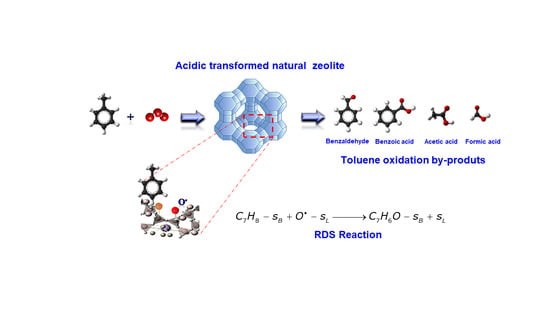
Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene over Acidic Surface Transformed Natural Zeolite: A Dual-Site Reaction Mechanism and Kinetic Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
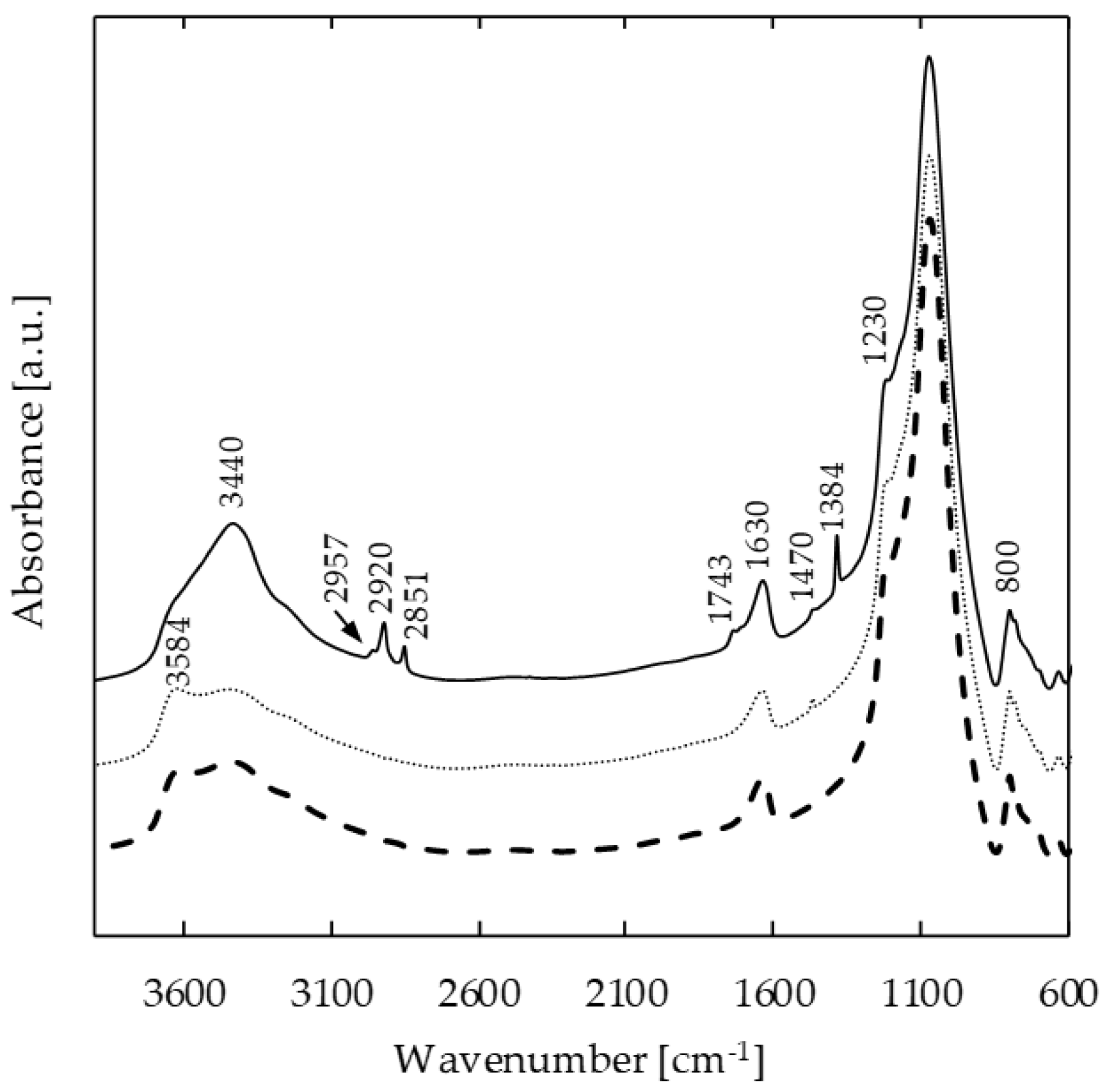
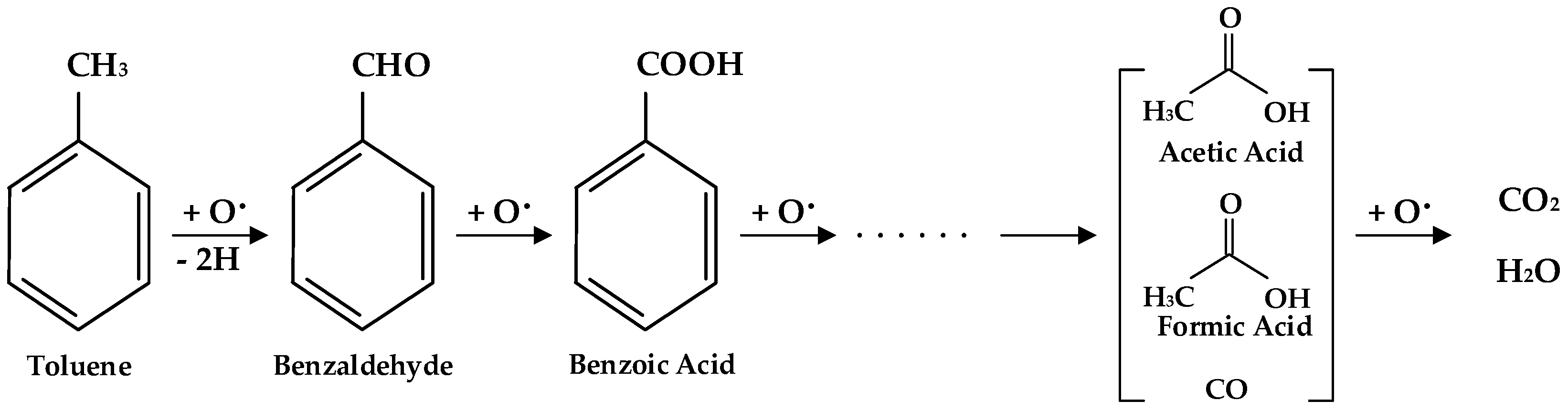
2.1. FTIR Evidence of the Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene
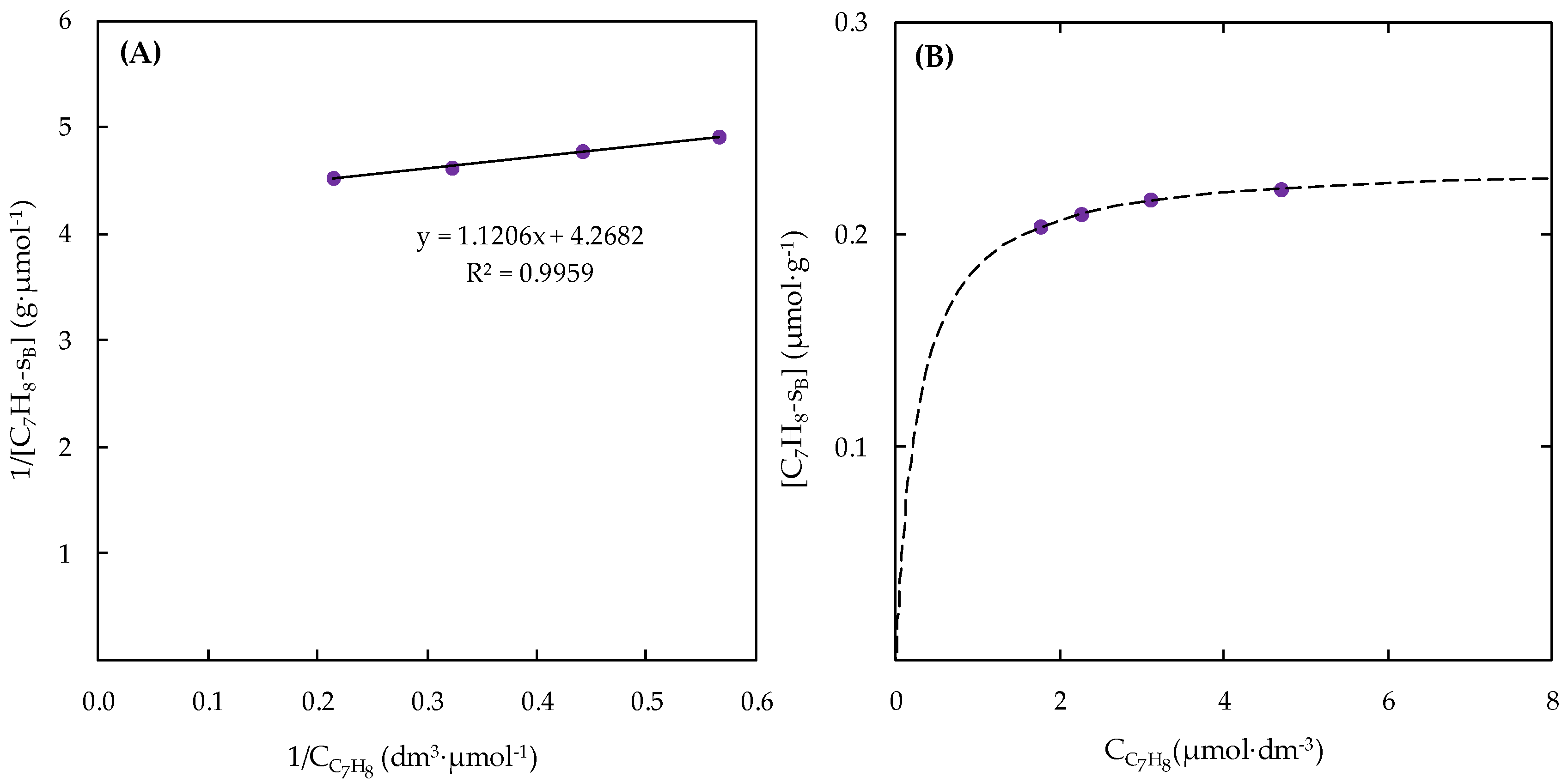
2.2. Kinetic Approaches of Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Transformation of As-Received Natural Zeolite into a Modified Zeolite Rich in Acidic Sites
3.3. Experimental Description of Catalytic Ozonation Studies
3.4. In Situ FTIR Study of Surface Interactions between Zeolite Sample and Toluene Oxidation By-Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parmar, G.R.; Rao, N.N. Emerging Control Technologies for Volatile Organic Compounds. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 39, 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-W.; Kim, J.-R.; Ihm, S.-K. Design of dual functional adsorbent/catalyst system for the control of VOC’s by using metal-loaded hydrophobic Y-zeolites. Catal. Today 2004, 93–95, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Lioy, P.; Weschler, C.; Fiedler, N.; Kipen, H.; Zhang, J. Ozone-Initiated Reactions with Mixtures of Volatile Organic Compounds under Simulated Indoor Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megías-Sayago, C.; Lara-Ibeas, I.; Wang, Q.; Le Calvé, S.; Louis, B. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) removal capacity of ZSM-5 zeolite adsorbents for near real-time BTEX detection. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Kabir, S. A review on the human health impact of airborne particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, X.; Creamer, A.E.; Annable, M.D.; Li, Y. Biochar for volatile organic compound (VOC) removal: Sorption performance and governing mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnew, G.A.; Meusinger, C.; Bork, N.; Gallus, M.; Kyte, M.; Rodins, V.; Rosenørn, T.; Johnson, M.S. Gas-phase advanced oxidation as an integrated air pollution control technique. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2016, 3, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, S.; Pitkäaho, S.; Laitinen, T.; Koivikko, N.N.; Brahmi, R.; Gaálová, J.; Kucherov, A.; Matejova, L.; Päivärinta, S.; Hirschmann, C.; et al. Catalysis in VOC Abatement. Top. Catal. 2011, 54, 1224–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidahy, H.L.; Siffert, S.; Lamonier, J.F.; Cousin, R.; Zhilinskaya, E.A.; Aboukaïs, A.; Su, B.L.; Canet, X.; De Weireld, G.; Frère, M.; et al. Influence of the exchanged cation in Pd/BEA and Pd/FAU zeolites for catalytic oxidation of VOCs. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 70, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.S.; You, D.W.; Park, H.O.; Jung, K.W. Catalytic oxidation of VOCs over CNT-supported platinum nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, A.P.; Ribeiro, M.F.; Silva, J.M.; Ribeiro, F.R.; Magnoux, P.; Guisnet, M. Catalytic oxidation of toluene over CuNaHY zeolites: Coke formation and removal. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 33, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Leung, D.Y.C. Low temperature catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: A review. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 2649–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenjian, A.; Khodiev, A. How ozone can affect volatile organic compounds. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2009, 3, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, E.; Soltan, J.; Chen, N. Catalytic oxidation of toluene by ozone over alumina supported manganese oxides: Effect of catalyst loading. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136–137, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.P.; Zhao, J.G.; Yang, L.X.; Fu, M.L.; Wu, J.L.; Huang, B.C.; Ye, D.Q. Room Temperature Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene over MnO2/Al2O3. Chin. J. Catal. 2011, 32, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, E.; Soltan, J. Low temperature oxidation of toluene by ozone over MnOx/alumina and MnOx/MCM-41 catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, J.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. The efficiency and mechanisms of catalytic ozonation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 99, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Moussavi, G.; Bakhtiari, A.R.; Yamini, Y. Toluene removal from waste air stream by the catalytic ozonation process with MgO/GAC composite as catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 306, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Shi, C.; Zhu, A. Ozone catalytic oxidation of benzene over AgMn/HZSM-5 catalysts at room temperature: Effects of Mn loading and water content. Cuihua Xuebao Chin. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ye, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Shao, Q.; Peng, Z.; Ou, G.; Shi, J.; et al. Ozone-catalytic oxidation of gaseous benzene over MnO2/ZSM-5 at ambient temperature: Catalytic deactivation and its suppression. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, H.; Maeda, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Teraoka, Y. Catalytic properties of copper-manganese mixed oxides supported on SiO2 for benzene oxidation with ozone. Catal. Today 2015, 245, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, T.; Swetha, G.; Shekar, S.C.; Krishna, R.; Ramakrishna, C.; Saini, B.; Rao, P.V.L.V.L. Ozone catalytic oxidation of toluene over 13X zeolite supported metal oxides and the effect of moisture on the catalytic process. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 12, 4502–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-H.; Sugasawa, M.; Hirata, H.; Teramoto, Y.; Kosuge, K.; Negishi, N.; Ogata, A. Ozone-assisted catalysis of toluene with layered ZSM-5 and Ag/ZSM-5 zeolites. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2013, 33, 1083–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ji, J.; Zhang, B.; Huang, W.; Gan, Y.; Leung, D.Y.C.; Huang, H. Catalytic ozonation of VOCs at low temperature: A comprehensive review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 126847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Liang, H.S.; Chang, M.B. Ozone-enhanced catalytic oxidation of monochlorobenzene over iron oxide catalysts. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Miao, G.; Pi, Y.; Xia, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J. Abatement of various types of VOCs by adsorption/catalytic oxidation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 1128–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wen, M.; Li, G.; An, T. Recent advances in VOC elimination by catalytic oxidation technology onto various nanoparticles catalysts: A critical review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 281, 119447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodu, N.; Zaitan, H.; Manero, M.-H.; Pic, J.-S. Removal of volatile organic compounds by heterogeneous ozonation on microporous synthetic alumina silicate. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2020–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, G.S.P.; Özçelik, Z.; Boz, İ.I. Total oxidation of toluene over metal oxides supported on a natural clinoptilolite-type zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, P.; Genov, K.; Konova, P.; Milenova, K.; Batakliev, T.; Georgiev, V.; Kumar, N.; Sarker, D.K.; Pishev, D.; Rakovsky, S. Ozone decomposition on Ag/SiO2 and Ag/clinoptilolite catalysts at ambient temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, H.; Tardón, R.F.; Zaror, C.A. Role of surface hydroxyl groups of acid-treated natural zeolite on the heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of methylene blue contaminated waters. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro-Martín, S.; Valdés, H.; Manero, M.-H.; Zaror, C. Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene Using Chilean Natural Zeolite: The Key Role of Brønsted and Lewis Acid Sites. Catalysts 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valdés, H.; Ulloa, F.J.; Solar, V.A.; Cepeda, M.S.; Azzolina-Jury, F.; Thibault-Starzyk, F. New insight of the influence of acidic surface sites of zeolite on the ability to remove gaseous ozone using operando DRIFTS studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 294, 109912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Su, T.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, X.; Qin, Z.; Ji, H. In situ DRIFTS study of O3 adsorption on CaO, γ-Al2O3, CuO, α-Fe2O3 and ZnO at room temperature for the catalytic ozonation of cinnamaldehyde. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 412, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque Malherbe, R.; Wendelbo, R. Study of Fourier transform infrared-temperature-programmed desorption of benzene, toluene and ethylbenzene from H-ZSM-5 and H-Beta zeolites. Thermochim. Acta 2003, 400, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, H.; Futamura, S. Catalytic oxidation of benzene with ozone over alumina-supported manganese oxides. J. Catal. 2004, 227, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, H.; Ogata, A. Benzene oxidation with ozone over supported manganese oxide catalysts: Effect of catalyst support and reaction conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandapani, B.; Oyama, S.T. Gas phase ozone decomposition catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1997, 11, 129–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Oyama, S.T. Mechanism of Ozone Decomposition on a Manganese Oxide Catalyst. 2. Steady-State and Transient Kinetic Studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9047–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, H.; Futamura, S. Comparative study on the catalytic activities of alumina-supported metal oxides for oxidation of benzene and cyclohexane with ozone. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2004, 81, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, S.T. Chemical and Catalytic Properties of Ozone. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2000, 42, 279–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Ziólek, M.; Nawrocki, J. Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulanin, K.M.; Lavalley, J.C.; Tsyganenko, A.A. IR spectra of adsorbed ozone. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 101, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulanin, K.M.; Lavalley, J.C.; Tsyganenko, A.A. Infrared Study of Ozone Adsorption on CaO. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 2917–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Hui, K.S.; Hui, K.N. Role of graphene in MnO2/graphene composite for catalytic ozonation of gaseous toluene. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Woo, S.I. Mechanistic study on the SCR of NO by C3H6 over Pt/V/MCM-41. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 44, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-M.; Yang, X.-F.; Zhu, A.-M.; Fan, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-K.; Xin, Q.; Zhou, X.-R.; Shi, C. In situ DRIFTS study on the partial oxidation of ethylene over Co-ZSM-5 catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, S.; Valdés, H.; Manéro, M.-H.; Zaror, C.A. Oxidative regeneration of toluene-saturated natural zeolite by gaseous ozone: The influence of zeolite chemical surface characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaei, E.; Soltan, J.; Chen, N.; Lin, J. Effect of noble metals on activity of MnOx/γ-alumina catalyst in catalytic ozonation of toluene. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 214, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kwon, E.E.; Lee, J.E.; Jang, S.-H.; Jeon, J.-K.; Song, J.; Park, Y.-K. Effect of zeolite acidity and structure on ozone oxidation of toluene using Ru-Mn loaded zeolites at ambient temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Durme, J.; Dewulf, J.; Sysmans, W.; Leys, C.; Van Langenhove, H. Abatement and degradation pathways of toluene in indoor air by positive corona discharge. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Na, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Z. In situ DRIFTS investigation for the oxidation of toluene by ozone over Mn/HZSM-5, Ag/HZSM-5 and Mn-Ag/HZSM-5 catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, W. Destruction of toluene by ozone-enhanced photocatalysis: Performance and mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 102, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ye, D.; Leung, D.Y.C.; Feng, F.; Guan, X. Byproducts and pathways of toluene destruction via plasma-catalysis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 336, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodu, N.; Manero, M.-H.; Andriantsiferana, C.; Pic, J.-S.; Valdés, H. Role of Lewis acid sites of ZSM-5 zeolite on gaseous ozone abatement. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brodu, N.; Manero, M.-H.; Andriantsiferana, C.; Pic, J.-S.; Valdés, H. Gaseous ozone decomposition over high silica zeolitic frameworks. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 96, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brodu, N.; Sochard, S.; Andriantsiferana, C.; Pic, J.-S.; Manero, M.-H. Fixed-bed adsorption of toluene on high silica zeolites: Experiments and mathematical modelling using LDF approximation and a multisite model. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.Y.H.; Kwong, C.W.; Hui, K.S. Potential use of a combined ozone and zeolite system for gaseous toluene elimination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, H.; Futamura, S. Catalytic oxidation of benzene with ozone over Mn ion-exchanged zeolites. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.C. Nonlinear least-squares curve fitting with Microsoft Excel Solver. J. Chem. Educ. 1998, 75, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toby, S.; Van de Burgt, L.J.; Toby, F.S. Kinetics and chemiluminescence of ozone-aromatic reactions in the gas phase. J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 1982–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yao, Z.; Hui, K.N.; Hui, K.S. Novel mechanistic view of catalytic ozonation of gaseous toluene by dual-site kinetic modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaei, E.; Soltan, J. EXAFS and kinetic study of MnOx/γ-alumina in gas phase catalytic oxidation of toluene by ozone. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 148–149, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbolaghy, M.; Soltan, J.; Chen, N. Low Temperature Catalytic Oxidation of Binary Mixture of Toluene and Acetone in the Presence of Ozone. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 3431–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.F. Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 54, ISBN 0133887820. [Google Scholar]
- Vannice, M.A. Kinetics of Catalytic Reactions; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-387-24649-9. [Google Scholar]
- Alejandro, S.; Valdés, H.; Zaror, C.A. Natural Zeolite Reactivity towards Ozone: The Role of Acid Surface Sites. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2011, 14, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, S.; Valdés, H.; Manero, M.-H.; Zaror, C.A. BTX abatement using Chilean natural zeolite: The role of Bronsted acid sites. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque-Malherbe, R.; Ivanov, V. Codiffusion and counterdiffusion of para-xylene and ortho-xylene in a zeolite with 10 MR/12 MR interconnected channels. An example of molecular traffic control. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 313, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque-Malherbe, R. Complementary approach to the volume filling theory of adsorption in zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 41, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, H.; Alejandro, S.; Zaror, C.A. Natural zeolite reactivity towards ozone: The role of compensating cations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227–228, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, H.; Farfán, V.J.; Manoli, J.A.; Zaror, C.A. Catalytic ozone aqueous decomposition promoted by natural zeolite and volcanic sand. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guisnet, M.; Ayrault, P.; Coutanceau, C.; Fernanda Alvarez, M.; Datka, J. Acid properties of dealuminated beta zeolites studied by IR spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1997, 93, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, N.J.; Valdés, H.; Zaror, C.A.; Azzolina-Jury, F.; Meléndrez, M.F. Ethylene adsorption onto natural and transition metal modified Chilean zeolite: An operando DRIFTS approach. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 274, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
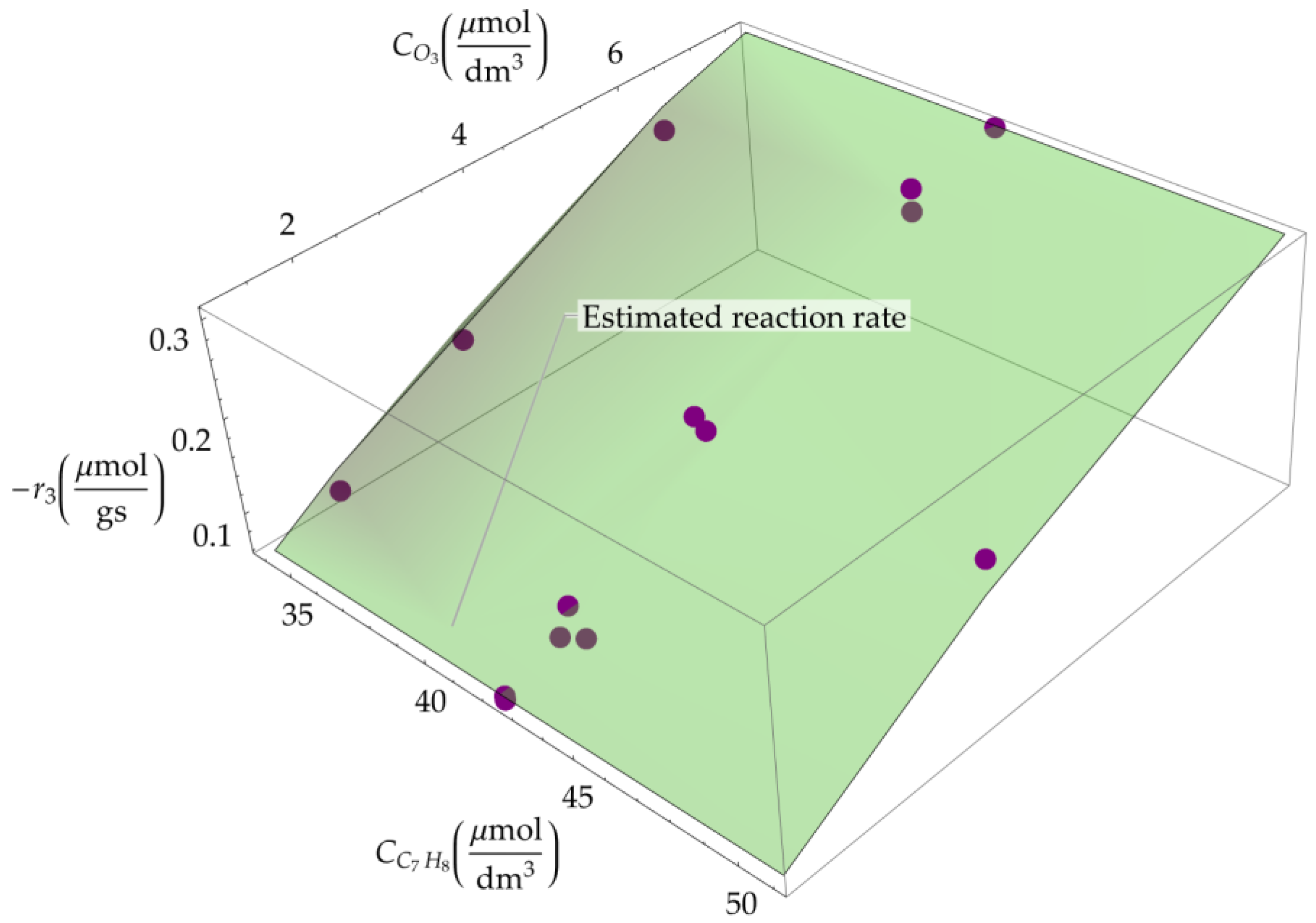
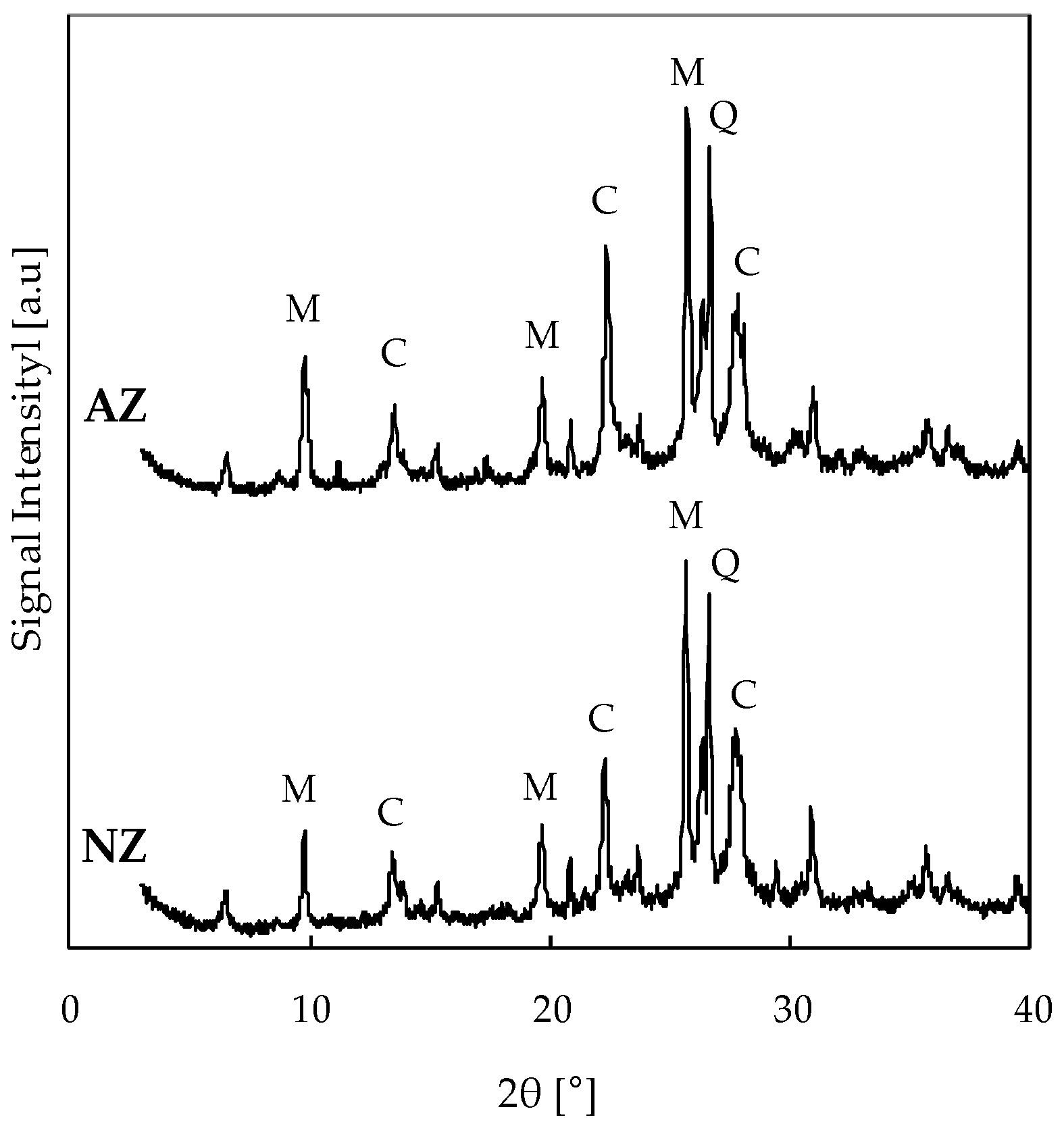

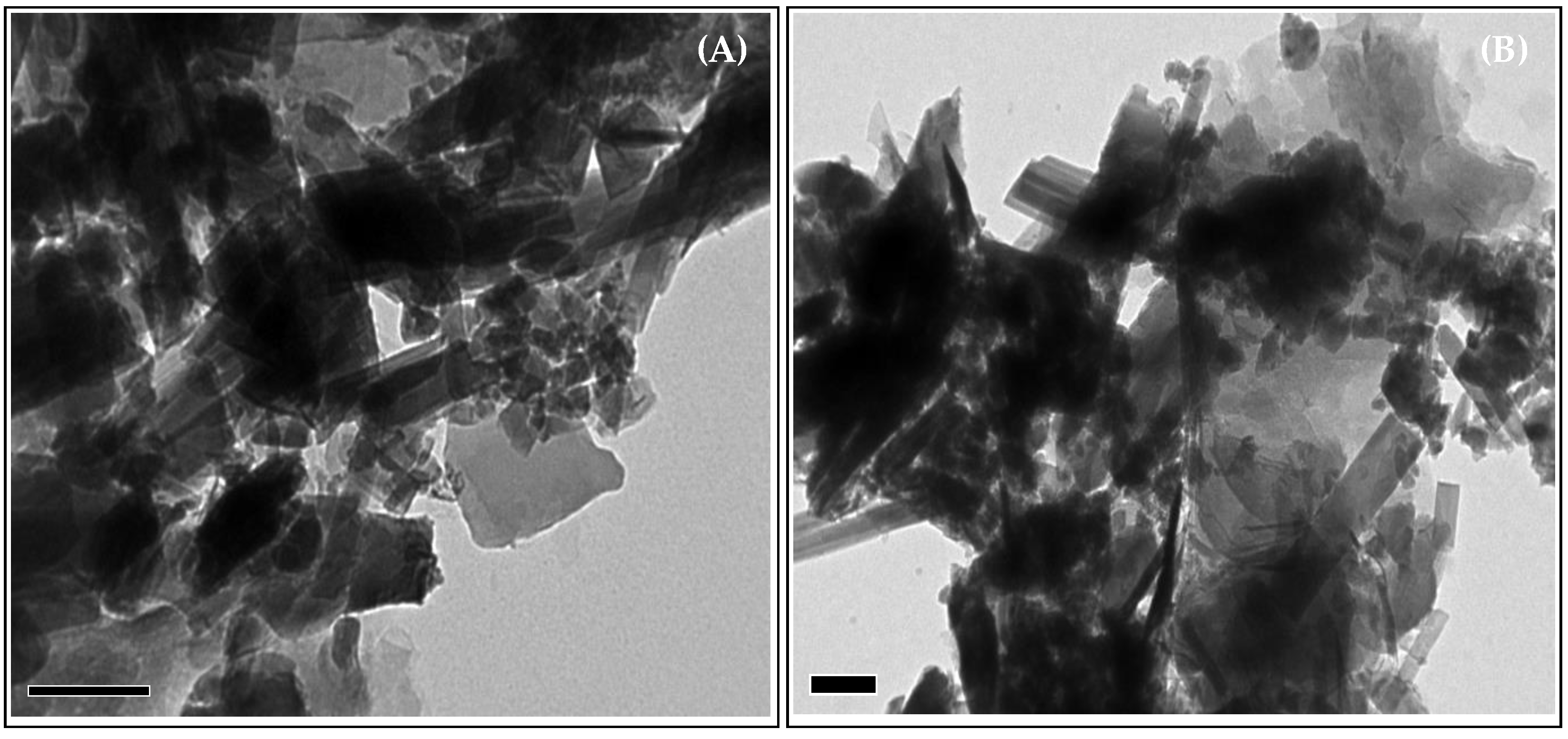
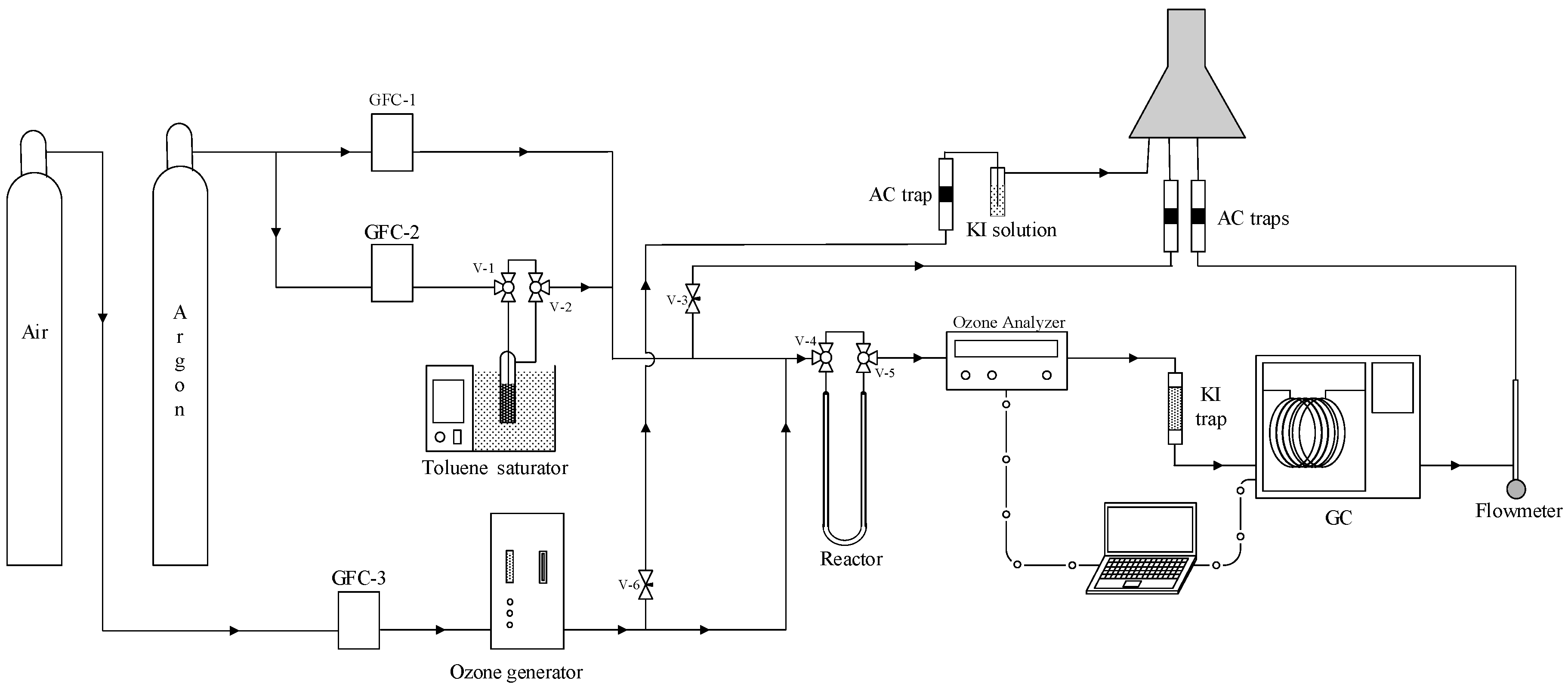
| Catalysts | Reaction Temperature (K) | × 103 (dm3∙μmol)1+α+β∙s−1) | EA app (kJ·mol−1) | α | β | R2 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ | 293 | 5.07 | 17.21 | 0.66 | 0.82 | 0.97 | This study |
| MnO2/graphene | 295 | 3.25 | 29.3 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.91 | [62] |
| MnOx/γ-alumina | 343 | n.r | 31 | −1 | 2 | n.r | [63] |
| MnOx/γ-alumina | 298 | n.r | 33 | 0.18 | 0.56 | 0.98 | [64] |
| Runs | Inlet Concentration (µmol·dm−3) | Conversion of Toluene (%) | −r3 (µmol·g−1·s−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toluene | Ozone | Experimental | Estimated by the Power Law Model | Estimated by the dsL-H Model | ||
| 1 | 42.36 | 3.57 | 11.0 | 0.207 | 0.1769 | 0.1810 |
| 2 | 42.36 | 6.48 | 15.7 | 0.295 | 0.2876 | 0.2871 |
| 3 | 42.36 | 6.48 | 14.4 | 0.272 | 0.2876 | 0.2871 |
| 4 | 42.36 | 1.92 | 5.6 | 0.106 | 0.1054 | 0.1060 |
| 5 | 42.36 | 1.12 | 3.0 | 0.057 | 0.0676 | 0.0646 |
| 6 | 42.36 | 1.12 | 3.2 | 0.061 | 0.0676 | 0.0646 |
| 7 | 42.86 | 1.92 | 4.3 | 0.081 | 0.1063 | 0.1068 |
| 8 | 33.99 | 3.57 | 10.6 | 0.160 | 0.1519 | 0.1562 |
| 9 | 33.85 | 6.43 | 16.8 | 0.253 | 0.2461 | 0.2456 |
| 10 | 33.96 | 1.92 | 5.4 | 0.081 | 0.0910 | 0.0914 |
| 11 | 50.99 | 3.57 | 9.3 | 0.212 | 0.1990 | 0.2032 |
| 12 | 42.71 | 3.57 | 10.4 | 0.198 | 0.1768 | 0.1820 |
| 13 | 42.36 | 1.79 | 4.3 | 0.081 | 0.0995 | 0.0995 |
| 14 | 42.56 | 7.59 | 16.4 | 0.311 | 0.3287 | 0.3218 |
| SBET a (m2∙g−1) | Brønsted b Acid Sites (µmol∙g−1) | Lewis b Acid Sites (µmol∙g−1) | Total Acidity (µmol∙g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 261 | 179.8 | 282.8 | 462.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alejandro-Martín, S.; Valdés, H.; Zaror, C.A. Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene over Acidic Surface Transformed Natural Zeolite: A Dual-Site Reaction Mechanism and Kinetic Approach. Catalysts 2021, 11, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11080958
Alejandro-Martín S, Valdés H, Zaror CA. Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene over Acidic Surface Transformed Natural Zeolite: A Dual-Site Reaction Mechanism and Kinetic Approach. Catalysts. 2021; 11(8):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11080958
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlejandro-Martín, Serguei, Héctor Valdés, and Claudio A. Zaror. 2021. "Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene over Acidic Surface Transformed Natural Zeolite: A Dual-Site Reaction Mechanism and Kinetic Approach" Catalysts 11, no. 8: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11080958
APA StyleAlejandro-Martín, S., Valdés, H., & Zaror, C. A. (2021). Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene over Acidic Surface Transformed Natural Zeolite: A Dual-Site Reaction Mechanism and Kinetic Approach. Catalysts, 11(8), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11080958