Fairness and Trust in Structured Populations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Model Description and Results
3. Evolution of Fairness: Ultimatum Game
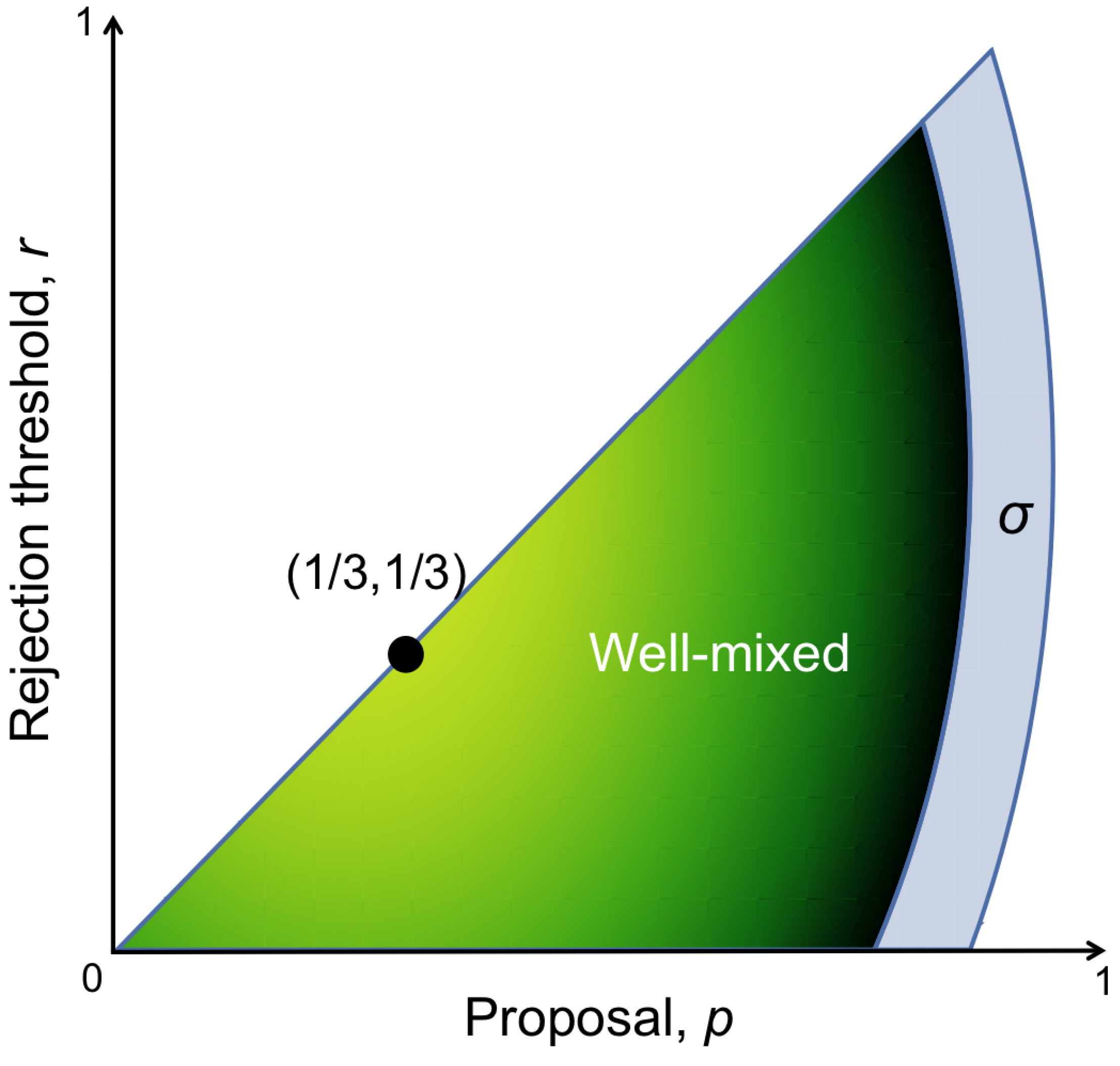
4. Evolution of Trust: Trust Game
4.1. Well-Mixed Population

4.2. Structured Populations
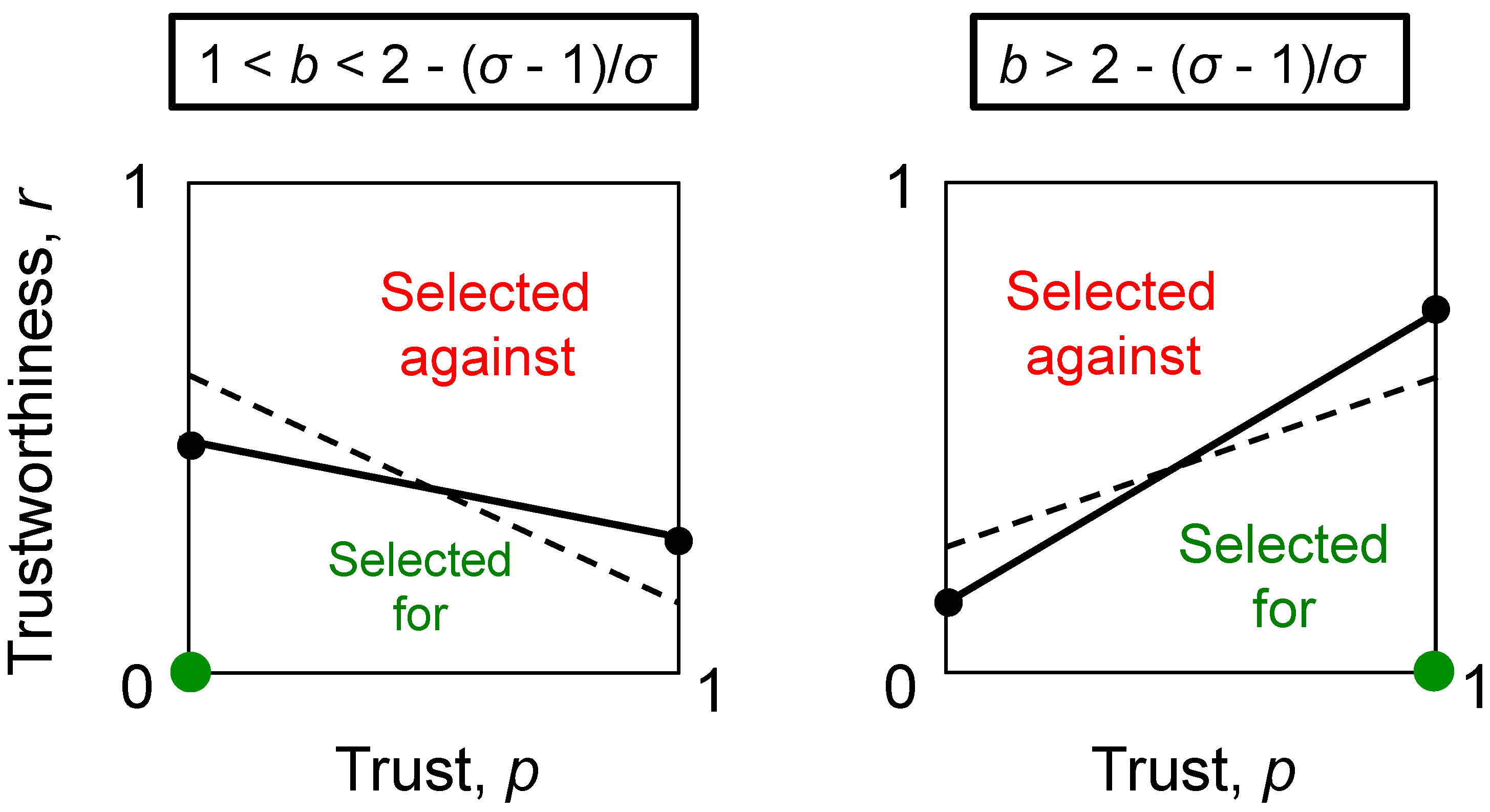
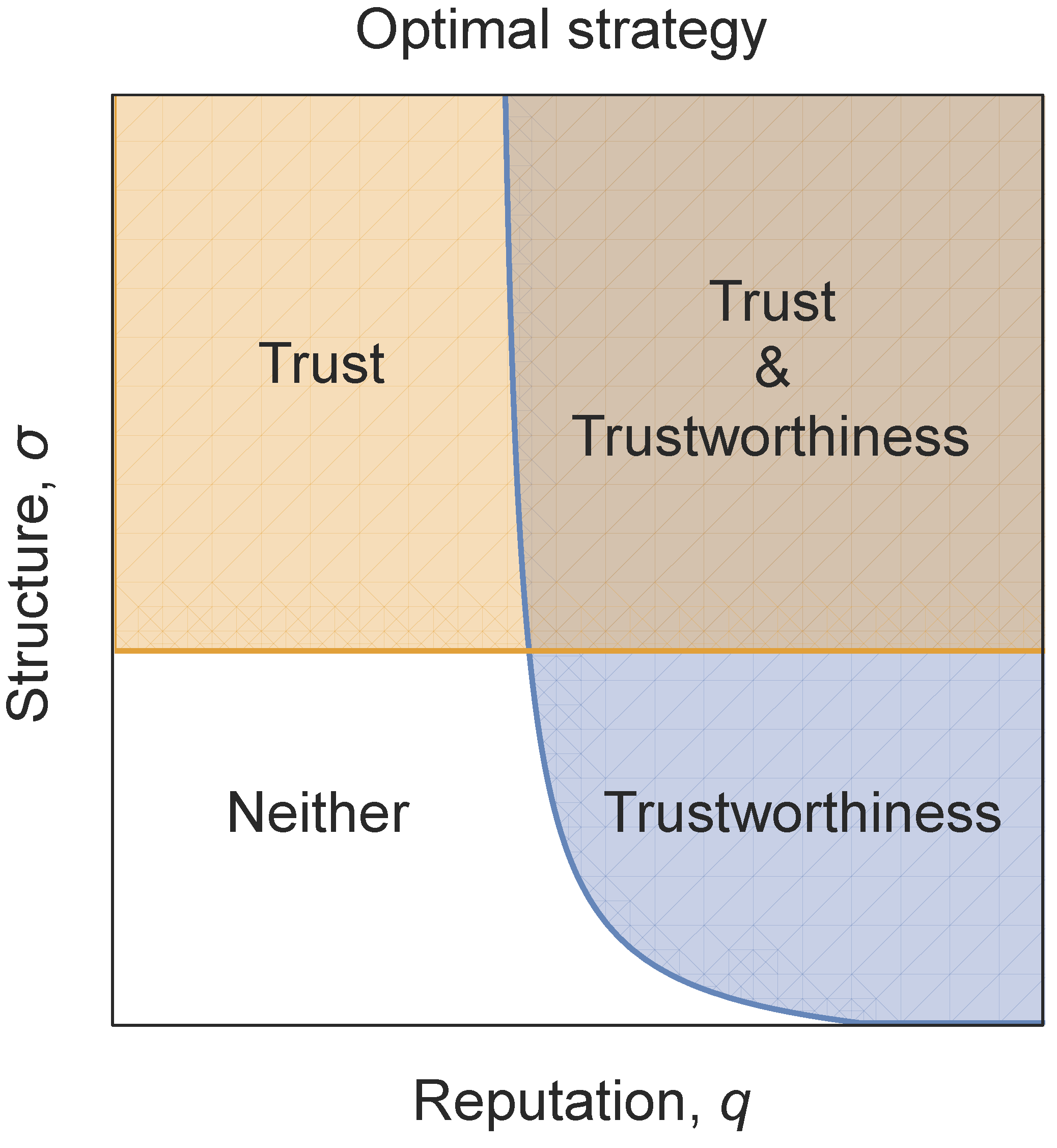
5. Evolution of Trust with Reputation

6. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
A. Selection of Continuous Strategies in a Structured Population
B. Trust Game: Two Well-Mixed Populations Formulation
C. Calculation of for the Trust Game with Reputation
References
- Camerer, C.F. Behavioral Game Theory: Experiments in Strategic Interaction; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.; Dickhaut, J.; McCabe, K. Trust, reciprocity, and social history. Games Econ. Behav. 1995, 10, 122–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.D.; Mislin, A.A. Trust games: A meta-analysis. J. Econ. Psychol. 2011, 32, 865–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.S.; Gowdy, J.M. Evolution as a general theoretical framework for economics and public policy. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2012, 90, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, S.J. Evolution and the Theory of Games; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, M.A.; Page, K.M.; Sigmund, K. Fairness versus reason in the ultimatum game. Science 2000, 289, 1773–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manapat, M.L.; Nowak, M.A.; Rand, D.G. Information, irrationality and the evolution of trust. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2013, 90, S57–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, D.G.; Tarnita, C.E.; Ohtsuki, H.; Nowak, M.A. Evolution of fairness in the one-shot anonymous Ultimatum Game. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 7, 2581–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, J.; Binmore, K.G.; Samuelson, L. Learning to be imperfect: The ultimatum game. Games Econ. Behav. 1995, 8, 56–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, K.M.; Nowak, M.A.; Sigmund, K. The spatial ultimatum game. Proc. Roy. Soc. B 2000, 267, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, E.; Hauert, C.; Nowak, M.A. Evolutionary dynamics on graphs. Nature 2005, 433, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuki, H.; Hauert, C.; Lieberman, E.; Nowak, M.A. A simple rule for the evolution of cooperation on graphs and social networks. Nature 2006, 441, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, M.A. Five rules for the evolution of cooperation. Science 2006, 314, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, M.A.; Tarnita, C.E.; Antal, T. Evolutionary dynamics in structured populations. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2006, 365, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, D.G.; Arbesman, S.; Christakis, N.A. Dynamic social networks promote cooperation in experiments with humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19193–19198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, D.G.; Nowak, M.A.; Fowler, J.H.; Christakis, N.A. Static network structure can stabilize human cooperation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17093–17098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, K.A.; Rigdon, M.L.; Smith, V.L. Sustaining Cooperation in Trust Games. Econ. J. 2007, 117, 991–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Antal, T.; Traulsen, A.; Ohtsuki, H.; Tarnita, C.E.; Nowak, M.A. Mutation-selection equilibrium in games with multiple strategies. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 258, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnita, C.E.; Antal, T.; Nowak, M.A. Mutation-selection equilibrium in games with mixed strategies. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 261, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnita, C.E.; Wage, N.; Nowak, M.A. Multiple strategies in structured populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2334–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnita, C.E.; Ohtsuki, H.; Antal, T.; Fu, F.; Nowak, M.A. Strategy selection in structured populations. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 259, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuki, H. Stochastic evolutionary dynamics of bimatrix games. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 264, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Casas, B.; Tomlin, D.; Anen, C.; Camerer, C.F.; Quartz, S.R.; Montague, P.R. Getting to know you: Reputation and trust in a two-person economic exchange. Science 2005, 308, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaliere, M.; Sedwards, S.; Tarnita, C.E.; Nowak, M.A.; Csikasz-Nagy, A. Prosperity is associated with instability in dynamical networks. J. Theor. Biol. 2012, 299, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Garcia, J.; Hauert, C.; Traulsen, A. Extrapolating weak selection in evolutionary games. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manapat, M.L.; Rand, D.G. Delayed and Inconsistent Information and the Evolution of Trust. Dyn. Games Appl. 2012, 2, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarnita, C.E. Fairness and Trust in Structured Populations. Games 2015, 6, 214-230. https://doi.org/10.3390/g6030214
Tarnita CE. Fairness and Trust in Structured Populations. Games. 2015; 6(3):214-230. https://doi.org/10.3390/g6030214
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarnita, Corina E. 2015. "Fairness and Trust in Structured Populations" Games 6, no. 3: 214-230. https://doi.org/10.3390/g6030214
APA StyleTarnita, C. E. (2015). Fairness and Trust in Structured Populations. Games, 6(3), 214-230. https://doi.org/10.3390/g6030214




