Abstract
Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) plays a vital role in supporting applications such as healthcare, human–computer interaction, and security. However, many existing approaches still face challenges in achieving robust generalization and maintaining high recall, particularly for emotions related to stress and anxiety. This study proposes a dual-stream hybrid model that combines prosodic features with spatio-temporal representations derived from the Multitaper Mel-Frequency Spectrogram (MTMFS) and the Constant-Q Transform Spectrogram (CQTS). Prosodic cues, including pitch, intensity, jitter, shimmer, HNR, pause rate, and speech rate, were processed using dense layers, while MTMFS and CQTS features were encoded with CNN and BiGRU. A Multi-Head Attention mechanism was then applied to adaptively fuse the two feature streams, allowing the model to focus on the most relevant emotional cues. Evaluations conducted on the RAVDESS dataset with subject-independent 5-fold cross-validation demonstrated an accuracy of 97.64% and a macro F1-score of 0.9745. These results confirm that combining prosodic and advanced spectrogram features with attention-based fusion improves precision, recall, and overall robustness, offering a promising framework for more reliable SER systems.
1. Introduction
Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) has emerged as a significant research area over the last two decades. Emotions play a crucial role in human communication, influencing social interactions, decision-making, and mental health conditions. SER systems offer broad opportunities in various applications, ranging from human–computer interaction (HCI) and technology-based education to mental health services, security systems, and intelligent vehicles [1,2,3]. Previous research has shown that speech signals contain two main components: linguistic information that conveys literal meaning and paralinguistic information that reflects emotional aspects [1]. Paralinguistic information is considered more relevant in identifying emotional states such as stress and anxiety because it is relatively independent of lexical and linguistic content. This makes paralinguistic-based SER very promising for detecting psychological conditions, especially those related to stress and anxiety.
Prosody, which encompasses variations in pitch, intensity, pauses, syllable duration, and rhythm of speech, has been recognized as an important indicator in emotion analysis [4]. Kuuluvainen et al. [5] asserted that prosody plays a role in facilitating the understanding of statistical patterns in the speech stream, thereby enhancing language learners’ ability to capture hidden structures. In the context of SER, prosodic cues have been shown to significantly contribute to the model’s ability to distinguish emotions, particularly those related to stress and anxiety. Shan [6] noted that intonation, stress, and rhythm have a direct impact on the interpretation of a speaker’s intent and emotions, making prosody a crucial element in understanding conversational dynamics. Furthermore, reference [7] shows that prosodic variations are often the most consistent nonverbal cues when someone is experiencing emotional distress. For example, higher pitch, increased speech rate, jitter, and unstable shimmer are often associated with stress or anxiety.
SER methodology has evolved rapidly, from classical machine learning (ML) approaches to deep learning. Traditional approaches typically rely on hand-crafted features such as Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) [8,9,10,11], Linear Predictor Coefficients (LPC) [12,13], and prosodic features [14,15] processed through classification models such as Support Vector Machine (SVM) [16], Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) [17,18], or Random Forest (RF) [19,20]. While quite effective on small and clean datasets, these approaches often fail to generalize to real-world environments with varying speakers, accents, and background conditions. With the advent of deep learning approaches, such as CNNs [21,22,23], RNNs [22,24], and Transformers [25,26], the accuracy of SER has significantly improved. CNNs are effective in extracting spectral patterns from speech spectrograms, while RNNs, such as GRUs and LSTMs, are capable of capturing long-term temporal dependencies [27,28,29]. Furthermore, the integration of attention mechanisms has been shown to help models focus more on emotion-relevant signal regions, thus improving performance [29,30,31,32].
With the development of deep learning-based methods, the use of spectrograms has become a popular approach for extracting speech acoustic patterns. One commonly used spectrogram is the Log–Mel Spectrogram; however, this representation still faces limitations in adaptive resolution and sensitivity to spectral leakage, which can reduce the model’s ability to distinguish emotions with similar acoustic characteristics [33,34]. Therefore, this study hypothesizes that the Multitaper Mel-Frequency Spectrogram (MTMFS) and Constant-Q Transform Spectrogram (CQTS) can provide richer representations than conventional spectrograms [1,35,36]. The MTMFS is expected to produce a more stable and detailed spectrum, while the CQTS is believed to capture low-frequency variations with higher resolution and fast temporal dynamics at high frequencies, thereby improving the accuracy of emotion detection, particularly in low-arousal and high-arousal classes.
Although various approaches have made significant progress, SER still faces several key challenges. First is the problem of overfitting on small datasets, which often occurs due to the limited number of available samples [37]. Second is the lack of in-depth exploration of prosodic features, despite prosody having long been recognized as a key indicator of stress. Third, research tends to prioritize overall accuracy over recall, which can result in missing cases of mental health-related emotions. Finally, the lack of multi-modal feature integration, as most studies still rely on a single feature type, results in an incomplete representation of complex emotional information.
Recall is one of the most crucial metrics in SER, reflecting the model’s ability to detect all relevant positive cases. Achieving high recall is crucial to ensure that no emotional samples are missed, especially for emotions that are difficult to recognize. In the context of stress and anxiety detection, recall becomes even more vital because incorrectly detecting individuals experiencing stress (false negatives) can have a direct impact on a person’s psychological well-being, risking more than false positives [38,39,40]. Unfortunately, most SER research still focuses on overall accuracy rather than maintaining optimal recall [29,30,31,32]. Several studies, such as [2,27,28], report that recall is often lower than accuracy, especially for emotion classes related to stress and anxiety.
Despite recent advances, three critical research gaps remain. First, most existing studies emphasize accuracy over recall, often leading to misclassification of stress- and anxiety-related emotions. Second, prosodic features, though long recognized as reliable indicators of emotional distress, have rarely been systematically combined with advanced spectro-temporal representations. Third, although MTMFS and CQTS have individually shown superior spectral stability and adaptive resolution, their joint fusion with prosodic cues under an attention mechanism has not yet been thoroughly explored.
To address this challenge, this study proposes a hybrid dual-stream architecture that combines prosodic modulation and spatio-temporal features based on the MTMFS and CQTS. The prosodic branch is designed to capture the temporal dynamics of prosody through dense layers, while the spectrogram branch uses CNN and BiGRU to extract spatio-temporal patterns from the MTMFS and CQTS. The results from both branches are then fused through a Multi-Head Attention (MHA) Fusion mechanism, which adaptively weights the most relevant features. With this design, this study contributes to improving recall without compromising overall accuracy, thereby providing more reliable emotion detection, especially under stressful and anxious conditions.
2. Related Works
Currently, research related to SER has been conducted using various feature and model approaches. Previously, many studies relied on conventional acoustic features such as MFCC, LPC, and prosodic cues, which were then processed using classical ML classification algorithms. Reference [2] employed MFCC on the RAVDESS dataset with SVM, achieving an accuracy of approximately 82%. However, this method is generally limited in its applicability and sensitive to noise, resulting in low recall performance for high-arousal emotions.
Advances in deep learning allow for richer feature representation. Reference [41] proposed a Multi-Scale Feature Pyramid Network (MSFPN), which combines a Multi-Scale CNN (MSCNN) with Convolutional Self-Attention (CSA) and BiLSTM to capture temporal context. Evaluations were conducted on the IEMOCAP and RAVDESS datasets. The results showed an Unweighted Accuracy (UA) of 86.5% on RAVDESS. This approach excels because it preserves multi-granularity information while improving local correlations between features through CSA. Furthermore, despite the relatively good accuracy performance, these studies still focused on UA and WA without an in-depth analysis of recall within specific emotional classes.
Multi-feature fusion-based approaches were also developed. Bhangale et al. [1] introduced the Parallel Emotion Network (PEmoNet), which combines the MTMFS, Gammatonegram (GS), and CQTS. Evaluations on EMODB and RAVDESS demonstrated accuracy of up to 97% with an average F1-score of 0.97. Ablation studies demonstrated that the MTMFS and CQTS contributed significantly to performance improvements compared to using a single spectrogram type alone. However, using all three spectrograms simultaneously increases computational complexity, making the integration more challenging.
Other studies have begun to emphasize the importance of prosodic features. Kuuluvainen et al. [5] showed that variations in pitch, intonation, and pauses can facilitate the learning of statistical dependencies in continuous speech. Meanwhile, Guo et al. [7] applied a prosody- and spectrogram-based dual-stream architecture to a Mandarin dataset and successfully improved the sensitivity of negative emotion detection. However, recall results still varied across classes, so the risk of false negatives for stress and anxiety emotions remained high.
The application of attention mechanisms has also been shown to improve performance. Makhmudov et al. [32] developed a hybrid CNN–LSTM model with attention, using RMS, ZCR, and MFCC features. Evaluation on TESS and RAVDESS yielded accuracies of up to 99.8% and 95.7%, respectively. The attention mechanism allows the model to focus on significant emotional segments, while the CNN handles spectral representation and the LSTM captures long-term temporal dependencies. However, this research is still limited to conventional acoustic features and tends to emphasize global accuracy.
Bhanbhro et al. [29] compared CNN-LSTM with Attention-Enhanced CNN-LSTM on the RAVDESS dataset. The use of attention improved accuracy by more than 2% compared to standard CNN-LSTM. The attention mechanism was demonstrated to enhance the separation between similar emotion classes while maintaining performance under noisy conditions. However, this research was still limited to Mel-spectrogram-based spectral features, without the integration of prosodic cues, which are important for detecting stress and anxiety.
Although various SER studies have achieved high accuracy, significant limitations remain. Conventional feature-based approaches (MFCC, LPC) are sensitive to noise and less effective in capturing the dynamics of high-arousal emotions, such as fear and anger. Multi-scale deep learning methods enhance representation but often prioritize global accuracy over recall. Multi-feature fusion studies have demonstrated the dominant contribution of the MTMFS and CQTS through ablation studies. Meanwhile, attention mechanism-based models improve accuracy and class separation but are still limited to spectral features without the integration of prosodic cues. Therefore, methods that integrate prosodic cues, spatio-temporal fusion of MTMFS and CQTS, and adaptive attention mechanisms are needed to improve recall and robustness, especially for stress and anxiety detection.
3. Proposed Method
The method proposed in this study aims to integrate prosodic and spectral features into a richer spatio-temporal representation, thereby improving emotion detection performance. The RAVDESS dataset was chosen as the experimental benchmark because it provides a corpus of emotional conversations under controlled conditions with professional actors. The dataset comprises eight distinct emotion classes, expressed by 24 speakers with both male and female voices, ensuring a diverse range of gender and vocal characteristics.
Importantly, RAVDESS offers emotions with both low and high arousal, making it well-suited for testing methods designed to improve recall in stress and anxiety detection scenarios. To address this challenge, the system is designed with a hybrid dual-stream architecture comprising a prosodic feature branch and a spectrogram feature branch, which are then combined through an attention-based fusion mechanism. To illustrate the flow of the proposed method, see below Figure, and its detailed configuration is shown in below Table.
3.1. Prosodic FeaturesExtraction Design
Figure 1 illustrate the flow of the proposed method. Prosodic features were extracted from the RAVDESS dataset (48 kHz, mono) using the openSMILE Python library (versions 2.6.0 and 3.0.1). The extracted features included pitch contour, intensity, jitter, shimmer, Harmonics-to-Noise Ratio (HNR), pause rate, and speech rate. Each segment yielded approximately 40–60 prosodic features. These features were processed through stacked dense layers (128 → 64 units, ReLU activation, dropout 0.3), resulting in a 64-dimensional representation vector.
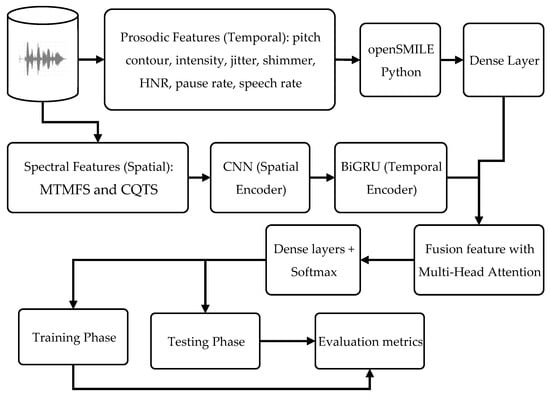
Figure 1.
Proposed dual-stream hybrid.
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Features
Spatial features were extracted using a parallel representation of the Multitaper Mel-Frequency Spectrogram (MTMFS) and the Constant-Q Transform Spectrogram (CQTS) to enhance the discriminative power of emotional cues. The MTMFS employed multiple orthogonal tapers instead of a single Hamming window, reducing spectral leakage and capturing subtle variations in pitch, timbre, and intonation. A 64-point Mel filterbank with a 25 ms frame size, 10 ms hop length, and a 2048-point FFT was applied, providing a stable and high-resolution spectral envelope. The CQTS offered an adaptive time–frequency resolution, providing superior frequency resolution at lower frequencies (suitable for low-arousal emotions, such as sadness and calmness) and higher temporal resolution at higher frequencies (critical for high-arousal emotions, such as anger and surprise).
Each spectrogram was processed independently using a CNN-based spatial encoder with 3 × 3 kernels to capture local time–frequency patterns. Each CNN comprised three convolutional blocks with filters of [32, 64, 128], each followed by Batch Normalization, ReLU activation, and Max Pooling. Instead of full flattening, the CNN outputs were retained as sequence embeddings (time steps × feature dimension) to preserve temporal information. The sequence embeddings from the MTMFS and CQTS were then individually passed through a BiGRU-based temporal encoder (2 layers, 128 hidden units each, dropout 0.3), allowing each branch to capture its long-term temporal dependencies.
The BiGRU outputs were subsequently concatenated and normalized using Layer Normalization to align feature scales and stabilize recurrent learning. This design enables the model to leverage both stable spectral envelopes from MTMFS and adaptive time–frequency dynamics from the CQTS in a balanced manner. Formally, the spatio-temporal representation is given by
where and denote the MTMFS and CQTS matrices of dimensions .
3.3. Fusion Configuration
The prosodic embedding and the spatio-temporal embedding from the BiGRU were combined through an MHA layer to weight the most relevant features for emotion recognition adaptively. Prior to fusion, the prosodic embedding was normalized using Layer Normalization, aligning its scale with the spatio-temporal embedding to ensure balanced contribution from both streams. This step is particularly crucial since prosodic features and spectrogram-derived embeddings differ in dimensionality and statistical distribution. An MHA module then processed the normalized embeddings with eight attention heads, which provided the best balance between recall improvement and computational efficiency. Formally, the fused vector can be expressed as
where and denote the normalized prosodic embedding and the spatio-temporal embedding, respectively, and denote the query, key, and value vectors of the respective feature branches.
3.4. Classifier
The fused representation was passed through fully connected layers [64, 128, 256] with ReLU activation and a dropout of 0.5. The final layer employed a Softmax function to classify eight emotional classes as defined by RAVDESS. The loss function used was Categorical Cross-Entropy:
where is the number of classes, is the true label, and is the predicted probability.
3.5. Training Strategy
The model was trained using the Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 1 × 10−4, a batch size of 32, and a maximum of 100 epochs. Early stopping was applied with a patience of 10 epochs, monitoring validation macro F1-score and validation loss to prevent overfitting and ensure balanced recall and precision across classes. This strategy allows the model to halt training when further improvements on the validation set become marginal, thereby reducing the risk of overfitting while maintaining generalization. To further enhance robustness, a 5-fold subject-independent cross-validation was conducted, ensuring that speakers in the training set did not appear in the testing set. This evaluation protocol provides a more reliable estimate of the model’s performance across different speakers.
3.6. Evaluation Metrics
The evaluation metrics included precision, recall, specificity, F1-score, AUC, and accuracy.
- Accuracy measures the proportion of correctly classified samples but may be misleading for imbalanced emotional classes.
- Precision indicates the fraction of correctly predicted positive samples among all predicted positives, ensuring the reliability of stress predictions.
- Recall (sensitivity) measures the proportion of correctly detected positive cases; in stress and anxiety detection, recall is critical since missing stressed cases (false negatives) can be more harmful than false positives.
- F1-score, the harmonic mean of precision and recall, balances sensitivity and reliability.
Table 1 illustrates its detailed configuration of the flow of the proposed method.

Table 1.
Configuration for the proposed model.
4. Results and Discussion
The dataset used in this study is the Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS), a widely used resource in Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) research. This dataset comprises 24 actors (12 men and 12 women) who voiced speech in eight emotion categories: neutral, calm, happy, sad, angry, fearful, disgusted, and surprised. Each emotion was recorded at two intensity levels, normal and strong, resulting in a total of 1440 records. The data distribution consisted of seven classes, with one other class being a minority (see Figure 2 for further details).
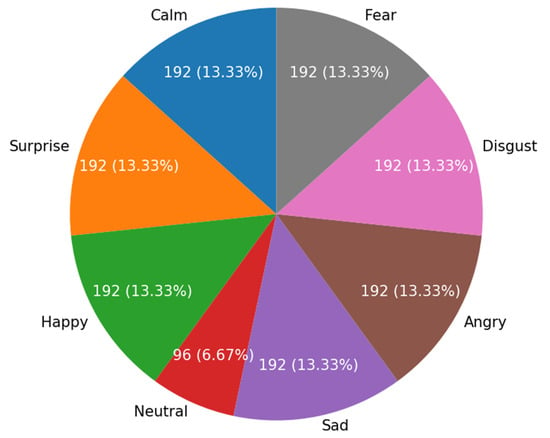
Figure 2.
Class distribution of the RAVDESS dataset.
4.1. Prosodic Features Analysis
Figure 3 displays a sample of prosodic extraction results, including pitch, intensity, HNR, loudness, jitter, shimmer, pause rate, and speech rate. The observed patterns illustrate acoustic dynamics over time. Pitch and intensity exhibit more fluctuating contours in segments with high arousal, such as fearful and angry emotions. HNR decreases in certain sections, which is typically associated with decreased voice quality resulting from vocal tension. Jitter and shimmer are relatively higher in segments with low vocal stability, which often occur in states of anxiety. Pause and speech rate reflect the rhythm of speech; fewer pauses and a faster speech rate are seen in emotionally intense sections.
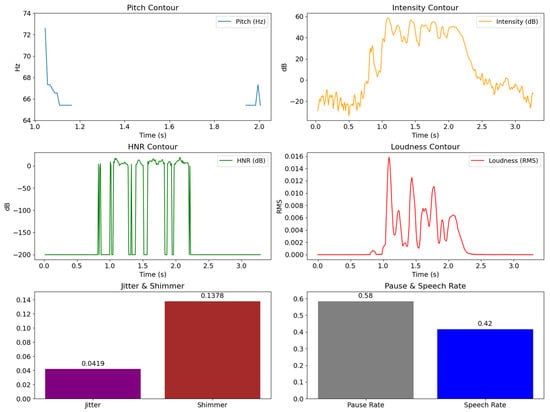
Figure 3.
Example of extracted prosodic features from a speech segment, including pitch contour, intensity contour, HNR contour, loudness contour, jitter, shimmer, pause rate, and speech rate.
This relationship is reinforced by Figure 4, which presents a statistical summary of prosodic features with openSMILE eGeMAPS. Loudness values are relatively higher in segments with high arousal, while jitter, shimmer, and HNR show variations that are in line with the temporal pattern in Figure 3. Thus, the values and patterns shown by Figure 3 and Figure 4 reinforce each other, indicating that prosodic features can be consistent markers in distinguishing certain emotional states, especially those related to stress and anxiety.
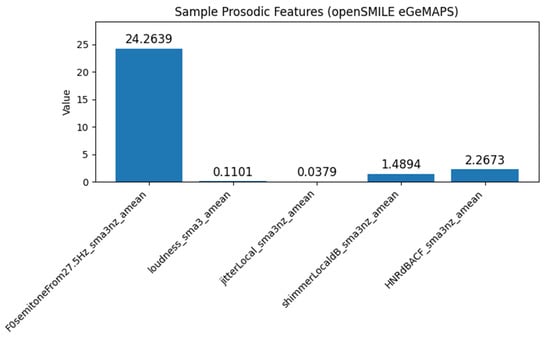
Figure 4.
Sample plot of prosodic features using openSMILE.
4.2. Spectrogram Features Analysis
Figure 5 shows an example of the MTMFS and CQTS for a voice sample in RAVDESS. MTMFS, shown on the left, produces a relatively smooth and stable representation with a clear energy distribution across the frequency range. This multitaper approach effectively reduces spectral leakage and improves the accuracy of identifying subtle variations in pitch, timbre, and intonation, which are highly relevant for distinguishing similar emotions.
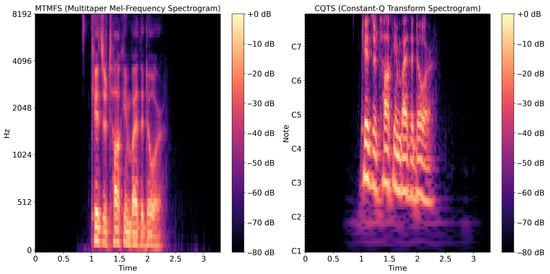
Figure 5.
Sample plot of spectrograms: (left) MTMFS; (right) CQTS.
Meanwhile, the CQTS on the right displays a more adaptive frequency pattern, characterized by high frequency resolution in low tones and high temporal resolution in high tones. This enables the CQTS to capture the subtle changes associated with low-arousal emotions, such as sadness or calm, while also representing the rapid dynamics common to high-arousal emotions, like anger or surprise. The combination of these two representations is expected to enrich the mapping of emotional features in speech signals, thereby improving the model’s accuracy in emotion recognition compared to using a single spectrogram.
4.3. Results
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of the proposed model, a confusion matrix representing the classification results of eight emotion classes on the RAVDESS dataset was used. The values displayed in this confusion matrix are the aggregated results of 5-fold cross-validation, providing a more stable picture and reducing bias caused by certain data splits. With this approach, each fold alternates as test data, while the other folds serve as training data, ensuring that all samples contribute to both the training and testing phases. The confusion matrix in Figure 6, the result of this aggregation, provides detailed information on the distribution of correct predictions and misclassifications for each emotion class, allowing for an in-depth analysis of the model’s strengths and weaknesses in each emotion category.
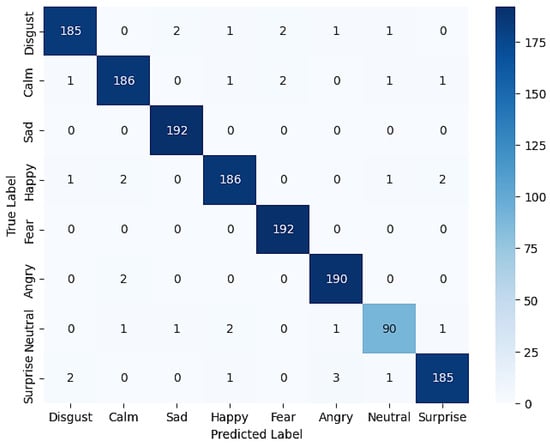
Figure 6.
Confusion matrix proposed method.
In general, the prediction distribution exhibits a dominant diagonal, indicating high accuracy across almost all classes. The Sad, Fear, and Calm classes show nearly perfect predictions with few misclassifications. However, some confusion is observed in the Neutral class, which is sometimes predicted as Happy or Calm. Similarly, a small number of Disgust and Surprise cases are swapped, although the numbers are relatively small. This pattern suggests that the model is quite reliable in recognizing emotions with explicit acoustic expressions, while confusion still occurs in classes with more subtle prosodic features, such as the Neutral class. For more details, see Table 2 for differences in precision, recall, and F1-score values for each class.

Table 2.
Classification report of the proposed model on the RAVDESS Dataset.
Table 2 shows that the model’s performance demonstrates high consistency across classes, with an average F1-score approaching 0.98. Two classes, Sad and Fear, achieved perfect recall (1.0000), indicating the model’s ability to detect these emotions without losing relevant samples. This indicates the model’s reliability in recognizing both low- and high-intensity emotions, which are often challenging in SER. Meanwhile, the Neutral class achieved the lowest recall value, which, although still a good performance considering its minority, suggests that its more subtle prosodic characteristics make it relatively difficult to distinguish from other classes. These findings confirm that integrating prosodic features with MTMFS and CQTS successfully enhances the model’s generalization, particularly for classes that are acoustically susceptible to confusion, while maintaining a balance between precision and recall across emotion categories.
Furthermore, to assess the contribution of each component in the proposed architecture, an ablation study was conducted by removing or replacing specific parts of the model. The primary goal of this ablation was to ensure that performance improvements stem not solely from model complexity but from the integration of the designed features and mechanisms. Specifically, this study focuses on three aspects: (i) the role of prosodic features in increasing sensitivity to stress and anxiety emotions, (ii) the contribution of MTMFS and CQTS spectral representations compared to using only one type of spectrogram, and (iii) the effectiveness of the attention mechanism in balancing the contributions of prosody and spatio-temporal features. The results of this study are expected to clarify the relative role of each component in achieving increased recall and robustness of the model.
Table 3 presents the results of an ablation study to assess the contribution of each component in the proposed architecture. It can be seen that removing prosodic features decreased performance to 93.78% accuracy and 93.85% F1-score, indicating that prosody plays a significant role in detecting both high- and low-arousal emotions. This is consistent with the expectation that prosodic cues provide additional sensitivity to stress and anxiety dynamics. Removing MTMFS features had the most significant impact, resulting in a 93.32% decrease in F1-score. This finding confirms the MTMFS’s dominant role in enriching spectral representation and reducing spectral leakage, consistent with previous studies that identified the MTMFS as the most stable representation in the RAVDESS dataset. Meanwhile, removing CQTS features resulted in a more moderate performance reduction (95.21% F1-score), indicating a significant but less significant contribution than the MTMFS. This can be explained by the CQTS being more prominent at low-frequency resolution, while RAVDESS is relatively rich in prosodic and mid-spectral variations.

Table 3.
Ablation study of the proposed method.
Removing the attention mechanism also had a significant impact (F1-score 95.61%). Although the CNN and BiGRU were still able to capture spatial and temporal patterns, the lack of attention caused an imbalance in the contributions between features, resulting in decreased recall in the minority class. Overall, the ablation results showed the following:
- The MTMFS makes the largest contribution to classification stability and accuracy.
- Prosodic features directly improve recall in the stress and anxiety classes.
- The CQTS adds depth to the representation but with a more moderate impact.
- The attention mechanism ensures adaptive integration between features, maintaining a balance between precision and recall.
The best performance of the proposed method (full) shows that the combination of prosodic cues, the MTMFS, the CQTS, and the attention mechanism synergistically contributes to achieving optimal generalization.
After confirming the contribution of each component through ablation studies, the next step was to compare the performance of the proposed model with previous research on the RAVDESS dataset. Table 4 summarizes the comparison results with several state-of-the-art models.

Table 4.
Results of the proposed model and comparison with prior works.
The results in Table 4 show the performance improvement of SER on the RAV-DESS dataset using various approaches. The SVM-based methods [16] and K-SVM + GWO [28] performed quite well in the classical machine learning category, with accuracies of 72.40% and 87.00%, respectively. The HuBERT + DPCNN + CAF approach [30] achieved an F1-score of 82.84%, confirming the potential of self-supervised learning-based representations. Model [2] achieved an F1-score of 90.80%, demonstrating the effectiveness of feature fusion. Reference [32] further improved recall to 94.99% with an F1-score of 94.20, thanks to LSTM’s ability to capture long-term temporal dependencies.
A study of PEmoNet [1] demonstrated competitive results, achieving an F1-score of 97.26 and confirming the effectiveness of multi-spectrogram fusion for enriching emotional representation. While the numerical difference between PEmoNet [1] and the proposed model may appear slight (0.1~0.2%), the key contribution of this work lies in the integration of prosodic features with MTMFS and CQTS under an attention-based fusion scheme. This architectural novelty provides a more balanced trade-off between precision and recall across all emotion classes, as reflected in the ablation results and confusion matrix. In practice, such a balance is often more critical than marginal accuracy gains, as it reduces bias toward dominant classes and enhances robustness under varied emotional conditions. Therefore, the significance of the proposed model should be understood not only in terms of absolute accuracy but in its ability to maintain consistent recall alongside precision, which offers a stronger foundation for future SER applications.
5. Conclusions
This study proposes a dual-stream hybrid architecture that integrates prosodic features with spatio-temporal representations from the MTMFS and the CQTS, combined through an MHA mechanism. The experimental results on the RAVDESS dataset using 5-fold subject-independent cross-validation demonstrated that the proposed model consistently outperformed state-of-the-art approaches, achieving an overall accuracy of 97.64% and a macro F1-score of 0.9745. More importantly, the model achieved a recall of 97.64%, which is higher than those of previous studies that often prioritize accuracy at the expense of recall. This improvement confirms the effectiveness of integrating prosodic cues with multi-spectrogram fusion to enhance sensitivity and robustness in emotion recognition. Furthermore, since prosodic cues are closely related to subtle psychological signals, the proposed framework may serve as a promising basis for future research focusing on stress- and anxiety-related emotion detection, where minimizing false negatives is especially critical.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.N. and D.R.I.M.S.; methodology, K.N.; software, K.N. and I.H.A.A.; validation, K.N., I.H.A.A. and N.A.N.; formal analysis, K.N. and I.H.A.A.; investigation, K.N. and N.A.N.; resources, K.N.; writing—original draft preparation, K.N.; writing—review and editing, D.R.I.M.S.; visualization, I.H.A.A.; supervision, K.N.; project administration, D.R.I.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education, Science, and Technology (Kemdiktisaintek) of the Republic of Indonesia with grant number 127/C3/DT.05.00/PL/2025, 026/LL6/AL.04/2025, and 081/DPPMP/UNISBANK/UM/VI/2025.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are publicly available. The experiments in this research were conducted using the RAVDESS Emotional Speech Audio dataset, which can be accessed at https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/uwrfkaggler/ravdess-emotional-speech-audio (accessed on 5 July 2025). No additional new data were created or analyzed in this study. The implementation code can be requested by contacting the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the Ministry of Higher Education, Science, and Technology (Kemdiktisaintek) of the Republic of Indonesia for providing financial support for this research. The authors also extend their appreciation to the Research and Community Service Institute (LPPM) of Universitas Stikubank for the administrative and technical assistance. During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used generative AI to assist in improving the clarity and structure of the writing. The ideas, study design, data analysis, and interpretation remain the sole responsibility of the authors, who have thoroughly reviewed and edited the final content.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bhangale, K.B.; Kothandaraman, M. Speech Emotion Recognition Using the Novel PEmoNet (Parallel Emotion Network). Appl. Acoust. 2023, 212, 109613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleed, G.T.; Shaker, S.H. Speech Emotion Recognition on MELD and RAVDESS Datasets Using CNN. Information 2025, 16, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liztio, L.M.; Sari, C.A.; Setiadi, D.R.I.M.; Rachmawanto, E.H. Gender Identification Based on Speech Recognition Using Backpropagation Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication (iSemantic), Semarang, Indonesia, 19–20 September 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Mai, G.; Mohammadi, Y.; Benzaquén, E.; Yukhnovich, E.A.; Sedley, W.; Griffiths, T.D. Neural Entrainment to Pitch Changes of Auditory Targets in Noise. Neuroimage 2025, 314, 121270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuuluvainen, S.; Kaskivuo, S.; Vainio, M.; Smalle, E.; Möttönen, R. Prosody Enhances Learning of Statistical Dependencies from Continuous Speech Streams in Adults. Cognition 2025, 262, 106169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y. Prosodic Modulation of Discourse Markers: A Cross-Linguistic Analysis of Conversational Dynamics. Speech Commun. 2025, 173, 103271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Huang, S.; Li, M. DDA-MSLD: A Multi-Feature Speech Lie Detection Algorithm Based on a Dual-Stream Deep Architecture. Information 2025, 16, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayvaz, U.; Gürüler, H.; Khan, F.; Ahmed, N.; Whangbo, T.; Akmalbek Bobomirzaevich, A. Automatic Speaker Recognition Using Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients Through Machine Learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 71, 5511–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, D.; Sriuppili, S. Speech Processing: MFCC Based Feature Extraction Techniques- An Investigation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1717, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, M.; Jain, S. Speech Recognition Employing MFCC and Dynamic Time Warping Algorithm. In Innovations in Information and Communication Technologies (IICT-2020); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wijaya, N.N.; Setiadi, D.R.I.M.; Muslikh, A.R. Music-Genre Classification Using Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory and Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients. J. Comput. Theor. Appl. 2024, 1, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, N.; Gao, J.; Khattak, M.I.; Rauf, H.T.; Kadry, S.; Shafi, M. DeepResGRU: Residual Gated Recurrent Neural Network-Augmented Kalman Filtering for Speech Enhancement and Recognition. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 238, 107914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kang, S. Deep Neural Network-based Linear Predictive Parameter Estimations for Speech Enhancement. IET Signal Process. 2017, 11, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapiperis, S.; Ellinas, N.; Vioni, A.; Oh, J.; Jho, G.; Hwang, I.; Raptis, S. Investigating Disentanglement in a Phoneme-Level Speech Codec for Prosody Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Macao, China, 2–5 December 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Sivasathiya, G.; Kumar, A.D.; Ar, H.R.; Kanishkaa, R. Emotion-Aware Multimedia Synthesis: A Generative AI Framework for Personalized Content Generation Based on User Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (IDCIoT), Bengaluru, India, 4–6 January 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1344–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Colunga-Rodriguez, A.A.; Martínez-Rebollar, A.; Estrada-Esquivel, H.; Clemente, E.; Pliego-Martínez, O.A. Developing a Dataset of Audio Features to Classify Emotions in Speech. Computation 2025, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Sharma, A. A Research on HMM Based Speech Recognition in Spoken English. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. (Former Recent Pat. Electr. Electron. Eng.) 2021, 14, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.R.K.; Pandey, D. Speech Recognition Using HMM and Soft Computing. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, T.; Roy, S.S. Novel Hate Speech Detection Using Word Cloud Visualization and Ensemble Learning Coupled with Count Vectorizer. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Li, Y. Simulation of English Speech Recognition Based on Improved Extreme Random Forest Classification. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1948159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, S.; Kumar, S.S.; Albagory, Y.; Ramalingam, R.; Dumka, A.; Singh, R.; Rashid, M.; Gehlot, A.; Alshamrani, S.S.; AlGhamdi, A.S. Developing a Speech Recognition System for Recognizing Tonal Speech Signals Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidhar, R.; Patilkulkarni, S.; Puneeth, S.B. Combining Audio and Visual Speech Recognition Using LSTM and Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2022, 14, 3425–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hema, C.; Garcia Marquez, F.P. Emotional Speech Recognition Using CNN and Deep Learning Techniques. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 211, 109492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruh, J.; Viriri, S.; Adegun, A. Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network for Automatic Speech Recognition. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 30069–30079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orken, M.; Dina, O.; Keylan, A.; Tolganay, T.; Mohamed, O. A Study of Transformer-Based End-to-End Speech Recognition System for Kazakh Language. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Sun, B.; Li, S. Multimodal Sparse Transformer Network for Audio-Visual Speech Recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 10028–10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondohanindijo, J.; Muljono; Noersasongko, E.; Pujiono; Setiadi, D.R.M. Multi-Features Audio Extraction for Speech Emotion Recognition Based on Deep Learning. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023, 14, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Szénási, S. Optimizing Speech Emotion Recognition with Deep Learning and Grey Wolf Optimization: A Multi-Dataset Approach. Algorithms 2024, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanbhro, J.; Memon, A.A.; Lal, B.; Talpur, S.; Memon, M. Speech Emotion Recognition: Comparative Analysis of CNN-LSTM and Attention-Enhanced CNN-LSTM Models. Signals 2025, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Meng, J.; Fan, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Q. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Dual-Stream Representation and Cross-Attention Fusion. Electronics 2024, 13, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Ge, C.; Su, C.; Chen, R.; Sun, J. A Deep Learning Model for Speech Emotion Recognition on RAVDESS Dataset. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2025, 16, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhmudov, F.; Kutlimuratov, A.; Cho, Y.-I. Hybrid LSTM–Attention and CNN Model for Enhanced Speech Emotion Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-H. Accuracy Enhancement Method for Speech Emotion Recognition From Spectrogram Using Temporal Frequency Correlation and Positional Information Learning Through Knowledge Transfer. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 128039–128048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ji, S.; Hu, Z.; Cai, C.; Luo, J.; Yang, X. ADFF: Attention Based Deep Feature Fusion Approach for Music Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2022, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 18–22 September 2022; ISCA: Singapore, 2022; Volume 2022-Septe, pp. 4152–4156. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, D.B.; Bakri, K.J.; de Souza Ferreira, F.; Inacio, J. Multitaper-Mel Spectrograms for Keyword Spotting. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 2028–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, T.; Gambäck, B. Music Style Transfer Using Constant-Q Transform Spectrograms. In Artificial Intelligence in Music, Sound, Art and Design; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, V.V.N.; Saravanakumar, R.; Yusuf, N.; Pradhan, R.; Hamdi, H.; Saravanan, K.A.; Rao, V.S.; Askar, M.A. Enhancing Emotion Prediction Using Deep Learning and Distributed Federated Systems with SMOTE Oversampling Technique. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 108, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; Tian, Y.; Dai, J. Trade-Offs between Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Mental Illness Detection on Social Media. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, N.; Kumar, Y.; Mehta, K.; Chaplot, N. Physiological Signal-Based Mental Stress Detection Using Hybrid Deep Learning Models. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2025, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, A.; Rajakaruna, D.K.; Kasthurirathna, D.; Atukorale, A.; Aththidiye, R.; Yatiipansalawa, M.; Yatipansalawa, M. A Reinforcement Learning-Based Approach for Promoting Mental Health Using Multimodal Emotion Recognition. J. Futur. Artif. Intell. Technol. 2024, 1, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Lan, H.; Zhang, X. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Multi-Scale Global–Local Representation Learning with Feature Pyramid Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).