Comparison of Catalytic Properties of the Easily Interconvertible, Water-Soluble [RuHCl(CO)(mtppms-Na)3] and [RuH(H2O)(CO)(mtppms-Na)3][BF4]
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hydrogenation of Phenylacetylene
2.1.1. Hydrogenation of Phenylacetylene in Homogeneous Organic Solution (MeOH)
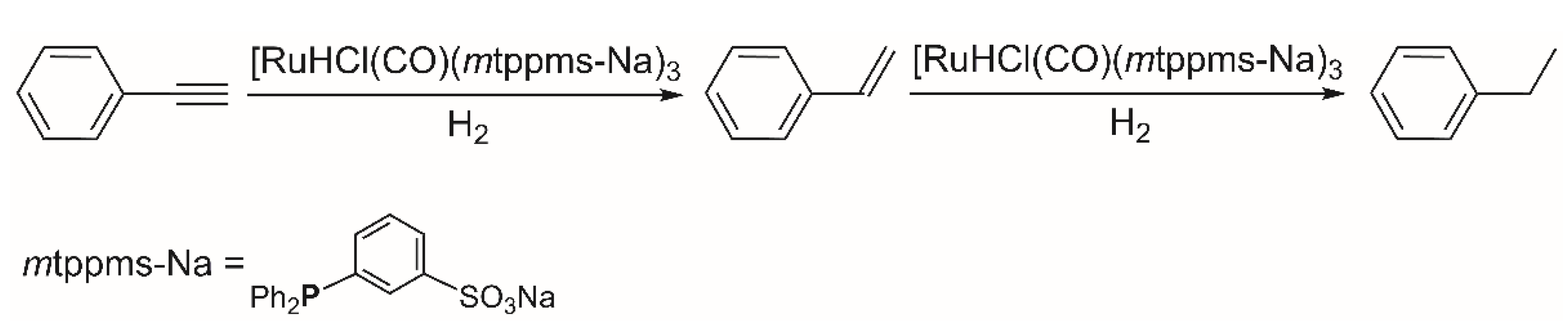
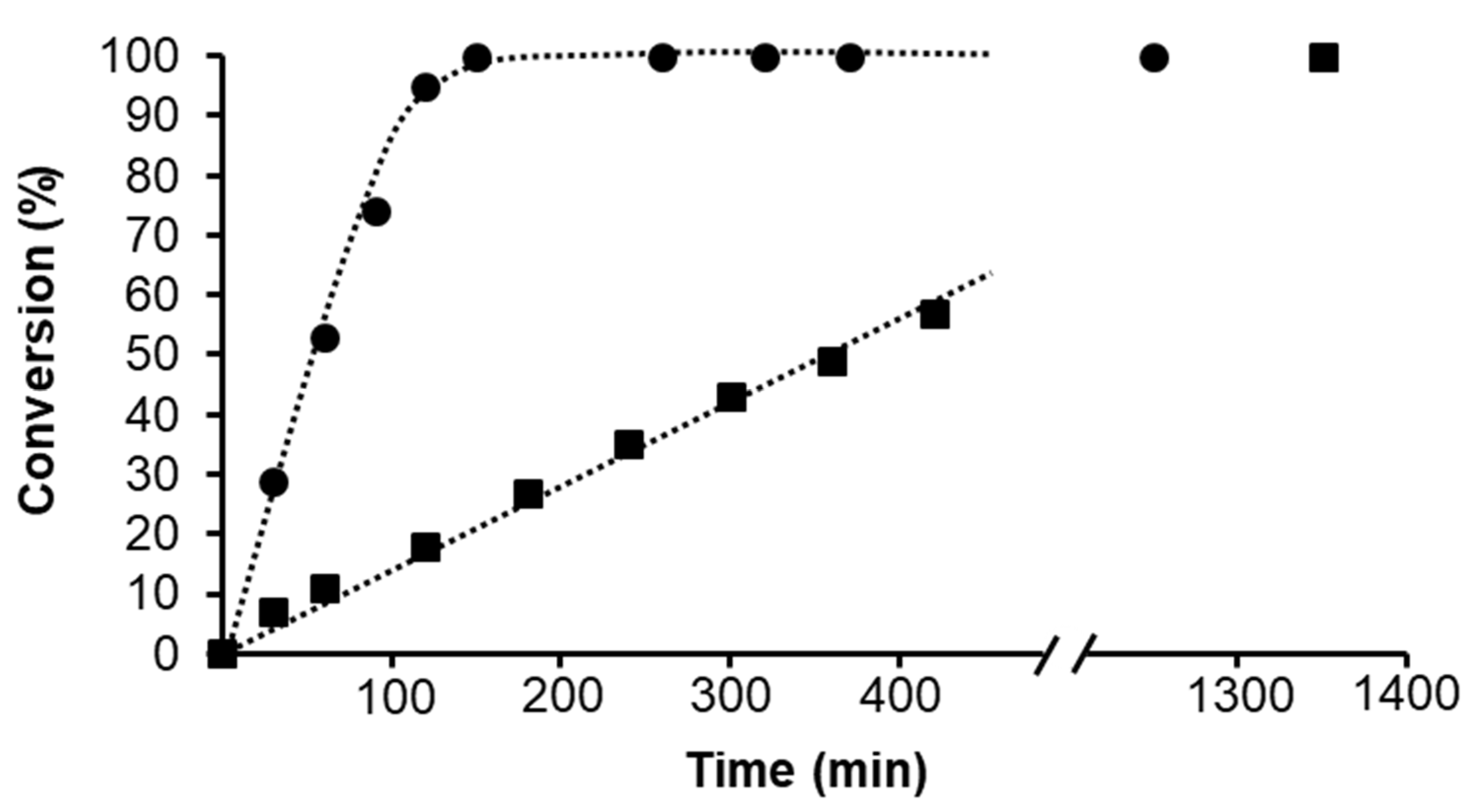
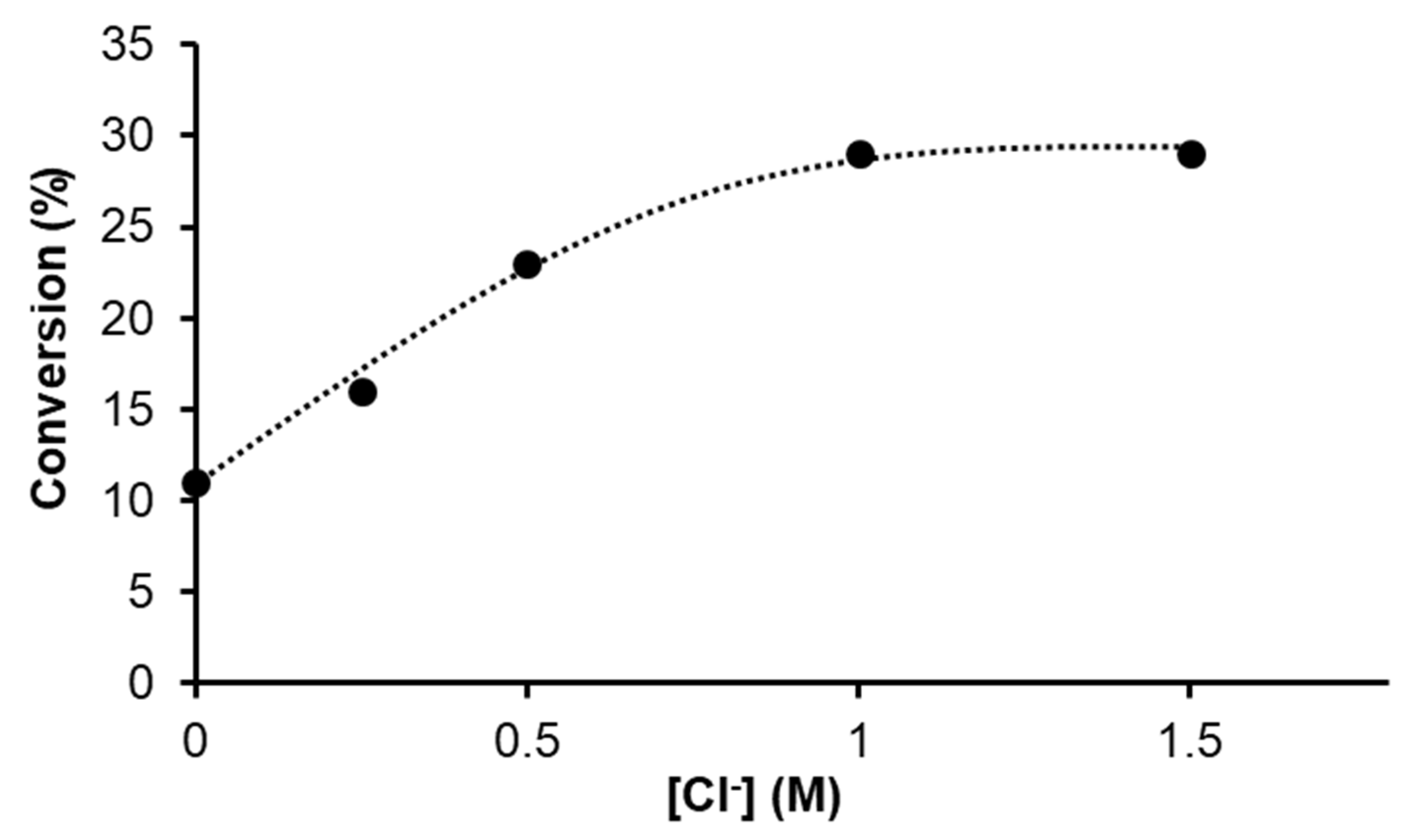
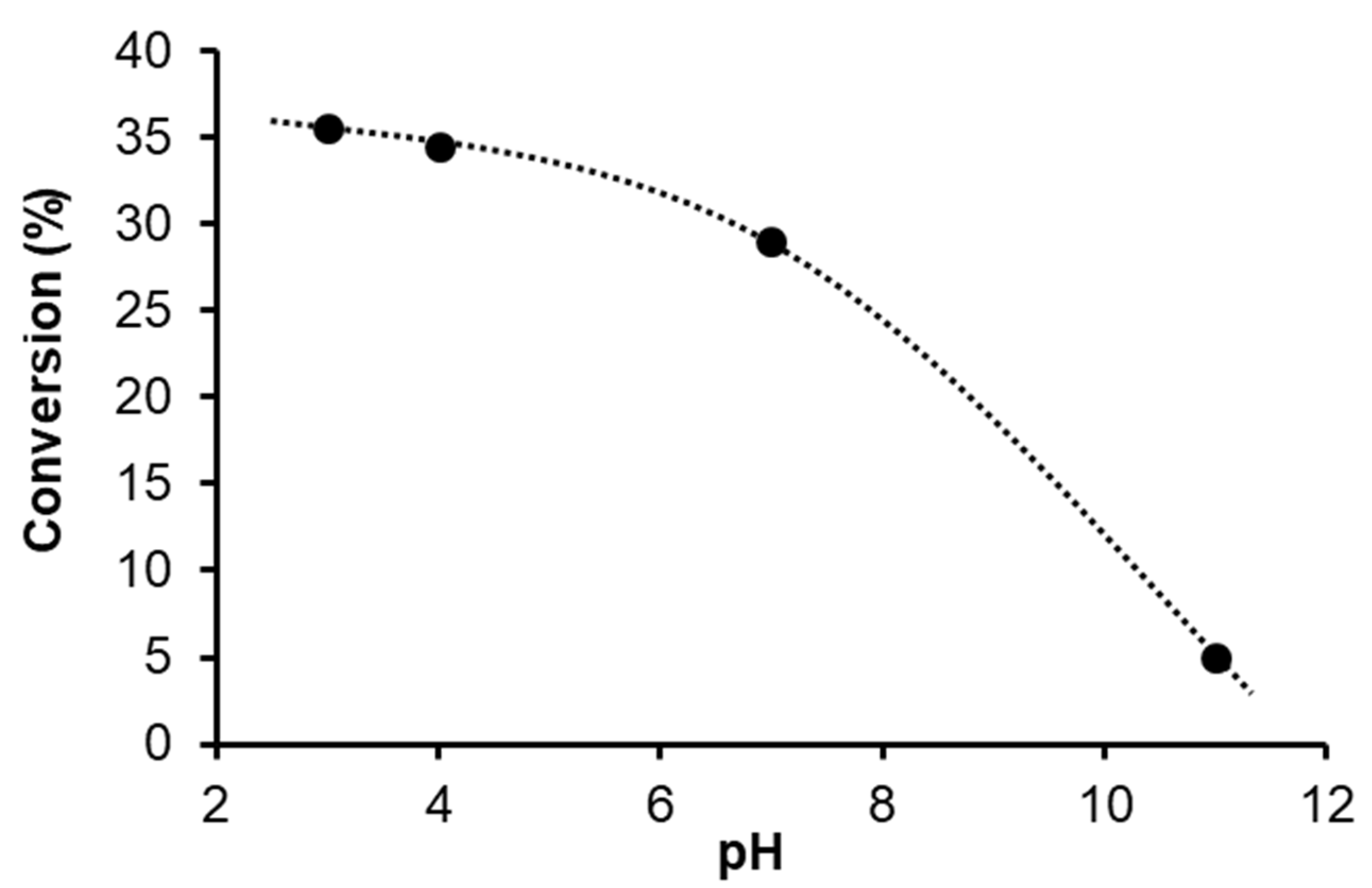
2.1.2. Hydrogenation of Phenylacetylene in water–1,2-dichloroethane (1,2-DCE) Biphasic System
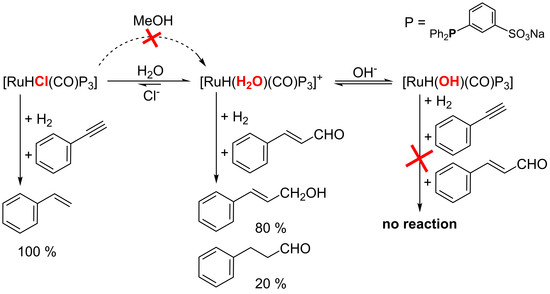
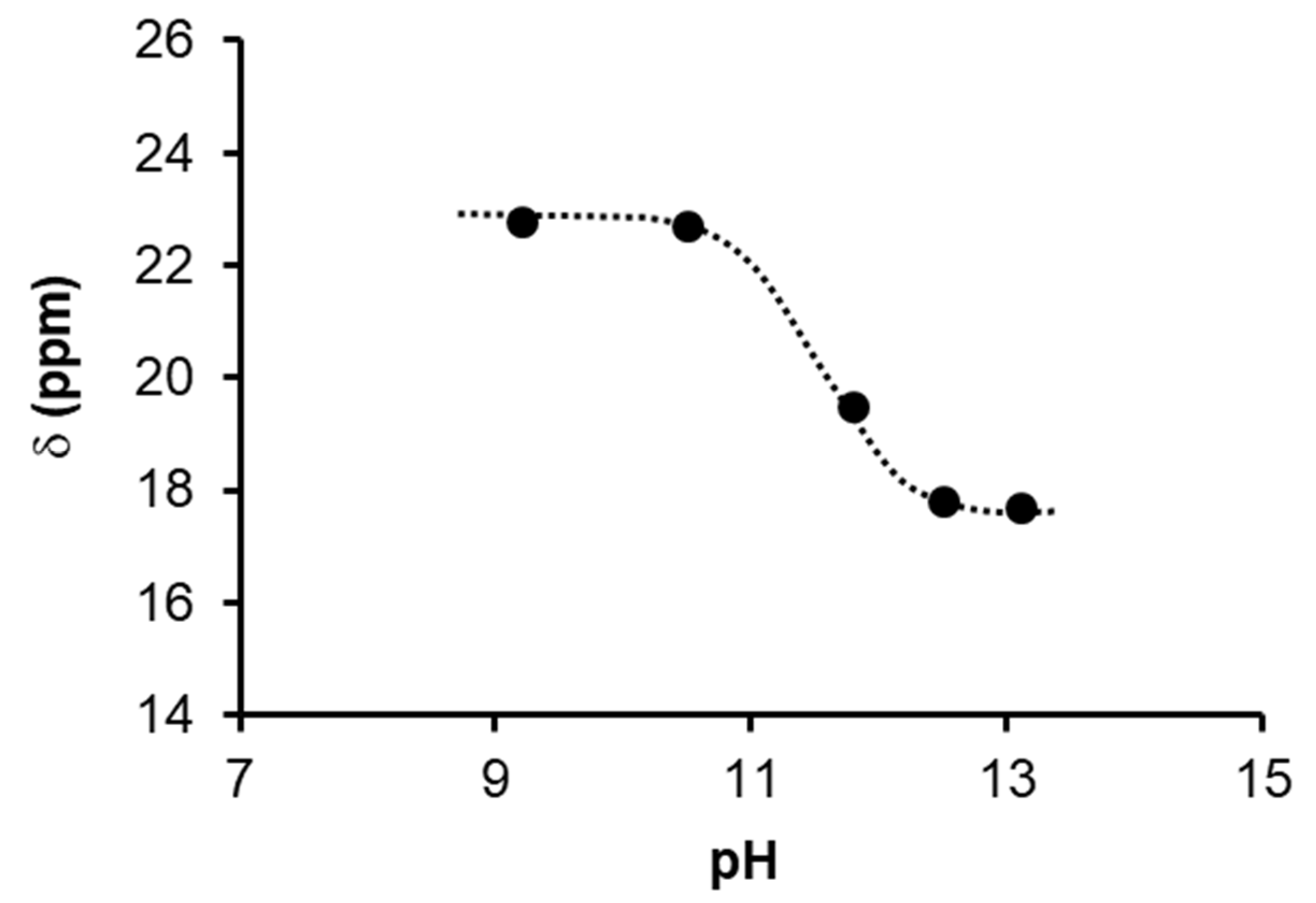
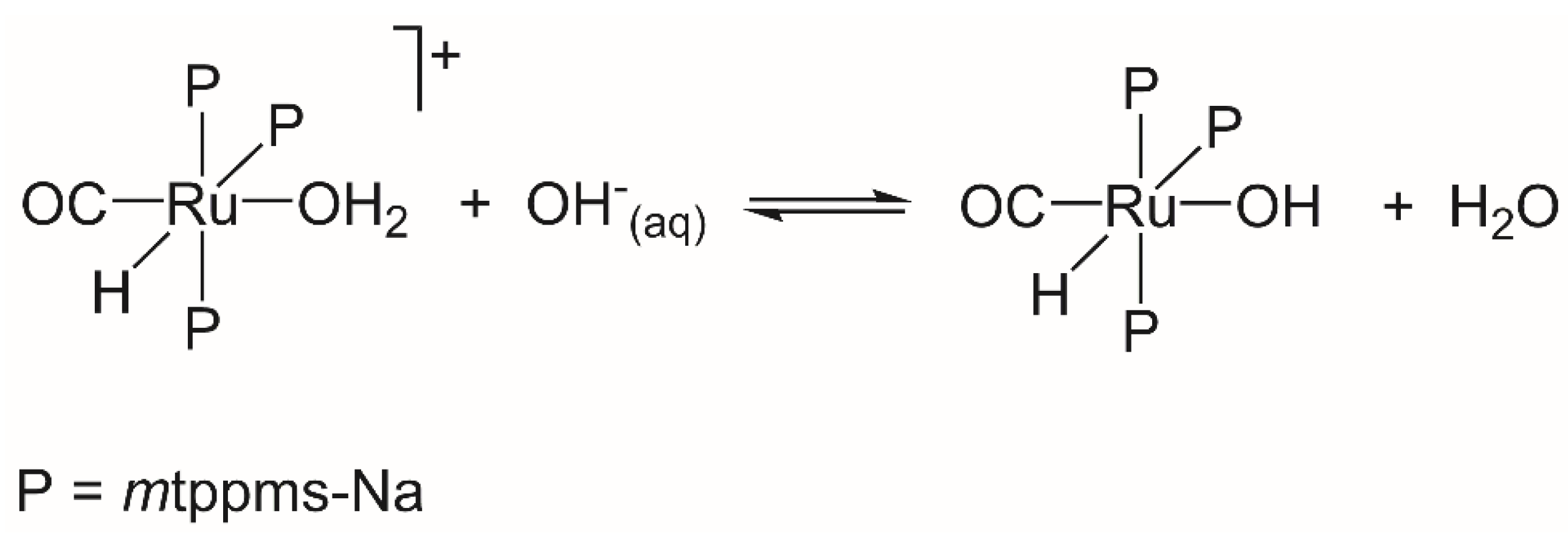
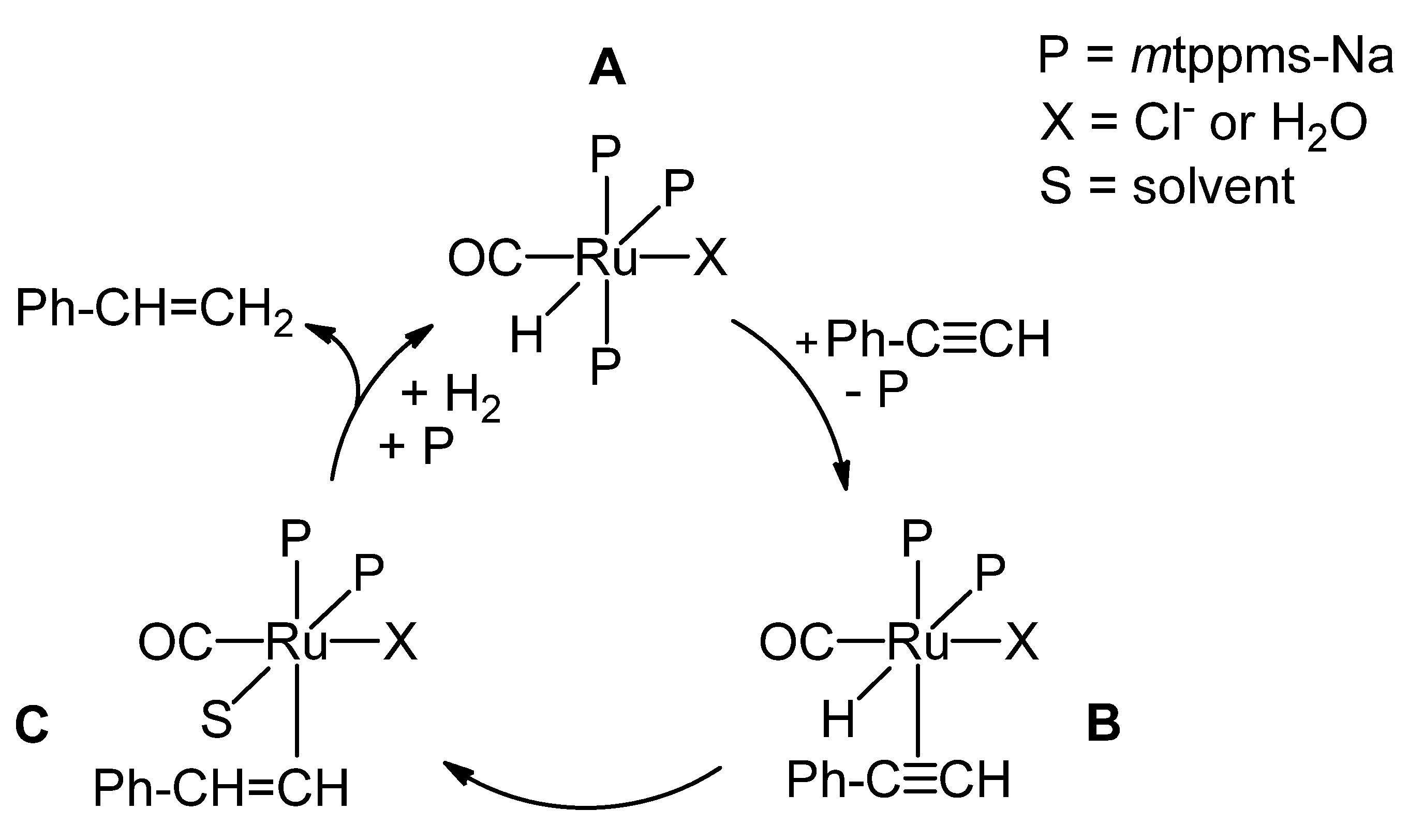
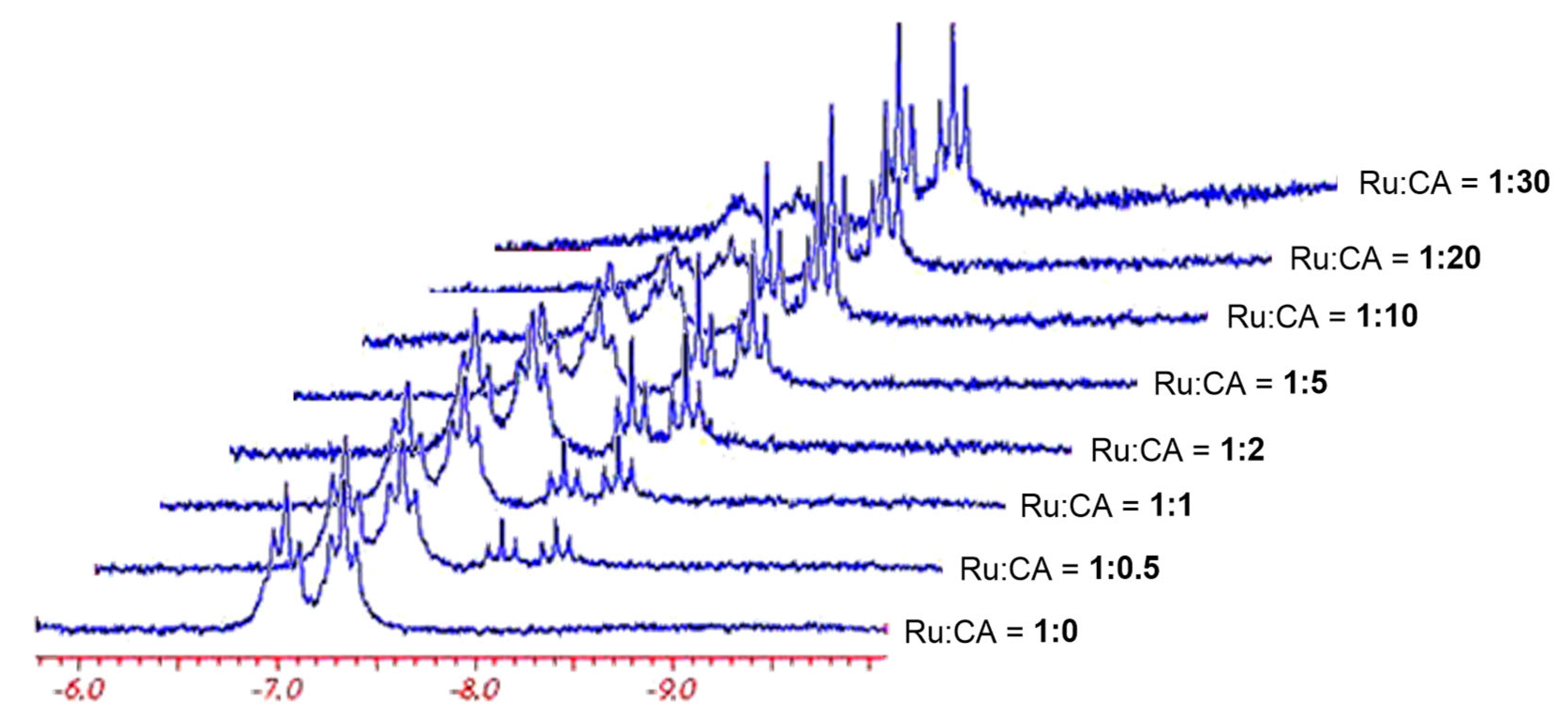
2.1.3. Mechanism of Phenylacetylene Hydrogenation in Aqueous–Organic Biphasic Solvent Mixtures Catalyzed by [RuHCl(CO)(mtppms-Na)3], 1, or [RuH(H2O)(CO)(mtppms-Na)3]+, 2
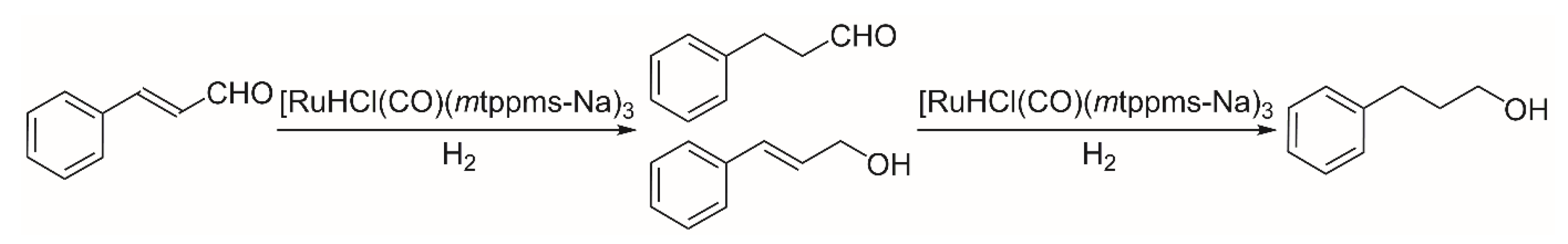
2.2. Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde
2.2.1. Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde in 2-Methoxyethanol
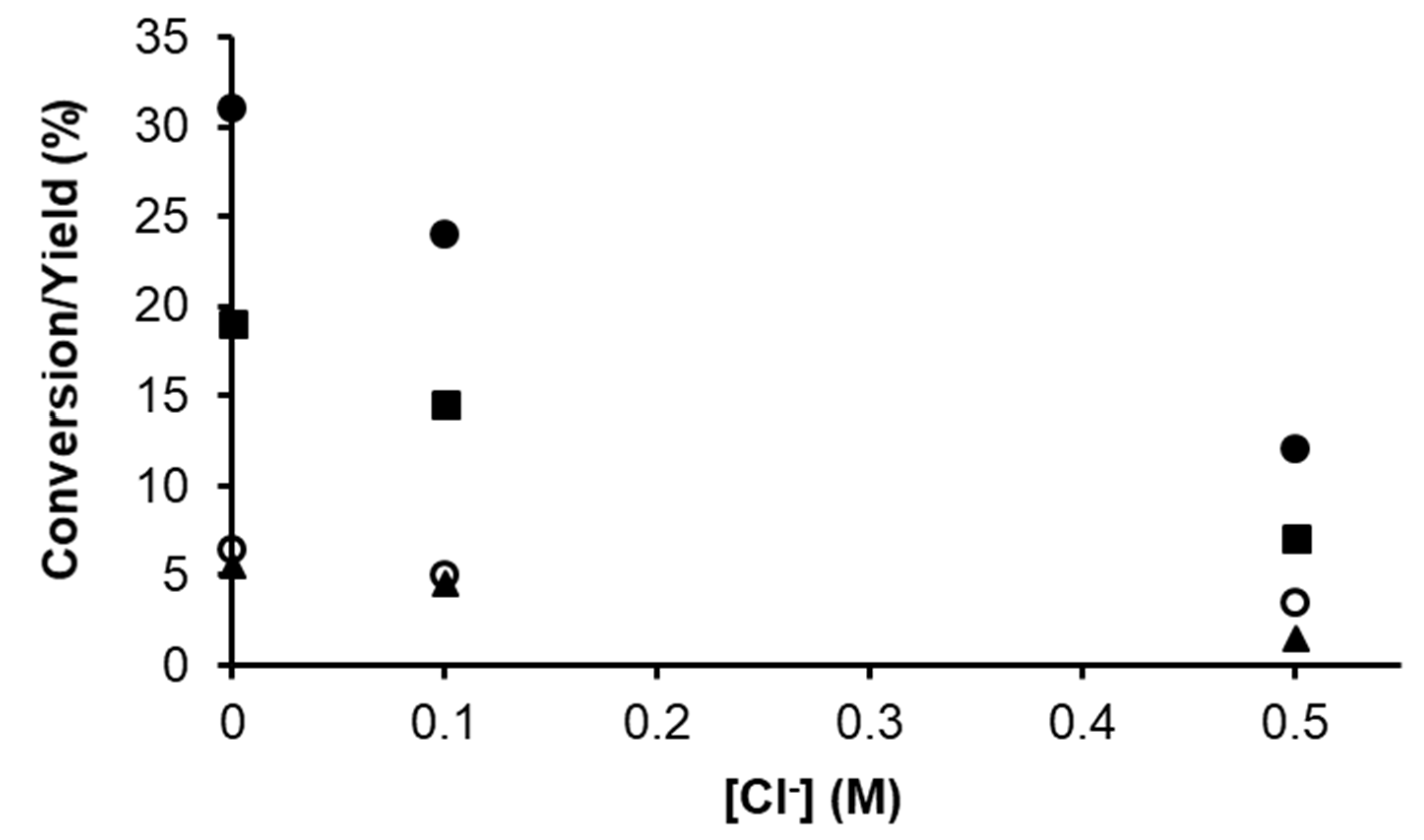
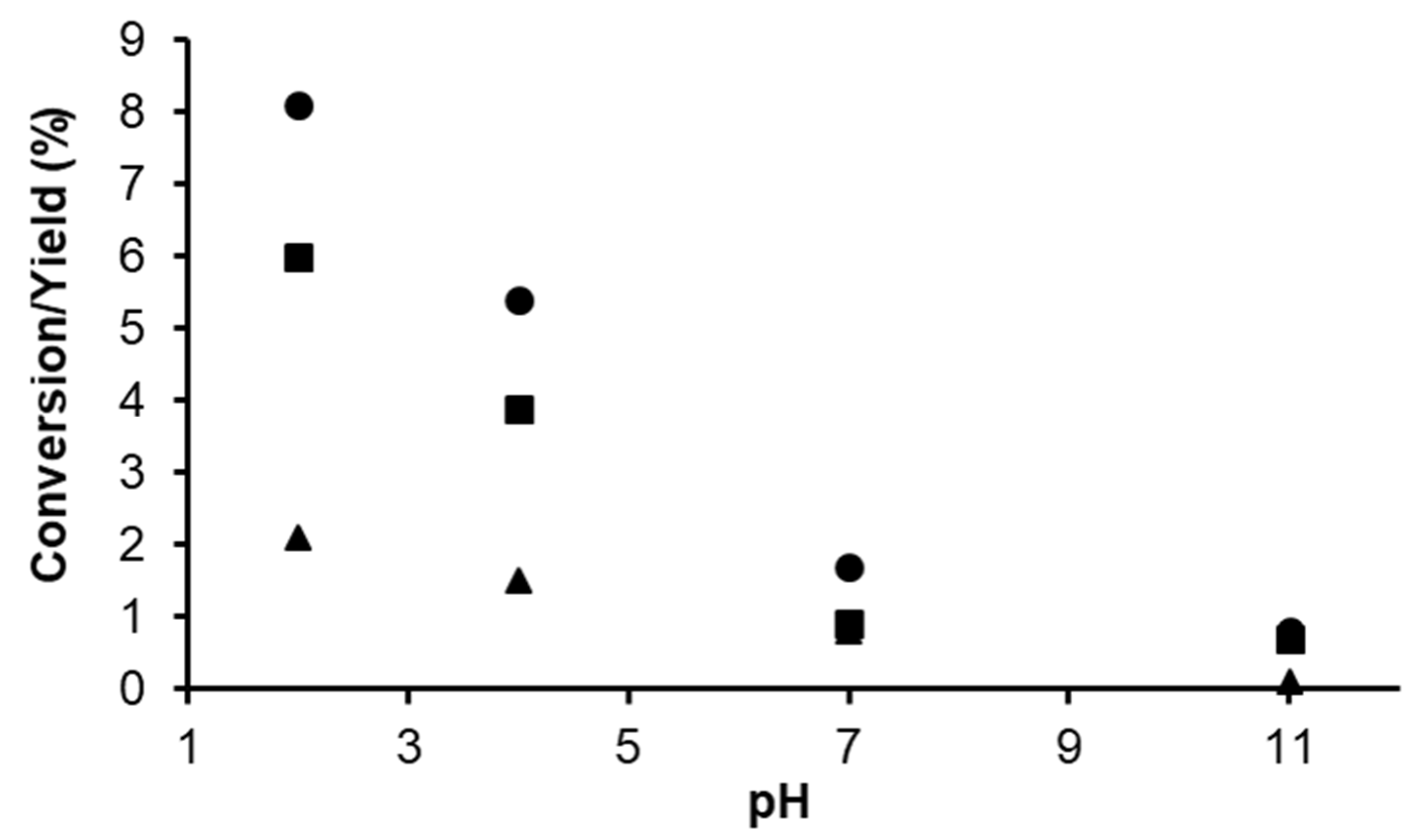
2.2.2. Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde in Aqueous–Organic Biphasic System (water–toluene)
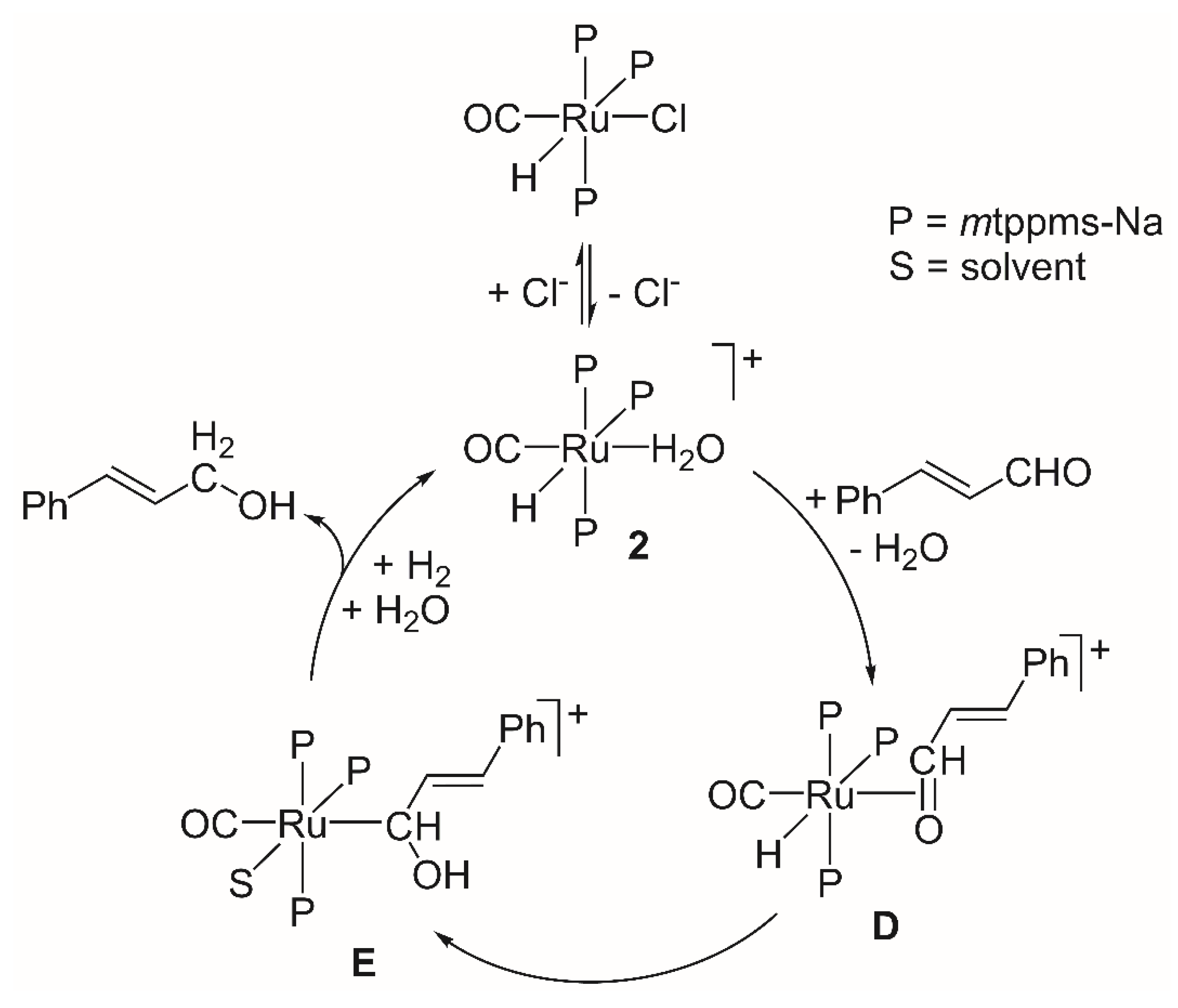
2.2.3. Mechanism of Cinnamaldehyde Hydrogenation Catalyzed by [RuHCl(CO)(mtppms-Na)3], 1, in Aqueous–Organic Biphasic Solvent Mixtures
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.3. General Procedure of Hydrogenation Reactions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaska, L. Homogeneous Catalysis by Five- and Six-Coordinated Metal Hydride Complexes (1,2). Inorg. Nucl. Chem. Lett. 1965, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Levison, J.J.; Robinson, S.D.; Uttley, M.F.; Wonchoba, E.R.; Parshall, G.W. Complexes of Ruthenium, Osmium, Rhodium, and Iridium Containing Hydride Carbonyl, or Nitrosyl Ligands. In Inorganic Syntheses; Parshall, G.W., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, N.J.; Dharmasena, U.L.; Drouin, S.D.; Fogg, D.E. Improved Syntheses of Versatile Ruthenium Hydridocarbonyl Catalysts Containing Electron-Rich Ancillary Ligands. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Delgado, R.A.; De Ochoa, O.L. Homogeneous Hydrogenation of Ketones to Alcohols with Ruthenium Complex Catalysts. J. Organomet. Chem. 1980, 202, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Delgado, R.A.; Valencia, N.; Marquez-Silva, R.; Andriollo, A.; Medina, M. Chemistry and Catalytic Properties of Ruthenium and Osmium Complexes. 3. Development of Highly Active Systems for the Homogeneous Hydrogenation of Aldehydes and Ketones. Inorg. Chem. 1986, 25, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, Y.; Yamamura, K.; Nakayama, I.; Yoshiuchi, K.; Ozawa, F. Mechanistic Study of Ruthenium-Catalyzed Hydrosilation of 1-(Trimethylsilyl)-1-Buten-3-yne. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z. C-Alkylation of Ketones and Related Compounds by Alcohols: Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Dehydrogenation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, T.; Fukuyama, T.; Ryu, I. RuHCl(CO)(PPh3)3-Catalyzed α-Alkylation of Ketones with Primary Alcohols. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4703–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Jia, G.; Liu, F.; Ou, G.; Xie, Y. RuHCl(CO)(PPh3)3-Catalyzed Direct Amidation of Arene C–H Bond with Azides. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 13811–13820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluwer, A.M.; Elsevier, C.J. Homogeneous Hydrogenation of Alkynes and Dienes. In The Handbook of Homogeneous Hydroge Nation; de Vries, J.G., Elsevier, C.J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 374–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathó, Á.; Horváth, H.H.; Papp, G.; Joó, F. Effect of Iodide on the pH-Controlled Hydrogenations of Diphenylacetylene and Cinnamaldehyde Catalyzed by Ru(II)-Sulfonated Triphenylphosphine Complexes in Aqueous–Organic Biphasic Systems. Catalysts 2022, 12, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloner, P.A.; Esteruelas, M.A.; Joó, F.; Oro, L.A. The Mechanisms of Homogeneous Hydrogenation. In Homogeneous Hydrogenation; Catalysis by Metal Complexes; Ugo, R., James, B.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 15, pp. 5–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joó, F.; Kovács, J.; Kathó, Á.; Bényei, A.C.; Decuir, T.; Darensbourg, D.J.; Miedaner, A.; Dubois, D.L. (Meta-Sulfonatophenyl) Diphenylphosphine, Sodium Salt and Its Complexes with Rhodium(I), Ruthenium(II), Iridium(I). In Inorganic Syntheses; Darensbourg, M.Y., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joó, F. Aqueous Organometallic Catalysis; Catalysis by metal complexes; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fache, E.; Santini, C.; Senocq, F.; Basset, J.M. Homogeneous Catalysis in Water Part III. The Catalytic Hydrogenation of Propionaldehyde with (RuCl2L2)2, RuHClL3, RuH(OAc)L3, RuH2L4, RuHIL3, RuCl2(CO)2L2 and [Ru(OAc)(CO)2L]2, (L=P(C6H4–mSO3Na)3·3H2O): A Kinetic Investigation of the Salt Effect in Water. J. Mol. Catal. 1992, 72, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriollo, A.; Bolívar, A.; López, F.A.; Páez, D.E. Homogeneous Catalysis in Water. On the Synthesis and Characterization of a Ruthenium Water-Soluble Complex: Preliminary Hydrogenation of Olefins in a Biphasic System. Inorganica Chim. Acta 1995, 238, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriollo, A.; Carrasquel, J.; Marino, J.; López, F.A.; Páez, D.E.; Rojas, I.; Valencia, N. On the synthesis and characterization of two ruthenium water-soluble complexes: Preliminary results on the hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde in a biphasic system. Surface activity of the ligands TPPMS and TPPTS. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chemical 1997, 116, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baricelli, P.J.; Izaguirre, L.; López, J.; Lujano, E.; López-Linares, F. Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Hydrogenation in Aqueous-Biphasic System of a New Water Soluble Complex RuH(CO)(NCMe)(mTPPMS)3[BF4]. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2004, 208, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, G.; Horváth, H.; Kathó, Á.; Joó, F. Aqueous Organometallic Chemistry. Synthesis and Solution Equilibria of Trisodium Carbonylchlorotris [3-(Diphenylphosphino-kP)Benzenesulfonato]Hydridoruthenate(3−) ([RuH(Cl)(CO){m-(Ph2P)-C6H4-SO3Na}3]) and Trisodium Aquacarbonyltris [3-(Diphenylphosphino-kP). Helv. Chim. Acta 2005, 88, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joó, F.; Kathó, Á. Two-Phase Aqueous Hydrogenations. In The Handbook of Homogeneous Hydrogenation; de Vries, J.G., Elsevier, C.J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 1326–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathó, Á.; Carmona, D.; Viguri, F.; Remacha, C.D.; Kovács, J.; Joó, F.; Oro, L.A. Enantioselective Hydride Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones Catalyzed by [(η6-p-Cymene)Ru(Amino Acidato)Cl] and [(η6-p-Cymene)Ru(Amino Acidato)]3(BF4)3 Complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2000, 593–594, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zékány, L.; Nagypál, I. PSEQUAD. In Computational Methods for the Determination of Stability Constants; Leggett, D.J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.; Horváth, H.; Sola, E.; Kathó, Á.; Joó, F. Water-Soluble Triisopropylphosphine Complexes of Ruthenium(II): Synthesis, Equilibria, and Acetonitrile Hydration. Organometallics 2009, 28, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csabai, P.; Joó, F. Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of New Water-Soluble Ruthenium(II)−N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes. Organometallics 2004, 23, 5640–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Parkinson, J.A.; Morris, R.E.; Sadler, P.J. Highly Selective Binding of Organometallic Ruthenium Ethylenediamine Complexes to Nucleic Acids: Novel Recognition Mechanisms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, J.; Joó, F.; Bényei, A.C.; Laurenczy, G. Reactions of [Ru(H2O)6 ]2+ with Water-Soluble Tertiary Phosphines. Dalton Trans 2004, 15, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, B.; Lorenzo-Luis, P.; Serrano-Ruiz, M.; Papp, É.; Fekete, M.; Csépke, K.; Ősz, K.; Kathó, Á.; Joó, F.; Romerosa, A. Catalysis of Redox Isomerization of Allylic Alcohols by [RuClCp(mPTA)2](OSO2CF3)2 and [RuCp(MPTA)2(OH2-kO)](OSO2CF3)3·(H2O)(C4H10O)0.5. Unusual Influence of the pH and Interaction of Phosphate with Catalyst on the Reaction Rate. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2010, 326, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merola, J.S.; Husebo, T.L.; Matthews, K.E. Aqueous Organometallic Chemistry of mer-Ir(H)2(PMe3)3X Complexes. Organometallics 2012, 31, 3920–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, G.; Ölveti, G.; Horváth, H.; Kathó, Á.; Joó, F. Highly Efficient Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid in Aqueous Solution Catalysed by an Easily Available Water-Soluble Iridium(iii)Dihydride. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 14516–14519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, G.; Horváth, H.; Laurenczy, G.; Szatmári, I.; Kathó, Á.; Joó, F. Classical and Non-Classical Phosphine-Ru(ii)-Hydrides in Aqueous Solutions: Many, Various, and Useful. Dalton Trans 2013, 42, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubas, G.J.; Burns, C.J.; Khalsa, G.R.K.; Van Der Sluys, L.S.; Kiss, G.; Hoff, C.D. Dihydrogen: A Better Ligand than Water? IR and x-Ray Evidence for Aquo Coordination in W(CO)3(PR3)2(H2O), Thermodynamics of H2O Binding versus η2-H2 Binding and H2O/D2 Isotopic Exchange. Implications for the Biological Activation of Hydrogen. Organometallics 1992, 11, 3390–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.R.; Vegas, A.; Santos, A.; Ros, J. Insertion Reactions of Acetylenes with Hydridocarbonyl-Chlorotris(Triphenylphosphine)Ruthenium(II). X-Ray Structure of Carbonylchloro(Cis-1,2-Diphenylethenyl)Bis(Triphenylphosphine)Ruthenium(II). J. Organomet. Chem. 1986, 309, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Wu, W.F.; Yeung, R.C.Y.; Xia, H. Reactions of RuHCl(CO)(PPh3)3 with 1-Alkynols. Preparation and Reactivity of Hydroxyvinyl Complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 1997, 538, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, B.; Bohome-Espinosa, A.B.; Scalambra, F.; Romerosa, A. Ru complexes containing N-methyl-1,3,5-triaza7-phosphaadamantane (mPTA) as catalysts for the isomerization of 2-cyclohexen-1-ol. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2022, e6971, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krȩżel, A.; Bal, W. A Formula for Correlating pKa Values Determined in D2O and H2O. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | 2[BF4] | |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion (%) | 13 | 10.9 |
| Cinnamyl alcohol (%) | 11.8 | 10.7 |
| 3-Phenylpropanal | 1.2 | 0.2 |
| Selectivity (%) | 90.8 | 98.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horváth, H.; Papp, G.; Joó, F.; Kathó, Á. Comparison of Catalytic Properties of the Easily Interconvertible, Water-Soluble [RuHCl(CO)(mtppms-Na)3] and [RuH(H2O)(CO)(mtppms-Na)3][BF4]. Catalysts 2023, 13, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010197
Horváth H, Papp G, Joó F, Kathó Á. Comparison of Catalytic Properties of the Easily Interconvertible, Water-Soluble [RuHCl(CO)(mtppms-Na)3] and [RuH(H2O)(CO)(mtppms-Na)3][BF4]. Catalysts. 2023; 13(1):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010197
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorváth, Henrietta, Gábor Papp, Ferenc Joó, and Ágnes Kathó. 2023. "Comparison of Catalytic Properties of the Easily Interconvertible, Water-Soluble [RuHCl(CO)(mtppms-Na)3] and [RuH(H2O)(CO)(mtppms-Na)3][BF4]" Catalysts 13, no. 1: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010197
APA StyleHorváth, H., Papp, G., Joó, F., & Kathó, Á. (2023). Comparison of Catalytic Properties of the Easily Interconvertible, Water-Soluble [RuHCl(CO)(mtppms-Na)3] and [RuH(H2O)(CO)(mtppms-Na)3][BF4]. Catalysts, 13(1), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010197