A “Superaerophobic” Se-Doped CoS2 Porous Nanowires Array for Cost-Saving Hydrogen Evolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
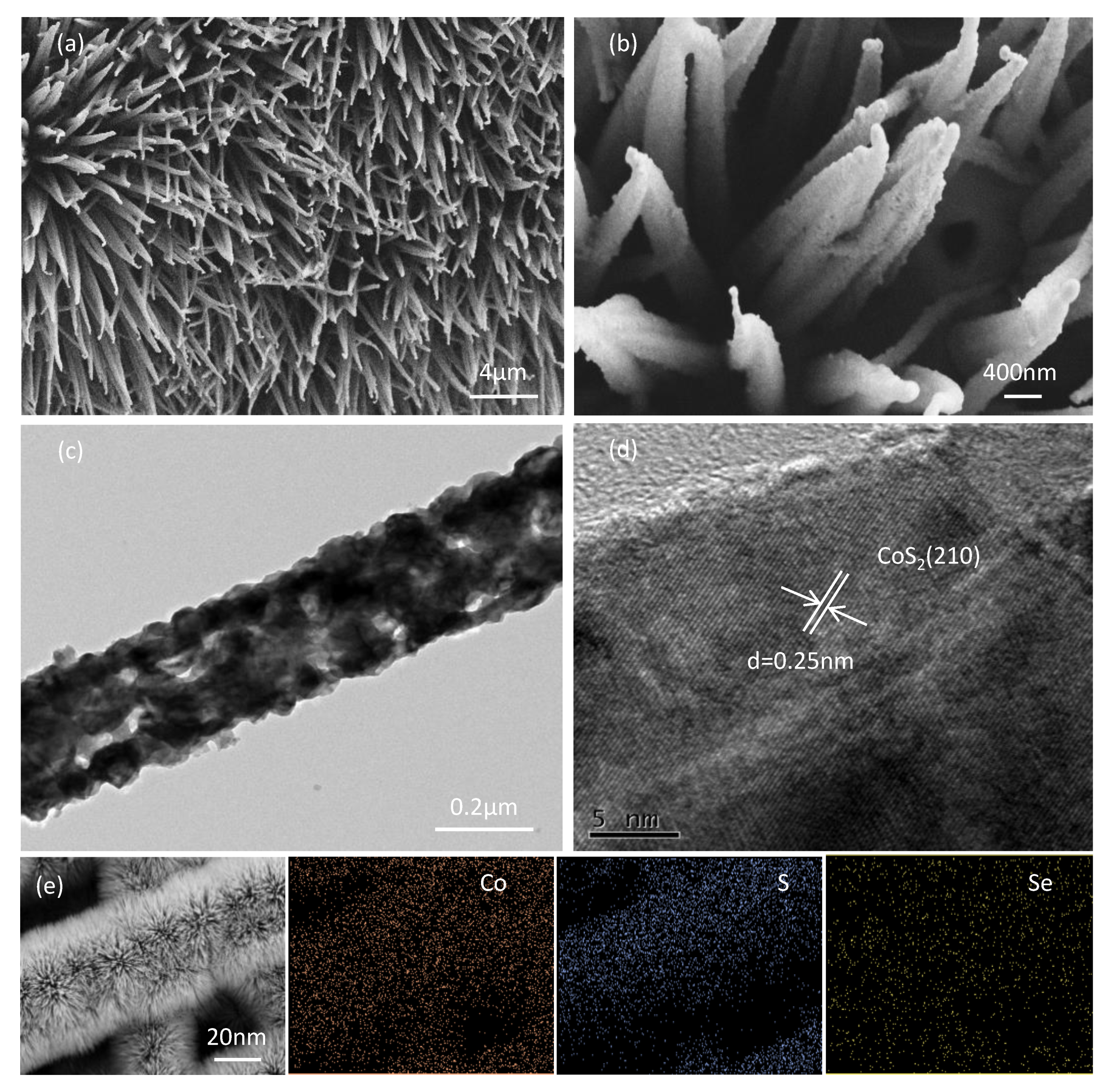
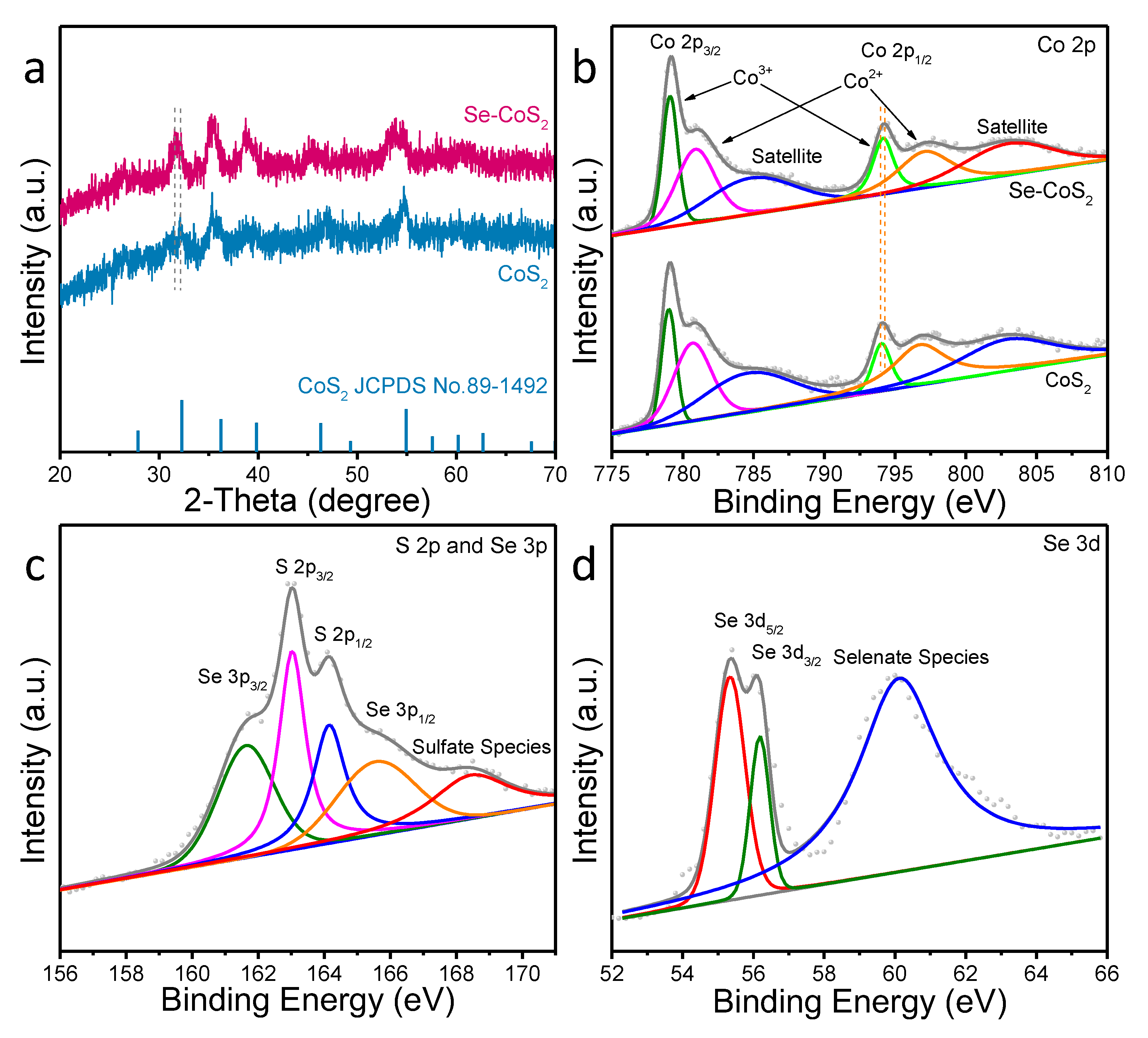
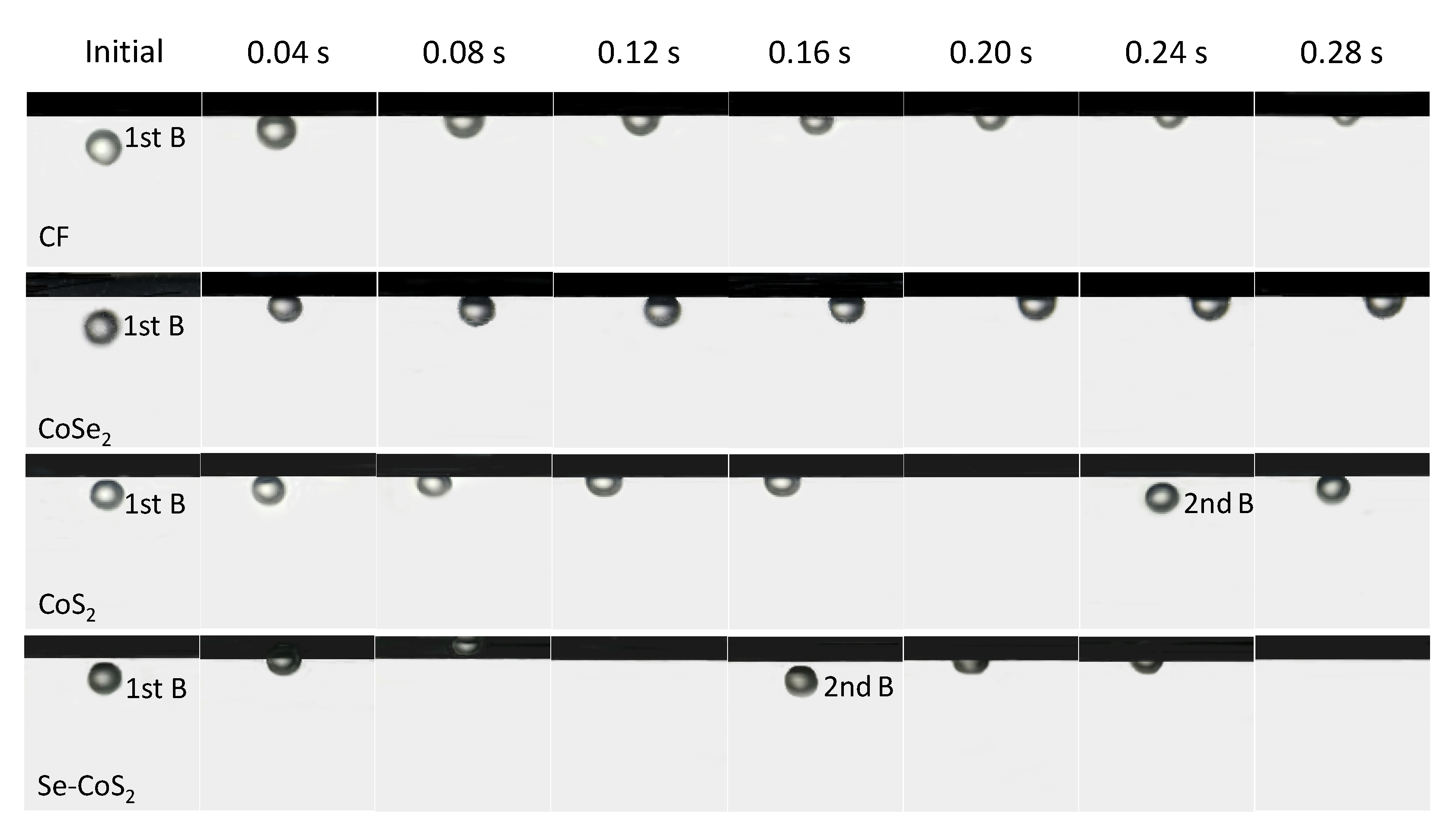
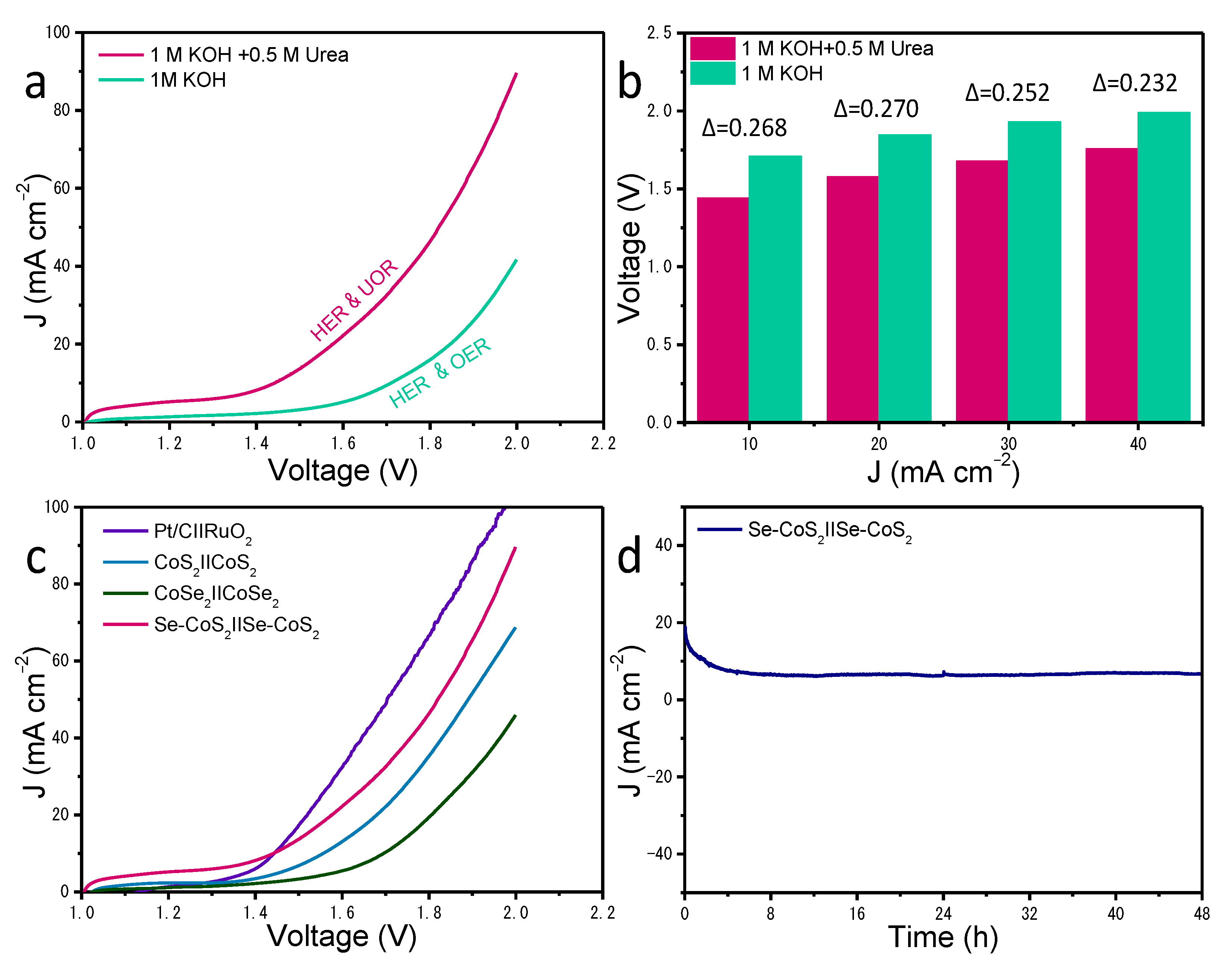
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. The Synthesis of Co(CO3)0.5(OH)·0.11H2O NW/CF
3.3. The Synthesis of Se-CoS2 NW/CF, CoS2 NW/CF, and CoSe2 NW/CF
3.4. Materials Characterization
3.5. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, J.W.; Wei, Z.D.; Xu, M.Q.; Jiang, Z.; Shang-Guan, W.F. Polyoxometalate template-based synthetic strategy to prepare Ni, Mo Co-doped CdS for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water splitting. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesuji, E.T.; Guardado-Villegas, E.; Fuentes, K.M.; Sánchez-Domínguez, M.; Videa, M. Pt-Co3O4 Superstructures by one-pot reduction/precipitation in bicontinuous microemulsion for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, W.L.; Xie, X.J.; Yang, X.L.; Chen, X.F.; Xu, X.G. synthesis and characterization of amorphous molybdenum sulfide (MoSx)/CdIn2S4 composite photocatalyst: Co-catalyst using in the hydrogen evolution reaction. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; He, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.W.; Li, H.Q.; Zhang, H.; Zha, T.Y. On-chip electrocatalytic microdevice: An emerging platform for expanding the insight into electrochemical processes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2916–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Xiao, C.; Huang, P.C.; Cheng, M.; Xie, Y. Regulating the charge and spin ordering of two-dimensional ultrathin solids for electrocatalytic water splitting. Chem 2018, 4, 1263–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Han, B.; Li, Z.; Fang, Y.S.; Feng, K.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Xu, A.B.; Yu, Y.Y.; Li, C.R.; et al. Ruthenium nanoparticles supported on Mg(OH)2 microflowers as catalysts for photothermal carbon dioxide hydrogenation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3028–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.C.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.Z.; Li, Z.; Zhao, K.N.; Zhao, Y.L.; Xu, L.; Zhou, L.; Moskaleva, L.V.; Mai, L.Q. Sisyphus effects in hydrogen electrochemistry on metal silicides enabled by silicene subunit edge. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Young, D.J.; Lang, J.P.; Li, H.X. Conjugated nanoporous polycarbazole bearing a cobalt complex for efficient visible-light driven hydrogen evolution. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 8736–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Z.; Zhou, T.P.; Chen, M.L.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, N.; Peng, X.; Chu, W.S.; Wu, X.J.; Wu, C.Z.; Xie, Y. Enhanced catalytic activity in nitrogen-anion modified metallic cobalt disulfide porous nanowire arrays for hydrogen evolution. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 7405–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Hou, J.X.; Wu, Z.X.; Guo, K.; Wang, D.L.; Zhai, T.Y.; Li, H.Q. Acid promoted Ni/NiO monolithic electrode for overall water splitting in alkaline medium. Sci. China Mater. 2017, 60, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Gao, G.H.; Du, M.L.; Zhou, J.H.; Wang, K.; Wu, W.B.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, P.M.; Dong, W.F.; et al. Atomic-scale core/shell structure engineering induces precise tensile strain to boost hydrogen evolution catalysis. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Gu, L.; Yu, D.N.; Sun, Y.J.; Wan, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.N.; Wu, W.W.; Yao, J.M.; et al. The marriage and integration of nanostructures with different dimensions for synergistic electrocatalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.N.; Zeng, J.H.; Yao, H.C.; Chen, Y. Iron doped cobalt phosphide ultrathin nanosheets on nickel foam for overall water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20658–20666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, S.; Dong, C.L.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Y.C.; Chen, J.L.; Tao, L.; Yan, D.; Chen, D.; Shen, S.; Chou, S.; et al. Atomic-scale CoOx species in metal-organic frameworks for oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Z.; Xu, K.; Zhou, T.P.; Tong, Y.; Wu, J.C.; Cheng, H.; Lu, X.L.; Ding, H.; Wu, C.Z.; Xie, Y. Strong-coupled cobalt borate nanosheets/graphene hybrid as electrocatalyst for water oxidation under both alkaline and neutral conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 2488–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Tan, Z.Y.; Mi, Y.; Huang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Yin, X.H.; Hu, F.L. On-site generated metal organic framework-deriving core/shell ZnCo2O4/ZnO nanoarray for better water oxidation. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 495405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhuo, Z.W.; Ju, H.X.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.P.; Wu, X.J.; Li, H.Q.; Zhai, T.Y. Local charge distribution engineered by schottky heterojunctions toward urea electrolysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Y.; Lang, C.C.; Gao, M.R.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Q.Q.; Duan, Y.; Yu, S.H. Ni–Mo–O nanorod-derived composite catalysts for efficient alkaline water-to-hydrogen conversion via urea electrolysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.; Jing, D.J.; Anthony, V.; Zhang, Q.S. Size fractionation of two-dimensional sub-nanometer thin manganese dioxide crystals towards superior urea electrocatalytic conversion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3804–3808. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.; Ye, K.; Cheng, K.; Wang, G.L.; Cao, D.X. Preparation of nickel nanowire arrays electrode for urea electro-oxidation in alkaline medium. J. Power Sources 2015, 278, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Xiong, T.; Tang, X.F.; Ma, Q.Y.; Hu, F.L.; Mi, Y. Engineering inner-porous cobalt phosphide nanowire based on controllable phosphating for efficient hydrogen evolution in both acidic and alkaline conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 481, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.Z.; Lv, F.; Lu, Y.D.; Yu, Y.L.; Niu, J.L.; Lang, J.P.; Deng, Y.Y.; Cao, X.Q.; Gu, H.W. In situ surface-derivation of AgPdMo/MoS2 nanowires for synergistic hydrogen evolution catalysis in alkaline solution. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6472–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, T.; Li, G.F.; Young, D.J.; Tan, Z.Y.; Yin, X.H.; Mi, Y.; Hu, F.L. In-situ surface-derivation of Ni-Mo bimetal sulfides nanosheets on Co3O4 nanoarrays as an advanced overall water splitting electrocatalyst in alkaline solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 791, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.R.; Lu, C.R.; Young, D.J.; Ren, Z.G.; Lang, J.P. Cobalt(II) and Nickel(II) complexes of a PNN type ligand as photoenhanced electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.M.; Wang, J.W.; Tan, J.B.; Zhang, Z.M.; Lu, T.B. Self-template synthesis of Co-Se-S-O hierarchical nanotubes as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution under alkaline and neutral conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8231–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Sun, C.Q.; Xi, P.X.; Peng, S.L.; Gao, D.Q.; Xue, D.S. Accelerated hydrogen evolution reaction in CoS2 by transition-metal doping. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Xia, Z.M.; Zhang, M.K.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.Y.; Qu, Y.Q. Ce-doped CoS2 pyrite with weakened O2 adsorption suppresses catalyst leaching and stabilizes electrocatalytic H2 evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 17775–17781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H.; Zhong, Z.X.; Wang, H.H.; Zheng, X.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Qi, J.L.; Cao, J.; Fei, W.D.; Huang, Y.D.; Feng, J.C. Rational constructing free-standing Se doped nickel-cobalt sulfides nanotubes as battery-type electrode for high-performance supercapattery. J. Power Sources 2018, 407, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Jian, C.Y.; Hong, W.T.; Cai, Q.; Liu, W. Tuning the electron status of urchin-like CoS2 nanowires by selenium doping toward highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Mater. Lett. 2019, 257, 126673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Qiu, Y.F.; Ji, X.Y.; Ma, T.G.; Ma, Z.; Hu, P.A. Direct growth of CNTs@CoSx Se2(1−x) on carbon cloth for overall water splitting. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 3792–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.Y.; Li, M.; Li, Y.L.; Dong, H.; Sun, D.M.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Tian, Z.Q.; Tang, Y.W. Regulating the electronic structure of CoP nanosheets by O incorporation for high-efficiency electrochemical overall water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1905252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.D.; Liang, Z.F.; Ji, K.Y.; Sun, Q.F.; Zhai, T.Y.; Xu, X.J. Hierarchical Ni-Co-S@Ni-W-O core–shell nanosheet arrays on nickel foam for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, H.J.; Shu, Y.W.; Zhen, P.; Chi, Z.; Peng, H.Z.; Dong, S.W. A nitrogen doping method for CoS2 electrocatalysts with enhanced water oxidation performance. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 4214–4220. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.D.; Xie, Z.Q.; Wang, Y. Novel CoS2 embedded carbon nanocages by direct sulfurizing metal-organic frameworks for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11984–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.J.; Jiang, L.J.; Ye, Z.F.; Liu, Y.Y.; Cen, T.L.; Peng, X.M.; Yuan, D.S. Phosphorus-doped Co3Mo3C/Co/CNFs hybrid: A remarkable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 325, 134962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, P.; Yao, N.; Cheng, G.Z.; Chen, S.L.; Luo, W.; Yin, Y.D. Phosphorus-doped Co3Mo3C/Co/CNFs hybrid: A remarkable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 4679–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, Y.N.; Li, P.; Yang, F.L.; Cheng, G.Z.; Chen, S.L.; Luo, W. Nitrogen-doped CoP as robust electrocatalyst for high-efficiency pH-universal hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 253, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.L.; Wang, F.M.; Xu, K.; Shifa, T.A.; Cheng, Z.Z.; Zhan, X.Y.; He, J. CoS2xSe2(1−x) nanowire array: An efficient ternary electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4699–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y.X.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, Y. Specific synthesis of CoS2 nanoparticles embedded in porous Al2O3 nanosheets for efficient hydrogen evolution and enhanced lithium storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, S.L.; Huang, S.W.; Xiao, L.Q.; Hou, L.X. Construction of uniform Co-Sn-X (X = S, Se, Te) nanocages with enhanced photovoltaic and oxygen evolution properties via anion exchange reaction. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 22012–22024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Wang, W.B.; Hu, F.L.; Mi, Y.; Wang, S.Z.; Liu, Y.W.; Ai, X.M.; Fang, J.K.; Li, H.Q.; Zhai, T.Y. 2D CoOOH sheet-encapsulated Ni2P into tubular arrays realizing 1000 mA cm−2-level-current-density hydrogen evolution over 100 h in neutral water. Nanomicro Lett. 2020, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.X.; Yu, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Zheng, Y.R.; Duan, Y.; Gao, Q.; Wu, R.; Sun, B.; Gao, M.R.; Wang, G.X.; et al. “Superaerophobic” nickel phosphide nanoarray catalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution at ultrahigh current densities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7537–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Ren, X.; Hao, S.; Ge, R.X.; Liu, Z.; Asiri, A.M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Q.J.; Sun, X.P. Selective phosphidation: An effective strategy toward CoP/CeO2 interface engineering for superior alkaline hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, X.B.; Huang, J.T.; Gao, X.M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, H.; Kang, B.B.; Yao, W.Q.; Zhu, Y.F. CN/rGO@BPQDs high-low junctions with stretching spatial charge separation ability for photocatalytic degradation and H2O2 production. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 266, 118602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Xiong, J.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Z.J.; Huang, J.T. Defect-assisted surface modification enhances the visible light photocatalytic performance of g-C3N4@C-TiO2 direct Z-scheme heterojunctions. Chin. J. Catal. 2019, 40, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.M.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, J.S.; Tang, J.; Zhou, J.; Tang, W.H. Metal-organic framework-templated synthesis of sulfur-doped core-sheath nanoarrays and nanoporous carbon for flexible all-solid-state asymmetric supercapacitors. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15454–15461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.M.; Hu, Y.W.; Tang, S.F.; Iljin, A.; Wang, J.W.; Zhang, Z.M.; Lu, T.B. Fe-CoP electrocatalyst derived from a bimetallic prussian blue analogue for large-current-density oxygen evolution and overall water splitting. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.J.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yang, S.Q.; Han, K.L.; Dong, F.; Ma, T.Y.; Huang, H.W. Three-in-one oxygen vacancies: Whole visible-spectrum absorption, efficient charge separation, and surface site activation for robust CO2 photoreduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 3880–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Cai, L.J.; Zhang, N.; Qiu, B.C.; Chai, Y. Robust photoelectrochemical oxygen evolution with N, Fe-CoS2 nanorod arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 44214–44222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Teng, X.; Meyer, T.J.; Chen, Z.F. CoP nanoframes as bifunctional electrocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting. ACS Catal. 2019, 10, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.L.; Ning, J.Q.; Zhao, D.; Xu, C.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Zhong, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Hu, Y. A room-temperature postsynthetic ligand exchange strategy to construct mesoporous Fe-doped CoP hollow triangle plate arrays for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting. Small 2018, 14, 1704233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Y.; Yin, Y.; Yin, X.; Lan, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, F.; Huang, Q.; Mi, Y. A “Superaerophobic” Se-Doped CoS2 Porous Nanowires Array for Cost-Saving Hydrogen Evolution. Catalysts 2021, 11, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020169
Tan Y, Yin Y, Yin X, Lan C, Wang Y, Hu F, Huang Q, Mi Y. A “Superaerophobic” Se-Doped CoS2 Porous Nanowires Array for Cost-Saving Hydrogen Evolution. Catalysts. 2021; 11(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Yan, Yijun Yin, Xianhong Yin, Chenghao Lan, Yu Wang, Feilong Hu, Qin Huang, and Yan Mi. 2021. "A “Superaerophobic” Se-Doped CoS2 Porous Nanowires Array for Cost-Saving Hydrogen Evolution" Catalysts 11, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020169
APA StyleTan, Y., Yin, Y., Yin, X., Lan, C., Wang, Y., Hu, F., Huang, Q., & Mi, Y. (2021). A “Superaerophobic” Se-Doped CoS2 Porous Nanowires Array for Cost-Saving Hydrogen Evolution. Catalysts, 11(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020169





