Synthesis, Characterization and Investigation of Cross-Linked Chitosan/(MnFe2O4) Nanocomposite Adsorption Potential to Extract U(VI) and Th(IV)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
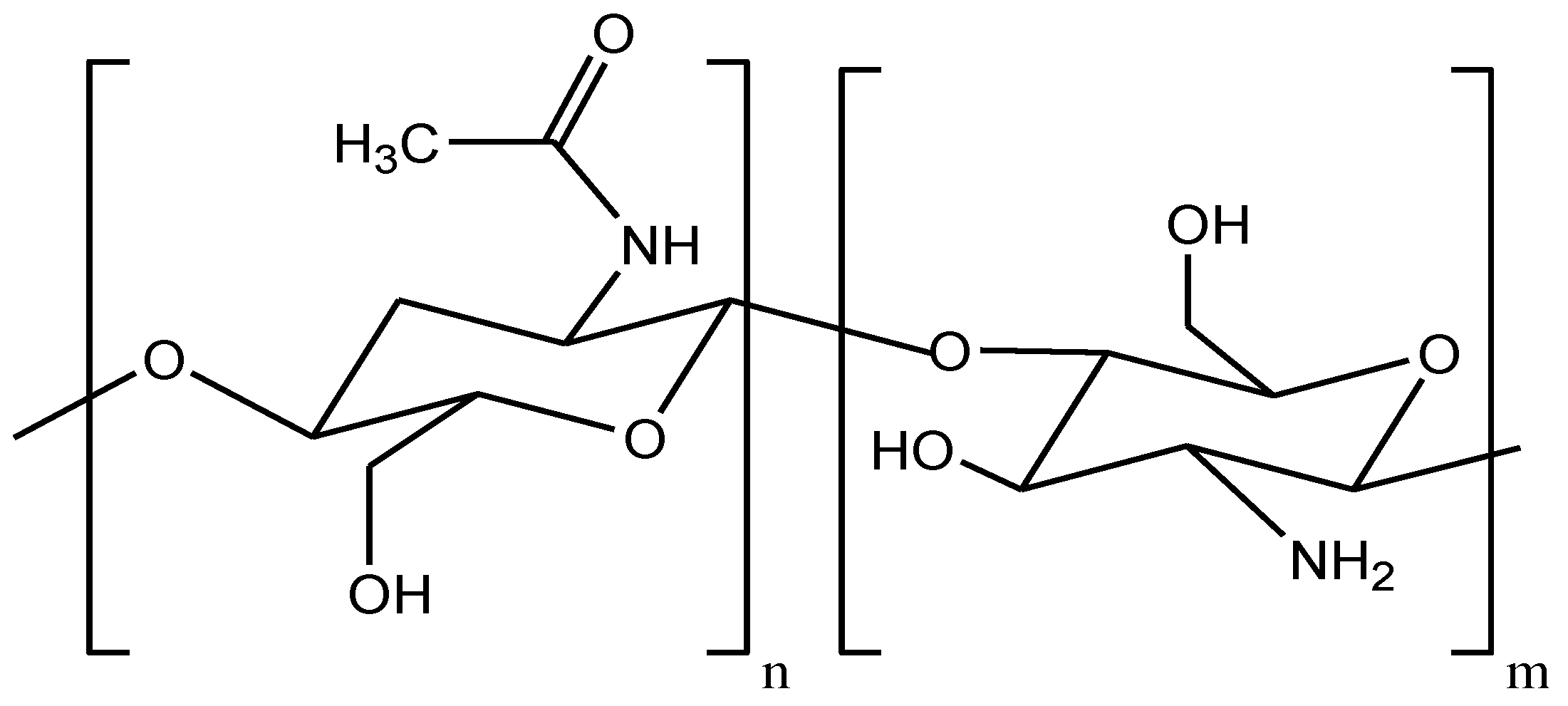
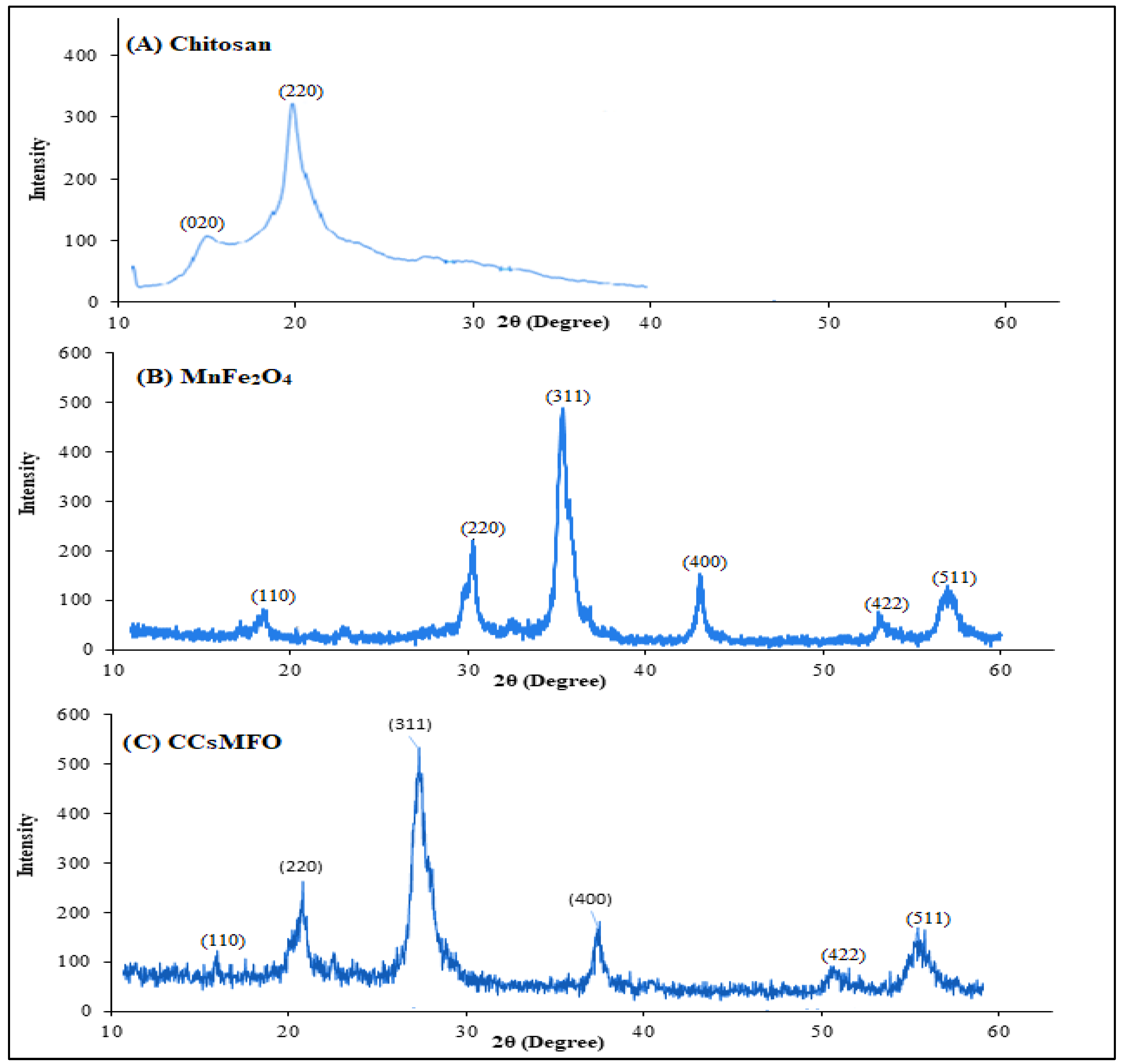
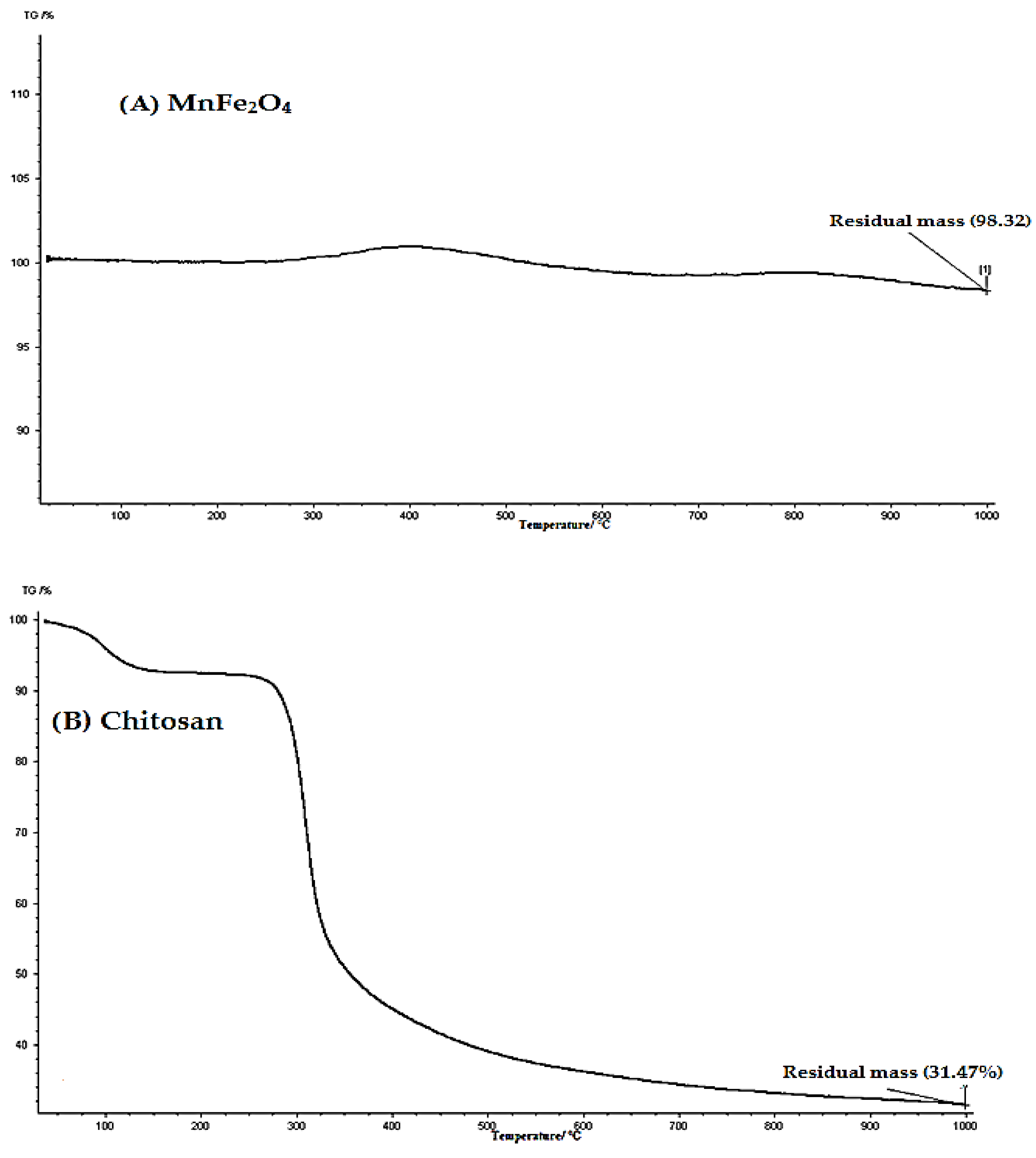
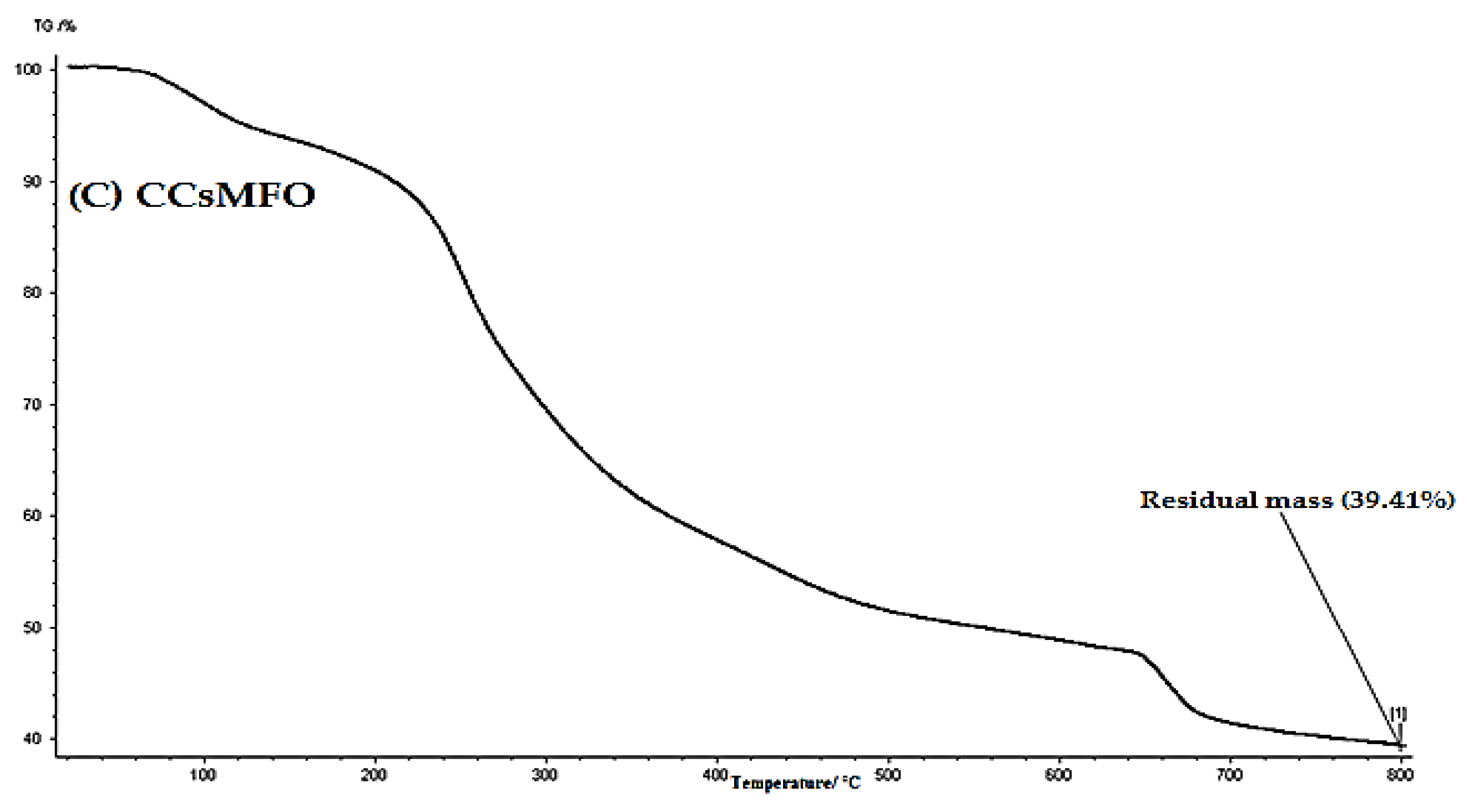
2.1. Characterization of (CCsMFO) Nanocomposite
2.2. Optimization Adsorption Protocols
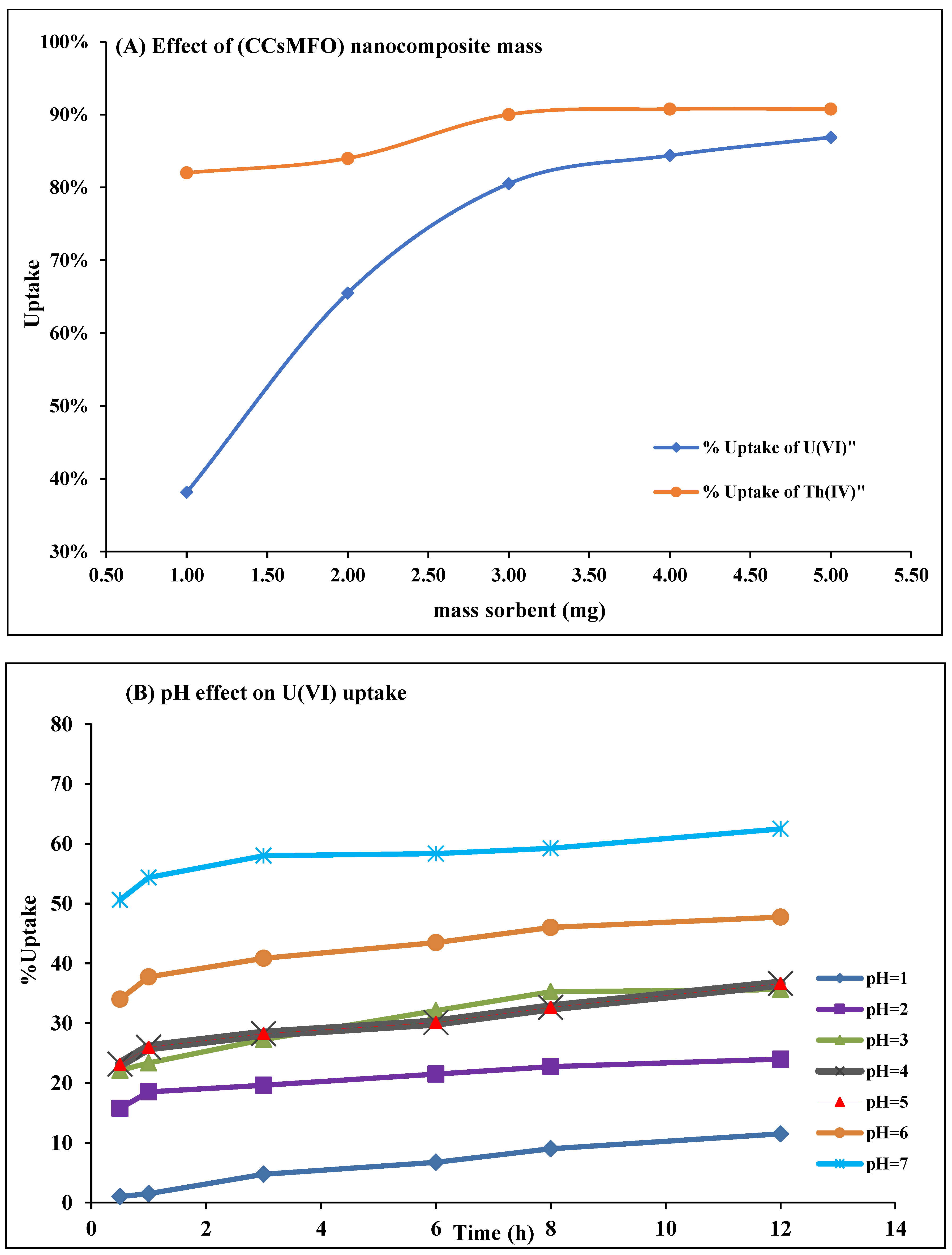
2.2.1. Effect of Adsorbent Amount
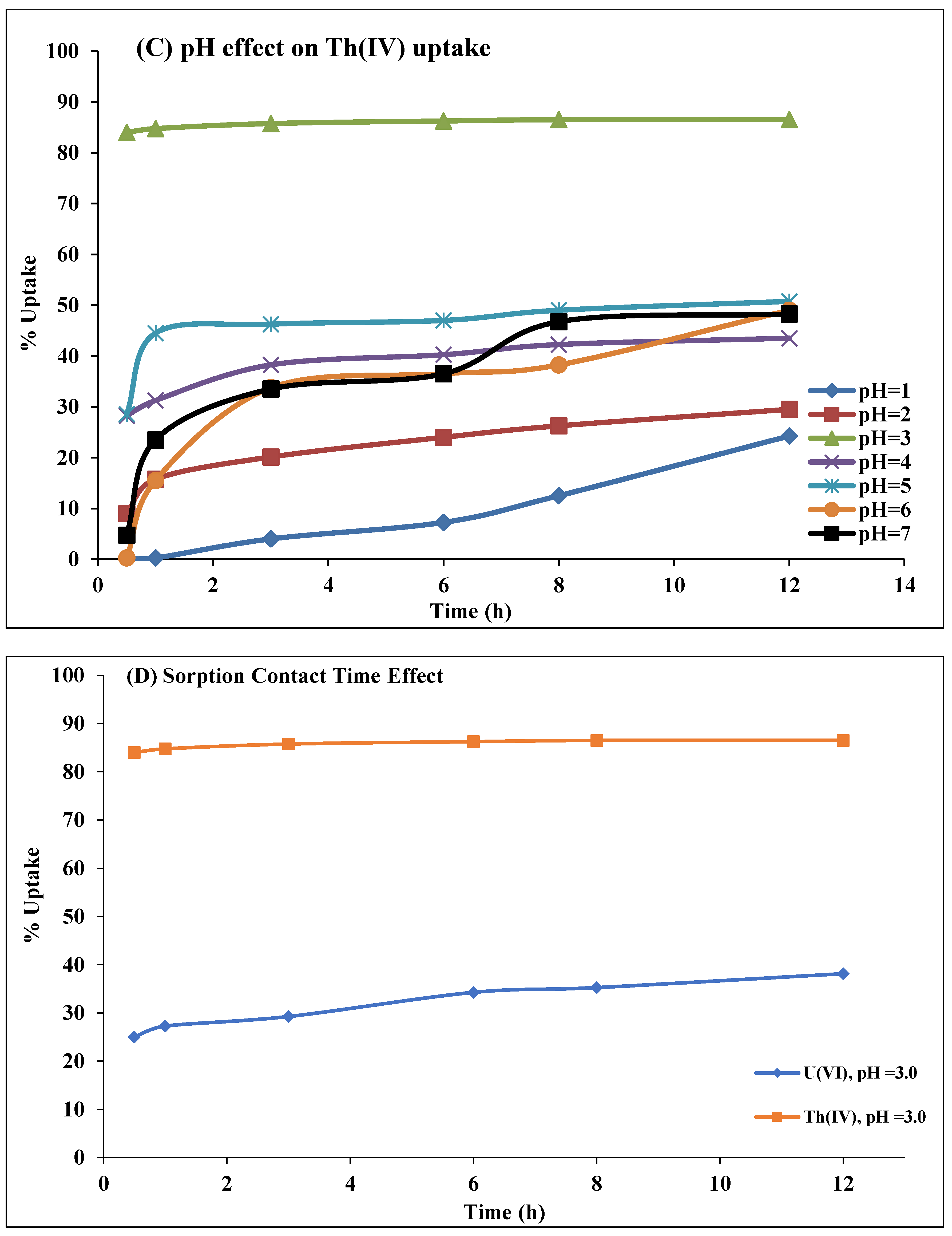
2.2.2. Solution pH Effect
2.2.3. Contact Time Effect
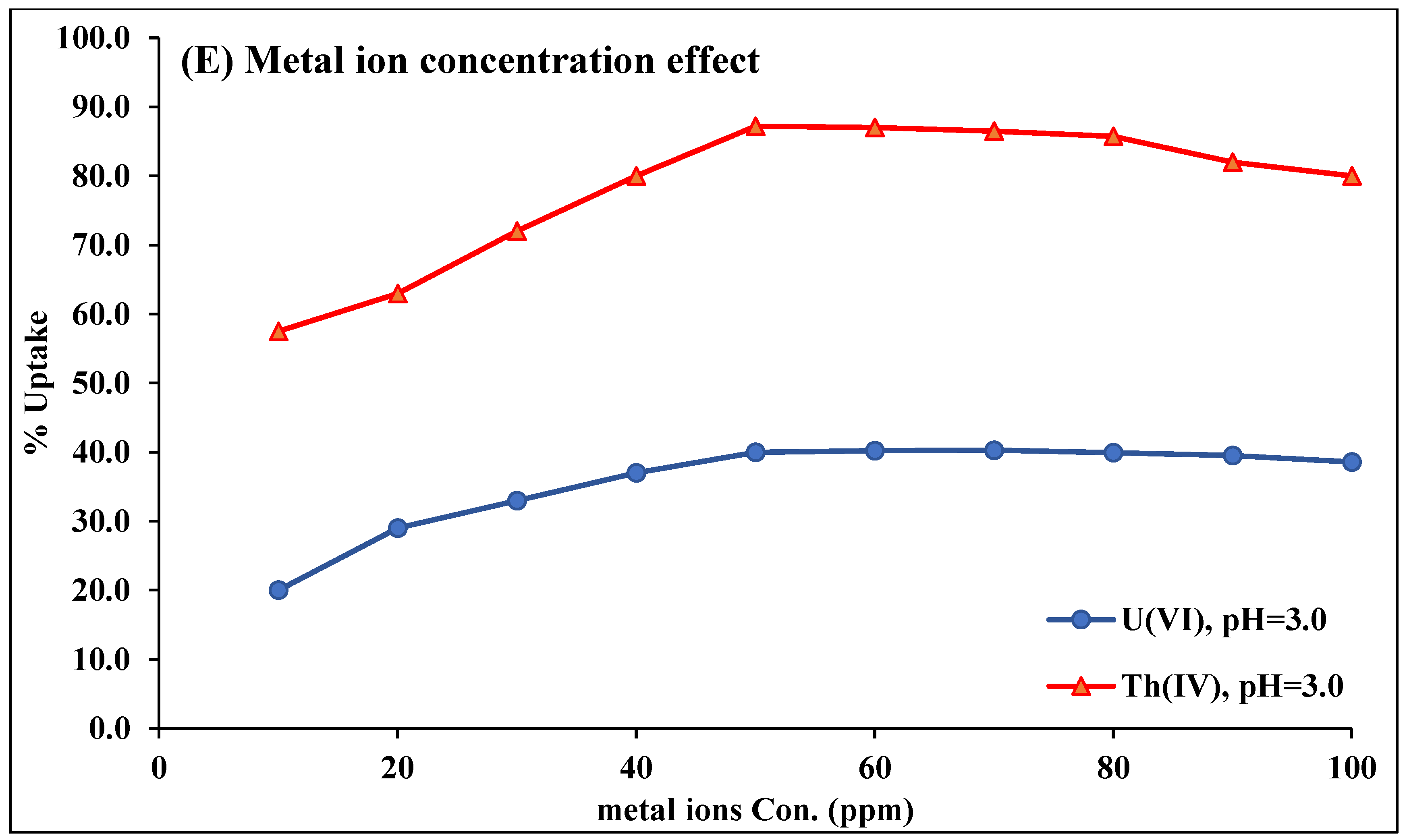
2.2.4. Metal Ion Concentration Effect
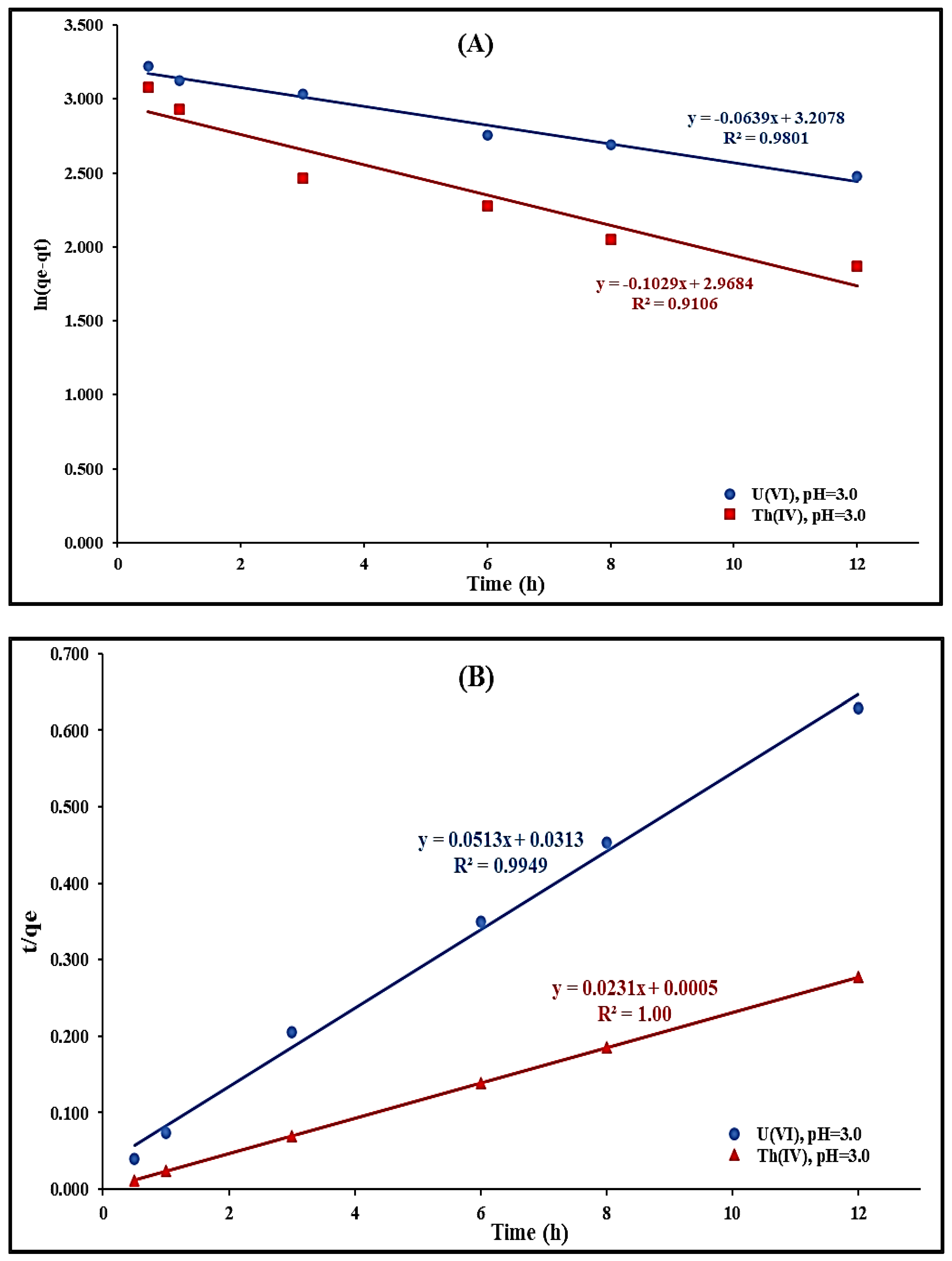
2.2.5. Adsorption Kinetics Modeling Studies
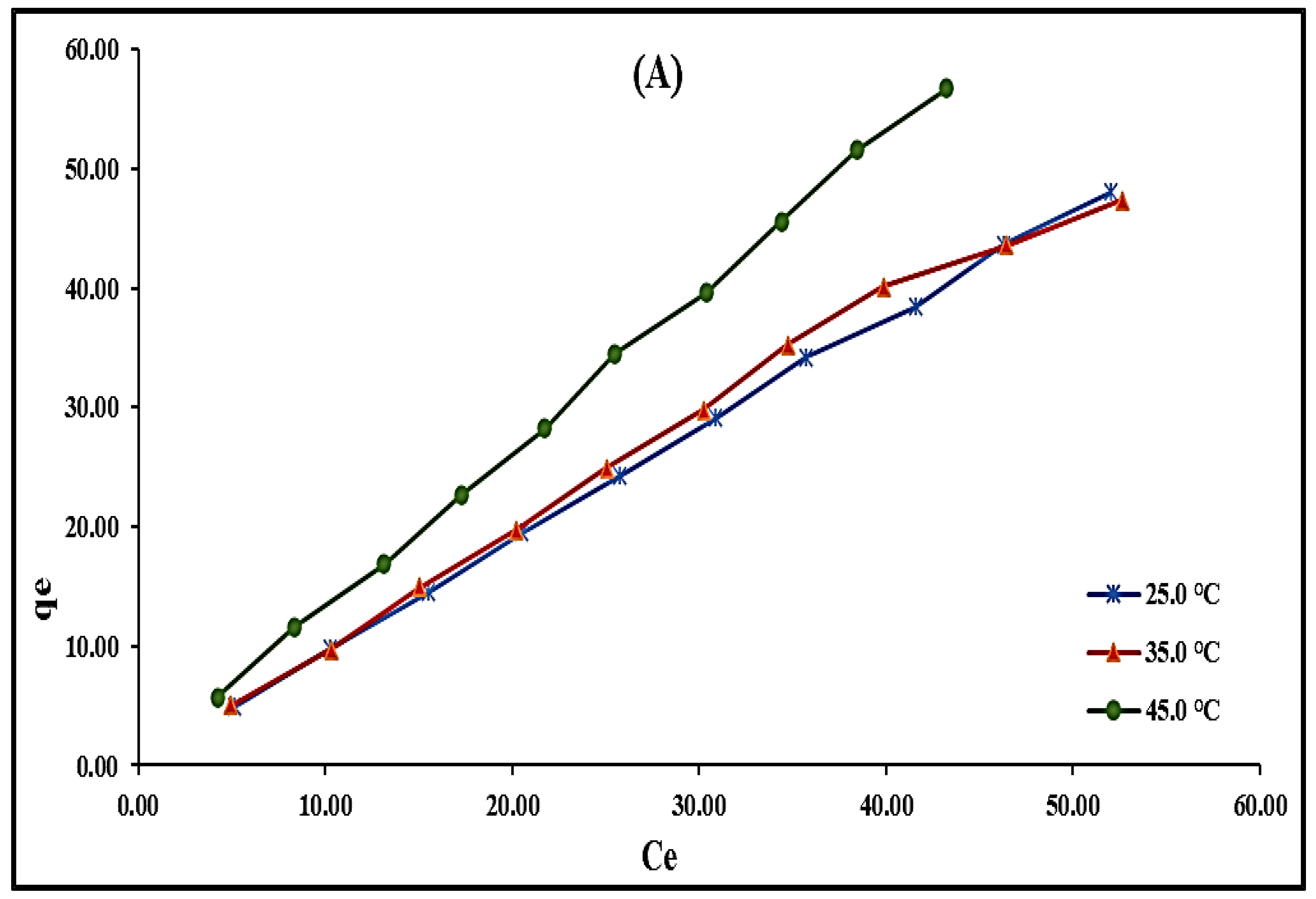
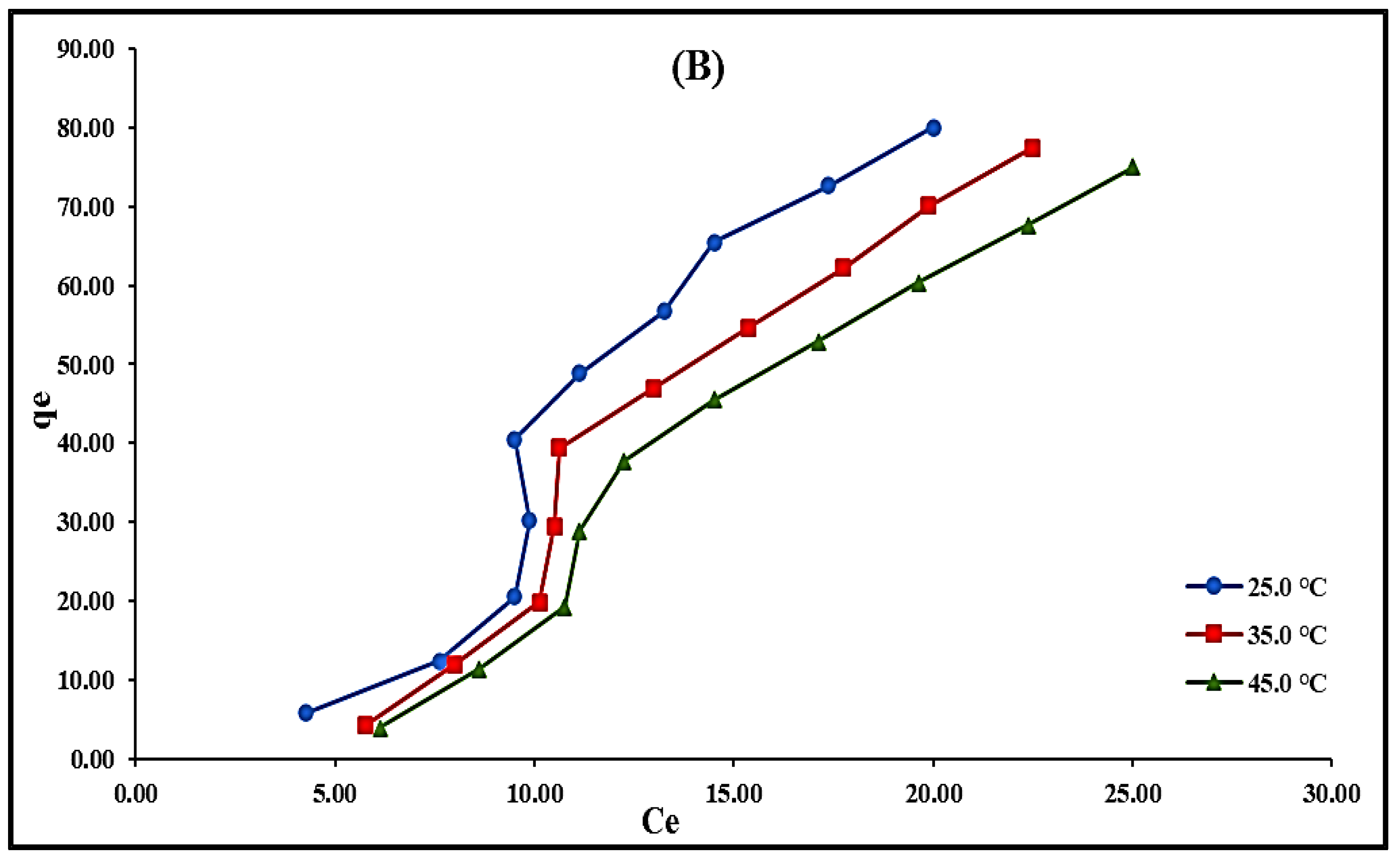
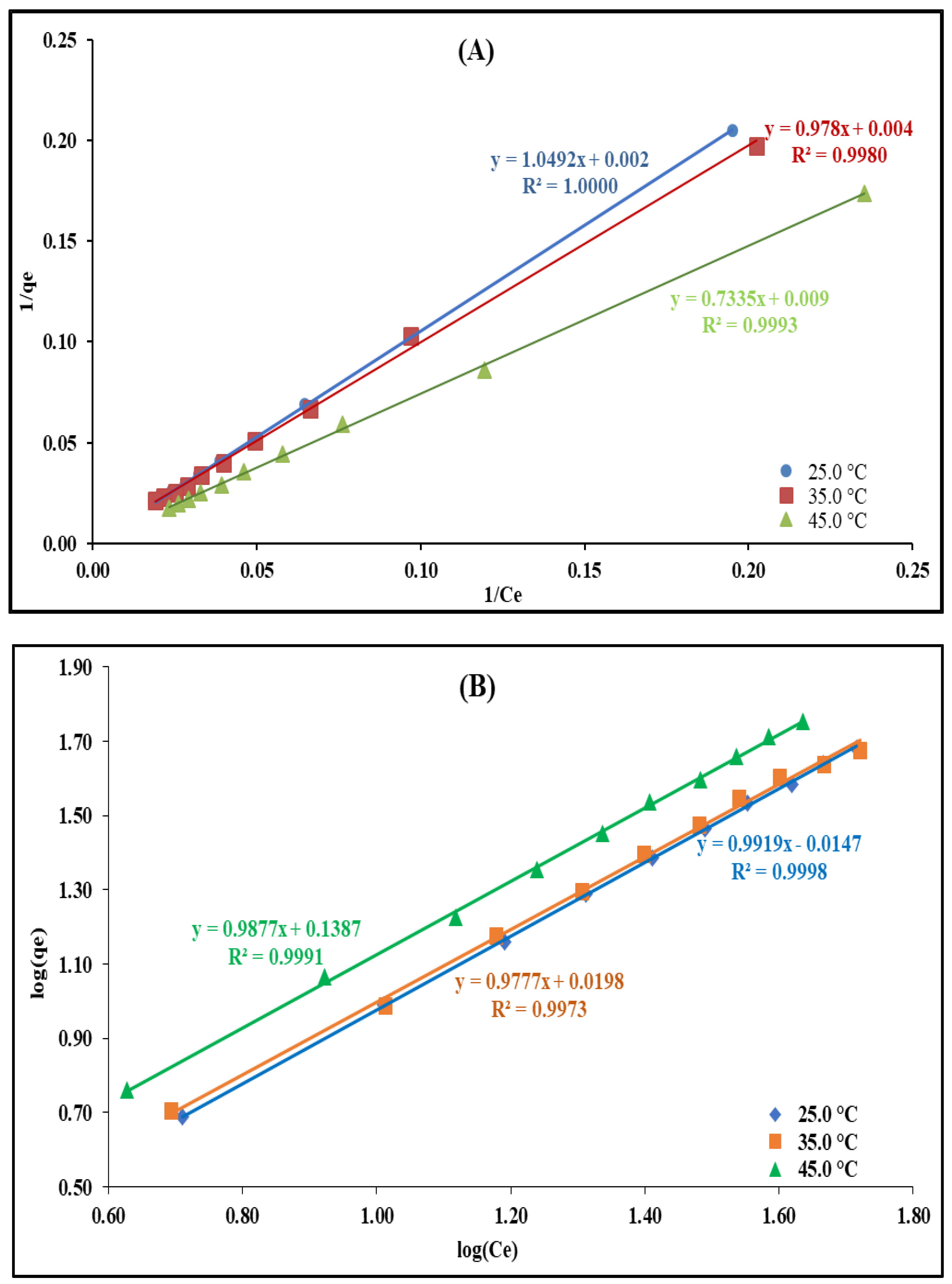
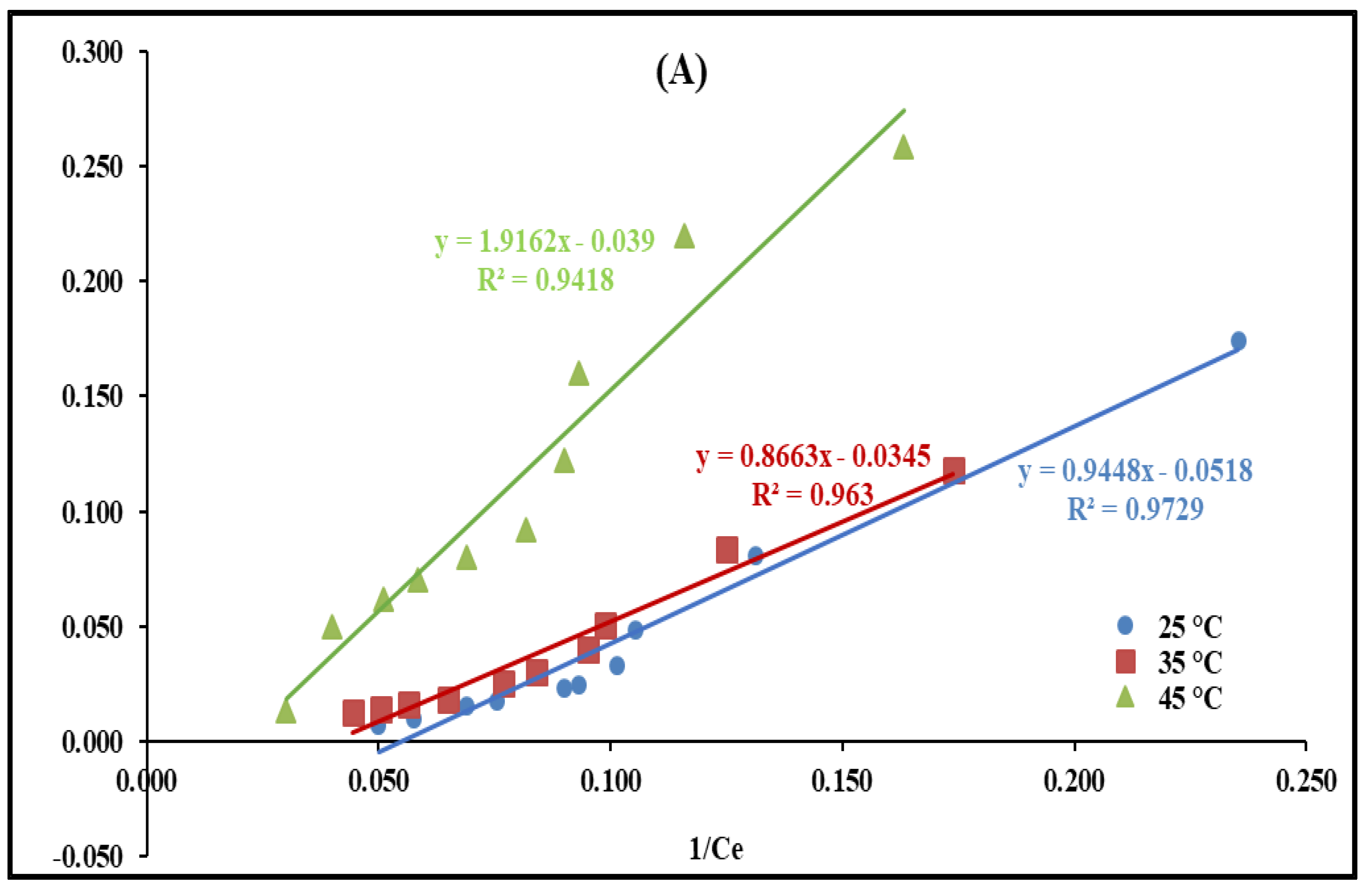
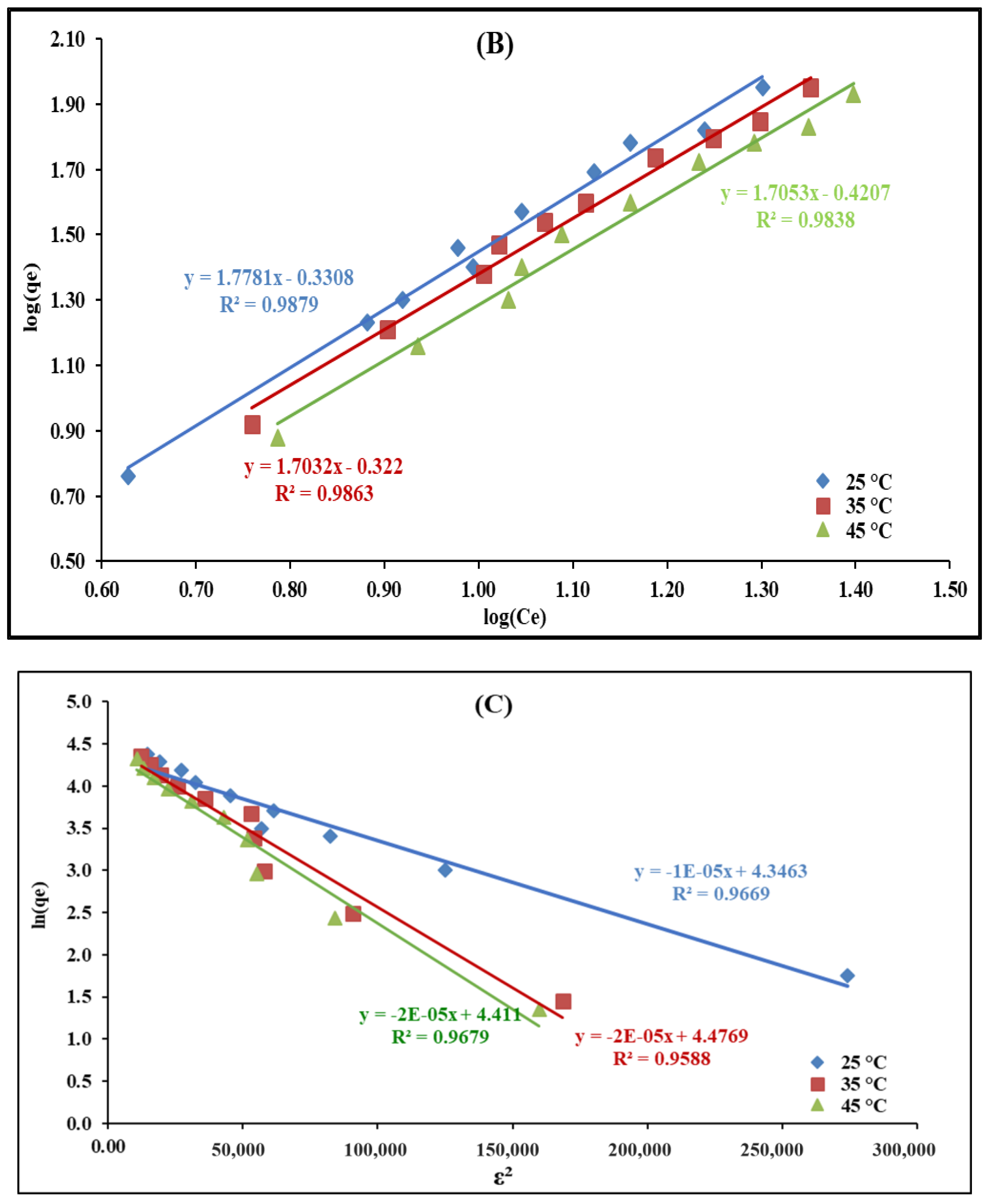
2.2.6. Temperature’s Effect and Adsorption Isotherms Modeling
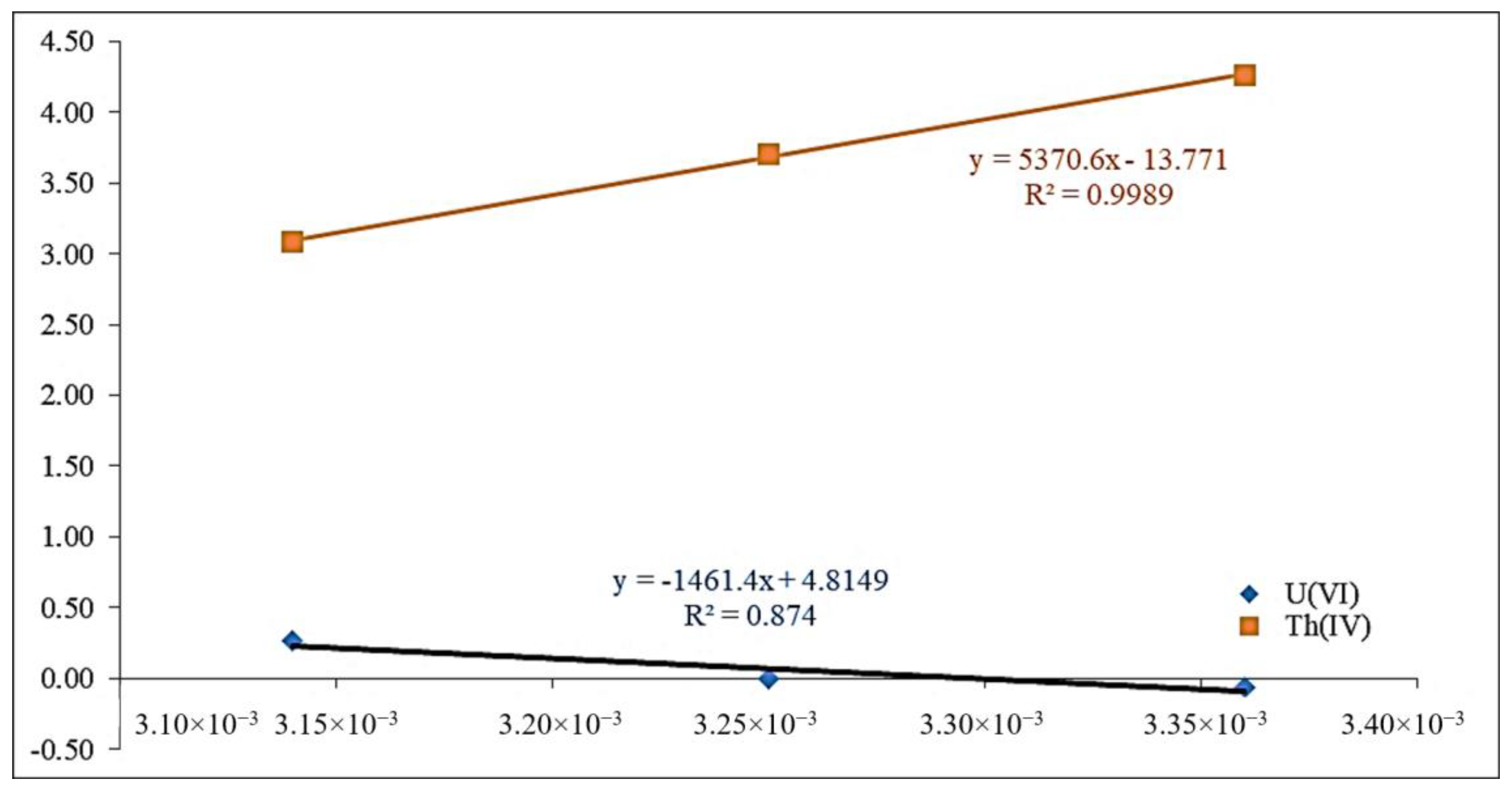
2.2.7. Adsorption Thermodynamics
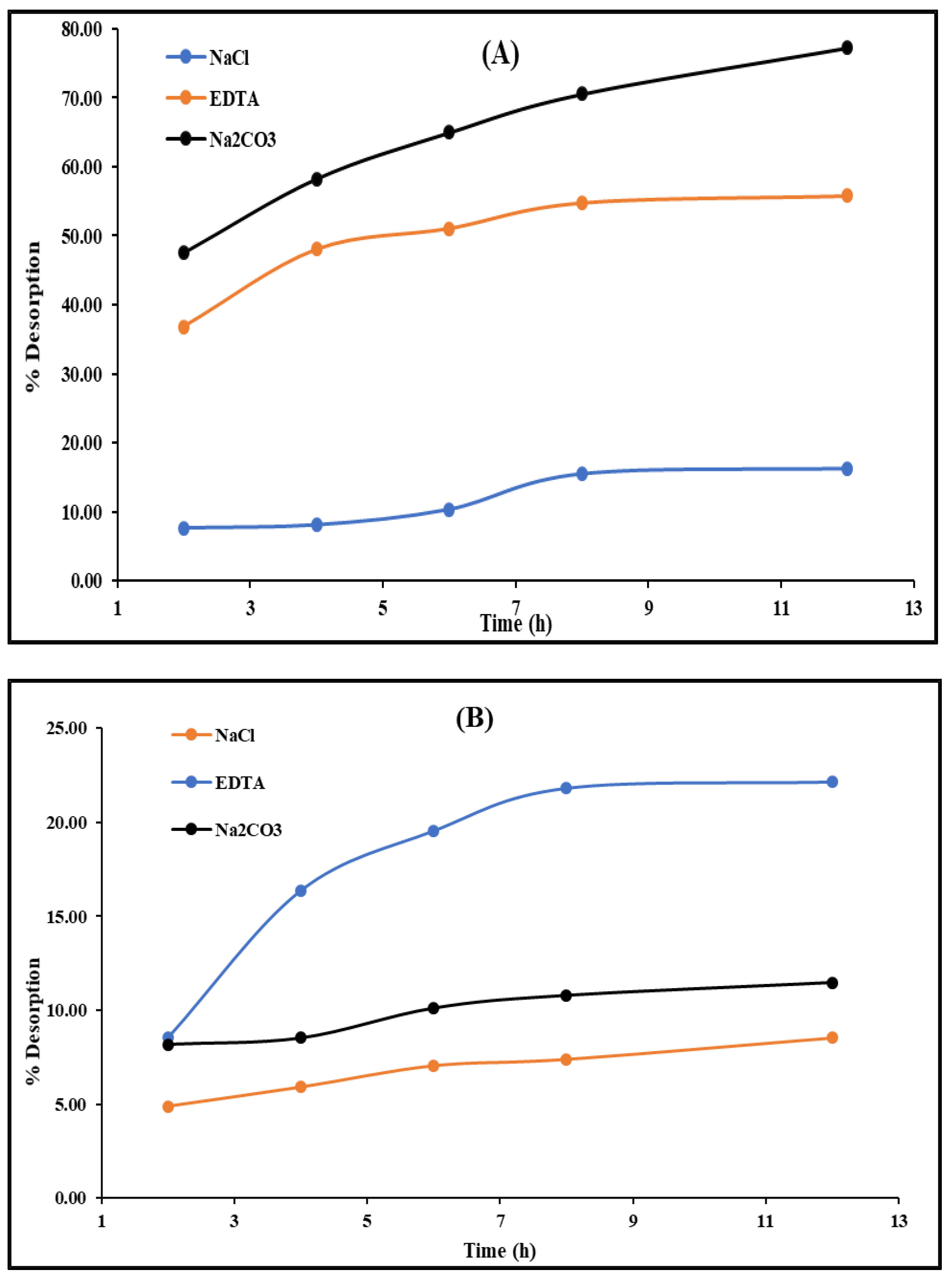
2.3. Reusability of CCsMFO Nanocomposite
2.4. Comparative Study
3. Material, Instruments, and Methods
3.1. Material
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Methods
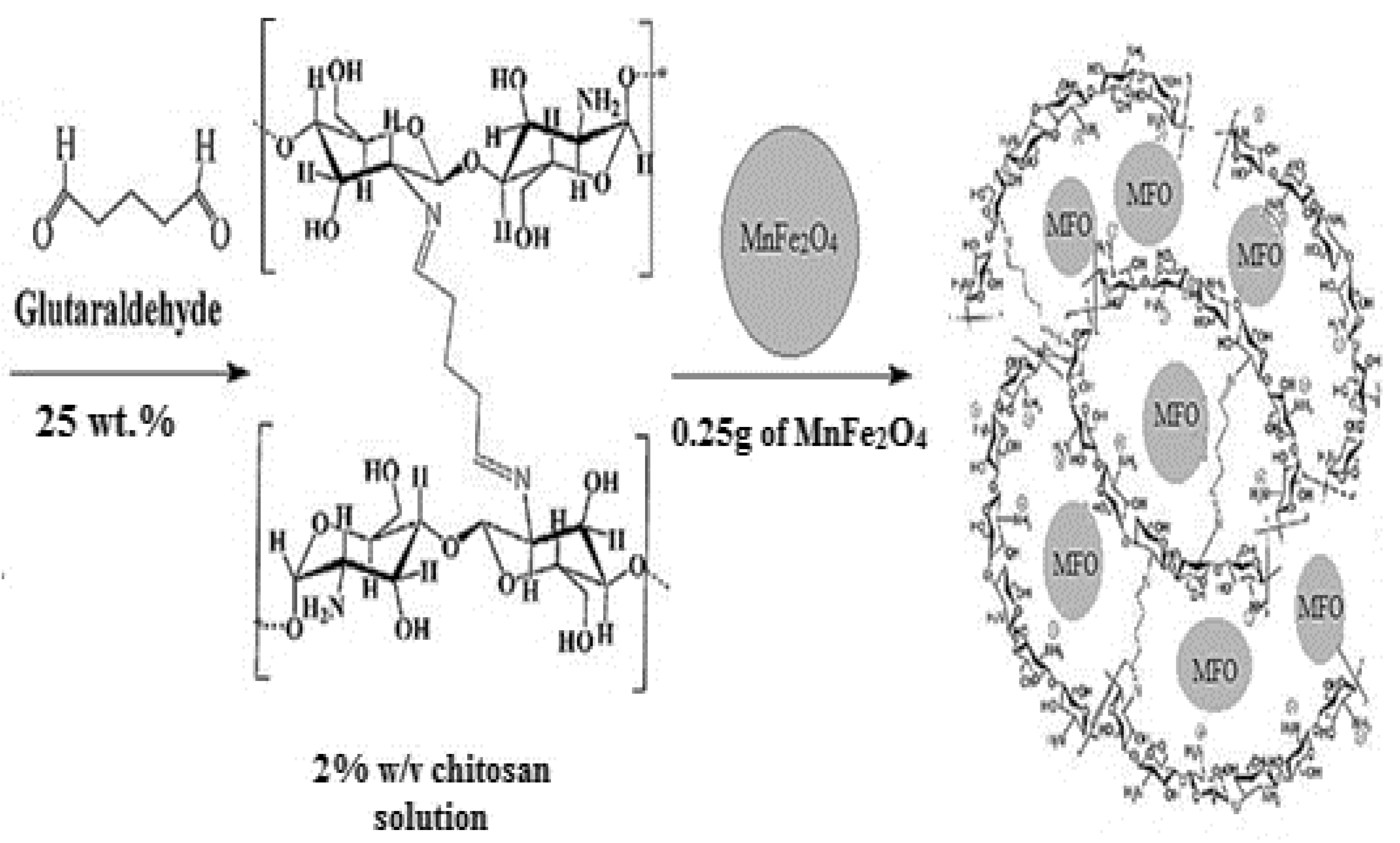
3.3.1. Cross-Linked Chitosan/MnFe2O4 (CCsMFO) Nanocomposite Synthesis
3.3.2. Sorption and Recovery Experiments
3.3.3. Determination of U(VI) and Th(IV) Concentration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Atawy, M.A.; Khalil, K.D.; Bashal, A.H. Chitosan Capped Copper Oxide Nanocomposite: Efficient, Recyclable, Heterogeneous Base Catalyst for Synthesis of Nitroolefins. Catalysts 2022, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjari, A.J.; Asghari, M. A Review on Chitosan Utilization in Membrane Synthesis. ChemBioEng Rev. 2016, 3, 134–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Dattajirao, V.; Shrivastava, V.; Bhardwaj, U. Isolation and Characterization of Chitosan-Producing Bacteria from Beaches of Chennai, India. Enzym. Res. 2012, 2012, 421683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Wirsen, A.; Albertsson, A.C. Effect of lactic/glycolic acid side chains on the thermal degradationkinetics of chitosan derivatives. Polymer 2000, 41, 4841–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, S.W.; Hanafiah, K.A.M. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xin, C.; Tan, C. Preparation, physicochemical and pharmaceutical characterization of chitosan from Catharsius molossus residue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontius, F.W. Chitosan as a Drinking Water Treatment Coagulant. Am. J. Civil Eng. 2016, 4, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, M.; Pal, K.; Anis, A.; Banthia, A.K. Development and Characterization of Chitosan based Polymeric Hydrogel Membranes. Des. Monomers Polym. 2010, 13, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pella, M.C.G.; Lima-Tenorio, M.K.; Tenório-Neto, E.T.; Guilherme, M.R.; Muniz, E.C.; Rubira, A.F. Chitosan-based hydrogels: From preparation to biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Nair, S.; Tamura, H. Novel chitin and chitosan nanofibers in biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 28, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ye, F.; Dobretsov, S.; Dutta, J. Chitosan Nanocomposite Coatings for Food, Paints, and Water Treatment Applications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, Y.; Dharaskar, S.; Khalid, M.; Sonawane, S. An environment friendly approach for heavy metal removal from industrial wastewater using chitosan based biosorbent: A review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 43, 100951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Fan, Z.; Su, G.; Pan, D.; Li, Z. Research progress of adsorption and removal of heavy metals by chitosan and its derivatives: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokila, S.; Gomathi, T.; Sudha, P.N.; Anil, S. Removal of the heavy metal ion chromiuim(VI) using chitosan and alginate nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanasrinivasan, V.; Mishra, M.; Paliwal, J.S.; Singh, S.K.; Selvarajan, E.; Suganthi, V.; Subathra Devi, C. Studies on heavy metal removal efficiency and antibacterial activity of chitosan prepared from shrimp shell waste. 3 Biotech 2014, 4, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Chitosan-based biosorbents: Modification and application for biosorption of heavy metals and radionuclides. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, M.L.; Arnal, M.C.; de la Guardia, M. Removal of heavy metals by using adsorption on alumina or chitosan. Anal Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 820–825. [Google Scholar]
- Annaduzzaman, M. Chitosan Biopolymer as an Adsorbent for Drinking Watertreatment-Investigation on arsenic and uranium. Trita-Lwr Lic 2015, 2, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Zemskova, L.; Egorin, A.; Tokar, E.; Ivanov, V. Chitosan-based biosorbents: Immobilization of metal hexacyanoferrates and application for removal of cesium radionuclide from aqueous solutions. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, W. Removal of Strontium Ions by Immobilized Saccharomyces Cerevisiae in Magnetic Chitosan Microspheres. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2017, 49, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Removal of radionuclide Sr2+ ions from aqueous solution using synthesized magnetic chitosan beads. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2012, 242, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, J. Removal of Co2+ from radioactive wastewater by polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/chitosan magnetic composite. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2014, 71, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Chitosan adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1800–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, L.E.; Bloom, T.F.; Hein, M.J. Mortality among a cohort of uranium mill workers: An update. Occup. Environ. Med. 2004, 61, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ara, A.; Khattak, R.; Khan, M.S.; Begum, B.; Khan, S.; Han, C. Synthesis, Characterization, and Solar Photo-Activation of Chitosan-Modified Nickel Magnetite Bio-Composite for Degradation of Recalcitrant Organic Pollutants in Water. Catalysts 2022, 12, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.A.; Onzi, G.R.; Morawski, A.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Contr, R.V. Chitosan as a coating material for nanoparticles intended for biomedicall applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 147, 104459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Arotiba, O.A.; Mamba, B.B. Chitosan-based nanomaterials: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Fu, J.; Gou, D.; Hu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Li, X. Chitosan-Derived Magnetic Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Characterization, and Nitrite Adsorption in Water. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 6420341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. A Review on Chitosan and its Nanocomposites in Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 109, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutirman, Z.A.; Sanagi, M.M.; Abd Karim, K.J.; Ibrahim, W.A.W.; Jume, B.H. Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism studies of Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions adsorption by modified chitosan beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Ayad, D.M.; Wei, Y.; Sarhanb, A.A. Adsorption of Cu(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) ions by modified magnetic chitosan chelating resin. J. Hazard. Mat. 2010, 177, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavan, N.; Mane, S.; Ponrathnam, S. Effect of Chemical Crosslinking on Properties of Polymer Microbeads. A Review. Can. Chem. Trans. 2016, 3, 473–485. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.M.; Reddy, D.H.K. Application of Magnetic Chitosan Composites for the Removal of Toxic Metal and Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 201–202, 68–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yanzhen, X.; Liang, H. MnFe2O4/Chitosan Nanocomposites as a Recyclable Adsorbent for the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 3910–3915. [Google Scholar]
- Khodadust, R.; Unsoy, G.; Yalcin, S.; Gunduz, G.; Gunduz, U. Synthesis Optimization and Characterization of Chitosan Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Produced for Biomedical Applications. J Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 964–977. [Google Scholar]
- Elwakeel, K.Z.; Atia, A.A.; Guibal, E. Fast removal of uranium from aqueous solutions using tetraethylenepentamine modified magnetic chitosan resin. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwakeel, K.Z. Removal of Cr(VI) from Alkaline Aqueous Solutions Using Chemically Modified Magnetic Chitosan Resins. Desalination 2010, 250, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaqarbeh, M.; Khalili, F.I.; Kanoun, O. Manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) as potential nanosorbent for adsorption of uranium(VI) and thorium(IV). J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2020, 323, 515–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesha, B.L.; Sharanagouda, H.; Udaykumar, N.; Ramachandr, C.T.; Dandekar, A.B. Removal of Pollutants from Water/Waste Water Using Nano-Adsorbents: A Potential Pollution Mitigation. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 4868–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbury, D.E. Mistakes encountered during automatic peak identification of minor and trace constituents in electron-excited energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis. Scanning 2009, 31, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczyk, A.; Fievet, P.; Mullet, M.; Reggiani, J.C.; Pagetti, J. Comparison of two electrokinetic methods-electroosmosis and streaming potential-to determine the zeta-potential of plane ceramic membranes. J. Membrane Sci. 1998, 143, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Removal of uranium from contaminated drinking water: A mini review of available treatment methods. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 2915–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, I.; Torapava, N.; Eriksson, I.; Lundberg, D. Hydration and Hydrolysis of Thorium(IV) in Aqueous Solution and the Structures of Two Crystalline Thorium(IV) Hydrates. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 11712–11723. [Google Scholar]
- Choppin, G. Actinide speciation in aquatic systems. Mar. Chem. 2006, 99, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenthe, I.; Szabo, Z.; Toraishi, T.; Vallet, V. Solution coordination chemistry of actinides: Thermodynamics, structure and reaction mechanisms. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 784–815. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaumik, M.; Setshedi, K.; Maity, A.; Onyango, M.S. Chromium(VI) removal from water using fixed bed column of polypyrrole/Fe3O4 nanocomposite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 110, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D. Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Equations for Modeling Adsorption Systems for Removal of Lead Ions Using Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2013, 3, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, S.I.Y.; Khalili, F.I.; Al-Dujaili, A.H. Removal of U(VI) and Th(IV) from Aqueous Solutions by Organically Modified Diatomaceous Earth: Evaluation of Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Data. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 168, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, F.I.; Al-Kakah, M.S.; Ayoub, M.M.; Ismail, L.S. Sorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) ions from aqueous solution using Jordanian kaolinite modified by the amino acids methionine or cysteine. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 151, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zou, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Luo, T.; Liu, Z.; Adesina, A.A. Adsorption of uranium(VI) from aqueous solution using magnetic carboxymethyl chitosan nano-particles functionalized with ethylenediamine. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 308, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. A General Treatment and Classification of the Solute Adsorption Isotherm. I. Theoretical. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humelnicu, D.; Dinu, M.V.; Dragan, E.S. Adsorption characteristics of UO22+ and Th4+ ions from simulated radioactive solutions onto chitosan/clinoptilolite sorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaqarbeh, M. Adsorption Phenomena: Definition, Mechanisms, and Adsorption Types: Short Review. RHAZES Green Appl. Chem. 2021, 13, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S. Cooperative adsorption on solid surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri, A.; Rajabi, S.; Amiri, A.; Fattahizade, M.; Hasani, O.; Lalehzari, A.; Hashemi, M. Adsorption of tetracycline using CuCoFe2O4@Chitosan as a new and green magnetic nanohybrid adsorbent from aqueous solutions: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic study. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Naglah, A.M.; Saad, F.A.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Modification of silica nanoparticles with 1-hydroxy-2-acetonaphthone as a novel composite for the efficient removal of Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), and Hg(II) ions from aqueous media. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, H.K.; Nasef, M.M.; Hadi, N.A.; Nordin, M.; Ting, T.M.; Harun, N.Y.; Saeed, A.A.H. Isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics of boron adsorption on fibrous polymeric chelator containing glycidol moiety optimized with response surface method. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, B.; Chen, Q.; Bai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Davaa, B. Synthesis, Structure, and Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2-Montmorillonite Composites. Catalysts 2022, 12, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatla, A.; Almanassra, I.W.; Kochkodan, V.; Laoui, T.; Alawadhi, H.; Atieh, M.A. Efficient Removal of Eriochrome Black T (EBT) Dye and Chromium (Cr) by Hydrotalcite-Derived Mg-Ca-Al Mixed Metal Oxide Composite. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouaini, F.; Knani, S.; Yahia, B.M.; Lamine, A.B. Statistical physics studies of multilayer adsorption isotherm in food materials and pore size distribution. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2015, 432, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastbaza, A.; Reza, K.A. Adsorption of Th4+, U6+, Cd2+, and Ni2+ from aqueous solution by a novel modified polyacrylonitrile composite nanofiber adsorbentprepared by electrospinning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 293, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Guo, X.; Mao, D.; Meng, T.; Yu, J.; Ma, Z. Phosphotungstic Acid-Modified MnOx for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Ebelegi, A.N.; Wankasi, D. Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3039817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Ren, X. Interaction of Th(IV) with graphene oxides: Batch experiments, XPS investigation, and modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 213, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Husnain, S.M.; Kim, H.J.; Um, W.; Chang, Y.Y.; Chang, Y.S. Superparamagnetic Adsorbent Based on Phosphonate Grafted Mesoporous Carbon for Uranium Removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 9821–9830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Lv, T.; Shi, J. Removal of thorium(IV) from aqueous solution using magnetic ion-imprinted chitosan resin. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 310, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Magied, M.O.; Tolba, A.A.; El-Gendy, H.S.; Zaki, S.A.; Atia, A.A. Studies on the recovery of Th(IV) ions from nitric acid solutions using amino-magnetic glycidyl methacrylate resins and application to granite leach liquors. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzabe, G.H.; Keshtkar, A.R. Application of response surface methodology for thorium adsorption on PVA/Fe3O4/SiO2APTES nanohybrid adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 26, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yao, C. Highly Efficient Removal of Uranium(VI) From Aqueous Solution Using the Polyethyleneimine Modified Magnetic Chitosan. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvin, S.B. Analytical Use of Arsenazo(III), Determination of Thorium, Zirconium, Uranium and Rare Earth Elements. Talanta 1961, 8, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

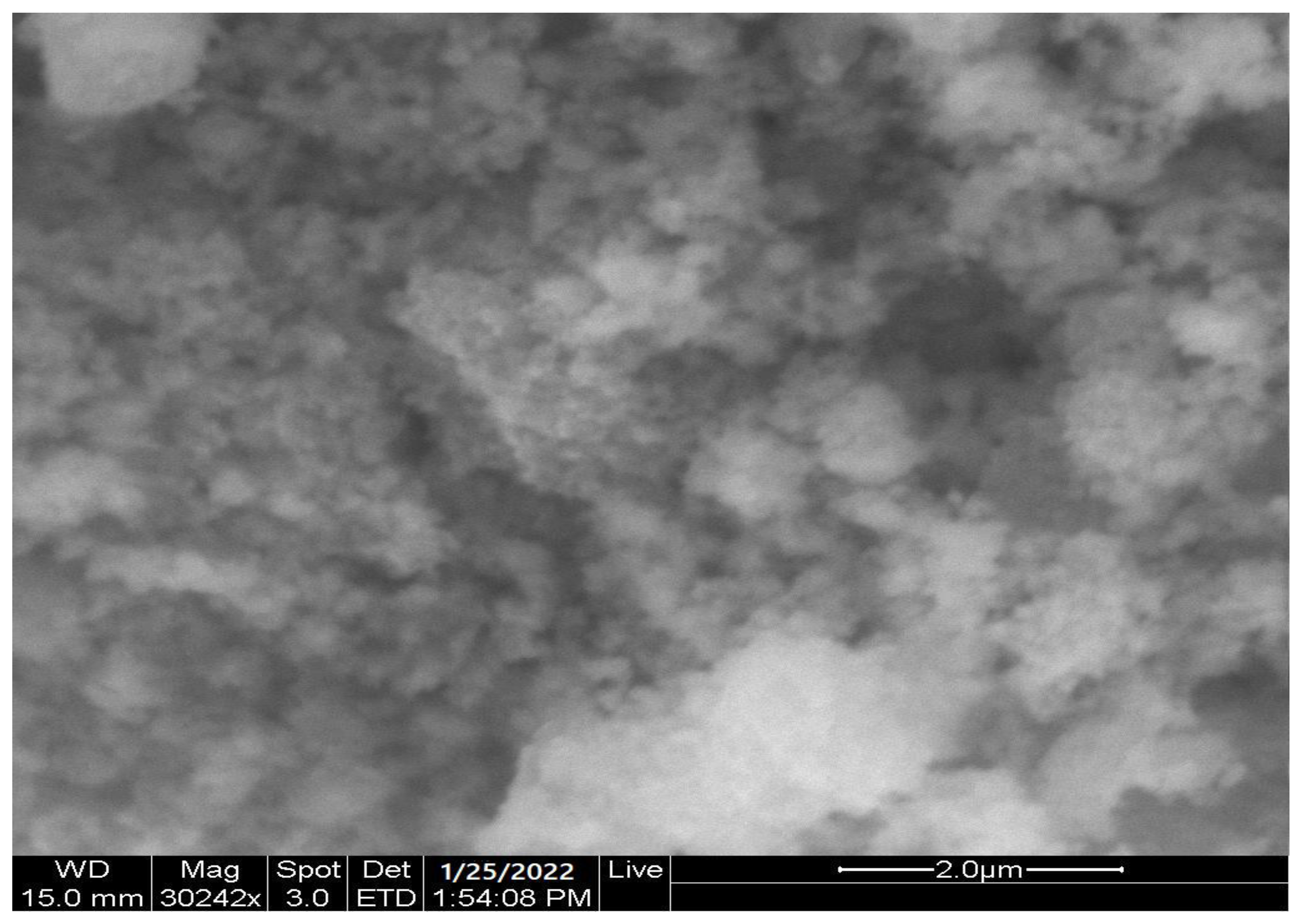
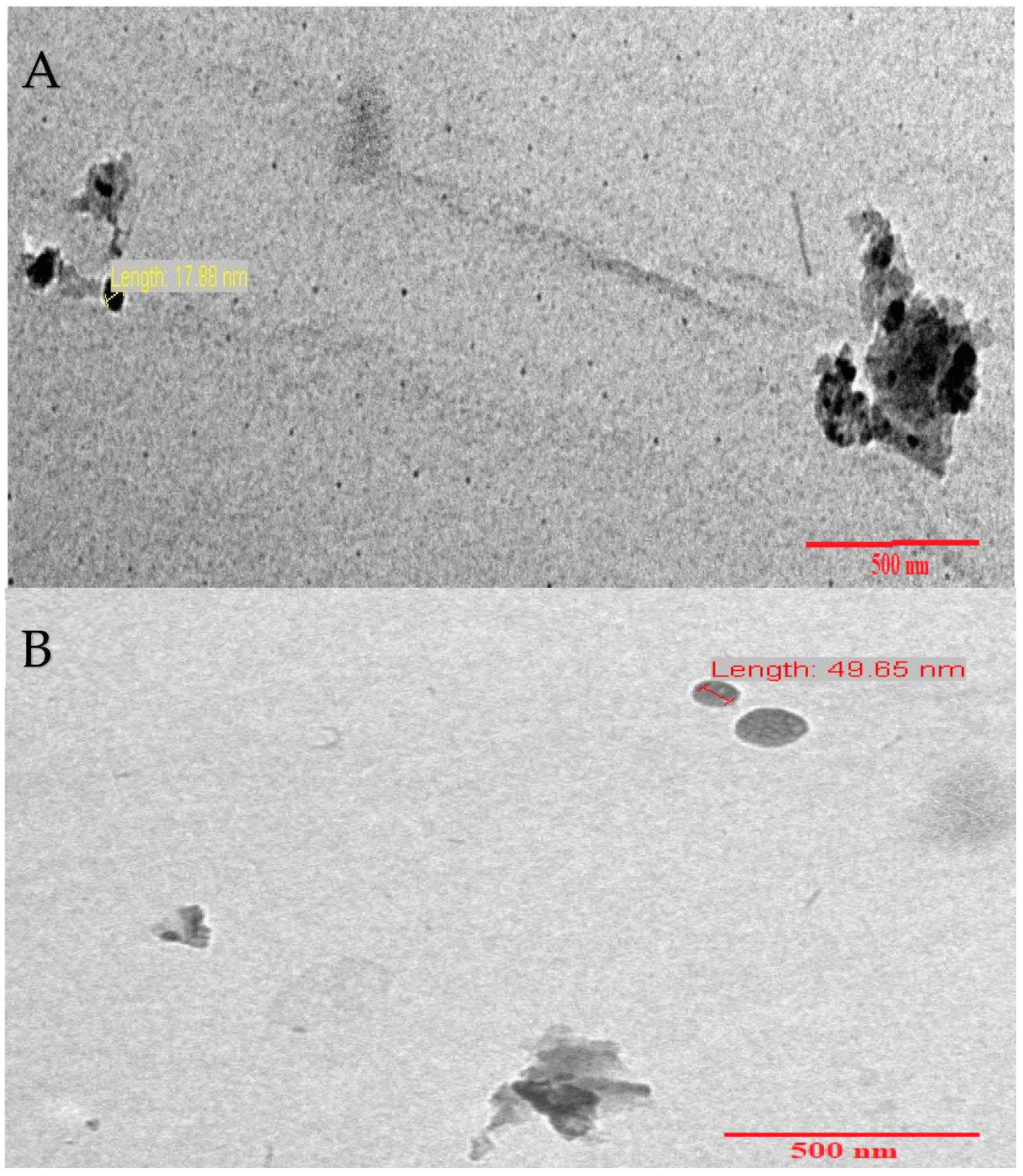

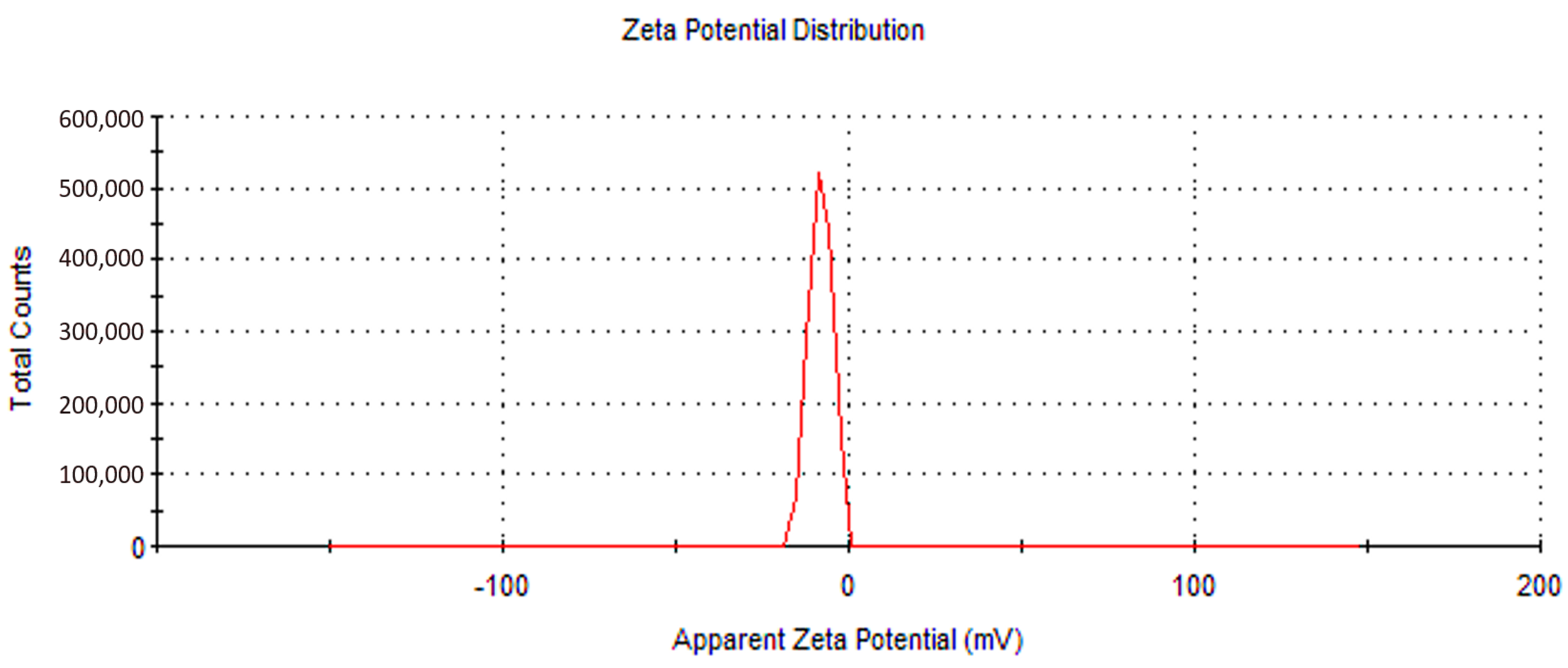

| Samples | Area (nm)2 | Length (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.24 | 15.10 |
| 2 | 13.85 | 17.65 |
| 3 | 12.11 | 17.88 |
| 4 | 20.96 | 49.65 |
| 5 | 28.16 | 63.29 |
| Average | 17.06 | 32.71 |
| Weight% | C Kα | O Kα | Mn Kα | Fe Kα | U Kα | Th Kα |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | ||||||
| MnFe2O4-CS | 35.02 | 18.24 | 12.78 | 34.44 | - | - |
| MnFe2O4-CS /U(VI) | 30.74 | 14.41 | 14.23 | 32.32 | 8.3 | - |
| MnFe2O4-CS /Th(IV) | 33.23 | 16.07 | 11.32 | 30.56 | - | 8.82 |
| Metal Ion, pH | Pseudo 1st Order | Pseudo 2nd Order | qe (mg·g−1) Experimental | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg·g−1) | k1 (h−1) | R2 | qe (mg·g−1) | k2 (g·mg−1·h−1) | R2 | ||
| U(VI), pH 3 | 24.72 | 0.06 | 0.98 | 19.49 | 0.08 | 0.99 | 19.06 |
| Th(IV), pH 3 | 19.45 | 0.10 | 0.91 | 43.29 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 43.33 |
| Mn+, pH | U(VI), pH 3.0 | Th(IV), pH 3.0 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | 25 | 35 | 45 | 25 | 35 | 45 |
| Langmuir | ||||||
| qm (mg/g) | 500.00 | 250.00 | 111.11 | 19.31 | 28.99 | 25.64 |
| KL (L/mg) | 1.90 × 10−3 | 4.10 × 10−3 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| RL (mg/g) | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.62 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.50 |
| R2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.94 |
| Freundlich | ||||||
| Kf (L/mg) | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.38 |
| n | 1.00 | 1.02 | 1.01 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.56 |
| R2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| D-R | ||||||
| qm (mg/g) | 77.19 | 87.96 | 82.35 | |||
| β (mol2/kJ2) | 1.00 × 10−5 | 2.00 × 10−5 | 2.00 × 10−5 | |||
| E (kJ/mol) | 223.71 | 158.13 | 158.13 | |||
| R2 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| Thermodynamic Parameters | U(VI) | Th(IV) |
|---|---|---|
| pH = 3.0 | pH = 3.0 | |
| ΔG° kJ/mol | 0.15 | −10.53 |
| ΔH° kJ/mol | 12.15 | −44.65 |
| ΔS° J/K·mol | 40.03 | −114.49 |
| Metal Ions | Nanosorbent | qm | pH | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U(VI) | Fe3O4 magnetic carboxymethyl chitosan nano- particles functionalizedwith ethylenediamine | 175.40 | 4.5 | [50] |
| U(VI) | phosphonate grafted mesoporous carbon | 150.00 | 4.0 | [65] |
| Th(IV) | Fe3O4 magnetic ion-imprinted chitosan | 147.10 | 4.0 | [66] |
| Th(IV) | amino- Fe3O4 magnetic glycidyl methacrylate nanoparticles | 50.89 | 3.7 | [67] |
| Th(IV) | amino- Fe3O4 magnetic glycidyl divinylbenzene nanoparticles | 68.98 | 3.7 | [67] |
| Th(IV) | Magnetic Fe3O4 /SiO2/ PVA/aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) nanoparticles | 62.50 | 5.0 | [68] |
| U(VI) | Polyethyleneimine Modified Magnetic Chitosan | 181.80 | 6.0 | [69] |
| U(VI) | MnFe2O4 | 80.96 | 3 | [38] |
| 104.04 | 4 | |||
| 76.50 | 5 | |||
| Th(IV) | MnFe2O4 | 179.81 | 3.0 | [38] |
| U(VI) | CCsMFO nanocomposite | 500.00 | 3.0 | Current study |
| Th(IV) | CCsMFO nanocomposite | 77.19 | 3.0 | Current study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alaqarbeh, M.; Khalili, F.; Bouachrine, M.; Alwarthan, A. Synthesis, Characterization and Investigation of Cross-Linked Chitosan/(MnFe2O4) Nanocomposite Adsorption Potential to Extract U(VI) and Th(IV). Catalysts 2023, 13, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010047
Alaqarbeh M, Khalili F, Bouachrine M, Alwarthan A. Synthesis, Characterization and Investigation of Cross-Linked Chitosan/(MnFe2O4) Nanocomposite Adsorption Potential to Extract U(VI) and Th(IV). Catalysts. 2023; 13(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlaqarbeh, Marwa, Fawwaz Khalili, Mohammed Bouachrine, and Abdulrahman Alwarthan. 2023. "Synthesis, Characterization and Investigation of Cross-Linked Chitosan/(MnFe2O4) Nanocomposite Adsorption Potential to Extract U(VI) and Th(IV)" Catalysts 13, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010047
APA StyleAlaqarbeh, M., Khalili, F., Bouachrine, M., & Alwarthan, A. (2023). Synthesis, Characterization and Investigation of Cross-Linked Chitosan/(MnFe2O4) Nanocomposite Adsorption Potential to Extract U(VI) and Th(IV). Catalysts, 13(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010047







