Mesoporous Carbon of Carbonized Human Urine Waste: A Valuable Heterogeneous Catalyst for Chromene and Xanthene Derivative Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Synthesis of Human Urine Carbon Nanomaterial
2.2. Synthesis of Chromene Derivatives
2.3. Synthesis of 1,8-Di-Oxo-Octahydroxanthene Derivatives
2.4. Synthesis of Benzyl Pyrazolyl Coumarin Derivatives
2.5. Synthesis of Biscoumarin Methane Derivatives
2.6. Spectral Data of 1H NMR and 13C NMR
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Characterizations
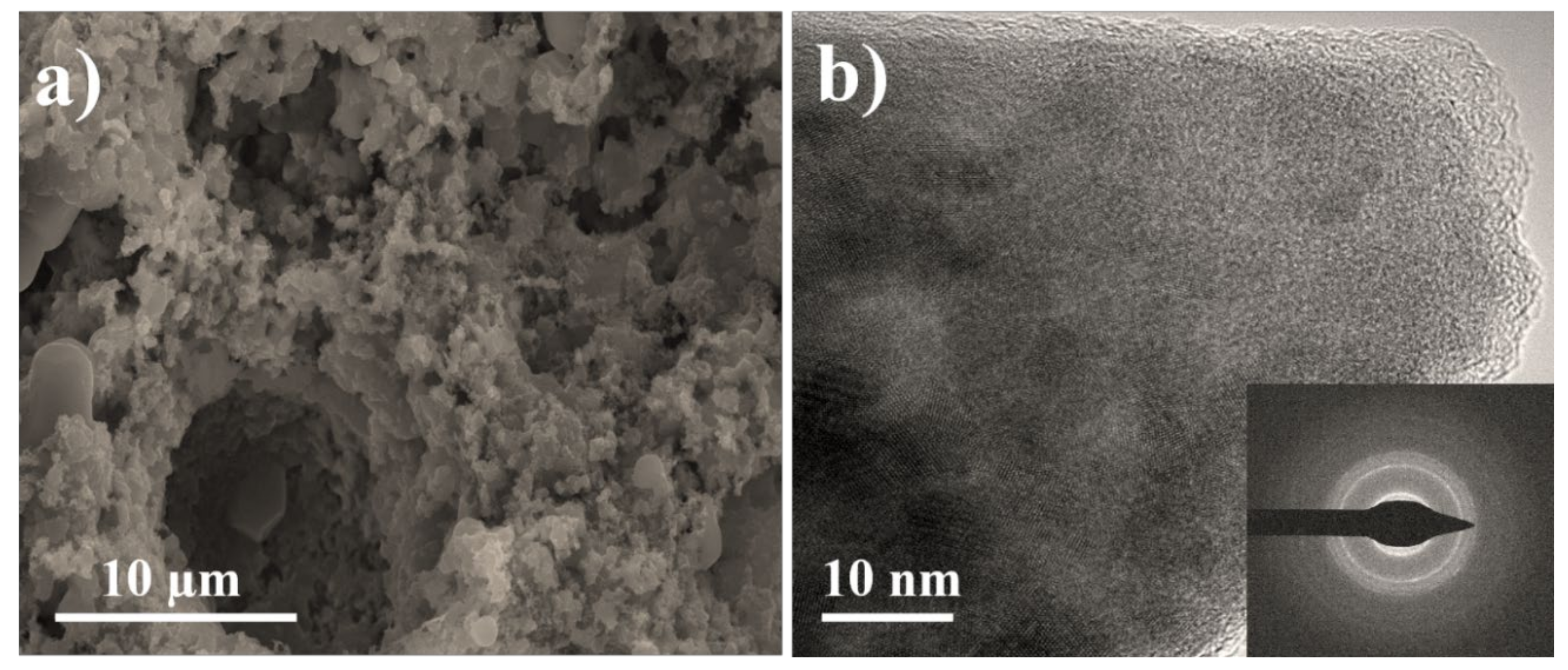
3.2. Surface Morphology Confirmation
3.3. Structural Elucidation
3.4. Surface Elements
3.5. Surface-Area and Pore-Size Distribution Studies
3.6. One-Pot Synthesis of Chromene Derivatives
3.7. One-Pot Synthesis of 1,8-Di-Oxo-Octahydroxanthene Derivatives
3.8. One-Pot Synthesis of Benzylpyrazolylcoumarin and Bis-Coumarin Derivatives
3.9. HUC Catalyst Reusability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schnorr, J.M.; Swager, T.M. Emerging Applications of Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Jia, H.-P.; Bielawski, C.W. Graphene Oxide: A Convenient Carbocatalyst for Facilitating Oxidation and Hydration Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6813–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Loh, K.P. Carbocatalysts: Graphene Oxide and Its Derivatives. ACC Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalon, S.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H. Carbocatalysis by Graphene-Based Materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6179–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahuguna, A.; Kumar, A.; Krishnan, V. Carbon-Support-Based Heterogeneous Nanocatalysts: Synthesis and Applications in Organic Reactions. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2019, 8, 1263–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Thanasekaran, P.; Subburaj, T.; Lin, K.-C. A Metal-Free Carbon-Based Catalyst: An Overview and Directions for Future Research. C J. Carbon Res. 2018, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, C.; Zammataro, A.; Pappalardo, A.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Catalysis with carbon nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27659–27664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Xie, X.; Xu, J.; Gu, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, X. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Nanosheets as Metal-Free Catalysts for Aerobic Selective Oxidation of Benzylic Alcohols. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhong, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Su, D.S.; Wang, J.; Bao, X.; Ma, D. Nitrogen-Doped sp2-Hybridized Carbon as a Superior Catalyst for Selective Oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2109–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cui, X.; Dai, X.; Deng, Y.; Shi, F. Carbon-catalysed reductive hydrogen atom transfer reactions. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Kinoshita, H.; Hashimoto, H.; Nishina, Y. Facile preparation of Pd nanoparticles supported on single-layer graphene oxide and application for the Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6501–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primo, A.; Neatu, F.; Florea, M.; Parvulescu, V.; Garcia, H. Graphenes in the absence of metals as carbocatalysts for selective acetylene hydrogenation and alkene hydrogenation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Tandiana, R.; Balapanuru, J.; Tang, W.; Pareek, K.; Nai, C.T.; Hayashi, T.; Loh, K.P. Tandem Catalysis of Amines Using Porous Graphene Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Acik, M.; Takai, K.; Lu, J.; Hao, S.J.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, P.; Bao, Q.; Enoki, T.; Chabal, Y.J.; et al. Probing the catalytic activity of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behaviour. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerf, A.; He, H.; Forster, M.; Klinowski, J. Structure of Graphite Oxide Revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 4477–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Matsuo, Y. Formation process and structure of graphite oxide. Carbon N. Y. 1994, 32, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.H. Solid Acids for Green Chemistry. ACC Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Green solvents for sustainable organic synthesis: State of the art. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, T.A.J.; Ghule, B.G.; Shaikh, S.; Shinde, P.V.; Gunturu, K.C.; Zubaidha, P.K.; Yun, J.M.; O’Dwyer, C.; Mane, R.S.; Kim, K.H. Metal-free heterogeneous and mesoporous biogenic graphene-oxide nanoparticle-catalyzed synthesis of bioactive benzylpyrazolyl coumarin derivatives. RSC Adv. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayank; Kaur Billing, B.; Agnihotri, P.K.; Kaur, N.; Singh, N.; Jang, D.O. Ionic Liquid-Coated Carbon Nanotubes as Efficient Metal-Free Catalysts for the Synthesis of Chromene Derivatives. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3714–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodal, D.; Przepiórski, J.; López Peinado, A.J.; Pérez-Mayoral, E. Basic-carbon nanocatalysts in the efficient synthesis of chromene derivatives. Valorization of both PET residues and mineral sources. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.K.; Song, M.Y.; Yu, J.-S. Heteroatom-doped highly porous carbon from human urine. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Lu, G.; Zhuang, H.; Yu, J. Synergistic catalytic effect of light rare earth element and other additives on the degree of graphitization and properties of graphite. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlgemuth, S.-A.; White, R.J.; Willinger, M.-G.; Titirici, M.-M.; Antonietti, M. A one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of sulfur and nitrogen doped carbon aerogels with enhanced electrocatalytic activity in the oxygen reduction reaction. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Bo, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, L. Nitrogen-doped ordered mesoporous carbons synthesized from honey as metal-free catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 108, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, T.; Naushad, M.; Ruksana; Alhabarah, A.N.; Alshehri, S.M. N/S doped highly porous magnetic carbon aerogel derived from sugarcane bagasse cellulose for the removal of bisphenol-A. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Shanbedi, M.; Ahmadi, G.; Eshghi, H.; Kazi, S.N.; Chew, B.T.; Savari, M.; Zubir, M.N.M. Mass production of highly-porous graphene for high-performance supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-L.; Wen, T.; Guo, H.-L.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, A.-W. Biomass-Derived Sponge-like Carbonaceous Hydrogels and Aerogels for Supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3589–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, K.; Yin, J. Biomass derived hierarchically porous and heteroatom-doped carbons for supercapacitors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 509, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gu, L.; Guo, S.; Shao, S.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Hao, S. N-Doped Mesoporous Carbons: From Synthesis to Applications as Metal-Free Reduction Catalysts and Energy Storage Materials. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Bhaumik, A.; Wu, K.C.-W. Hierarchically porous carbon derived from polymers and biomass: Effect of interconnected pores on energy applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3574–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Bai, Z. Three-Dimensional Heteroatom-Doped Nanocarbon for Metal-Free Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysis: A Review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, K.N.; Song, M.Y.; Yu, J.-S. Transforming Hair into Heteroatom-Doped Carbon with High Surface Area. Small 2014, 10, 2625–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, Q.; Pan, F.; Wang, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheets as metal-free catalyst with excellent oxygen reduction performance in alkaline and acidic media. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjooei, F.; Singh, K.; Kang, T.H.; Chaudhari, N.; Yuan, J.; Yu, J.-S. Urine to highly porous heteroatom-doped carbons for supercapacitor: A value added journey for human waste. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Ubaidullah, M.; Ahmed, J.; Ahamad, T.; Ahmad, T.; Shaikh, S.F.; Naushad, M. Synthesis of NiOx@NPC composite for high-performance supercapacitor via waste PET plastic-derived Ni-MOF. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 183, 107655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Ahmed, J.; Ubaidullah, M.; Shaikh, S.F.; Ahamad, T.; Naushad, M.; Zheng, G. Utilization of waste polyethylene terephthalate bottles to develop metal-organic frameworks for energy applications: A clean and feasible approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaidullah, M.; Ahmed, J.; Ahamad, T.; Shaikh, S.F.; Alshehri, S.M.; Al-Enizi, A.M. Hydrothermal synthesis of novel nickel oxide@nitrogenous mesoporous carbon nanocomposite using costless smoked cigarette filter for high performance supercapacitor. Mater. Lett. 2020, 266, 127492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subodh; Mogha, N.K.; Chaudhary, K.; Kumar, G.; Masram, D.T. Fur-Imine-Functionalized Graphene Oxide-Immobilized Copper Oxide Nanoparticle Catalyst for the Synthesis of Xanthene Derivatives. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 16377–16385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sr. No | Catalyst (mg) | Solvent | Temp. (°C) | Time (h) | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | No solvent | RT | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | - | No solvent | 100 | 3 | Trace |
| 3 | 10 | No solvent | 100 | 1.5 | 70 |
| 4 | 10 | CH3OH | RT | 5 | 85 |
| 5 | 20 | CH3OH | RT | 5 | 90 |
| 6 | 20 | CH3CN | RT | 5 | Trace |
| 7 | 20 | H2O | RT | 6 | 40 |
| 8 | 20 | H2O | Reflux | 1 | 80 |
| 9 | 20 | IPA | Reflux | 1 | Trace |
| 10 | 20 | CH2Cl2 | RT | 6 | Trace |
| 11 | 20 | CH2Cl2 | Reflux | 1.5 | 50 |
| 12 | 20 | Toluene | RT | 3 | 70 |
| 13 | 20 | EtOH | RT | 5 | 90 |
| 14 | 20 | H2O/EtOH | RT | 4 | 97 |
| 15 | 30 | H2O/EtOH | RT | 4 | 97 |
| Entry | Ar | Product | Time (h) | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C6H5 | 4a | 2 | 97 |
| 2 | 4-OMe-C6H5 | 4b | 2 | 95 |
| 3 | 4-Br-C6H5 | 4c | 2.5 | 93 |
| 4 | 3,4-Di-Cl-C6H5 | 4d | 3 | 85 |
| 5 | 4-NO2-C6H5 | 4e | 3.5 | 93 |
| 6 | 3,4-Di-OMe-C6H5 | 4f | 4 | 90 |
| 7 | 3-OMe-C6H5 | 4g | 4 | 92 |
| 8 | 3,5-Di-OMe-C6H5 | 4h | 4 | 93 |
| 9 | 3-Br-C6H5 | 4i | 3 | 90 |
| 10 | 4-F-C6H5 | 4j | 5 | 80 |
| 11 | 4-Cl-C6H5 | 4k | 3 | 95 |
| 12 | 4-OH-C6H5 | 4l | 3 | 85 |
| 13 | 2-Cl-C6H5 | 4m | 4 | 80 |
| Entry | Ar | Product | Time (h) | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4-NO2-C6H5 | 9a | 1 | 97 |
| 2 | 4-MeO-C6H5 | 9b | 1.5 | 93 |
| 3 | 4-Cl-C6H5 | 9c | 1 | 95 |
| 4 | 4-Br-C6H5 | 9d | 1 | 95 |
| 5 | 3-MeO-C6H5 | 9e | 2 | 90 |
| 6 | 3-Br-C6H5 | 9f | 2.5 | 88 |
| 7 | 3,5-Di-OMe-C6H5 | 9g | 3 | 85 |
| Entry | Ar | Product | Time (h) | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4-Me-C6H5 | 10a | 1.5 | 97 |
| 2 | 4-MeO-C6H5 | 10b | 1 | 95 |
| 3 | 4-Cl-C6H5 | 10c | 1 | 96 |
| 4 | 3,4-DI-OMe-C6H5 | 10d | 2 | 90 |
| 5 | 3-OMe-C6H5 | 10e | 2.5 | 85 |
| Entry | Time (h) | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 97 |
| 2 | 2 | 97 |
| 3 | 2 | 97 |
| 4 | 2 | 96 |
| 5 | 2 | 96 |
| 6 | 2 | 95 |
| 7 | 2 | 95 |
| 8 | 2 | 94 |
| 9 | 2.30 | 93 |
| 10 | 2.50 | 92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siddiqui, T.A.J.; Shaikh, S.F.; Sangale, S.S.; Raut, S.D.; Mane, R.S.; Ubaidullah, M.; Thamer, B.M.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Totawar, B.B.; Samdani, M.S. Mesoporous Carbon of Carbonized Human Urine Waste: A Valuable Heterogeneous Catalyst for Chromene and Xanthene Derivative Synthesis. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10121369
Siddiqui TAJ, Shaikh SF, Sangale SS, Raut SD, Mane RS, Ubaidullah M, Thamer BM, Al-Enizi AM, Totawar BB, Samdani MS. Mesoporous Carbon of Carbonized Human Urine Waste: A Valuable Heterogeneous Catalyst for Chromene and Xanthene Derivative Synthesis. Catalysts. 2020; 10(12):1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10121369
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiddiqui, T. A. J., Shoyebmohamad F. Shaikh, Sushil S. Sangale, Siddheshwar D. Raut, Rajaram S. Mane, Mohd Ubaidullah, Badr M. Thamer, Abdullah M. Al-Enizi, Balaji B. Totawar, and Mohammad Shahzad Samdani. 2020. "Mesoporous Carbon of Carbonized Human Urine Waste: A Valuable Heterogeneous Catalyst for Chromene and Xanthene Derivative Synthesis" Catalysts 10, no. 12: 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10121369
APA StyleSiddiqui, T. A. J., Shaikh, S. F., Sangale, S. S., Raut, S. D., Mane, R. S., Ubaidullah, M., Thamer, B. M., Al-Enizi, A. M., Totawar, B. B., & Samdani, M. S. (2020). Mesoporous Carbon of Carbonized Human Urine Waste: A Valuable Heterogeneous Catalyst for Chromene and Xanthene Derivative Synthesis. Catalysts, 10(12), 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10121369








