Abstract
Various types of mesoporous silica were used as carriers to synthesize a series of immobilized imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Their activity was tested in the synthesis of styrene carbonate from CO2 and styrene. This is one-pot process, whereby two stages are carried out in one reactor and there is no need to isolate the intermediate product, epoxide. A systematic study on the influence of parameters such as temperature, the reaction time, CO2 pressure, as well as the amount and type of catalyst used was carried out. A strong synergistic catalytic effect of ionic liquid and Lewis acid was observed in promoting this reaction. The addition sequence of regents and amount of immobilized catalyst were considered crucial for the synthesis of styrene carbonate from CO2 and styrene. The tested silica-supported ionic liquids gave an easily-recyclable system which under the most favorable conditions ([mtespim]Cl/@SiO2; ZnBr2, 0.1 mol%; 110 °C, 4 h, 1 MPa) can be reused without a significant loss of catalytic activity nor selectivity.
1. Introduction
Five-membered ring cyclic carbonates are widely used as, among other purposes, polar aprotic high boiling solvents for natural and synthetic polymers, in the production of polyacrylic fibers, selective solvents in separation processes, electrolytes in the production of batteries, or starting materials for the production of polycarbonates and intermediates for many useful chemicals [1,2]. On an industrial scale, these compounds are mainly obtained by the 100% atom-economic reaction of carbon dioxide with an epoxide. A wide spectrum of compounds have been studied as catalysts for this synthesis, both homogeneous and heterogeneous, as well as immobilized ones, such as onium quaternary salts [3,4,5,6], metal complexes [7,8,9,10], metal-organic frameworks [11,12], and ionic liquids [13,14,15,16,17]. However, the direct synthesis of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and olefin as raw materials is of growing interest [18,19]. This process, i.e., an oxidative carboxylation of olefins with CO2, proceeds in two stages. In the first stage, epoxidation of terminal olefins takes place, and in the second, the in situ formed epoxide reacts with CO2. The advantage of this method is that both process steps can take place in one reaction vessel (one-pot synthesis), so there is no need to isolate and purify the resulting intermediate product, which is the epoxide. However, designing an effective catalyst system to perform multiple reactions in one reactor is still a challenge for researchers. Great emphasis is placed not only on the search for active and selective catalysts, but also on those that can be easily separated from the reaction mixture. In this regard, the immobilization of homogeneous catalysts on the surface of organic or inorganic supports are of particular interest. Examples of the use of immobilized catalysts in the direct synthesis of cyclic carbonates can be found in the literature [18,19].
Mesoporous silicas are convenient and frequently used inorganic catalyst supports [20,21]. The ease of functionalization, thermal and mechanical stability and also chemical resistance within a certain pH range are just some of their advantages. They were successfully used to anchor various catalysts applied in the reaction of obtaining cyclic carbonates from CO2 and olefins. Arai et al. used a ternary catalytic system consisting of silica-supported gold (Au/SiO2), zinc bromide and tetrabutylammonium bromide (TBAB) for the synthesis of styrene carbonate (SC) from styrene (ST) and CO2—using tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) as an oxidant [22]. Under optimal conditions (80 °C, 1 MPa, 4 h), the product was obtained with a yield of 42%. Recently, the easily recyclable heterobimetalic catalytic system, consisting of the manganese and chromium metalloporphyrin magnetic nanoparticles MNP@SiO2-8Mn and MNP@SiO2-4Cr, was used for the oxidative carboxylation of olefins with O2 as an oxidant [23].
Herein, a series of ionic liquids, immobilized on various mesoporous silica carriers, were synthesized and their catalytic performance was tested in the model reaction of synthesis styrene carbonate from CO2 and styrene oxide or styrene. To the best of our knowledge, immobilized ionic liquids on silica were, for the first time, used in the direct synthesis of cyclic carbonates.
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis of Immobilized Catalysts
The synthesis of ionic liquids covalently bound to a silica support was performed according to the procedure described earlier, with some modifications [24]. The first stage of ionic liquid immobilization on silica supports involved the reaction of (3-chloropropyl)triethoxysilane with 1-alkylimidazole under an inert atmosphere. The obtained ionic liquids were then anchored onto solid support (Scheme 1). As a carrier, we used macro/mesoporous silica obtained by the sol-gel method with simultaneous phase separation. In this method, the selection of the appropriate composition and temperature of the reaction system led to phase separation, induced by the polymerization reaction. The following hydrolysis and condensation reactions of the silica precursor led to the freezing/consolidation of the structure [25,26]. As supports, we also used the commercially available mesoporous silicas: MCM-41 (Mobil Composition of Matter No. 41 or Mobil Crystalline Materials), MSU-F (mesostructured silica, cellular foam), MSU-H (mesostructured silica, large pore 2D hexagonal).
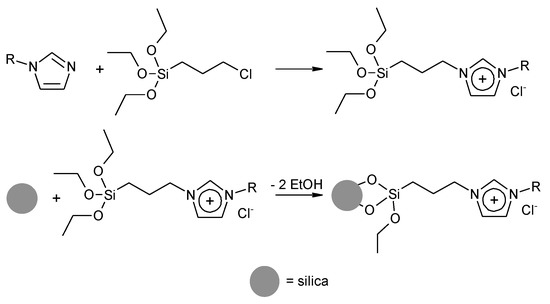
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of immobilized ionic liquid on SiO2.
The surface area, pore size and pore volume of synthesized silica (@SiO2) and commercial carriers are summarized in Table 1. The surface area of @SiO2 was lower than the commercial ones, while pore size and pore volume were comparable as for MSU-H, which has large 2D hexagonal pores. As shown in Figure 1a, the nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm of @SiO2 can be classified as a type IV isotherm with a H1 hysteresis loop, which is typical for mesoporous materials [27,28]. @SiO2 had a bimodal pore size distribution (Figure 1a and Figures S1 and S2 in Supplementary Materials). The fine pore sizes clustered at approximately 3 nm and the mesopores at about 20 nm. The morphology of the obtained @SiO2 is shown in Figure 2a (Figures S3 and S4 in Supplementary Materials). The particles of silica were of irregular shape and different size (Figure 2a).

Table 1.
Morphological characterization of silica carriers and IL immobilized catalyst.
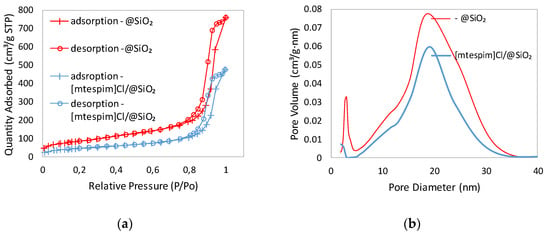
Figure 1.
(a) Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms; and (b) Size distribution plots of synthesized silica @SiO2 and the catalyst immobilized on the @SiO2 ([mtespim]Cl/@SiO2) (see also in ESI, Figures S1–S4).
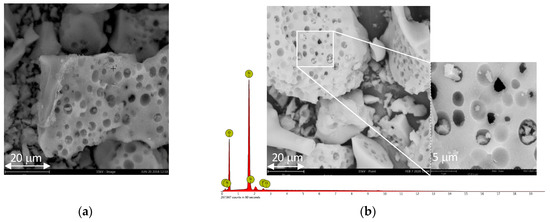
Figure 2.
SEM images of: (a) @SiO2; (b) Functionalized @SiO2 sample ([mtespim]Cl/@SiO2).
As expected, the surface areas and the pore volume of the immobilized catalyst [mtespim]Cl/@SiO2 were reduced (Table 1, entry 2) compared to the values for the carrier itself. The pore size of large mesopores at about 20 nm did not change, while the small ones – in the range of 3 nm - practically disappear (Figure 1b). However, the SEM images prove that the surface morphology of the carrier remained unchanged (Figure 2). The number of functional groups attached to the supports was determined based on elemental analysis and ranged from 0.86 to 2.20 mmol/g (Table 2).

Table 2.
The number of functional groups attached to the supports.
2.2. Catalytic Tests
First, the immobilized ionic liquids were tested in the model reaction between CO2 and styrene oxide (SO) which is the second stage in one-pot synthesis of cyclic carbonate. All preliminary reactions were conducted under the same conditions (100 °C, 1 MPa, 6 h, 700 rpm) using [mtespim]Cl/@SiO2 as the catalyst together with a cocatalyst, namely Lewis acid. Zinc bromide was chosen as it is known to exhibit high activity in the cycloaddition reactions of CO2 [29]. The use of a two-component catalytic system resulted in obtaining of styrene carbonate (SC) with yield of 72% (Table 3, entry 5). This result shows the strong synergistic effect of this binary catalyst system, as a reaction in the presence of zinc bromide itself practically did not occur while using only [mtespim]Cl/@SiO2, SC was obtained with yield of 16% (Table 3, entries 3, 4). For comparison, a control experiment without any catalyst showed that no reaction took place (Table 3, entry 1).

Table 3.
Choice of catalytic system for the reaction of CO2 with SO. Reaction conditions: Reaction conditions: SO, 0.13 mol; 100 °C; CO2 pressure, 1 MPa; 6 h; 700 rpm.
Studies on the effect of the amount of catalyst showed that a two-fold increase in the amount of [mtespim]Cl/@SiO2 from 0.25 to 0.5 mol% using the same amount of cocatalyst caused a three-fold increase in SC yield (Table 3, entries 5 and 7). However, a further increase in the amount of immobilized catalyst (from 0.5 to 1.0 mol%) did not affect the yield of styrene carbonate, while the conversion of styrene oxide increased. Most likely, styrene oxide undergoes side reactions leading to the formation of SO or SC dimers and oligomers [30]. In turn, the use of a five-fold increase in the amount of cocatalyst (0.10 mol% instead of 0.02 mol%) resulted in only a two-fold higher yield of SC. This outcome confirms the synergistic effect of the catalytic system, consisting of ionic liquid and Lewis acid, in promoting the studied reaction.
The effect of temperature in the range of 90 to 120 °C and reaction time (from 2 to 6 h) on the synthesis of styrene carbonate was investigated (Figure 3a). It can be seen that as the temperature increased up to 100 °C, the SC yield also increased. Above this value, the product yield remained practically unchanged for the reactions carried out for 4 and 6 h. However, the conversion of styrene oxide increased and reached almost 100% for the reactions conducted at a temperature above 110 °C for 6 h. GC-MS revealed that apart from benzaldehyde, phenyl glycol was observed at elevated temperatures. In addition, dimers and oligomers of styrene oxide and styrene carbonate also formed during the process. Therefore, further experiments were carried out at 110 °C for 4 h. The SC yield increased from 58% to 75% with increasing pressure from 0.5 MPa to 1.0 MPa (Figure 3b). A further pressure increase did not affect SO conversion and SC yield.
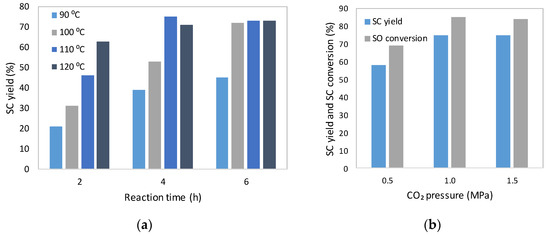
Figure 3.
The effect of: (a) the temperature and reaction time; (b) CO2 pressure; on the synthesis of styrene carbonate from CO2 and styrene oxide. Reaction conditions: SO, 0.13 mol; [mtespim]Cl/@SiO2, 0.5 mol%; ZnBr2, 0.1 mol%; 700 rpm.
For the sake of comparison, we carried out the reactions using supported ionic liquids on various silica carriers (Table 4). Immidazolium ionic liquids with an alkyl chain of different lengths were immobilized on solid support. It can be observed that the styrene carbonate yield increased with the lengthening of the alkyl chain in ionic liquid. Probably due to the increased lipophilicity of these ionic liquids, substrates such as SO and CO2 dissolve better in the ILs, which facilitates their contact with the active sites of the catalyst [31]. Similar phenomenon was observed in the literature [16,31]. In turn, the immobilization of the same ionic liquid on different carriers showed that the best results were obtained for the synthesized @SiO2. The order of their activities was as follows: @SiO2 > MSU-F > MSU-H > MCM-41. These results may indicate that the specific surface area had no significant effect on catalyst activity. The key factor affecting its activity seems to be the pore size. The reaction with [mtespim]Cl immobilized on MCM-41, which is characterized by the largest surface area and the smallest pore size among tested supports, proceeded with the lowest efficiency. Despite the large surface area, access to pores is limited.

Table 4.
Reaction of CO2 with SO using various catalysts. Reaction conditions: SO, 0.13 mol; immobilized catalyst, 0.5 mol%; ZnBr2, 0.1 mol%; 110 °C; 4 h; 700 rpm.
The activity of the immobilized catalyst in consecutive reaction cycles was examined. After reaction, the catalyst was recovered by simple filtration, washed with ethyl acetate, and dried in the air. Recycling studies showed that the supported catalyst can be used in up to three cycles without significant loss in its catalytic activity and selectivity (Figure 4). A decrease in styrene carbonate efficiency was observed in the fourth cycle. Styrene carbonate yield dropped to 53%. Based on the results of elemental analysis, it can be stated that after the fourth cycle the amount of nitrogen decreased, which suggests partial release of the catalyst (Table 2). Thermogravimetric analysis of the supported catalysts revealed that weight loss in the range 130 to 1000 °C was slightly higher for the catalyst after the third reaction cycle (24.20%) than for a fresh one (20.47%). However, much higher weight loss (30.79%) was observed for the catalyst after the fourth cycle (Figure 5 and Figures S5–S7 in Supplementary Materials). This might indicate that contaminants were retained on the catalyst surface. Most likely they were by-products, such as dimers or oligomers that might not have been wash out after the reaction cycle. A slight change in the surface roughness of the catalysts after consecutive runs can be observed (Figure 6).
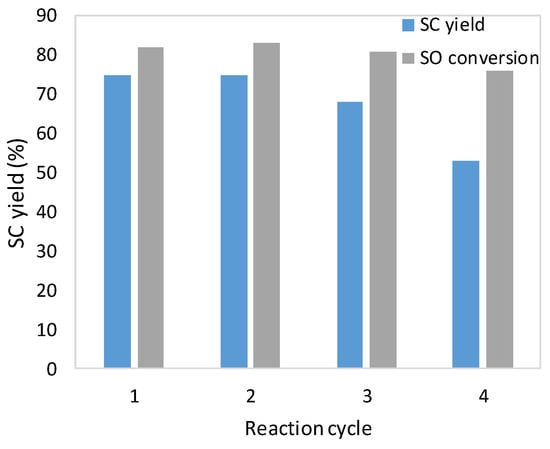
Figure 4.
Catalyst recycling tests. Reaction conditions: SO, 0.13 mol; [mtespim]Cl/@SiO2, 0.5 mol%; ZnBr2, 0.1 mol%; 110 °C; 4 h; 700 rpm.
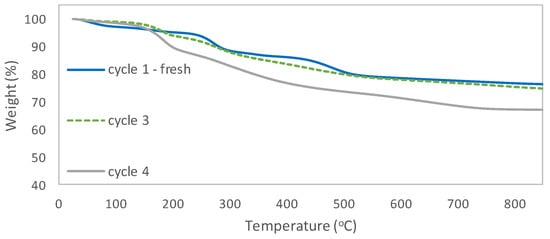
Figure 5.
TGA curves for [mtespim]Cl/@SiO2.
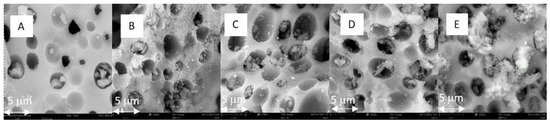
Figure 6.
SEM images of [mtespim]Cl/@SiO2: (A) fresh; (B) after the first cycle; (C) after the second cycle; (D) after the third cycle; (E) after the fourth cycle.
The one-pot process of oxidative carboxylation of olefins with carbon dioxide can be carried out in two different ways: in a single-step approach or a two-step approach [18,19]. Both methods are one-pot processes differing in that, in the first case, all the reactants and catalysts for the two subsequent reactions are added at one time, in the second, after the first stage, the regents are added to carry out the subsequent reaction. However, in both cases, the process is carried out in one vessel without isolating and purifying the intermediate. Therefore, the research began with determining the impact of the reaction method on styrene carbonate yield. A solution of TBHP in decane was used as an oxidant while molybdenyl acetylacetonate (MoO2(acac)2) was chosen for the epoxidation step. Molybdenum complexes next to tungsten and titanium, are among the most active transition metals used as catalysts for epoxidation using alkyl hydroperoxide as an oxidant [32]. The reaction conditions for the first step were chosen on the basis of literature report [33] and our previous experience [34]. The second stage was carried out under the best conditions, as detailed above.
A single-step approach for conducting the synthesis of styrene carbonate turned out to be inappropriate for conducting a one-pot reaction using the proposed catalytic system (Table 5, entry 1). A fairly large amount of unreacted styrene oxide in the post-reaction mixture might indicate that when the catalyst system for the second stage was introduced at the beginning of the process it may have been deactivated under the reaction conditions. Therefore, the catalytic system for the second stage together with carbon dioxide were charged after the first reaction stage. This solution enabled the obtainment of styrene carbonate with yield of 8% (Table 5, entry 2). It should be emphasized that the second step of styrene carbonate synthesis use was conducted under solvent-free conditions and truly catalytic amounts of immobilized ionic liquid (0.5 mol%) was required to obtain good results. However, in a direct one-pot reaction the system was diluted because together with TBHP, the solvent (decane) was introduced and during the reaction the by-product tert-butanol was formed. Thus, the influence of the concentration of immobilized catalyst on the reaction course was investigated. With an increase in the amount of catalyst increased yield of styrene carbonate (Table 5, entry 3–6). Increasing the amount of catalyst from 5 mol% to 6 mol% resulted in a slight increase in styrene carbonate yield from 46% to 49%. A slight catalytic activity drop was observed when the recycled immobilized catalyst was used (Table 5, entry 7).

Table 5.
Synthesis of styrene carbonate from CO2 and styrene.
The outcome is comparable with the results obtained for styrene carbonate synthesis in the reaction of CO2 and styrene using TBHP as an oxidant and in the presence of immobilized catalysts. As mentioned above, in the presence a ternary catalytic system consisting of Au/SiO2, ZnBr2 and TBAB (80 °C, 1 MPa, 4 h), styrene carbonate was obtained with yield of 42% [22]. A similar catalytic system but using Au/Fe(OH)3 allowed to obtain styrene carbonate with yield of 53%, but higher CO2 pressure and longer reaction times were required (4 MPa, 10 h) [35]. Styrene carbonate was obtained in a higher yield of 60% using another three-component catalytic system in which a gold immobilized on the multi-walled carbon nanotubes was the catalyst of the epoxidation stage (80 °C, 4 h) while 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ([bmim]Br) along with zinc bromide catalyzed CO2 addition to epoxide (1.2 MPa at 120 °C) [36]. In our previous work, we obtained styrene carbonate with a yield of 67% using of immobilized tributylammonium chloride [34]. Sun et al. used a nano-gold supported on basic R201 resin and after the first stage which was carried out at 80 °C for 3 h, and the second stage at 150 °C, under CO2 pressure of 4 MPa for 4h, yield of styrene reached 51% [37].
The reaction in the presence of a binary catalytic system involving only immobilized catalyst and ZnBr2 allowed to obtain the styrene carbonate with yield of 16% (Table 5, entry 8).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Carbon dioxide (99.2%, from Air Liquide Polska Sp., Cracow, Poland) was used without further purification. Bis(acetylacetonato)dioxomolybdenum(VI) (molybdenyl acetylacetonate, MoO2(acac)2), 1-methylimidazole (99%), hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide, and tetraethoxysilane (98%) were provided by Acros Organics (Waltham, MA, USA). Further, 1-Octyl-1H-imidazole (96%) was obtained from AmBeed, Inc. (Arlington Hts, IL, USA). Mesostructured MSU-F (cellular foam), mesostructured MSU-H (large pore 2D hexagonal), (3-chloropropyl)triethoxysilane (95%), MCM-41, 1-butylimidazole (98%), anhydrous toluene (99.8%), octane (>99%), ~5.5 M solution of tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) in decane, styrene oxide (97%), styrene (>99%), and polyethylene glycol 35 000 were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
3.2. Apparatus
EM60-100-HC pressure reactor (100 cm3) placed in EasyMax 102 thermostat system (Mettler-Toledo, GmbH., Greifensee, Switzerland) was used for the reactions under pressure.
Gas chromatography analyses (GC) were performed on a Shimadzu chromatograph GC-2010 Plus (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) equipped with flame ionization detector (FID) and capillary column Zebron ZB-50: 30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 µm (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA). GC-MS analyses were carried out using a gas chromatograph Agilent Technologies GC 7890A (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) coupled with mass spectrometer Agilent Technologies MS 5975C MSD, Triple-AxisDetector (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and a capillary column (Zebron ZB-5HT: 30 m × 250 μm × 0.25 μm).
Scanning electron microscopy was performed on Phenom Pro Desktop SEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with EDS detector.
Nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms were recorded at −195.8 °C using a Micrometrics ASAP 2420 instrument (Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, Norcross, GA, USA). Samples were degassed at 200 °C. The surface area of synthesized silica support was determined using the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method and pore sizes by the Barret-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) method.
Elemental analyses were performed on Vario MACRO elemental analyzer (Elementar Analysesysteme GmbH, Langenselbold, Germany).
Thermogravimetric analyses (TGA) were conducted using a Mettler-Toledo termobalance (Mettler-Toledo, GmbH., Greifensee, Switzerland). Sample mass: 9–11 mg, corundum crucible (70 μL), temperature range: 25–1000 °C, heating rate: 10 °C/min, gas atmosphere: nitrogen, flow rate: 80 cm3/min.
3.3. Synthetic Procedures
3.3.1. Synthesis of Silica Support
In typical procedure polyethylene glycol 35,000 (PEG, 8.67 g) was dissolved in 1M HNO3 (100 cm3). After that, tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS, 82.8 cm3) was added dropwise in an ice bath and then hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 3.8 g) was introduced. The solution was mixed left to gel at 40 °C and aged for 7 days at 40 °C. Next, the white aclogels obtained were impregnated in a 1 M NH4OH solution for 9 h at 90 °C, washed with deionized water, dried for 4 days at 60 °C and then calcined at 550 °C for 8 h under air. The size and shape of the monoliths were determined by the size and the shape of the vessel used. Composition led to the formation of a macroporous, interconnected, open network with a bimodal system of macropores of micrometer size. Apart from macropores, the material also exhibited textural mesopores [25,26].
3.3.2. Synthesis of 1-alkyl-3-(triethosysilylpropyl) Imidazolium Chloride [atespim]Cl
An equimolar mixture of 1-alkylimidazole (freshly distilled) and (3-chloropropyl)triethoxysilane was heated to 90–95 °C and stirred at 1000 rpm for 24 h under an inert gas atmosphere. Then, after cooling the reaction mixture, the volatile substances were removed under reduced pressure. The crude ionic liquid was washed with diethyl ether (5 × 10 cm3) and dried under vacuum. The products were obtained as viscous liquids [24].
3.3.3. Immobilization of 1-alkyl-3-(triethosysilylpropyl) Imidazolium Chloride on Silica
Briefly, 2 g of silica, 25 cm3 of anhydrous toluene and 2.7 mmol of [atespim]Cl were introduced to a round-bottom flask. The reaction mixture was heated at a temperature of 90 °C for 16–24 h under reflux under an inert atmosphere of Ar. The mixture was then filtered and washed with methylene chloride (4 × 25 cm3). The resulting product was extracted in a Soxhlet apparatus with CH2Cl2 for 24 h. The obtained catalyst was dried under reduced pressure [24].
3.3.4. Reaction of Styrene Oxide with CO2
Typical procedure is as follow: 0.50 mol% of immobilized catalyst, 0.13 mol of styrene oxide and 0.10 mol% of 77% aqueous solution of ZnBr2 were introduced into a pressure reactor. The reactor was sealed, purged twice with CO2 and pressurized with CO2 to a constant pressure. The mixture was heated to the desired temperature and stirred at 700 rpm. From this moment, the reaction was carried out for 4 h. Afterwards, the reactor was cooled to 25 °C and depressurized. The catalyst was removed by filtration and washed with 35 cm3 of ethyl acetate. The sample was analysed by GC. Octane was used as an internal standard. Purification of styrene carbonate was achieved by column chromatography (hexane:ethyl acetate 3:1 v/v). Styrene carbonate was obtained as a solid.
3.3.5. One-Pot Synthesis of Styrene Carbonate
Briefly, 0.052 mmol of styrene, 0.052 mmol of TBHP, 0.05 mol% of MoO2(acac)2 were charged into the reactor. The reactor was sealed and heated to 100 °C. The reaction was carried out for 1 h. Then the reactor was cooled to 25 °C and the appropriate amount of immobilized catalyst and ZnBr2 were added. Then, the reaction was carried out according to the described-above procedure.
3.3.6. Recycling of the Immobilized Catalyst
After completion of the reaction, the immobilized catalyst was filtered off and washed with methylene chloride (10 mL) and ethyl acetate (3 × 10 mL). Then, the catalyst was dried under vacuum on a Schlenk line and used in the next reaction cycle. The fresh 77% aqueous solution zinc bromide was added to each run.
4. Conclusions
Mesoporous silicas were used as supports for the immobilization of the ionic liquids. These catalysts have proven to be active in the synthesis reaction of styrene carbonate with CO2. The most important feature of silica carriers affecting a catalyst activity was the pore size. Styrene carbonate was obtained in high yield in the reaction of carbon dioxide and styrene oxide (second step of one-pot reaction of synthesis of cyclic carbonates) and in moderate yield in direct synthesis from CO2 and styrene under mild reaction conditions. The immobilized catalyst retained its activity and stability in two cycles, but a loss of catalytic activity in the fourth cycle was observed most likely due to the partial release of the catalyst and the deposition of side-products on the catalyst.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4344/10/11/1363/s1, Figures S1 and S2: Nitrogen adsorption/desorption curves, Figures S3 and S4: Pore size distribution, Figures S5–S7: TGA curves.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.; investigation, A.F. and A.S.; preparation of silica support, K.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.S.; supervision, A.S.; funding acquisition, A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Science Centre (NCN), Poland, Project No. 2018/02/X/ST8/03066 in the framework of MINIATURA program. The APC was funded by Silesian University of Technology, Poland, Grant No. 04/050/BK_20/0097 in the framework of the BK program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shaikh, R.R.; Pornpraprom, S.; D’Elia, V. Catalytic Strategies for the Cycloaddition of Pure, Diluted, and Waste CO2 to Epoxides under Ambient Conditions. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 419–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, M.; Pasquale, R.; Young, C. Synthesis of cyclic carbonates from epoxides and CO2. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1514–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, J.; Yang, H.J.; Ban, B.; Wang, L.; Lei, B.; Guo, C.Y.; Hu, J.; Zhu, J.; Han, B. β-Cyclodextrin/Quaternary Ammonium Salt as an Efficient Catalyst System for Chemical Fixation of CO2. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 3263–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbauer, J.; Kubis, C.; Ludwig, R.; Werner, T. Mechanistic Study on the Addition of CO2 to Epoxides Catalyzed by Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts: A Combined Spectroscopic and Kinetic Approach. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 10778–10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, C.A.; Paninho, A.B.; Felix, P.M.; Zakrzewska, M.E.; Vital, J.; Najdanovic-Visak, V.; Nunes, A.V.M. Styrene carbonate synthesis from CO2 using tetrabutylammonium bromide as a non-supported heterogeneous catalyst phase. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 100, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ema, T.; Fukuhara, K.; Sakai, T.; Ohbo, M.; Bai, F.Q.; Hasegawa, J. Quaternary ammonium hydroxide as a metal-free and halogen-free catalyst for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from epoxides and carbon dioxide. J. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 2314–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Xu, Y.C.; Gan, Z.L.; Peng, X.; Yi, X.Y. Zinc Complexes with Tridentate Pyridyl-Pyrrole Ligands and their Use as Catalysts in CO2 Fixation into Cyclic Carbonates. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 13, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaishi, K.; Nath, B.D.; Yamada, Y.; Kosugi, H.; Ema, T. Unexpected Macrocyclic Multinuclear Zinc and Nickel Complexes that Function as Multitasking Catalysts for CO2 Fixations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9984–9988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, H.J.; Wang, S.; Ban, B.; Wei, Z.; Lei, B.; Guo, C.Y. Efficient solvent-free fixation of CO2 catalyzed by new recyclable bifunctional metal complexes. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cao, Z. Catalytic Preparation of Cyclic Carbonates from CO2 and Epoxides by Metal–Porphyrin and −Corrole Complexes: Insight into Effects of Cocatalyst and meso-Substitution. Organometallics 2018, 37, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, T.K.; De, D.; Bharadwaj, P.K. Metal–organic frameworks for the chemical fixation of CO2 into cyclic carbonates. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2020, 408, 213173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. A novel metal-organic framework as a heterogeneous catalysis for the solvent-free conversion of CO2 and epoxides into cyclic carbonate. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2018, 88, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Wu, D.; Pan, H.; Zhao, T.; Hu, X. Imidazolium hydrogen carbonate ionic liquids: Versatile organocatalysts for chemical conversion of CO2 into valuable chemicals. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 39, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Yin, L. Progress in the Heterogeneous Catalytic Cyclization of CO2 with Epoxides Using Immobilized Ionic Liquids. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaugule, A.A.; Tamboli, A.H.; Kim, H. Ionic liquid as a catalyst for utilization of carbon dioxide to production of linear and cyclic carbonate. Fuel 2017, 200, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiak, K.; Siewniak, A.; Kopczyńska, K.; Chrobok, A.; Baj, S. Hydrogensulphate ionic liquids as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from carbon dioxide and epoxides. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 2827–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.H.; Wang, J.Q.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, S.J. Fixation of CO2 into cyclic carbonates catalyzed by ionic liquids: A multi-scale approach. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Que, S.; Ding, Z.; Vessally, E. Oxidative carboxylation of olefins with CO2: Environmentally benign access to five-membered cyclic carbonates. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9103–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Hu, C. Synthesis of Cyclic Carbonates from Alkenyl and Alkynyl Substrates. Chin. J. Chem. 2017, 35, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilia, J.A.; Tost, R.M.; Millán, M.R. Mesoporous Materials: From Synthesis to Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresge, C.T.; Roth, W.J. The discovery of mesoporous molecular sieves from the twenty year perspective. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Fujita, S.; Zhao, F.; Hasegawa, M.; Arai, M. A direct synthesis of styrene carbonate from styrene with the Au/SiO2–ZnBr2/Bu4NBr catalyst system. J. Catal. 2005, 230, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.D.; Carrilho, R.M.B.; Henriques, C.A.; Calvete, M.J.F.; Masdeu-Bultó, A.M.; Claver, C.; Rossi, L.M.; Pereira, M.M. Hybrid Metalloporphyrin Magnetic Nanoparticles as Catalysts for Sequential Transformation of Alkenes and CO2 into Cyclic Carbonates. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 2792–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrobok, A.; Baj, S.; Pudło, W.; Jarzębski, A. Supported hydrogensulfate ionic liquid catalysis in Baeyer–Villiger reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 366, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, K.; Pietrowska, M.; Kocurek, J.; Maresz, K.; Koreniuk, A.; Mrowiec-Białoń, J.; Widłak, P.; Magner, E.; Jarzębski, A. Low back-pressure hierarchically structured multichannel microfluidic bioreactors for rapid protein digestion—Proof of concept. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, K.; Odrozek, K.; Zniszczoł, A.; Pudło, W.; Jarzębski, A. A novel hierarchically structured siliceous packing to boost the performance of rotating bed enzymatic reactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.U.; Staudt, R. Adsorption isotherms. In Gas Adsorption Equilibria. Experimental Methods and Adsorptive Isotherms; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 359–413. [Google Scholar]
- Rouquerol, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.; Llewellyn, P.; Maurin, G. Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids. Principles, Methodology and Applications, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.S.; Zhang, X.W.; Dai, W.L.; Yin, S.F.; Li, W.S.; Ren, Y.Q.; Au, C.T. ZnBr2–Ph4PI as highly efficient catalyst for cyclic carbonates synthesis from terminal epoxides and carbon dioxide. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 341, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fujita, S.; Bhanage, B.M.; Arai, M. One-pot synthesis of styrene carbonate from styrene in tetrabutylammonium bromide. Catal. Today 2004, 93–95, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanami, H.; Sasaki, A.; Matsui, K.; Ikushima, Y. A rapid and effective synthesis of propylene carbonate using a supercritical CO2–ionic liquid system. Chem. Commun. 2003, 7, 896–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ted Oyama, S. Rates, Kinetics, and Mechanisms of Epoxidation: Homogeneous, Heterogeneous, and Biological Routes. In Mechanisms in Homogenous and Heterogeneous Epoxidation Catalysis, 1st ed.; Ted Oyama, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Dong, T.; Xu, T.; Li, X.; Hu, C. Direct synthesis of cyclic carbonates from olefins and CO2 catalyzed by a MoO2(acac)2-quaternary ammonium salt system. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2518–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewniak, A.; Jasiak-Jaroń, K.; Kotyrba, Ł.; Baj, S. Efficient Catalytic System Involving Molybdenyl Acetylacetonate and Immobilized Tributylammonium Chloride for the Direct Synthesis of Cyclic Carbonates from Carbon Dioxide and Olefins. Catal Lett. 2017, 147, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Xiang, D.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Xiao, F.S. A Facile, Direct Synthesis of Styrene Carbonate from Styrene and CO2 Catalyzed by Au/Fe(OH)3–ZnBr2/Bu4NBr System. Catal. Lett. 2009, 129, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiak, K.; Krawczyk, T.; Pawlyta, M.; Jakóbik-Kolon, A.; Baj, S. One-Pot Synthesis of Styrene Carbonate from Styrene and CO2 Over the Nanogold-Ionic Liquid Catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Xiao, F.S.; Sun, J. A novel route for synthesis of styrene carbonate using styrene and CO2 as substrates over basic resin R201 supported Au catalyst. Catal. Today 2009, 148, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).