Shaking Rate during Production Affects the Activity of Escherichia coli Surface-Displayed Candida antarctica Lipase A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Gene Construction and Protein Expression
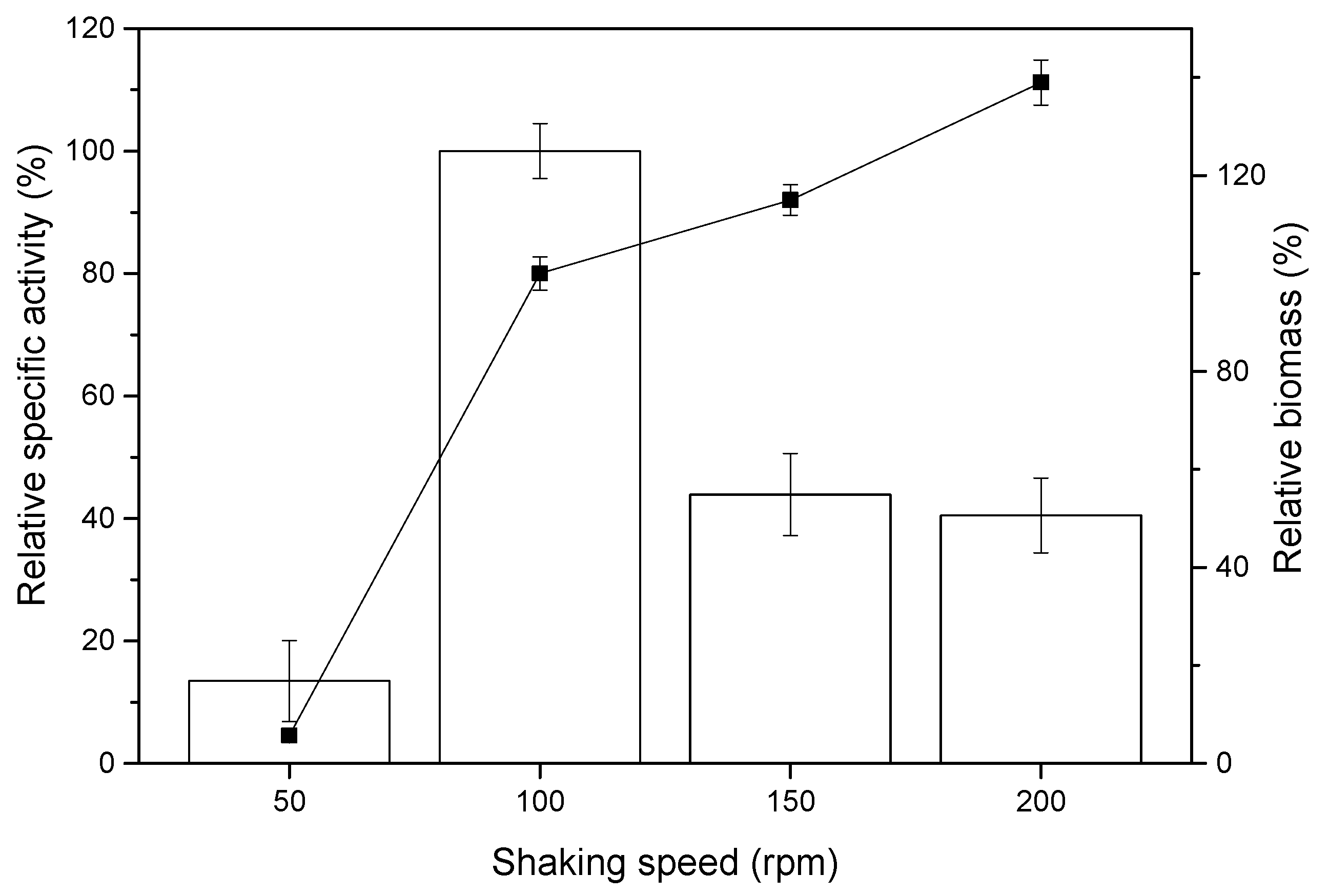
2.2. Effect of Shaking Rate on sdCALA Activity and Biomass
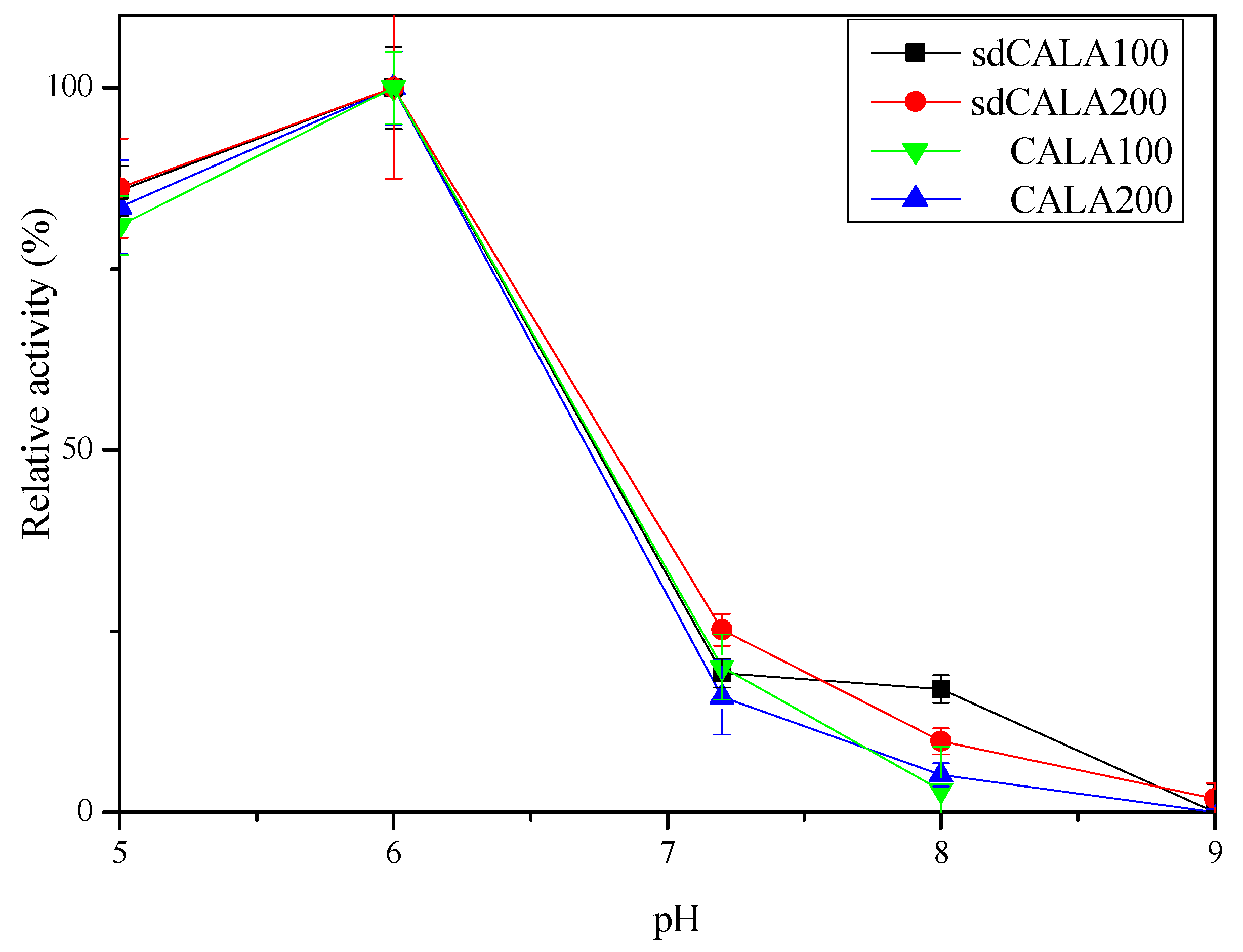
2.3. Optimal Temperature and pH for Production of CALA and sdCALA
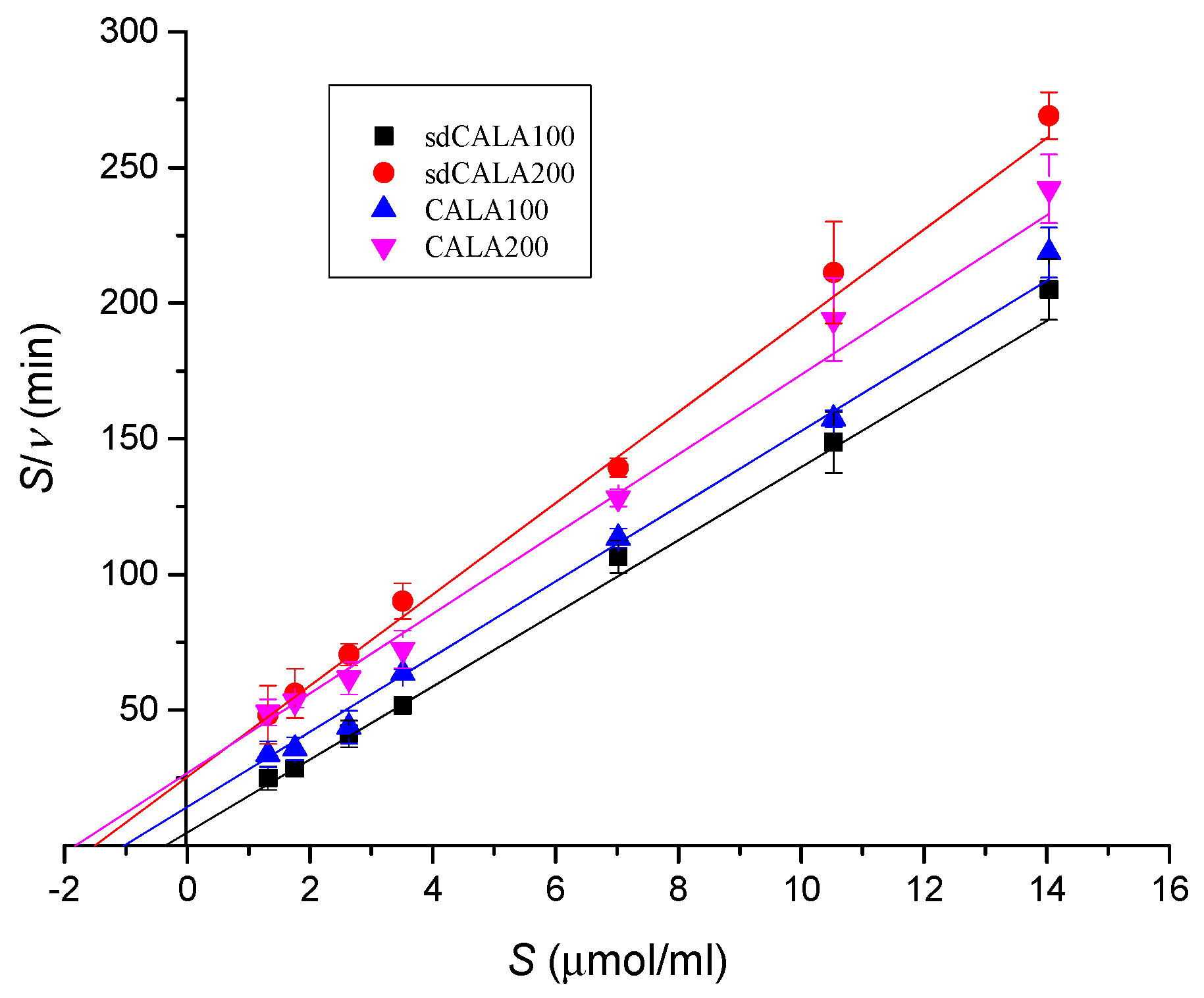
2.4. Kinetic Analyses of Various CALA Enzymes
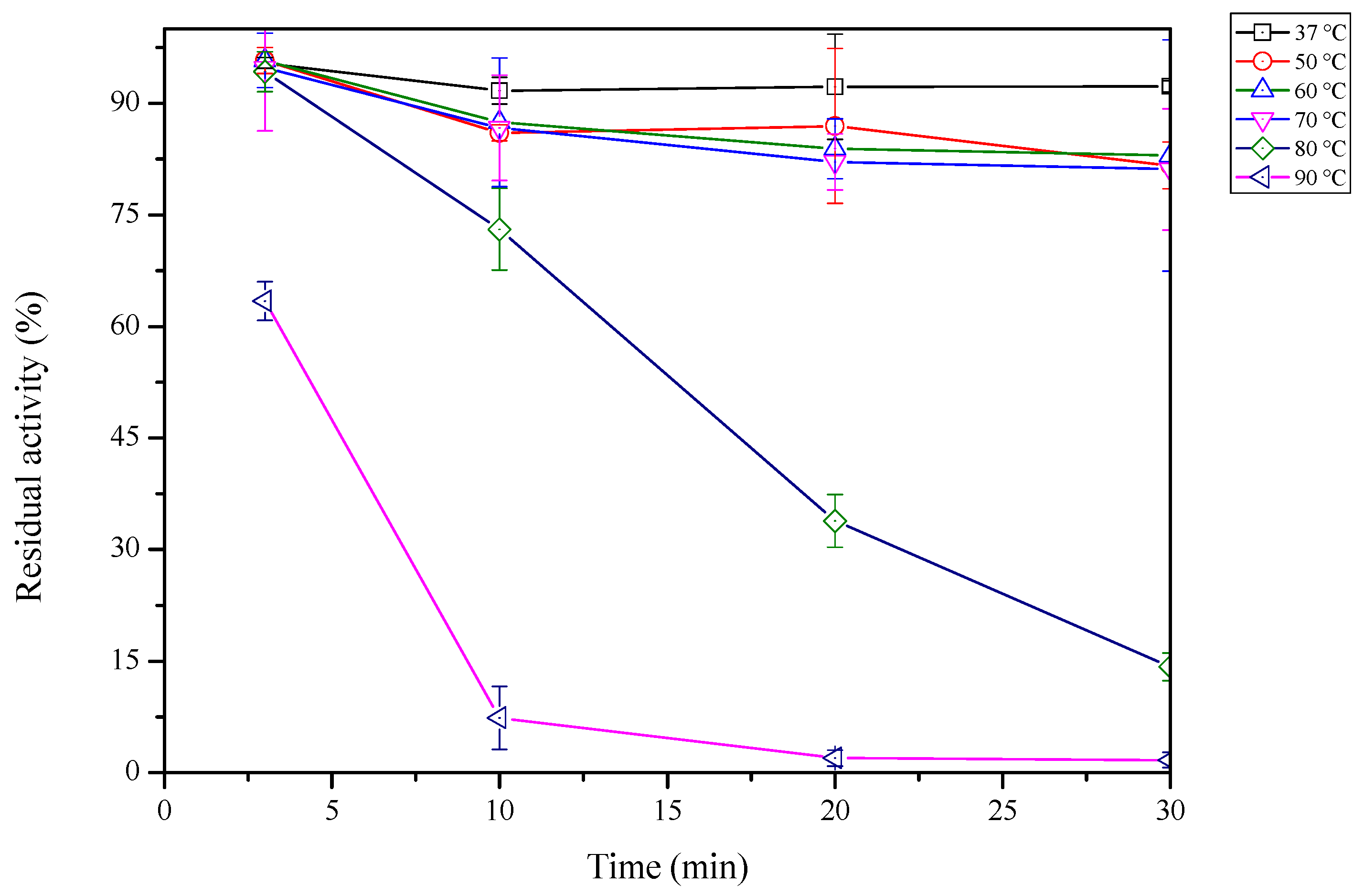
2.5. Thermal Stability of sdCALA
2.6. Effect of Organic Solvents on sdCALA Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Strains, Plasmids, and Source
3.2. Construction of Expression Systems
3.3. Cultivation Conditions
3.4. Estimation of Shear Stress and Mass Transfer Coefficient
3.5. Kinetics Models
3.6. Assays
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirk, O.; Christensen, M.W. Lipases from Candida antarctica: Unique biocatalysts from a unique origin. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2002, 6, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppenberg, J.; Parkar, S.; Bergfors, T.; Jones, T.A. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray studies of lipase B from Candida antarctica. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 235, 790–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, K.; Morfill, J.; Gumpp, H.; Gaub, H.E. Functional expression of Candida antarctica lipase B in Eschericha coli. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 125, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, M.; Juhl, P.B.; Pleiss, J. Structural classification by the lipase engineering database: A case study of Candida antarctica lipase A. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de María, P.D.; Carboni-Oerlemans, C.; Tuin, B.; Bargeman, G.; van der Meer, A.; van Gemert, R. Biotechnological applications of Candida antarctica lipase A: State-of-the-art. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 2005, 37, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh, I.; Patkar, S.; Halkier, T.; Hansen, M.T. Two lipases from Candida antarctica: Cloning and expression in Aspergillus oryzae. Can. J. Bot. 1995, 73, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, J.; Richter, S.; Nieveler, J.; Hansen, C.E.; Rhlid, R.B.; Schmid, R.D.; Rusnak, M. High yield expression of lipase A from Candida antarctica in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris and its purification and characterisation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, J.; Rusnak, M.; Hansen, C.-E.; Rhlid, R.B.; Schmid, R.D.; Maurer, S.C. Functional expression of lipase A from Candida antarctica in Escherichia coli—A prerequisite for high-throughput screening and directed evolution. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 2007, 45, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.W.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Hult, K. Expression of Candida antarctica lipase B in Pichia pastoris and various Escherichia coli systems. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 62, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larios, A.; Garcia, H.S.; Oliart, R.M.; Valerio-Alfaro, G. Synthesis of flavor and fragrance esters using Candida antarctica lipase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognjanovic, N.; Bezbradica, D.; Knezevic-Jugovic, Z. Enzymatic conversion of sunflower oil to biodiesel in a solvent-free system: Process optimization and the immobilized system stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5146–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.P. Filamentous fusion phage-novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science 1985, 228, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Xu, Z. Microbial cell-surface display. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernerus, H.; Stahl, S. Biotechnological applications for surface engineered bacteria. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2004, 40, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Margaritis, A.; Bassi, A.S. Principles and biotechnological applications of bacterial ice nucleation. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 1991, 11, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, A.R.; Van Den Bussche, R.A.; Wichman, H.A.; Orser, C.S. Unusual pattern of bacterial ice nucleation gene evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1994, 11, 911–920. [Google Scholar]
- van Bloois, E.; Winter, R.T.; Kolmar, H.; Fraaije, M.W. Decorating microbes: Surface display of proteins on Escherichia coli. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, P.; Gunneriusson, E.; Nygren, P.A.; Stahl, S. Display of proteins on bacteria. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 96, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, Z.; Shao, X.; He, J.; Li, L. Improved phosphate biosorption by bacterial surface display of phosphate binding protein utilizing ice nucleation protein. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 299, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, M.; Mulchandani, A.; Chen, W. Cell surface display of organophosphorus hydrolase using ice nucleation protein. Biotechnol. Prog. 2001, 17, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.H.; Giridhar, R.; Wu, W.T. Surface display of transglucosidase on Escherichia coli by using the ice nucleation protein of Xanthomonas campestris and its application in glucosylation of hydroquinone. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 95, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Fukuda, H.; Ueda, M.; Tanaka, A.; Kondo, A. Construction of yeast strains with high cell surface lipase activity by using novel display systems based on the Flo1p flocculation functional domain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4517–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, M.V.H.; Silva, G.P.D.; Machado, A.C.D.O.; Torres, F.A.G.; Freire, D.M.G.; Almeida, R.V. Displaying lipase B from Candida antarctica in Pichia pastoris using the yeast surface display approach: Prospection of a new anchor and characterization of the whole cell biocatalyst. PLoS ONE 2015, 12, e0141454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, H.; Jia, B.; Xu, L.; Yan, Y. Surface display of active lipase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using Cwp2 as an anchor protein. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Rosenau, F.; Becker, S.; Buest, S.; Hausmann, S.; Kolmar, H.; Jaeger, K.-E. Functional cell-surface display of a lipase-specific chaperone. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.-H.; Han, C.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Kwon, H.-J.; Lee, H.-H. Surface display expression of Bacillus licheniformis lipase in Escherichia coli using Lpp’OmpA Chimera. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, S.-C.; Chen, C.-M.; Lin, C.-C.; Wu, J.-Y.; Shieh, C.-J.; Liu, Y.-C. Deciphering EGFP production via surface display and self-cleavage intein system in different hosts. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 55, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Liu, T.-T.; Kan, S.-C.; Zang, C.-Z.; Yeh, C.-W.; Wu, J.-Y.; Chen, J.-H.; Shieh, C.-J.; Liu, Y.-C. Production of D-Hydantoinase via surface display and self-cleavage system. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-I.; Chen, C.-M.; Lin, C.-C.; Kan, S.-C.; Shieh, C.-J.; Liu, Y.-C. Cell disruption enhanced the pure EGFP recovery from an EGFP-intein- surface protein production system in recombinant E. coli. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 68, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Liu, T.-T.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Yang, S.-C.; Shieh, C.-J.; Liu, Y.-C. Production of recombinant EGFP via surface display of ice nucleation protein and self-cleavage intein. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 54, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamel, M.M.; Ramachandran, K.B.; Hasan, M. Operational stability of lipase enzyme: Effect of temperature and shear. Dev. Chem. Eng. Min. Process. 2005, 13, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijevic, A.; Velickovic, D.; Bihelovic, F.; Bezbradica, D.; Jankov, R.; Milosavic, N. One-step, inexpensive high yield strategy for Candida antarctica lipase A isolation using hydroxyapatite. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamost, B.L.; Nielsen, H.K.; Starnes, R.L. Thermostable enzymes for industrial applications. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1991, 8, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpipat, W.; Xu, X.; Guo, Z. Improved acylation of phytosterols catalyzed by Candida antarctica lipase A with superior catalytic activity. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 70, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boran, R.; Ugur, A. Partial purification and characterization of the organic solvent-tolerant lipase produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens RB02-3 isolated from milk. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 40, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Batal, A.I.; Farrag, A.A.; Elsayed, M.A.; El-Khawaga, A.M. Effect of environmental and nutritional parameters on the extracellular lipase production by Aspergillus niger. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2016, 60, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, F.; Lan, D.; Whiteley, C.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y. Effects of organic solvents on activity and conformation of recombinant Candida antarctica lipase A produced by Pichia pastoris. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.L.; Duque, E.; Rodríguez-Herva, J.J.; Godoy, P.; Haïdour, A.; Reyes, F.; Fernández-Barrero, A. Mechanisms for solvent tolerance in bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3887–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, A.; Duque, E.; Mosqueda, G.; Ramos, J.L.; Junker, F. Multiple responses of Gram-negative bacteria to organic solvents. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 1, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russel, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, C.E.G.; Martınez-Trujillo, A.; Osorio, G.A. Oxygen transfer coefficient and the kinetic parameters of exo-polygalacturonase production by Aspergillus flavipes FP-500 in shake flasks and bioreactor. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 55, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, F.G.; Rodrıguez, J.J.G.; Miron, A.S.; Garcıa, M.C.C.; Belarbi, E.H.; Grima, E.M. Determination of shear stress thresholds in toxic dinoflagellates cultured in shaken flasks Implications in bioprocess engineering. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, S.H.; Wu, W.T. Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase on chitosan with activation of the hydroxyl groups. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.C.; Ko, S.; Ju, S.J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, M.K.; Pan, J.G. Bacterial cell surface display of lipase and its randomly mutated library facilitates high-throughput screening of mutants showing higher specific activities. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 2003, 26, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
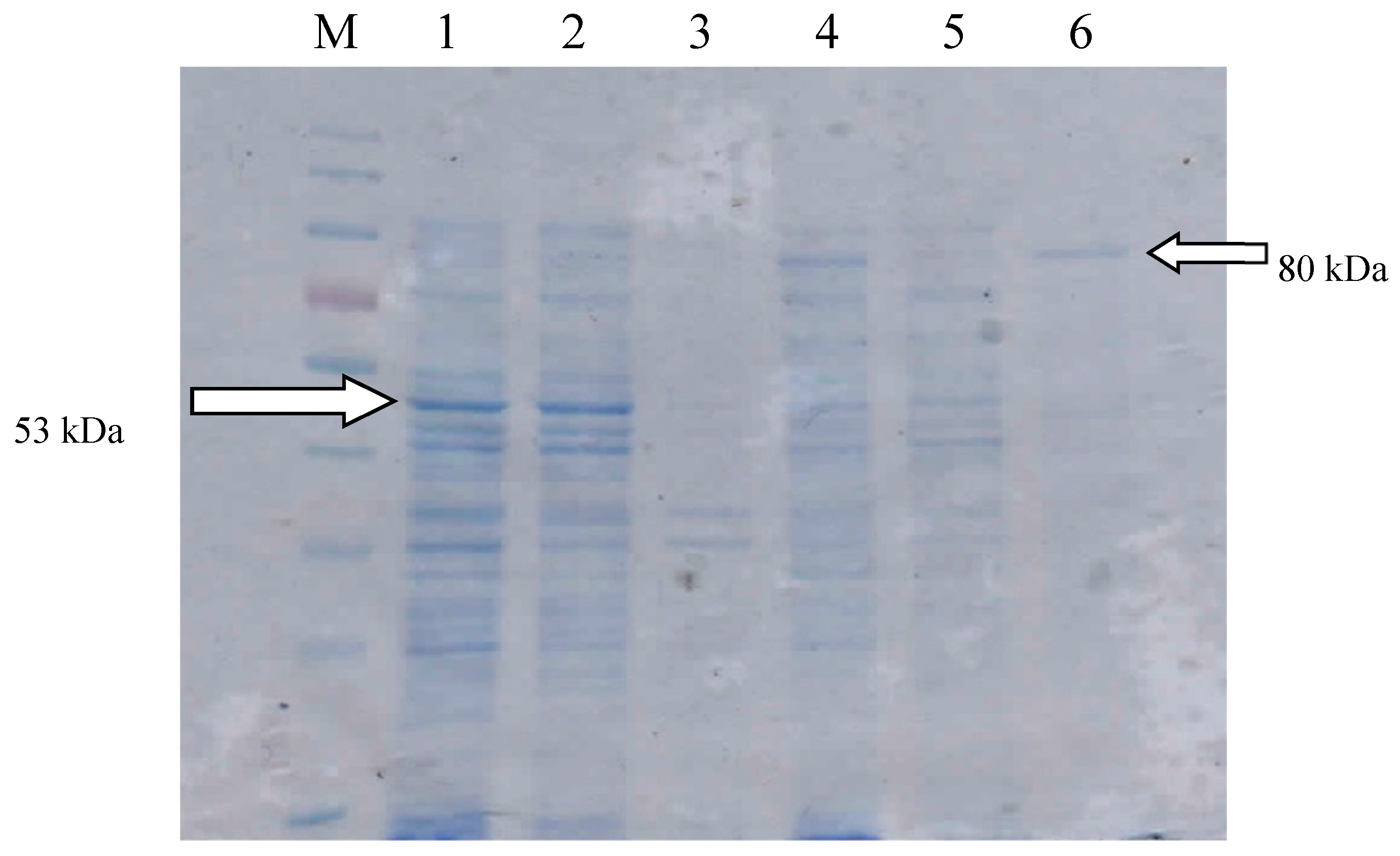
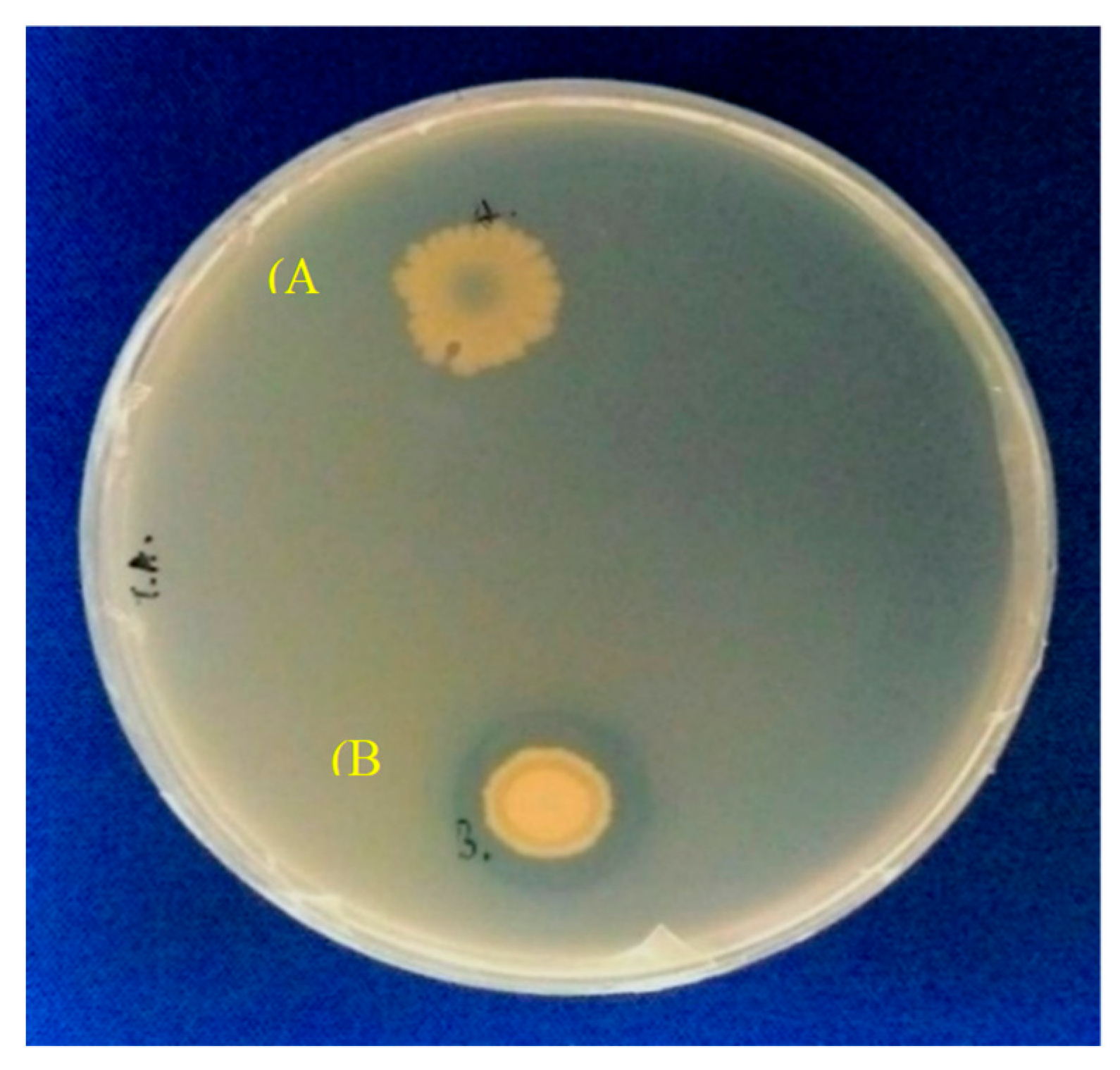




| Expression System | Biomass (mg/mL) | Activity (U/mL) | Specific Activity (U/mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intracellular a (pET22b-calawt) | 1.298 ± 0.232 | 0.326 ± 0.11 | 0.251 ± 0.047 |
| Surface display b (pINP-CALA) | 0.999 ± 0.052 | 0.285 ± 0.07 | 0.285 ± 0.013 |
| Shaking Rate (rpm) | KLa (h−1) | γ (h−1) | Relative Specific Activity (%) | Relative Biomass (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 9.6 | 13 | 13.5 ± 6.6 | 5.7 ± 1.2 |
| 100 | 21.4 | 89 | 100 ± 4.5 | 100 ± 3.4 |
| 150 | 34.2 | 276 | 43.9 ± 6.7 | 115 ± 3.1 |
| 200 | 47.8 | 617 | 40.5 ± 6.1 | 139 ± 4.6 |
| Lipase | νm (μmol/mL/min) | Km (μmol/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| sdCALA100 | 0.074 | 0.360 |
| sdCALA200 | 0.059 | 1.510 |
| CALA100 | 0.072 | 1.032 |
| CALA200 | 0.068 | 1.821 |
| Strain or Plasmid | Genotype and Relevant Characteristics | Source |
|---|---|---|
| DH5α | F- endA1 glnV44 thi-1 recA1 relA1 gyrA96 deoR nupG Φ80dlacZΔM15 Δ(lacZYA-argF)U169, hsdR17(rk − mk +), λ– | Novagen |
| JM109 (DE3) | endA1 glnV44 thi-1 relA1 gyrA96 recA1 mcrB+ Δ(lac-proAB) e14- (F’ traD36 proAB+ lacIq lacZΔM15) hsdR17(rk − mk +) λ(DE3) | NEB |
| pET22b-calawt | CALA (calA) gene fragment in pET22b | Professor Bornscheuer (Greifswald University, Germany) |
| pET26b-inaX | INP (inaX) gene fragment in pET26b | Professor Wu (NCKU, Taiwan) |
| yT&A | pBluescript IISK(–) with modified MCS | Yeastern Biotech |
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5’3’) | Template |
|---|---|---|
| CALA-F | GAATTCATGCGTGTGAGCCTGCGTAG (EcoRI) | pET22b-calawt |
| CALA-R | CACTCGAGCACCACCACCA (XhoI) | pET22b-calawt |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, C.-F.; Lin, S.-C.; Juang, T.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C. Shaking Rate during Production Affects the Activity of Escherichia coli Surface-Displayed Candida antarctica Lipase A. Catalysts 2020, 10, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040382
Chung C-F, Lin S-C, Juang T-Y, Liu Y-C. Shaking Rate during Production Affects the Activity of Escherichia coli Surface-Displayed Candida antarctica Lipase A. Catalysts. 2020; 10(4):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040382
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Chen-Fu, Shih-Che Lin, Tzong-Yuan Juang, and Yung-Chuan Liu. 2020. "Shaking Rate during Production Affects the Activity of Escherichia coli Surface-Displayed Candida antarctica Lipase A" Catalysts 10, no. 4: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040382
APA StyleChung, C.-F., Lin, S.-C., Juang, T.-Y., & Liu, Y.-C. (2020). Shaking Rate during Production Affects the Activity of Escherichia coli Surface-Displayed Candida antarctica Lipase A. Catalysts, 10(4), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040382






