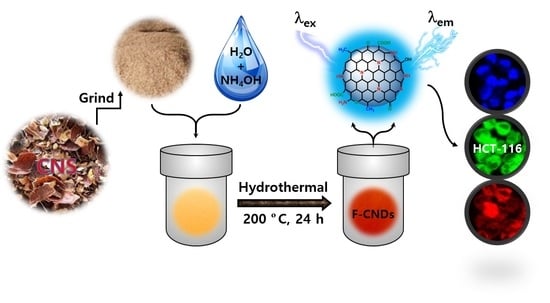
Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Functionalized Carbon Nanodots from Cashew Nut Skin Waste for Bioimaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
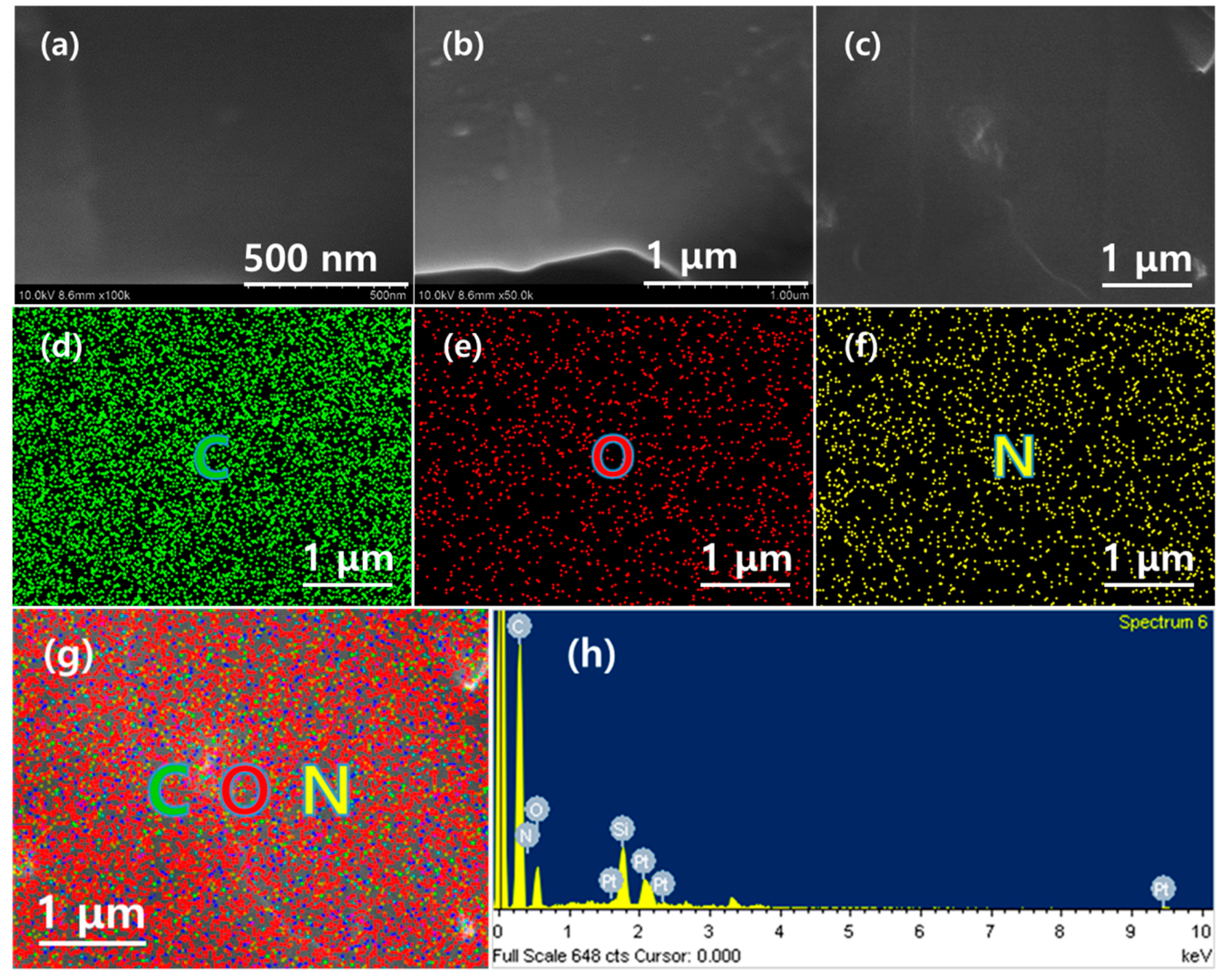
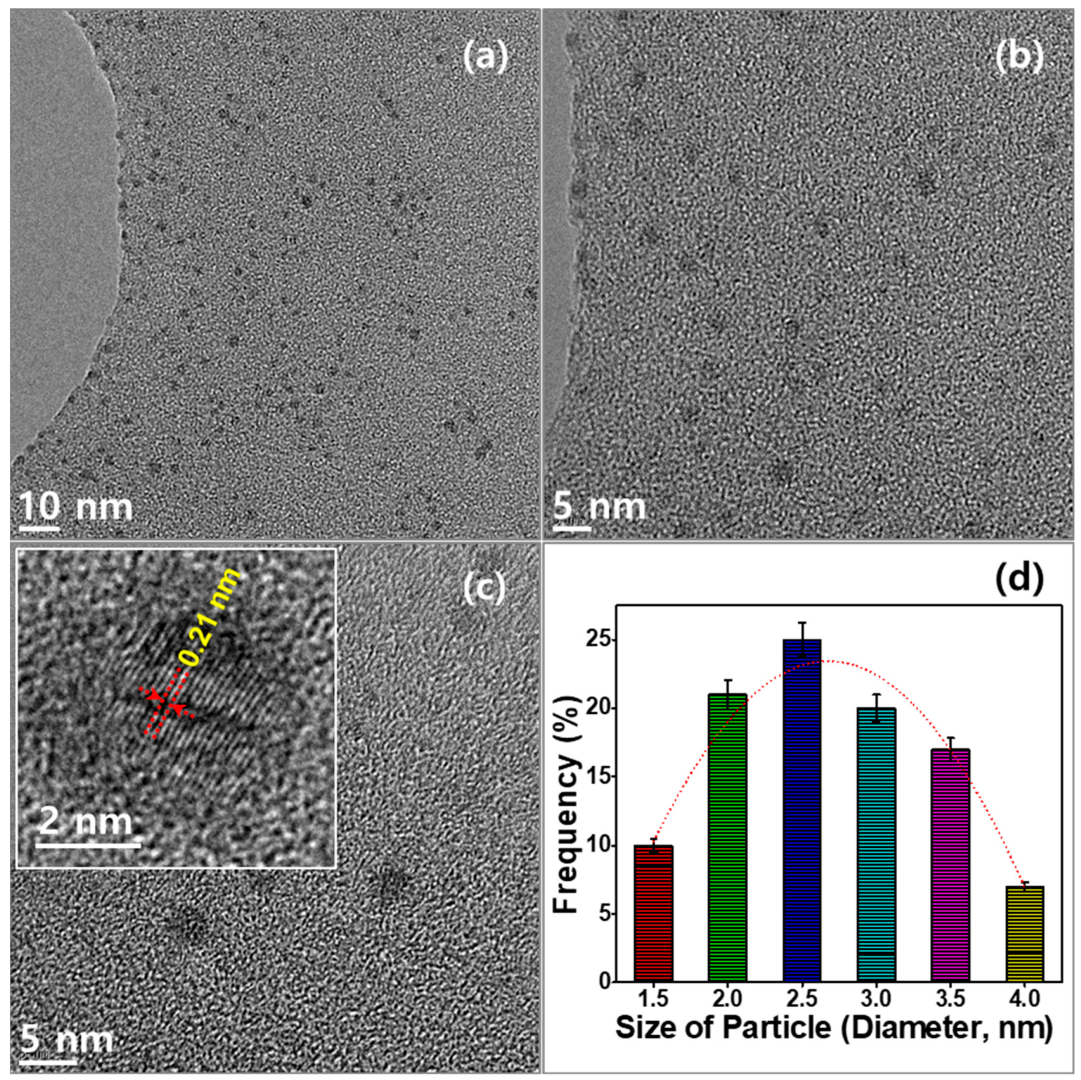
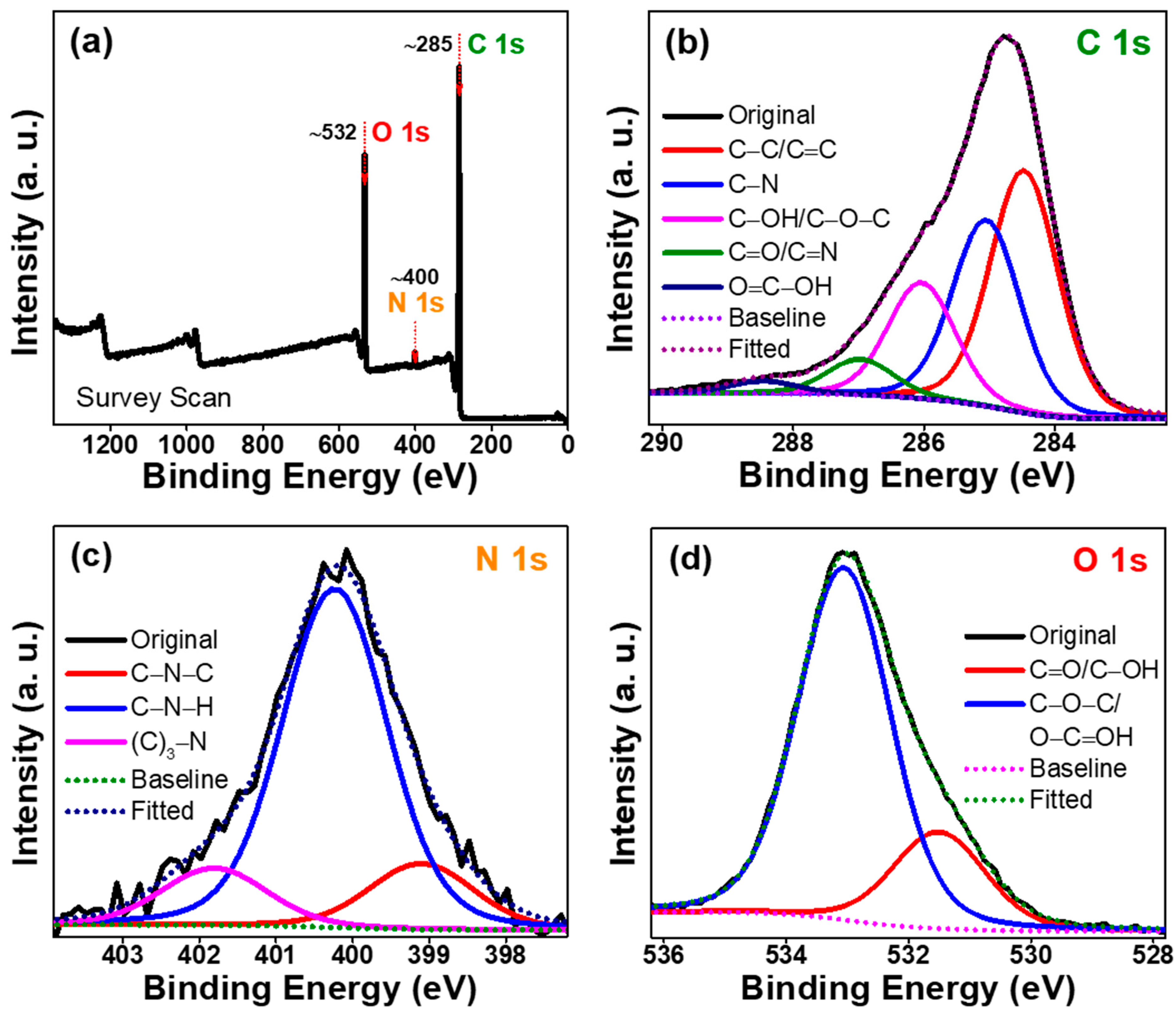
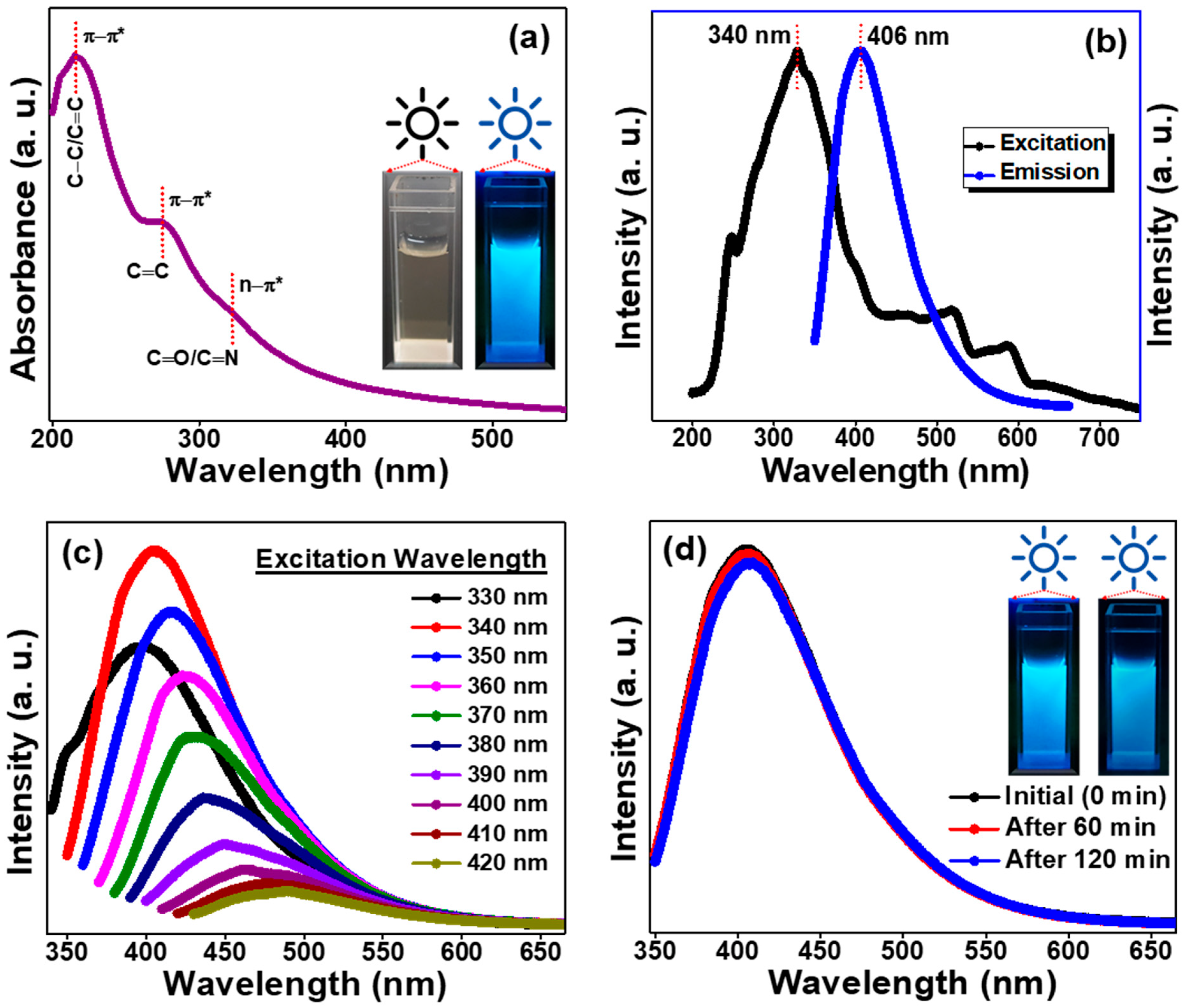
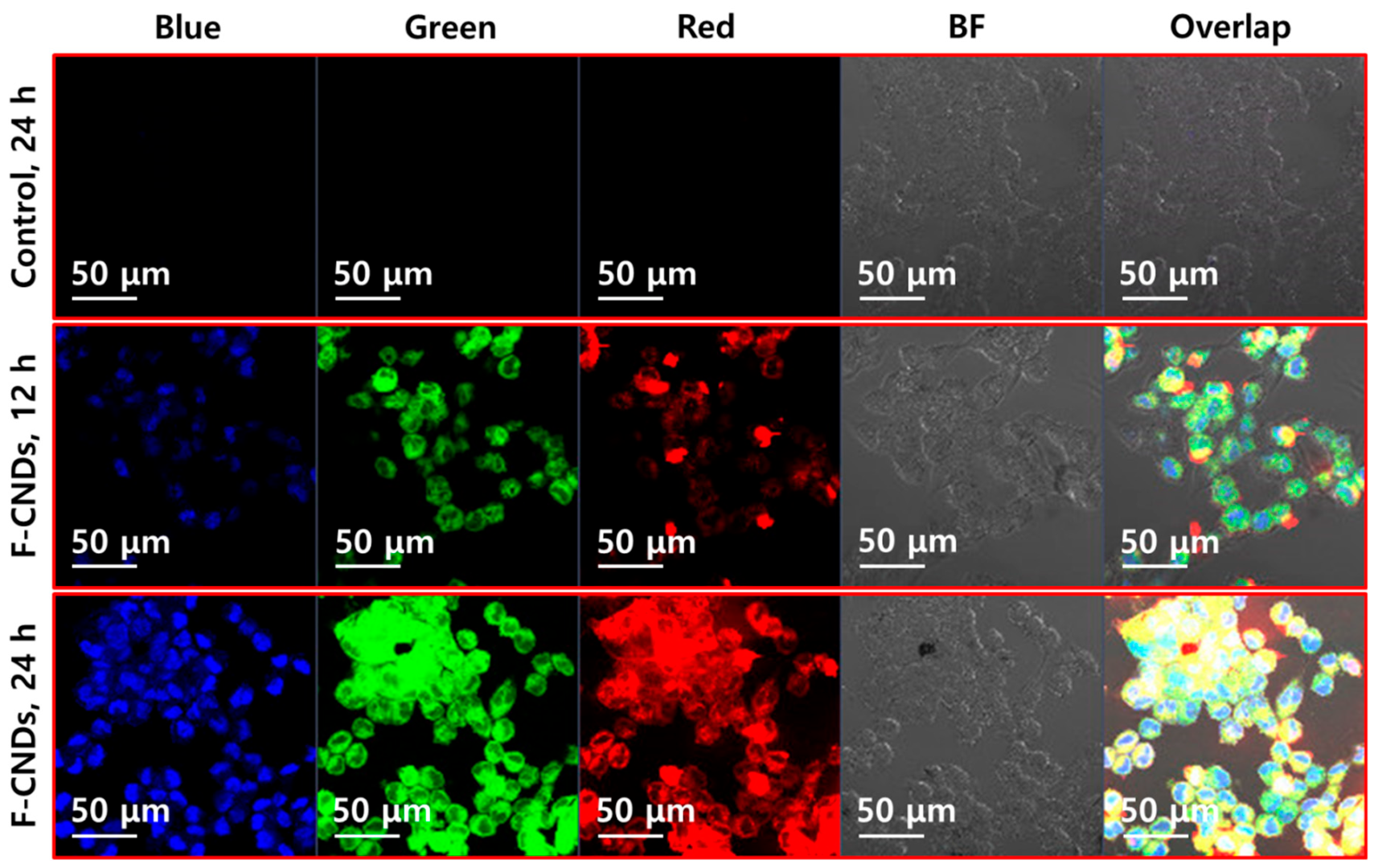
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. The Synthesis of Functionalized Carbon Nanodots
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Lu, S. The light of carbon dots: From mechanism to applications. Matter 2022, 5, 110–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Lewis, R.E.; Haynes, C.L. Synthesis Processes, Photoluminescence Mechanism, and the Toxicity of Amorphous or Polymeric Carbon Dots. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 3312–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Meng, T.; Shi, Y.; Song, X.; Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L. Toward phosphorescent and delayed fluorescent carbon quantum dots for next-generation electroluminescent displays. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarkhah, A.; Hosseini, E.; Kamkar, M.; Sehat, A.A.; Dordanihaghighi, S.; Allahbakhsh, A.; van der Kuur, C.; Arjmand, M. Synthesis, applications, and prospects of graphene quantum dots: A comprehensive review. Small 2022, 18, 2102683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, X. The Emerging Development of Multicolor Carbon Dots. Small 2022, 18, 2205099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falara, P.P.; Zourou, A.; Kordatos, K.V. Recent advances in Carbon Dots/2-D hybrid materials. Carbon 2022, 195, 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, A.; Selvaraj, R.; Vinayagam, R.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Kumar, P.S.; Duc, P.A.; Rangasamy, G. A critical review on the environmental applications of carbon dots. Chemosphere 2022, 313, 137308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, M.R.; Bhatia, S. Carbon Dot Nanoparticles: Exploring the Potential Use for Gene Delivery in Ophthalmic Diseases. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; Xiang, Y.; Zou, G.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. Functionalized carbon dots for advanced batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 37, 8–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-T.; Wang, L.-N.; Xu, J.; Huang, K.-J.; Wu, X. Synthesis and modification of carbon dots for advanced biosensing application. Analyst 2021, 146, 4418–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Verma, G. Converting fruit waste into carbon dots for bioimaging applications. Mater. Today Sustain. 2022, 18, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Kong, B.; Wu, H.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, G. Carbon nanodots featuring efficient FRET for real-time monitoring of drug delivery and two-photon imaging. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6569–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashkoulinejad-Kouhi, T.; Sawalha, S.; Safarian, S.; Arnaiz, B. A carbon-based nanocarrier for efficient gene delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2021, 12, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yang, J.H.; Zeng, H.B.; Chen, Y.M.; Yang, S.C.; Wu, C.; Zeng, H.; Yoshihito, O.; Zhang, Q. Carbon dots with high fluorescence quantum yield: The fluorescence originates from organic fluorophores. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14374–14378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Schneider, J.; Reckmeier, C.J.; Huang, H.; Kasák, P.; Rogach, A.L. Carbonization conditions influence the emission characteristics and the stability against photobleaching of nitrogen doped carbon dots. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 11730–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmadadi, M.; Rahmani, E.; Rajabzadeh-Khosroshahi, M.; Samadi, A.; Behzadmehr, R.; Rahdar, A.; Ferreira, L.F.R. Properties and application of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) in biosensors for disease detection: A comprehensive review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 80, 104156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Gangadharan, D.; Venkatanarasimhan, S. Synthetic strategies toward developing carbon dots via top-down approach. In Carbon Dots in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.-L.; Niu, K.-Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, N.-Q.; Du, X.-W. One-step synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by laser irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Tian, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y.; Qi, B.; Pang, D.W. Electrochemical tuning of luminescent carbon nanodots: From preparation to luminescence mechanism. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5801–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchudan, R.; Kishore, S.C.; Gangadaran, P.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Perumal, S.; Rajendran, R.L.; Alagan, M.; Al-Rashed, S.; Ahn, B.-C.; Lee, Y.R. Tunable fluorescent carbon dots from biowaste as fluorescence ink and imaging human normal and cancer cells. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoharan, P.; Dhanabalan, S.C.; Alagan, M.; Muthuvijayan, S.; Ponraj, J.S.; Somasundaram, C.K. Facile synthesis and characterisation of green luminescent carbon nanodots prepared from tender coconut water using the acid-assisted ultrasonic route. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; He, Y.; Li, S.; Cui, H. Amino acids as the source for producing carbon nanodots: Microwave assisted one-step synthesis, intrinsic photoluminescence property and intense chemiluminescence enhancement. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9634–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Liebana, M.; Chung, N.; Limpens, R.; Gomez, L.; Hueso, J.; Santamaria, J.; Gregorkiewicz, T. Uniform luminescent carbon nanodots prepared by rapid pyrolysis of organic precursors confined within nanoporous templating structures. Carbon 2017, 117, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Pan, K.; Yu, H.; Wang, F.; Kang, Z. Large scale electrochemical synthesis of high quality carbon nanodots and their photocatalytic property. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9526–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Kishore, S.C.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Perumal, S.; Vinodh, R.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Babu, R.S.; Alagan, M.; Lee, Y.R. Highly fluorescent carbon dots as a potential fluorescence probe for selective sensing of ferric ions in aqueous solution. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Q.; Yang, X.; Liu, K.; Ding, Z.; Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Lv, C.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Pressure-induced photoluminescence enhancement and ambient retention in confined carbon dots. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 2545–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Sheardy, A.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chevva, H.; Allado, K.; Yin, Z.; Wei, J. Tuning the functional groups on carbon nanodots and antioxidant studies. Molecules 2019, 24, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, X.; Qin, B.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y. Highly fluorescent near-infrared emitting carbon dots derived from lemon juice and its bioimaging application. J. Lumin. 2019, 211, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarah, R.; Karak, N. Facile and ultrafast green approach to synthesize biobased luminescent reduced carbon nanodot: An efficient photocatalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9454–9466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huo, X.; Zhao, H.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Li, Y. One-pot green synthesis of N, S co-doped biomass carbon dots from natural grapefruit juice for selective sensing of Cr (VI). Chem. Phys. Impact 2022, 5, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandani, S.; Dey, D.; Sharma, B.; Sarma, T.K. Natural occurrence of fluorescent carbon dots in honey. Carbon 2017, 119, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Ban, R.; Zhang, P.-H.; Wu, G.-H.; Zhang, J.-R.; Zhu, J.-J. Hair fiber as a precursor for synthesizing of sulfur-and nitrogen-co-doped carbon dots with tunable luminescence properties. Carbon 2013, 64, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Akanda, M.R.; Park, B.-Y.; Kim, H.Y. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from carrot juice for in vitro cellular imaging. Carbon Lett. 2017, 21, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lan, M.; Zhu, X.; Xue, H.; Ng, T.-W.; Meng, X.; Lee, C.-S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W. Green synthesis of bifunctional fluorescent carbon dots from garlic for cellular imaging and free radical scavenging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17054–17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Kumar, G.S.; Devi, P.S. Egg-shell derived carbon dots for base pair selective DNA binding and recognition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 20476–20488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchudan, R.; Gangadaran, P.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Perumal, S.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Vinodh, R.; Rajendran, R.L.; Ahn, B.-C.; Lee, Y.R. Betel leaf derived multicolor emitting carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for imaging mouse normal fibroblast and human thyroid cancer cells. Phys. E: Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2022, 136, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.U.; Park, E.S.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, J.-W.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Huh, Y.S.; Lee, J. Photoluminescent green carbon nanodots from food-waste-derived sources: Large-scale synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3365–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Q.; Ni, Q.; Niu, C.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, W.; Shen, C.; Qin, C.; Zheng, G.; Liu, K. Carbon nanodots with nearly unity fluorescent efficiency realized via localized excitons. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2203622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Shang, Y.; Lou, Q.; Zhu, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, W.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Shan, C.X. A Molecular Engineering Strategy for Achieving Blue Phosphorescent Carbon Dots with Outstanding Efficiency Above 50%. Adv. Mater. 2022, 35, 2207970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramashivappa, R.; Kumar, P.P.; Vithayathil, P.; Rao, A.S. Novel method for isolation of major phenolic constituents from cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) nut shell liquid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2548–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekara, N.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidative potential of cashew phenolics in food and biological model systems as affected by roasting. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Parpia, H. Polyphenols of cashew kernel testa. J. Food Sci. 1970, 35, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison, T.N.J.I.; Atchudan, R.; Sethuraman, M.G.; Lee, Y.R. Reductive-degradation of carcinogenic azo dyes using Anacardium occidentale testa derived silver nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 162, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, S.; Yin, K.; Ng, W.J. Nitrogen-doped durian shell derived carbon dots for inner filter effect mediated sensing of tetracycline and fluorescent ink. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temerov, F.; Belyaev, A.; Ankudze, B.; Pakkanen, T.T. Preparation and photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots by decomposition of graphene-encapsulated metal nanoparticles derived from Kraft lignin and transition metal salts. J. Lumin. 2019, 206, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dager, A.; Baliyan, A.; Kurosu, S.; Maekawa, T.; Tachibana, M. Ultrafast synthesis of carbon quantum dots from fenugreek seeds using microwave plasma enhanced decomposition: Application of C-QDs to grow fluorescent protein crystals. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Shah, K.A.; Islam, S. Investigation of effects produced by chemical functionalization in single-walled and multi-walled carbon nanotubes using Raman spectroscopy. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 2013, 31, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Muthuchamy, N.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Perumal, S.; Vinodh, R.; Park, K.H.; Lee, Y.R. An ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical biosensor for glucose based on bio-derived nitrogen-doped carbon sheets wrapped titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammina, S.K.; Yang, D.; Koppala, S.; Cheng, C.; Yang, Y. Highly photoluminescent N, P doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensor for the detection of dopamine and temperature. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 194, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Chakradhar, D.; Perumal, S.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, Y.R. Facile green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots using Chionanthus retusus fruit extract and investigation of their suitability for metal ion sensing and biological applications. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2017, 246, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza da Costa, R.; Ferreira da Cunha, W.; Simenremis Pereira, N.; Marti Ceschin, A. An Alternative Route to Obtain Carbon Quantum Dots from Photoluminescent Materials in Peat. Materials 2018, 11, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.; Abellán, C.; Zougagh, M.; Jimenez-Jimenez, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; da Silva, J.E.; Ríos, A.; Algarra, M. Fluorescent chemosensor for pyridine based on N-doped carbon dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 458, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Feng, M.; Zhan, H. Generation of nitrogen-doped photoluminescent carbonaceous nanodots via the hydrothermal treatment of fish scales for the detection of hypochlorite. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 44636–44641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; An, X.; Yan, X. A novel rapid and green synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots with good biocompatibility for cell imaging. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 1376–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Fu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zeng, J.; Xia, Z.; Gao, D. Green synthesis of carbon dots using the flowers of Osmanthus fragrans (Thunb.) Lour. as precursors: Application in Fe3+ and ascorbic acid determination and cell imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2715–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Perumal, S.; Vinodh, R.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Babu, R.S.; Lee, Y.R. Morus nigra-derived hydrophilic carbon dots for the highly selective and sensitive detection of ferric ion in aqueous media and human colon cancer cell imaging. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 635, 128073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, W. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: Facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Gong, X.; Liu, L.; Choi, M.M. Characterization and analytical separation of fluorescent carbon nanodots. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 1804178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Perumal, S.; Muthuchamy, N.; Lee, Y.R. Hydrophilic nitrogen-doped carbon dots from biowaste using dwarf banana peel for environmental and biological applications. Fuel 2020, 275, 117821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.B.; Pramanick, A.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Ray, M. Amorphous carbon dots and their remarkable ability to detect 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Shen, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, T.; Ge, J. Facile synthesis of biomass waste-derived fluorescent N, S, P co-doped carbon dots for detection of Fe 3+ ions in solutions and living cells. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan, L.; Volf, I.; Stan, C.S.; Albu, C.; Coroaba, A.; Ursu, L.E.; Popa, M. Intense Blue Photo Emissive Carbon Dots Prepared through Pyrolytic Processing of Ligno-Cellulosic Wastes. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Ehrat, F.; Wang, Y.; Milowska, K.Z.; Reckmeier, C.; Rogach, A.L.; Stolarczyk, J.K.; Urban, A.S.; Feldmann, J. Carbon dots: A unique fluorescent cocktail of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6030–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kishore, S.C.; Perumal, S.; Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Alagan, M.; Sangaraju, S.; Lee, Y.R. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Functionalized Carbon Nanodots from Cashew Nut Skin Waste for Bioimaging. Catalysts 2023, 13, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030547
Kishore SC, Perumal S, Atchudan R, Edison TNJI, Sundramoorthy AK, Alagan M, Sangaraju S, Lee YR. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Functionalized Carbon Nanodots from Cashew Nut Skin Waste for Bioimaging. Catalysts. 2023; 13(3):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030547
Chicago/Turabian StyleKishore, Somasundaram Chandra, Suguna Perumal, Raji Atchudan, Thomas Nesakumar Jebakumar Immanuel Edison, Ashok K. Sundramoorthy, Muthulakshmi Alagan, Sambasivam Sangaraju, and Yong Rok Lee. 2023. "Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Functionalized Carbon Nanodots from Cashew Nut Skin Waste for Bioimaging" Catalysts 13, no. 3: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030547
APA StyleKishore, S. C., Perumal, S., Atchudan, R., Edison, T. N. J. I., Sundramoorthy, A. K., Alagan, M., Sangaraju, S., & Lee, Y. R. (2023). Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Functionalized Carbon Nanodots from Cashew Nut Skin Waste for Bioimaging. Catalysts, 13(3), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030547