Abstract
A series of FeOx-MnO2-CeO2 catalysts were synthesized by the surfactant-templated coprecipitation method and applied for HCHO removal. The influence of Fe/Mn/Ce molar ratio on the catalytic performance was investigated, and the FeOx-MnO2-CeO2 catalyst exhibited excellent catalytic activity, with complete HCHO conversion at low temperatures (40 °C) when the molar ratio of Fe/Mn/Ce was 2/5/5. The catalysts were characterized by N2 adsorption and desorption, XRD, H2-TPR, O2-TPD and XPS techniques to illustrate their structure–activity relationships. The result revealed that the introduction of FeOx into MnO2-CeO2 formed a strong interaction between FeOx-MnO2-CeO2, which facilitated the improved dispersion of MnO2-CeO2, subsequently increasing the surface area and aiding pore development. This promotion effect of Fe enhanced the reducibility and produced abundant surface-active oxygen. In addition, a great number of Oα is beneficial to the intermediate decomposition, whereas the existence of Ce3+ favors the formation of oxygen vacancies on the surface of the catalyst, all of which contributed to HCHO oxidation at low temperatures.
1. Introduction
As a common indoor air pollutant, formaldehyde (HCHO), mainly from building and decoration materials, causes strong irritation, teratogenicity and carcinogenicity, and it is therefore harmful to human health. In 2004, the World Health Organization identified formaldehyde as a group I carcinogen for humans [1]. Hence, from the perspective of protecting human health and the air environment, it is vital to reduce and eliminate formaldehyde. Many technologies have been proposed for indoor HCHO removal, such as adsorption [2], photocatalytic oxidation [3], plasma degradation [4] and catalytic oxidation [5]. Among these, catalytic oxidation of HCHO has been proven to be the most economical and effective technology, because the process involves the complete conversion of HCHO into CO2 and H2O without by-products at low or even room temperature [6]. The key factor of this method lies in the selection and preparation of effective catalysts to eliminate HCHO.
Two types of catalysts for the catalytic oxidation of HCHO have been applied in the reaction process, namely supported noble metals and transition metal oxides [7]. Comparing both types of catalysts, supported noble metal catalysts exhibit superior catalytic properties for HCHO elimination at low or even room temperature. However, due to the scarce resources and high costs of noble metals, many researchers are shifting their attention to the development of inexpensive and effective transition metal oxide catalysts. It has been reported that [MnOx] [8], [Co3O4] [9], [CeO2] [10] and [CuO] [11], being characteristic rich oxygen species and exhibiting rapid electron transfer, are promising alternative catalysts for the catalytic oxidation of HCHO. For example, a MnOx-CeO2 catalyst was prepared by the redox reaction method and it achieved 100% HCHO conversion at 100 °C [12]. Additionally, Co3O4-CeO2 was synthesized by a citric acid sol-gel method, and it fully oxidized HCHO at a temperature as low as 80 °C [13]. According to the literature [14], the use of metal oxides with promoters for the synthesis of trimetal oxide catalysts can increase the amount of surface-active oxygen species and, thus, significantly enhance the catalytic oxidation processes. Jiang et al. [15] reported that Mn-Cu-Ce mixed oxide networks had higher catalytic activity than Mn-Cu and pure Mn due to the inclusion of Cu, which improved the oxygen activation and transport ability. Lu et al. [16] discovered that the addition of MnOx to Co3O4-CeO2 resulted in high dispersion and easy reducibility of a MnOx-Co3O4-CeO2 catalyst at lower temperatures.
However, only a few reports exist on ternary mixed oxide catalysts for the elimination of formaldehyde, and these have failed to address some vital research questions. In an attempt to expand the general knowledge of the application of ternary mixed oxide catalysts for the removal of formaldehyde, it is necessary to develop multi-component metal oxide catalysts for the low-temperature catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde. Therefore, we report the development of Fe-Mn-Ce ternary mixed oxide catalysts for the purification of formaldehyde by the surfactant-templated coprecipitation method. The influence of the Fe/Mn/Ce molar ratio on the structure-activity relationship of the FeOx-MnO2-CeO2 catalysts was investigated.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Catalysts
2.1.1. N2 Adsorption and Desorption
The N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms and pore size distributions of the Fe-Mn-Ce ternary mixed oxides are presented in Figure 1A, B and C, while the specific surface area (SBET), pore diameter and pore volume are summarized in Table 1. All the catalysts exhibited the type Ⅳ isotherm with H3 hysteresis loops in the relative pressure (P/P0) range of 0.6–1.0; the pore structure of the sample caused agglomeration in the capillary, indicating the existence of mesoporous structures [17,18]. It was noted that the FeOx-MnO2-CeO2-2:5:5(FMC-2:5:5) catalyst significantly increased the amount of adsorbed N2, which indicates that the catalyst had large specific surface area and pore volume. This observation is supported by the data in Table 1. The specific surface area and pore volume of FMC-2:5:5 catalyst were 99 m2 g−1 and 0.4 cm3 g−1, respectively. The pure CeO2, Fe3O4 and MnO2 presented similar results for surface area (22 m2 g−1) and pore volume of (0.1 cm3 g−1), while the SBET values and pore volume of MnO2-CeO2 increased to 73 m2 g−1 and 0.2 cm3 g−1, respectively. This is consistent with the investigation by Zhu et al. [12], which reported that the interaction between MnO2 and CeO2 could restrain the structure growth of mixed oxide and thus increase the specific surface area. The addition of an Fe promoter further increased the specific surface area and pore volume of the FMC catalyst; while the Fe content increased to 3 mol (FMC-3:5:5), the SBET value of the sample decreased. This indicates that while the introduction of Fe enhanced the dispersion of the FMC catalyst, excessive Fe may lead to the agglomeration of particles and decrease the specific surface area. Meanwhile, the average pore diameter also increased in comparison with that of MnO2-CeO2, which may be due to the formation of developed pores promoted by Fe incorporation into MnO2-CeO2. This is confirmed by the pore size distribution curve shown in Figure 1C. However, when the Fe content increased to 3 mol (FMC-3:5:5), the SBET value decreased, indicating that excessive Fe may cause particle agglomeration and decrease the specific surface area. Generally, higher values of SBET and pore volume are beneficial to the adsorption of HCHO and could provide more reactive sites, thus improving the catalytic performance [19].
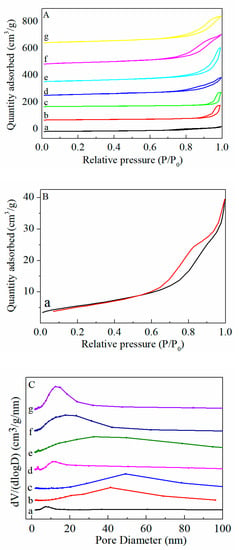
Figure 1.
(A) N2 adsorption isotherms, (B) N2 adsorption isotherms of CeO2 and (C) pore size distribution of (a) CeO2, (b) Fe3O4, (c) MnO2, (d) MnO2-CeO2, (e) FMC-1:5:5, (f) FMC-2:5:5 and (g) FMC-3:5:5.

Table 1.
Specific surface area, average pore diameter and pore volume of the catalysts.
2.1.2. XRD Patterns
The crystal phase of FMC ternary mixed oxide catalysts was characterized by the X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique and the results are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3. As observed from Figure 2, the CeO2 showed sharp and intense peaks at 2θ = 28.7°, 33.1°, 47.6° and 56.4°, which are assigned to the cubic fluorite structure of CeO2 [20]. The pure Fe2O3 exhibited the typical α-Fe2O3 pattern (Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards No.33-0664) [21]. MnO2 exhibited its main peak at 28.6° and several weak peaks at 37.3°, 44.8°and 55.5°, which are all attributed to α-MnO2 (JCPDS No.44-0141) [22]. From the XRD spectra of the different Fe contents (Figure 3), it can be seen that the MnO2-CeO2 and FMC catalysts still retained the cube structure of CeO2 and displayed four diffraction peaks belonging to the plane facet (111), (200), (220) and (311), respectively. Compared with CeO2, the intensity of MnO2-CeO2 decreased steadily, suggesting that the Mn species entered the CeO2 lattice to form a Mn-Ce solid solution. The diffraction peak of the FMC catalyst became broader and weaker than that of the MnO2-CeO2 catalyst, leaving only the peak related to CeO2 to be detected, thus indicating that Fe existed in highly dispersed or amorphous form [23]. The cerium-based solid solution formed as the active center of oxygen promoted the transport of reactive oxygen species, while the highly dispersed Fe and Mn mixed oxides as an active center had stronger activation ability for HCHO; hence, the FMC catalyst exhibited better catalytic performance [24].
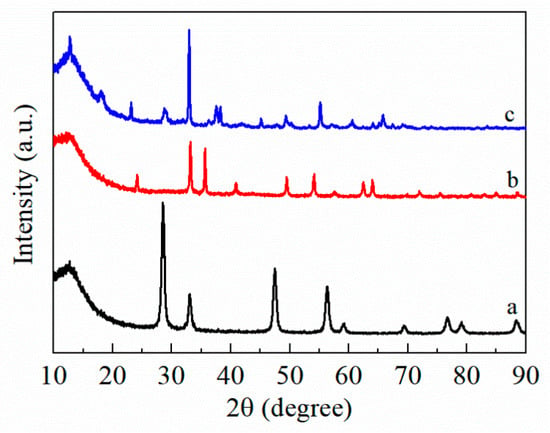
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of (a) CeO2, (b) Fe2O3, (c) MnO2.
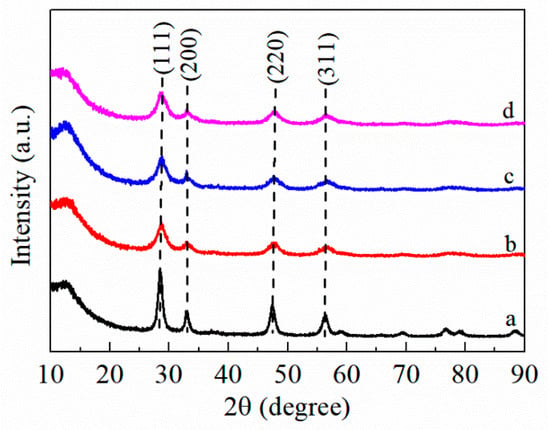
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of (a) MnO2-CeO2, (b) FMC-1:5:5, (c) FMC-2:5:5 and (d) FMC-3:5:5.
2.1.3. H2-TPR
The H2-TPR test was used to observe the redox properties of CeO2, Fe3O4, MnO2 and MnO2-CeO2 catalysts and the results are illustrated in Figure 4A,B. According to the literature, CeO2 has only one weak reduction peak at around 500 °C, which is ascribed to the reduction of Ce4+ species on the surface [25]. The TPR spectrum of CeO2 in this work is consistent with the literature, with the observation of small peaks at 494 °C (see Figure 4B). The Fe2O3 exhibited three peaks, a reduction peak centered at 393 °C, and two overlapping peaks at 577 and 645 °C, relating to the reductions of Fe2O3 to Fe3O4, Fe3O4 to FeO, FeO to Fe, respectively [26]. Mnn+ is easily reduced from MnO2 → Mn2O3 → Mn3O4 from 200–500 °C. The MnO2 spectrum displayed an obvious reduction peak at 310 °C with a slight shoulder at 336 °C. The shoulder peak is related to the easily reduced surface manganese oxides and the main peak represents the reduction of MnO2 to Mn2O3. Another peak located at 423 °C is assigned to the reduction of Mn2O3 to Mn3O4 [27]. By contrast, the incorporation of Ce resulted in the reduction peak shifting towards low temperatures. The decrease in reduction temperature indicates that the interactions between manganese and cerium promoted the reduction of Mn species through the formation of Mn-Ce solid solution, and thus increased the mobility of oxygen species [28].
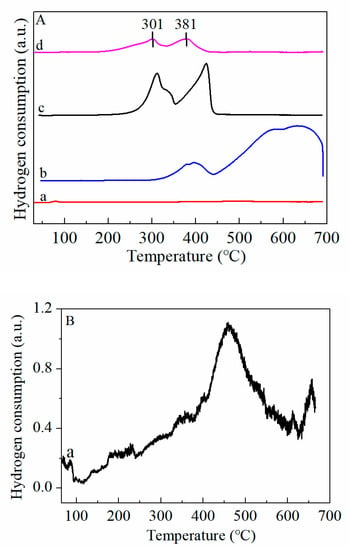
Figure 4.
(A) H2-TPR profiles of (a) CeO2, (b) Fe3O4, (c) MnO2 and (d) MnO2-CeO2, (B) Enlarged H2-TPR profiles of (a) CeO2.
As displayed in Figure 5, the TPR profiles of the FMC samples were categorized into two peaks, labeled as α and β, respectively. These are similar to the MnO2-CeO2 peak, although the position changed. The low-temperature reduction peak (<500 °C) shifted slightly towards a high temperature, and a new reduction peak appeared in the high-temperature region (>500 °C), which is attributed to the reduction of FeO to metallic Fe. This implies that a strong redox interaction was generated between Mn-Ce and Fe, and the oxygen species in the system exhibited strong mobility. From FMC-1:5:5 to FMC-3:5:5, the peak value of H2 consumption first decreases and then increases at low temperatures. At the same time, it also shows that the added amount of co-active component Fe does not necessarily conform to the rule of “more is better”. According to Figure 5 and Table 2, the order of low-temperature reduction capacity is FMC-2:5:5 > FMC-3:5:5 > FMC-1:5:5 > MnO2-CeO2. Such results suggest that the appropriate amount of Fe can improve the reduction behavior of the FMC catalyst. FMC-2:5:5 shows the first reduction peak at 314 °C, lower than FMC-1:5:5 (318 °C) and FMC-3:5:5 (327 °C), and the FMC-2:5:5 sample has the highest hydrogen consumption. A similar phenomenon was reported by Lu et al. [16], where they discovered that the inclusion of MnOx enhanced the dispersion of Co3O4 and CeO2, causing the reduction temperature to move slightly towards lower temperatures. In conclusion, both Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) and XRD results proved that the addition of FeOx promoted the dispersion of MnOx and CeO2.
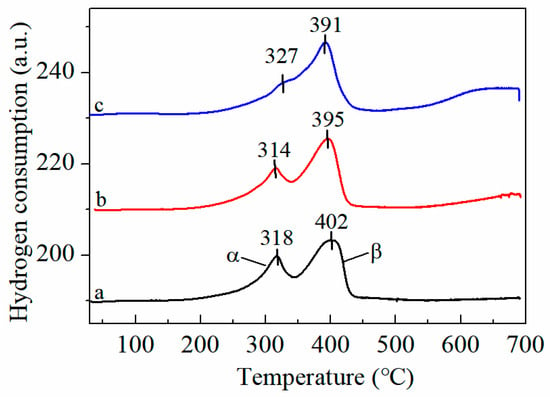
Figure 5.
H2-TPR profiles of (a) FMC-1:5:5, (b) FMC-2:5:5 and (c) FMC-3:5:5. α refers to the reduction peak at 250–350 °C; β refers to the reduction peak at 350–450 °C.

Table 2.
Hydrogen consumption of FMC samples with different ratios of Fe/Mn/Ce.
2.1.4. O2-TPD
The O2-TPD profiles of the FMC catalysts were tested to investigate the mobility of the surface oxygen species. It has been reported that chemically adsorbed oxygen species (such as O2− and O−) are desorbed at temperatures below 500 °C, and the desorption peaks of lattice oxygen occur above 500 °C [29]. As presented in Figure 6, due to the weak signal of the oxygen desorption peak in CeO2, no oxygen desorption peak was characterized in the test temperature range. A small desorption peak detected for Fe3O4 around 200–500 °C indicates the existence of a small amount of chemically adsorbed oxygen species. There are two obvious desorption peaks of MnO2 at 268 and 626 °C, which are assigned to surface oxygen and lattice oxygen species, respectively. After the fusion of MnO2-CeO2, the intensity of the desorption peak at around 300 °C decreased, meaning that the concentration of surface-active oxygen decreased; the intensity of the desorption peak at 500–700 °C increased significantly, meaning that the concentration of lattice oxygen increased, which may be the consequence of MnOx transition through the loss of lattice oxygen at high temperatures [30]. The desorption temperature of the FMC catalyst series moved to 200–500 °C with the introduction of FeOx to MnO2-CeO2. The O2 desorption peak shifted to low temperatures and the signals became stronger, indicating that Fe enhanced the mobility of the surface oxygen species and effectively activated Olatt to Oads. This phenomenon is consistent with the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) results. Compared with FMC-1:5:5 and FMC-3:5:5, it is obvious that FMC-2:5:5 exhibited the largest O2 desorption peak area in the low-temperature region, indicating that the sample had the largest desorbed oxygen content. According to Table 3, the desorption O2 content of FMC-2:5:5 (1.89 mmol/g) is higher than that of FMC-1:5:5 (1.68 mmol/g) and FMC-3:5:5 (1.71 mmol/g). FMC-2:5:5 had abundant surface-active oxygen species. It is general knowledge that surface oxygen exhibits higher mobility than lattice oxygen, and this can facilitate the catalytic oxidation reaction.
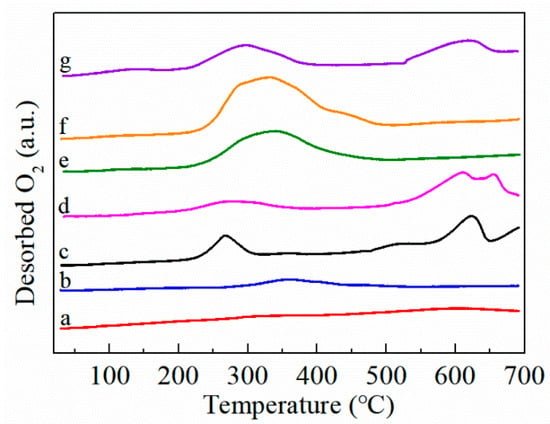
Figure 6.
O2-TPD profiles of (a) CeO2, (b) Fe3O4, (c) MnO2, (d) MnO2-CeO2, (e) FMC-1:5:5, (f) FMC-2:5:5 and (g) FMC-3:5:5.

Table 3.
Oxygen desorption of FMC samples with different ratios of Fe/Mn/Ce.
2.1.5. XPS
To further evaluate the surface elemental composition and chemical states of the FMC catalysts, XPS measurements were performed and the results are shown in Figure 7 and Table 4. Two obvious peaks located at 651.8 and 640.3 eV are observed in Figure 7A, and these peaks were assigned to the signal of Mn 2p1/2 and Mn 2p3/2, respectively. The spin orbital splitting energy of Mn 2p was 11.5 eV, which is close to that of MnO2 (11.7 eV) [31]. The Mn 2p3/2 peak for MnO2 and the FMC ternary mixed oxides were deconvoluted into three peaks at binding energies of 640.5 eV, 641.2 eV and 642.3 eV, corresponding to the Mn2+, Mn3+ and Mn4+ species, respectively [32]. However, the absence of a satellite peak at +5 eV from the Mn 2p3/2 peak indicates that Mn2+ was not present while Mn3+ and Mn4+ co-existed [33]. In addition, Table 4 shows that the concentration of Mn4+ (54.81%) in the MnO2-CeO2 samples was lower than those of the FMC samples (56.28–57.63%). These results indicate that the structural distribution of Mn and Ce was more homogeneous with the addition of Fe. From Table 4, the order of surface Mn4+ concentration is as follows: MnO2-CeO2 < FMC-3:5:5 < FMC-1:5:5 < FMC-2:5:5, suggesting that the FMC-2:5:5 catalyst possessed the largest Mn4+ concentration. The high-valence state of Mn species could enhance the redox properties of the catalyst, and the high content of Mn4+ will be favorable to the oxidation reaction [34].
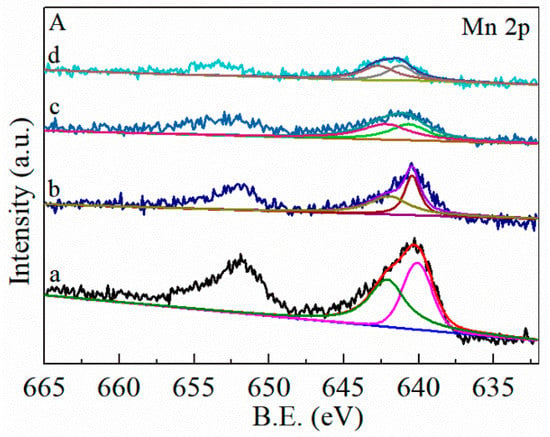
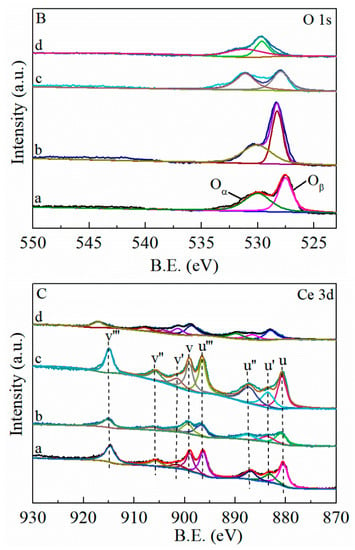
Figure 7.
XPS spectra of (a) MnO2-CeO2, (b) FMC-1:5:5, (c) FMC-2:5:5 and (d) FMC-3:5:5. (A) Mn 2p, (B) O 1s, (C) Ce 3d. Oα represent the surface-absorbed oxygen, Oβ represent the surface lattice oxygen. The peak u (880.6 eV), u’ (883.3 eV), u″ (887.0 eV), u‴ (896.3 eV), v (899.1 eV), v′ (901.7 eV), v″ (905.7 eV) and v‴ (914.7 eV).

Table 4.
Surface elemental composition of FMC catalysts.
Figure 7B shows that the O 1s spectra in the binding energy range of 525.8–534.0 eV were broad with shoulder peaks. This may have resulted from the overlapping signals of different oxygen species. The peak corresponding to the higher Binding Energy (BE) (531.4 eV) is associated with the surface-absorbed oxygen, such as, O22−,O2− and O−, and it is denoted as Oα, while the peak corresponding to the lower BE (527.5 eV) is related to surface lattice oxygen, and denoted as Oβ [35]. It is known that Oα ions are electrophilic, and a large amount of Oα is beneficial to the decomposition of intermediates [33]. The FMC catalysts have a higher Oα/(Oα + Oβ) ratio than MnO2-CeO2, implying that the promotional effect of Fe between Mn and Ce enhanced the concentration and mobility of adsorbed oxygen on the surface. In addition, the relative concentration of Oα species increased with increasing amount of Fe, with the highest Oα/(Oα + Oβ) value of 66.76% achieved for FMC-2:5:5, indicating that the sample had the most abundant surface-adsorbed oxygen species.
Ce is a rare earth metal element located in the lanthanide series. During the X-ray excitation process, multiple electrons are excited at the same time, thus complicating the peak shape. In the Ce 3d spectra of CeO2 (Figure 7C), four pairs of spin-orbit coupling were assigned to two orbits, Ce 3d3/2 and Ce 3d5/2, which were divided into eight peaks and labeled as u and v, respectively. The peak u (880.6 eV), u″ (887.0 eV), u‴ (896.3 eV), v (899.1 eV), v″ (905.7 eV) and v‴ (914.7 eV) are characteristic of Ce4+, while u’ (883.3 eV), and v′ (901.7 eV) are assigned to Ce3+ [36]. Ce3+ is closely related to oxygen vacancies; hence, when Ce3+ appears on the surface of CeO2, oxygen vacancies are usually formed in order to observe the charge conservation [37].The calculated Ce3+/(Ce3+ + Ce4+) ratios of the samples are presented in Table 4, and the table shows that the value for FMC-2:5:5 was 25.79%, which is higher than the recorded values for the FMC-1:5:5 (23.29%) and FMC-3:5:5 (21.26%) catalysts. The formation of oxygen vacancies and defects helps to improve the catalytic performance of HCHO oxidation [38].
2.2. Catalytic Activity
Figure 8 reveals the catalytic activity of pure FeOx, CeO2, MnO2 and the FMC catalysts for HCHO oxidation at different temperatures (20–120 °C), and it can be seen that pure FeOx, CeO2 and MnO2 exhibited low catalytic activity even at temperatures as high as 120 °C, with MnO2 achieving the highest HCHO conversion rate of 80% of this catalyst category. After combining MnO2 and CeO2, the catalytic activity of MnO2-CeO2 obviously improved, reaching a conversion rate of 93% at 100 °C. Furthermore, the introduction of FeOx into the MnO2-CeO2 resulted in the enhanced catalytic performance of the FMC catalysts. Notably, the catalytic activity of the FMC catalyst initially increased with increasing iron content, and then decreased. With low Fe content addition, the small amount of surface compounds will contribute little to the catalytic activity. As the Fe content gradually increases, the amount of surface compounds also increases, which is beneficial to the oxidation reaction of formaldehyde, thereby enhancing the catalytic activity. An optimum catalytic performance is achieved when the amount of surface compounds reaches the maximum for a certain Fe content. When this value is exceeded, the Fe particles will agglomerate and cover part of the active center, which will weaken the interactions between the Fe particles and Mn-Ce, thus discouraging the enhancement of the catalyst’s performance, therefore exhibiting no promotional effect on the catalytic activity. Hence, it can be inferred that the order of catalytic activity of these seven catalysts is FeOx < CeO2 < MnO2 < MnO2-CeO2 < FMC-3:5:5 < FMC-1:5:5 < FMC-2:5:5. FMC-2:5:5 exhibited the highest catalytic activity, achieving complete HCHO conversion at the lowest temperature (40 °C). This means that the Fe content was at its optimum value in the FMC-2:5:5 catalyst.
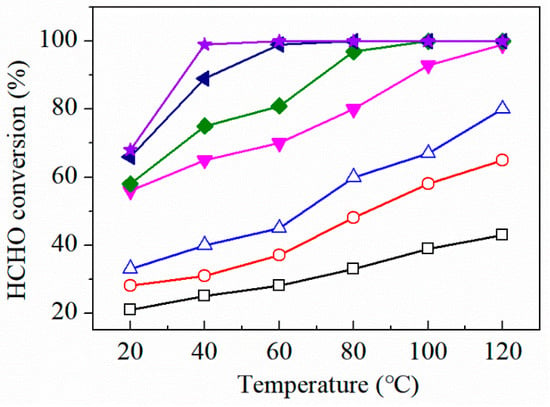
Figure 8.
The HCHO conversion over prepared catalysts: (□) FeOx, (○) CeO2, (△) MnO2, (▼) MnO2-CeO2, (◆) FMC-3:5:5, (►) FMC-1:5:5, (★) FMC-2:5:5. Reaction conditions: 200 ppm HCHO, 21 vol% O2 and N2 (balance). The total flow rate and WHSV were 30 mL min−1 and 36,000 mL gcat−1 h−1, respectively.
The stability test results of the FMC-2:5:5 catalyst for HCHO oxidation at 40 °C are shown in Figure 9. The reaction conditions were 200 ppm HCHO, 21 vol% O2 and N2 (balance). It can be observed that with the extension of time, the FMC-2:5:5 catalyst performed with good stability and still maintained complete conversion of HCHO over 68 h.
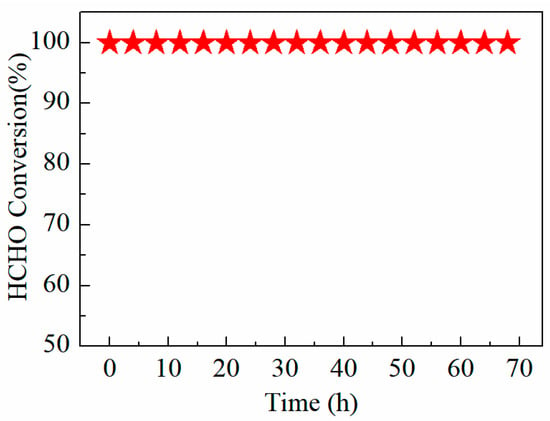
Figure 9.
Stability test of the FMC-2:5:5 catalyst at 40 °C.
For the practical application of the HCHO oxidation catalyst, the effect of H2O on the catalytic performance of FMC-2:5:5 was measured under the feed gas adding 5% water. As shown in Figure 10, FMC-2:5:5 was investigated under dry and humid conditions at 230 °C for 24 h. Introducing 5% H2O to the gas stream at 230 °C, the formaldehyde conversion increased from 87% to 91% and remained active for 15 h. As the H2O was stopped, the activity was immediately reduced to the original level. This indicates that the existence of water vapor is beneficial to the catalytic oxidation of HCHO.
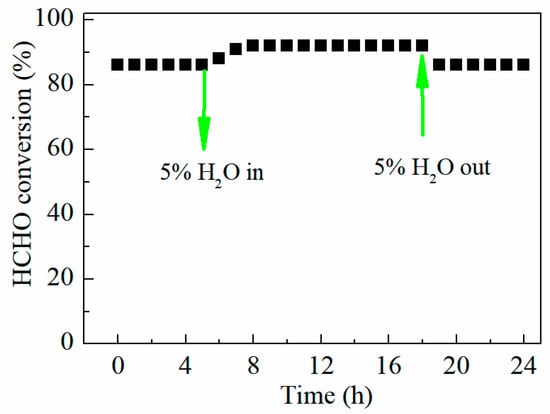
Figure 10.
Effect of water vapor on catalytic performance of FMC-2:5:5 at 30 °C with 200 ppm HCHO, 21 vol% O2 and N2 (balance), WHSV = 36,000 mL gcat−1 h−1.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
The FeOx-MnO2-CeO2 ternary mixed oxide catalysts were synthesized by a surfactant-templated coprecipitation method [33]. The different molar ratios of Fe/Mn/Ce were 1:5:5 (referred to as FMC-1:5:5, where the numbers represent the contents of Fe, Mn and Ce), 2:5:5 (FMC-2:5:5) and 3:5:5 (FMC-3:5:5). In a typical synthesis such as FMC-2, 2 g CTAB was first dissolved in 100 mL deionized water to obtain a transparent and clear solution. Then, Mn(CH3COO)2·4H2O (5 mmol)(Fuchen, Tianjin, China), Ce(NO3)3·6H2O (5 mmol)(Damao, Tianjin, China) and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (1 mmol) (Tianli, Tianjin, China) were added to the above solution in succession and the mixture was stirred at 30 °C for 0.5 h. A suitable amount of NaHCO3 solution was added to the mixed solution under vigorous stirring. The obtained precipitate was aged by steaming at 100 °C for 2 h, filtered and washed to neutral with deionized water and ethanol. The resultant solid material was dried overnight at 80 °C to remove excess solution, and then calcined at 500 °C for 3 h under air atmosphere. Finally, the obtained black powder was crushed to 40–60 mesh particles. Other catalysts with different elemental molar ratios and pure MnO2, CeO2, Fe3O4, MnO2-CeO2 were prepared with the same procedure.
3.2. Characterization
The specific surface area was calculated using the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method. The BET measurements were performed on a micromeritics apparatus (Micromeritics, USA) at −196 °C. Prior to the analysis, the samples were degassed for 4 h at 250 °C under N2 atmosphere, and the pore size distribution was determined by the Barret Joyner Halenda (BJH) method using the desorption branch of the nitrogen adsorption-desorption data.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) was tested on an X-ray polycrystalline diffractometer (Bruker, Germany) fitted with Cu-Ka radiation source (λ = 1.5406 nm, 40 kV and 30 mA). The 2θ of the angle XRD was in the range of 10° to 80° at a step rate of 2°·min−1.
Hydrogen temperature-programmed reduction (H2-TPR) was measured using gas chromatography (Jiedao GC1690, Hangzhou, China) instrument with the reducing gas of 10 vol% H2/N2 (60 mL·min−1). The heating temperature ranged from 25 to 700 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C·min−1. The amount of H2 consumption was analyzed by a thermal conductivity detector (TCD) (Jiedao, Hangzhou, China).
Oxygen temperature-programmed desorption (O2-TPD) was performed using the same apparatus as H2-TPR. A 50 mg sample was first purified with He at 200 °C for 1 h to remove surface impurities, followed by cooling to room temperature. Then, the catalyst was made to absorb O2 (21 vol% O2/N2) at room temperature. Thereafter, the sample was blown with 40 mL/min He for 30 min to remove the physisorbed O2. Finally, the temperature increased from 25 to 700 °C at a ramp of 10 °C·min−1 in He stream.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements were conducted on an Escalab250xi spectrometer (Thermo, USA). Al Ka X-ray line (1653.6 eV) was used for the excitation, and all binding energies were calibrated with the C 1s line (284.6 eV).
3.3. Catalytic Activity Test
HCHO oxidation activity test was conducted between 20 and 120 °C on a quartz fixed-bed microreactor (Chunlong, Xi’an, China). First, 50 mg of catalyst (40–60 mesh) was packed in a quartz tube (Chunlong, Xi’an, China) with external and internal diameters of 6 and 3 mm, respectively. Gaseous HCHO was generated by passing N2 over paraformaldehyde in a water bath set at 30 °C, and then mixed with 21 vol% O2/N2 gas flow to obtain the feed gas of 200 ppm HCHO, 21 vol% O2/N2 (balance). The concentration of formaldehyde was controlled by the weight of paraformaldehyde, the temperature of the constant temperature water bath and the flow rate of the carrier gas. The gas flow rate was controlled by a mass flow meter, and the temperature of the catalyst bed was controlled by tubular resistance furnace and K-type thermocouple. The total flow rate was 30 mL·min−1, corresponding to a gas hourly space velocity (GHSV) of 36,000 mL gcat−1 h−1. The outlet gas of the reactor was analyzed online by gas chromatograph (GC) equipped with thermal conductivity detector (TCD) and hydrogen flame ionization detector (FID) ((Jiedao, Hangzhou, China)). A catalyst convertor was installed in front of the FID detector, whose function was to quantitatively convert COx into methane in an H2 atmosphere. No other carbon-containing compounds except CO2 in the products were detected for the tested catalysts. Thus, HCHO conversion is equal to the yield of CO2 and calculated as follows:
where [CO2]out is the CO2 concentration in the products, and [HCHO]in is the concentration of HCHO in the gas flow.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have successfully developed FeOx-MnO2-CeO2 catalysts with different Fe/Mn/Ce molar ratios, synthesized using the surfactant-templated coprecipitation method and applied for HCHO removal at low temperatures. FeOx-MnO2-CeO2 exhibited excellent catalytic activity at a 2/5/5 molar ratio of Fe/Mn/Ce, and complete conversion of HCHO at a temperature as low as 40 °C. Through a series of characterization analyses, it was proven that Fe ions were successfully introduced into MnO2-CeO2. XRD analysis revealed that the introduction of Fe ions promoted the dispersion of MnO2-CeO2, and FeOx-MnO2-CeO2 existed in highly dispersed or amorphous form. Comparatively, BET results show that the FeOx-MnO2-CeO2 catalyst had a larger specific surface area, and the pores were more developed than those of the MnO2-CeO2 catalyst. The results of H2-TPR and O2-TPD indicate that the strong interactions between iron, manganese and cerium improved the reducibility of the catalyst, and, at the same time, the mobility of oxygen species was enhanced. From the XPS results, it was shown that a large amount of Oα is beneficial to the intermediate decomposition, and the existence of Ce3+ is favorable for the formation of oxygen vacancies on the catalyst surface. All of these play an important role in improving the oxidation activity of HCHO. Therefore, this work demonstrated that the introduction of Fe promoters into binary mixed oxides is an effective strategy for improving the HCHO catalytic performance.
Author Contributions
Methodology, data curation, and writing—original draft. Y.D.; conceptualization, formal analysis. C.S.; investigation, formal analysis. Y.D., K.L. and H.W.; software. Z.Z. and W.Z.; conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing. S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Young Talent fund of the University Association for Science and Technology in Shanxi (No. 20180604), the postgraduate Innovative Entrepreneurial Training Program of Xi’an Shiyou University (No. YCS18211014 and YCS19211024), and the college student Innovative Entrepreneurial Training Program of Nation (No. 201910705024). Meanwhile, the modern analysis and testing center of Xi’an Shiyou University provided strong support.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bai, B.; Qiao, Q.; Li, J.; Hao, J. Progress in research on catalysts for catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamravaei, S.; Shariaty, P.; Lashaki, M.J.; Atkinson, J.D.; Hashisho, Z.; Phillips, J.H.; Anderson, J.E.; Nichols, M. Effffect of beaded activated carbon flfluidization on adsorption of volatile organic compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Q.; Sun, L.; Hu, S.; Zhong, J.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Construction of homojunction-adsorption layer on anatase TiO2 to improve photocatalytic mineralization of volatile organic compounds. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 202, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.B.; Gao, X.; Qin, R.; Zeng, Y.X.; Qu, R.Y.; Zheng, C.H.; Tu, X. Plasma-cata lytic removal of formaldehyde over Cu-Ce catalysts in a dielectric barrier discharge reactor. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 170, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M.; Tao, F.F. Room-temperature catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde on catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3649–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.H.; Han, W.D.; Si, Y.; Chen, W.K.; Zhang, M.; Kim, H.Y.; Ding, B. In situ synthesis of MnO2@SiO2–TiO2 nanofifibrous membranes for room temperature degradation of formaldehyde. Compos. Commun. 2019, 16, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Rong, S.; Zhang, P.; Gao, L. One-step synthesis of nanocarbon-decorated MnO2 with superior activity for indoor formaldehyde removal at room temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 235, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.P.; Zhang, P.Y.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.J. Engineering Crystal Facet of α-MnO2 Nanowire for Highly Efficient Catalytic Oxi-dation of Carcinogenic Airborne Formaldehyde. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3435–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Qin, L.F.; Xiao, W.; Zeng, C.; Li, N.; Lv, T.; Zhu, H. Oriented growth of layered-MnO2 nanosheets over ɑ-MnO2 nanotubes for enhanced room-temperat ure HCHO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 207, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Long, B.; Tang, M.; Rui, Z.; Balogun, M.-S.; Tong, Y.; Ji, H. Bifunctional catalytic material: An ultrastable and high-performance surface defect CeO2 nanosheets for formaldehyde thermal oxidation and photocatalytic oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 181, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wei, G.; Liang, X.; Chen, D.; He, H.; Chen, T.; Xi, Y.; Chen, H.; Han, D.; Zhu, J. Synergetic effect of Cu and Mn oxides supported on palygorskite for the catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde: Dispersion, microstructure, and catalytic performance. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Rong, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P. Cerium modified birnessite-type MnO2 for gaseous formaldehyde oxidation at low temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 211, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, F.; Chen, C.; Huang, F.; Li, K. Catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde over CeO2-Co3O4 catalysts. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genty, E.; Siffert, S.; Cousin, R. Investigation of reaction mechanism and kinetic modelling for the toluene total oxidation in presence of CoAlCe catalyst. Catal. Today 2019, 333, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Long, D.; Ling, L.; Qiao, W. Three-dimensional Mn–Cu–Ce ternary mixed oxide networks prepared by polymer-assisted deposition for HCHO catalytic oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 2740–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.H.; Li, K.L.; Huang, F.L.; Chen, C.C.; Sun, B. Efficient MnOx-Co3O4-CeO2 catalysts for formaldehyde elimination. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 400, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yi, H.; Tang, X.; Zhao, S.; Xu, J.; Meng, J.; Li, Q. Catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde by MnCo3MOx catalyst: Effect of rare earth elements and temperature. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Xu, X.; Zhen, W.J.; Jing, H.P. Homogeneous introduction of CeOy into MnOx-based catalyst for oxidation of aromatic VOCs. Appl. Catal B Environ. 2018, 224, 825–835. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.R.; Zheng, Y.M.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Dong, Y.X.; Li, K.L. MnOx-CeO1 derived from Mn-Ce-MOFs with Highly Efficient Removal of Formaldehyde. Catal. Surv. Asia 2020, 24, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, C.A.; de Souza, E.F.; Manfro, R.L.; Landi, S.M.; Souza, M.M.; Schmal, M. Copper as promoter of the NiO-CeO2 cata-lyst in the preferential CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 182, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Peng, C.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, W. Heterostructured Fe2O3@SnO2 core-shell nanospindles for enhanced Room-temperature HCHO oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.H.; Cheng, G.; Liu, Q.; Yu, W.X.; Yu, L. Novel Ordered Mesoporous γ MnO2 Catalyst for High-Performance Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene and o Xylene. Ing. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 13926–13934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.L.; Asencios, Y.J.; Bellido, J.D.; Assaf, E.M. Bio-ethanol steam reforming for hydrogen production over Co3O4/CeO2 catalysts synthesized by one-step polymerization method. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 142, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Hu, Z.H.; Branton, P.; Li, W.C. The effect of doping transition metal oxides on copper manganese oxides for the cata-lytic oxidation of CO. Chin. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Pham, P.T.M.; Bruneel, E.; Van Driessche, I. Activated MnO2-Co3O4-CeO2 catalysts for the treatment of CO at room temperature. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 480, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, W.J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, J.Z.; Jia, H.P.; Chen, J. Hydrolysis driving redox reaction to synthesize Mn-Fe binary oxides as highly active catalysts for the removal of toluene. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Qing, C.; Zou, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of palygorskite-supported Mn1−xCexO2 clusters and their performance in catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 159, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataswamy, P.; Rao, K.N.; Jampaiah, D.; Reddy, B.M. Nanostructured manganese doped ceria solid solutions for CO oxidation at lower temperatures. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 162, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yu, X.L.; Ma, X.Y.; Yang, X.Q.; Lin, M.Y.; Ge, M.F. Mnx-CeO2 catalyst derived from metal-organic frameworks for toluene oxidation. Catal Today 2020, 355, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Huang, H.; Deng, W.; Dai, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Catalytic combustion of 1,2-dichlorobenzene at low temperature over Mn-modified Co3O4 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 166–167, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Mi, R.; Liu, H.; Li, F.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, W.; He, S.X.; Zhang, Y.X. Layered manganese oxides-decorated and nickel foam-supported carbon nanotubes as advanced binder-free supercapacitor electrodes. J. Power Sources 2014, 269, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyjoo, Y.; Rochard, G.; Giraudon, J.M.; Liu, J.; Lamonier, J.F. Mesoporous MnO2 hollow spheres for enhanced catalytic oxi-dation of formaldehyde. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2018, 17, e00091. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Zhao, S.; Li, K.Z.; Si, W.Z. Toluene catalytic combustion over copper modified Mn0.5Ce0.5Ox solid solution sponge-like structures. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 540, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Du, J.; Xie, B.; Yu, Y.; Yu, W.C.; Tao, C.Y. Rare earth metal modified three dimensionally ordered macroporous MnOx-CeO2 catalyst for diesel soot combustion. J. Rare Earth. 2018, 36, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wan, Z.T.; Yang, X.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Niu, X.X.; Sun, B.M.; Wang, T.; Wan, Z.T.; Yang, X.C.; Zhang, X.Y. Promotion-al effect of iron modification on the catalytic properties of Mn-Fe/ZSM-5 catalysts in the Fast SCR reaction. Fuel Process Technol. 2018, 169, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Hou, Z.-Y.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-L.; Cheng, T.-Q.; Lin, T.; Chen, Y.-Q. Low-temperature catalytic oxidation of toluene over Mn–Co–O/Ce0.65Zr0.35O2 mixed oxide catalysts. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaf, M.; Aouad, S.; Hany, S.; Cousin, R.; Abi-Aad, E.; Aboukaïs, A. Physicochemical characterization and catalytic performance of 10% Ag/CeO2 catalysts prepared by impregnation and deposition-precipitation. J. Catal. 2014, 320, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Song, Z.; Liu, W.; Du, H.X. The catalytic oxidation performance of toluene over the Ce-Mn-Ox catalysts: Effect of synthetic routes. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2020, 562, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).