Photocatalytic Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Greywater
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Their resistance to biodegradation;
- Due to their small molecular sizes, the filtration modules are unable to create a suitable barrier to hold them back.
2. Results
2.1. Photocatalysts Used and Their Characterization
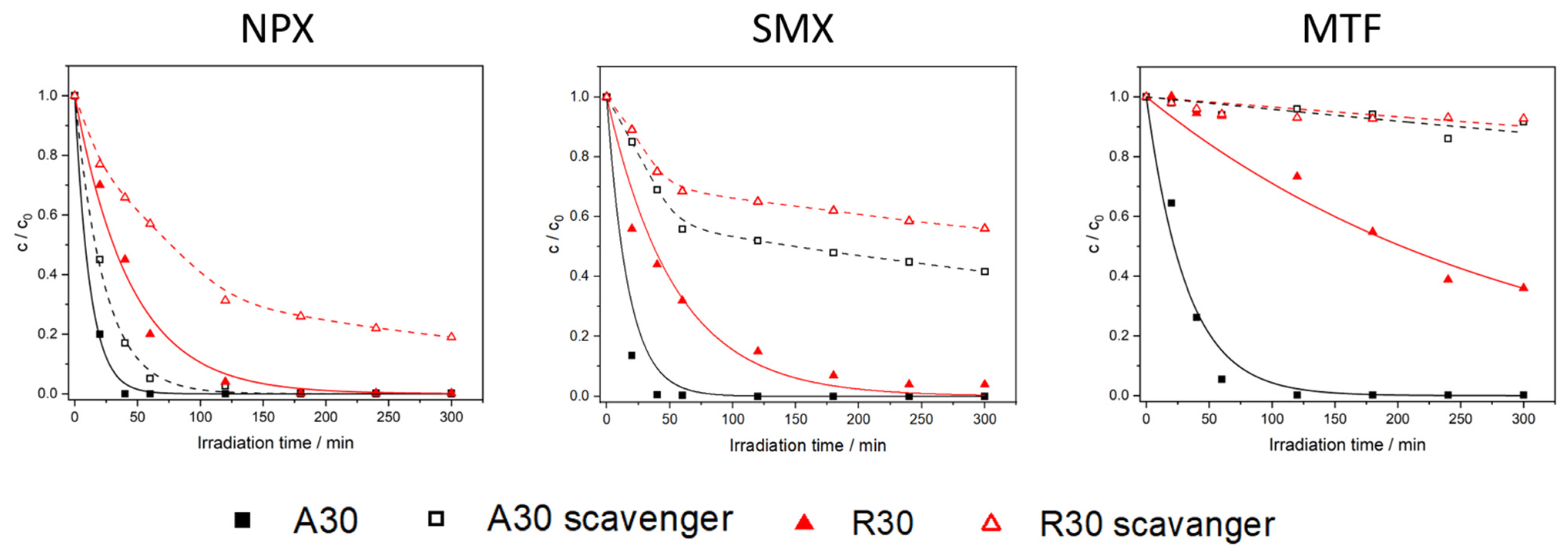
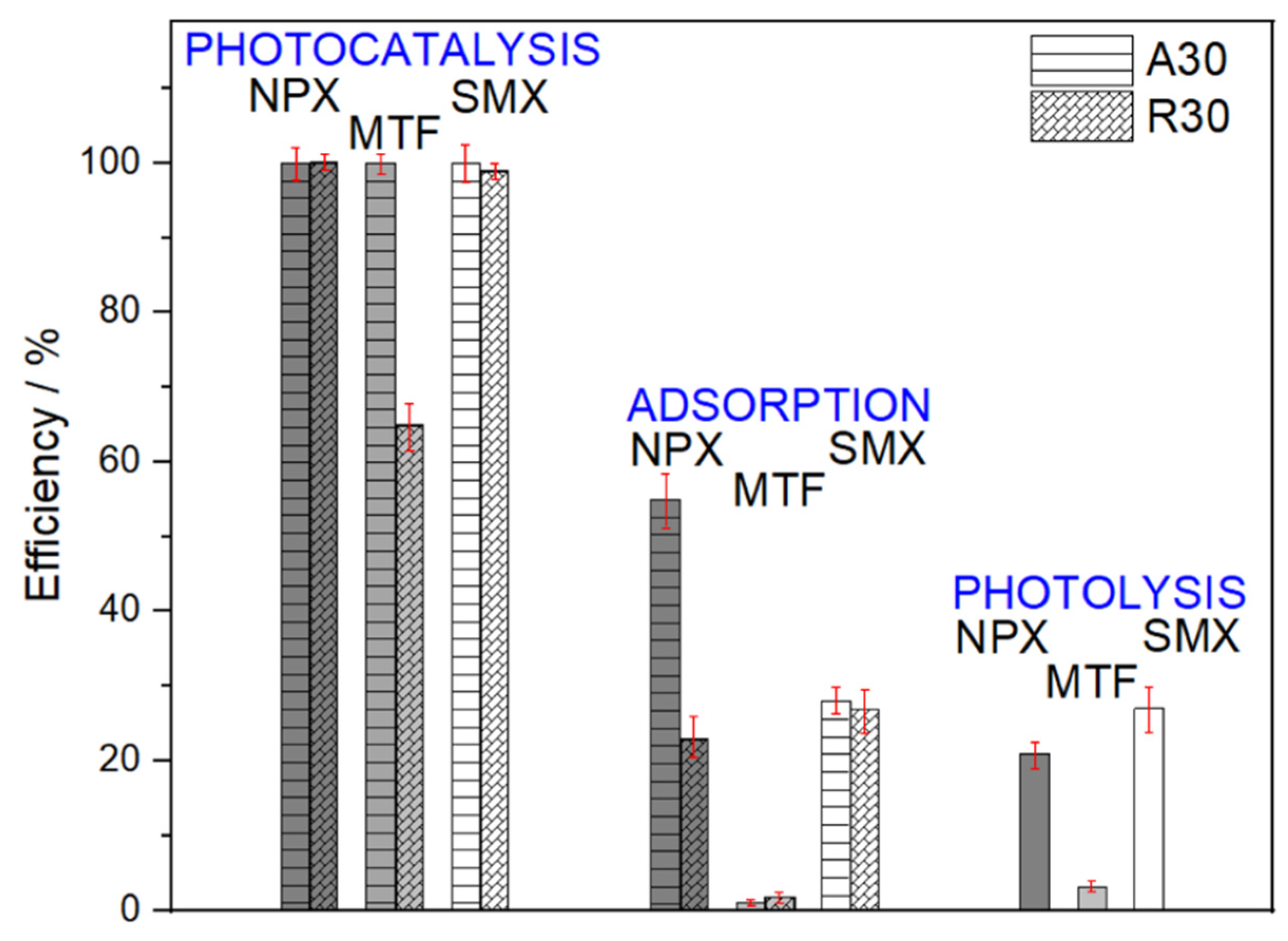
2.2. Photocatalytic Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Ultrapure Water and in the Presence of a Radical Scavenger
2.2.1. Naproxen
2.2.2. Sulfamethoxazole
2.2.3. Metformin
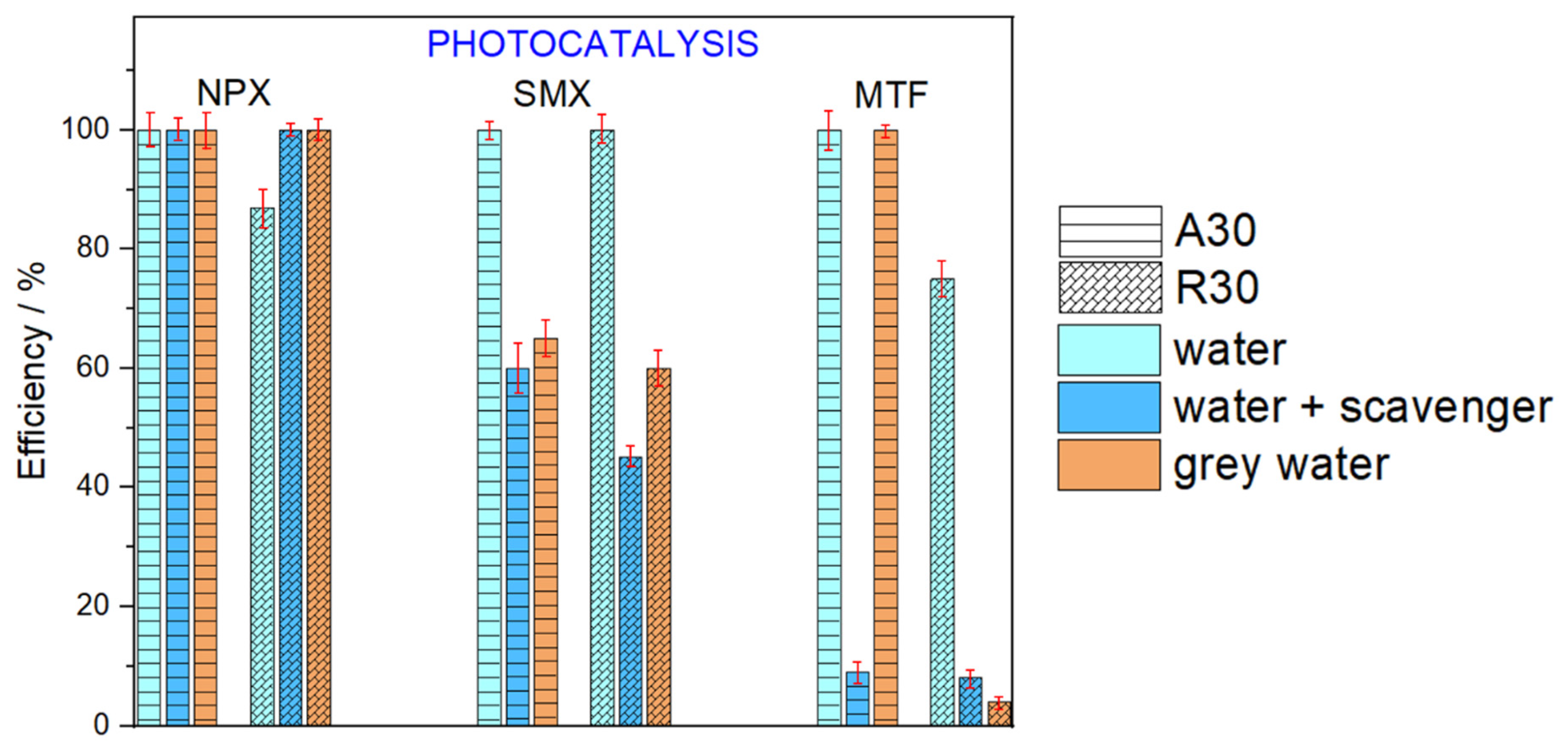
2.3. Photocatalytic Removal of Pharmaceuticals in MBR-Treated Greywater
3. Discussion
Degradation of Pharmaceuticals Using TiO2
4. Materials and Methods
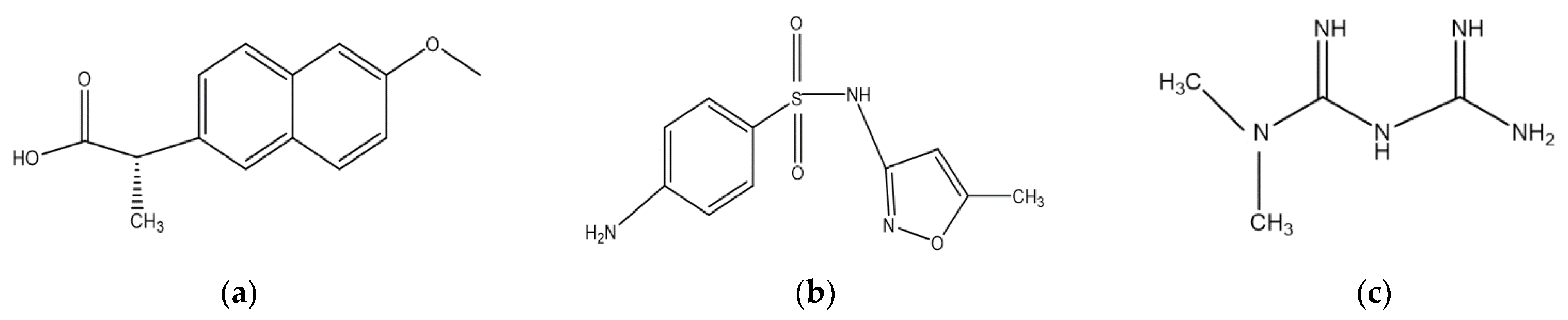
4.1. Pharmaceuticals
4.2. TiO2 Photocatalysts
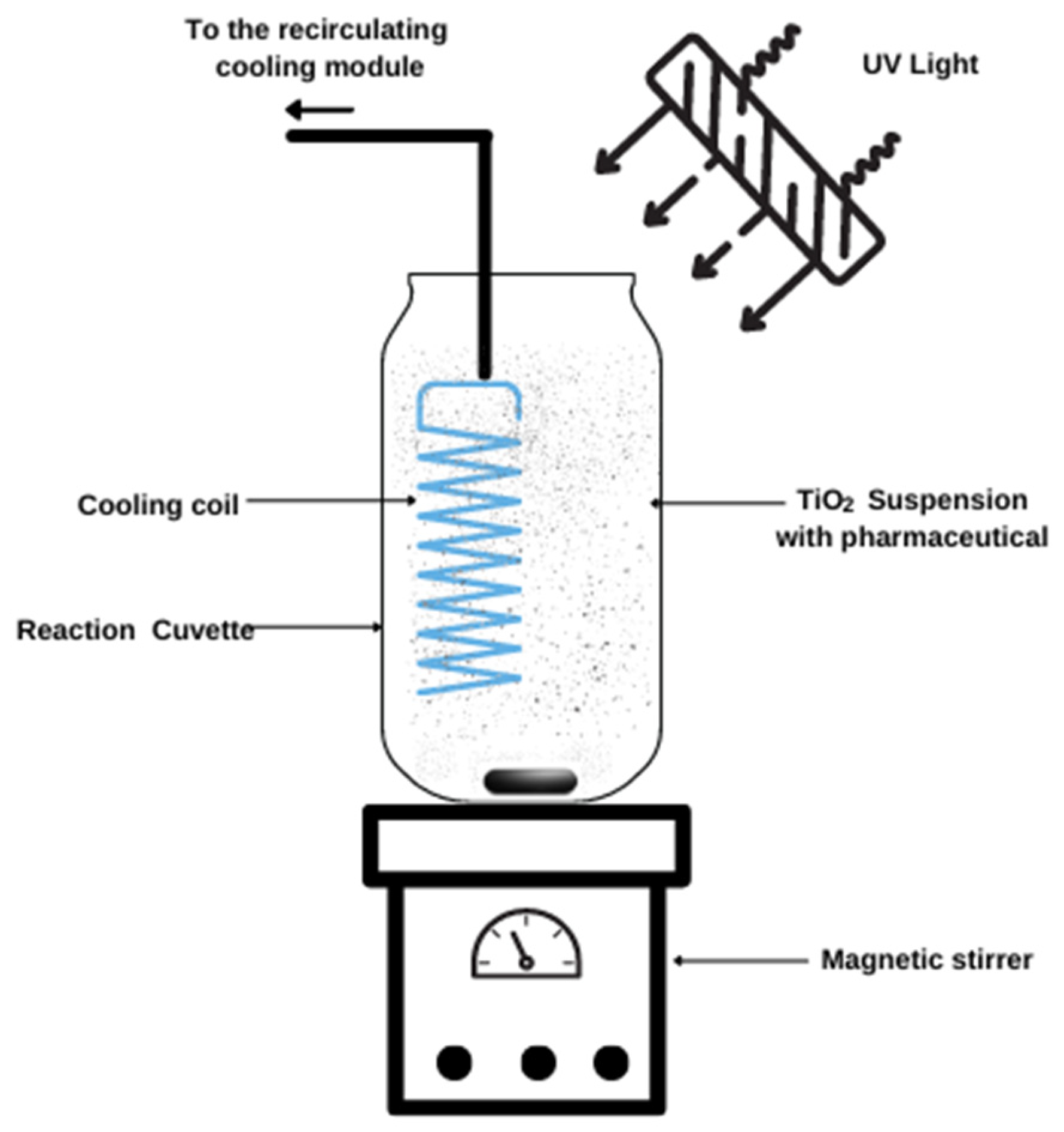
4.3. Photocatalytic Experiments
4.4. Adsorption, Photolysis and Scavenger Experiments
4.5. Lab-Scale MBR Treatment of Greywater
4.6. Analytical Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Li, B. Occurrence, transformation, and fate of antibiotics in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 951–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benotti, M.J.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.J.; Holady, J.C.; Stanford, B.D.; Snyder, S. Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in U.S. drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.E.; Newton, I.; Shultz, S.; Cunningham, A.A.; Gilbert, M.; Pain, D.J.; Prakash, V. Diclofenac poisoning as a cause of vulture population declines across the Indian subcontinent. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 41, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.-A.; der Beek, T.A.; Carius, A.; Grüttner, G.; Hickmann, S.; Ebert, I.; Hein, A.; Küster, A.; Rose, J.; Koch-Jugl, J. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment—The Global Perspective Occurrence, Effects, and Potential Cooperative Action under SAICM; German Environment Agency: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2014.
- Bolong, N.; Ismail, A.; Salim, M.R.; Matsuura, T. A review of the effects of emerging contaminants in wastewater and options for their removal. Desalination 2009, 239, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyjoo, Y.; Pareek, V.K.; Ang, M. A review of greywater characteristics and treatment processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1403–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Butler, D.; Memon, F.; Makropoulos, C.; Avery, L.; Jefferson, B. Impacts of residence time during storage on potential of water saving for grey water recycling system. Water Res. 2010, 44, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etchepare, R.; van der Hoek, J.P. Health risk assessment of organic micropollutants in greywater for potable reuse. Water Res. 2015, 72, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Hoek, J.P.; Tenorio, J.L.I.; Hellinga, C.; Van Lier, J.B.; Van Wijk, A.J.M. Green village delft—Integration of an autarkic water supply in a local sustainable energy system. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2014, 4, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Butkovskyi, A.; Sevenou, L.; Meulepas, R.J.W.; Leal, L.H.; Zeeman, G.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M. Micropollutant removal from black water and grey water sludge in a UASB-GAC reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 77, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Angelin, A.; Kalpana, M.; Rangarajan, M.; Shankar, P.; Jang, A. Electrocoagulants characteristics and application of electrocoagulation for micropollutant removal and transformation mechanism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 12, 1775–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, E.K.; O’Malley, K.N.; Dollhopf, M.E.; Mayer, B.K.; McNamara, P.J. Removal of estrogenic compounds from water via energy efficient sequential electrocoagulation-electrooxidation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2020, 37, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Palaniandy, P.; Dahlan, I. Pharmaceutical residues in aquatic environment and water remediation by TiO2 heterogeneous photocatalysis: A review. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foteinis, S.; Borthwick, A.G.; Frontistis, Z.; Mantzavinos, D.; Chatzisymeon, E. Environmental sustainability of light-driven processes for wastewater treatment applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, O.; García-Araya, J.; Beltrán, F.; Rivas, F.; Espejo, A. Removal of emerging contaminants from a primary effluent of municipal wastewater by means of sequential biological degradation-solar photocatalytic oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassie, L.W.; Englehardt, J.D. Advanced oxidation and disinfection processes for onsite net-zero greywater reuse: A review. Water Res. 2017, 125, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-García, N.; Suárez, S.; Sanchez, B.; Coronado, J.; Malato, S.; Maldonado, M.I. Photocatalytic degradation of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plant effluents using immobilized TiO2 in a solar pilot plant. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 103, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirilä, M.; Saouabe, M.; Ojala, S.; Rathnayake, B.; Drault, F.; Valtanen, A.; Huuhtanen, M.; Brahmi, R.; Keiski, R.L. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater. Top. Catal. 2015, 58, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Pisani, P.L. Direct reclamation of potable water at Windhoek’s Goreangab reclamation plant. Desalination 2006, 188, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Richard, J.; Liu, Y.; Dopp, E.; Tuerk, J.; Bester, K. Ozonation products of triclosan in advanced wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, V.; Priyanka, K.; Remya, N. Solar photocatalytic degradation of metformin by TiO2 synthesized using Calotropis gigantea leaf extract. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallouli, N.; Elghniji, K.; Hentati, O.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Silva, A.; Ksibi, M. UV and solar photo-degradation of naproxen: TiO2 catalyst effect, reaction kinetics, products identification and toxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 304, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakaraju, D.; Motti, C.; Glass, B.D.; Oelgemöller, M. Solar photolysis versus TiO2-mediated solar photocatalysis: A kinetic study of the degradation of naproxen and diclofenac in various water matrices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17437–17448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roncaroli, F.; Blesa, M.A. Kinetics of adsorption of carboxylic acids onto titanium dioxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 9938–9944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, K.D.; McQuillan, A. In situ infrared spectroscopic analysis of the adsorption of aliphatic carboxylic acids to TiO2, ZrO2, Al2O3, and Ta2O5 from aqueous solutions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 1999, 55, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, A.; Bruni, M.; Maldotti, A. Chemo- and Regio-Selectivity in the TiO2-Mediated Photooxidation of 1,n-diols. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2008, 11, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, B.; Pflüger, F.; Kruglik, S.G.; Cohen, R.; Ghomi, M. Protonation–deprotonation and structural dynamics of antidiabetic drug metformin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 114, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brame, J.; Long, M.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P. Inhibitory effect of natural organic matter or other background constituents on photocatalytic advanced oxidation processes: Mechanistic model development and validation. Water Res. 2015, 84, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samayamanthula, D.R.; Sabarathinam, C.; Bhandary, H. Treatment and effective utilization of greywater. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Bashirzadeh, Y.; Bernadowski, T.A.; Zhang, X. UV Light-Induced Aggregation of Titania Submicron Particles. Micromachines 2016, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Photocatalyst | Phase Content a/% Anatase Rutile | Crystallite Size a/nm Anatase Rutile | Particle Size b/nm | Particle Size c/nm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A30 | 100 | 0 | 16 | - | 31 | 20–40 |
| R30 | 0 | 100 | - | 29 | 100 | 30–100 |
| Parameter Range | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dissolved oxygen/mg L−1 | 6.7–8.5 | |
| Temperature/°C | 22.6–26.0 | |
| Total nitrogen/mg L−1 | 0.2–11.7 | |
| Total phosphorus/mg L −1 | 0.1–0.4 | |
| Electric conductivity/µS cm−1 | 412–500 | |
| pH | 6.5–7.6 | |
| Dissolved organic carbon/mg L−1 | 3.4–5.4 | |
| Solids/mg L−1 | Total suspended solids | Not detected |
| Total dissolved solids | 310–358 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ojobe, B.; Zouzelka, R.; Satkova, B.; Vagnerova, M.; Nemeskalova, A.; Kuchar, M.; Bartacek, J.; Rathousky, J. Photocatalytic Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Greywater. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091125
Ojobe B, Zouzelka R, Satkova B, Vagnerova M, Nemeskalova A, Kuchar M, Bartacek J, Rathousky J. Photocatalytic Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Greywater. Catalysts. 2021; 11(9):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091125
Chicago/Turabian StyleOjobe, Bukola, Radek Zouzelka, Barbora Satkova, Magdalena Vagnerova, Alzbeta Nemeskalova, Martin Kuchar, Jan Bartacek, and Jiri Rathousky. 2021. "Photocatalytic Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Greywater" Catalysts 11, no. 9: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091125
APA StyleOjobe, B., Zouzelka, R., Satkova, B., Vagnerova, M., Nemeskalova, A., Kuchar, M., Bartacek, J., & Rathousky, J. (2021). Photocatalytic Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Greywater. Catalysts, 11(9), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091125








