Viscosity Reduction and Mechanism of Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil Co-Catalyzed by Bentonite and Transition Metal Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Influence of Different Conditions on the Aquathermolysis
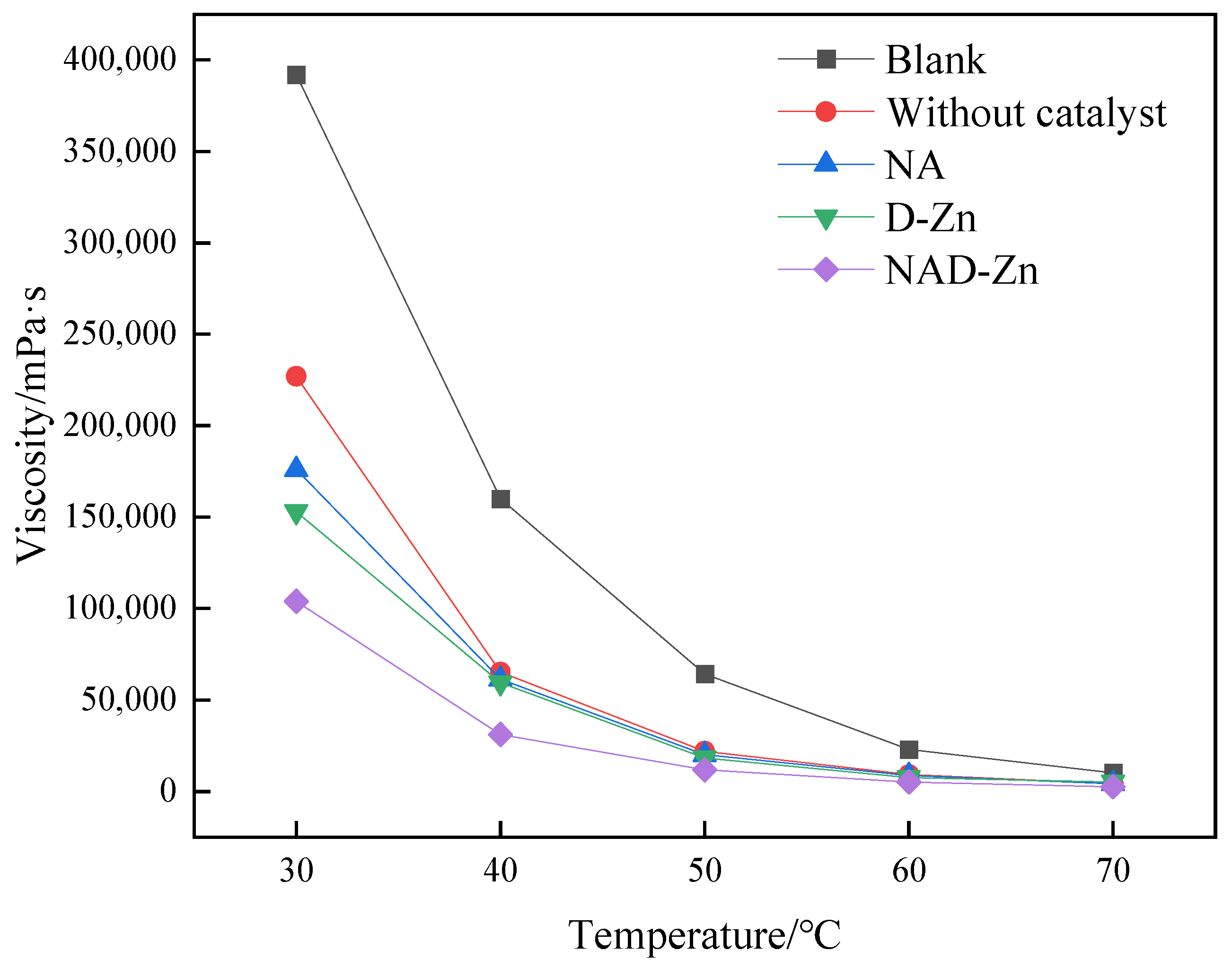
2.1.1. Effect of Catalysts on Aquathermolysis
2.1.2. Evaluation of the Catalytic Effect of NA and D–Zn Separately
2.1.3. Effect of Ethanol on Aquathermolysis
2.2. Characterization of Heavy Oil
2.2.1. Group Composition and Elemental Analysis
2.2.2. Wax Crystal Morphology
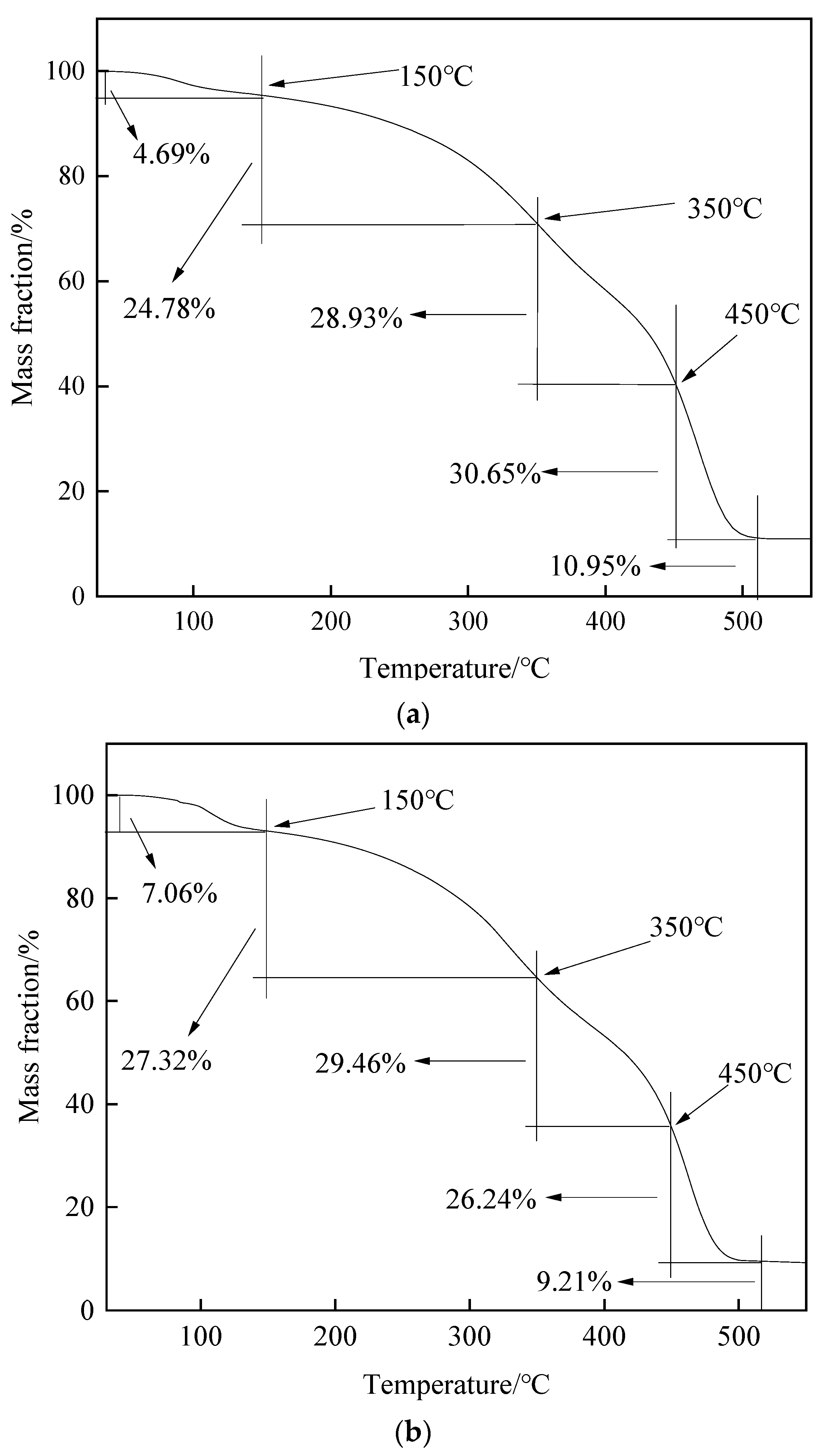
2.2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Heavy Oil
2.2.4. Distribution of Distillation Ranges
2.3. Characterization of the Catalyst
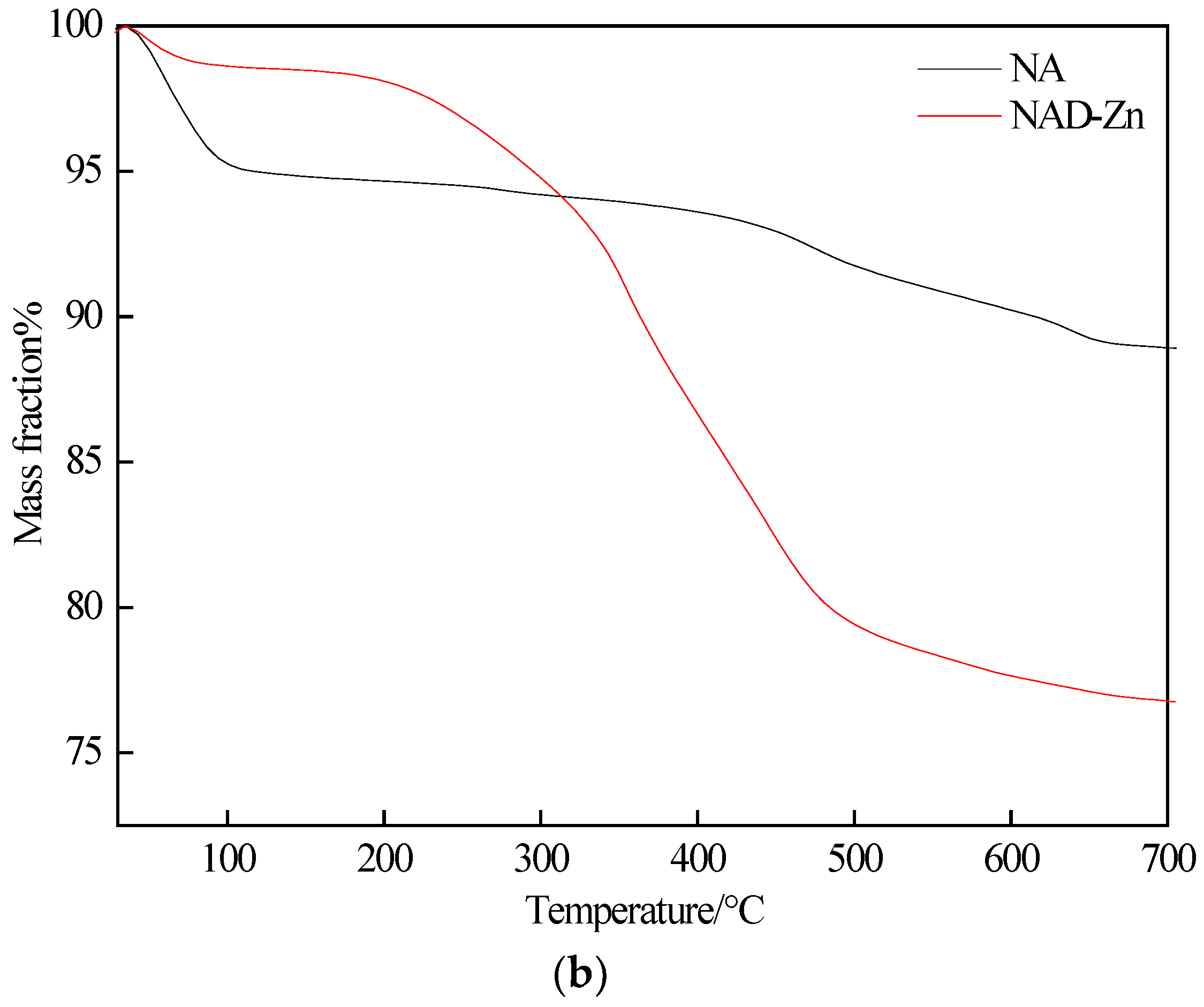
2.3.1. IR Characterization and Thermogravimetric Analysis of the NAD–Zn
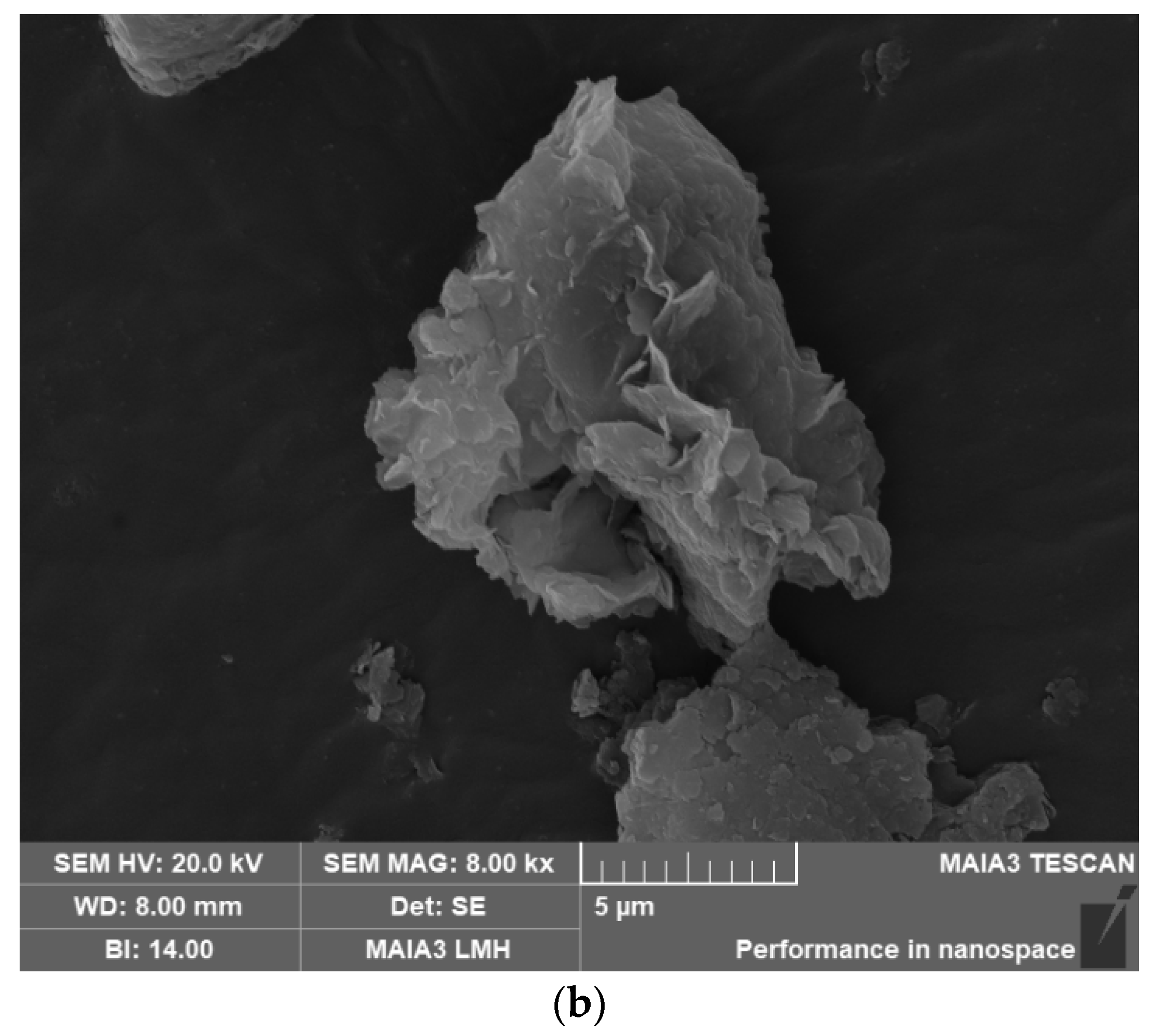
2.3.2. The SEM of NAD–Zn
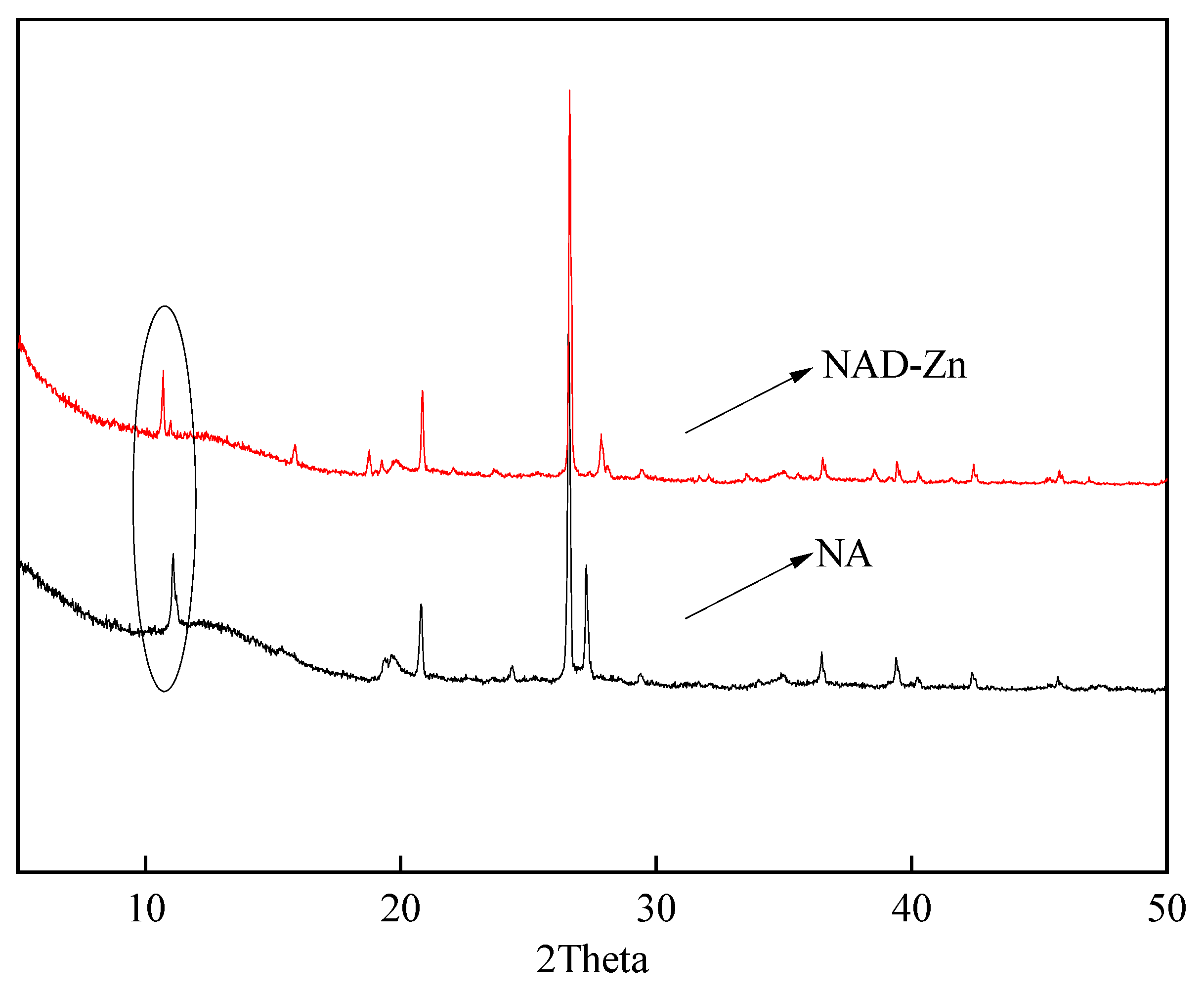
2.3.3. The XRD of NAD–Zn
2.4. Mechanism of Aquathermolysis
2.4.1. Selection of Model Compounds
2.4.2. The Role of High-Temperature Water
2.4.3. GC-MS of Model Compounds after Aquathermolysis
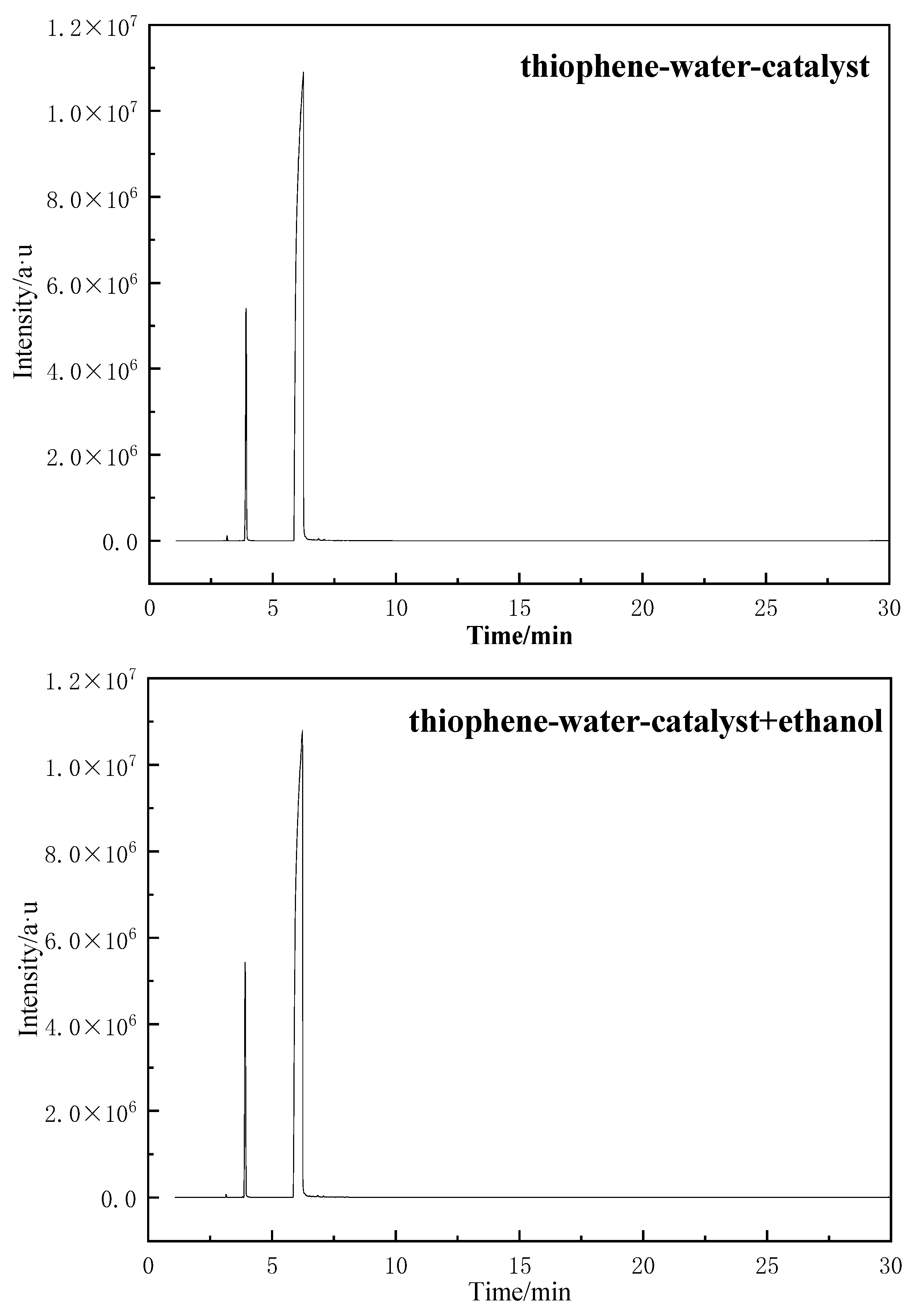
2.4.4. The Reaction Mechanism of Thiophene
2.4.5. The Reaction Mechanism of Nonylphenol
2.4.6. The Reaction Mechanism of Quinoline
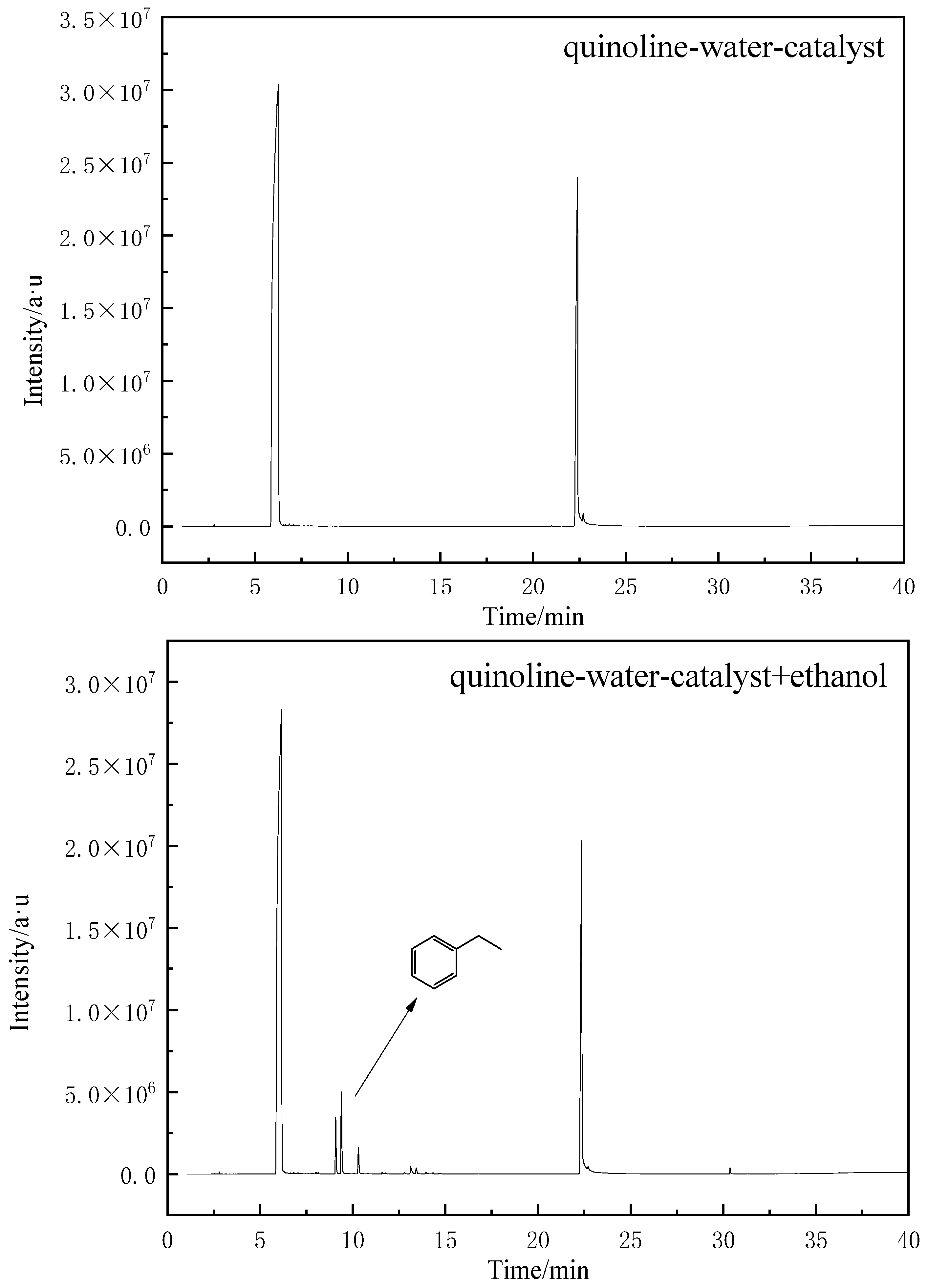
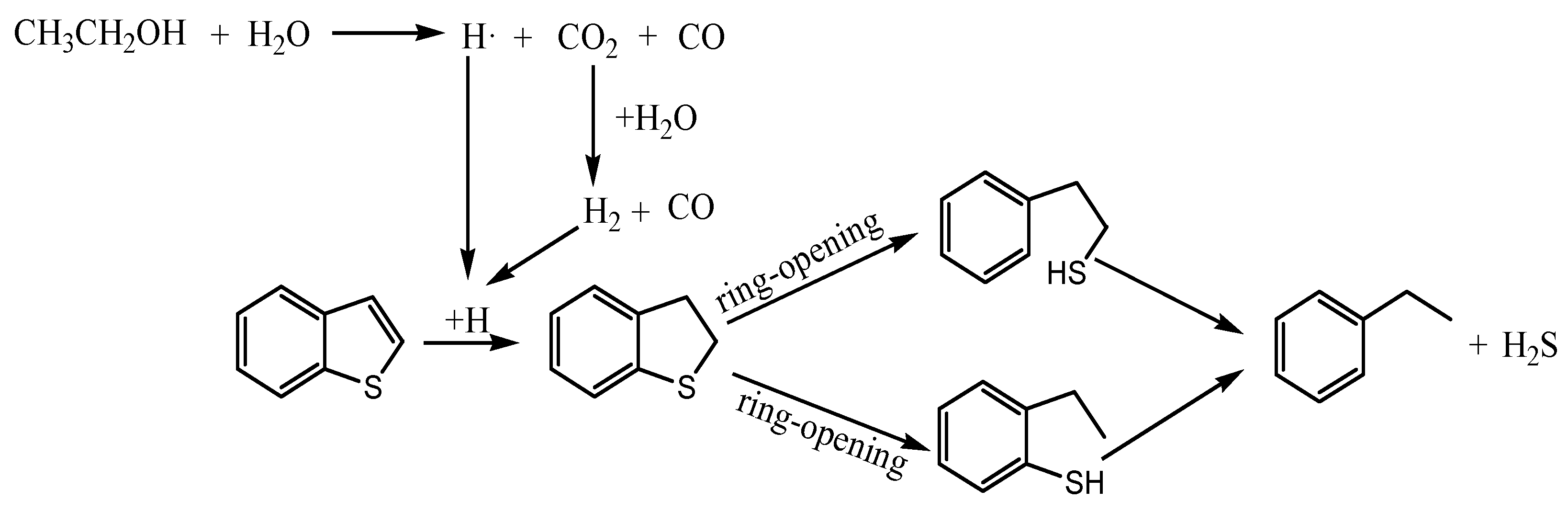
2.4.7. The Reaction Mechanism of Benzothiophene
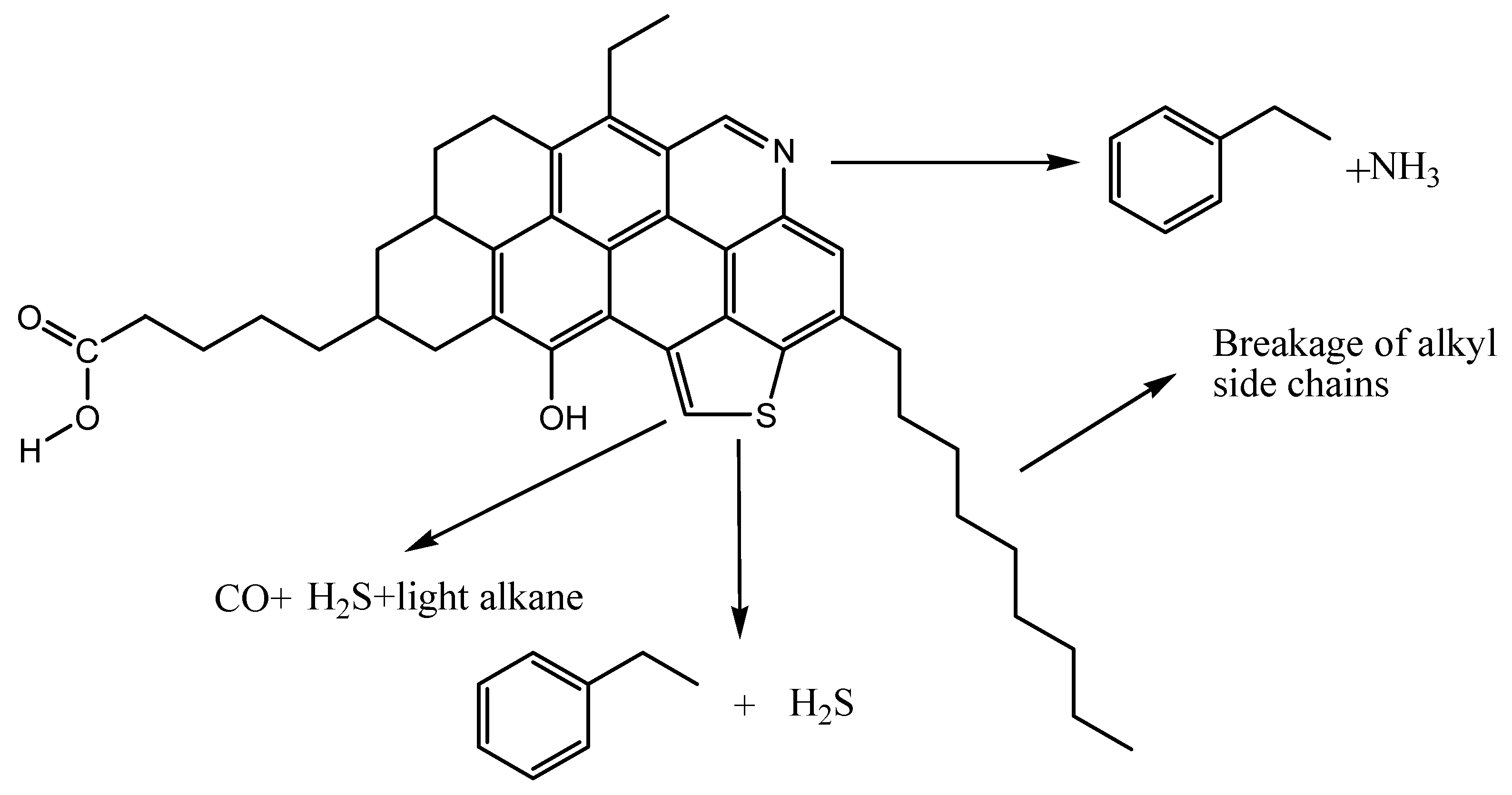
2.4.8. Mechanisms of Aquathermolysis Reactions in Heavy Oil
2.5. The Catalytic Mechanism of NAD–Zn
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material
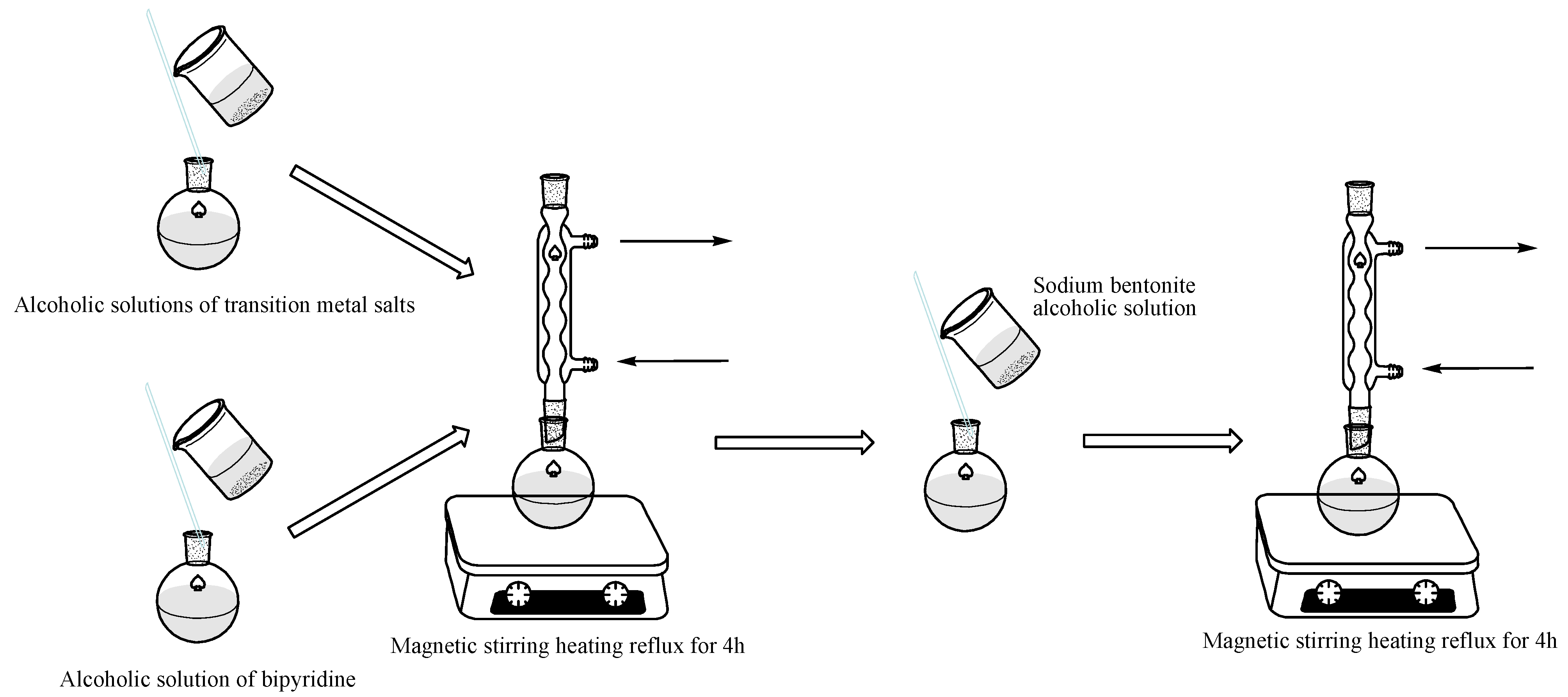
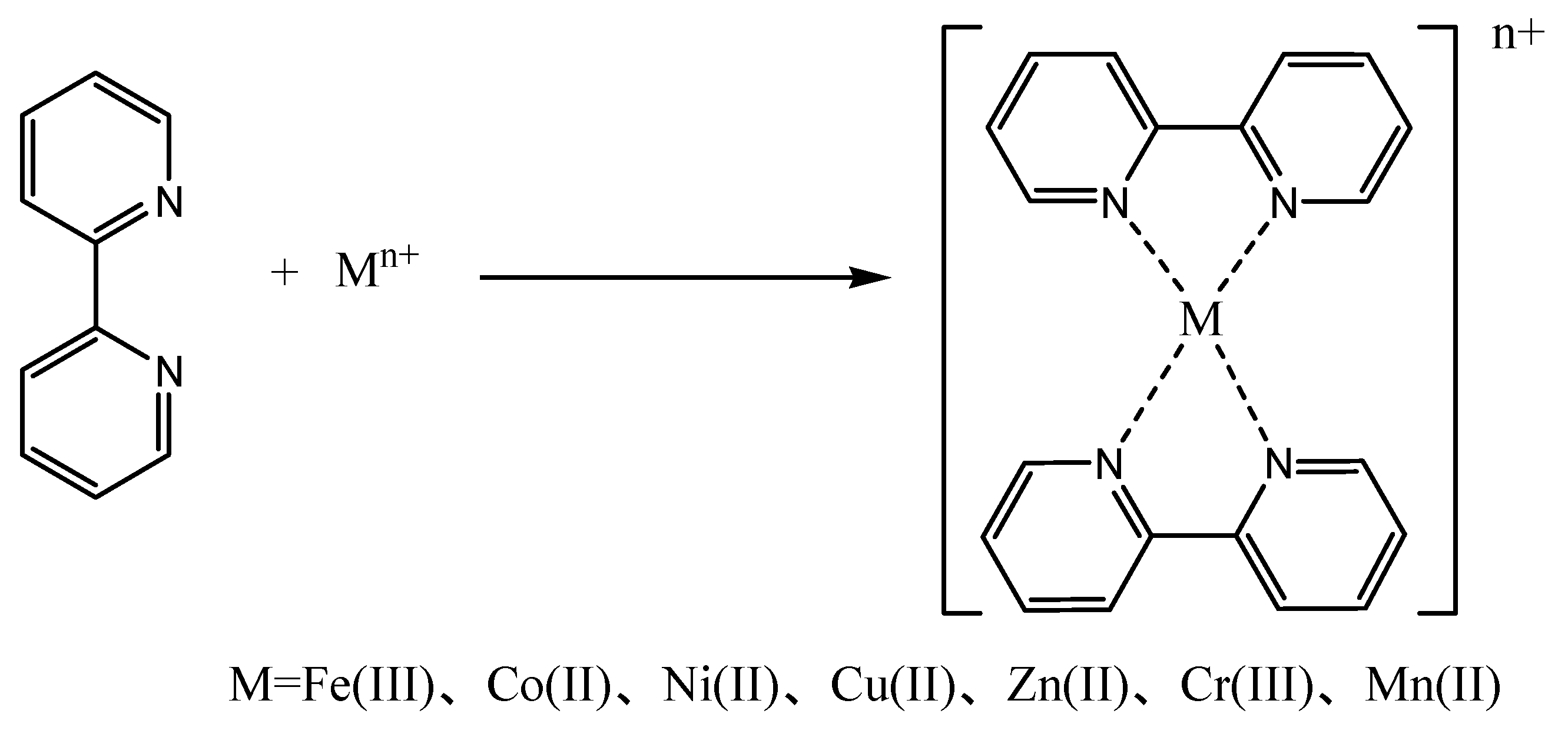
3.2. Synthesis of the Catalysts
3.3. Characterisations of Catalysts
3.4. Experimental Conditions
3.5. Characterization of Heavy Oil before and after Reaction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, P.; Yang, H.Y.; Wu, P.Y.; Liao, Y.Q.; Tan, D.C.; Ma, Z.F.; Yan, X.M. Study on catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil by simple synthesis of highly dispersed nickel-loaded nitrogen-doped carbon catalysts. Mol. Catal. 2022, 529, 112528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Zhou, G.Q.; Lu, Y.K.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, J.Q.; Xu, H. Catalytic aquathermolysis of Mackay River bitumen with different types of Mo-based catalysts. Fuel 2022, 326, 125134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.K.; Semen, E.L.; Aleksey, V.B.; Nikita, E.I.; Elvira, I.S.; Irek, I.M.; Alexey, V.V. Thermal behavior of heavy oil catalytic pyrolysis and aquathermolysis. Catalysts 2022, 12, 449. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandra, S.U.; Vladislav, Z.; Mohammed, A.K.; Sergey, A.S.; Alexey, V.V. In situ combustion of heavy, medium, and light crude oils: Low-temperature oxidation in terms of a chain reaction approach. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 7710–7721. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Fu, W.; Qu, L.; Li, Y.F.; Yuan, W.H.; Chen, G. Methanol enhanced Fe(III) oleate catalyzed aquathermolysis of heavy oil. Processes 2022, 10, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yuan, W.H.; Yan, J.; Meng, M.; Guo, Z.; Gu, X.F.; Zhang, J.; Qu, C.T.; Song, H.; Ayodeji, J.J. Zn(II) complex catalyzed coupling aquathermolysis of water-heavy oil-methanol at low temperature. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, G.; Yan, J.; Zhang, J.; Meng, M.; Qu, C.T.; Ayodeji, J.J. Water-Soluble complexes catalyzed coupling aquathermolysis of water-heavy oil-methanol at low temperature. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.F.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.J. The catalytic effects of minerals on aquathermolysis of heavy oils. Fuel 2004, 83, 2035–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.L.; Dong, S.B.; Yu, T.; Slaný, M.; Chen, G. Enhanced aquathermolysis of heavy oil catalysed by bentonite supported Fe(III) complex in the present of ethanol. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 97, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.F.; Guo, Z.; Bai, Y.; Gu, X.F.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.Q.; Zhang, Z.F. The use of a tartaric-Co(II) complex in the catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Gu, X.F.; Li, B.Q.; Qu, C.T.; Song, H. MeOH enhanced aquathermolysis of heavy oil catalyzed by hydroxamic acid-Ni(II) complex at low temperature. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2018, 40, 487–494. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; Feng, X.; Wu, Y.N.; Ding, B.D.; Lu, T.; Liu, Y.B.; Chen, X.B.; Chen, D.; Yang, C.H. Insights into the synergy between recyclable magnetic Fe3O4 and zeolite for catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy crude oil. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 456, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.R.; Li, Q.Y.; Wang, X.D.; Yu, L.G.; Yang, J.J. Aquathermolysis of heavy crude oil with ferric oleate catalyst. Pet. Sci. 2018, 15, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yuan, W.H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, H.; Ayodeji, J.J.; Song, S.F.; Qu, C.T. Catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil by coordination complex at relatively low temperature. Pet. Chem. 2017, 57, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhin, A.V.; Sitnov, S.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Onishchenko, Y.V.; Feoktistov, D.A. Aquathermolysis of high-viscosity oil in the presence of an oil-soluble iron-based catalyst. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2017, 53, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Gu, M.; Yu, Z.Y. Carbon Nanocatalysts for aquathermolysis of heavy crude oil: Insights into thiophene hydrodesulfurization. Energy Technol. 2017, 5, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yan, J.; Bai, Y.; Gu, X.F.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.F.; Ayodeji, J.J. Clean aquathermolysis of heavy oil catalyzed by Fe(III) complex at relatively low temperature. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.R.; Chen, Y.; An, Y.; Chen, L.Y. Catalytic aquathermolysis of super-heavy oil: Cleavage of CS bonds and separation of light organosulfurs. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 153, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, T.K.; Johannes, I.; Luik, H.; Gregor, H. Synergy in the hydrothermal pyrolysis of oil shale/sawdust blends. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 117, 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Alexey, V.V.; Firdavs, A.A.; Irek, I.M.; Sergey, A.S.; Andrey, V.S.; Sergey, I.K.; Igor, S.A.; Oleg, V.P.; Danis, K.N. Catalytic aquathermolysis of boca de iaruco heavy oil with nickel-based oil-soluble catalyst. Processes 2020, 8, 532. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.L.; Li, Y.G.; Zhang, Z.J.; Li, X.H.; Zhao, M.Y.; Su, C.M. Synthesis of silica/metatitanic acid nanocomposite and evaluation of its catalytic performance for aquathermolysis reaction of extra-heavy crude oil. J. Energy Chem. 2015, 24, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, J.S.; Li, Q.; Lv, K.H.; Wang, J.T.; Wang, Z.Y. Mechanism of organosilicate polymer as high-temperature resistant inhibitor in water-based drilling fluids. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 641, 128489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Yang, Z.C.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhao, M.Y.; Su, C.M. Preparation of silica-supported nanoFe/Ni alloy and its application in viscosity reduction of heavy oil. Micro Nano Lett. 2015, 10, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Wu, Y.B.; Zhao, X.; Tan, L.R. Study of catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil in the presence of a hydrogen donor. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2012, 48, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Slaný, M.; Kuzielová, E.; Zhang, W.Y.; Ma, L.W.; Dong, S.B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Influence of reservoir minerals and ethanol on catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil. Fuel 2022, 307, 121871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Slaný, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.F.; Zang, Y.L.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, G. Acetylation modification of waste polystyrene and its use as a crude oil flow improver. Polymers 2021, 13, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Pu, C. Mechanism of underground heavy oil catalytic aquathermolysis. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2018, 53, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.L.; He, G.; Li, P.; Yang, C. Mechanism of catalytic aquathermolysis: Influences on heavy oil by two types of efficient catalytic ions: Fe3+ and Mo6+. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Dong, B. Upgrading and visbreaking of super- heavy oil by catalytic aquathermolysis with aromatic sulfonic copper. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 104, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Laboratory experiments and field test of a difunctional catalyst for catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Liu, Y. Downhole catalyst upgrades heavy oil. Oil Gas J. 2002, 100, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Shokrlu, Y.; Babadagli, T. Viscosity reduction of heavy oil/bitumen using micro-and nano-metal particles during aqueous and non-aqueous thermal applications. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 119, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, L. Studies on the synergetic effects of mineral and steam on the composition changes of heavy oils. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhu, H.H.; Wu, Y.N.; Lu, T.; Liu, Y.B.; Chen, X.B.; Peng, C.; Yang, C.H.; Feng, X. Morphological insights into the catalytic aquathermolysis of crude oil with an easily prepared high-efficiency Fe3O4-containing catalyst. Fuel 2019, 245, 420–428. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, P.; Kirk, M. Studies on the upgrading of bituminous oils with water and transition metal catalysts. Energy Fuels 1994, 8, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.Y.; Cui, L.R.; Xu, X.B.; Cen, L.; Xu, J.; Cao, F.H. Investigation on aquathermolysis desulfurization by cutting off C-S bond in thiophene over Fe-Zr-Al catalyst facilitated by surfactants. Energy Sources Part A 2022, 44, 5755–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, M.; Richard, W.C.; Andrew, C.R.; Mark, A.S. High temperature reactions of water with heavy oil and bitumen: Insights into aquathermolysis chemistry during steam-assisted recovery. Fuel 2013, 113, 426–434. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.W.; Michal, S.; Guo, R.; Du, W.C.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, G. Study on synergistic catalysis of ex-situ catalyst and in-situ clay in aquathermolysis of water-heavy oil-ethanol at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.J.; Li, C.; Gao, H.; Chen, M.; Huang, W.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhou, C.G. Recyclable oleic acid modified magnetic NiFe2O4 nanoparticles for catalytic aquathermolysis of Liaohe heavy oil. Fuel 2017, 200, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitnov, S.A.; Khelkhal, M.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Feoktistov, D.A.; Vakhin, A.V. Iron oxide nanoparticles impact on improving reservoir rock minerals catalytic effect on heavy oil aquathermolysis. Fuel 2022, 327, 124956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Z.; Liu, H.M.; Bu, H.L.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Du, P.X. Effects of montmorillonite charge reduction on the high-temperature/high-pressure pyrolysis of organic matter. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 213, 106243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







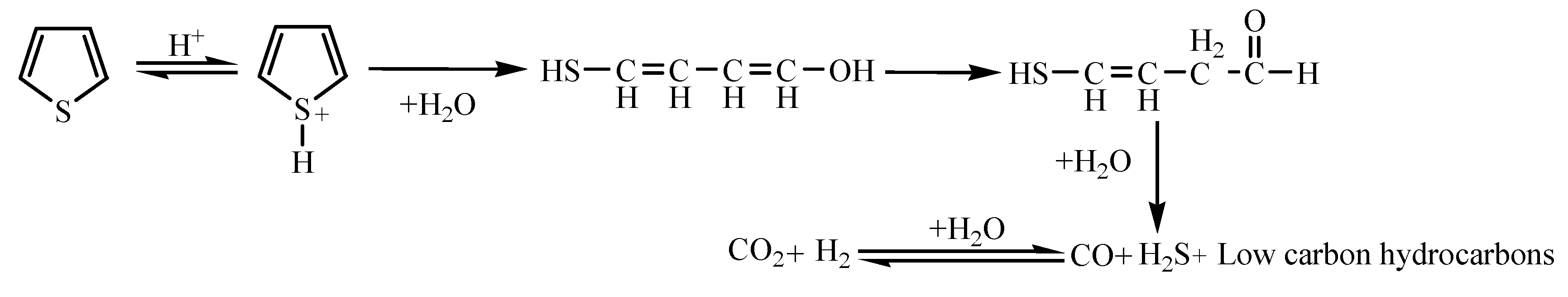





| Sample | Saturated HC, % | Aromatic HC, % | Resin, % | Asphaltene, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before reaction | 32.53 | 26.68 | 18.15 | 22.64 |
| NAD–Zn | 33.71 | 27.96 | 16.87 | 21.46 |
| NAD–Zn + ethanol | 35.28 | 29.23 | 15.17 | 20.32 |
| Sample | C/% | H/% | N/% | S/% | H/C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before reaction | 86.26 | 9.90 | 0.91 | 0.53 | 0.1148 |
| NAD–Zn | 85.91 | 10.15 | 0.82 | 0.43 | 0.1181 |
| NAD–Zn + ethanol | 84.97 | 10.34 | 0.76 | 0.41 | 0.1217 |
| Boiling Range/°C | Blank | NAD–Zn | NAD–Zn + Ethanol | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cut Fraction /% | Cumulative /% | Cut Fraction /% | Cumulative /% | Cut Fraction /% | Cumulative /% | |
| initial boiling point −100 | 3.22 | 3.22 | 6.69 | 6.69 | 2.49 | 2.49 |
| 100–150 | 2.06 | 5.28 | 1.82 | 8.51 | 5.30 | 7.79 |
| 150–200 | 2.42 | 7.70 | 1.90 | 10.41 | 2.41 | 10.20 |
| 200–250 | 4.29 | 11.99 | 3.82 | 14.23 | 4.83 | 15.03 |
| 250–300 | 7.62 | 19.61 | 7.10 | 21.33 | 9.33 | 24.36 |
| 300–350 | 13.52 | 33.13 | 14.07 | 35.40 | 15.79 | 40.15 |
| >350 | 66.90 | 100 | 64.60 | 100 | 59.89 | 100 |
| Pour Point/°C | Saturated HC, % | Aromatic HC, % | Resin, % | Asphaltene, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24.0 | 32.53 | 22.68 | 18.15 | 22.64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Dong, S.; Peng, S.; Chen, G. Viscosity Reduction and Mechanism of Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil Co-Catalyzed by Bentonite and Transition Metal Complexes. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12111383
Zhang W, Li Q, Li Y, Dong S, Peng S, Chen G. Viscosity Reduction and Mechanism of Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil Co-Catalyzed by Bentonite and Transition Metal Complexes. Catalysts. 2022; 12(11):1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12111383
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wangyuan, Qi Li, Yongfei Li, Sanbao Dong, Sen Peng, and Gang Chen. 2022. "Viscosity Reduction and Mechanism of Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil Co-Catalyzed by Bentonite and Transition Metal Complexes" Catalysts 12, no. 11: 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12111383
APA StyleZhang, W., Li, Q., Li, Y., Dong, S., Peng, S., & Chen, G. (2022). Viscosity Reduction and Mechanism of Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil Co-Catalyzed by Bentonite and Transition Metal Complexes. Catalysts, 12(11), 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12111383







