Abstract
Responsiveness—the speed at which a text-to-speech (TTS) system produces audible output—is critical for real-time voice assistants yet has received far less attention than perceptual quality metrics. Existing evaluations often touch on latency but do not establish reproducible, open-source standards that capture responsiveness as a first-class dimension. This work introduces a baseline benchmark designed to fill that gap. Our framework unifies latency distribution, tail latency, and intelligibility within a transparent and dataset-diverse pipeline, enabling a fair and replicable comparison across 13 widely used open-source TTS models. By grounding evaluation in structured input sets ranging from single words to sentence-length utterances and adopting a methodology inspired by standardized inference benchmarks, we capture both typical and worst-case user experiences. Unlike prior studies that emphasize closed or proprietary systems, our focus is on establishing open, reproducible baselines rather than ranking against commercial references. The results reveal substantial variability across architectures, with some models delivering near-instant responses while others fail to meet interactive thresholds. By centering evaluation on responsiveness and reproducibility, this study provides an infrastructural foundation for benchmarking TTS systems and lays the groundwork for more comprehensive assessments that integrate both fidelity and speed.
1. Introduction
Voice assistants have become increasingly prevalent in modern society, integrating seamlessly into smartphones, smart speakers, and various IoT devices. The widespread adoption of virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and Google Assistant underscores the growing demand for intuitive and hands-free interaction with technology [1]. This trend is propelled by advancements in speech recognition and synthesis technologies, enabling more natural and efficient human–computer communication [2].
The primary and most widely adopted approach for designing voice assistant systems is the modular pipeline architecture. This structure divides the system into specialized components that each handle a distinct task. First, a speech-to-text (STT) engine transcribes the user’s spoken input into text. Next, a natural language processing (NLP) component—typically powered by a large language model (LLM)—interprets the text and generates a response. Finally, a text-to-speech (TTS) engine converts the generated text back into natural-sounding speech for the user [3]. This clear division allows for each part of the system to leverage domain-specific advances: STT models focus on acoustic and linguistic accuracy, LLMs handle semantics and intent reasoning, and TTS models synthesize expressive, human-like speech.
An emerging alternative to this modular design is an integrated, end-to-end trainable system that combines all stages—recognition, understanding, and synthesis—into a single model. One prominent example is Moshi [4], a real-time speech-to-speech dialogue model developed by Kyutai (https://kyutai.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2025)). Although Moshi eliminates explicit interfaces between components (no separate ASR (automatic speech recognition), NLP (natural language processing), or TTS (text-to-speech) modules), its architecture remains logically modular: it uses a large language model core to reason over internally predicted text tokens, while audio tokenizers encode and decode the speech signals. The entire system is trained end-to-end, allowing for tight integration and low latency, but it still relies on internal text-based reasoning and separate token streams for input and output speech.
Overall, the base quality of the integrated approach remains behind that of modular pipelines. Moshi, for example, prioritizes conversational fluidity and low latency over raw quality, and while it achieves decent intelligibility and speaker similarity, it is not yet intended to be competitive against state-of-the-art commercial TTS systems in terms of naturalness and expressiveness, as acknowledged by its authors [4], making the more common modular approach the preferred choice for voice assistant systems. This approach, with distinct components for speech-to-text (STT), natural language processing (NLP), and text-to-speech (TTS), allows for higher-quality outputs by leveraging advancements in each field. Benchmarking the performance of these individual components is critical not only for selecting the most effective models but also for ensuring system reliability and maintainability—since failures or bottlenecks in a modular pipeline can be isolated and resolved at the component level without retraining the entire system. This enables more targeted optimization and efficient integration of new models, which is essential for building robust voice assistant applications. Moreover, because the system is not end-to-end but modular, any quality or latency issues can be systematically traced to and addressed within the responsible module, streamlining both development and debugging processes.
Among the three core components of voice assistants—speech-to-text (STT), large language models (LLMs), and text-to-speech (TTS)—LLMs have received the most research attention due to rapid advancements in AI. Several benchmarks have been developed to assess their capabilities, such as BIG-Bench, which evaluate over 200 tasks spanning linguistics, logic, and world knowledge to test generalization limits [5], while MMLU measures accuracy across 57 academic subjects to assess reasoning depth [6]. HumanEval focuses on code generation accuracy using pass@k execution metrics [7], and MLPerf Inference benchmarks model latency and throughput under standardized deployment scenarios [8]. Project MPG introduces a combined “Goodness” and “Fastness” score to balance correctness with query-per-second efficiency [9]. Holistic chatbot evaluations such as the E2E Chatbot Benchmark assess semantic similarity against expert responses [10], MT-Bench-101 scores multi-turn conversational coherence [11], and Malode analyzes deployment feasibility in domain-specific contexts [12]. Finally, FACTS Grounding measures faithful, document-grounded generation using multi-judge evaluations across real-world enterprise domains [13]. Together, these benchmarks reflect a shift from accuracy-only metrics toward comprehensive evaluations incorporating latency, grounding, and real-world applicability.
There are also benchmarks that evaluate voice assistants holistically, assessing the entire end-to-end system rather than isolating individual modules, such as AudioBench [14], End-to-End Speech Benchmark (ESB) [15], S2S-Bench [16], VoiceBench [17], and CURATe [18], which will be discussed in subsequent sections. While these works provide critical insights into the LLM component and end-to-end systems’ performance, they leave a major gap in evaluating TTS performance—particularly its responsiveness, which is essential for real-time voice interactions. Unlike LLMs, TTS systems have received relatively little benchmarking attention, despite their direct impact on perceived latency, fluidity of conversation, and overall user experience.
This work addresses the gap in TTS benchmarking by introducing a baseline open-source benchmark for evaluating responsiveness in real-time voice assistants. While it can be seen as a testbed, its contribution goes beyond reporting latency values by providing a reproducible, extensible framework with transparent methodology, diverse datasets, and breadth of model comparison. Unlike prior evaluations that emphasize perceptual naturalness, raw timing outputs, or commercial API-based throughput, our framework unifies latency distribution, tail latency, and speech quality within a single open-source pipeline, ensuring that results are both replicable and directly relevant to user-perceived responsiveness. A key component of this design is a structured dataset approach that spans single words, two-word phrases, and full-length sentences of 12 and 18 words, reflecting the linguistic variability in real conversations from short backchannels to typical sentence-level utterances. By anchoring measurements in this systematically categorized dataset, the benchmark avoids the ad hoc or proprietary inputs used in prior work and provides a representative basis for fair evaluation. Furthermore, by adapting MLPerf’s latency methodology to the speech domain and reframing it around per-utterance responsiveness using median and P90 as representative statistics, we capture typical and worst-case experiences rather than isolated runs or bulk throughput. The benchmark also establishes standardized procedures for fair comparison, baseline results across representative models, and explicit rationale for metric choice, allowing the community to build upon a shared foundation rather than relying on closed or proprietary baselines. In this sense, our contribution is infrastructural: like MLPerf, it offers a benchmark that unifies fragmented evaluation practices and sets a baseline standard for fair progress measurement in TTS responsiveness, complementing quality-focused efforts and pointing toward more comprehensive future benchmarks. While we acknowledge that our work does not propose a novel model or algorithm, benchmarks themselves are infrastructural contributions: their value lies in defining standards, ensuring reproducibility, and enabling fair comparisons across systems. Our study plays this role for TTS responsiveness, providing a structured, open-source foundation that integrates dimensions previously addressed only in isolation and thereby moves the field toward a unified and reproducible evaluation standard.
As follows, Section 2 reviews the related work on LLMs, STT, and TTS; Section 3 details the benchmarking methodology; Section 4 describes the experimental setup; Section 5 presents the empirical findings; and Section 6 discusses broader implications and future directions. To orient the reader, Figure 1 summarizes the overall pipeline, from controlled text inputs through TTS generation and vocoding to audio output, followed by latency and quality evaluation and final aggregation. This figure provides a high-level overview, while Section 4 expands on the technical details and measurement procedures.
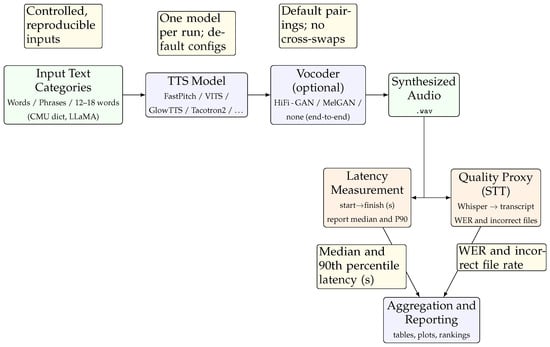
Figure 1.
End-to-end benchmarking pipeline: input text → TTS (and optional vocoder) → audio, with latency (s) and STT-based quality evaluation aggregated into tables/plots.
2. Related Works
Modern voice assistant systems build on transformer architectures that have rapidly become the dominant paradigm across modalities. As highlighted in [19], transformers differ fundamentally from earlier sequence models such as recurrent neural networks (RNNs) by enabling parallel input processing and more effective modeling of long-range dependencies, overcoming challenges such as vanishing gradients that limited recurrent approaches. Their minimal reliance on inductive biases makes them broadly adaptable across text, vision, audio, and speech, supported by design elements such as positional encodings to preserve sequence order and multi-headed attention to capture global context. Originally developed to address inefficiencies in signal processing, transformers were later applied to vision tasks, where a range of variants illustrate how architectural refinements balance scalability, data efficiency, and computational cost. The Vision Transformer (ViT), for example, demonstrated that pure transformer blocks could rival convolutional neural networks in image recognition, while the Data-efficient Image Transformer (DeiT) reduced the data requirements for training by leveraging knowledge distillation. The Swin Transformer introduced hierarchical attention windows to capture both local and global features efficiently, and the Pyramid Vision Transformer (PVT) extended scalability to dense prediction tasks, such as detection and segmentation. These innovations highlight how transformer design choices affect performance and efficiency, lessons that directly inform speech models where input sequences are similarly long, variable, and context-dependent. Taken together, these architectural insights provide the foundation of today’s large language models (LLMs) and speech-to-text (STT) and text-to-speech (TTS) systems and provide the backdrop for this section, where we review how benchmarking approaches for text-to-speech (TTS) systems and broader benchmarks designed to evaluate voice assistants end to end, including their TTS components, have evolved—from an early emphasis on accuracy alone toward more comprehensive evaluations that also consider responsiveness, latency, and real-time performance.
2.1. Text-to-Speech (TTS)
Benchmarking text-to-speech (TTS) models have historically emphasized speech quality, naturalness, and intelligibility while largely neglecting computational efficiency and real-time responsiveness. Most evaluations rely on subjective measures such as Mean Opinion Scores (MOSs) [20], where listeners rate naturalness on a scale, or on preference tests and crowdsourced judgments. While useful for capturing perceptual quality, these approaches are inherently limited: they are expensive to scale, difficult to reproduce consistently across studies, and provide no insight into latency or tail latency—metrics central to real-time virtual assistants. More recent efforts attempt to broaden the scope by adding structured intelligibility metrics or focusing on inference speed, yet each remains partial. Quality-oriented frameworks capture fidelity but omit responsiveness; latency-focused tools provide timing data but fail to integrate accuracy or robustness; and API-based evaluations often lack transparency and reproducibility, especially for open-source models. This fragmentation leaves a gap in benchmarking methodologies: no existing approach rigorously unites latency-sensitive evaluation with reproducible, open-source comparisons of TTS systems. Our study directly addresses this gap by placing responsiveness at the center of evaluation while maintaining a reproducible, model-agnostic framework.
Hugging Face’s TTS Arena [21,22] is one of the most well-known benchmarking efforts, offering a crowdsourced evaluation platform where users compare TTS models by listening to side-by-side samples and voting on which sounds more natural, clear, and expressive. While this approach provides valuable human feedback, it does not explicitly or systematically assess output accuracy; however, inaccuracies in word generation can indirectly affect scores since they influence user preference. The platform also has notable limitations: evaluations are inherently subjective and may shift with changing user preferences, it does not measure latency or computational efficiency, and it relies on participant activity—causing newer models to be underrepresented or unevenly rated.
Picovoice (https://github.com/Picovoice/tts-latency-benchmark (accessed on 1 August 2025)) [23] takes a different approach by focusing specifically on TTS inference speed. Their benchmark is lightweight and extensible, measuring latency at individual processing stages such as text preprocessing, model inference, and waveform generation. While this provides useful raw measurements of system components, the framework is limited in two key ways. First, it emphasizes speed in isolation, without incorporating quality assessment, which means models that produce unnatural or less intelligible speech may still appear favorable. Second, its scope is largely restricted to embedded or on-device scenarios, overlooking broader deployment settings. Most importantly, Picovoice reports raw timing breakdowns but does not synthesize them into representative indicators of user-perceived responsiveness. In contrast, our framework complements theirs by not only collecting latency data but also interpreting it through descriptive statistics—such as median latency and tail latency (P90)—that better capture typical and worst-case experiences of real-time interaction. Moreover, unlike Picovoice, we incorporate speech quality alongside latency, evaluating if models are not only fast but also intelligible and natural. Thus, while Picovoice demonstrates how latency can be measured at a granular level, our contribution advances this line of work by translating raw measurements into reproducible, user-centered benchmarks that integrate both responsiveness and quality, providing a more faithful representation of end-to-end performance in real-time virtual assistants.
Artificial Analysis (https://artificialanalysis.ai/text-to-speech (accessed on 1 August 2025)) [24] presents a more holistic evaluation framework, assessing both quality and performance. Their methodology benchmarks various commercial and open-source TTS models across key dimensions, including naturalness, intelligibility, and latency. They employ serverless API-based evaluation, where models are tested in real-world conditions to measure their inference time and quality trade-offs. However, like TTS Arena, Artificial Analysis relies on human evaluations for speech quality, which introduces subjectivity. Moreover, their focus on commercial API-based models may not fully capture open-source or offline TTS systems, limiting its applicability in resource-constrained environments.
Another work [25] extends benchmarking efforts by providing a comparative analysis of six leading TTS models, using a structured dataset of 500 diverse text prompts. Each output was rated by three expert human evaluators using structured criteria, ensuring a controlled and consistent evaluation process. Unlike previous works, this study incorporates structured feedback on intelligibility, pronunciation accuracy, and audio quality. However, it does not explicitly benchmark latency or responsiveness, making it less relevant for real-time applications. Additionally, since Labelbox focuses on commercial solutions, open-source models are not evaluated, leaving gaps in benchmarking freely available TTS systems.
Finally, Minixhofer et al. (2024) provide one of the most comprehensive attempts to establish an objective, scalable evaluation metric for TTS models [26]. The Text-to-Speech Distribution Score (TTSDS) benchmark quantifies synthetic speech quality by analyzing how closely a model’s output distribution aligns with real human speech. Unlike MOS-based benchmarks, it removes reliance on subjective ratings, enabling reproducible and cross-study comparisons. Intelligibility is evaluated by passing the generated speech through speech-to-text (STT) models (wav2vec 2.0 and Whisper) to obtain transcripts, which are then compared with the original text using the word error rate (WER). Alongside intelligibility, the TTSDS incorporates four additional factors—prosody, speaker identity, environmental artifacts, and general distribution similarity—summarized below.
- Intelligibility—this is measured using the word error rate (WER) from STT models.
- Prosody—this is evaluated via pitch variation and rhythm consistency.
- Speaker Identity—this measures how closely the generated voice matches natural human speech by comparing voice features (e.g., tone and timbre) between synthetic and real recordings.
- Environmental Artifacts—this measures unwanted noise or distortions in the generated audio, with higher artifact levels indicating lower audio quality.
- General Distribution Similarity—this uses self-supervised embeddings to compare TTS outputs with real speech data.
It benchmarks 35 TTS systems developed between 2008 and 2024, demonstrating that objective factor-based scoring correlates strongly with human evaluations. However, the TTSDS does not explicitly evaluate latency, meaning it does not fully address responsiveness, which is critical for real-time TTS applications.
Across these efforts, a clear pattern emerges: existing benchmarks each address part of the problem space but none sufficiently capture the requirements of real-time virtual assistants. TTS Arena [21,22] provides breadth through crowdsourced judgments but is entirely subjective, lacking reproducibility and ignoring latency. Picovoice [23] focuses narrowly on latency and provides raw timing outputs for each run, but it does not synthesize these into representative indicators of user-perceived responsiveness and does not account for speech quality. Moreover, its design is oriented toward embedded and on-device contexts, limiting its relevance to broader deployments. Artificial Analysis [24] goes further by reporting both latency and quality, yet its methodology is concentrated on commercial API-based models and emphasizes throughput-style metrics, such as characters per second. While valuable for understanding large-scale efficiency, this approach does not capture the per-utterance responsiveness that defines interactive assistants, and its reliance on proprietary systems leaves no reproducible path for open-source evaluation. Labelbox [25] improves on earlier work by introducing structured expert ratings for intelligibility and pronunciation, but it omits latency entirely and focuses exclusively on commercial solutions, excluding open-source models. By contrast, the TTSDS framework [26] represents the strongest step toward objective and reproducible quality evaluation, offering metrics for intelligibility, prosody, speaker identity, environmental artifacts, and distributional similarity. Yet, it explicitly omits latency, leaving responsiveness—the defining requirement for real-time assistants—unaddressed. Our contribution fills this gap by providing a reproducible, open-source methodology that not only reports latency but also interprets it through descriptive statistics (median and tail latency) and integrates speech quality. In this way, we directly complement the TTSDS: their framework establishes rigorous, distribution-based measures of fidelity, while ours establishes rigorous measures of responsiveness. Our contribution fills this gap by providing a reproducible, open-source methodology that not only reports latency but also interprets it through descriptive statistics (median and tail latency) and integrates speech quality, thereby directly reflecting user experience in real-time settings. In addition, our benchmark is grounded in a structured dataset design that spans single words, two-word phrases, and full-length sentences, ensuring that evaluations reflect the linguistic diversity of real conversations rather than ad hoc or proprietary inputs. This structured approach, combined with our open-source implementation, enables broad cross-model comparisons under a unified methodology—something missing from prior efforts that were limited to embedded, commercial, or proprietary contexts. In this sense, our work extends the landscape of existing benchmarks: unlike Picovoice [23], which reports unsynthesized raw timings, we provide representative measures of responsiveness grounded in a structured and diverse dataset; unlike Artificial Analysis [24], which emphasizes proprietary API-based throughput, we prioritize reproducibility, open-source accessibility, and broad cross-model comparison under a unified methodology. Most importantly, our framework complements TTSDS [26], which rigorously quantifies fidelity but omits latency, by supplying the missing responsiveness dimension. Together, these contributions point toward the possibility of a unified benchmark that addresses both fidelity and speed while maintaining objectivity and reproducibility.
2.2. End-to-End Systems
In addition to benchmarks that evaluate the three modular components separately, several recent works have introduced benchmarks that assess speech-enabled systems in an end-to-end manner.
AudioBench [14] was introduced as a benchmark for audio large language models (AudioLLMs) that take audio as input and generate textual responses to natural language instructions. It unifies evaluation across speech semantics, environmental audio understanding, and paralinguistic voice traits through eight tasks and 26 datasets, 7 of which are newly collected or adapted. These tasks span areas such as speech understanding (e.g., automatic speech recognition and question answering), audio-scene understanding (e.g., audio captioning), and voice-related attributes (e.g., emotion and accent recognition). The benchmark tests robustness by varying prompt templates and input lengths (from seconds to minutes), totaling over 400 h and 100k samples. Since the benchmark outputs are free-form text rather than fixed choices, AudioBench uses a model-as-judge approach, where large language models automatically evaluate the generated answers instead of relying on human annotators. The authors report high agreement between different judge models, validating the reliability of this automated scoring method.
S2S-Bench [16] is designed to measure “intelligence degradation,” or the drop in reasoning ability when a model processes audio tokens instead of text tokens. It compares two conditions: speech-to-text (S → T), where audio input is tokenized and processed by the model, and a text-to-text (T → T) upper bound using the same semantic content. Each test sample contains two continuations—a correct (positive) and an incorrect (negative) option—and the model’s task is to prefer the positive one. Perplexity, a standard language modeling metric indicating how confident the model is about a sequence (lower means more confident), is used to score each option. Accuracy is defined as the proportion of times the positive continuation receives lower perplexity than the negative, and the benchmark also analyzes the perplexity “gap” between the two options to gauge how strongly the model prefers the correct answer. Results show a consistent performance drop in the S → T setting across all tested reasoning tasks, confirming that audio tokenization introduces a measurable degradation relative to the text-only upper bound.
VoiceBench [17] introduces a benchmark for assessing how effectively LLM-based voice assistants interpret spoken commands in realistic conditions. Unlike traditional speech-to-text (STT) tests, it examines robustness to factors like speaker variation, background noise, and linguistic complexity, covering tasks in knowledge retrieval, instruction following, and safety adherence. Results show notable performance gaps between end-to-end voice assistants and modular ASR-LLM pipelines, with current models struggling under noisy or diverse inputs, underscoring the need for greater real-world resilience.
Conversely, CURATe [18] evaluates the ability of conversational AI to sustain personalized alignment during interactions. It benchmarks ten leading LLM-based assistants across 337 scenarios, focusing on their capacity to respect user-specific safety constraints and contextual preferences. Findings highlight recurring issues such as neglecting safety-critical instructions, excessive agreement (sycophancy), and inattentiveness to personalized context while demonstrating that prompting models to explicitly acknowledge safety cues can enhance adherence. CURATe thus offers a structured framework for measuring consistency and trustworthiness in conversational AI.
While end-to-end benchmarks are less directly aligned with our focus on modular TTS responsiveness, they are nonetheless relevant in framing how speech-enabled assistants are evaluated holistically. AudioBench [14] demonstrates breadth across multiple audio tasks, but its reliance on model-as-judge raises concerns about evaluation stability, and it does not isolate latency or responsiveness—critical factors for real-time use cases. S2S-Bench [16] makes an important contribution by quantifying “intelligence degradation” when models process audio tokens, yet it is confined to perplexity-based reasoning tasks and does not extend to end-to-end responsiveness or speech quality. VoiceBench [17] brings evaluation closer to practical voice assistants by testing robustness to noise, speaker variation, and linguistic complexity, but its emphasis remains on interpretation accuracy, leaving system latency and user-perceived responsiveness unmeasured. CURATe [18] highlights safety and personalization, which are crucial dimensions of conversational AI, but again operates at the interaction and alignment level rather than capturing the computational performance of speech systems. Together, these efforts illustrate how end-to-end benchmarks excel at assessing semantic fidelity, robustness, and safety but consistently lack integration of efficiency and responsiveness metrics. Future work may entail bridging these perspectives—integrating latency- and quality-focused measures, such as those in our framework, into broader end-to-end evaluations—so that benchmarks capture not only what assistants understand and how safely they respond but also how quickly and reliably they do so in real time.
3. Benchmarking Methodology
This project is influenced by the MLPerf Inference framework [8], a widely recognized benchmark suite for evaluating machine learning systems across different deployment scenarios. Among its four scenarios—single-stream, multistream, server, and offline—we adopt the single-stream setting because it matches our target deployment: a virtual assistant running on a single local device where interaction is strictly one-to-one and sequential (one user utterance leads to one model response that is synthesized into speech). In contrast, the multistream and server scenarios are not relevant to this study. The server scenario assumes a backend capable of handling many independent clients with stochastic request arrivals, measuring throughput (queries per second) under service-level latency constraints—conditions that presuppose a distributed serving infrastructure, which we do not set up. Similarly, the multistream scenario evaluates systems that process multiple streams in parallel with tight time synchronization, but a local virtual assistant does not multiplex requests or handle simultaneous sessions. In practice, the quality-of-service objective for voice assistants is perceived latency for a single user, not aggregate throughput across many users, and even when cloud-based TTS services are called, they are still consumed as a single response per utterance. Moreover, many open-source TTS implementations lack thread-safe or multi-instance streaming modes, meaning artificial concurrency would introduce backend-dependent biases without reflecting real usage. For these reasons, we evaluate models under the single-stream configuration, feeding category-stratified text inputs, recording per-utterance latency, and reporting both median and tail (90th percentile) latency to capture typical and worst-case responsiveness, thereby reflecting realistic single-user interaction rather than throughput-oriented load tests.
This paper defines TTS input processing as the sequence where text is received and converted into an output audio file. Because streaming support varies—some models offer native streaming while others rely on external tools—evaluating only file generation time ensures fair, consistent measurement of responsiveness across all models.
For speech processing models, the task is to transcribe audio input into text accurately and efficiently. The following metrics are chosen for evaluating model responsiveness and quality:
- Latency: This measures the time from when the model begins processing the text input to when the generated audio file is fully produced. This study reports the median latency, which summarizes typical synthesis speed across the dataset while minimizing the effect of outliers. Lower median latency directly indicates faster audio generation, which is critical for real-time voice assistant performance.where
- −
- is the timestamp when the text input is passed to the TTS model;
- −
- is the timestamp when the audio file generation is completed.
- Tail Latency: This captures worst-case performance by measuring the 90th percentile latency across all samples. This reflects edge-case delays relevant to voice assistant interactions; keeping this value low is essential for maintaining smooth and responsive user experiences.where
- −
- is the 90th percentile latency across the dataset.
While we did compute throughput-style metrics (queries per second under load), we do not report them here, as they are strongly correlated with latency statistics and add little beyond what is already captured by median and 90th percentile latencies; including them would risk overwhelming readers and distract from our focus on per-utterance responsiveness, which is the critical factor for interactive voice assistants.
In addition to latency metrics, this paper evaluates audio quality as a primary measure of synthesis performance. These metrics directly assess the clarity, naturalness, and intelligibility of the generated speech, focusing on phrases and sentences rather than isolated single-word utterances. In this study, audio quality is further examined alongside responsiveness to investigate whether there is any trade-off between synthesis speed and perceived quality.
To evaluate audio quality, this study uses a speech-to-text (STT) model to transcribe the audio generated by each TTS system back into text. The resulting transcription is then compared against the original input text to measure how accurately the TTS model preserved the intended content. Both the ground-truth input text and the STT-produced transcription undergo normalization following Whisper’s evaluation guidelines [27], which include lowercasing, punctuation removal, whitespace standardization, contraction normalization, and numeric formatting. This preprocessing ensures that the comparison focuses on semantic accuracy rather than superficial formatting differences, providing a fair assessment of how faithfully each TTS model conveys the intended speech content.
- Percentage of Incorrect Audio Files: The proportion of generated audio files whose transcriptions, after being converted back to text via STT and normalized as described above, do not exactly match the original input text. In other words, this metric is based on strict string equality between the normalized input and output texts.
- Overall WER: This is a cumulative measure of the word error rate (WER) across all transcriptions. The word error rate (WER) is a common metric used to evaluate transcription accuracy, calculated for a single sample aswhere
- −
- S is the number of substitutions (incorrectly transcribed words);
- −
- D is the number of deletions (missing words);
- −
- I is the number of insertions (extra words added);
- −
- N is the total number of words in the reference transcript.
For multiple transcriptions, the overall WER, used by Whisper [27], aggregates the WER across all samples by summing the total number of errors (substitutions, deletions, and insertions) across all transcriptions and dividing by the total number of words in all reference transcripts:where i represents each individual sample in the dataset. This method provides a cumulative error rate that reflects the overall performance of the transcription system across a dataset rather than an average of individual WER values. - Median WER (Mismatched Files): In addition to the Summation-Based WER following Whisper’s methodology, we also compute the median WER specifically for files with mismatched transcriptions, providing further insight into transcription accuracy variability.
We acknowledge that relying on Whisper’s STT for audio quality evaluation has shortcomings, as transcription errors may conflate with TTS inaccuracies and introduce bias into intelligibility estimates. However, because the same STT model is applied consistently across all TTS systems, the comparison remains fair in relative terms and provides a scalable, reproducible basis for benchmarking. We also recognize that user-centered evaluations such as MOS or AB preference testing could capture perceptual naturalness more directly, but these approaches were excluded in this study due to the high cost and annotation effort required to evaluate all generated audio at scale. While not feasible here, hybrid evaluations that combine structured automated metrics with selective human assessments would be a valuable direction for future work and could further strengthen the conclusions of benchmarks like ours.
Finally, as secondary metrics, we monitored system-level resource utilization during inference, but only for the top-performing models. This choice reflects our focus on deployment-relevant considerations without expanding the scope of measurement to all models. The following metrics were collected:
- GPU memory usage (MB): peak allocation per inference, reported by PyTorch (version 2.1.0 for Fastpitch and VITS, 2.8.0 for Microsoft Windows Speech) We report the median of peak values across sampled inputs, as this provides a more robust measure than the mean when outliers occur.
- GPU utilization (%) and power draw (W): sampled via nvidia-smi at 0.1-s intervals. For each input, we compute the average utilization and power, and across the dataset we report the mean.
- CPU utilization (%): collected using the psutil library, sampled at the same interval. Per-input averages are calculated, and the mean across inputs is reported.
A key limitation is that GPU utilization reported by nvidia-smi is system-wide rather than process-specific. While per-process tracking could in principle be achieved through NVML, this was not available on the devices used in our benchmarking environment. Consequently, our measurements may include minor background GPU activity unrelated to the TTS models. However, this constraint also reflects deployment reality: TTS systems are rarely executed in isolation, and real-world hardware is often shared with other processes. Thus, system-level monitoring provides a practical and conservative estimate of the true resource demands of these models. In practice, GPU memory usage is reported with the median to reduce sensitivity to rare spikes, while GPU/CPU utilization and power draw are summarized with the mean to capture overall system load. These metrics are treated as secondary indicators: results are presented only for the top-performing models in the Results Section, with broader implications discussed in the Discussion Section.
4. Experiments—Benchmarked Text Inputs
This section describes the experiments conducted to measure each model’s performance, detailing the datasets of text inputs used as well as models tested.
4.1. Evaluation Categories
First, to reflect the models’ capabilities of naturally transforming text into speech in conversations, we look into various elements in human speech—where certain sentence types consist solely of words or short phrases that can function as complete, standalone utterances. We also take into account the elements that are present in dialogues, including utterances; backchannel words such as “uh-huh” and “I see”; or filler and transition words such as “well”, “so”, and “anyway”, to define the range of inputs for models testing. Accordingly, this project evaluates single-word utterances and two-word phrases that can function as complete sentences. Furthermore, full-length sentences are incorporated to capture typical structures observed in standard written and spoken communication. A guideline for scientific writings suggested 12–17 words to be the optimal length [28], while another one indicated today’s experts recommended 15–18 words per sentence [29]. To accommodate these guidelines, we incorporate 12-word sentences and 18-word sentences into our benchmarking, and to sum up, these criteria for experimentation are presented in Table 1:

Table 1.
Categorization of benchmarked text input types with word count, sources, and data size.
This dataset was designed in a structured way to test different aspects of TTS performance step by step. The single-word sets from the CMU Dictionary let us check whether models handle words with different numbers of syllables consistently—for example, whether a one-syllable word like “yes” is processed differently from a two-syllable word like “okay.” These short, controlled cases help us spot issues in how models deal with very small speech units. We then add the most common standalone words and two-word phrases, which cover frequent items in everyday conversation, such as short answers, imperatives, and filler or backchannel words (“uh-huh,” “I see,” and “well”). These are especially relevant because virtual assistants often need to produce quick, simple utterances rather than long sentences. To capture the kinds of outputs that are likely to come from modern assistant pipelines, we also include phrases and sentences generated by an LLM, since in real use the TTS system typically speaks text produced by an LLM. Finally, we include 12-word and 18-word sentences, which represent more natural, full sentences and align with recommended ranges for effective communication. Together, this progression from single syllables to common words and phrases, and then to realistic sentence-level utterances, provides both targeted tests for specific challenges and broader coverage of the kinds of speech virtual assistants actually need to produce.
To ensure a robust evaluation, while latency is computed for all input categories, audio quality metrics are assessed only on 12-word and 18-word sentences generated by Llama3-8B. This choice avoids the limitations of single-word evaluations: while the benchmark includes standalone words (e.g., “Yes” and “Stop”), such cases can yield misleading accuracy scores because multiple pronunciations may be valid and the lack of surrounding context provides few cues for disambiguation. Multi-word phrases and sentences, by contrast, more closely resemble natural speech patterns and offer richer contextual information, resulting in a more reliable assessment of audio quality.
4.2. TTS Models
This study focuses on evaluating the most popular and widely used TTS models, as identified through extensive literature and community engagement metrics—such as GitHub stars or likes—alongside models developed by reputable service providers. Since voice assistants typically do not require voice cloning or dynamic multi-voice capabilities, we prioritize models trained on single-speaker datasets. We also include models trained on multiple voices, provided that each voice is independently preset—meaning the model is trained on specific voices individually and allows users to choose from those predefined options.
In many TTS systems, the core model is responsible for converting input text into intermediate audio representations, typically mel-spectrograms. These spectrograms must then be transformed into actual audio waveforms using a vocoder. Therefore, unless the TTS model is fully end-to-end, a separate vocoder is required to synthesize the final audio output. In this study, we focus on TTS models that perform the text-to-spectrogram transformation, however still making use of vocoders where applicable. The list of models and architectures evaluated is presented in Table 2:

Table 2.
Summary of TTS models evaluated in this study.
It is important to note the varying role of vocoders across the evaluated systems. Certain models, such as VITS, are designed to be fully end-to-end and therefore do not require a separate vocoder stage. Others, such as BarkTTS and VALL-E X, employ EnCodec as an integral part of their design, which cannot be trivially substituted or exchanged for alternative components. Meanwhile, several Coqui models (e.g., FastPitch, Overflow, Glow-TTS, and Tacotron variants) rely on default vocoder pairings such as HiFi-GAN or Multiband MelGAN, which are recommended and optimized by their developers. As these pairings are provided and tuned specifically for each model, systematically re-evaluating all possible combinations of TTS models and vocoders would be both impractical and of limited analytical value. For this reason, the present study evaluates each model using its default, developer-recommended configuration, ensuring consistency with common usage patterns and fair comparison across systems.
The experiments are conducted on a machine equipped with a 13th Gen Intel Core i9-13900HX processor (24 cores; 32 threads) and an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop GPU with 8 GB of VRAM. This setup reflects the capabilities of a high-end consumer device rather than specialized server hardware, making the results relevant for real-world virtual assistant deployments on powerful laptops or desktops. However, this configuration does not capture the constraints of edge devices with low-power CPUs or mobile hardware, nor the scalability of cloud-based environments. Future iterations of this benchmark should therefore extend evaluations across a wider range of device tiers—including edge, mobile, cloud, and high-performance systems—to provide a more complete picture of TTS responsiveness under diverse deployment conditions. All experiments in this study are run with each model’s default configurations and pre-trained weights as released by their developers, without fine-tuning or manual hyperparameter adjustments, to ensure fair and consistent comparison.
5. Results
This section provides an overview of model performance, focusing on both responsiveness and audio quality for the 12-word and 18-word sentence input types. We begin with a broad discussion of overall trends before examining the results and their implications in greater details in the subsequent section.
5.1. Responsiveness
Overall, as shown in Table 3 and further illustrated in Figure 2 and Figure 3, FastPitch consistently achieves the best performance across both median and 90th percentile rankings. It ranks first or second in nearly every category, achieving first place in both the median and 90th percentile for most inputs such as two-syllable words, most common words, and LLM two-word phrases. Even in longer sequences like 12-word and 18-word sentences, it maintains the top-three positions (median rank 1; P90 rank 3). This highlights FastPitch’s exceptional balance between typical and worst-case latency, ensuring predictable real-time responsiveness across varying input complexities.

Table 3.
Median (M) and 90th percentile (P90) latencies across all benchmarked text input categories (s).
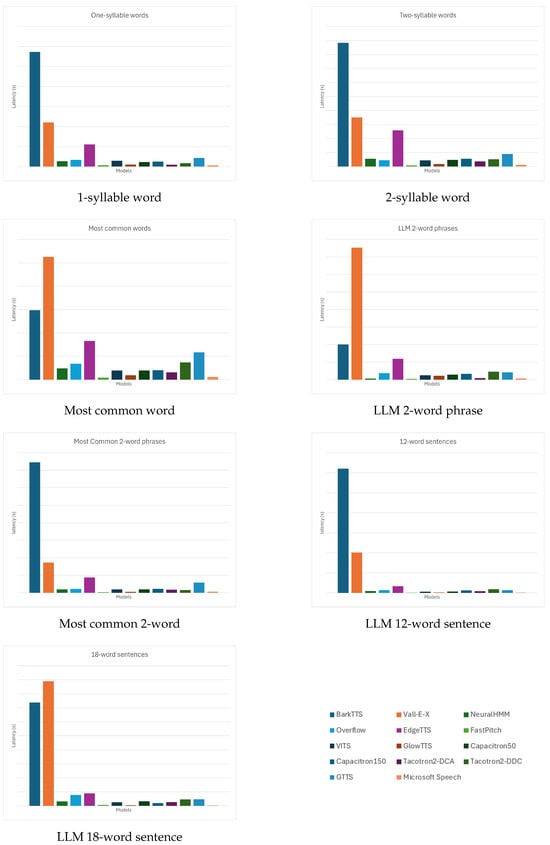
Figure 2.
Median latency across seven input categories.
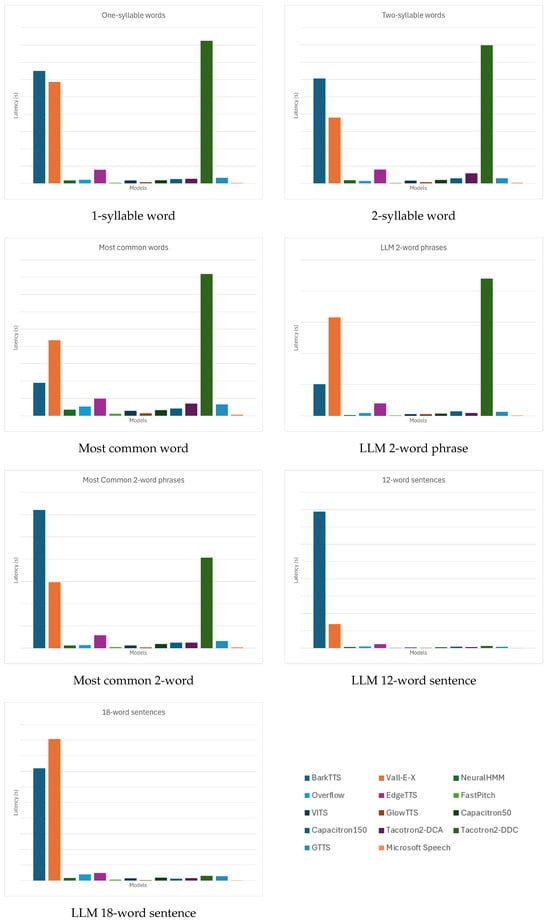
Figure 3.
The 90th percentile latency across seven input categories.
Microsoft Speech follows closely behind and frequently secures first or second place in both the median and P90 rankings across almost all categories. It is ranked first in median latency for one-syllable words, tied first for most common words, and first again for 12-word sentences. Even at the 90th percentile, Microsoft Speech rarely falls below rank 3, showing remarkable stability despite being a non-neural, CPU-based system. Its consistent top-tier performance demonstrates how deterministic architectures can outperform many neural models under variable conditions.
GlowTTS and VITS also perform strongly, staying within the top five in most categories. GlowTTS achieves ranks as high as third for both median and P90 in shorter inputs (e.g., one-syllable and two-syllable words) and second for 18-word sentences at P90, though occasionally dropping to fifth in LLM 2-word phrases. VITS shows similar behavior, with steady mid-upper rankings (median rank 4–6) and slightly worse tail performance (P90 ranks 4–5), indicating minor degradation as inputs grow more complex.
The middle tier consists of NeuralHMM, Overflow, and Tacotron2-DCA. NeuralHMM ranks mid-table, for example, 8th in median and 6th in P90 for one-syllable words, and improves to 4th in most common words (median). However, its P90 scores degrade with input length, reaching 7th for 18-word sentences. Overflow follows a similar trajectory, ranking around 6th–10th across categories; for instance, it is 10th median and 7th P90 for one-syllable words and 9th/8th for most common words. Tacotron2-DCA places better at median (2nd–4th in shorter phrases) but worsens in P90, hitting 10th for two-syllable words and 9th for most common words, indicating occasional latency spikes.
Capacitron50 and Capacitron150 occupy mid-lower rankings. Capacitron50 is typically 6th–7th median (e.g., 6th for one-syllable words and 7th for most common words) and similarly placed for P90. Capacitron150 fares slightly worse, with 9th median and 9th P90 for one-syllable words and 7th–8th across other categories. The minimal performance gap between the 50- and 150-unit variants suggests increased model size does not significantly alleviate tail latency issues.
At the bottom, Vall-E-X and BarkTTS consistently rank last, with extremely high median and P90 latencies across all input lengths. Vall-E-X sits consistently at 13th–14th for both median and P90, for example, 13th median and 13th P90 in most common words, and 14th in 18-word sentences. BarkTTS is similarly poor, often tied for 14th (e.g., 14th median and 14th P90 in one-syllable and two-syllable words) and showing no improvement even in shorter inputs. These rankings reflect their computationally heavy architectures and lack of optimization for low-latency inference.
A particularly striking outlier is Tacotron2-DDC. While its median ranks are mid-tier (e.g., 4th for one-syllable words and 8th for two-syllable words), its P90 ranks collapse to last place in almost every input (14th P90 for one-syllable words; 13th–14th for longer inputs). This discrepancy stems from pathological inference behavior, where stop-token failures and alignment drift cause excessively long outputs even for short inputs.
Cloud-based systems like GTTS and EdgeTTS show distinct patterns. GTTS generally ranks in the 10th–11th range for both median and P90, such as 10th median and 10th P90 for one-syllable words, reflecting moderate but stable performance. EdgeTTS fares slightly worse, 12th in both median and P90 for one-syllable words and 11th–12th for most categories, with tail latencies particularly affected by network fluctuations. These results highlight how cloud services, while convenient, struggle to match the deterministic low-latency performance of local neural models, like FastPitch or GlowTTS.
5.2. Audio Quality
Table 4 shows the audio quality tradeoff Microsoft Windows Speech, GTTS, and EdgeTTS emerge as the best overall performers. All three achieve extremely low incorrect file rates—between 2 and 4% for 12-word inputs and around 4% for 18-word inputs—with an overall WER consistently below 0.5. The median WER remains low (approx. 10–16), demonstrating both stability and precision. Their consistent accuracy across sentence lengths places them firmly at the top of the ranking. Notably, Microsoft Windows Speech achieves this despite being CPU-based and non-neural, highlighting the efficiency of its deterministic synthesis pipeline. GTTS and EdgeTTS, despite being cloud-based, maintain similarly high quality, with minimal degradation even as the input length doubles.

Table 4.
TTS Models’ Audio Quality for LLM-Generated 12-Word and 18-Word Sentence Inputs.
Among locally hosted neural models, VITS demonstrates the strongest performance in audio quality. It records incorrect rates of just 5.11% (12 word) and 7.11% (18 word), combined with the lowest overall WER among local models (approx. 0.65) and consistently low median WER values (approx. 5–8%). FastPitch and GlowTTS follow closely, with slightly higher incorrect rates (7–20%) and WER values around 0.7–1.8, remaining highly competitive in quality despite their focus on speed.
Mid-tier results are observed for Tacotron2-DCA, Tacotron2-DDC, and Overflow. These models maintain moderate incorrect rates (approx. 12–20%) and an overall WER between 1 and 3. While Tacotron2-DDC suffers from severe tail latency issues in responsiveness, its quality metrics remain stable, suggesting that overly long outputs do not necessarily lead to higher transcription mismatches. Overflow and Tacotron2-DCA show similar performance, with modest error rates but less consistency compared to top-tier models.
NeuralHMM and the Capacitron series perform worse in terms of quality. NeuralHMM exhibits error rates exceeding 50% and an overall WER around 8.5, indicating frequent synthesis failures or alignment errors. Capacitron50 and Capacitron150 fare slightly better but still remain in the lower tier, with 17–28% incorrect rates and overall WER between 4 and 8, reflecting inconsistent handling of longer phrases.
Vall-E-X and BarkTTS consistently deliver the lowest quality scores. Both models show incorrect rates exceeding 25–32% and an overall WER above 3.5–5, with the median WER comparable to low-performing models despite significantly heavier architectures. Their degradation worsens with longer inputs, highlighting poor optimization for short prompts and limited robustness to input length scaling.
Overall, cloud-based models (GTTS and EdgeTTS) and in-built Microsoft Windows Speech dominate the quality metrics, showing the most accurate and stable outputs, while VITS leads among locally hosted neural architectures. FastPitch and GlowTTS also maintain high quality with slightly more variability, while models like Vall-E-X, BarkTTS, and Capacitron variants consistently trail behind due to higher error rates and poor robustness.
5.3. Secondary Metric: System Resource Utilization
Table 5 report secondary system-level resource utilization metrics for a set of representative categories from the top-performing models only. This restriction avoids diluting the reader’s focus while still providing practical insight into deployment feasibility. These metrics capture GPU memory usage, GPU utilization and power draw, and CPU utilization, which serve as relevant references for deployment on resource-constrained environments such as consumer devices and edge platforms.

Table 5.
System-level resource utilization metrics for top-performing models across input lengths.
By including these results, we provide context beyond responsiveness and audio quality, highlighting how models interact with underlying hardware during inference. The reported values are intended as indicative references rather than exhaustive benchmarks across all evaluated systems. A more detailed interpretation of their implications for efficiency and deployment trade-offs is provided in the Discussion Section.
6. Discussions and Future Works
6.1. High-Performing Models: Responsiveness, Quality Balance, and Deployment Considerations
One of the primary aims of this benchmarking study was to identify whether any text-to-speech (TTS) models could deliver both low latency and high audio quality consistently across a range of input lengths. Most models exhibited trade-offs—excelling in one dimension while underperforming in the other. However, Microsoft Speech stands out as the clear overall leader. Despite being a CPU-based, non-neural system, it achieves top-tier responsiveness and audio quality simultaneously, ranking first or second in nearly every median and 90th percentile latency category and also securing the lowest error rates in audio quality metrics (approximately 2–4% incorrect files; overall WER around 0.39–0.41). Its deterministic design avoids pathological tail latency spikes and maintains pristine transcription fidelity even for long inputs, making it uniquely suited for latency-critical real-time applications.
In terms of pure responsiveness, FastPitch remains the fastest neural model in this benchmark. Its feed-forward, non-autoregressive design consistently ranks first in median and tail latency across almost every category, including one- and two-syllable words, most common words, and short phrases. Even in longer sentences (12 word and 18 word), it maintains the top-three positions, highlighting its predictability under load. However, FastPitch’s audio quality lags behind the top tier: its incorrect rates are slightly higher (around 7–9%), and its overall WER (around 0.7–0.8) is above the best performers. While still competitive and suitable for real-time systems where speed is paramount, its quality ceiling prevents it from unseating Microsoft Speech as the best all-rounder. This performance reflects FastPitch’s feed-forward, non-autoregressive architecture, which avoids the sequential bottlenecks inherent to autoregressive models like Tacotron2 or Bark. By predicting mel-spectrogram frames in parallel rather than step-by-step, FastPitch achieves highly predictable runtimes and avoids catastrophic attention failures that plague autoregressive baselines [42]. However, this architectural choice also introduces limitations in expressivity and prosody modeling, which helps explain its higher error rates and weaker WER relative to more flexible but slower models. In practice, this positions FastPitch as a latency-optimized architecture that excels in real-time settings but with a ceiling in quality that prevents it from displacing more balanced contenders.
Conversely, EdgeTTS and Google’s GTTS dominate the audio quality leaderboard. Both achieve error rates in the 2–4% range and an overall WER below 0.5, rivaling or even matching Microsoft Speech for transcription fidelity. However, their cloud-based nature introduces significant responsiveness issues. GTTS performs mid-tier in latency (10th–11th ranks across most inputs), while EdgeTTS frequently ranks near the bottom (11th–12th at P90) due to network variability and API response times. These results underline a key trade-off: while cloud services can deliver exceptional quality, their unpredictable latency makes them unsuitable for deterministic real-time deployments.
Among locally hosted neural architectures, VITS strikes the best balance between speed and quality. It ranks mid-upper for latency (median ranks 4–6; P90 ranks 4–5) and delivers the lowest WER among all neural models (approximately 0.65), with incorrect rates around 5–7%. This combination makes VITS a strong candidate where moderate latency is acceptable but higher audio fidelity is desired, such as offline synthesis or user-facing content generation. VITS’s competitive showing stems from its integrated end-to-end architecture, which unifies acoustic modeling, duration prediction, and vocoding in a single variational framework [43]. Unlike two-stage pipelines that combine separate TTS and vocoder models, VITS benefits from joint training, reducing error propagation and improving robustness across input lengths. The model further leverages normalizing flows and adversarial training to capture natural prosody and reduce alignment errors, which accounts for its lower WER compared to other neural systems. While this comes at the cost of slightly higher computational demand than FastPitch, VITS represents a more balanced design—sacrificing some responsiveness for a noticeable gain in fidelity and stability.
While occupying the mid-tier in our benchmarks, models such as GlowTTS, NeuralHMM, OverFlow, and Tacotron2-DCA/Capacitron variants illustrate important architectural contrasts with the top performers. GlowTTS, for instance, was originally reported to deliver strong efficiency due to its non-autoregressive, flow-based design coupled with monotonic alignments [44]. However, in our results, FastPitch consistently outperformed GlowTTS in latency despite earlier reports favoring GlowTTS. This divergence can be explained by FastPitch’s fully feed-forward architecture, which bypasses both flow sampling and complex alignment mechanisms. In contrast, GlowTTS retains computational overhead from flow inversion steps, which can inflate per-sentence synthesis time even if the model remains parallel in principle.
Neural HMM-based models and their extension, OverFlow, were proposed to remedy common attention failures by enforcing monotonicity and introducing exact probabilistic training [37,40]. While these designs improve robustness—reducing catastrophic failures and yielding natural speech under constrained training—their autoregressive generation limits throughput and makes them slower on longer sentences compared to FastPitch or VITS. OverFlow’s integration of normalizing flows further increases model expressiveness but at additional computational cost, which helps explain the degradation in responsiveness we observe at scale.
At the bottom, Tacotron2-DDC, Vall-E-X, and BarkTTS show severe limitations. Tacotron2-DDC suffers catastrophic tail latency failures (e.g., 16.49 s P90 for one-syllable words) due to attention/stop-token misalignment, despite decent median scores. This demonstrates why attention-based autoregressive systems are increasingly disfavored for low-latency scenarios. As the prior literature notes, Tacotron2’s recurrent sequence-to-sequence design with attention is prone to alignment errors and stop-token mispredictions [48]. These pathologies were confirmed in our benchmarks, where Tacotron2-DDC suffered catastrophic tail latency failures despite reasonable median scores. Capacitron variants, despite scaling efforts, inherit these inefficiencies and thus lag behind non-autoregressive baselines. Vall-E-X and BarkTTS, meanwhile, consistently rank last in both latency and quality: their heavy autoregressive pipelines result in extreme latencies (median > 2 s; P90 > 12–45 s) and high error rates (25–32%), making them impractical for any interactive use case. This performance can be traced back to architectural choices. Vall-E-X is a cross-lingual neural codec model that extends the VALL-E framework with autoregressive and non-autoregressive codec LMs, trained on very large multilingual corpora to support zero-shot cross-lingual synthesis [36]. While powerful in expressivity and speaker transfer, the autoregressive stage inherently incurs sequential decoding costs, which accumulate severely for longer inputs, explaining its extreme tail latencies in our benchmarks. BarkTTS, on the other hand, is not designed as a conventional TTS system but as a fully generative text-to-audio model capable of producing not only speech but also music, ambient noise, and sound effects [34]. Its GPT-style architecture, optimized for open-ended generation rather than deterministic TTS, introduces high variance in outputs and compounds inference delays due to its autoregressive decoding over audio tokens. These design decisions, while enabling flexibility and multimodal audio creativity, make both Vall-E-X and BarkTTS poorly suited for real-time or latency-sensitive TTS applications despite their research significance.
The resource utilization metrics indicate that the top-performing models—Microsoft Speech, FastPitch, and VITS—deliver responsive synthesis while maintaining hardware demands that are broadly compatible with consumer devices. Microsoft Speech, as a CPU-based and largely deterministic system, effectively avoids GPU usage altogether. Its resource profile shows negligible CPU/GPU load (beyond background processes), making it an especially attractive option for deployment in environments where dedicated accelerators are absent or where battery and thermal budgets are highly constrained.
By contrast, FastPitch and VITS, as neural architectures, leverage the GPU but differ in their efficiency characteristics. FastPitch exhibits relatively high median peak GPU memory (∼1.2–1.3 GB), reflecting its modular architecture that separately predicts phoneme duration and pitch before conditioning the synthesis [42]. While this design drives its state-of-the-art responsiveness, it also introduces transient bursts of GPU computation that can cause localized spikes in utilization and power draw. VITS, on the other hand, integrates alignment, duration modeling, and waveform generation into a single end-to-end generative framework [43]. This design reduces auxiliary predictors and stabilizes inference, yielding lower median GPU memory usage (600–700 MB) at the cost of slightly higher average GPU utilization on some longer inputs. The result is a more consistent resource profile, though with latency that trails FastPitch.
These observations are consistent with the broader literature on deploying TTS in constrained environments, such as mobile hardware, embedded boards, and edge devices. Typical deployment challenges include RAM ceilings, power caps, and the need for predictable latency under load. Non-autoregressive architectures like FastPitch and its successors are often preferred for their low-latency inference [51], while unified designs like VITS trade some speed for improved efficiency and stability in memory-constrained scenarios. Prior work on edge TTS deployment further notes that models consuming over a gigabyte of GPU memory may exceed the limits of embedded accelerators, motivating techniques such as pruning, quantization, or lightweight vocoders to reduce footprint [52].
In practical terms, Microsoft Speech emerges as the most suitable option for low-resource deployments, since it operates entirely on the CPU with negligible hardware overhead. However, its applicability is limited by the fact that it is a Windows-exclusive, proprietary engine. This constrains portability to other platforms (e.g., Linux- or Android-based embedded devices) and may restrict adoption in edge deployments where open-source or cross-platform solutions are required.
FastPitch, in contrast, provides the best option when raw speed is paramount and GPU memory budgets are not severely constrained. Its non-autoregressive design ensures near real-time responsiveness even for longer utterances, albeit at the cost of higher peak GPU memory demand. VITS offers a middle ground: it requires less GPU memory overall and maintains stable performance across varied input lengths, making it a strong candidate where moderate GPU capacity is available but higher quality and stability guarantees are prioritized. Together, these trade-offs underscore how architectural choices and platform dependencies shape deployment viability across consumer, cloud, and edge scenarios.
Taken together, these results highlight clear architectural trends in modern TTS. FastPitch, with its fully feed-forward and non-autoregressive design, emerges as the strongest neural architecture for scenarios where latency dominates other considerations. By predicting spectrogram frames in parallel rather than sequentially, it eliminates the autoregressive bottlenecks that cripple models such as Tacotron2, Vall-E-X, or Bark, and in doing so, it achieves highly predictable, near real-time performance even on longer inputs [42]. Thus, the architecture sets a benchmark for deployment in low-latency, interactive applications where speed is paramount. In practice, FastPitch demonstrates that carefully constrained design choices can yield substantial gains in responsiveness without catastrophic quality losses, explaining why it consistently outperforms earlier flow-based or attention-driven approaches.
VITS, by contrast, demonstrates the benefits of integration and joint optimization. Its end-to-end variational framework unifies alignment, duration prediction, and waveform generation into a single model, reducing error propagation and capturing prosody more effectively than modular pipelines [43]. This explains its superior word error rates and lower incorrect rates compared to other neural baselines, even though its latency lags slightly behind FastPitch. VITS therefore represents the most balanced option in our benchmark: an architecture that sacrifices some responsiveness in exchange for improved stability and fidelity, making it an attractive candidate for offline synthesis and user-facing applications where naturalness is prioritized over absolute speed.
Finally, Microsoft Speech underscores the enduring strength of non-neural, deterministic systems. Despite its proprietary and Windows-exclusive nature, it achieves an unrivaled combination of ultra-low latency and near-perfect audio quality. Its negligible hardware footprint, operating entirely on the CPU with minimal overhead, positions it as uniquely well-suited for edge deployments and resource-constrained devices. Yet its closed-source and platform-specific limitations restrict its generalizability to broader deployment scenarios, particularly in open or cross-platform environments.
In sum, these findings demonstrate that not all TTS architectures are equally viable for deployment, and clear winners emerge. Among neural approaches, FastPitch stands out as the go-to architecture when responsiveness is the overriding priority. Its feed-forward, non-autoregressive design consistently delivers sub-second synthesis even for long inputs, decisively outperforming flow-based and attention-driven competitors. VITS, while slower, is currently the superior choice when audio fidelity and stability matter more than raw speed: its end-to-end integration reduces error propagation and produces more natural prosody than any other neural model tested. Microsoft Speech remains unmatched in efficiency, requiring virtually no GPU resources, but its closed-source, Windows-only availability limits its role to niche deployments where platform constraints align.
Looking forward, these results carry several implications for future TTS design. First, there is a strong case for hybrid architectures that merge FastPitch’s latency advantage with VITS’s prosody modeling, producing systems that can sustain real-time responsiveness without sacrificing naturalness. Second, it is important to note that the present benchmarks are restricted to English, reflecting the training corpora of the evaluated systems. The architectural trends we observe—feed-forward decoding for responsiveness and end-to-end modeling for stability—should generalize across languages when sufficient training data are available. However, multilingual and code-switching contexts introduce additional complexity in phonetic coverage, prosody, and dataset balance, underscoring the need for systematic benchmarking beyond English. Finally, deployment cost must be understood as a function of both latency and model size. FastPitch’s relatively high GPU memory footprint makes it attractive for cloud deployments where accelerators are plentiful but costly under pay-as-you-go inference billing. VITS, with its lower peak memory footprint but higher average utilization, is better suited for edge devices with moderate VRAM and stable power availability. By contrast, Microsoft Speech demonstrates that lightweight, CPU-only solutions can still dominate where resource budgets are minimal, even if portability is restricted by operating system lock-in.
Taken together, FastPitch and VITS represent today’s state-of-the-art paradigms: the former defining the ceiling for latency-critical use cases, and the latter offering the most reliable balance of speed and quality. Future TTS systems should be guided by these blueprints but extended to meet multilingual demands and deployment realities across both cloud and edge environments.
6.2. Unusual Patterns in Performance Metrics
While most models exhibit predictable behavior in terms of latency and synthesis quality, certain models display unexpected performance trends that merit closer examination. These anomalies provide deeper insights into the internal workings of the architectures and highlight potential optimizations or inefficiencies in model design.
A particularly notable irregularity arises in the performance of Tacotron2-DDC (Double Decoder Consistency). While most models maintain predictable scaling between median and tail latencies, Tacotron2-DDC exhibits extreme instability. For example, in the one-syllable word category it records a median latency of 0.17 s, yet its P90 latency spikes to 16.49 s. This pattern repeats across all inputs—two-syllable words (median 0.26 s vs. P90 15.95 s) and LLM two-word phrases (median 0.45 s vs. P90 21.99 s)—indicating severe tail latency issues irrespective of text length or complexity. Such behavior suggests systemic alignment failures in its dual-decoder mechanism: when the coarse and fine decoders desynchronize, the model enters extended decoding loops, inflating inference times even on otherwise short prompts. These anomalies render Tacotron2-DDC unsuitable for latency-critical deployments, despite its competitive median responsiveness.
Beyond individual strengths at specific input lengths, the latency rankings also reveal which models maintain stable performance across all text categories. Microsoft Speech stands out as the clearest example of consistency: its median latency remains at 0.06–0.07 s across every input type, from single-syllable words to 18-word sentences, with the 90th percentile latency barely exceeding 0.08 s. This indicates virtually no degradation as inputs grow longer, a rare trait among all evaluated models. Combined with its leading audio quality—consistently achieving the lowest incorrect-file rates and word error rates across both 12-word and 18-word sentences—Microsoft Speech delivers exceptional balance between responsiveness and fidelity. These qualities make it particularly well-suited for general-purpose voice assistants, where reply lengths can vary widely yet both latency and intelligibility must remain predictably high.
FastPitch also displays relatively stable trends, with the median latency increasing only modestly from 0.06 s for one-syllable words to 0.13 s for 18-word sentences. This consistency reflects its feed-forward, non-autoregressive architecture, which synthesizes frames in parallel and avoids the sequential decoding bottlenecks that cause latency to grow with input length [42]. Its audio quality is competitive, though less consistently strong than Microsoft Speech or VITS due to more limited prosody modeling. By contrast, autoregressive systems such as Tacotron2-DDC and BarkTTS suffer sharp degradation as the input length grows: their 90th percentile latencies balloon from 16.49 s and 13.01 s (one-syllable words) to 31.99 s and 78.86 s, respectively, for 2-word and 18-word phrases. These extreme tails stem from attention misalignment in Tacotron2 [48] and token-by-token generative overhead in Bark [34], both of which make inference inherently unpredictable. As a result, models like Microsoft Speech—and, to a slightly lesser degree, FastPitch and GlowTTS—deliver more predictable real-time performance by structurally limiting these bottlenecks, a critical property for interactive systems where worst-case latency and transcription accuracy jointly determine user experience.
A notable anomaly is observed in GlowTTS, where latency for longer inputs is sometimes comparable to—or even lower than—that of shorter ones. For instance, GlowTTS records a median latency of 0.10 s for one-syllable words but achieves 0.09 s for the most common single words and maintains 0.23 s for LLM-generated two-word phrases. Despite handling more content, its per-word latency does not scale upward as expected, and in some cases, longer phrases are synthesized proportionally faster. This counterintuitive stability can be traced to GlowTTS’s flow-based parallel decoder and its reliance on monotonic alignment search rather than autoregressive attention [44]. Unlike FastPitch, which predicts durations in a strictly feed-forward fashion, GlowTTS samples latent variables through invertible flows, enabling it to transform text-conditioned priors into mel-spectrograms with nearly constant computational overhead per sequence. The hard monotonic alignment further ensures robust mapping across longer utterances, preventing the alignment drift and stop-token failures that plague autoregressive baselines. Together, these design choices explain why GlowTTS maintains efficiency across variable input lengths, even yielding anomalously low latency for some longer sequences. In practical terms, this stability makes GlowTTS attractive for use cases where input length can vary unpredictably—such as conversational agents, interactive dialogue systems, or narration pipelines—since it guarantees consistent synthesis times without the sharp latency growth observed in autoregressive systems. While it does not outperform FastPitch in absolute responsiveness, GlowTTS’s predictable scaling profile positions it as a reliable option in deployment scenarios where input variability is a primary concern.
In contrast, Vall-E-X and BarkTTS perform markedly worse than other models in terms of latency, with inefficiencies evident across every input length tested. For short single-word inputs, Vall-E-X records a median latency of 2.20 s with the 90th percentile latency spiking to 11.72 s, while BarkTTS fares even worse at 5.73 s median and 13.01 s P90. Performance deteriorates further with longer sequences: for LLM-generated 18-word sentences, Vall-E-X reaches 17.79 s median and 45.38 s P90, and BarkTTS records 14.75 s median with an extreme 36.00 s at the 90th percentile. These values place both models firmly at the bottom of the ranking across all categories, reflecting their computationally heavy autoregressive architectures and lack of optimization for low-latency inference. Vall-E-X, as an extension of the VALL-E framework, relies on autoregressive codec language models to decode discrete audio tokens sequentially [36]. While this approach enables powerful cross-lingual and zero-shot synthesis, the inherent sequential decoding severely penalizes latency, especially for long utterances. BarkTTS, meanwhile, is not a conventional TTS system but a fully generative GPT-style text-to-audio model designed to produce not only speech but also music, ambient noise, and nonverbal cues [34]. Its open-ended generative scope, while expressive, compounds inefficiencies during inference, as the autoregressive decoding of long audio token sequences leads to extreme tail latencies and inconsistent outputs. Taken together, these design choices explain why both Vall-E-X and BarkTTS, despite their research significance in expressive and multimodal synthesis, are poorly suited for real-time or interactive deployment scenarios. Their high computational cost and severe tail latency failures make them viable primarily for offline or experimental use rather than for practical latency-sensitive applications, such as voice assistants or embedded systems.
These results indicate that while these models prioritize high-fidelity synthesis and expressive speech generation, their computational demands render them impractical for latency-sensitive applications.
These unusual performance patterns underscore the inherent complexities of benchmarking modern text-to-speech systems, where small architectural choices can produce disproportionately large effects on responsiveness and stability. Future research must prioritize mitigating tail latency failures, particularly in hybrid or multi-stage decoder architectures such as Tacotron2-DDC. Promising strategies include blockwise or speculative decoding to cap worst-case sequential operations [53], the use of monotonic alignment constraints or probabilistic duration models as seen in Neural HMMs [37], and redesigning decoder pipelines to explicitly separate coarse and fine-grained generation stages with convergence guarantees.
At the same time, the unexpected efficiency gains observed in models like GlowTTS for longer sequences suggest unexplored opportunities: batching phonemes or words into hierarchical context windows could amortize computation, while curriculum-based training regimes (progressively increasing input length) or targeted fine-tuning for structured versus unstructured text may further stabilize inference. Such counterintuitive trends highlight that benchmarking is not merely evaluative but diagnostic, revealing hidden bottlenecks as well as architectural advantages. By systematically surfacing these anomalies, detailed benchmarks can inform the next generation of TTS models, guiding both algorithmic refinements and deployment strategies for real-world, latency-sensitive applications.
6.3. Cloud-Based TTS Services: GTTS vs. EdgeTTS
Cloud-based TTS services provide an alternative to locally deployed models, offering scalable synthesis capabilities with varying constraints on performance and accessibility. Two cloud-based models evaluated in this study are GTTS (Google Text-to-Speech) and EdgeTTS. These models differ significantly in availability, with GTTS imposing usage limits while EdgeTTS allows for unrestricted access. This distinction is crucial for real-time applications, where consistent availability is essential.
When examining responsiveness, GTTS demonstrates moderate yet stable latency behavior across input types. As shown in Table 3, its median latency ranges from 0.43 s on single-word inputs to 0.93 s for 18-word sentences, with the 90th percentile latencies remaining between 0.65 s and 1.39 s. While this performance does not match the ultra-low latency of models such as FastPitch or Microsoft Speech, it remains predictable and comfortably within real-time thresholds across all tested scenarios. EdgeTTS, by contrast, performs notably worse in responsiveness: its median latency spans 1.11 s to 1.78 s, and the 90th percentile latencies rise as high as 2.41 s for longer inputs. The disparity is most evident in shorter phrases, where GTTS sustains sub-0.5 s median latency, whereas EdgeTTS more than doubles that figure.
Audio quality results for 12-word and 18-word sentence synthesis, summarized in Table 4, further highlight differences between the two cloud-based systems. GTTS achieves overall word error rates (WERs) of 0.40 for 12-word inputs and 0.39 for 18-word inputs, with median WERs of 16.67 and 10.82, respectively. EdgeTTS records nearly identical overall WER values (0.41 and 0.38) and slightly higher median WERs (16.67 and 11.11). Both models therefore provide comparable transcription fidelity, and both substantially outperform models like NeuralHMM (overall WER 8.48–8.50) or BarkTTS (5.28–4.20), which suffer from high misalignment and token omission rates.
Incorrect transcription rates reinforce this finding: GTTS produces 2.84% incorrect files for 12-word inputs and 4.25% for 18-word inputs, while EdgeTTS reports 3.02% and 4.02%, respectively. These errors primarily arise from phoneme-duration misalignments rather than network instability, indicating that both cloud systems are robust to input length. Taken together, GTTS offers a slight advantage in responsiveness, while EdgeTTS delivers similar audio quality but suffers higher latency—a trade-off that may constrain its use in latency-critical deployments while remaining viable for general-purpose synthesis scenarios.
In addition to GTTS and EdgeTTS, prior reports on commercial APIs such as Amazon Polly and Google Cloud TTS help contextualize our findings. While official latency benchmarks are not published by these vendors, user measurements suggest that Amazon Polly can return speech in under 0.10 s for short inputs, whereas Google Cloud TTS responses typically average around 0.50 s, with occasional variability into the multi-second range (https://stackoverflow.com/questions/76709700/my-google-cloud-tts-speech-to-text-latency-almost-2-min (accessed on 1 August 2025)). Independent benchmarking by Artificial Analysis (https://artificialanalysis.ai/text-to-speech/model-family/aws#speed (accessed on 1 August 2025)) further highlights throughput differences across providers, reporting that Polly Neural voices sustain approx. 853 characters per second (corresponding to 0.06 s per 50-character phrase), while Google WaveNet achieves approx. 424 characters per second (0.12 s per 50-character phrase) (https://artificialanalysis.ai/ (accessed on 1 August 2025)). These observations reinforce that commercial platforms are heavily optimized for responsiveness, albeit subject to quota segmentation and usage costs, whereas our open-source benchmark emphasizes transparency and reproducibility even if absolute latencies are higher in some cases.
The primary trade-off between gTTS and EdgeTTS is an availability versus quality balance. Looking ahead, major TTS providers already expose configurable performance profiles, e.g., OpenAI’s Realtime API for low-latency speech interactions (https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/realtime (accessed on 1 August 2025)) (and its separate, higher-latency Chat Completions audio path) (https://openai.com/index/introducing-the-realtime-api/ (accessed on 1 August 2025)), Microsoft Azure’s guidance on chunked/streamed synthesis to cut first-byte and finish latency (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/speech-service/how-to-lower-speech-synthesis-latency (accessed on 1 August 2025)), and ElevenLabs’ streaming endpoints for real-time audio generation (https://elevenlabs.io/docs/api-reference/text-to-speech/stream (accessed on 1 August 2025)).
Commercial tiers and usage limits are likewise segmented: Google Cloud TTS prices Standard, WaveNet, and Neural2 voices separately (https://cloud.google.com/text-to-speech/pricing (accessed on 1 August 2025)), while Amazon Polly differentiates Standard, Neural, Long-Form, and Generative voices with distinct quotas and rates (https://aws.amazon.com/polly/pricing/ (accessed on 1 August 2025)). Beyond these service tiers, existing reports provide useful context on responsiveness. Although neither Polly nor Google Cloud TTS publish official latency benchmarks, user measurements suggest that Polly can return speech in under 0.10 s for short inputs, whereas Google Cloud TTS responses typically average around 0.50 s, with occasional variability into the multi-second range (https://stackoverflow.com/questions/76709700/my-google-cloud-tts-speech-to-text-latency-almost-2-min (accessed on 1 August 2025)). Independent benchmarking by Artificial Analysis (https://artificialanalysis.ai/text-to-speech/model-family/aws#speed (accessed on 1 August 2025); https://artificialanalysis.ai/text-to-speech/model-family/google (accessed on 1 August 2025)) further highlights throughput differences across providers. Their results indicate that Google Standard and Google Neural2 achieve approx. 600 and 588 characters per second, respectively (corresponding to 0.05–0.06 s per 30-character phrase), while Google WaveNet reaches approx. 424 characters per second (0.12 s per 50-character phrase). By contrast, Amazon Polly Neural sustains approx. 853 characters per second (0.06 s per 50-character phrase), but specialized voices such as Polly Long-Form drop sharply to 68 characters per second. Taken together, these findings show that commercial platforms are highly optimized for responsiveness, though performance varies significantly across tiers and configurations. They remain subject to quota segmentation, usage costs, and access restrictions, whereas our open-source benchmark emphasizes transparency and reproducibility even if absolute latencies are higher in some cases. Meanwhile, industry forecasts project the voice user interface market to grow at CAGR through 2032, reflecting rising demand for scalable yet stable voice tech—pressure that will drive convergence toward offerings blending reliability with accessibility (https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/voice-user-interface-market (accessed on 1 August 2025)).
In conclusion, the results demonstrate that cloud services such as GTTS and EdgeTTS excel in audio quality but remain constrained by network-induced latency, with median responsiveness in the 0.4–1.8 s range and long-tail delays extending beyond 2.0 s. Commercial platforms such as Google Cloud TTS and Amazon Polly are also widely used in practice, but as closed-source services with usage quotas and costs, they fall outside the scope of our benchmark. By contrast, several lightweight, locally hosted models tested in this study—most notably FastPitch, VITS, and GlowTTS—consistently achieved sub-second responsiveness on consumer hardware, outperforming the tested cloud baselines in both median and tail latency while maintaining competitive fidelity. Other architectures, including Tacotron variants, Vall-E-X, and BarkTTS, lagged significantly behind, confirming that not all open-source systems are suitable for real-time use. Within the scope of our analysis, these findings indicate that top-performing local models now provide stronger responsiveness than commonly used cloud services, underscoring the viability of open-source solutions for latency-critical virtual assistant deployments.
7. Conclusions
This work introduced a reproducible, open-source benchmark for assessing responsiveness in text-to-speech systems, filling a long-standing gap in real-time voice assistant evaluation. By combining latency distributions, tail latency, and intelligibility within a structured dataset, the study established a transparent baseline across 13 open-source models. The results showed clear architectural trade-offs: feed-forward and flow-based models consistently delivered sub-second responsiveness, while autoregressive designs struggled with stability and tail latency spikes. Notably, FastPitch emerged as the most latency-optimized neural system, while deterministic baselines such as Microsoft Speech combined low latency with strong audio quality, underscoring that both architecture and design philosophy shape deployment readiness.
The benchmark’s contribution is infrastructural—defining standards rather than rankings—yet several limitations remain. Experiments were confined to high-end consumer hardware, excluded multilingual scenarios, and relied on automated STT proxies that cannot fully capture perceptual naturalness. Future iterations should broaden evaluations across device tiers, integrate hybrid human–automated quality assessments, and extend to multilingual and code-switching contexts.
By reframing responsiveness as a first-class evaluation dimension, this work complements existing quality-focused efforts and provides a foundation for unified benchmarks that balance speed, fidelity, and robustness in speech synthesis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.P.T.D., A.C. and R.A.P.; methodology, H.P.T.D., A.C. and R.A.P.; software, H.P.T.D.; validation, H.P.T.D.; formal analysis, H.P.T.D.; investigation, H.P.T.D.; resources, H.P.T.D.; writing—original draft preparation, H.P.T.D.; writing—review and editing, A.C., R.A.P. and M.L.; visualization, H.P.T.D.; supervision, A.C. and M.L.; project administration, A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset utilized for the experiments in this study is publicly accessible on Hugging Face at the following URL: https://huggingface.co/datasets/sebdinh61/benchmarked_text_inputs (accessed on 8 August 2025). It is hosted under the Apache License 2.0 (Apache-2.0), permitting broad reuse with attribution.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hoy, M. Alexa, Siri, Cortana, and More: An Introduction to Voice Assistants. Med. Ref. Serv. Q. 2018, 37, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainath, T.N.; Parada, C. Convolutional Neural Networks for Small-Footprint Keyword Spotting. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH), Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; pp. 1478–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Kaur, G.; Bansal, A. How Voice Assistants Are Taking Over Our Lives—A Review. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2019, 6, 355–357. [Google Scholar]
- Défossez, A.; Mazaré, L.; Orsini, M.; Royer, A.; Pérez, P.; Jégou, H.; Grave, E.; Zeghidour, N. Moshi: A speech-text foundation model for real-time dialogue. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.00037. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.; Rastogi, A.; Rao, A.; Shoeb, A.A.M.; Abid, A.; Fisch, A.; Brown, A.R.; Santoro, A.; Gupta, A.; Garriga-Alonso, A.; et al. Beyond the imitation game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.04615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrycks, D.; Burns, C.; Basart, S.; Zou, A.; Mazeika, M.; Song, D.; Steinhardt, J. Measuring massive multitask language understanding. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.03300. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Tworek, J.; Jun, H.; Yuan, Q.; Pinto, H.P.D.O.; Kaplan, J.; Edwards, H.; Burda, Y.; Joseph, N.; Brockman, G.; et al. Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, V.J.; Cheng, C.; Kanter, D.; Mattson, P.; Schmuelling, G.; Wu, C.J.; Anderson, B.; Breughe, M.; Charlebois, M.; Chou, W.; et al. Mlperf inference benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM/IEEE 47th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Virtual, 30 May–3 June 2020; pp. 446–459. [Google Scholar]
- Spangher, L.; Li, T.; Arnold, W.F.; Masiewicki, N.; Dotiwalla, X.; Parusmathi, R.; Grabowski, P.; Ie, E.; Gruhl, D. Project MPG: Towards a generalized performance benchmark for LLM capabilities. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.22368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Singh, P.; Avadhanam, A.; Srivastava, S. Benchmarking LLM powered chatbots: Methods and metrics. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.04624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Liu, J.; Bu, X.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, Z.; Su, W.; Ge, T.; Zheng, B.; et al. Mt-bench-101: A fine-grained benchmark for evaluating large language models in multi-turn dialogues. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.14762. [Google Scholar]
- Malode, V.M. Benchmarking Public Large Language Model. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Hochschule Ingolstadt, Ingolstadt, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jacovi, A.; Wang, A.; Alberti, C.; Tao, C.; Lipovetz, J.; Olszewska, K.; Haas, L.; Liu, M.; Keating, N.; Bloniarz, A.; et al. The FACTS Grounding Leaderboard: Benchmarking LLMs’ Ability to Ground Responses to Long-Form Input. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.03200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zou, X.; Lin, G.; Sun, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Aw, A.; Chen, N.F. Audiobench: A universal benchmark for audio large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.16020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Von Platen, P.; Rush, A.M. Esb: A benchmark for multi-domain end-to-end speech recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.13352. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, W.; Xing, X.; Xu, X. S2SBench: A Benchmark for Quantifying Intelligence Degradation in Speech-to-Speech Large Language Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.14438. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; Tan, R.T.; Li, H. Voicebench: Benchmarking llm-based voice assistants. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17196. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, L.; Ellis, B.; Lupu, A.; Foerster, J. CURATe: Benchmarking Personalised Alignment of Conversational AI Assistants. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.21159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fnu, N.; Bansal, A. Understanding the architecture of vision transformer and its variants: A review. In Proceedings of the 2024 1st International Conference on Innovative Engineering Sciences and Technological Research (ICIESTR), Muscat, Oman, 14–15 May 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, M.; Viswanathan, M. Measuring speech quality for text-to-speech systems: Development and assessment of a modified mean opinion score (MOS) scale. Comput. Speech Lang. 2005, 19, 55–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- mrfakename; Srivastav, V.; Fourrier, C.; Pouget, L.; Lacombe, Y.; main; Gandhi, S. Text to Speech Arena. 2024. Available online: https://huggingface.co/spaces/TTS-AGI/TTS-Arena (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- mrfakename; Srivastav, V.; Fourrier, C.; Pouget, L.; Lacombe, Y.; main.; Gandhi, S.; Passos, A.; Cuenca, P. TTS Arena 2.0: Benchmarking Text-to-Speech Models in the Wild. 2025. Available online: https://huggingface.co/spaces/TTS-AGI/TTS-Arena-V2 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Picovoice. Picovoice TTS Latency Benchmark. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/Picovoice/tts-latency-benchmark (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Artificial Analysis. Text-to-Speech Benchmarking Methodology. 2024. Available online: https://artificialanalysis.ai/text-to-speech (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Labelbox. Evaluating Leading Text-to-Speech Models. 2024. Available online: https://labelbox.com/guides/evaluating-leading-text-to-speech-models/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Minixhofer, C.; Klejch, O.; Bell, P. TTSDS-Text-to-Speech Distribution Score. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Macau, China, 2–5 December 2024; pp. 766–773. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Xu, T.; Brockman, G.; McLeavey, C.; Sutskever, I. Robust speech recognition via large-scale weak supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 28492–28518. [Google Scholar]
- Griffies, S.M.; Perrie, W.A.; Hull, G. Elements of style for writing scientific journal articles. In Publishing Connect; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 20–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wallwork, A. English for Writing Research Papers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie Mellon University Speech Group. The Carnegie Mellon Pronouncing Dictionary (CMUdict). 1993–2014. Available online: http://www.speech.cs.cmu.edu/cgi-bin/cmudict (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Day, D.L. CMU Pronouncing Dictionary Python Package. 2014. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/cmudict/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Davies, M. Word Frequency Data from the Corpus of Contemporary American English (COCA). 2008. Available online: https://www.wordfrequency.info (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Davies, M. The iWeb Corpus: 14 Billion Words of English from the Web. 2018. Available online: https://www.english-corpora.org/iweb/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Suno-AI. Bark: A Transformer-Based Text-to-Audio Model. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/suno-ai/bark (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Défossez, A.; Copet, J.; Synnaeve, G.; Adi, Y. High fidelity neural audio compression. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.13438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; et al. Speak foreign languages with your own voice: Cross-lingual neural codec language modeling. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.03926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Székely, É.; Beskow, J.; Henter, G.E. Neural HMMs are all you need (for high-quality attention-free TTS). In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 7457–7461. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Jin, Z.; Finkelstein, A. HiFi-GAN-2: Studio-quality speech enhancement via generative adversarial networks conditioned on acoustic features. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), New Paltz, NY, USA, 17–20 October 2021; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Johnson, L. The LJ Speech Dataset. 2017. Available online: https://keithito.com/LJ-Speech-Dataset/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Mehta, S.; Kirkland, A.; Lameris, H.; Beskow, J.; Székely, É.; Henter, G.E. OverFlow: Putting flows on top of neural transducers for better TTS. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.06892. [Google Scholar]
- rany2. Edge-tts: Microsoft Edge Text-to-Speech Library. 2021. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/edge-tts/ (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Łańcucki, A. Fastpitch: Parallel text-to-speech with pitch prediction. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 6588–6592. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kong, J.; Son, J. Conditional variational autoencoder with adversarial learning for end-to-end text-to-speech. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 5530–5540. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Kong, J.; Yoon, S. Glow-tts: A generative flow for text-to-speech via monotonic alignment search. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 8067–8077. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Yang, S.; Liu, K.; Fang, P.; Chen, W.; Xie, L. Multi-band melgan: Faster waveform generation for high-quality text-to-speech. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Online, 19–22 January 2021; pp. 492–498. [Google Scholar]
- Battenberg, E.; Mariooryad, S.; Stanton, D.; Skerry-Ryan, R.; Shannon, M.; Kao, D.; Bagby, T. Effective use of variational embedding capacity in expressive end-to-end speech synthesis. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.03402. [Google Scholar]
- King, S.; Karaiskos, V. The Blizzard Challenge 2013. In Proceedings of the Blizzard Challenge Workshop, Barcelona, Spain, 3 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Pang, R.; Weiss, R.J.; Schuster, M.; Jaitly, N.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Skerrv-Ryan, R.; et al. Natural TTS Synthesis by Conditioning Wavenet on Mel Spectrogram Predictions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4779–4783. [Google Scholar]
- Durette, P.N. gTTS: Documentation. 2014. Available online: https://gtts.readthedocs.io/ (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Microsoft Corporation. Speech API 5.4 Documentation. 2009. Available online: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/desktop/ee125663(v=vs.85) (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- NVIDIA. How to Deploy Real-Time Text-to-Speech Applications on GPUs Using TensorRT. 2023. Available online: https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/how-to-deploy-real-time-text-to-speech-applications-on-gpus-using-tensorrt/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Milvus AI. What Are the Challenges of Deploying TTS on Embedded Systems? 2023. Available online: https://blog.milvus.io/ai-quick-reference/what-are-the-challenges-of-deploying-tts-on-embedded-systems (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Stern, M.; Shazeer, N.; Uszkoreit, J. Blockwise parallel decoding for deep autoregressive models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).