Facile Synthesis of Fe(0)@Activated Carbon Material as an Active Adsorbent towards the Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Media
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
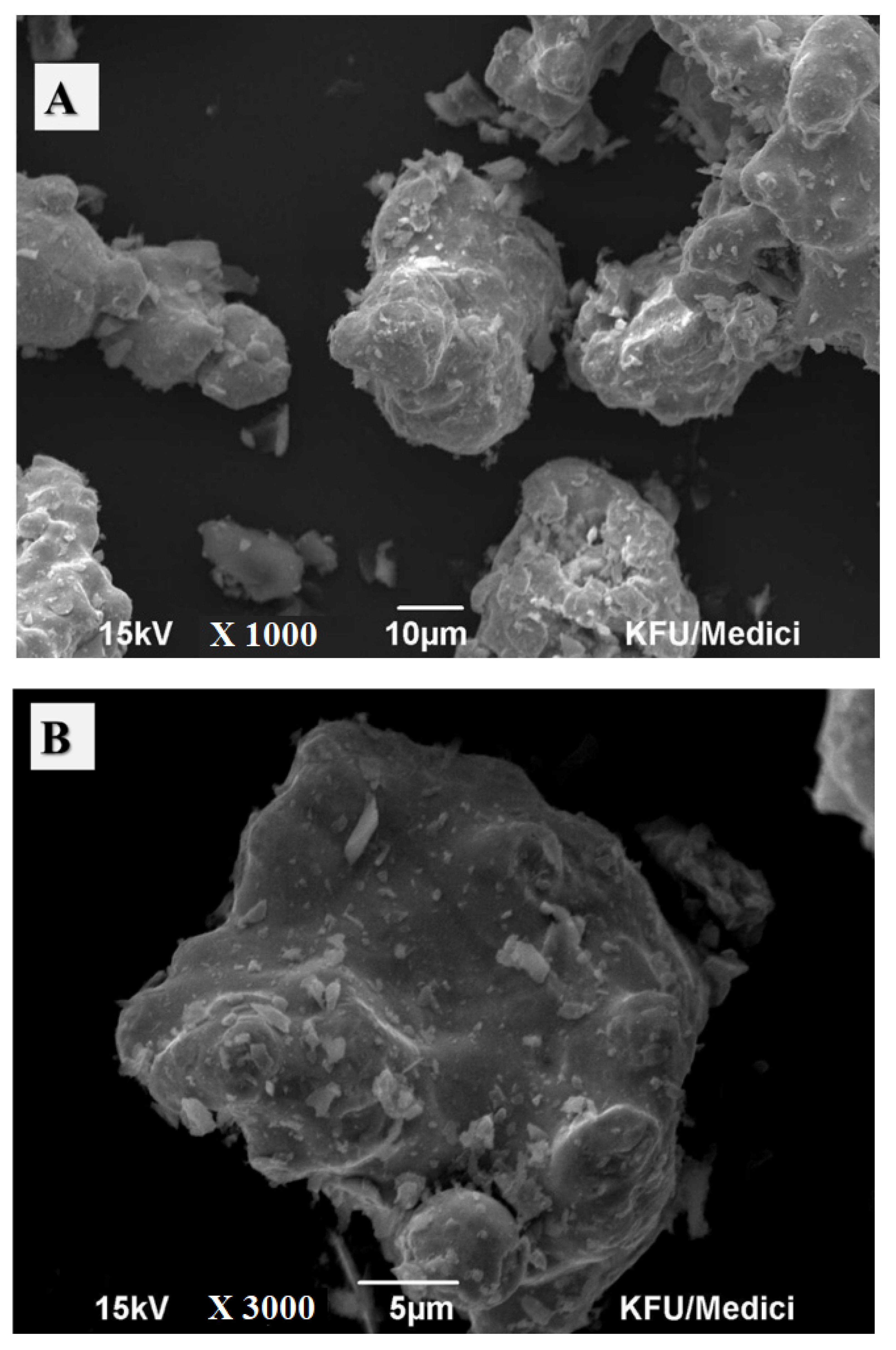
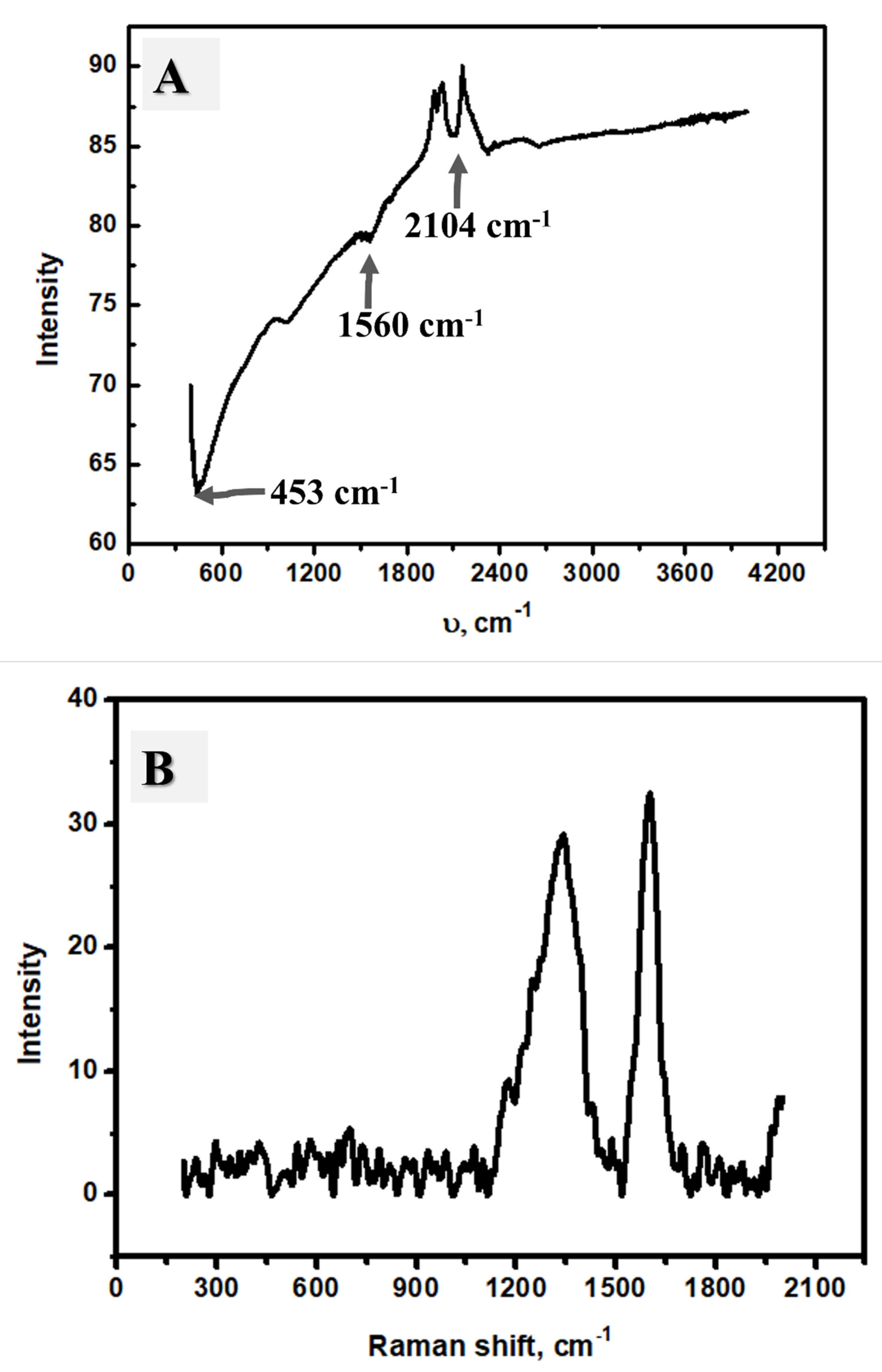
2.1. Material Characterization
2.2. Cr(VI) Adsorption Study

2.3. Adsorption Isotherm Studies
2.4. Adsorbent Characterization after Adsorption
2.5. The Adsorption Capacity Comparison and pH of Solution for Cr (VI) Removal of with Some Reported Adsorbent Materials
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Fe(0)@Activated Carbon Material
3.2. Material Categorization
3.3. Batch Adsorption Experimentations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, J.; Pu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Yu, A.; Zhang, X.; Pan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, G. Adsorption and Reduction of Cr(VI) Together with Cr(III) Sequestration by Polyaniline Confined in Pores of Polystyrene Beads. Environ. Sci. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12602–12611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Hua, S.; Wang, C.; Qiu, M.; Jin, L.; Hu, B. Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using cost-effective caffeic acid functionalized corn starch. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Tian, X.; Yang, C.; Luo, W.; Nie, Y.; Wang, Y. Polyethylenimine-Functionalized Corn Bract, an Agricultural Waste Material, for Efficient Removal and Recovery of Cr(VI) from Aqueous, Solution. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7153–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, J.; Duan, M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.; Liu, R.; Zhang, R. Insight into the adsorption-interaction mechanism of Cr (VI) at the silica adsorbent surface by evanescent wave measurement. Langmuir 2019, 35, 14414–14427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Z.; Liu, L.; Qiu, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Tan, W.; Liu, C.; Wu, F. Photochemical Formation Process of Schwertmannite on Montmorillonite and Corresponding Cr(VI) Adsorption Capacity. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.P.; Chakraborty, P.; Ghosh, R.; Paul, S.; Mondal, S.; Panja, A.; Nandi, A.K. Folic Acid-Polyaniline Hybrid Hydrogel for Adsorption/Reduction of Chromium(VI) and Selective Adsorption of Anionic Dye from Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9325–9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, G.; Tolba, R.; Chen, A. Integrated lignin-mediated adsorption-release process and electrochemical reduction for the removal of trace Cr(vi). RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 27843–27849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. A super biosorbent from dendrimer poly(amidoamine)-grafted cellulose nanofibril aerogels for effective removal of Cr(vi). J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14703–14711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ayati, A.; Ghanbari, S.; Orooji, Y.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Rouhi, J.; Fu, L.; Sillanpää, M. Recent advances in removal techniques of Cr (VI) toxic ion from aqueous solution: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-X.; Han, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-C. Fabrication strategies and Cr (VI) elimination activities of the MOF-derivatives and their composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orooji, Y.; Nezafat, Z.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Kamali, T.A. Polysaccharide-based (nano) materials for Cr (VI) removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 950–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y. Highly efficient and ultrafast removal of Cr (VI) in aqueous solution to ppb level by poly (allylamine hydrochloride) covalently cross-linked amino-modified graphene oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, N.; Gong, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. Cu–Fe embedded cross-linked 3D hydrogel for enhanced reductive removal of Cr (VI): Characterization, performance, and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhao, H.; Lyu, H.; Li, D. Development of a novel pyrite/biochar composite (BM-FeS2@ BC) by ball milling for aqueous Cr (VI) removal and its mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Zhang, G.; Du, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, J. Preparation and application of BiOBr-Bi2S3 heterojunctions for efficient photocatalytic removal of Cr (VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhao, X.; Sun, H.; Geng, Z.; She, D. Synthesis of a novel three-dimensional porous carbon material and its highly selective Cr (VI) removal in wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhao, J.; He, F.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, F.; Bashir, M.A. Ball milling biochar iron oxide composites for the removal of chromium (Cr (VI)) from water: Performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-H.; Dong, M.; Li, R.-Q.; Cui, Y.-Q.; Xie, G.-X.; Wang, X.-X.; Long, Y.-Z. Enhancement of Cr (VI) removal efficiency via adsorption/photocatalysis synergy using electrospun chitosan/g-C3N4/TiO2 nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, I.M.A.; Dao, V.-D.; Yasin, A.S.; Barakat, N.A.M.; Choi, H.-S. Design of an efficient photoanode for dye-sensitized solar cells using electrospun one-dimensional GO/N-doped nanocomposite SnO2/TiO2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 400, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, A.S.; Mohamed, I.M.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Design of novel electrode for capacitive deionization using electrospun composite titania/zirconia nanofibers doped-activated carbon. Mater. Lett. 2018, 213, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, A.; Sun, Y.; Peng, M.; Gu, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W. Amino-functionalized MXenes for efficient removal of Cr (VI). Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 617, 126388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsini, A.; Naciri, Y.; Laabd, M.; Bouziani, A.; Navío, J.A.; Puga, F.; Boukherroub, R.; Lakhmiri, R.; Albourine, A. Development of a novel PANI@ WO3 hybrid composite and its application as a promising adsorbent for Cr (VI) ions removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Myslin, M.; Lapchuk, I.; Shyichuk, A.; Murthy, A.P.; Gargula, R.; Kurzydło, P.; Bogacz, B.F.; Pędziwiatr, A.T. Magnesium-zinc ferrites as magnetic adsorbents for Cr (VI) and Ni (II) ions removal: Cation distribution and antistructure modeling. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qian, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Han, L.; Shang, X.; Li, J.; Gu, M.; Chen, M. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by attapulgite produced at different acid modification: Synthesis mechanism and the role of silicon on Cr (VI) removal. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounab, N.; Duclaux, L.; Reinert, A.; Oumedjbeur, A.; Boukhalfa, C.; Penhoud, P.; Muller, F. Improvement of zero valent iron nanoparticles by ultrasound-assisted synthesis, study of Cr (VI) removal and application for the treatment of metal surface processing wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasili, E.; Bavasso, I.; Petruccelli, V.; Vilardi, G.; Valletta, A.; Bosco, C.D.; Gentili, A.; Pasqua, G.; Di Palma, L. Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated water through zero-valent iron nanoparticles and effects on tomato plant growth performance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.-L.; Sun, Y. Remediation of arsenic(III) from aqueous solutions using improved nanoscale zero-valent iron on pumice. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Jin, Z.; Li, T.; Qi, X. Kinetics of hexavalent chromium removal from water by chitosan-Fe0 nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhang, M.; Qian, T.; Zhao, D. Transport of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized iron nanoparticles in porous media: Column experiments and modeling. J. Colloid Inter. Face Sci. 2009, 334, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jones, H.; Zhang, P.; Bowman, R.S. Chromate transport through columns packed with surfactant-modified zeolite/zero valent iron pellets. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, A.S.; Mohamed, I.M.; Amen, M.T.; Barakat, N.A.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Incorporating zirconia nanoparticles into activated carbon as electrode material for capacitive deionization. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 772, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, A.S.; Jeong, J.; Mohamed, I.M.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Fabrication of N-doped &SnO2-incorporated activated carbon to enhance desalination and bio-decontamination performance for capacitive deionization. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 729, 764–775. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, I.M.; Yasin, A.S.; Liu, C. Synthesis, surface characterization and electrochemical performance of ZnO @ activated carbon as a supercapacitor electrode material in acidic and alkaline electrolytes. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 3912–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Ou, X.; Wei, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, K.; Qin, Q.; Meng, L.; Fan, M.; Li, B.; Dong, L. Insight into the effect of oxygen vacancies and OH groups on anatase TiO2 for CO oxidation: A combined FT-IR and density functional theory study. Mol. Catal. 2021, 511, 111755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, W.; Zhang, L.; Kong, Q.; Wang, W. Efficient adsorption of sulfamethazine onto modified activated carbon: A plausible adsorption mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Santos, A.M.d.S.; Cunha, J.R.; Dasgupta, A.; Fujisawa, K.; Ferreira, O.P.; Lobo, A.O.; Terrones, M.; Terrones, H.; Viana, B.C. CO2 Sensing by in-situ Raman spectroscopy using activated carbon generated from mesocarp of babassu coconut. Vib. Spectrosc. 2018, 98, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Lateef, H.M.A.; Al-Omair, M.A.; Touny, A.H.; Saleh, M.M. Enhanced adsorption and removal of urea from aqueous solutions using eco-friendly iron phosphate nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.-X.; Yan, L.; Zhou, X.-H.; Huang, S.-T.; Liang, J.-Y.; Zhang, W.-X.; Guo, Z.-W.; Guo, P.-R.; Qian, W.; Kong, L.-J. Simultaneous adsorption of Cr(VI) and phenol by biochar-based iron oxide composites in water: Performance, kinetics and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Adsorptive removal of Cr (VI) by Fe-modified activated carbon prepared from Trapa natans husk. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, D.; Goyal, M.; Bansal, R.C. Adsorption of chromium by activated carbon from aqueous solution. Carbon 1999, 37, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Fan, M.; Yang, D.; He, H.; Liu, D.; Yuan, A.; Zhu, J.; Chen, T. Montmorillonite-supported magnetite nanoparticles for the removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiral, H.; Demiral, I.; Tümsek, F.; Karabacakoğlu, B. Adsorption of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution by activated carbon derived from olive bagasse and applicability of different adsorption models. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, N.R.; Bajaj, M.; Sharma, N.; Gupta, A. Adsorption of Cr(VI) on activated rice husk carbon and activated alumina. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 91, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Duan, Y.; Xu, X. Facile Preparation of Amine-Rich Polyamidoamine (PAMAM) Gel for Highly Efficient Removal of Cr(VI) Ions. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 579, 123685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Weeks, B.L.; Connor, O.R.; Huang, X.; Wei, S.; Guo, Z. Cr(vi) Removal by Magnetic Carbon Nanocomposites Derived from Cellulose at Different Carbonization Temperatures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9817–9825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, W.; Vasiliev, A.L.; Zhu, K.; Padture, N.P. Room-Temperature Crystallization of Hybrid-Perovskite Thin Films via Solvent–Solvent Extraction for High-Performance Solar Cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 8178–8184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, U.C.; Goswami, S. Studies on Adsorption Behaviour of Cr(VI) onto Synthetic Hydrous Stannic Oxide. Water SA 2006, 31, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baral, S.S.; Das, S.N.; Rath, P. Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption on Treated Sawdust. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 31, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabour, B.; Belattmani, Z.; Tahiri, S.; Zrid, R.; Reani, A.; Elatouani, S.; Loukili, H.; Hassouani, M.; El Krati, M.; Bentiss, F. Bioremoval of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solutions by the Brown Seaweed Dictyopteris Polypodioides. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 9, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parlayici, Ş.; Pehlivan, E. Comparative Study of Cr(VI) Removal by Bio-Waste Adsorbents: Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanthi, T.; Selvarajan, V.M. Removal of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Carbon Prepared from Henna Leaves. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badessa, T.S.; Wakuma, E.; Yimer, A.M. Bio-Sorption for Effective Removal of Chromium(VI) from Wastewater Using Moringa Stenopetala Seed Powder (MSSP) and Banana Peel Powder (BPP). BMC Chem. 2020, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owalude, S.O.; Tella, A.C. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption on Modified Groundnut Hull. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Jiang, Z.; Chang, G.; Hu, B. Simultaneous On-Line Preconcentration and Determination of Trace Metals in Environmental Samples by Flow Injection Combined with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Using a Nanometer-Sized Alumina Packed Micro-Column. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2005, 540, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Guo, D.; Liang, W.; Liu, Y. Facile Synthesis of Magnetic Biochar Derived from Burley Tobacco Stems towards Enhanced Cr (VI) Removal: Performance and Mechanism. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



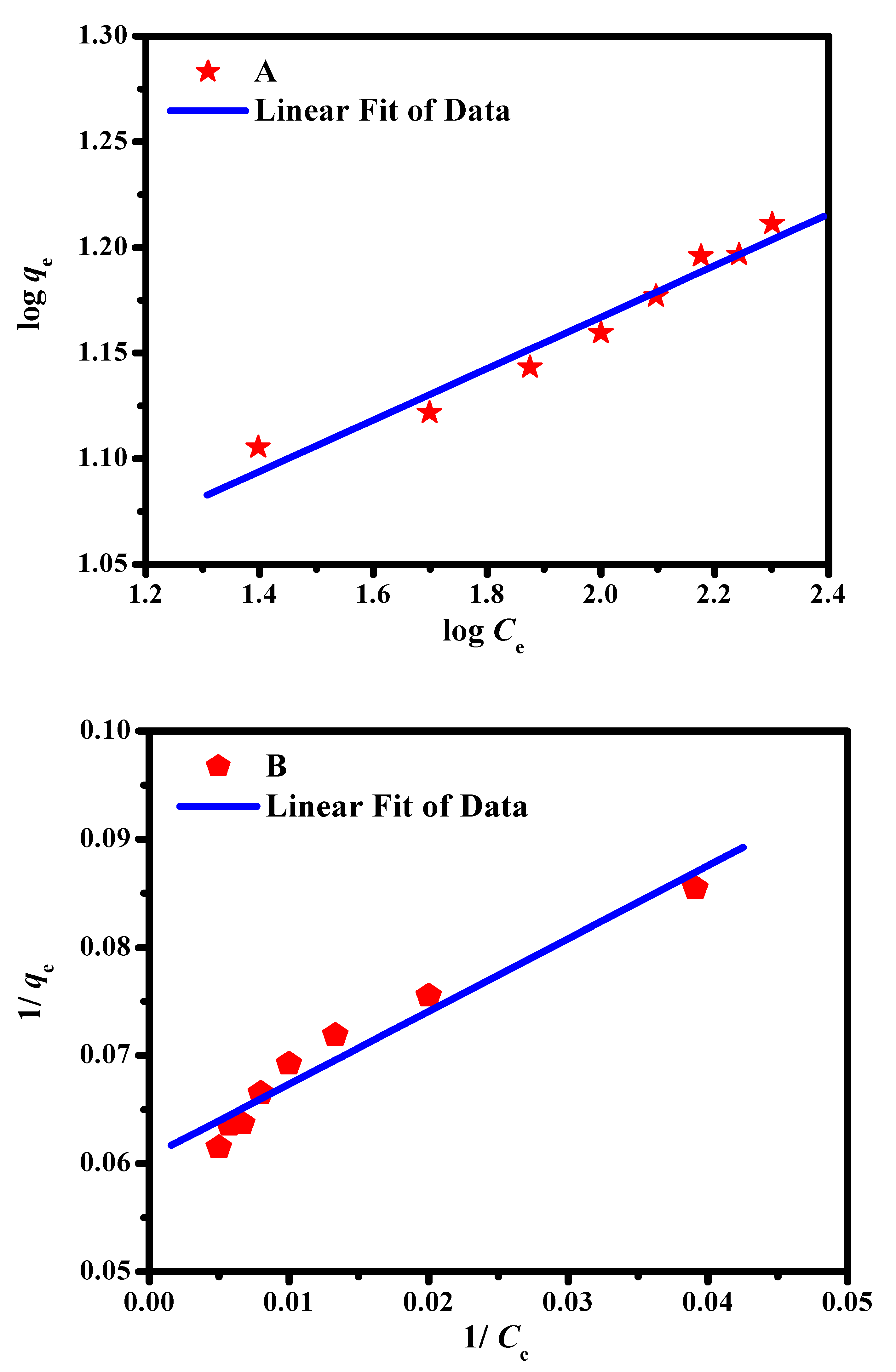


| Model | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | Kf | n | R2 |
| Values | 38.4 | 0.038 | 0.977 | 6.32 | 8.33 | 0.971 |
| Sorbents | Optimum pH | Sorbent/Solution Ratio (g L−1) | Adsorption Capacity qm (mg g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(0)@AC | 2 | 6 | 38.4 | This study |
| Hydrous stannic oxide | 2 | 4 | 3.48 | [47] |
| Treated sawdust of sal tree | 3.5 | 0.1 | 9.55 | [48] |
| Dictyopteris polypodioides | 1 | 10 | 21.78 | [49] |
| Banana peel | 2 | - | 10.42 | [50] |
| Henna Leaves | 4 | - | 0.078 | [51] |
| banana peel powder | 3 | - | 7.35 | [52] |
| modified groundnut hull | 2 | - | 31.0 | [53] |
| Nano-Al2O3 | 4 | 5 | 17.7 | [54] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almujaybil, M.J.; Abunaser, D.F.M.; Gouda, M.; Khalaf, M.M.; Mohamed, I.M.A.; Abd El-Lateef, H.M. Facile Synthesis of Fe(0)@Activated Carbon Material as an Active Adsorbent towards the Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Media. Catalysts 2022, 12, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050515
Almujaybil MJ, Abunaser DFM, Gouda M, Khalaf MM, Mohamed IMA, Abd El-Lateef HM. Facile Synthesis of Fe(0)@Activated Carbon Material as an Active Adsorbent towards the Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Media. Catalysts. 2022; 12(5):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050515
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmujaybil, Mohammed J., Dania Fathi Mohammed Abunaser, Mohamed Gouda, Mai M. Khalaf, Ibrahim M. A. Mohamed, and Hany M. Abd El-Lateef. 2022. "Facile Synthesis of Fe(0)@Activated Carbon Material as an Active Adsorbent towards the Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Media" Catalysts 12, no. 5: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050515
APA StyleAlmujaybil, M. J., Abunaser, D. F. M., Gouda, M., Khalaf, M. M., Mohamed, I. M. A., & Abd El-Lateef, H. M. (2022). Facile Synthesis of Fe(0)@Activated Carbon Material as an Active Adsorbent towards the Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Media. Catalysts, 12(5), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050515










