Green Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles for Sustainable and Environmentally Benign Processes
Abstract
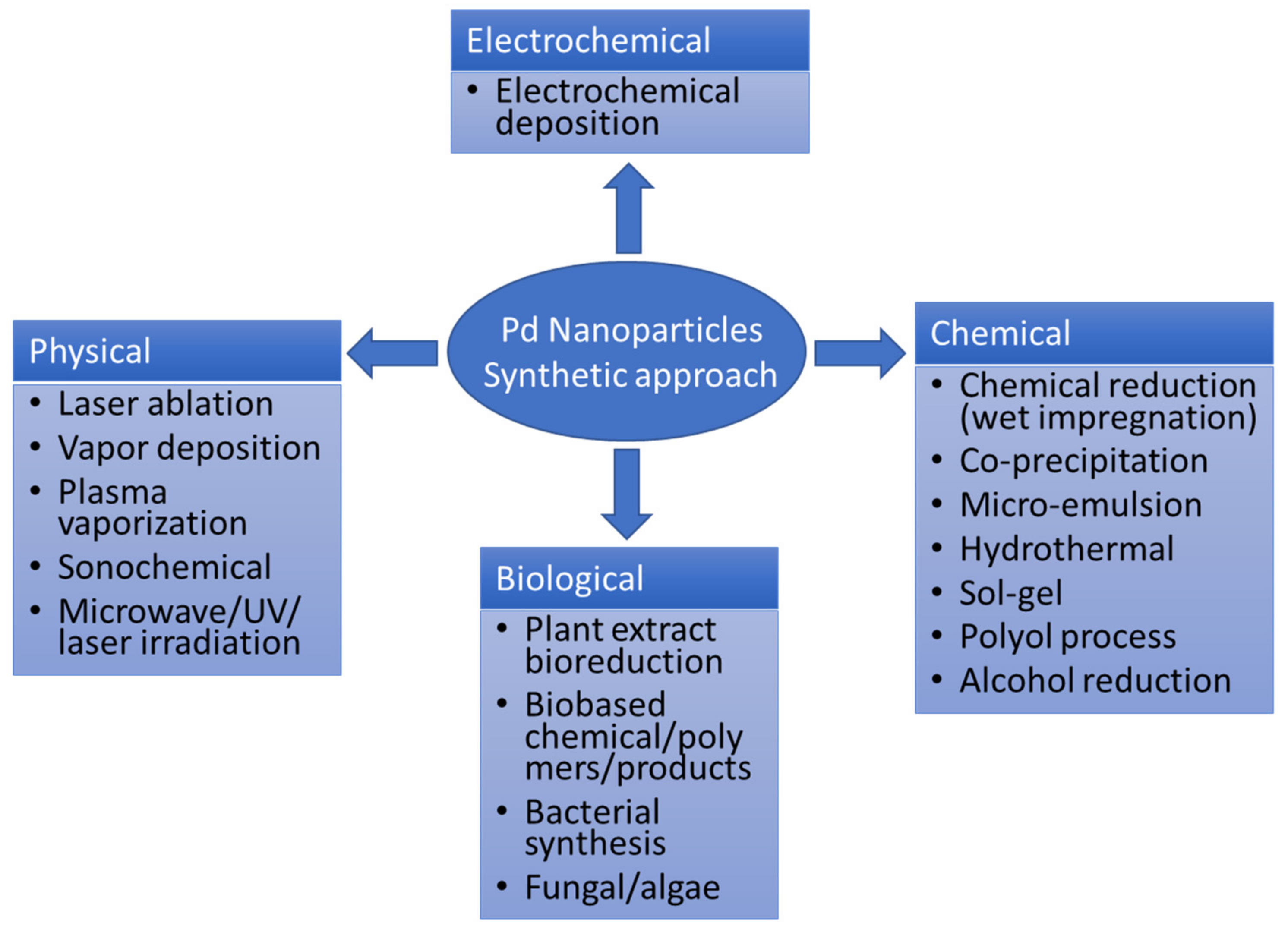
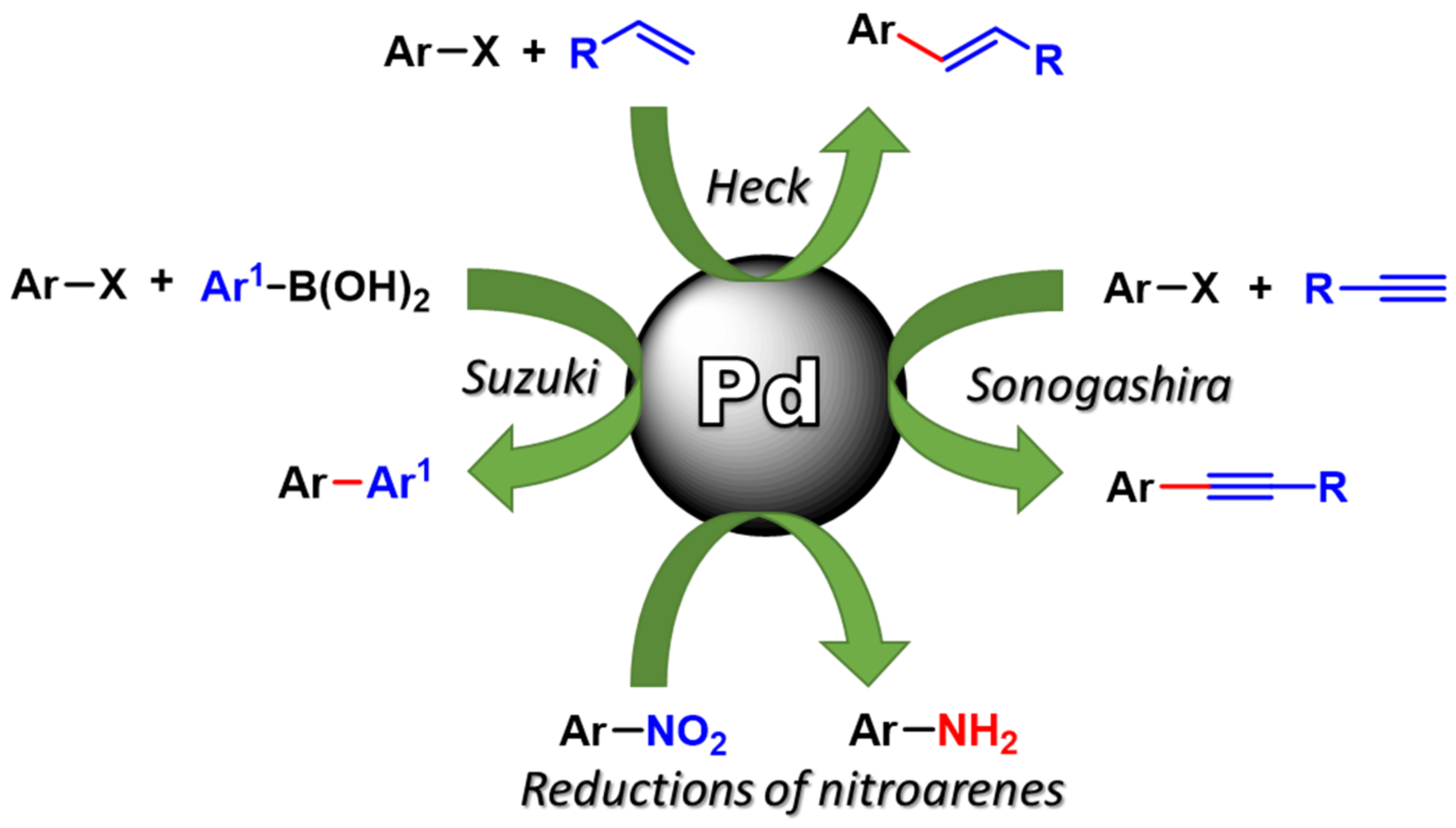
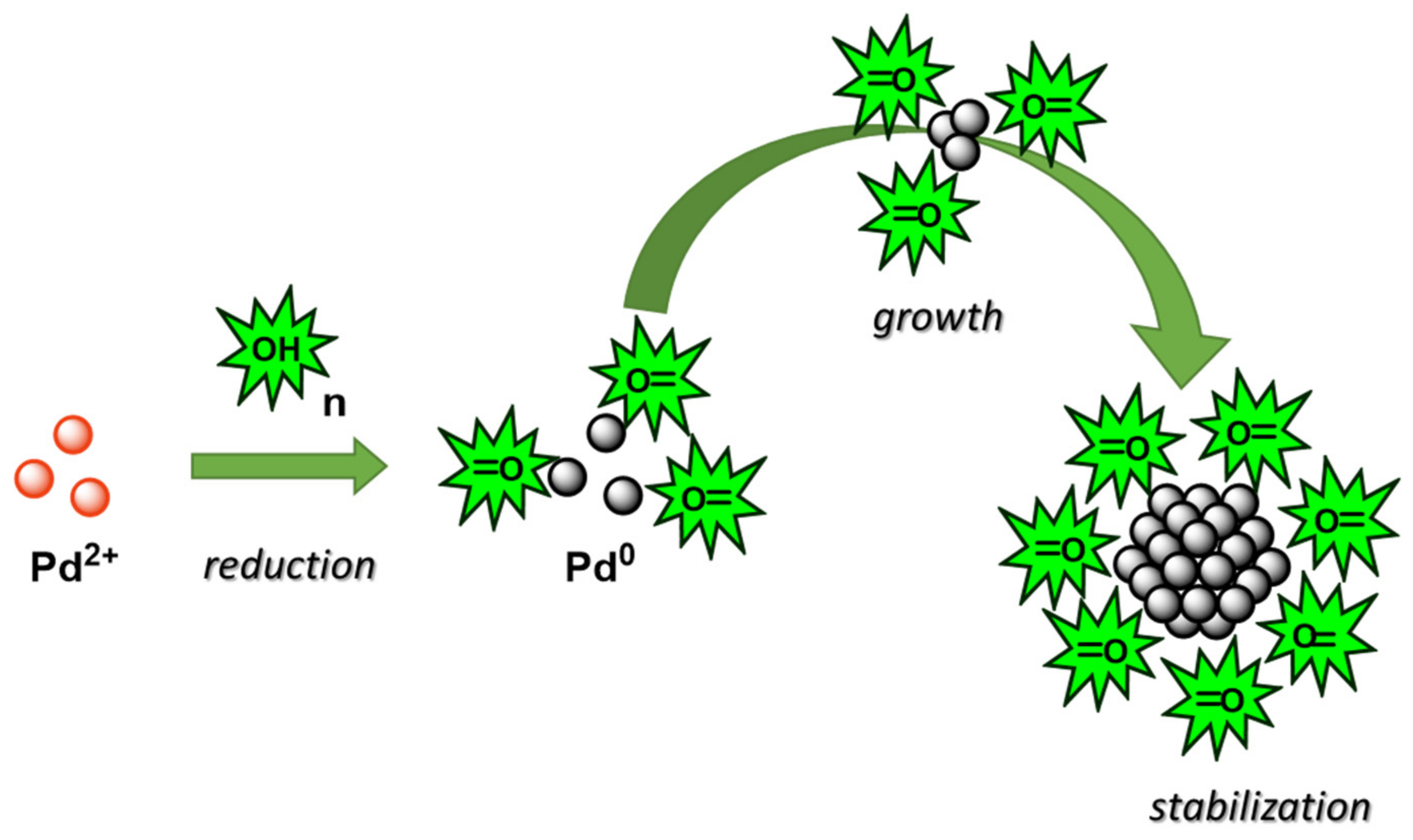
:1. Introduction
2. PdNPs Preparation by Pd(II) Chemical Reduction
2.1. Natural Reductant
2.2. Plant Extracts
2.3. Biopolymers as Supports
2.4. Carbonaceous Supports
2.5. Polyol as Liquid Supports
2.6. Hydrothermal Coprecipitation
3. Ultrasonic and Laser Irradiation
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanchi, S.; Ahmed, S. (Eds.) Green Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Applications; Wiley-Scrivener: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shafey, A.M. Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles from plant leaf extracts and their applications: A review. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 304–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bej, A.; Ghosh, K.; Sarkar, A.; Knight, D.W. Palladium nanoparticles in the catalysis of coupling reactions. RSC Adv. 2016, 14, 11446–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, G.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, R.; Chen, M.; Tang, L.; Tang, W.; Lai, C.; Cheng, M.; et al. Metal Organic Frameworks as Robust Host of Palladium Nanoparticles in Heterogeneous Catalysis: Synthesis, Application, and Prospect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 36, 32579–32598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.; Sajjadi, M.; Suh, J.M.; Zhang, K.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Jang, H.W.; Varma, R.S.; Shokouhimehr, M. Palladium Nanoparticles on Assorted Nanostructured Supports: Applications for Suzuki, Heck, and Sonogashira Cross-Coupling Reactions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 2070–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Astruc, D. Development of the Applications of Palladium on Charcoal in Organic Synthesis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 3426–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldan, I.; Semenyuk, Y.; Marchuk, I.; Reshetnyak, O. Chemical synthesis and application of palladium nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 2337–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, R.; Varma, R.S. (Eds.) Sustainable Preparation of Metal Nanoparticles: Methods and Applications; RSC Green Chemistry; Royal Society Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnukumar, P.; Vivekanandhan, S.; Muthuramkumar, S. Plant-Mediated Biogenic Synthesis of Palladium Nanoparticles: Recent Trends and Emerging Opportunities. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Dadashi, J.; Ghafuri, H. Pd-based nanoparticles: Plant-assisted biosynthesis, characterization, mechanism, stability, catalytic and antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 276, 102103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Ishak, N.A.I.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Timmiati, S.N. Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles via plant extracts: An overview. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 112004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadi, M.; Mostafavi, E.; Saleh, B.; Davaran, S.; Aliyeva, I.; Khalilov, R.; Nikzamir, M.; Nikzamir, N.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Panahi, Y.; et al. Current developments in green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, S336–S343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Uses of Palladium/Platinum Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, I.; Singh, N.B.; Singh, A.; Singh, H.; Singh, S.C. Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, L. (Ed.) Sustainable Flow Chemistry: Methods and Applications; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co: Weinheim, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, L.; Curini, M.; Ferlin, F.; Lanari, D.; Marrocchi, A.; Piermatti, O.; Trombettoni, V. Definition of green synthetic tools based on safer reaction media, heterogeneous catalysis, and flow technology. Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 90, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, C.; Cappelletti, M.; Piermatti, O.; Nocchetti, M.; Pica, M.; Pizzo, F.; Vaccaro, L. Immobilized Palladium Nanoparticles on Potassium Zirconium Phosphate as an Efficient Recoverable Heterogeneous Catalyst for a Clean Heack Reaction in Flow. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 401, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, F.; Vivani, R.; Bastianini, M.; Ortolani, L.; Piermatti, O.; Nocchetti, M.; Vaccaro, L. Accessing stable zirconium carboxyaminophosphonate nanosheets as support for highly active Pd nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15990–15993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozell, V.; Giannoni, T.; Nocchetti, M.; Vivani, R.; Piermatti, O.; Vaccaro, L. Immobilized Palladium Nanoparticles on Zirconium Carboxy-Aminophosphonates Nanosheets as an Efficient Recoverable Heterogeneous Catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura and Heck Coupling. Catalysts 2017, 7, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferlin, F.; Trombettoni, V.; Luciani, L.; Fusi, S.; Piermatti, O.; Santoro, S.; Vaccaro, L. A waste-minimized protocol for copper-catalyzed Ullmann-type reaction in a biomass derived furfuryl alcohol/water azeotrope. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlin, F.; Luciani, L.; Viterritti, O.; Brunori, F.; Piermatti, O.; Santoro, S.; Vaccaro, L. Polarclean as a Sustainable Reaction Medium for the Waste Minimized Synthesis of Heterocyclic Compounds. Front. Chem. 2019, 6, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferlin, F.; Cappelletti, M.; Vivani, R.; Pica, M.; Piermatti, O.; Vaccaro, L. Au@zirconium-phosphonate nanoparticles as an effective catalytic system for the chemoselective and switchable reduction of nitroarenes. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlin, F.; Giannoni, T.; Zuliani, A.; Piermatti, O.; Luque, R.; Vaccaro, L. Sustainable Protocol for the Reduction of Nitroarenes by Heterogeneous Au@SBA-15 with NaBH4 under Flow Conditions. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 3178–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valentini, F.; Mahmoudi, H.; Bivona, L.A.; Piermatti, O.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Fusaro, L.; Aprile, C.; Marrocchi, A.; Vaccaro, L. Polymer-Supported Bis-1,2,4-triazolium Ionic Tag Framework for an Efficient Pd(0) Catalytic System in Biomass Derived γ-Valerolactone. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6939–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, F.; Massaccesi, M.B.; Santoro, S.; Piermatti, O.; Vaccaro, L. Polarclean/Water as a Safe and Recoverable Medium for Selective C2-Arylation of Indoles Catalyzed by Pd/C. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16441–16450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Green chemistry for nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5778–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.L.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Yun, Y.S. Facile synthesis of monodisperse Pt and Pd nanoparticles using antioxidants. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2015, 15, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, A.I.; Marín, C.B.; Colaco, E.; Lefevre, C.; Méthivier, C.; Driss, A.O.; Landoulsi, J.; Guénin, E. “Water soluble” palladium nanoparticle engineering for C-C coupling, reduction and cyclization catalysis. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 6646–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Begum, T.; Gogoi, P.K.; Bora, U. Gallic Acid Derived Palladium(0) Nanoparticles: An In Situ Formed “Green and Recyclable” Catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling in Water. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 4645–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, J.E.; Dunsford, J.J.; Dacosta, O.S.G.; Blundell, R.K.; Adams, J.; Britton, J.; Smith, R.J.; Bousfield, T.W.; Fay, M.W. Recyclable glucose-derived palladium(0) nanoparticles as in situ-formed catalysts for cross-coupling reactions in aqueous media. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 16115–16121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, F.; Hussain, Z.; Tahir, M.N. Advances in biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60277–60286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anila, P.A.; Keerthiga, B.; Ramesh, M.; Muralisankar, T. Synthesis and characterization of palladium nanoparticles by chemical and green methods: A comparative study on hepatic toxicity using zebrafish as an animal model. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2021, 244, 108979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, X.L.; Gu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, G.W. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Potential Applications to Treat Cancer. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Gautam, P.K.; Verma, A.; Singh, V.; Shivapriya, P.M.; Shivalkar, S.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles as effective alternatives to treat antibiotics resistant bacterial infections: A review. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 25, e00427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaqoob, S.B.; Adnan, R.; Rameez Khan, R.M.; Rashid, M. Gold, Silver, and Palladium Nanoparticles: A Chemical Tool for Biomedical Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, S.A.; Fawzy, I.M.; Saleh, B.M.; Issa, M.Y.; Bakowsky, U.; Azzazy, H.M.E.S. Green synthesis of platinum and palladium nanoparticles using Peganum harmala L. Seed alkaloids: Biological and computational studies. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbagca, F.; Aygün, A.; Gülcan, M.; Ozdemir, S.; Gonca, S.; Şen, F. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, and investigation of antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer, and DNA cleavage activities. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonbol, H.; Ameen, F.; AlYahya, S.; Almansob, A.; Alwakeel, S. Padina boryana mediated green synthesis of crystalline palladium nanoparticles as potential nanodrug against multidrug resistant bacteria and cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirubaharan, C.J.; Fang, Z.; Sha, C.; Yong, Y.C. Green synthesis of Ag and Pd nanoparticles for water pollutants treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Shahri, M.M.; Rahman, H.S.; Rahim, R.A.; Rasedee, A.; Mohamad, R. Green synthesis palladium nanoparticles mediated by white tea (Camellia sinensis) extract with antioxidant, antibacterial, and antiproliferative activities toward the human leukemia (MOLT-4) cell line. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 8841–8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surendra, T.V.; Roopan, S.M.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Rayalu, G. MRSM optimized Moringa oleifera peel extract for green synthesis of M. oleifera capped palladium nanoparticles with antibacterial and hemolytic property. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 162, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kora, A.J. Plant Arabinogalactan Gum Synthesized Palladium Nanoparticles: Characterization and Properties. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2019, 29, 2054–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsiya, F.; Sayadi, M.H.; Sobhani, S. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Chlorella vulgaris. Mater. Lett. 2017, 186, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. “Green” synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, R.V.; Ghosh, A.; Jadhav, A.H.; Nizam, A.; Patil, S.A.; Peter, F.; Dateer, R.B. Biogenic synthesis of Pd-nanoparticles using Areca Nut Husk Extract: A greener approach to access α-keto imides and stilbenes. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 16213–16222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathula, C.K.S.; Kumar, K.A.; Yadav, H.; Ramesh, S.; Shinde, S.; Shrestha, N.K.; Mallikarjuna, K.; Kim, H. Ultrasonically driven green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles by Coleus amboinicus for catalytic reduction and Suzuki-Miyaura reaction. Colloids Surfaces B 2020, 192, 111026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Kiani, M.; Ghadiri, A.M. Rosmarinus officinalis directed palladium nanoparticle synthesis: Investigation of potential anti-bacterial, anti-fungal and Mizoroki-Heck catalytic activities. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, J.; Madiwale, S.; Bashte, B.; Dindorkar, S.; Dhawal, P.; More, P. Green mediated synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Gymnema sylvestre for catalytic reduction of Cr (VI). SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arde, S.M.; Rashinkar, G.S.; Jadhav, S.N.; Patil, A.D.; Salunkhe, R.S. Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Boswellia sarrata and their applications in cross-coupling reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ün, Ş.Ş.; Ünlü, A.; Ün, İ.; Ok, S. Green synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity evaluation of palladium nanoparticles facilitated by Punica granatum peel extract. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2021, 51, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahri, M.M. Highly efficient of cross-coupling reaction supported green synthesized palladium nanoparticles coated natural ligands as heterogeneous reusable nanocatalyst. J. Nanostruct. 2019, 9, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, M.; Neog, A.B.; Boruah, P.K.; Das, M.R.; Bharali, P.; Bora, U. Effect of Substrates on Catalytic Activity of Biogenic Palladium Nanoparticles in C-C Cross-Coupling Reactions. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 3329–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaikwad, D.S.; Undale, K.A.; Kalel, R.A.; Patil, D.B. Acacia concinna pods: A natural and new bioreductant for palladium nanoparticles and its application to Suzuki–Miyaura coupling. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukan, S.; Mahanta, A.; Kakati, D.; Rashid, M.H. Green chemical synthesis of Pd nanoparticles for use as efficient catalyst in Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garole, V.J.; Choudhary, B.C.; Tetgure, S.R.; Garole, D.J.; Borse, A.U. Palladium nanocatalyst: Green synthesis, characterization, and catalytic application. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 7885–7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, C.; Hasan, S.N.; Barai, A.C.; Ghorai, S.; Panja, S.K.; Bag, B.G. Green synthesis of Terminalia arjuna-conjugated palladium nanoparticles (TA-PdNPs) and its catalytic applications. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2018, 8, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewan, A.; Sarmah, M.; Thakur, A.J.; Bharali, P.; Bora, U. Greener Biogenic Approach for the Synthesis of Palladium Nanoparticles Using Papaya Peel: An Eco-Friendly Catalyst for C-C Coupling Reaction. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5327–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandathil, V.; Dateer, R.B.; Sasidhar, B.S.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A. Green Synthesis of Palladium Nanoparticles: Applications in Aryl Halide Cyanation and Hiyama Cross-Coupling Reaction under Ligand Free Conditions. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 1562–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanreh, S.; Hallajian, S.; Hamedani, Y.P.; Nazari, P.; Darvishi, K.; Hekmati, M. Green Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles Mediated by Thymbra Spicata Leaves Extract and Its Application as a Recyclable Nanocatalyst for Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Suzuki Reactions. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2018, 28, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Adib, M.; Karimi-Nami, R.; Yasaei, Z.; Tajik, M.; Mosavat, T.S.; Hemmati, S. Suzuki–Miyaura coupling catalyzed by palladium nanoparticles biosynthesized using Glycyrrhiza glabra as reducing and stabilyzing agent. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Hekmati, M.; Yousefi, M.; Veisi, H. Biogenic synthesis of Palladium nanoparticles mediated by Artemisia abrotanumaqueous extract and its catalytic evaluation for Suzuki coupling reactions. Asian J. Nanosci. Mater. 2018, 1, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebaschi, S.; Hekmati, M.; Veisi, H. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles mediated by black tea leaves (Camellia sinensis) extract: Catalytic activity in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction under ligand-free conditions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 485, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasaiah, P.; Kumar Mandal, B.; Sarada, N.C. Green synthesis of Pd NPs from Pimpinella tirupatiensis plant extract and their application in photocatalytic activity dye degradation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 263, 022013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi Shaik, M.; Ali, Z.J.Q.; Khan, M.; Kuniyil, M.; Assal, M.E.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Al-Warthan, A.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Khan, M.; Adil, S.F. Green synthesis and characterization of palladium nanoparticles using Origanum vulgare L. extract and their catalytic activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, R.; Tantayanon, S.; Bag, B.G. Synthesis of palladium nanoparticles with leaf extract of Chrysophyllum cainito (Star apple) and their applications as efficient catalyst for C–C coupling and reduction reactions. Int. Nano Lett. 2017, 7, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallikarjuna, K.; Bathula, C.; Buruga, K.; Shrestha, N.K.; Noh, Y.Y.; Kim, H. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using fenugreek tea and their catalytic applications in organic reactions. Mater. Lett. 2017, 205, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Albalawi, G.H.; Shaik, M.R.; Khan, M.; Adil, S.F.; Kuniyil, M.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Al-Warthan, A.; Siddiqui, M.R.H. Miswak mediated green synthesized palladium nanoparticles as effective catalysts for the Suzuki coupling reactions in aqueous media. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borah, R.K.; Mahanta, A.; Dutta, A.; Bora, U.; Thakur, A.J. A green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles by Sapindus mukorossi seed extract and use in efficient room temperature Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmati, M.; Bonyasi, F.; Javaheri, H.; Hemmati, S. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Hibiscus sabdariffa L. flower extract: Heterogeneous and reusable nanocatalyst in Suzuki coupling reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Rostami, A.; Shirinbayan, M. Greener approach for synthesis of monodispersed palladium nanoparticles using aqueous extract of green tea and their catalytic activity for the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction and the reduction of nitroarenes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Bai, X. Biosynthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Poplar leaf extract and its application in Suzuki coupling reaction. IET Nanobiotech. 2017, 11, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Mohammad Sajadi, S. Pd nanoparticles synthesized in situ with the use of Euphorbia granulate leaf extract: Catalytic properties of the resulting particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 462, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Rashtiani, A.; Barjasteh, V. Biosynthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Rosa canina fruit extract and their use as a heterogeneous and recyclable catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions in water. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 30, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Maham, M. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Hippophae rhamnoides Linn leaf extract and their catalytic activity for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling in water. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 396, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Ghorbani-Vaghei, R.; Hemmati, S.; Haji Aliani, M.; Ozturk, T. Green and effective route for the synthesis of monodispersed palladium nanoparticles using herbal tea extract (Stachys lavandulifolia) as reductant, stabilizer and capping agent, and their application as homogeneous and reusable catalyst in Suzuki coupling reactions in water. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 29, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Maham, M.; Ehsani, A. Facile and surfactant-free synthesis of Pd nanoparticles by the extract of the fruits of Piper longum and their catalytic performance for the Sonogashira coupling reaction in water under ligand- and copper-free conditions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 2562–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Honarmand, E.; Maham, M. Preparation of palladium nanoparticles using Euphorbia thymifolia L. leaf extract and evaluation of catalytic activity in the ligand-free Stille and Hiyama cross-coupling reactions in water. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 4745–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmipathy, R.; Palakshi Reddy, B.; Sarada, N.C.; Chidambaram, K.; Khadeer Pasha, S. Watermelon rind-mediated green synthesis of noble palladium nanoparticles: Catalytic application. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veisi, H.; Karmakar, B.; Tamoradi, T.; Tayebee, R.; Sajjadifar, S.; Lotfi, S.; Maleki, B.; Hemmati, S. Bio-inspired synthesis of palladium nanoparticles fabricated magnetic Fe3O4 nanocomposite over Fritillaria imperialis flower extract as an efficient recyclable catalyst for the reduction of nitroarenes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, S.; Yousefi, M.; Salehi, M.H.; Amiri, M.; Hekmati, M. Palladium nanoparticles immobilized over Strawberry fruit extract coated Fe3O4 NPs: A magnetic reusable nanocatalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Pirhayati, M.; Kakanejadifard, A.; Mohammadi, P.; Abdi, M.R.; Gholami, J.; Hemmati, S. In Situ Green Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles on Tannic Acid-Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles as a Green Reductant and Stabilizer Agent: Its Application as a Recyclable Nanocatalyst (Fe3O4@TA/Pd) for Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Suzuki Reactions. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Rostami-Vartooni, A.; Khalaj, M. Green synthesis of Pd/Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Euphorbia condylocarpa M. bieb root extract and their catalytic applications as magnetically recoverable and stable recyclable catalysts for the phosphine-free Sonogashira and Suzuki coupling reactions. J. Mol. Catal A Chem. 2015, 396, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjuna, K.; Reddy, L.V.; Al-Rasheed, S.; Mohammed, A.; Gedi, S.; Kim, W.K. Green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide-supported palladium nanoparticles by Coleus amboinicus and its enhanced catalytic efficiency and antibacterial activity. Crystals 2021, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.H.; Yousefi, M.; Hekmati, M.; Balali, E. In Situ biosynthesis of palladium nanoparticles on Artemisia abrotanum extract-modified graphene oxide and its catalytic activity for Suzuki coupling reactions. Polyhedron 2019, 165, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, C.; Borah, G. Green synthesis of Pd@rGO nanocomposite using Piper (Piper nigrum) leaf extract and its catalytic activity towards alcohol oxidation in water at room temperature. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1250i1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Tamoradi, T.; Karmakar, B.; Mohammadi, P.; Hemmati, S. In Situ biogenic synthesis of Pd nanoparticles over reduced graphene oxide by using a plant extract (Thymbra spicata) and its catalytic evaluation towards cyanation of aryl halides. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 109919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Kuniyil, M.; Shaik, M.R.; Khan, M.; Adil, S.F.; Al-Warthan, A.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Tremel, W.; Tahir, M.N.; Siddiqui, M.R.H. Plant extract mediated eco-friendly synthesis of pd@graphene nanocatalyst: An efficient and reusable catalyst for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling. Catalysts 2017, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seyedi, N.; Saidi, K.; Sheibani, H. Green Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles Supported on Magnetic Graphene Oxide by Origanum vulgare Leaf Plant Extract: Catalytic Activity in the Reduction of Organic Dyes and Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, K.S.; Peng, Y.P.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, S.W.; Huang, C.E.; Lai, H.W.; Li, H.W. Green synthesized palladium coated titanium nanotube arrays for simultaneous azo-dye degradation and hydrogen production. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S. M Green synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of the Pd/TiO2 nanoparticles for the ligand-free Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 465, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Rostami-Vartooni, A.; Bagherzadeh, M. Green synthesis of Pd/CuO nanoparticles by Theobroma cacao L. seeds extract and their catalytic performance for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and phosphine-free Heck coupling reaction under aerobic conditions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 448, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjare, S.B.; Chaudhari, R.A. Environment-friendly synthesis of palladium nanoparticles loaded on Zeolite Type-Y (Na-form) using Anacardium Occidentale shell extract (Cashew nut shell extract), characterization and application in -C-C- coupling reaction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Bai, X. FGreen synthesis of Pd nanoparticles supported on LDHs and its application in the Suzuki coupling reaction. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. and Eng. 2018, 292, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, N.; Bordoloi, P.; Borah, G.; Gogoi, P.K. Synthesis of Palladium Nanoparticle by Bio-reduction Method and Its Effectiveness as Heterogeneous Catalyst Towards Selective Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohols in Aqueous Media. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, P.K.; Bhattacharjee, R.P.; Sarmah, P.P.; Saikia, L.; Dutta, D.K. A green synthesis of Pd nanoparticles supported on modified montmorillonite using aqueous: Ocimum sanctum leaf extract: A sustainable catalyst for hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 110011–110018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, M.; Khazaei, A.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Tahsili, M.R. Highly efficient reusable Pd nanoparticles based on eggshell: Green synthesis, characterization and their application in catalytic reduction of variety of organic dyes and ligand-free oxidative hydroxylation of phenylboronic acid at room temperature. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 5613–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, R.K.; Saikia, H.J.; Mahanta, A.; Das, V.K.; Bora, U.; Thakur, A.J. Biosynthesis of poly(ethylene glycol)-supported palladium nanoparticles using Colocasia esculenta leaf extract and their catalytic activity for Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72453–72457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. Fast-growing field of magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6949–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sánchez, M.; Díaz-García, D.; Prashar, S.; Gómez-Ruiz, S. Palladium nanoparticles supported on silica, alumina or Titania: Greener alternatives for Suzuki–Miyaura and other C–C coupling reactions. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1585–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Thanasekaran, P.; Lu, K.L.; Liu, S.B.; Rajagopal, S. Functionalized Silica Matrices and Palladium: A Versatile Heterogeneous Catalyst for Suzuki, Heck, and Sonogashira Reactions. ACS Sust. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6357–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Lin, K.C. An overview of palladium supported on carbon-based materials: Synthesis, characterization, and its catalytic activity for reduction of hexavalent chromium. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholinejad, M.; Naghshbandi, Z.; Nájera, C. Carbon-Derived Supports for Palladium Nanoparticles as Catalysts for Carbon-Carbon Bonds Formation. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 1792–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, R.; Ma, X.; Wei, X.; Jin, Y.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, W. Porous organic polymer material supported palladium nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17360–17391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H. Celluloses as Green Support of Palladium Nanoparticles for Application in Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Brief Review. J. Cluster Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, A.; Levy-Ontman, O. Development and application of palladium nanoparticles on renewable polysaccharides as catalysts for the Suzuki cross-coupling of halobenzenes and phenylboronic acids. Mol. Catal. 2020, 493, 111048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aabaka, S.R.; Mao, J.; Lavanya, M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Huang, Z.; Mao, J.; Yang, X.; Lin, C. Nanocellulose Supported PdNPs as in situ Formed Nano Catalyst for the Suzuki Coupling Reaction in Aqueous Media: A Green Approach and Waste to Wealth. J. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 937, 121719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.D.; Le, T.C.H.; Chau, V.T.; Le, T.N.D.; Dang, C.H.; Vo, T.T.N.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, T.D. Palladium nanoparticles in situ synthesized on Cyclea barbata pectin as a heterogeneous catalyst for Heck coupling in water, the reduction of nitrophenols and alkynes. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 4746–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempasiddaiah, M.; Kandathil, V.; Dateer, R.B.; Sasidhar, B.S.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A. Immobilizing biogenically synthesized palladium nanoparticles on cellulose support as a green and sustainable dip catalyst for cross-coupling reaction. Cellulose 2020, 27, 3335–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempasiddaiah, M.; Kandathil, V.; Dateer, R.B.; Sasidhar, B.S.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A. Palladium-catalyzed denitrogenative cross-coupling of aryl halides with arylhydrazines under mild reaction conditions. Transit. Met. Chem. 2021, 46, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, E.; Bahrami, K. Palladium Nanoparticles Doped on the Chitosan Nanofibers Modified with 2-Aminobenzaldehyde as a Nanocatalyst in Cross-Coupling Reactions. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 5489–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easson, M.W.; Jordan, J.H.; Bland, J.M.; Hinchliffe, D.J.; Condon, B.D. Application of Brown Cotton-Supported Palladium Nanoparticles in Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reactions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 6304–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bai, X. One-pot synthesis of bio-supported Pd nanoparticles by using clove leaf and their catalytic performance for Suzuki coupling reaction. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1219, 128538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, T.; Nasrollahzadeh, M. Cyanation of aryl halides and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction using palladium nanoparticles anchored on developed biodegradable microbeads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Zeng, X.; Du, F.; Zhang, L.; Peng, X. Palladium Nanoparticles Anchored on Thiol Functionalized Xylose Hydrochar Microspheres: An Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst for Suzuki Cross-Coupling Reactions. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, I.; Shahsavari, H.R.; Beitle, R.; Beyzavi, M.H. Recombinant Peptide Fusion Protein-Templated Palladium Nanoparticles for Suzuki-Miyaura and Stille Coupling Reactions. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 2942–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendre, A.D.; Patil, V.P.; Terdale, S.S.; Kodam, K.M.; Waghmode, S.B. A simple, efficient and green approach for the synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Oxytocin: Application for ligand free Suzuki reaction and total synthesis of aspongpyrazine A. J. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 909, 121093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.; Islami, M.R.; Tikdari, A.M. Green synthesis of Pd nanoparticles supported on modified Nonpareil almond shell using almond hull extract: A beneficial nanocatalyst for convenient reduction of organic dyes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 18111–18122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalanthoden, A.N.; Shaikh, M.N.; Aziz, M.A.; Rani, S.K. Pd Nanoparticles Decorated on Jute Sticks: Dip-Catalyst of Suzuki-Miyaura and Mizoroki-Heck C–C Bond Formation Reactions in Water. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 12832–12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.N. Pd nanoparticles on green support as dip-catalyst: A facile transfer hydrogenation of olefins and: N -heteroarenes in water. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 28199–28206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Z.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T.; Chen, S.; Ma, G.; Guo, X.; Wang, L. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using lentinan for catalytic activity and biological applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 38265–38270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolatkhah, Z.; Javanshir, S.; Bazgir, A. Isinglass–palladium as collagen peptide–metal complex: A highly efficient heterogeneous biocatalyst for Suzuki cross-coupling reaction in water. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marulasiddeshwara, M.B.; Kumar, P.R. Phosphine and Copper-free Sonogashira coupling reaction catalyzed by lignin supported palladium nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 20811–20818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kora, A.J.; Rastogi, L. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using gum ghatti (Anogeissus latifolia) and its application as an antioxidant and catalyst. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baran, T. Ultrasound-accelerated synthesis of biphenyl compounds using novel Pd(0) nanoparticles immobilized on bio-composite. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 45, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, N.Y.; Baran, T.; Menteş, A. Production of novel palladium nanocatalyst stabilized with sustainable chitosan/cellulose composite and its catalytic performance in Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, T.; Baran, N.Y.; Menteş, A. Sustainable chitosan/starch composite material for stabilization of palladium nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and investigation of catalytic behaviour of Pd@chitosan/starch nanocomposite in Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Bai, X.; Lv, H. Biosynthesis of supported Pd nanoparticles using poplar leaf as a reducing agent and carrier: A green route to highly efficient and reusable Suzuki coupling reaction catalyst. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2017, 47, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, S.; Arabi, A.; Khazaei, A.; Khazaei, M. In Situ stabilization of Pd(0) nanoparticles into a mixture of natural carbohydrate beads: A novel and highly efficient heterogeneous catalyst system for Heck coupling reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Bai, X.; Lv, H. Green synthesis of supported palladium nanoparticles employing pine needles as reducing agent and carrier: New reusable heterogeneous catalyst in the Suzuki coupling reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, R.; Tantayanon, S.; Gopal Bag, B. A Novel Trihybrid Material Based on Renewables: An Efficient Recyclable Heterogeneous Catalyst for C−C Coupling and Reduction Reactions. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 2406–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Nasrabadi, N.H.; Mohammadi, P. Biosynthesis of palladium nanoparticles as a heterogeneous and reusable nanocatalyst for reduction of nitroarenes and Suzuki coupling reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 30, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Peng, X.; Zhong, L.; Li, X.; Sun, R. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles via branched polymers: A bio-based nanocomposite for C-C coupling reactions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 32202–32211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frindy, S.; Primo, A.; Lahcini, M.; Bousmina, M.; Garcia, H.; El Kadib, A. Pd embedded in chitosan microspheres as tunable soft-materials for Sonogashira cross-coupling in water-ethanol mixture. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, D.; Das, R.N.; Hazarika, S.; Konwar, D. Biogenic synthesis of cellulose supported Pd(0) nanoparticles using hearth wood extract of Artocarpus lakoocha Roxb—A green, efficient and versatile catalyst for Suzuki and Heck coupling in water under microwave heating. Catal. Commun. 2015, 72, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Faraji, A.R.; Hemmati, S.; Gil, A. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Pistacia atlantica kurdica gum and their catalytic performance in Mizoroki-Heck and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions in aqueous solutions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 29, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affrose, A.; Suresh, P.; Azath, I.A.; Pitchumani, K. Palladium nanoparticles embedded on thiourea-modified chitosan: A green and sustainable heterogeneous catalyst for the Suzuki reaction in water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27533–27539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, A.; Khazaei, M.; Rahmati, S. A green method for the synthesis of gelatin/pectin stabilized palladium nano-particles as efficient heterogeneous catalyst for solvent-free Mizoroki-Heck reaction. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 398, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A.S.; Martín-García, I.; Contreras-Celedón, C.; Chacón-García, L.; Alonso, F. DNA-supported palladium nanoparticles as a reusable catalyst for the copper- and ligand-free Sonogashira reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 2262–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Lin, L.; Sun, D.; Chen, H.; Yang, D.; Li, Q. Bio-inspired synthesis of metal nanomaterials and applications. Chem. Soci. Rev. 2015, 44, 6330–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, L.H.; Xing, H.; Lu, Y. DNA as a powerful tool for morphology control, spatial positioning, and dynamic assembly of nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veisi, H.; Joshani, Z.; Karmakar, B.; Tamoradi, T.; Heravi, M.M.; Gholami, J. Ultrasound assisted synthesis of Pd NPs decorated chitosan-starch functionalized Fe3O4 nanocomposite catalyst towards Suzuki-Miyaura coupling and reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K. Methyl Salicylate Functionalized Magnetic Chitosan Immobilized Palladium Nanoparticles: An Efficient Catalyst for the Suzuki and Heck Coupling Reactions in Water. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 7129–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamatmanesh, A.; Heydari, A.; Nahzomi, H.T. Stabilizing Pd on magnetic phosphine-functionalized cellulose: DFT study and catalytic performance under deep eutectic solvent assisted conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 235, 115947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharamanagowda, M.M.; Panchangam, R.K. Fe3O4-Lignin@Pd-NPs: A highly efficient, magnetically recoverable and recyclable catalyst for Mizoroki-Heck reaction under solvent-free conditions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, T.; Sargin, I. Green synthesis of a palladium nanocatalyst anchored on magnetic lignin-chitosan beads for synthesis of biaryls and aryl halide cyanation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, T. Production and Application of Highly Efficient and Reusable Palladium Nanocatalyst Decorated on the Magnetically Retrievable Chitosan/Activated Carbon Composite Microcapsules. Catal. Lett. 2019, 49, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, T.; Nasrollahzadeh, M. Facile synthesis of palladium nanoparticles immobilized on magnetic biodegradable microcapsules used as effective and recyclable catalyst in Suzuki-Miyaura reaction and p-nitrophenol reduction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatkhah, Z.; Javanshir, S.; Bazgir, A.; Hemmati, B. Palladium on magnetic Irish moss: A new nano-biocatalyst for suzuki type cross-coupling reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, A.R.; Tavangar-Rizi, Z. Palladium nanoparticles immobilized on magnetic methionine-functionalized chitosan: A versatile catalyst for Suzuki and copper-free Sonogashira reactions of aryl halides at room temperature in water as only solvent. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Motamedi, A.; Marvdashti, Z.; Hosseini, S.H. Magnetic nanocomposite based on functionalized salep as a green support for immobilization of palladium nanoparticles: Reusable heterogeneous catalyst for Suzuki coupling reactions. Catal. Commun. 2017, 97, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghipour, A.; Fakhri, A. Heterogeneous Fe3O4@chitosan-Schiff base Pd nanocatalyst: Fabrication, characterization and application as highly efficient and magnetically-recoverable catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura and Heck-Mizoroki C-C coupling reactions. Catal. Commun. 2016, 73, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandathil, V.; Kempasiddaiah, M.; Nataraj, S.K.; Somappa, S.B.; Patil, S.A. DNA as a bioligand supported on magnetite for grafting palladium nanoparticles for cross-coupling reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalışkan, M.; Baran, T. Decorated palladium nanoparticles on chitosan/δ-FeOOH microspheres: A highly active and recyclable catalyst for Suzuki coupling reaction and cyanation of aryl halides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 174, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzad, E.; Veisi, H. Fe3O4/SiO2 nanoparticles coated with polydopamine as a novel magnetite reductant and stabilizer sorbent for palladium ions: Synthetic application of Fe3O4/SiO2@PDA/Pd for reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Suzuki reactions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 60, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalanpour, N.; Nejati, S.; Keshipour, S. Pd nanoparticles/graphene quantum dot supported on chitosan as a new catalyst for the reduction of nitroarenes to arylamines. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2021, 18, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putta, C.; Sharavath, V.; Sarkar, S.; Ghosh, S. Palladium nanoparticles on β-cyclodextrin functionalised graphene nanosheets: A supramolecular based heterogeneous catalyst for C-C coupling reactions under green reaction conditions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 6652–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargin, I.; Baran, T.; Arslan, G. Environmental remediation by chitosan-carbon nanotube supported palladium nanoparticles: Conversion of toxic nitroarenes into aromatic amines, degradation of dye pollutants and green synthesis of biaryls. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, A.R.; Khorsandi, Z. Efficient Suzuki and Sonogashira coupling reactions catalyzed by Pd/DNA@MWCNTs in green solvents under mild conditions. Nanochem. Res. 2019, 4, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Shafiei, N.; Baran, T.; Pakzad, K.; Tahsili, M.R.; Baran, N.Y.; Shokouhimehr, M. Facile synthesis of Pd nanoparticles supported on a novel Schiff base modified chitosan-kaolin: Antibacterial and catalytic activities in Sonogashira coupling reaction. J. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 945, 121849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, N.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Baran, T.; Baran, N.Y.; Shokouhimehr, M. Pd nanoparticles loaded on modified chitosan-Unye bentonite microcapsules: A reusable nanocatalyst for Sonogashira coupling reaction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 262, 117920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Yuan, X.; Zuo, S.; Qi, C. Novel chitosan-based/montmorillonite/palladium hybrid microspheres as heterogeneous catalyst for Sonogashira reactions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37995–38000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, F.; Ferlin, F.; Lilli, S.; Marrocchi, A.; Ping, L.; Gu, Y.; Vaccaro, L. Valorisation of urban waste to access low-cost heterogeneous palladium catalysts for cross-coupling reactions in biomass-derived γ-valerolactone. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 5887–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, P.; Hajjami, M.; Valizadeh-Kakhki, F. Biochar as heterogeneous support for immobilization of Pd as efficient and reusable biocatalyst in C–C coupling reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enneiymy, M.; Le Drian, C.; Ghimbeu, C.M.; Becht, J.M. Mesoporous carbon supported ultrasmall palladium particles as highly active catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Asatkar, A.; Patel, G.; Banerjee, S. Synthesis of Rice Husk Derived Activated Mesoporous Carbon Immobilized Palladium Hybrid Nano-Catalyst for Ligand-Free Mizoroki-Heck/Suzuki/Sonogashira Cross-Coupling Reactions. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 5577–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketike, T.; Velpula, V.R.K.; Madduluri, V.R.; Kamaraju, S.R.R.; Burri, D.R. Carbonylative Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Over Pd NPs/Rice-Husk Carbon-Silica Solid Catalyst: Effect of 1,4-Dioxane Solvent. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 7164–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Habibi, Z. Palladium nanoparticle-decorated magnetic pomegranate peel-derived porous carbon nanocomposite as an excellent catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura and Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, C.; Derible, A.; Becht, J.M.; Kiener, J.; le Drian, C.; Parmentier, J.; Fierro, V.; Girleanu, M.; Ersen, O. Biosourced mesoporous carbon with embedded palladium nanoparticles by a one pot soft-template synthesis: Application to Suzuki reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 12297–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholinejad, M.; Zareh, F.; Nájera, C. Nitro group reduction and Suzuki reaction catalysed by palladium supported on magnetic nanoparticles modified with carbon quantum dots generated from glycerol and urea. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholinejad, M.; Najera, C.; Hamed, F.; Seyedhamzeh, M.; Bahrami, M.; Kompany-Zareh, M. Green synthesis of carbon quantum dots from vanillin for modification of magnetite nanoparticles and formation of palladium nanoparticles: Efficient catalyst for Suzuki reaction. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 5585–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholinejad, M.; Seyedhamzeh, M.; Razeghi, M.; Najera, C.; Kompany-Zareh, M. Iron oxide nanoparticles modified with carbon quantum nanodots for the stabilization of palladium nanoparticles: An efficient catalyst for the Suzuki reaction in aqueous media under mild conditions. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Mao, Z.; Wang, K.; Phan, N.T.S.; Zhang, F. Microwave-assisted aqueous carbon-carbon cross-coupling reactions of aryl chlorides catalysed by reduced graphene oxide supported palladium nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 3239–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, I.; Pla, D.; Gómez, M. Palladium Nanoparticles in Polyols: Synthesis, Catalytic Couplings, and Hydrogenations. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1146–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Duaso, A.; Mayoral, J.A.; Pires, E. Steps Forward toward the Substitution of Conventional Solvents in the Heck-Mizoroki Coupling Reaction: Glycerol-Derived Ethers and Deep Eutectic Solvents as Reaction Media. ACS Sust. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13076–13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Duaso, A.; Favier, I.; Pla, D.; Pires, E.; Gómez, M. Design of Glycerol-Based Solvents for the Immobilization of Palladium Nanocatalysts: A Hydrogenation Study. ACS Sust. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 6875–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Rudra, S.; Rahman, P.; Khatua, S.; Pradhan, M.; Chatterjee, P.N. Synthesis and characterization of Pd-γ-Fe2O3 nanocomposite and its application as a magnetically recyclable catalyst in ligand-free Suzuki-Miyaura reaction in water. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 871, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J. One-pot synthesis of magnetic palladium-NiFe2O4-graphene oxide composite: An efficient and recyclable catalyst for Heck reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 30, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, G.K.; Sunkara, S.; Gadupudi, P.C.R. One-step synthesis of magnetically recyclable palladium loaded magnesium ferrite nanoparticles: Application in synthesis of anticancer drug PCI-32765. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2020, 50, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadjarodi, A.; Dehghani, M.; Imani, M. Green synthesis and characterization of palladium nanoparticles supported on zeolite Y by sonochemical method, powerful and efficient catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of aryl halides with phenylboronic acid. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias Batista, L.M.; Kunzler, K.; John, M.G.; Clark, B.; Bullock, A.; Ferri, J.; Gupton, B.F.; Tibbetts, K.M. Laser synthesis of uncapped palladium nanocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 557, 149811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Plant | Part Used | Size/Shape of PdNPs | Catalytic Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Areca Nut | husk | 16 nm, spherical | Synthesis of α-cheto imide Heck coupling reaction Denitrogenative coupling rection | [46] |
| Coleus amboinicus | leaf | 20 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [47] |
| Rosmarinus officinalis | leaf | 15–90 nm, semi-spherical | Heck coupling reaction | [48] |
| Gymnema sylvestre | leaf | 10–20 nm, quasi-spherical | Reduction of Cr(IV) | [49] |
| Boswellia sarrata | leaf | 6 nm, spherical | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [50] |
| Punica granatum | peel | 22 ± 5 nm, spherical | Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [51] |
| White tea | leaf | 11 ± 2 nm, spherical | C-O cross coupling reaction | [52] |
| Ocimum sanctum Aloe vera | leaf | 4–5 nm, spherical 4–5 nm, spherical | Sonogashira coupling reaction Suzuki coupling reaction | [53] |
| Acacia concinna | pods | 20 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [54] |
| Lantana camara | flower | from 4.6 to 6.3 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [55] |
| Lagerstroemia speciosa | leaf | 136 nm, aggregates | Reduction of 4-nitophenol and dyes | [56] |
| Terminalia arjuna | bark | 8.94 nm, most spherical, few hexagonal, triangular | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [57] |
| Papaya | peel | 2.4 nm, spherical | Suzuki and Sonogashira coupling | [58] |
| Piper nigrum | fruit | 2–7 nm, spherical | Hiyama coupling reaction | [59] |
| Thymbra Spicata | leaf | 5–7 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [60] |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra | root and branches | 3–6 nm, not reported | Suzuki coupling reaction | [61] |
| Artemisia abrotanum | leaf | 20 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [62] |
| Camelia sinensis (black tea) | leaf | 7 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [63] |
| Pimpinella tirupatiensis | leaf | 12 nm, spherical | Reduction of dyes | [64] |
| Origanum vulgare L. | leaf | 2.2 nm, spherical | Oxidation of alcohols. | [65] |
| Chrysophyllum cainito | leaf | 25–50 nm, flower-like aggregates | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction Reduction of nitrophenols | [66] |
| Fenugreek tea | seeds | 20–50 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [67] |
| Salvadora persica L. | root | 2.2–15 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [68] |
| Sapindus mukorossi | seed | 3.6 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [69] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa L. | flower | 5–8 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [70] |
| Green tea | leaf | 7–10 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of nitroarenes | [71] |
| Poplar | leaf | 4.2 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [72] |
| Euphorbia granulate | leaf | 25–35 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [73] |
| Rosa canina | fruit | 10 ± 3 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [74] |
| Hippophae rhamnoides Linn | leaf | 5 ± 2.5 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [75] |
| Stachys lavandulifolia | leaf | 5–7 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [76] |
| Piper longum | fruit | 5–40, spherical | Sonogashira coupling | [77] |
| Euphorbia thymifolia L. | leaf | 20–30 nm, spherical | Hiyama and Stille coupling reaction | [78] |
| Water melon | rind of fruit | 96 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [79] |
| Support | Plant Extract | Size/Shape of PdNPs | Catalytic Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 magnetic NPs | Fritillaria imperialis flower extract | 20–30 nm, quasi-spherical | Reduction nitroarenes | [80] |
| Strawberry fruit extract | <20 nm, quasi-spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [81] | |
| Tannic acid | 5–25 nm, quasi-spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [82] | |
| Euphorbia condylocarpa M. bieb root extract | 39 nm, not reported | Suzuki and Sonogashira coupling reaction | [83] | |
| Graphene Oxide (GO) | Coleus amboinicus leaf extract | 20–30 nm, spherical | Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [84] |
| Artemisia abrotanum leaf extract | Not reported | Suzuki coupling reaction | [85] | |
| Piper nigrum leaf extract | 6–20 nm, not reported | Oxidation of alcohols | [86] | |
| Thymbra spicata leaf extract | 12–15 nm, cubic | Cyanation of Arylaldehydes | [87] | |
| Pulicaria glutinosa leaf extract | 15–18 nm, triangle 7–8 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [88] | |
| GO-F3O4 | Origanum vulgare leaf extract | 10–40 nm, not reported | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [89] |
| TiO2 | Green tea leaf extract or Coffee powder extract | 10 nm, not reported | Azo-Dyes degradation Hydrogen production | [90] |
| Myrtus communis L. leaf extract | 17–25 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [91] | |
| CuO | Theobroma cacao L. seeds extract | 40 nm, not reported | Heck coupling reaction (DMF) Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [92] |
| Zeolite | Anacardium Occidentale shell extract | 1–2 nm, spherical | Suzuki coupling reaction | [93] |
| LDH | Pine needle extract | 1.75 nm, not reported | Suzuki coupling reaction | [94] |
| MMT-K10 | Ocimum sanctum leaf extract | 3–6 nm, not reported | Oxidation of alcohols | [95] |
| MMT | Ocimum sanctum leaf extract | 10–80 nm, not reported | Hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol | [96] |
| Egg shell | Barberry fruit extract | <20 nm, spherical | Hydroxylation phenylboronic acid Reduction of 4-nitrophenol and dyes | [97] |
| PEG | Colocasia esculenta leaf extract | Irregular shape and size | Suzuki coupling reaction | [98] |
| Biopolymer | Reducing Agent | Size of PdNPs | Catalytic Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanocellulose from waste cotton cloth | - | 2.46 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [107] |
| Cyclea barbata pectin | - | 6–12 nm | Heck coupling reaction Reduction of nitrophenols | [108] |
| Cellulose from waste banana pseudostem | Waste banana pseudostem extract a | 8–18 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction Denitrogenative cross-coupling | [109,110] |
| Chitosan nanofiber | EtOH | 5–50 nm | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [111] |
| Brown cotton fiber | - | 8 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [112] |
| Clove leaf powder | - | 4.49 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [113] |
| Chitosan/agarose/beta-cyclodextrin microbeads | EtOH | 50 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [114] |
| Xylose hydrocar microsphere | EtOH | 8–18 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [115] |
| (Pd4)3-GFPuv fusion protein | NaBH4 | 2.4 ± 0.7 | Suzuki and Stille coupling reaction | [116] |
| Oxytocin | - | 16–18 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [117] |
| Modified Nonpareil almond shell | Nonpareil almond hull extract | 20 nm | Reduction of Dyes | [118] |
| Jute plant sticks | NaBH4 | 7–10 nm | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [119] |
| Jute plant sticks | HCOOH | 15–20 nm | Hydrogenation of olefins and N-heteroarenes | [120] |
| Lentinan | - | 2.3–3.3 nm | Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [121] |
| Collagen | - | 20–25 | Suzuki coupling reaction | [122] |
| Lignin | - | 1–5 nm | Sonogashira | [123] |
| Gum gatti | - | 4.8 ± 1.6 | Reduction of 4-nitrophenol and dyes | [124] |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose/agar | - | 37–55 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [125] |
| Chitosan/cellulose composite | NaBH4 | 26–30 | Suzuki coupling reaction | [126] |
| Chitosan/starch composite | NaBH4 | 16–21 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [127] |
| Residue of Poplar leaf | Poplar leaf extract | 3.1 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [128] |
| Gum Arabic/pectin beads | - | 3–6 nm | Heck coupling reaction | [129] |
| Pine needle powder | Pine needle extract | 3.25 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [130] |
| Pentacyclic triterpenoid arjunolicacid from Terminalia arjuna | Chrysophyllum caimito leaf extract | 9 nm | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [131] |
| Oak gum | - | 5–7 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of nitroarenes | [132] |
| Carboxymethyl functionalized hemicelluloses | EtOH | 11–19 | Heck coupling reaction | [133] |
| Native and modified Chitosan microspheres | EtOH | 5 nm | Sonogashira coupling reaction | [134] |
| Cellulose | hearth wood extract of Artocarpus lakoocha Roxb | 10–30 nm | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [135] |
| Pistacia atlantica kurdica gum | EtOH | 4–7 nm | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [136] |
| Thiourea modified chitosan | Ellagic acid | 3–5 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [137] |
| Gelatin/pectin | - | 2–5 nm | Heck coupling reaction | [138] |
| DNA | - | 7.1 ± 3.5 | Sonogashira coupling reaction | [139] |
| Support | Biopolymer/Reducing Agent | Size of PdNPs | Catalytic Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 magnetic NPs | Chitosan-Starch | 5–6 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [142] |
| Modified Chitosan (NaBH4) | 60 nm | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [143] | |
| Modified Cellulose (NaBH4) | 6–8 nm | Suzuki and Sonogashira coupling reaction | [144] | |
| Lignin | 5–10 nm | Heck coupling reaction | [145] | |
| Lignin-Chitosan (EtOH) | <20 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [146] | |
| Chitosan-activated carbon | 31–48 | Suzuki coupling reaction | [147] | |
| Chitosan-Agar | 28–39 | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [148] | |
| Polysaccharides from algae | 25–35 | Suzuki coupling reaction | [149] | |
| Modified Chitosan (EtOH) | 6–7 nm | Suzuki and Sonogashira coupling reaction | [150] | |
| Modified Salep (NaBH4) | 5 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [151] | |
| Modified Chitosan (EtOH) | 31 nm | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [152] | |
| DNA | 11–15 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [153] | |
| δ-FeOOH Magnetic | Chitosan (EtOH) | 10 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [154] |
| Fe3O4/SiO2 | Polydopamine | 5 nm | Suzuki coupling reactions Reduction of 4-nitrophenol | [155] |
| Graphene QD | Chitosan (NaBH4) | 6–8 nm | Reduction of nitroarenes | [156] |
| Graphene nanosheet | Cyclodextrin (EtOH) | 5–15 nm | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [157] |
| Carbon Nanotube | Chitosan (EtOH) | not reported | Suzuki coupling reactions Reduction of nitroarene and dyes | [158] |
| DNA (NaBH4) | not reported | Suzuki and Sonogashira coupling reaction | [159] | |
| Kaolin | Modified Chitosan (EtOH) | 15–20 nm | Sonogashira coupling reaction | [160] |
| Bentonite | Chitosan (EtOH) | 13 ± 2 | Sonogashira coupling reaction | [161] |
| MMT | Chitosan | 5 nm | Sonogashira coupling reaction | [162] |
| Carbonaceous Material | Bio-Source | Size of PdNPs | Catalytic Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porous active carbon | pine needle urban waste | 4.5 nm | Heck and Hiyama coupling reaction | [163] |
| Modified biochar | dried chicken manure | 6–8 nm | Suzuki and Heck coupling reaction | [164] |
| Mesoporous carbon | phenolic resin | 1.2 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [165] |
| Activated mesoporous carbon | Rice husk biomass | 7 nm | Suzuki, Heck and Sonogashira coupling reaction | [166] |
| Carbon-SiO2 | Rice husk biomass | 3.5–4.5 nm | Carbonylative Suzuki coupling reaction | [167] |
| Fe3O4@Porous Carbon | Pomegranate peel waste. | not reported | Suzuki and Sonogashira coupling reaction | [168] |
| Mesoporous carbon | Tannin | 25 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [169] |
| CDQ@Fe3O4 | Glycerol/urea | 15–20 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction Reduction of nitroarenes | [170] |
| CQD@Fe3O4 | Vanillin | 3.6 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [171] |
| CDQ@Fe3O4 | Citric acid/urea | 20 nm | Suzuki coupling reaction | [172] |
| rGO | - | 2 nm | Suzuki and Ulman reaction | [173] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piermatti, O. Green Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles for Sustainable and Environmentally Benign Processes. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111258
Piermatti O. Green Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles for Sustainable and Environmentally Benign Processes. Catalysts. 2021; 11(11):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111258
Chicago/Turabian StylePiermatti, Oriana. 2021. "Green Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles for Sustainable and Environmentally Benign Processes" Catalysts 11, no. 11: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111258
APA StylePiermatti, O. (2021). Green Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles for Sustainable and Environmentally Benign Processes. Catalysts, 11(11), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111258






