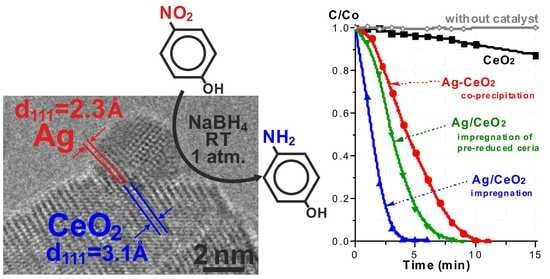
Room-Temperature Nitrophenol Reduction over Ag–CeO2 Catalysts: The Role of Catalyst Preparation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Result of N2 Sorption
2.2. XRD
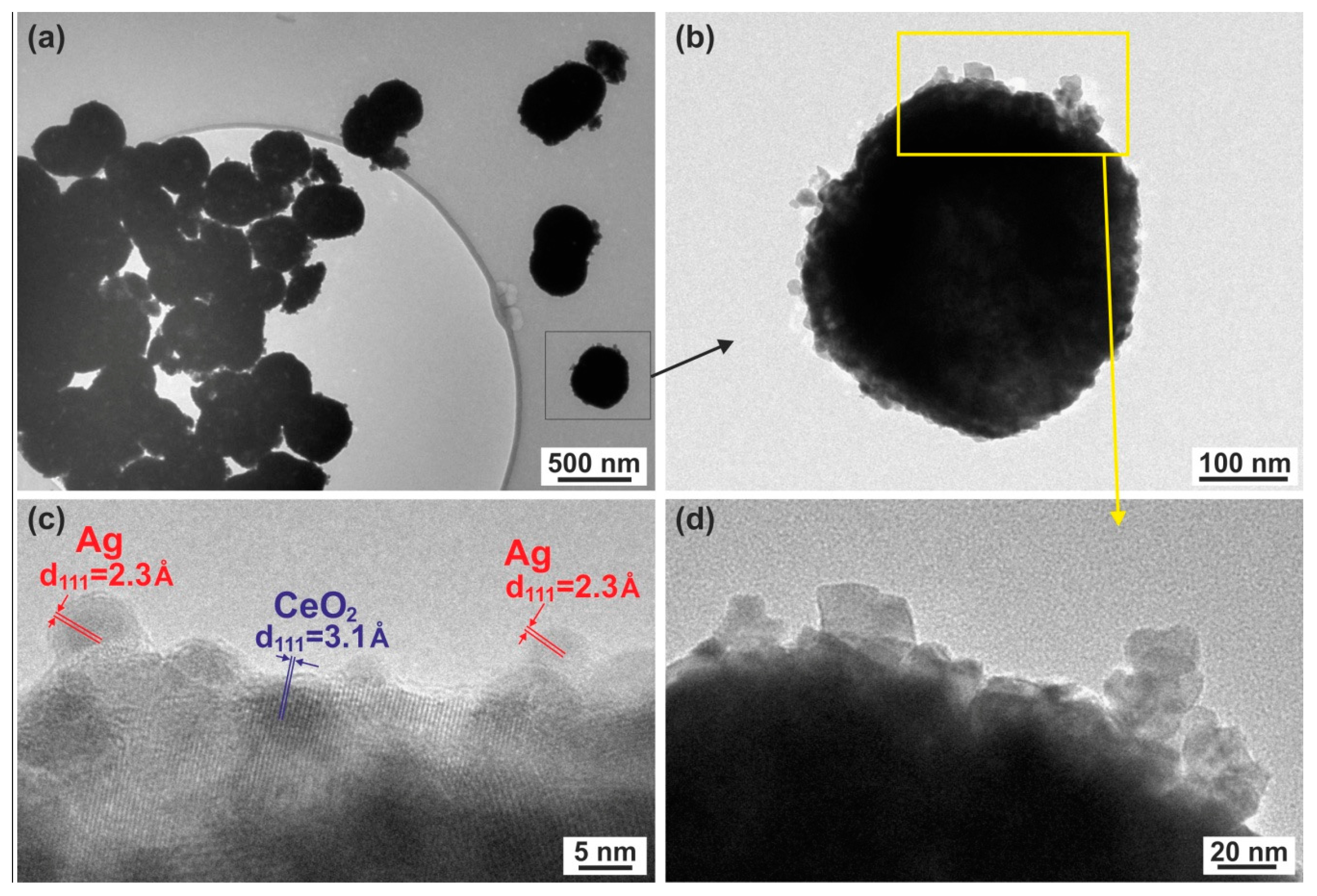
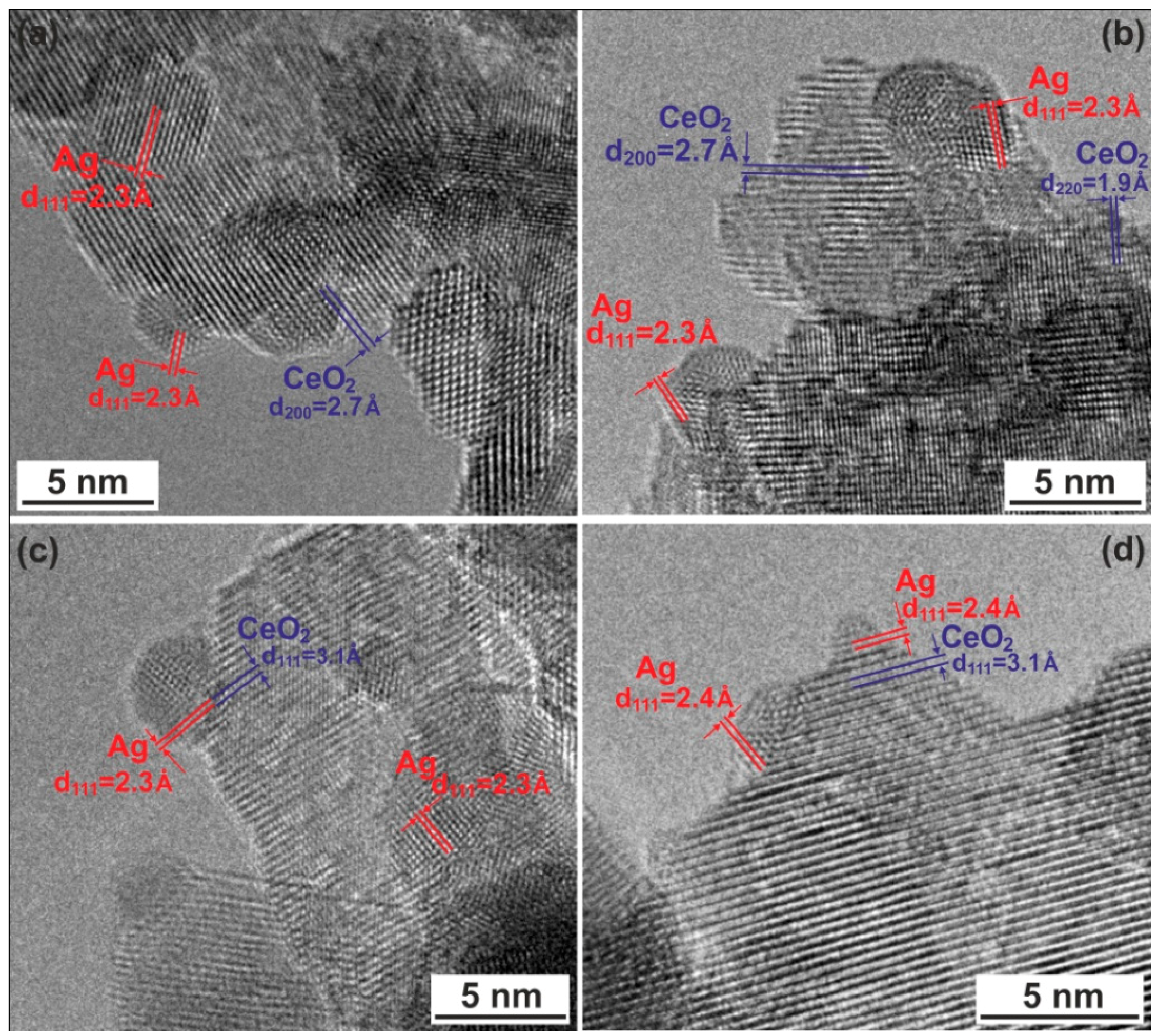
2.3. TEM Studies
2.4. H2-TPR
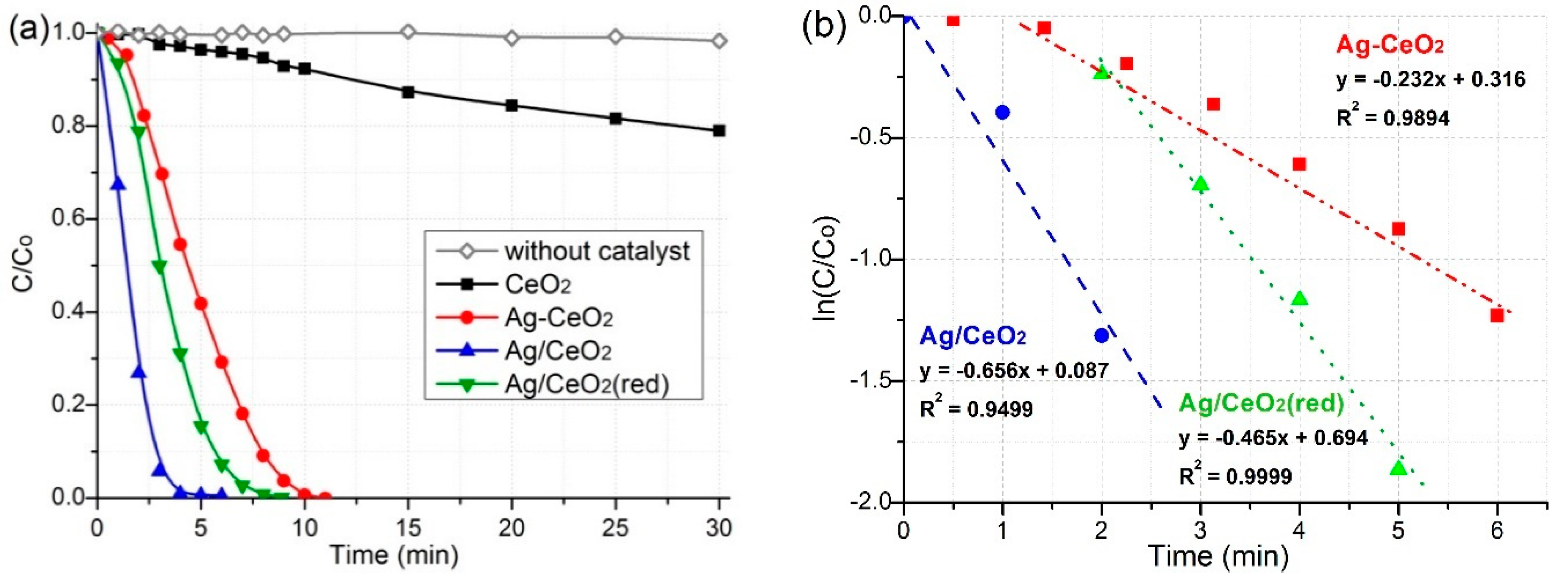
2.5. Catalytic Properties
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Catalysts
4.2. Materials Characterization
4.3. Catalytic Activity Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bamba, D.; Coulibaly, M.; Robert, D. Nitrogen-containing organic compounds: Origins, toxicity and conditions of their photocatalytic mineralization over TiO2. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, J.; Ferreira, L.F.; Silva, V.C.; Oliveira, A.C.; De Oliveira, R.R.; Jacinto, M.J. Facile fabrication of functionalized core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2@Pd microspheres by urea-assisted hydrothermal route and their application in the reduction of nitro compounds. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 11, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, C.M.; Agathos, S.N. Biodegradation of nitroaromatic pollutants: From pathways to remediation. Biotechnol. Ann. Rev. 2010, 6, 197–220. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao-Qiong, W.; Xing-Wen, W.; Qing, H.; Jiang-Shan, S.; Hong-Wu, Z. In situ synthesized gold nanoparticles in hydrogels for catalytic reduction of nitroaromatic compounds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 331, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, T.; Chen, B. Facile fabrication of Shewanella@graphene core-shell material and its enhanced performance in nitrobenzene reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 658, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Khorsandi, S. Photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol with ZnO supported nano-clinoptilolite zeolite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 20, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhong, Y. Electrochemical degradation of p-nitrophenol with different processes. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.; Rehan, R.; Farooqi, H.Z.; Butt, Z.; Ashraf, S. Physical chemistry of catalytic reduction of nitroarenes using various nanocatalytic systems: Past, present, and future. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, M.; Estrada, M.; Miridonov, S.; Simakov, A. Synthesis of cerium oxide (IV) hollow nanospheres with tunable structure and their performance in the 4-nitrophenol adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 278, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Qi, Y.; Liu, R. Pilot-Scale Production, Properties and Application of Fe/Cu Catalytic-Ceramic-Filler for Nitrobenzene Compounds Wastewater Treatment. Catalysts 2019, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Huang, Z.-F.; Pan, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, J.-J. Review on selective hydrogenation of nitroarene by catalytic, photocatalytic and electrocatalytic reactions. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 227, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Satsuma, A. Size- and support-dependent silver cluster catalysis for chemoselective hydrogenation of nitroaromatics. J. Catal. 2010, 270, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Gupta, A.; Pandey, O.P. Role of oxygen vacancies in Ag/Au doped CeO2 nanoparticles for fast photocatalysis. Sol. Energy 2018, 165, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.K.; Vo, N.T.; Kim, D. Highly robust magnetically recoverable Ag/Fe2O3 nanocatalyst for chemoselective hydrogenation of nitroarenes in water. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 538, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhong, L.; Fang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Gao, H.; Fang, B. Unlocking the door to highly efficient Ag-based nanoparticles catalysts for NaBH4-assisted nitrophenol reduction. Nanoresearch 2019, 12, 2407–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabchenko, M.V.; Mamontov, G.V.; Zaikovskii, V.I.; La Parola, V.; Liotta, L.F.; Vodyankina, O.V. The role of metal–support interaction in Ag/CeO2 catalysts for CO and soot oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 260, 118148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, J.; Zou, Y.; Yu, G.; Luo, J.; Dong, C.-L.; et al. Interface Engineering of Pt and CeO2 Nanorods with Unique Interaction for Methanol Oxidation. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.T.; Azeeva, E.; Zhang, K.; Zell, E.T.; Bernard, D.T.; Balaz, S.; Wang, R. A comparative study of CO oxidation over Cu-O-Ce solid solutions and CuO/CeO2 nanorods catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, Z.; Ni, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Qu, Y. Strong electronic metal-support interaction of Pt/CeO2 enables efficient and selective hydrogenation of quinolines at room temperature. J. Catal. 2018, 359, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Kuwahara, Y.; Mori, K.; Yamashita, H. Plasmonic catalysis of Ag nanoparticles deposited on CeO2 modified mesoporous silica for the nitrostyrene reduction under light irradiation conditions. Catal. Today 2018, 324, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubina, E.V.; Lokteva, E.S.; Erokhin, A.V.; Veligzhanin, A.A.; Zubavichus, Y.V.; Likholobov, V.A.; Lunin, V.V. The role of metal–support interaction in catalytic activity of nanodiamond-supported nickel in selective phenylacetylene hydrogenation. J. Catal. 2016, 344, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, R.; Spitaleri, L.; Gulino, A.; Sciré, S. High-Performing Au-Ag Bimetallic Catalysts Supported on Macro-Mesoporous CeO2 for Preferential Oxidation of CO in H2-Rich Gases. Catalysts 2020, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabchenko, M.V.; Mikheeva, N.N.; Mamontov, G.V.; Salaev, M.A.; Liotta, L.F.; Vodyankina, O.V. Ag/CeO2 Composites for Catalytic Abatement of CO, Soot and VOCs. Catalysts 2018, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Kayama, T.; Dong, F.; Shinjoh, H. A mechanistic study on soot oxidation over CeO2-Ag catalyst with ‘rice-ball’ morphology. J. Catal. 2011, 282, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montini, T.; Melchionna, M.; Monai, M.; Fornasiero, P. Fundamentals and Catalytic Applications of CeO2-Based Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5987–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamontov, G.V.; Grabchenko, M.V.; Sobolev, V.I.; Zaikovskii, V.I.; Vodyankina, O.V. Ethanol dehydrogenation over Ag-CeO2/SiO2 catalyst: Role of Ag-CeO2 interface. Appl. Catal. A 2016, 528, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Han, G.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, H.W.; Choung, J.W.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, K.-Y. CeO2 promoted Ag/TiO2 catalyst for soot oxidation with improved active oxygen generation and delivery abilities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutov, V.V.; Mamontov, G.V.; Zaikovskii, V.I.; Liotta, L.F.; Vodyankina, O.V. Low-temperature CO oxidation over Ag/SiO2 catalysts: Effect of OH/Ag ratio. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 221, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabchenko, M.V.; Mamontov, G.V.; Zaikovskii, V.I.; La Parola, V.; Liotta, L.F.; Vodyankina, O.V. Design of Ag CeO2/SiO2 catalyst for oxidative dehydrogenation of ethanol: Control of Ag–CeO2 interfacial interaction. Catal. Today 2019, 333, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlivskaya, M.V.; Mikheeva, N.N.; Zaikovskii, V.I.; Mamontov, G.V. Influence of Preparation Method of Ag–CeO2 Catalysts on Their Structure and Activity in Soot Combustion. Kinet. Catal. 2019, 60, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, P.; Huang, D.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Qin, L.; Li, B.; He, J.; Yi, H.; Cheng, M.; et al. Au nanoparticles decorated on activated coke via a facile preparation for efficient catalytic reduction of nitrophenols and azo dyes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Feng, X.; Huang, D.; Yang, G.; Astruc, D. Basic concepts and recent advances in nitrophenol reduction by gold- and other transition metal nanoparticles. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 287, 114–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Liu, Q.; Song, M.X.; Huang, C. Hydrogenation of nitroarenes into aromatic amines over Ag@BCN colloidal catalysts. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 447, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, G.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, T.; Du, X. Silver nanoparticles supported on electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous mats for catalytic applications. MRS Commun. 2016, 6, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Shu, Y.; Xu, J.; Pang, H. Facile one-step synthesis of Ag@CeO2 core–shell nanospheres with efficient catalytic activity for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. CrystEngComm. 2017, 19, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhu, Y.M.; Tan, H.L.; Chen, X.S.; Lu, Z.H. Core–shell structured nanocomposites Ag@CeO2 as catalysts for hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol and 2-nitroaniline. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 47966–47973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-F.; Ling, L.-L.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.-J.; Jiang, H. Enhancing the Catalytic Activity and Stability of Noble Metal Nanoparticles by the Strong Interaction of Magnetic Biochar Support. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 13055–13064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, N.; Chen, B.H. Constructing nano-structure on silver/ceria-zirconia towards highly active and stable catalyst for soot oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabchenko, M.V.; Mamontov, G.V.; Zaikovskii, V.I.; Vodyankina, O.V. Effect of the metal−support interaction in Ag/CeO2 catalysts on their activity in ethanol oxidation. Kinet. Catal. 2017, 58, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
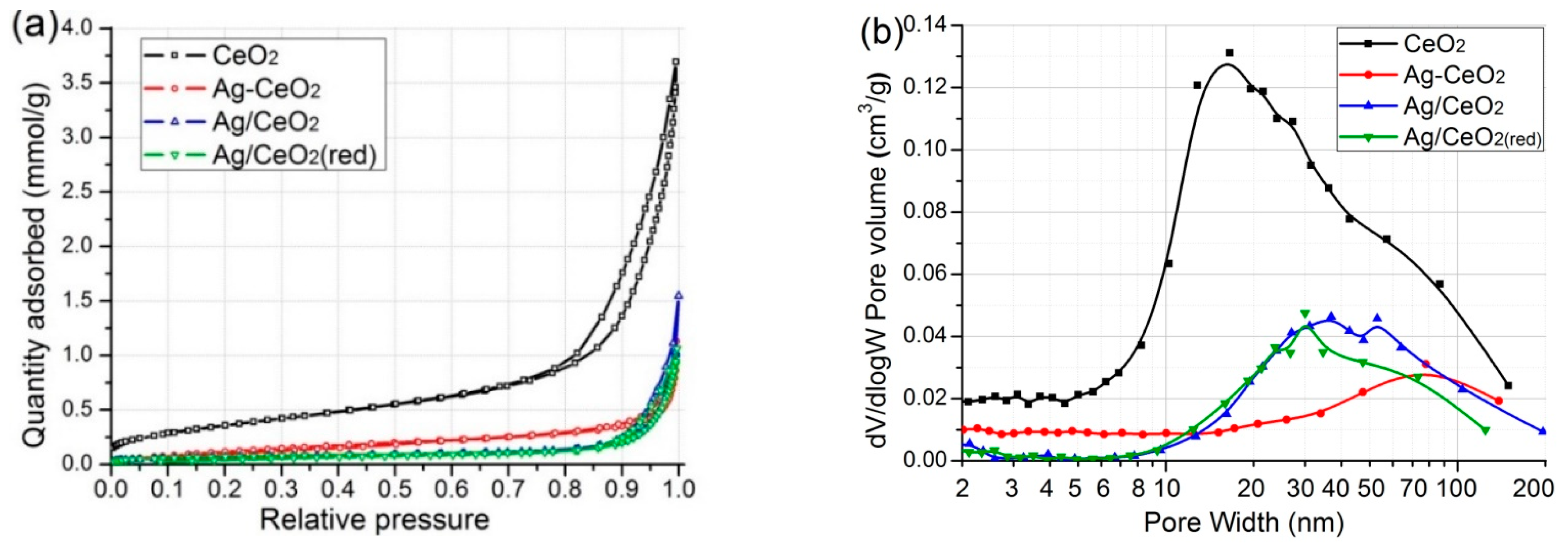



| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | Vpore (сm3/g) | Dpore (nm) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 | 30.4 | 0.128 | 13 |
| Ag–CeO2 | 11.9 | 0.039 | - |
| Ag/CeO2 | 5.6 | 0.054 | 27 |
| Ag/CeO2 (red) | 5.6 | 0.037 | 27 |
| Sample | d(111)CeO2 (Å) | DCeO2 (nm) a | d (111)Ag (Å) | DAg (nm) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 | 3.131 | 8.8 ± 1.0 | - | - |
| Ag–CeO2 | 3.121 | 16.7 ± 1.8 | 2.361 | 17.0 ± 1.1 |
| Ag/CeO2 | 3.130 | 9.9 ± 1.3 | - | - |
| Ag/CeO2 (red) | 3.126 | 14.1 ±1.5 | 2.362 | 12.3 ± 0.7 |
| ICSD * reference files b | 3.121 | - | 2.359 | - |
| Сatalysts | t (min) | k (min−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/CeO2 (red) | 6 | 0.465 | This work |
| Ag-CeO2 | 11 | 0.232 | This work |
| Ag/CeO2 | 8 | 0.656 | This work |
| Ag@BCN | 6 | 0.196 | [34] |
| AgNPs/PAN | 70 | 0.046 | [35] |
| Ag@CeO2 | 7 | 0.32 | [36] |
| Ag@CeO2 | - | 1.96 | [37] |
| Pd/C (commercial) | 6 | 0.77 | [38] |
| Pt/C | 30 | 0.058 | [38] |
| Pd/Fe2O3 | 5 | 0.359 | [38] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chernykh, M.; Mikheeva, N.; Zaikovskii, V.; Salaev, M.; Liotta, L.F.; Mamontov, G. Room-Temperature Nitrophenol Reduction over Ag–CeO2 Catalysts: The Role of Catalyst Preparation Method. Catalysts 2020, 10, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050580
Chernykh M, Mikheeva N, Zaikovskii V, Salaev M, Liotta LF, Mamontov G. Room-Temperature Nitrophenol Reduction over Ag–CeO2 Catalysts: The Role of Catalyst Preparation Method. Catalysts. 2020; 10(5):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050580
Chicago/Turabian StyleChernykh, Mariia, Natalia Mikheeva, Vladimir Zaikovskii, Mikhail Salaev, Leonarda F. Liotta, and Grigory Mamontov. 2020. "Room-Temperature Nitrophenol Reduction over Ag–CeO2 Catalysts: The Role of Catalyst Preparation Method" Catalysts 10, no. 5: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050580
APA StyleChernykh, M., Mikheeva, N., Zaikovskii, V., Salaev, M., Liotta, L. F., & Mamontov, G. (2020). Room-Temperature Nitrophenol Reduction over Ag–CeO2 Catalysts: The Role of Catalyst Preparation Method. Catalysts, 10(5), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050580