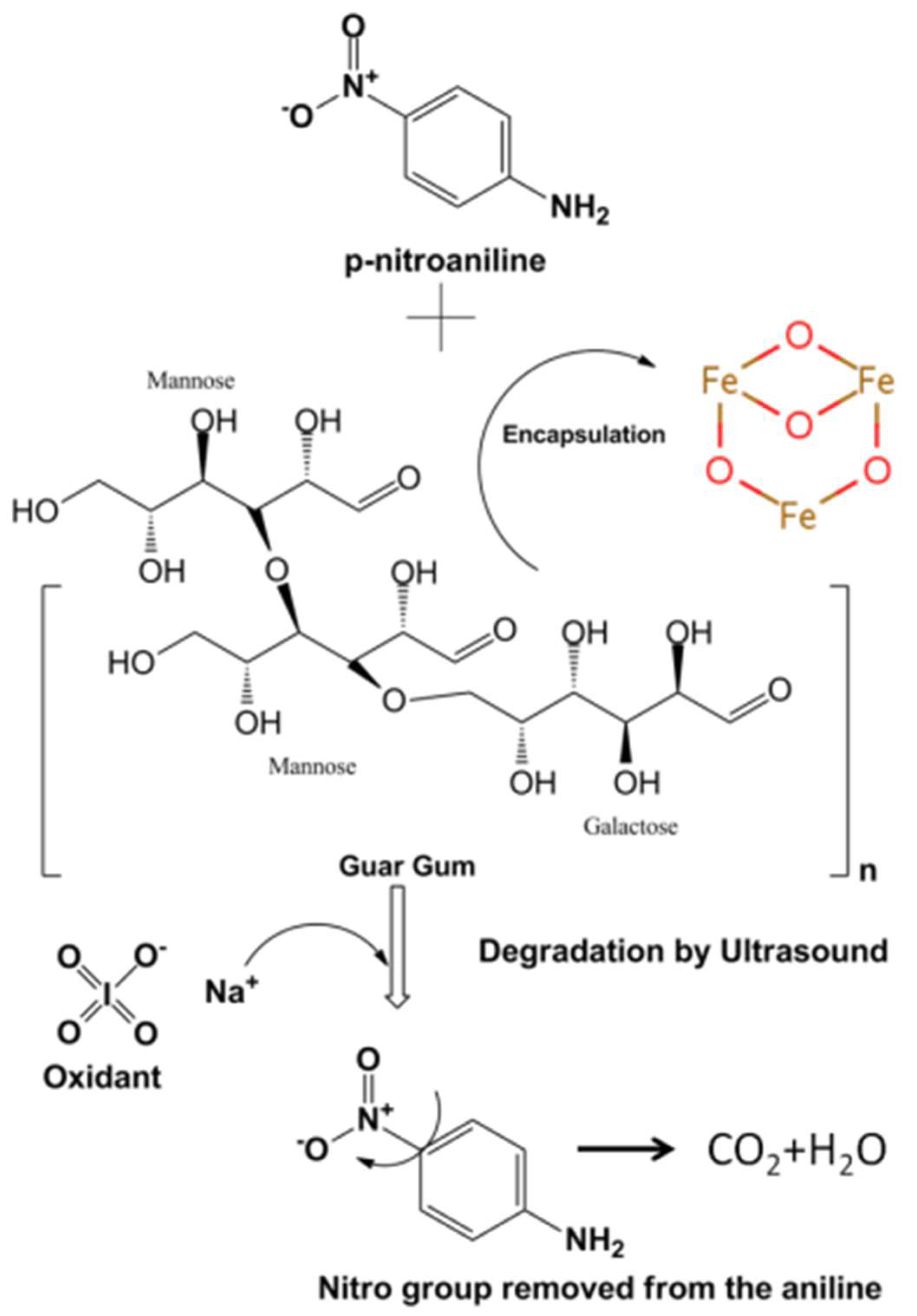
Natural Polymer-Based Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Synthesis, Characterization and Its Application for 1-Amino-Nitrobenzene Degradation in Assistance with Oxidants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
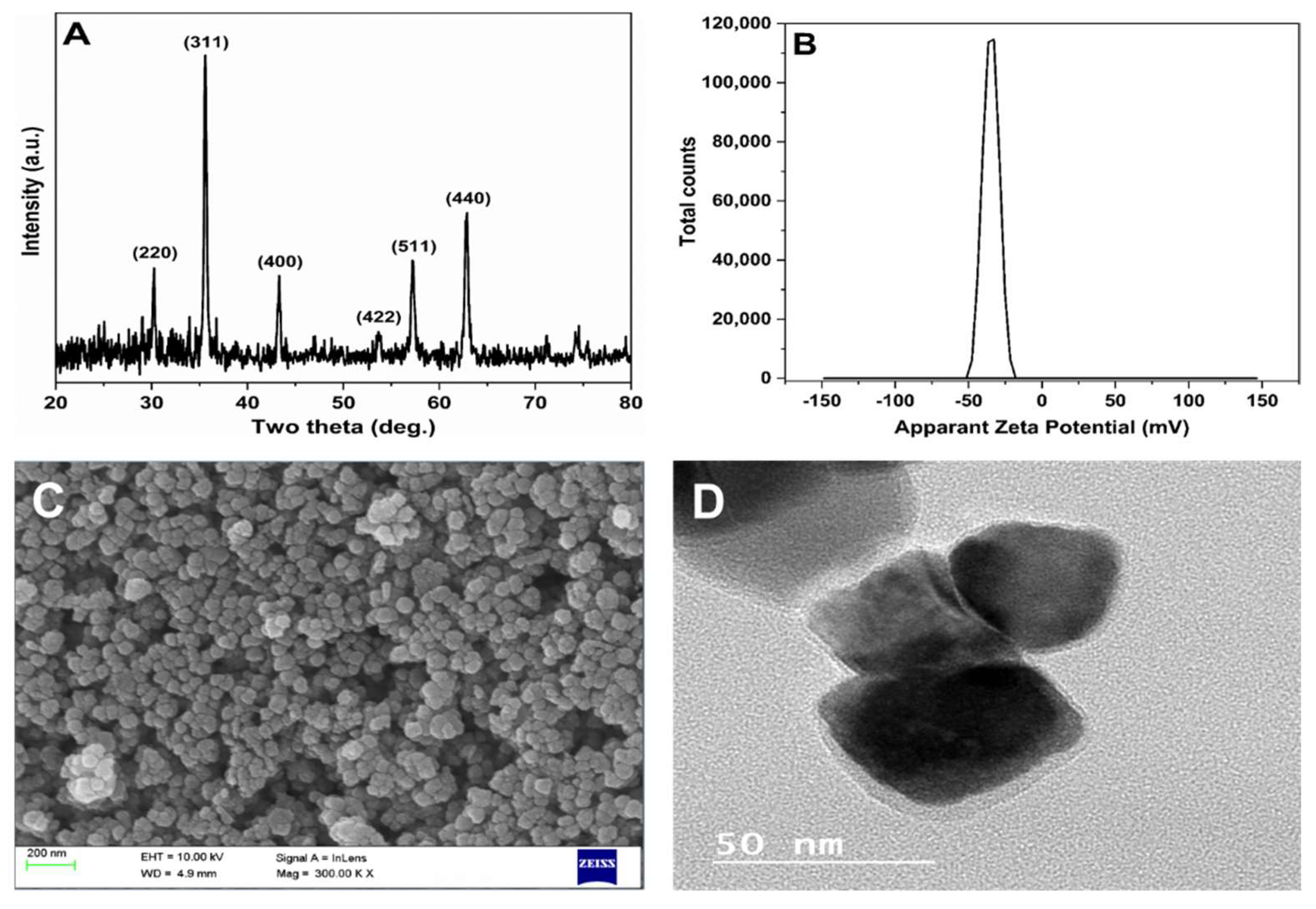
2.1. Characterization of Synthetic Ferroferric Oxide-Guaran Nanocomposite
2.2. Sonophotochemical Degradation of ANB
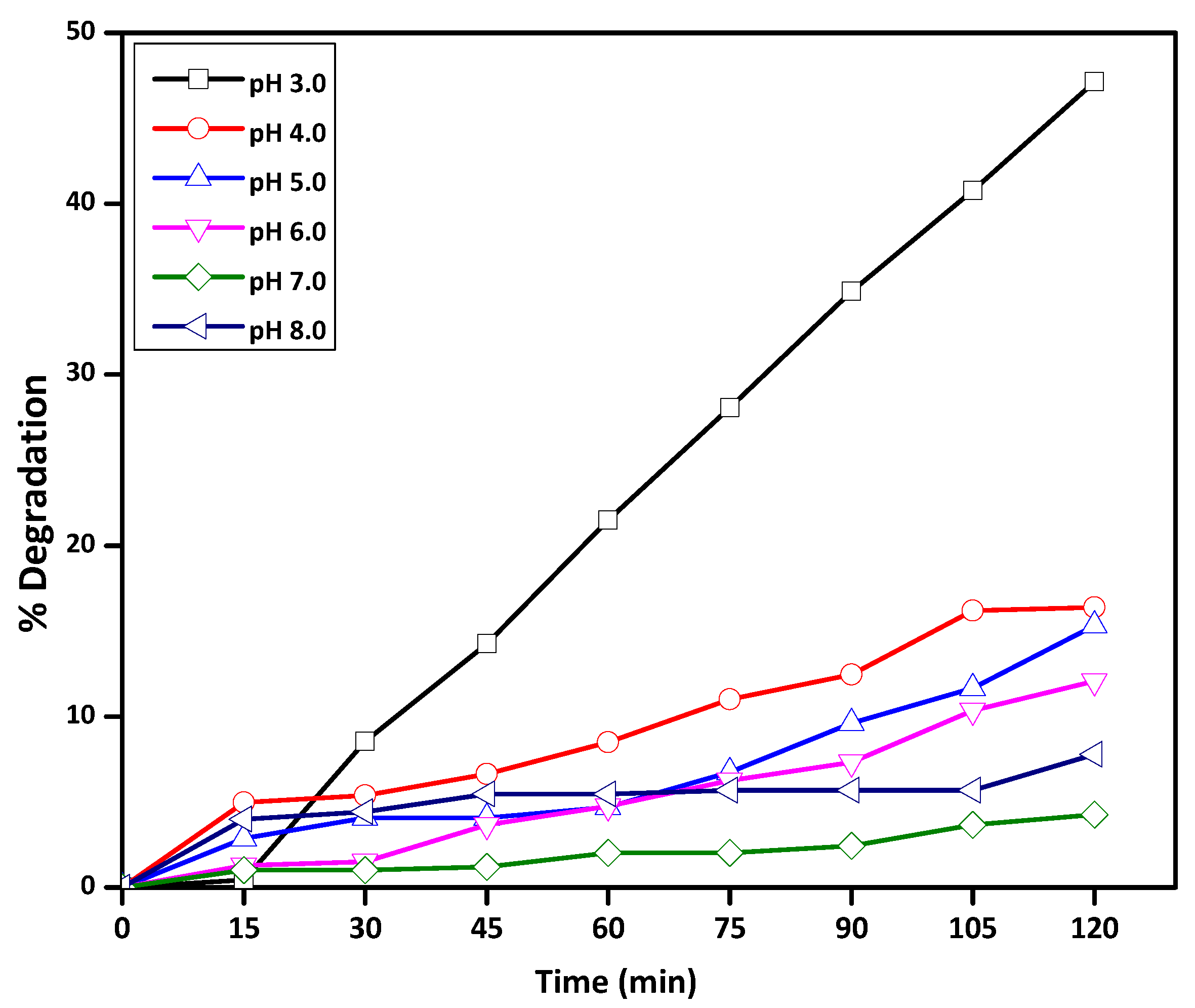
2.2.1. Effect of Initial Solution pH
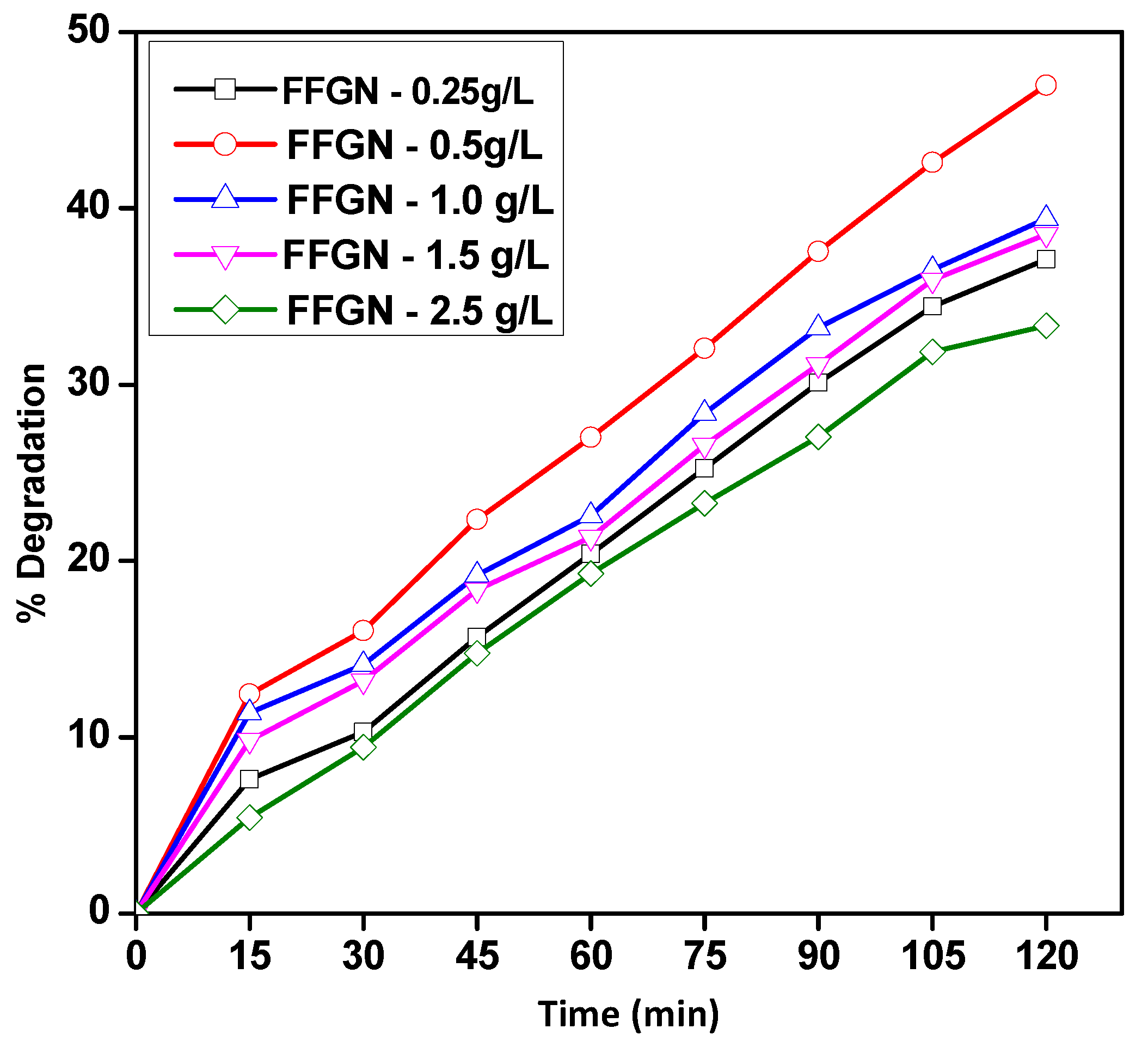
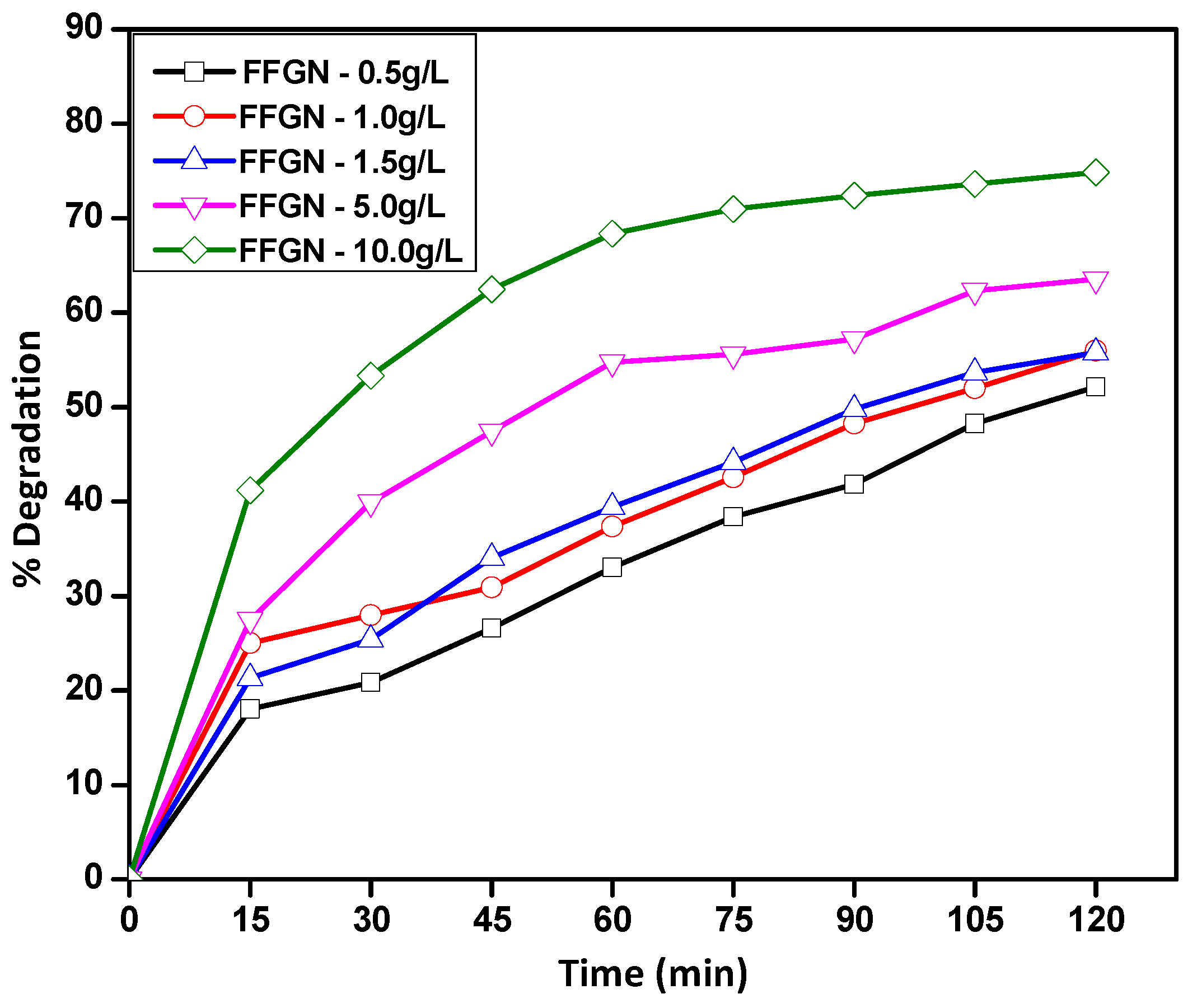
2.2.2. Effect of FFGN Concentration
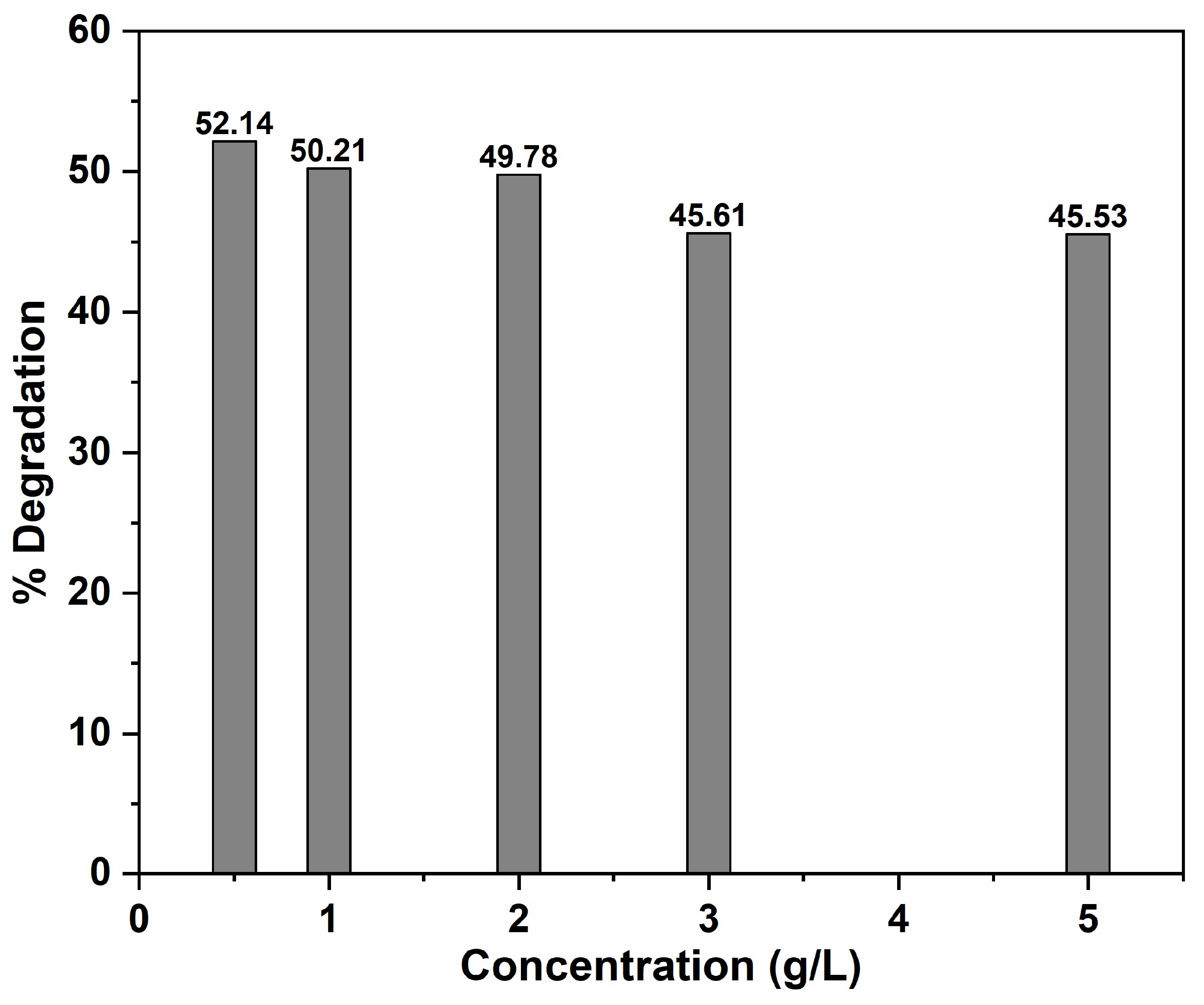
2.2.3. Effect of NaIO4 Concentration
2.2.4. Mechanism of ANB Degradation by Sodium Periodate
2.2.5. Effect of FFGN with Fixed NaIO4 Concentration
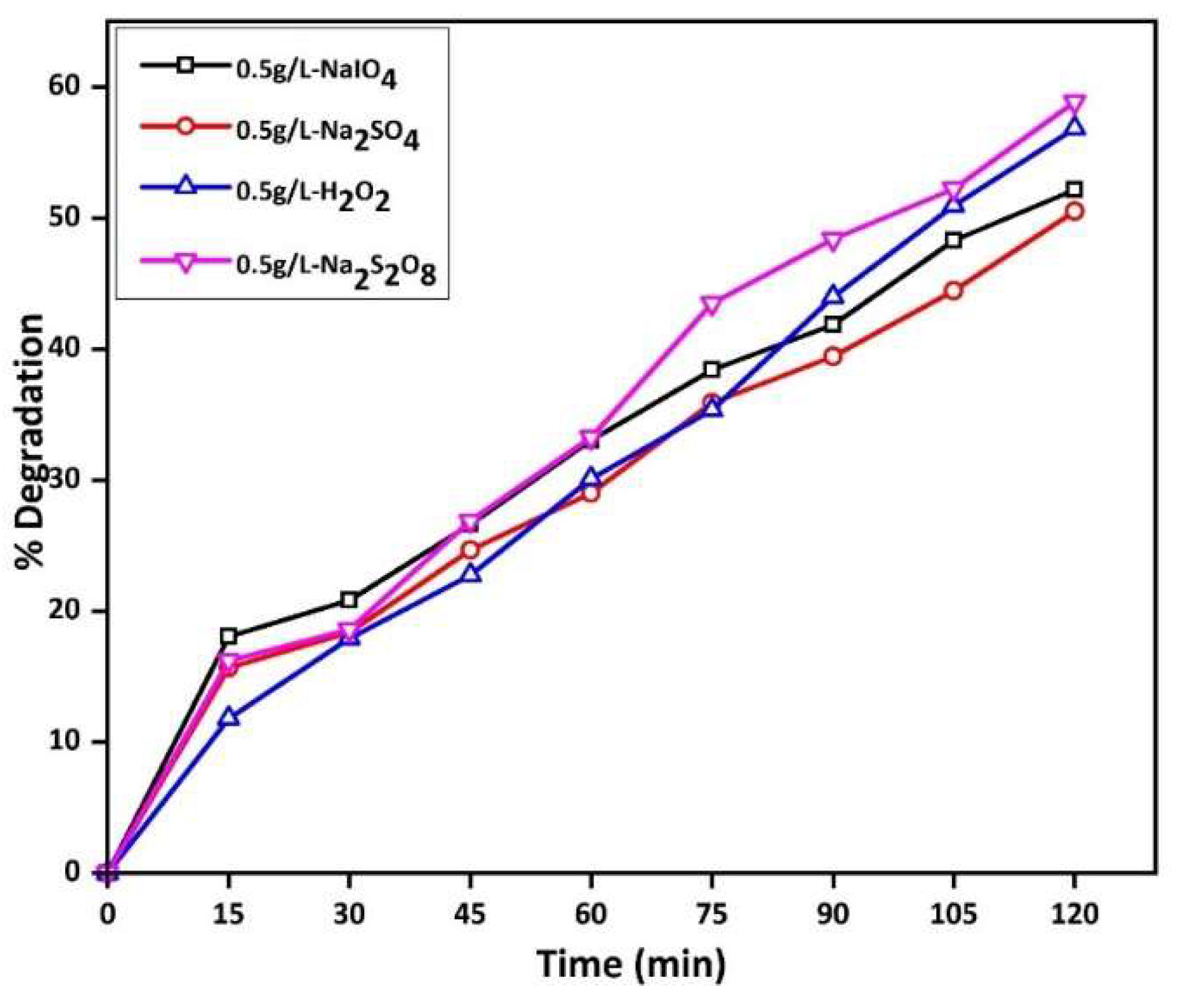
2.2.6. Effect of FFGN with Different Oxidants
2.2.7. Effect of Na2S2O8 Concentration
| Catalyst Synthesis | Degradation Method | Degradation Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AgBiO3 photocatalyst by Ion exchange followed by hydrothermal treatment | Photocatalytic degradation, reaction temperature 25 °C, 4-NP with initial concentration of 20 ppm, 5 h | 90% removal with catalyst loading of 0.3 g/L | Boruah et al., 2019 [53] |
| Carbon nanotube-containing cathode | Heterogeneous electro-Fenton-like oxidation, 200 mL 4-nitrophenol (100 mg L−1) solution containing Na2SO4 (0.10 M) with pH 3.0, 3.0 V (75 mA of average current), 240 min | 100% removal with 10.0 g catalyst amount | Chu et al., 2020 [54] |
| In2S3/α-Fe2O3 composites by hydrothermal treatment | 4-nitrophenol (20 mg/L), Visible light irradiation by a xenon lamp with a 420 nm filter, 0.05 g In2S3/α-Fe2O3, 50 mL reaction volume | 95% of PNP was removed using the 60% In2S3/α-Fe2O3 catalyst after 100 min, 8% and 20% of PNP were degraded using the pure α-Fe2O3 and In2S3 | Fang et al., 2021 [55] |
| Porous PbO2-CNTs electrode was prepared by oxygen bubble template method | Electrocatalytic degradation, p-nitrophenol concentration of 50 mg·L−1 and 0.25 mol·L−1 Na2SO4, Electrode working area is 2 cm2, current density of 30 mA·cm−2, temperature of 30 °C, 120 min | 96%—3D PbO2-CNTs electrode, 85.2%—3D PbO2, 86.4%—flat PbO2-CNTs electrodes | You et al., 2021 [56] |
| Silver/carbon co-decorated hollow TiO2 photocatalyst (Ag/C-TiO2) by depositing Ag NPs on the surface of carbon decorated hollow TiO2 sphere | Ag/C-TiO2 (10 mg in 50 mL), 4-NP (10 mg/L), simulated sunlight irradiation (300 W Xe lamp equipped with an AM 1.5 filter), 60 min | Complete removal for the Ag/C-TiO2 photocatalyst, 86% removal of 4-NP for C-TiO2 | Zhang et al., 2022 [57] |
| Natural polymer-based iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanocomposites by sonochemical precipitation method | pH = 3.0 ± 0.2, ANB = 50 ppm, Na2S2O8 = 0.06 mol/L, Amplitude = 40%, Ultrasound Probe = 25 mm, T = 25 ± 1 °C, UV light, 60 min | 95% degradation efficiency | This study |
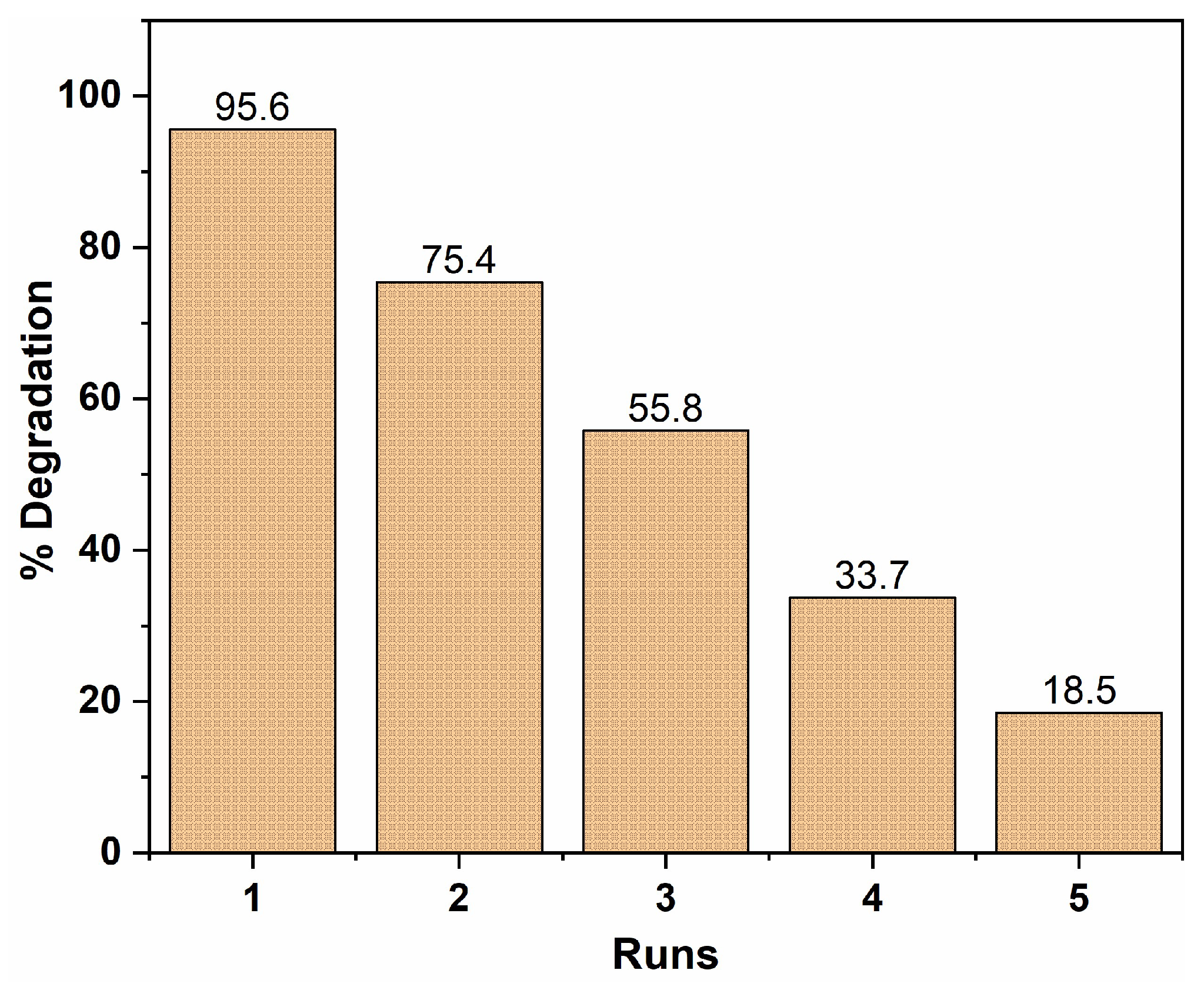
2.2.8. Recycling Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Ferroferric Oxide-Guaran Nanocomposite Synthesis
3.3. Degradation Study
3.4. Characterization and Analytical Techniques
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shanker, V.; Rayabandla, S.M.; Kumavath, R.N.; Chintalapati, S.; Chintalapati, R. Light-Dependent Transformation of Aniline to Indole Esters by the Purple Bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides OU5. Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, A.S. Manufacture and uses of the Anilines: A Vast Array of Processes and Products. Chem. Anilines. 2007, 715–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, E.; Sundaraganesan, N.; Sebastian, S. Molecular structure, vibrational spectroscopic and HOMO, LUMO studies of 4-nitroaniline by density functional method. Indian J. Pure. Appl. Phys. 2010, 48, 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Oturan, M.A.; Peiroten, J.; Chartrin, P.; Acher, A.J. Complete Destruction of p -Nitrophenol in Aqueous Medium by Electro-Fenton Method. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3474–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-H.; Sun, S.-P.; Fan, M.; Guo, H.-Q.; Lee, Y.-F.; Sun, R.-X. Oxidative decomposition of p-nitroaniline in water by solar photo-Fenton advanced oxidation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yao, S.; Zhang, J.; Pu, C.; Zhao, S.; Wang, M.; Xiong, J. Steady-state and transient photolysis of p-nitroaniline in acetonitrile. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2009, 202, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Zhao, G.; Wu, M.; Li, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Electrosorptive photocatalytic degradation of highly concentrated p-nitroaniline with TiO2 nanorod-clusters/carbon aerogel electrode under visible light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Arshad, M.; Crowley, D.E. Biodegradation potential of pure and mixed bacterial cultures for removal of 4-nitroaniline from textile dye wastewater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.; Torati, R.S.; Oh, S.; Kim, C. Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Assisted by Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn. Fruit Pericarp and Their Catalytic Application for the Reduction of p-Nitroaniline. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Park, K.S.; Nam, Y.W.; Kim, Y.-C.; Lee, C.H. Hydrothermal decomposition and oxidation of p-nitroaniline in supercritical water. J. Hazard. Mater. 1997, 56, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-H.; Sun, S.-P.; Fan, M.-H.; Guo, H.-Q.; Qiao, L.-P.; Sun, R.-X. A kinetic study on the degradation of p-nitroaniline by Fenton oxidation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, S.; Kamble, S.P.; Sawant, S.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitroaniline using solar and artificial UV radiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 110, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saupe, A. High-rate biodegradation of 3- and 4-nitroaniline. Chemosphere 1999, 39, 2325–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Pan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Pan, B.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Enhanced adsorption of p-nitroaniline from water by a carboxylated polymeric adsorbent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhao, G.; Huang, X. Adsorption of p-nitroaniline from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon fiber prepared from cotton stalk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Liang, S.; Chen, Y.; Shen, L.; Zheng, H.; Wu, L. High efficient photocatalytic reduction of 4-nitroaniline to p-phenylenediamine over microcrystalline SrBi2Nb2O9. Catal. Commun. 2012, 17, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, G.; Liang, S.; Chen, Y.; Shen, L.; Zheng, H.; Yuan, R.; Hou, Y.; Wu, L. Efficient visible-light-induced photocatalytic reduction of 4-nitroaniline to p-phenylenediamine over nanocrystalline PbBi2Nb2O9. J. Catal. 2012, 290, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wen, L.; Shen, L.; Liang, R.; Yuan, R.; Wu, L. A new insight into the photocatalytic reduction of 4-nitroaniline to p-phenylenediamine in the presence of alcohols. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 130–131, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S. The Chemical Effects of Ultrasound. Sci. Am. 1989, 260, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirgaonkar, I.Z.; Pandit, A.B. Sonophotochemical destruction of aqueous solution of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol. Ultrason. Sonochem. 1998, 5, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritikos, D.E.; Xekoukoulotakis, N.P.; Psillakis, E.; Mantzavinos, D. Photocatalytic degradation of reactive black 5 in aqueous solutions: Effect of operating conditions and coupling with ultrasound irradiation. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2236–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejarano-Perez, N.J.; Suarez-Herrera, M.F. Sonophotocatalytic degradation of congo red and methyl orange in the presence of TiO2 as a catalyst. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, C.G.; Li Puma, G.; Bono, A.; Krishnaiah, D. Sonophotocatalysis in advanced oxidation process: A short review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzigallo, M.D.R.; Ruggiero, P.; Crecchio, C.; Mascolo, G. Oxidation of Chloroanilines at Metal Oxide Surfaces. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2049–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, N.H.; Hoa, T.T.K.; Van Tan, N.; Thang, H.V.; Le Ha, P. Characterization and activity of Fe-ZSM-5 catalysts for the total oxidation of phenol in aqueous solutions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 34, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-F.; Phonthammachai, N.; Ramesh, K.; Zhong, Z.; White, T. Removing Organic Compounds from Aqueous Medium via Wet Peroxidation by Gold Catalysts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelmanov, G.; Semiat, R. Iron(3) oxide-based nanoparticles as catalysts in advanced organic aqueous oxidation. Water Res. 2008, 42, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Wang, M.; Pu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Yao, S.; Xiong, J. Transient and steady-state photolysis of p-nitroaniline in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.Q.; Zhou, R. Kinetic modeling and efficiency of sulfate radical-based oxidation to remove p-nitroaniline from wastewater by persulfate/Fe3O4 nanoparticles process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 142, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Zada, N.; Khan, I.; Sadiq, M.; Saeed, K. Enhancement of photocatalytic potential and recoverability of Fe3O4 nanoparticles by decorating over monoclinic zirconia. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1473–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Goswami, G.K.; Nanda, K.K. Green synthesis of polysaccharide/gold nanoparticle nanocomposite: An efficient ammonia sensor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Son, N.; Kim, S.; Balakrishnan, D.; Kang, M. Locust Bean gum-based hydrogels embedded magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles nanocomposite: Advanced materials for environmental and energy applications. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Yeasmin, S.; Khatua, S.; Acharyab, K.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Influence of a blend of guar gum and poly(vinyl alcohol) on long term stability, and antibacterial and antioxidant efficacies of silver nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 54059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Naushad, M.; Ghfar, A.A.; Ahamad, T.; Stadler, F.J. Fabrication and characterization of novel Fe0@Guar gum-crosslinked-soya lecithin nanocomposite hydrogel for photocatalytic degradation of methyl violet dye. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, N.K. Industrial Galactomannan Polysaccharides; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, V.M.; Loosli, F.; Santagapita, P.R.; Buera, M.P.; Stoll, S. Formation of complexes between hematite nanoparticles and a non-conventional galactomannan gum. Toward a better understanding on interaction processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 556–563. [Google Scholar]
- Bocchinfuso, G.; Mazzuca, C.; Sandolo, C.; Margheritelli, S.; Alhaique, F.; Coviello, T.; Palleschi, A. Guar Gum and Scleroglucan Interactions with Borax: Experimental and Theoretical Studies of an Unexpected Similarity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 13059–13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Aerry, S.; Saxena, A.; de, A.; Mozumdar, S. Copper nanoparticulates in Guar-gum: A recyclable catalytic system for the Huisgen [3 + 2]-cycloaddition of azides and alkynes without additives under ambient conditions. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiraferri, A.; Chen, K.L.; Sethi, R.; Elimelech, M. Reduced aggregation and sedimentation of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in the presence of guar gum. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 324, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandramohan, J.; Anandan, S.; Sivasankar, T. A simple approach for the sonochemical synthesis of Fe3O4-guargum nanocomposite and its catalytic reduction of p-nitroaniline. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidhin, M.; Indumathy, R.; Sreeram, K.J.; Nair, B.U. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles of narrow size distribution on polysaccharide templates. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2008, 31, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Goswami, G.K.; Nanda, K.K. Green synthesis of biopolymer–silver nanoparticle nanocomposite: An optical sensor for ammonia detection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Mishra, S.B. Catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol by using platinum nanoparticles stabilised by guar gum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandramohan, J.; Sivasankar, T. Sonication-assisted synthesis of a new heterostructured schiff base ligand Silver-Guar gum encapsulated nanocomposite as a visible light photocatalyst. J. Microencapsul. 2020, 37, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandramohan, J.; Sivasankar, T.; Sivakumar, M. Facile sonochemical synthesis of Ag2O-guar gum nanocomposite as a visible light photocatalyst for the organic transformation reactions. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 385, 121621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amritha, A.S.; Manu, B. Low cost Fenton’s oxidative degradation of 4-nitroaniline using iron from laterite. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remucal, C.K.; Sedlak, D.L. The Role of Iron Coordination in the Production of Reactive Oxidants from Ferrous Iron Oxidation by Oxygen and Hydrogen Peroxide. In Aquatic Redox Chemistry; ACS Symposium Series; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 177–197. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Ali, N.; Khan, I.; Zhang, B.; Sadiq, M. Heterogeneous photodegradation of industrial dyes: An insight to different mechanisms and rate affecting parameters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Zekker, I.; Zhang, B.; Hendi, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zada, N.; Ahmad, H.; Shah, L.A.; et al. Review on Methylene Blue: Its Properties, Uses, Toxicity and Photodegradation. Water 2022, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Yang, P.; Lu, X. Degradation of 4-chlorophenol by a microwave assisted photocatalysis method. J. Hazard Mater. 2005, 124, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, S.R.M.; Ngatenah, S.N.I.; Johan, N.A.; Amat, K.A.C. Removal of Zn (II), Cu (II), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Colour from Anaerobically Treated Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) using Microwave Incinerated Rice Husk Ash (MIRHA). Int. Conf. Environ. Ind. Innov. 2011, 12, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, J.; De Luis, A.M.; Ortueta, M.; Varona, F.; Lombraña, J.I. Microwave and Fenton’s reagent oxidation of wastewater. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2003, 1, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Chen, B.; Lv, Z.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Preparation of a three-dimensional porous PbO2-CNTs composite electrode and study of the degradation behavior of p-nitrophenol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Yin, Z.; Cao, S. Silver/carbon co-decorated hollow TiO2 catalyst drives the efficient photocatalytic degradation/catalytic hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 133, 104274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Munthali, R.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z. Enhanced photocatalytic activity for 4-nitrophenol degradation using visible-light-driven In2S3/α-Fe2O3 composite. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 303, 122461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Miao, B.; Zhang, X.; Lv, R. Heterogeneous electro-Fenton-like oxidation for the degradation of 4-nitrophenol characterized by immobilized Fe(III): Performance, mechanism and chlorinated organic compounds formation. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 38, 101662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, B.; Gupta, R.; Modak, J.M.; Madras, G. Novel insights into the properties of AgBiO3 photocatalyst and its application in immobilized state for 4-nitrophenol degradation and bacteria inactivation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2019, 373, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandramohan, J.; Sivasankar, T. Ultrasound assisted synthesis of guar gum-zero valent iron nanocomposites as a novel catalyst for the treatment of pollutants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balachandramohan, J.; Kumar, M.; Sivasankar, T.; Sivakumar, M. Natural Polymer-Based Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Synthesis, Characterization and Its Application for 1-Amino-Nitrobenzene Degradation in Assistance with Oxidants. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101161
Balachandramohan J, Kumar M, Sivasankar T, Sivakumar M. Natural Polymer-Based Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Synthesis, Characterization and Its Application for 1-Amino-Nitrobenzene Degradation in Assistance with Oxidants. Catalysts. 2022; 12(10):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101161
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalachandramohan, Jayachandrabal, Mithun Kumar, Thirugnanasambandam Sivasankar, and Manickam Sivakumar. 2022. "Natural Polymer-Based Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Synthesis, Characterization and Its Application for 1-Amino-Nitrobenzene Degradation in Assistance with Oxidants" Catalysts 12, no. 10: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101161
APA StyleBalachandramohan, J., Kumar, M., Sivasankar, T., & Sivakumar, M. (2022). Natural Polymer-Based Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Synthesis, Characterization and Its Application for 1-Amino-Nitrobenzene Degradation in Assistance with Oxidants. Catalysts, 12(10), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101161








