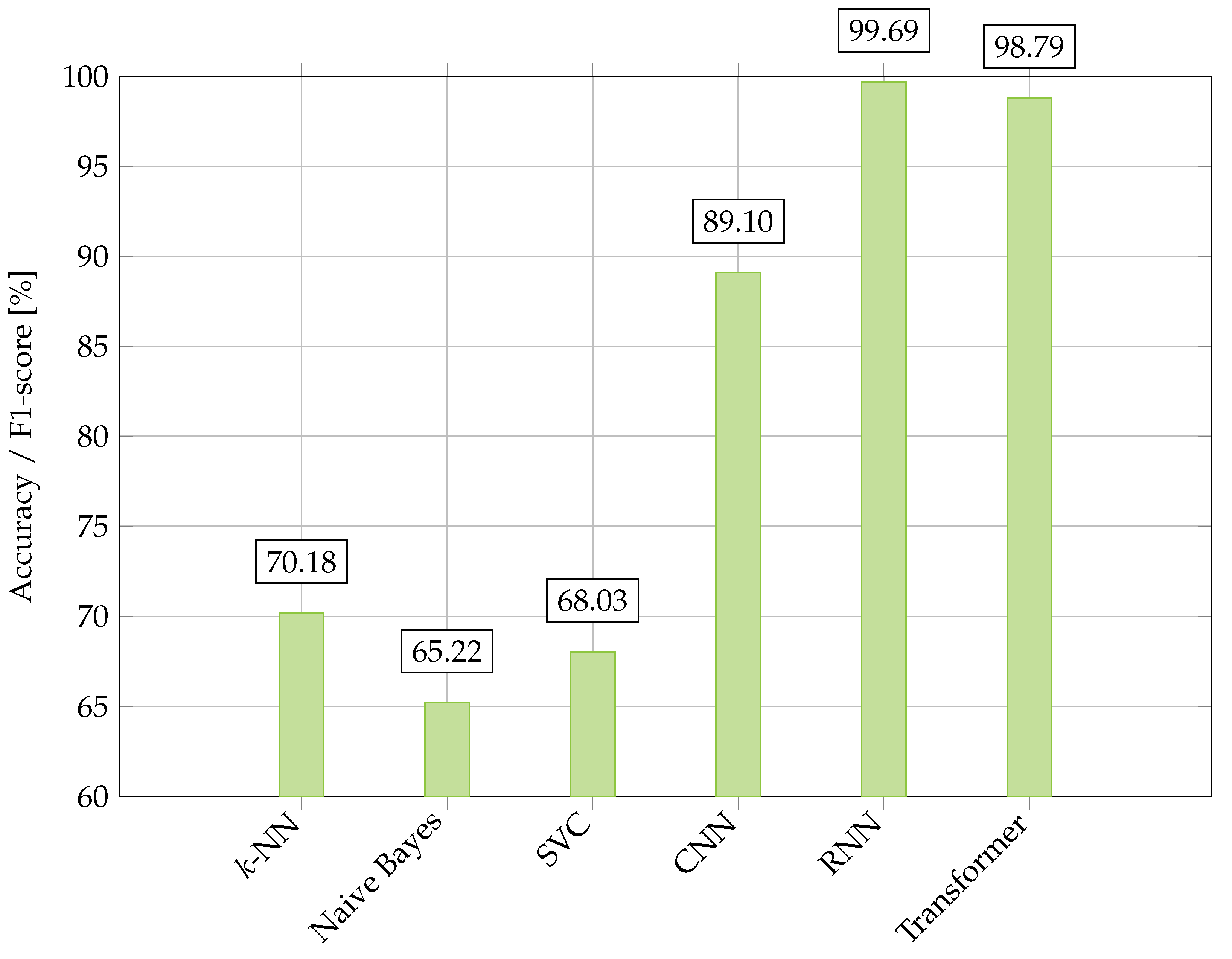Abstract
The Persian language, also known as Farsi, is distinguished by its intricate morphological richness, yet it contends with a paucity of linguistic resources. With an estimated 110 million speakers, it finds prevalence across Iran, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Iraq, Russia, Azerbaijan, and Afghanistan. However, despite its widespread usage, scholarly investigations into Persian document retrieval remain notably scarce. This circumstance is primarily attributed to the absence of standardized test collections, which impedes the advancement of comprehensive research endeavors within this realm. As data corpora are the foundation of natural language processing applications, this work aims at Persian language datasets to address their availability and structure. Subsequently, we motivate a learning-based framework for the processing of Persian texts and their recognition, for which current state-of-the-art approaches from deep learning, such as deep neural networks, are further discussed. Our investigations highlight the challenges of realizing such a system while emphasizing its possible benefits for an otherwise rarely covered language.
1. Introduction and Motivation
In 1993, Iran became the second Middle Eastern country to establish an Internet connection [1]. With the Internet becoming the predominant source of information, containing billions of documents across its vast networks, the swift growth of the World Wide Web has introduced several challenges but also opportunities for information retrieval (IR) systems [2,3]. Today, the World Wide Web has become a central source of information in Iran, reflecting its global ascent as an indispensable resource.
The evolution of information retrieval has progressed from mechanized systems for literature searches to the modern ubiquity of web search engines, emphasizing the growing significance of this field. Originally defined by Calvin Mooers, information retrieval addresses the challenge of guiding users to previously stored information, which may be unknown to them [4]. Typically, information retrieval systems generate outcomes that include references aimed at providing users with relevant information about potential items of interest [5]. Therefore, developers must evaluate the effectiveness of their systems based on the relevance of the results to user queries [3]. Evaluating the effectiveness of an information retrieval system involves measuring how efficiently users can locate the desired documents within a list of results. Usually, this evaluation begins by assembling a collection of documents alongside a set of queries. Establishing benchmarks for performance requires predefined answers, which can serve as a basis for comparison. In addition, relevance judges are often tasked with assessing the pertinence of the information retrieved, contributing to the development of standard test collections [6] to gauge a system’s accuracy.
The field of information retrieval, particularly in the form of text and image, intersects significantly with human language, attracting substantial interest from researchers in language engineering and natural language processing (NLP) [7]. The effectiveness of information retrieval systems can vary notably across languages due to their unique linguistic structures. Challenges in word segmentation present significant obstacles in languages such as Chinese and Japanese, whereas in German, the prevalence of varied compound constructions can degrade retrieval performance [8]. For instance, ref. [9] showed that decompounding German words can significantly improve retrieval performance. Additionally, divergent syntactic orders, such as the subject-object-verb word order (SOV) in Persian vs. the subject-verb-object word order (SVO) in English, can further complicate verb alignment and translation, potentially impacting the accuracy of information retrieval systems.
The work of [10] highlights several foundational concepts and theories that underpin the development and functioning of NLP models. These include, for instance, considerations on the concepts of: (i) nativism vs. empiricism [11,12], (ii) symbolic vs. statistical learning, (iii) the role of symbols and numbers, (iv) human and artificial neural networks, and (v) challenges and future directions [10], which are summarized as follows:
(i) Nativism vs. empiricism. The debate between nativist and empiricist theories of knowledge is crucial. Nativist theories, such as those proposed by Chomsky [13,14], argue that certain structures of knowledge are innate. In contrast, empiricist theories, aligned with thinkers such as Locke [15] and contemporary artificial intelligence (AI) practices, suggest that knowledge is primarily acquired through sensory experiences and interactions with the environment. AI architectures such as transformers, including generative pre-trained transformers (GPT), are grounded in empiricism, learning from vast datasets without inherent a priori knowledge of (feature) space, time, or objects.
(ii) Symbolic vs. statistical learning. Historically, AI has relied on symbolic syntactic interpretations, but modern transformers employ statistical learning. This shift from symbolic AI, which uses explicit rules and representations, to statistical methods allows for more flexible and scalable learning from data. However, this comes with challenges in interpretability and reliability, as the knowledge acquired by statistical models is often superficial and context-dependent.
(iii) The role of symbols and numbers. The representation of knowledge in AI involves encoding information in symbolic or numerical forms. In learning-based models, knowledge is most commonly embedded in vectors or matrices derived from the training corpus, allowing the model to predict and generate language patterns. This numerical representation contrasts with traditional symbolic AI, which uses predefined rules and logic to process information.
(iv) Human and artificial neural networks. The relationship between human neural networks and artificial ones is another area of focus. While human cognition involves complex, often innate structures [16], artificial neural networks learn through backpropagation and optimization algorithms. This difference emphasizes the need for AI systems to integrate some aspects of human-like knowledge representation to enhance their understanding and generalization capabilities.
(v) Challenges and future directions. The current empirical approach in AI, while powerful, is not without its limitations. The knowledge acquired by models such as GPT can be shallow and unreliable, highlighting the need for incorporating more robust, perhaps hybrid, approaches that blend empirical data with structured, symbolic knowledge. This might involve integrating aspects of nativist theories to create more comprehensive AI systems.
The accuracy of Persian information retrieval is predominantly compromised by two main issues. The first is improper text tokenization, where stop words are erroneously identified as significant content keywords. Tokenization refers to the process of dividing a continuous stream of “textual content up into words, terms, symbols, or some other meaningful elements called tokens” [17]. Tokenization is beneficial both in linguistics and in computer science, where it is concerned with text segmentation and lexical analysis. Typically, tokenization occurs at the word level. However, defining what constitutes a “word” can be challenging. Oftentimes, tokenizers rely on straightforward heuristics to make decisions [18]. The second issue involves the potential inadequate handling of word variants, which can severely affect the retrieval process [1].
Despite these challenges, international initiatives such as the Text REtrieval Conference (TREC) (https://trec.nist.gov/, accessed on 31 May 2024) [19] and the Cross-Language Evaluation Forum (Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, CLEF, https://www.clef-initiative.eu/, accessed on 31 May 2024) [20] have played pivotal roles in the systematic evaluation of information retrieval systems and their datasets.
2. Current Challenges
The objectives of research in Persian information retrieval are primarily focused on enhancing the reproducibility and reliability of IR systems. To achieve these objectives, it is imperative to conduct detailed investigations into the existing data corpora (see also Figure 1) and current models, especially in the context of Persian letter recognition. The fundamental goals associated with these objectives typically encompass the following key points:

Figure 1.
Illustration of different Persian language datasets. The examples have been obtained from the datasets’ project pages and repositories: Arshasb [21] (top left, https://github.com/persiandataset/Arshasb, accessed on 31 May 2024), IDPL-PFOD [22] (bottom left, https://github.com/FtmsdtHosseini/IDPL-PFOD, accessed on 31 May 2024), persis [23] (top right, https://github.com/mehrdad-dev/persis, accessed on 31 May 2024), and Iranis-dataset [24] (bottom right, https://github.com/alitourani/Iranis-dataset, accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Linguistic features exploration. To discuss common linguistic features of the Persian language that are crucial for optimizing information retrieval systems [25,26].
- Linguistic specificity. To address language-specific challenges inherent to Persian to enhance the performance of information retrieval systems [27].
- Corpus investigation. To construct a robust and extensive list of Persian datasets in the form of text and images that can serve as a reliable collection for further developments [28].
- Model review. To evaluate how Persian data corpora can be assessed via learning-based approaches, for which their disadvantages/advantages and origins are investigated [29].
These goals aim to advance the field of IR by refining the tools and methodologies applied in the evaluation and implementation of Persian language systems, for which we set our focus on emerging approaches of AI in machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) [30], including artificial neural networks (ANN) such as deep neural networks (DNN) [31,32].
3. Properties of the Persian Language
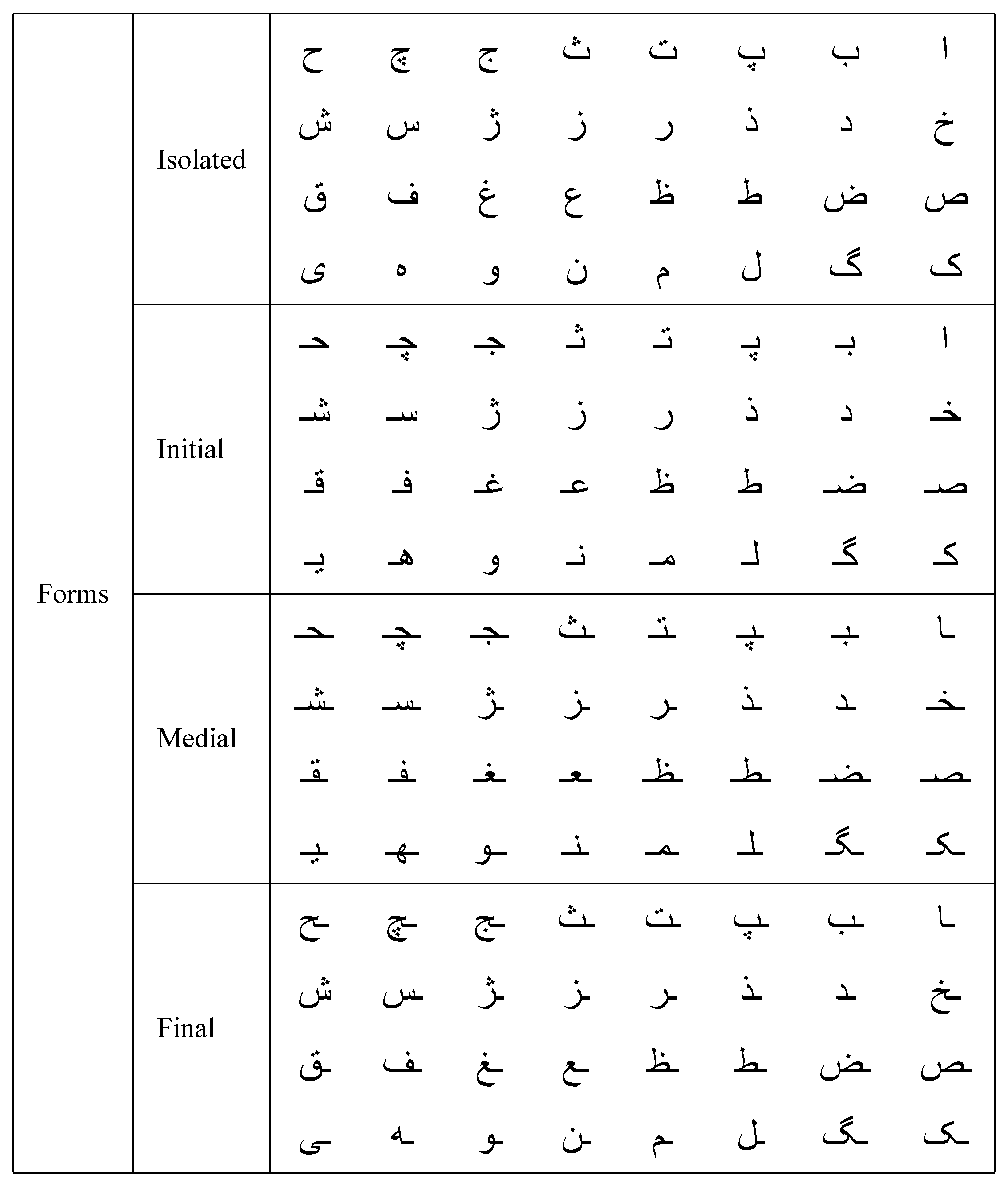
Persian, which is a part of the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European language families, utilizes a script derived from Arabic, belonging to the Semitic language family. Commonly referred to as Farsi in Iran, where it is predominantly spoken, Persian employs a modified version of the Arabic alphabet. However, there are distinct differences between the two. For instance, compared to the 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet, the Persian alphabet consists of 32 letters. Yet, both languages share the right-to-left writing direction where the form of each letter varies based on its position within a word [1]. Figure 2 displays the complete alphabets for English, Persian, and Arabic, with Figure 3 addressing the writing direction in Persian and Arabic. Similar to Arabic, Persian letters can exhibit either joiner or non-joiner forms depending on their position within a word, while most Persian letters can take on one of four possible forms (Figure 4). These forms change when a letter is at the beginning, middle, or end of a word where it typically connects to adjacent letters. The alternative non-joiner form appears when the letter stands alone or at the end of a word, remaining isolated from other letters. Certain Persian letters manifest only in two forms: non-joiner and end-joiner. Notably, when these letters are positioned in the middle of a word, the subsequent letter adopts a form that corresponds to the start of a word. This morphological feature is crucial for understanding Persian [6].

Figure 2.
The English, Persian, and Arabic alphabets in comparison. (a) The English alphabet with upper and lower case letters. (b) The Persian alphabet. (c) The Arabic alphabet. In comparison to Persian, red letters are omitted in the Arabic language.

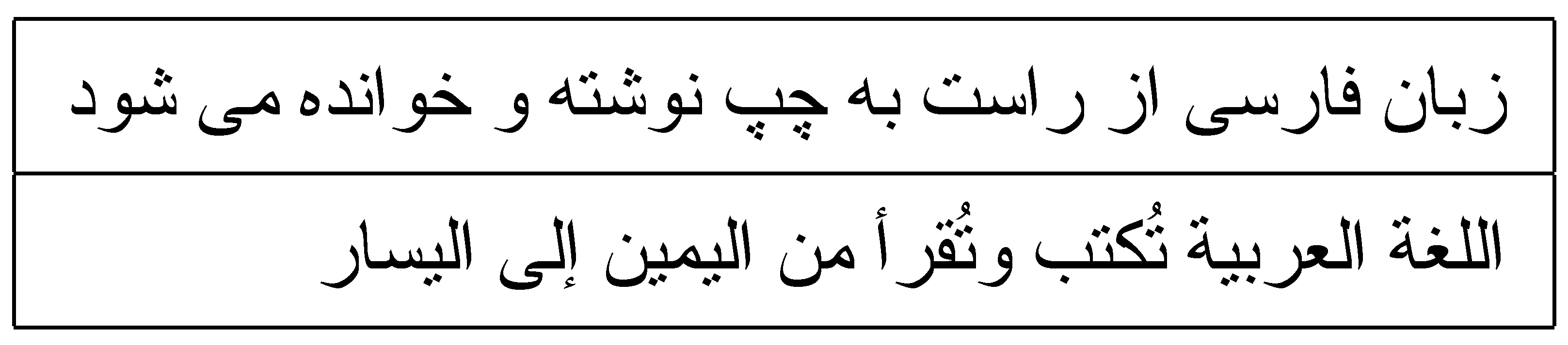
Figure 3.
In comparison to English, Persian (top) and Arabic (bottom) are written from right to left. The provided text states, in Persian and Arabic, “[The] Persian language is written and read from right to left”, which is transliterated as “zabān-e fārsi neveshteh va khāndeh az rāst be chap” (Persian) and “al-lughat al-arabiyyah tuktabu wa tuqra min al-yameen ila al-yasaar” (Arabic).
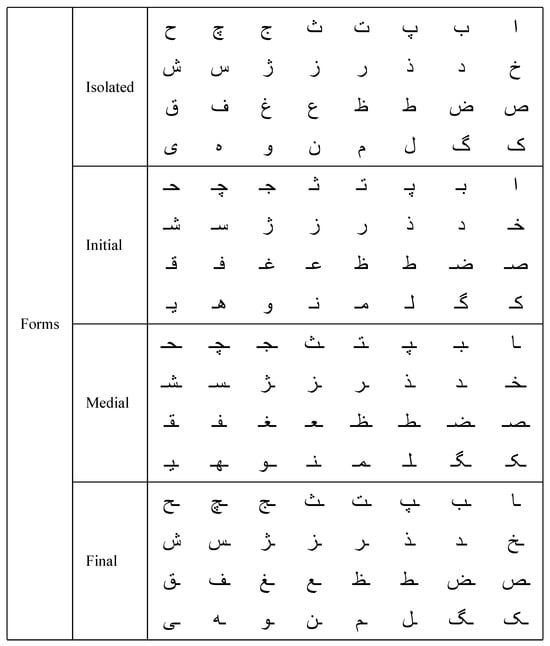
Figure 4.
Construction of Persian letters with the forms isolated, initial, medial, and final.
The Persian vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Arabic and, to a lesser extent, by French, English, as well as Russian, leading to a significant number of borrowed words. In syntactic terms, Persian is unique in that it inflects only verbs, offering six distinct inflections, while predominantly utilizing the subjunctive mood. The language primarily follows a SOV order, which allows for flexibility at the constituent level. Phonetically, Persian features three short vowels and three long vowels. The short vowels are often spoken. However, they are inconsistently represented in writing. A notable grammatical feature is the Ezāfeh morpheme, a spoken short vowel /e/ that connects constituents in a sentence but is generally not written, except when linking words ending in vowels. Both Persian and Arabic utilize four distinct letters that represent the /z/ sound. However, in Persian, these letters are pronounced identically, whereas in Arabic, each letter corresponds to a different pronunciation. This uniformity in pronunciation does not diminish their role in differentiating word meanings, despite the letters being visually distinct [6].
Several characters in the Persian vocabulary are directly borrowed from Arabic, including the diacritic mark Tanvin, which is applied to denote the phonetic endings /an/, /on/, and /en/. Additionally, Persian has adopted not only specific Arabic characters but also the structural composition of certain words, such as the short Alef /ā/ found in /mūsā/ (“Moses”). In Persian, explicit spaces indicate word boundaries, whereas a pseudo-space within words, such as between ‘N’ and ‘L’ in /beynolmelali/ (“international”), suggests a break that does not affect the word’s continuity. The incorrect use of pseudo-spaces can lead to errors in writing, either by inappropriately connecting letters or by creating malformed words. Character encoding is crucial for using Persian, with specific codes significantly impacting text representation [6].
Unlike Arabic, Persian does not differentiate between upper and lower case letters, complicating the identification of proper nouns, foreign names, and terms borrowed from other languages, which makes the formation of acronyms challenging. Additionally, the positioning and presence of dots above or below letters are critical for distinguishing different pronunciations and, hence, meanings within the Persian language. The number and placement of these dots can significantly affect word interpretation, which often introduces ambiguity. Moreover, the Persian script employs a right-to-left format for textual content and a left-to-right orientation for numerical data, mirroring the Arabic system but contrasting with the left-to-right textual and numerical arrangement used in European languages. This bidirectional system introduces complexities, especially in texts that incorporate both script and numerical data. The alignment necessitates managing words from right to left and numbers from left to right, which can complicate the readability and processing of a sentence [6].
4. Availability of Persian Datasets
The significance of supporting less-resourced languages has been increasingly recognized by the NLP community, which is dedicated to this task and often emphasizes it at various international gatherings. For instance, the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC) regularly addresses issues related to low-resource languages. Similarly, the First International Conference on Speech and Language Technologies for Low-Resource Languages (SPELLL 2022) specifically focused on advancements in this field [33]. Additionally, the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL) has featured various contributions and workshops dedicated to low-resource languages. Another notable event is the ELLORA project, which was highlighted in conferences such as the International Conference on Natural Language Processing (ICON) and the UNESCO International Conference on Language Technologies for All (LT4All) [34].
Several specialized corpora have been developed for Persian [35,36,37], targeting various linguistic and computational applications. These corpora are indispensable for researchers focused on natural language processing, machine translation, and other linguistic studies involving Persian, details of which are outlined below for a selected few of these datasets. These corpora are further detailed in Table 1.
- Tehran English–Persian parallel corpus (TEP) [38]. Launched by a natural language processing lab in Tehran in 2011, the Tehran English–Persian parallel corpus is publicly accessible and comprises approximately 550,000 sentence pairs with 8 million terms derived from movie subtitles.
- MIZAN [39]. The manually aligned Persian–English parallel corpus MIZAN features one million sentence pairs along with 25 million terms, providing a rich resource for translation studies and linguistic algorithms.
- hmBlogs [40]. This corpus addresses the unique challenges of Persian orthography and font recognition, highlighting the complexity and diversity of research within Persian linguistic studies.
- MirasText [41]. Generated automatically, MirasText aggregates content from over 250 Persian websites, encompassing a wide array of metadata including keywords, descriptions, and titles, to facilitate extensive text analysis.
- Hamshahri Corpus [1,42]. With 308 MB of text covering a vast range of topics from politics to sports, the Hamshahri Corpus includes 300,000 news articles, each enriched with semantic tags for advanced text processing tasks.
- Shiraz Corpus [43]. Designed for machine translation, the Shiraz Corpus is a bilingual corpus developed from Persian texts sourced online, incorporating a bilingual dictionary with 50,000 terms, alongside sophisticated morphological and syntactic analysis tools.
- Peykare Corpus [44]. This corpus serves as a fundamental resource for language resources and evaluations, particularly in linguistic research.
- FLDB [45]. The Persian Linguistic Database, also referred to as the Farsi Linguistic Database (FLDB), comprises over 3 million words, featuring a blend of contemporary modern Persian literature, spoken varieties, and comprehensive lists of dictionary entries and word lists.
- Mahak Samim [46]. Focused on academic integrity, Mahak Samim consists of Persian academic texts from peer-reviewed journals designed to test and refine plagiarism detection systems.
- PerKey [47]. This extensive corpus of 553,000 news articles, sourced from six Persian news sites, includes high-quality key phrases that are filtered and cleaned to ensure the integrity of the data.
The Tehran English–Persian parallel corpus used movie subtitles to underscore the significance of multilingual (parallel) corpora in NLP. It addressed challenges in data extraction and sentence alignment while introducing the parameter , a language-dependent parameter determined via grid search [48], to align subtitles accurately. Investigations into translated sentences with a statistical machine translation model trained on TEP revealed an average sentence length ratio of Persian to English of approximately 0.7. This ratio, uncommon in human translations, suggests that TEP may not be ideal for machine translation purposes, highlighting a need to enrich datasets such as TEP.

Table 1.
Overview of currently developed Persian datasets with their corpus name and dataset source, size, description, and use cases, separated into text- and image-based datasets. Additionally, further datasets are listed that are not publicly available.
Table 1.
Overview of currently developed Persian datasets with their corpus name and dataset source, size, description, and use cases, separated into text- and image-based datasets. Additionally, further datasets are listed that are not publicly available.
| Corpus | Source | Size | Description | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text-based datasets | ||||
| Tehran English–Persian parallel corpus (TEP) [38] | University of Tehran, 2011 | 550,000 sentences | Movie subtitles | For use in NLP areas (statistical machine translation, cross-lingual information retrieval, and bilingual lexicography) |
| MIZAN [39] | 250 Persian websites from 2018 | 1 million sentence pairs collected from masterpieces of literature | Persian corpus with focus on Islamic studies | Islamic studies, cultural analysis, and machine translation |
| Persica Corpus [49] | Not specified | More than 1.5 million categorized news | Standard text document formats | Persian news articles |
| hmBlogs [40] | Persian blogs from 2021 | 20 million blog posts | Semantic analogy dataset | Used by the Blogfa hosting service |
| Digikala Magazine (DigiMag) [37] | Digikala Online Magazine | 8515 articles | Seven different classes | Persian text classification |
| Persian News Dataset [50] | Various news articles | 16,438 articles | Eight different classes: economic, international, political, science, technology, cultural art, sport, and medical | Persian text classification |
| PEYMA [51] | 10 news websites | 7145 sentences with 302,530 tokens | Seven different classes: organization, money, location, date, time, person, and percent | Persian named-entity recognition |
| EmoPars Dataset [52] | Persian social media texts | 30,000 social media texts | Emotion-annotated texts | Used for sentiment analysis |
| MirasText [41] | An automatically generated text corpus for Persian | 1000 documents | Automatically generated corpus by crawling more than 250 Persian news websites | Language modeling, title extraction, and named-entity recognition for unsupervised learning approaches |
| Image-based datasets | ||||
| Arshasb [21] | Persian text | 33,000 pages | Not specified | Public texts and news texts |
| Persian-OCR [53,54] | Persian alphabets | 570,000 images | Labeled images of Persian alphabets, created by the zarnevis Python library | Image recognition |
| Unavailable datasets | ||||
| Hamshahri Corpus [1,42] | University of Tehran | 700 MB | 166,774 newspaper articles with approximately 380 terms per document | General NLP applications and information retrieval |
| Shiraz Corpus [43] | New Mexico State University, 2000 | Approximately 50,000 terms | Is a bilingual Persian-to-English dictionary | Machine translation for Persian to English, NLP applications, morphological analysis, and syntax parsing |
| Peykare Corpus [44] | Institute for Humanities and Cultural Studies, Tehran | 2.6 million manually tagged words, containing 550 Persian part-of-speech tags | Persian corpus with daily news and common texts | Linguistic studies |
The construction of data corpora often entails the creation of test collections, followed by the extraction of topics from a broad array of subjects including politics, literature, and art. This step is often succeeded by a processing phase that refines the retrieved content to form the final corpus, holding a significant role within text mining methodologies and their practical applications, frequently serving as the initial phase in the overall text mining procedure [55]. Subsequently, the corpus should undergo a validation process, for example by utilizing Word2Vec, a method for word representation learning that encodes each word into a fixed-length vector based on its contextual usage [56]. This process also includes the evaluation of the average word length in queries, alongside detailed information on the number of topics, collection size, and format.
For instance, the work of [56] introduced two novel model architectures for learning word embeddings: Continuous Bag of Words (CBOW) and skip-gram, which were designed to efficiently learn high-quality word vectors from large datasets. CBOW predicts a target word given its surrounding context words, for which it uses the context (a few preceding and following words) to predict the target word. Subsequently, the context words are averaged or summed to form a combined context representation. Finally, this combined context representation is used to predict the target word. Skip-gram, however, does the reverse of CBOW. It predicts the surrounding context words given a target word, where the goal is to maximize the probability of the context words given the target word. The processes is as follows: The input to the model is a single word (the target word). The model predicts the words in the context window around the target word. Each word in the context is treated independently, and the model tries to predict each one. For the training method, both CBOW and skip-gram are trained using stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and backpropagation. The loss function used is typically the negative log-likelihood, which aims to maximize the probability of the correct target word (CBOW) or the context words (skip-gram). To handle large datasets efficiently, techniques such as hierarchical softmax and negative sampling were used. The learned word vectors are evaluated using various linguistic tasks, such as word similarity, word analogy tasks (e.g., “” [56]), and downstream NLP tasks. In [56], the approach primarily used was to compute vectors from the corpus, which were then evaluated. They trained the Word2Vec model (both CBOW and skip-gram architectures) directly on their data corpus. This involved learning word vectors from scratch using the specific text data provided by the corpus, for which word embeddings that capture semantic meanings based on the context within these data were obtained. The learned vectors were then evaluated intrinsically by assessing word similarities and analogies, and extrinsically by their performance in downstream NLP tasks.
5. Persian Language Information Retrieval
Recent advancements in NLP and text recognition have leveraged sophisticated pattern modeling techniques for optical character recognition (OCR) systems to enhance their accuracy and efficiency [57]. Different approaches have been explored, ranging from the integration of vision encoders and decoders for feature extraction and sequence prediction to the use of language models (LM) for output refinement, particularly in handling low-quality text and image [58]. In the following sections, we explore conventional as well as current learning-based models to assess their development and application across different tasks, including complex scenarios involving Persian scripts and their integration into broader applications, highlighting the role of deep learning including convolutional neural networks (CNN). Subsequently, we explore different state-of-the-art methodologies employed within the field.
5.1. Optical Character Recognition
In 2021, Persian emerged as the fifth most widely used language on the internet, highlighting a significant demand for developing novel algorithms capable of understanding Persian across various fields [23]. Optical Character Recognition played a pivotal role in this development by converting different types of documents, such as scanned papers or images, into editable and searchable formats. Recognized for its utility in pattern recognition and AI, OCR has become a cornerstone application in these domains [59]. Character recognition is a specific area within pattern recognition that incorporates techniques from OCR, pattern recognition, and image processing [59]. OCR systems are crucial for document classifiers that rely on textual data, using natural language processing to categorize the extracted text. Although NLP has advanced in text classification, OCR presents unique challenges, particularly with complex scripts including Persian, which complicate text extraction and recognition processes [60].
OCR are typically structured into three main stages: document layout analysis (DLA), text line detection (TLD), and optical character recognition itself. In the DLA phase, the system distinguishes and isolates textual from non-textual components in the image, a vital step that allows the OCR to focus on textual areas, thereby enhancing the accuracy of text recognition [61,62]. The success of OCR technology heavily depends on the precision of the DLA and TLD phases, as the reliability of character recognition closely ties to these initial stages’ effectiveness. DLA and TLD are resource-intensive, requiring significant computation to process a large number of pixels [63]. Modern OCR systems have increasingly integrated advanced DL algorithms to enhance their performance. For instance, a study by [64] highlights the use of deep learning models and a voting system in DLA to improve OCR accuracy, particularly for Persian language documents.
Developing effective OCR systems necessitates engineering highly efficient algorithms that optimize both performance and resource utilization. Variability in image quality, due to factors such as blur, low resolution, and inconsistent lighting, can significantly degrade OCR accuracy if not addressed during preprocessing [65]. A major challenge stems from the lack of a uniform layout across different documents. Some documents might have simple layouts, while others may include complex features such as irregular shapes, tables, or graphs [66]. Complex backgrounds, noise, poor image quality, and image rotation further complicate text region detection and extraction. Furthermore, the difficulty of managing curved text lines poses a substantial challenge, impacting OCR accuracy when the baseline of the text does not align with the line’s baseline [65,67].
In [64], researchers introduced a novel approach to overcome prevalent challenges in OCR, aiming to enhance both accuracy and efficiency. Their DLA module focused on precisely identifying the layout of the document, which includes organizing text blocks, images, and other visual elements. It aimed to separate the primary text for a structured representation of the document’s contents. On the other hand, the TLD module was dedicated to the accurate detection and segmentation of text lines, which aided in precise character recognition in the subsequent OCR stages. Both the DLA and TLD processes were carefully crafted to maximize performance and minimize resource consumption, accommodating documents of varied complexity.
Another separation of OCR frameworks can also be made with the following three primary phases: preprocessing, segmentation, and recognition [68]. Initially, preprocessing techniques such as binarization [68,69] or grayscale conversion, edge smoothing and image rotation correction [69], as well as noise reduction and the correction of letter spacing irregularities are applied to improve the quality of the image and thereby enhance the accuracy of text recognition. Segmentation occurs when the processed output is divided into lines, words, and characters. This step is crucial as it prepares the segmented content for the subsequent recognition phase, ensuring that meaningful data are presented for accurate interpretation [68]. For example, Tesseract [70,71] emerged as an influential open-source OCR engine. It was developed to address the shortcomings of existing commercial OCR technologies that performed poorly with suboptimal print quality [70]. Nowadays, Tesseract excels in text recognition owing to its deep learning framework, providing high accuracy while supporting multiple languages [72], making it a versatile tool in both software and hardware applications.
5.2. Algebraic and Statistical Approaches
The evaluation of the Hamshahri Corpus [1,42] focused on building and validating a large-scale text collection for Persian text retrieval experiments and NLP by judging the relevance of retrieved documents for a given topic. A performance evaluation of various retrieval systems was conducted with 65 different queries. Notably, the 4-gram-based vector space model showed good performance for Persian text, which was evaluated via the trec_eval program [42]. Additionally, different language models denoted as LM1 to LM4 [73], and different vector space models, denoted as VS1 to VS5 [73], have been evaluated with varying results, showing precision scores in the range of 5% to 30% at different cut-off thresholds.
Focusing on machine translation, the MIZAN dataset [39] introduced the largest known Persian–English parallel corpus, containing over one million sentence pairs collected from Persian masterpieces of different literature sources. The methodology included data collection, cleaning, alignment, and validation, with experiments conducted on a baseline statistical machine translation (SMT) [74] system. The SMT system’s performance was evaluated using the BLEU score [75], achieving scores of approximately 25.52 for in-domain and 24.26 for simple out-of-domain test sets [39]. Based on comparisons between translation outputs and post-edited translations, a performance variability of 43% when compared with reference sentences, but only 11% with post-edited results, was reported, indicating that the SMT system meets about 50% of human expectations [39].
The EmoPars Dataset [52] involved the collection, labeling, and analysis of 30,000 Persian tweets according to Paul Ekman’s six basic emotions [76]: anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, and surprise. It introduced the first known publicly available emotion dataset in the Persian language, focusing on the automatic detection of emotions in social media posts. Sentiment analysis was performed on the dataset via Quecst [52], successfully detecting sentiment in 21,485 texts (71%). Their analysis underscores a distribution with 45% of tweets having a positive sentiment (>0.5), 37% with negative sentiment (<0.5), and 17% with neutral sentiment (=0.5), highlighting the prevalence of both positive and negative sentiments in Persian social media posts.
Focusing on linguistic analysis methodologies, the Peykare Corpus [44] defined linguistic varieties and registers, for which linguistic analyses to explore cross-register differences have been conducted. In order to address Persian tokenization challenges [77], they proposed a descriptive generalization to standardize orthographic variations. For annotating Peykare, the EAGLES guidelines [78] were used, employing a semi-automatic approach to establish tag hierarchies. This work emphasized linguistic features such as the Ezafe construction [79] and homographs, combining linguistic analysis techniques with established guidelines to build a contemporary Persian language resource. Word frequency for each linguistic parameter was counted across subtexts, and an analysis of variance (ANOVA) test [80] was used to differentiate levels of varieties. The use of EAGLES guidelines provided a rule-based approach for part-of-speech tagging and other annotation tasks, ensuring consistency and accuracy in the annotation process.
5.3. Learning-Based Approaches
In the domain of information retrieval, the recognition of individual letters is essential for the accurate identification and categorization of textual data. Machine learning techniques have become increasingly popular for this purpose due to their effectiveness in handling complex recognition tasks. The choice of a specific machine learning method depends on several factors, including data characteristics, available computational resources, and the particular demands of the task at hand. Conducting comparative analyses is vital for identifying the most efficient and accurate solutions for letter recognition, especially for languages with unique orthographic structures such as Persian.
5.3.1. Classical Machine Learning Approaches
The Persica Corpus [49], a corpus for news article analysis, addressed the lack of multi-application text corpora in Persian. The methodology involved modified category classification and data normalization processes applied to Persian news articles. To validate the corpus, three classification approaches were evaluated: the k-nearest neighbors algorithm (abbreviated as k-NN) [81], a naive Bayes classifier [82], and a support vector classifier (SVC) [83]. The 1-NN classifier and the naive Bayes classifier achieved accuracies of 70.18% and 65.22%, while the 2-NN and 3-NN classifiers and the SVC achieved an accuracy of 68.03%. Different comparisons of minimum, maximum, and average accuracies between the Persica Corpus and the Reuters Corpus dataset (Volume 1, RCV1) [84] indicated that Persica shows a slightly improved average score with the SVC, while the naive Bayes classifier resulted in a reduced average.
With the hmBlogs corpus [40], word embedding models [85] have been generated from preprocessed data, which have been compared with related, existing Persian corpora. Word embedding models, a type of learning-based models that learn the representation of a word, are employed for evaluation, for which various hyperparameters have been evaluated. The results obtained show that the model created with a 50% separation threshold of “common words of the post” [40] outperformed the model based on a 75% threshold model. Word embeddings were prepared using Word2Vec (skip-gram) and Word2Vec (CBOW) [56], GloVe [86], and FastText (skip-gram) [87]. The Pearson correlation coefficient [88] was evaluated for the SemEval2017-Task2 dataset [89] with, among others, the processed datasets hmBlogsW2V (0.571), irBlogsW2V (0.459), hmBlogsGloVe (0.540), irBlogsGloVe (0.480) [90], and hmBlogsFastText (0.679). These results demonstrated the effectiveness of word embedding methods on the hmBlogs corpus, showing a moderate to strong correlation [91].
MirasText [41] was automatically generated by crawling content from over 250 different Persian websites, for which [41] employed approaches to topic and language modeling. To ensure its validity, the corpus was validated using Word2Vec [56] to encode words into fixed-length vectors based on their context. Subsequently, MirasText and the Google N-gram dataset [92] were trained via Word2Vec to generate word clusters. Comparing these clusters revealed a high correlation, confirming MirasText’s coherence and validity. The manual evaluation yielded an F1-score of 75%, indicating a strong correlation between the word clusters from Google N-gram and MirasText, thereby demonstrating the reliability of the learned word representations.
Another common approach is random forests [93], a type of ensemble learning technique that utilizes multiple decision trees to enhance predictive accuracy and control over-fitting. Within the realm of letter recognition, each letter is depicted as a set of definable features, and a random forest classifier is adept at processing these labeled examples to classify letters effectively. This method extends beyond simple letter recognition. It is also applicable in more complex NLP tasks that require the analysis and categorization of text, such as sentiment analysis and topic classification. By characterizing words and phrases through feature sets and employing a random forest classifier, various textual elements can be identified and classified with considerable accuracy. A comparative study by [94] highlighted that classical machine learning approaches such as random forests can outperform other classifiers in recognizing letters, particularly in accuracy and robustness, albeit with increased processing times. Their primary aim was to ascertain the most effective classifier for letter recognition. Their findings demonstrated the utility of random forests in automating and enhancing text-based operations by investigating the influence of different dataset split ratios with cross-validation. Their “results show that the highest average accuracy of the test option is given by 80%-split, 10-fold Cross-validation, 90%-split, and 5-fold Cross-validation, respectively” [94].
5.3.2. Deep Neural Networks
DNNs such as Multilayer perceptrons (MLP) [95,96] and CNNs [97,98,99,100] have proven to be effective for letter recognition in various languages, including Persian. Its fundamental idea is to treat the Persian text document as an image, for which a DNN architecture is utilized to extract relevant features, classifying present instances of letters. Such DNNs can be trained on large datasets of labeled Persian letters, allowing them to learn the specific patterns and characteristics of the Persian alphabet. For example, in [98], the input of the network consisted of normalized images of isolated digits. Their results show a 1% error rate with a reject rate of about 9% on zipcode digits provided by the United States Postal Service.
In the study conducted by [23], novel datasets were introduced for Persian font recognition, utilizing CNNs to tackle the challenges of font identification effectively. The CNNs showcased effectiveness, achieving top-1 accuracies of 78.0% on the persis dataset, 89.1% on the IDPL-PFOD dataset [22], and 94.5% on the KAFD dataset (King Fahd Univeristy Arabic Font Database) [101]. These results validate the practicality of employing CNNs for Persian font recognition, eliminating the necessity for separate preprocessing steps such as feature extraction, binarization, and normalization. The findings highlight the ability of CNN-based methods to identify fonts accurately and efficiently within linguistically diverse contexts, particularly in Persian [23].
Subsequently, a CNN was developed for the recognition of handwritten Arabic letters, as detailed in [102]. This model introduced a sophisticated approach to effectively discern handwritten Arabic characters, where it demonstrated improved accuracy, achieving an accuracy of 96.78%. This study not only confirmed the proposed model’s performance but also considered various evaluation metrics to underscore its effectiveness [102].
5.3.3. Recurrent Neural Networks
Deep neural network variants such as recurrent neural networks (RNN) [103,104], particularly their long short-term memory (LSTM) [103] and gated recurrent unit (GRU) [104] variants, can be instrumental in enhancing Persian language models. These networks are highly adept at performing a range of tasks, including text generation, sentiment analysis, and machine translation. The inherent ability of RNNs to process sequential data makes them exceptionally suitable for NLP tasks involving Persian. This suitability stems from their architecture, which efficiently handles the dependencies and context in language sequences, thereby improving the performance and accuracy of related NLP applications [105].
The PEYMA dataset [51] focused on the creation of a standard, tagged Persian NER dataset by collecting documents from news websites while establishing annotation guidelines based on existing English NER datasets. Emphasizing dataset construction and annotation, PEYMA supports learning-based models that require annotated data for their training process for an RNN with LSTM. The NER task achieved a Cohen’s kappa [106] of 95% for labeled named entities. Using a hybrid system combining statistical and list-based models, an F1-score of 84% for seven different labels was achieved: person, location, organization, date, time, percent, and currency. The system included a rule-based part with lists of frequently named entities and regular expressions, as well as a statistical part that utilized a conditional random fields model [107]. In addition, an RNN-based system with LSTM was envisioned to further assess the usage of advanced deep learning techniques.
In [67], an RNN-based system with LSTM has been proposed, exploring various parameter adjustments to address false recognition issues of the Persian sub-word “LA”. The methodology included a preprocessing algorithm to remove justification through image processing techniques. A dataset comprising 5 million images with eight popular Persian fonts in 10 different sizes was evaluated, demonstrating a 2% accuracy improvement over already existing Persian OCR systems. Experimental results show an average letter-level accuracy of 99.69%, with 98.1% accuracy for “zero-width non-breaking space(s)” and 98.64% accuracy for “LA” at the word level.
5.3.4. Transformers
Introduced by [108], transformer models have emerged as a pivotal DL architecture extensively adopted across various scientific fields including NLP, computer vision (CV), and speech processing [109,110]. These transformer models [110], originally developed for machine translation, have been adapted through numerous modifications, extensions, and adaptations—collectively referred to as Xformers or transformer variants—to enhance performance and address specific challenges in these disciplines. The extensive application of the transformer architecture beyond its initial NLP focus—to areas such as CV and audio processing—can be attributed to its flexible and versatile design, which allows for innovations across three principal dimensions: architectural modifications, pre-training methodologies, and a wide range of applications. These adaptations have enabled the transformer to set new benchmarks in efficiency and accuracy, making it a cornerstone technology in modern AI research [110].
Substantial efforts have been invested in the pre-training of transformer models on extensive text corpora [110], including their application to a multitude of NLP tasks such as machine translation, language modeling, and named-entity recognition. A notable example is the BERT model (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) [111], which is specifically designed to develop rich bidirectional representations by simultaneously considering the left and right contexts across all layers from unlabeled text. This extensive pre-training enables BERT to be fine-tuned with just an additional output layer, enabling question-answering and language inference, without the need for significant modifications to the architecture tailored to specific tasks. This methodology underscores the versatility and efficiency of pre-trained transformer models in handling complex NLP challenges [112].
For the processing of datasets such as the Digikala Magazine (DigiMag) dataset [37], a monolingual BERT model for the Persian language (ParsBERT) has been developed that demonstrated state-of-the-art performance compared to other architectures and multilingual models. The results obtained on the DigiMag and SnappFood [37] datasets showed that ParsBERT surpassed the baseline multilingual BERT model in its accuracy and F1-score. For the named-entity recognition [113] task, ParsBERT achieved an improved model performance with F1-scores of 93.10% on the PEYMA dataset and 98.79% on the ARMAN dataset. Subsequently, downstream tasks including named-entity recognition, sentiment analysis, and text classification have been realized. Based on ParsBERT version V1.0, ParsBERT V2.0 [37] is highlighted for its Persian language understanding capabilities, which enabled the labeling of Persian texts in supervised tasks on the DigiMag dataset and the Persian News Dataset.
Frequently, current approaches also include refinement modules that enhance the readability of texts derived from low-quality images. In addition, LMs are oftentimes employed to correct and refine the output text. In comparison, [114] proposed a Decoder-only Transformer for Optical Character Recognition (DTrOCR) for English or Chinese. This approach transforms a pre-trained generative LM into an effective text recognition model. Unlike traditional generative models that generate text sequences autoregressively, DTrOCR processes image inputs by converting them into a sequence of patches, which may also be a promising approach for other languages such as Persian.
Subsequently, large language models (LLM) utilize the transformer architecture. Yet, they pose additional challenges [115] due to their generative nature, necessitating precise evaluation methods [116]. Furthermore, evaluating non-English LLMs lag behind their English counterparts, leading to limited availability for many languages. The Khayyam Challenge (also known as PersianMMLU) [116], for instance, is a curated set comprising 20,192 multiple-choice questions sourced from 38 diverse Persian exams. Its primary goal is to enable rigorous evaluation of LLMs supporting the Persian language. Distinctive features of the Khayyam Challenge include comprehensive coverage of topics such as literary comprehension, mathematics, sciences, logic, and intelligence testing. It aims at assessing different aspects of LLM performance such as language understanding, reasoning, and information retrieval across educational levels from primary to secondary school. It incorporates detailed metadata including human response rates, difficulty levels, and descriptive answers. The Khayyam Challenge utilizes original, non-translated data tailored for Persian speakers to avoid translation challenges and accurately capture cultural nuances. A built-in scalability for future updates and evaluations without additional human effort is warranted. In addition, a diverse array of existing LLMs were evaluated that support Persian through statistical analyses and interpretations of their outcomes.
LLMs achieve their highest performance in English. However, their proficiency in other languages is also noteworthy. Conversely, open-source models such as the Large Language Model Meta AI (Llama) are mainly trained on English data, which results in weaker performance in non-English languages. To address this problem authors in [117] present PersianMind, an open-source bilingual large language model that achieved performance similar to the closed-source GPT-3.5-turbo in Persian. By augmenting Llama 2’s vocabulary with 10,000 Persian tokens and training it on a dataset containing nearly 2 billion Persian tokens, [117] demonstrated that their method maintains the model’s English proficiency and uses transfer learning effectively to transfer task knowledge between languages. They further assessed the results of their model with the recently released multilingual masked language model XLM-V [118], the original Llama 2 7B-chat, and GPT-3.5-turbo. The findings show that PersianMind improved the performance of Llama 2 7B-chat by 43% on English subsets and 48% on Persian subsets. “Although its performance in English was 1% lower than that of GPT-3.5-turbo, it surpassed GPT-3.5-turbo by 12%” [117] for Persian text.
The work of “Cross-lingual Transfer Learning with Persian” investigated cross-lingual transfer learning using Persian as the source language [119]. It examined the effectiveness of Persian in improving part-of-speech (POS) tagging and sentiment analysis for low-resource languages. The study highlights the importance of typological and genetic similarities between languages for successful cross-lingual transfer. Results show that Persian can effectively aid in POS tagging for related languages such as Kurmanji and Tagalog, and sentiment analysis for various languages. Yet, possible benefits also vary significantly by task [119]. In comparison, [120] proposed a cross-lingual DL framework for sentiment analysis in Persian to address the critical issue of data scarcity in low-resource languages by leveraging English training data through cross-lingual word embeddings. This approach demonstrated substantial improvements over monolingual approaches, achieving a 22% improvement with static embeddings and 9% with dynamic embeddings in Persian sentiment analysis. Their model’s flexibility and language independence highlight its potential applicability to other low-resource languages, contingent upon the availability of cross-lingual embeddings.
However, evaluating transformers such as LLMs also requires multi-dimensional measurements while balancing model performance trade-offs. One such example is the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking [121] to assess creative performance across various tasks [122]. LLMs are vulnerable to security and privacy attacks, such as jailbreaking and data poisoning, which highlights the need for robust evaluation methods to mitigate risks [123]. Evaluating LLMs on symbolic reasoning tasks reveals that “increasing the scale of the model and fine-tuning it on relevant tasks lead to significant performance gains” [124], particularly in tasks related to mathematical reasoning.
5.4. Discussion
With the rise of Persian as an upcoming digital language, advancements in Persian OCR have significantly impacted various fields of application. Yet, Persian script presents unique challenges, requiring precise document layout analysis and text line detection to isolate text accurately. Robust preprocessing techniques, such as image rotation correction and noise reduction, have been necessary in the past to address image quality variability and complex document layouts.
Algebraic and statistical methods are a vital baseline in Persian text processing. For example, evaluations of the Hamshahri Corpus showed a strong performance utilizing a vector space model with 65 queries. The MIZAN dataset’s statistical machine translation achieved BLEU scores of 25.52 for in-domain and 24.26 for out-of-domain data. In comparison, the EmoPars dataset’s sentiment analysis detected sentiment in 71% of texts. Standardized annotations, such as those provided by the Peykare Corpus, can ensure consistent data processing, crucial for reliable NLP models. Machine learning techniques, particularly classical approaches including k-nearest neighbors (70.18% accuracy) and support vector machines (68.03% accuracy), have shown success in text classification on different datasets. Deep neural networks, including CNNs and RNNs, have enhanced OCR and text recognition, with CNNs achieving 94.5% accuracy on the KAFD dataset and 78.0% on the persis dataset. Consequently, RNN-based systems demonstrated an average letter-level accuracy of 99.69% and word-level accuracy of 98.64% (sub-word “LA”). Transformer models, such as BERT, may offer superior performance in various NLP tasks due to their robust pre-training. ParsBERT, for example, achieved F1 scores of 93.10% on the PEYMA dataset and 98.79% on the ARMAN dataset. Subsequently, these methods may collectively contribute to more accurate and efficient language information retrieval systems. Opportunities lie in refining these techniques further, while challenges focus on the handling of complex scripts and varied document formats.
Figure 5 presents a set of different results from the previous sections, for which different models have been evaluated with different datasets as provided by the respective authors. It is noted that a direct comparison of these results is difficult as there is no known unified evaluation of different models and datasets. Therefore, Figure 5 can only serve as an overview of the previously discussed results. Their respective classes and class distributions are as follows.
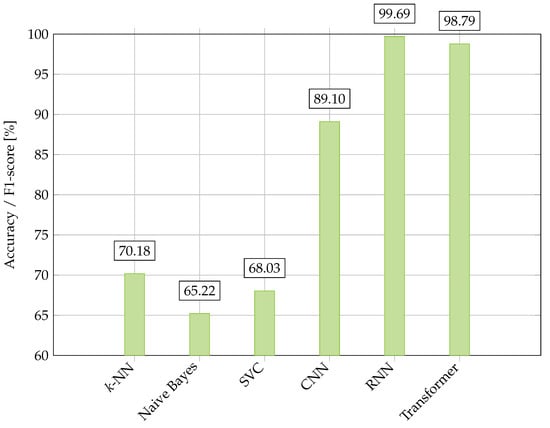
Figure 5.
Performance comparison of learning-based approaches on different Persian datasets from Section 5.3. The best k-NN (1-NN) [49], naive Bayes [49], SVC [49], CNN [22], and RNN (LSTM) [67] scores are reported in accuracy, while the best transformer score (ParsBERT) [37] is reported in F1-score. Please note: As different evaluation scores have been provided by the respective works, with all scores, except for the transformer [37], being reported in accuracy, a direct comparison of all results is difficult.
The evaluated models’ datasets can be summarized as follows: (i) The Persica Corpus [49] contains 11 classes on sports, economy, culture, religion, history, politics, science, society, education, judiciary, and hygiene. Overall, 1,454,745 samples are reported, with a minimum and a maximum sample-class distribution of 1720 (history) and 456,602 (politics). (ii) The IDPL-PFOD dataset [22] contains 30,138 lines (parts of sentences) with 452,070 words. These can be differentiated via their fonts, font styles, font sizes, and (background) textures, as well as applied distortions, noise, and blurring. OCR was applied to these samples. (iii) In [67], a dataset comprising 5 million images with eight popular Persian fonts in 10 different sizes was evaluated. Its task was to classify 110 different classes, which correspond to a set of Persian letters and symbols with different, not specified occurrences that have been evaluated [67]. (iv) The DigiMag dataset [37] contains 8515 articles with seven different classes, which are not further elaborated on.
6. Conclusions and Outlook
This research has emphasized the critical importance of developing advanced information retrieval systems tailored specifically to the Persian language, which is characterized by its intricate morphological structure and wide linguistic diversity. With its global speaker base, Persian presents unique challenges and opportunities within the realm of information retrieval. Technological advancements, particularly the incorporation of deep learning in the form of deep neural networks, have shown promising potential in improving the processing and recognition of Persian in text and image. These advancements are crucial for effectively managing the syntactic and semantic complexities of the Persian language more efficiently.
By addressing these challenges while strategically leveraging modern technological advancements, the field of Persian language retrieval can advance toward a more inclusive and effective digital information environment. With this work, we intend to provide a comprehensive overview to make Persian language datasets more accessible and navigable. The continued refinement of these datasets, the enhancement of machine learning models, and the expansion of system applicability are essential to meeting the practical needs of Persian language users and implementing these advancements.
Author Contributions
S.M., T.S. and D.K. conducted this work’s writing process and the related research project’s literature research. S.M., T.S. and D.K. designed this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| CV | Computer vision |
| DL | Deep learning |
| DLA | Document layout analysis |
| DNN | Deep neural network |
| DTrOCR | Decoder-only Transformer for Optical Character Recognition |
| GRU | Gated recurrent unit |
| IR | Information retrieval |
| k-NN | k-nearest neighbors |
| LM | Language model |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| ML | Machine learning |
| MLP | Multilayer perceptron |
| NLP | Natural language processing |
| OCR | Optical character recognition |
| RNN | Recurrent neural network |
| SMT | Statistical machine translation |
| SVC | Support vector classifier |
| TLD | Text line detection |
| VS | Vector space (model) |
References
- Sadeghi, M.; Vegas, J. How well does Google work with Persian documents? J. Inf. Sci. 2017, 43, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Takeda, K. Information retrieval on the web. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2000, 32, 144–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Sharma, D. Information Retrieval on the Web and its Evaluation. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 975, 8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooers, C. Information retrieval viewed as temporal signaling. In Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians, Cambridge, MA, USA, 30 August–6 September 1950; Volume 1, pp. 572–573. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, V. As we may think. Atl. Mon. 1945, 176, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Masood Ghayoomi Saeedeh Momtazi, M.B. A Study of Corpus Development for Persian. Int. J. Asian Lang. Process. 2010, 20, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg, J.; Manning, C.D. Advances in natural language processing. Science 2015, 349, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoy, J. Comparative study of monolingual and multilingual search models for use with Asian languages. ACM Trans. Asian Lang. Inf. Process. (TALIP) 2005, 4, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braschler, M.; Ripplinger, B. How effective is stemming and decompounding for German text retrieval? Inf. Retr. 2004, 7, 291–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaldi, L.; Pucci, G. Knowing knowledge: Epistemological study of knowledge in transformers. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valian, V. Arguing about innateness. J. Child Lang. 2014, 41, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Allen, J.W.; Bickhard, M.H. Emergent constructivism: Theoretical and methodological considerations. Hum. Dev. 2022, 66, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomsky, N. Syntactic Structures; Mouton de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chomsky, N. On certain formal properties of grammars. Inf. Control 1959, 2, 137–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soles, D.E. Locke’s Empiricism and the Postulation of Unobservables. J. Hist. Philos. 1985, 23, 339–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spelke, E.S.; Kinzler, K.D. Innateness, learning, and rationality. Child Dev. Perspect. 2009, 3, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayarani, S.; Janani, R. Text mining: Open source tokenization tools-an analysis. Adv. Comput. Intell. Int. J. (ACII) 2016, 3, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grefenstette, G. Tokenization. In Syntactic Wordclass Tagging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Harman, D.K. The First Text Retrieval Conference (TREC-1); US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1993; Volume 500.
- Braschler, M. CLEF 2000—Overview of results. In Proceedings of the Workshop of the Cross-Language Evaluation Forum for European Languages; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- GitHub User “Persiandataset”. GitHub Repository “Arshasb”. Available online: https://github.com/persiandataset/Arshasb (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Hosseini, F.; Kashef, S.; Shabaninia, E.; Nezamabadi-pour, H. Idpl-pfod: An image dataset of printed Farsi text for OCR research. In Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on NLP Solutions for Under Resourced Languages (NSURL 2021) Co-Located with ICNLSP 2021, Trento, Italy, 12–13 November 2021; pp. 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadian, M.; Maleki, N.; Olsson, T.; Ahlgren, F. Persis: A Persian Font Recognition Pipeline Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 12th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE), Mashhad, Iran, 17–18 November 2022; pp. 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourani, A.; Soroori, S.; Shahbahrami, A.; Akoushideh, A. Iranis: A large-scale dataset of iranian vehicles license plate characters. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis (IPRIA), Kashan, Iran, 28–29 April 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pallotti, G. A simple view of linguistic complexity. Second. Lang. Res. 2015, 31, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, A.; Shabani-Jadidi, P. The Oxford handbook of Persian linguistics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khashabi, D.; Cohan, A.; Shakeri, S.; Hosseini, P.; Pezeshkpour, P.; Alikhani, M.; Aminnaseri, M.; Bitaab, M.; Brahman, F.; Ghazarian, S.; et al. Parsinlu: A suite of language understanding challenges for persian. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2021, 9, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaresi, A. Challenges in web corpus construction for low-resource languages in a post-BootCaT world. In Proceedings of the 6th Language & Technology Conference, Less Resourced Languages Special Track, Poznań, Poland, 7–9 December 2013; pp. 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Mohtaj, S.; Roshanfekr, B.; Zafarian, A.; Asghari, H. Parsivar: A Language Processing Toolkit for Persian. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T.; Hazarika, D.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E. Recent trends in deep learning based natural language processing. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2018, 13, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, D.W.; Medina, J.R.; Kalita, J.K. A survey of the usages of deep learning for natural language processing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 604–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand Kumar, M.; Chakravarthi, B.R.; Bharathi, B.; O’Riordan, C.; Murthy, H.; Durairaj, T.; Mandl, T. Speech and Language Technologies for Low-Resource Languages. In Proceedings of the First International Conference, SPELLL 2022, Kalavakkam, India, 23–25 November 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Strassel, S.; Tracey, J. LORELEI Language Packs: Data, Tools, and Resources for Technology Development in Low Resource Languages. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khosrobeigi, Z.; Veisi, H.; Hoseinzadeh, E. Persian Optical Character Recognition Using Deep Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory. Appl. Sci. 2022, 22, 11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A. Large Dataset of Persian License Plate Characters. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/amirebrahimi66/large-dataset-of-persian-license-plate-characters (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Farahani, M.; Gharachorloo, M.; Farahani, M.; Manthouri, M. ParsBERT: Transformer-based Model for Persian Language Understanding. Neural Process. Lett. 2021, 53, 3831–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilevar, M.T.; Faili, H.; Pilevar, A.H. TEP: Tehran English–Persian parallel corpus. In International Conference on Intelligent Text Processing and Computational Linguistics; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 6609 LNCS; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashefi, O. MIZAN: A large persian–English parallel corpus. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.02107. [Google Scholar]
- Khansari, H.M.; Shamsfard, M. HmBlogs: A big general Persian corpus. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.02362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, B.; Firouzjaee, H.A.; Choobbasti, A.J.; Najafabadi, S.M.; Vaheb, A. Mirastext: An automatically generated text corpus for persian. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- AleAhmad, A.; Amiri, H.; Darrudi, E.; Rahgozar, M.; Oroumchian, F. Hamshahri: A standard Persian text collection. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2009, 22, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amtrup, J.W.; Rad, H.M.; Megerdoomian, K.; Zajac, R. Persian–English machine translation: An overview of the Shiraz project. In Memoranda in Computer and Cognitive Science MCCS-00-319; New Mexico State University: Las Cruces, New Mexico, 2000; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bijankhan, M.; Sheykhzadegan, J.; Bahrani, M.; Ghayoomi, M. Lessons from building a Persian written corpus: Peykare. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2011, 45, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, S. Farsi linguistic database (FLDB). Int. J. Lexicogr. 1997, 10, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifabadi, M.R.; Eftekhari, S.A. Mahak Samim: A Corpus of Persian Academic Texts for Evaluating Plagiarism Detection Systems. In Proceedings of the Working Notes of FIRE 2016—Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation, Tehran, Iran, 17–19 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Doostmohammadi, E.; Bokaei, M.H.; Sameti, H. PerKey: A Persian News Corpus for Keyphrase Extraction and Generation. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th International Symposium on Telecommunications (IST), Tehran, Iran, 17–19 December 2018; pp. 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibrahim, H.; Ludwig, S.A. Hyperparameter optimization: Comparing genetic algorithm against grid search and bayesian optimization. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Kraków, Poland, 28 June–1 July 2021; pp. 1551–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Eghbalzadeh, H.; Hosseini, B.; Khadivi, S.; Khodabakhsh, A. Persica: A Persian corpus for multi-purpose text mining and natural language processing. In Proceedings of the 2012 6th International Symposium on Telecommunications, IST 2012, Tehran, Iran, 6–8 November 2012; pp. 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub User “Milad-4274”. GitHub Repository “Persian_News”: Persian News Dataset. Available online: https://github.com/milad-4274/persian_news (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Shahshahani, M.S.; Mohseni, M.; Shakery, A.; Faili, H. PEYMA: A Tagged Corpus for Persian Named Entities. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.09936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, N.; Akhavan, R.; Bahrak, B. Emopars: A collection of 30k emotion-annotated persian social media texts. In Proceedings of the Student Research Workshop Associated with RANLP, Online, 1–3 September 2021; pp. 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- GitHub Repository “Persian OCR Using LeNet5”. Available online: https://github.com/mostafamhmdi/Persian-OCR (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Team, Z.D. Zarnevis: A Python Package for Persian Text Processing. 2024. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/zarnevis/ (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Vijayarani, S.; Ilamathi, M.J.; Nithya, M. Preprocessing techniques for text mining-an overview. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Commun. Netw. 2015, 5, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Mandaviya, K.; Badelia, P.; K Ghosh, S.; Chaudhuri, A.; Mandaviya, K.; Badelia, P.; Ghosh, S.K. Optical Character Recognition Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kasem, M.S.; Mahmoud, M.; Kang, H.S. Advancements and Challenges in Arabic Optical Character Recognition: A Comprehensive Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.11812. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Mandaviya, K.; Badelia, P.; Ghosh, S.K. Optical Character Recognition Systems. In Optical Character Recognition Systems for Different Languages with Soft Computing; Chaudhuri, A., Mandaviya, K., Badelia, P., K Ghosh, S., Eds.; Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 9–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashef, S.; Nezamabadi-pour, H.; Shabaninia, E. A review on deep learning approaches for optical character recognition with emphasis on Persian, Arabic and Urdu scripts. J. Mach. Vis. Image Process. 2021, 8, 51–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ehikioya, S.A.; Zeng, J. Mining web content usage patterns of electronic commerce transactions for enhanced customer services. Eng. Rep. 2021, 3, e12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fateh, A.; Rezvani, M.; Tajary, A.; Fateh, M. Providing a voting-based method for combining deep neural network outputs to layout analysis of printed documents. J. Mach. Vis. Image Process. 2022, 9, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Bauer, P.; Allebach, J.P.; Bouman, C.A. Text line detection based on cost optimized local text line direction estimation. In Proceedings of the Color Imaging XX: Displaying, Processing, Hardcopy, and Applications, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 February 2015; Volume 9395, pp. 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Fateh, A.; Fateh, M.; Abolghasemi, V. Enhancing optical character recognition: Efficient techniques for document layout analysis and text line detection. Eng. Rep. 2023, e12832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.S.; Shafait, F.; Breuel, T.M. Coupled snakelets for curled text-line segmentation from warped document images. Int. J. Doc. Anal. Recognit. (IJDAR) 2013, 16, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, I.M.; Hamdy, S.; Mostafa, M.G.M. Deep Arabic document layout analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Information Systems (ICICIS), Cairom, Eygpt, 5–7 December 2017; pp. 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Fateh, M.; Rezvani, M.; Tajary, A.; Abolghasemi, V. Printed Persian OCR system using deep learning. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 3920–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, F.; Abu Doush, I.; Albsoul, A. Arabic optical character recognition software: A review. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 2017, 27, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plötz, T.; Fink, G.A. Markov models for offline handwriting recognition: A survey. Int. J. Doc. Anal. Recognit. (IJDAR) 2009, 12, 269–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R. An overview of the Tesseract OCR engine. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR 2007), Curitiba, Brazil, 23–26 September 2007; Volume 2, pp. 629–633. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, C.; Patel, A.; Patel, D. Optical character recognition by open source OCR tool tesseract: A case study. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 55, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, E.; Teuchler, M.; Bernier, B. Image Processing Based Scene-Text Detection and Recognition with Tesseract. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, D. Using Language Models for Information Retrieval. 2001. Available online: https://ris.utwente.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/6042641/t000001d.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Duh, K.; McNamee, P.; Post, M.; Thompson, B. Benchmarking Neural and Statistical Machine Translation on Low-Resource African Languages. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 2667–2675. [Google Scholar]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 6–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P. Basic emotions. In Handbook of Cognition and Emotion; John Wiley& Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 98, p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Ghayoomi, M.; Momtazi, S. Challenges in developing Persian corpora from online resources. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Asian Language Processing, Singapore, 7–9 December 2009; pp. 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbon, D.; Moore, R.; Winski, R. Handbook of Standards and Resources for Spoken Language Systems; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, S. Persian: A Comprehensive Grammar; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- St, L.; Wold, S. Analysis of variance (ANOVA). Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1989, 6, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, D.J.; Yu, K. Idiot’s Bayes—Not so stupid after all? Int. Stat. Rev. 2001, 69, 385–398. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, D.D.; Yang, Y.; Russell-Rose, T.; Li, F. Rcv1: A new benchmark collection for text categorization research. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2004, 5, 361–397. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, T. Word embedding for understanding natural language: A survey. Guide to Big Data Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 83–104. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Bojanowski, P.; Grave, E.; Joulin, A.; Mikolov, T. Enriching word vectors with subword information. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2017, 5, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Benesty, J.; Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cohen, I. Pearson correlation coefficient. Noise Reduction in Speech Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho-Collados, J.; Pilehvar, M.T.; Collier, N.; Navigli, R. Semeval-2017 task 2: Multilingual and cross-lingual semantic word similarity. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2017), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–4 August 2017; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- AleAhmad, A.; Zahedi, M.; Rahgozar, M.; Moshiri, B. irBlogs: A standard collection for studying Persian bloggers. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 57, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation coefficients: Appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Michel, J.B.; Lieberman, E.A.; Orwant, J.; Brockman, W.; Petrov, S. Syntactic annotations for the google books ngram corpus. In Proceedings of the ACL 2012 System Demonstrations, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 8–14 July 2012; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J.H.; Friedman, J.H. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Prayogo, R.D.; Karimah, S.A. Comparison Study of Machine Learning Techniques for Letter Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2022 1st International Conference on Technology Innovation and Its Applications (ICTIIA), Tangerang, Indonesia, 23 September 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, H.; Monro, S. A Stochastic Approximation Method. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 400–407. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E. Connectionist learning procedures. In Machine Learning; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 555–610. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation Applied to Handwritten Zip Code Recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L. Handwritten digit recognition with a back-propagation network. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; NeurIPS Proceedings: New Orleans, LA, USA, 1989; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Luqman, H.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Awaida, S. KAFD Arabic font database. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Jamjoom, M. An intelligent approach for Arabic handwritten letter recognition using convolutional neural network. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2022, 8, e995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Weeks, D.E.; Xin, H.; Swaroop, A.; Chew, E.Y.; Huang, H.; Ding, Y.; Chen, W. Deep-learning-based prediction of late age-related macular degeneration progression. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, C.; McCallum, A. An introduction to conditional random fields. Found. Trends® Mach. Learn. 2012, 4, 267–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, X. A survey of transformers. AI Open 2022, 3, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers); Minneapolis, Minnesota, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau, D.; Sekine, S. A survey of named entity recognition and classification. Lingvisticae Investig. 2007, 30, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitake, M. DTrOCR: Decoder-only Transformer for Optical Character Recognition. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.15996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jin, R.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Shi, D.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Xiong, B.; Xiong, D.; et al. Evaluating large language models: A comprehensive survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.19736. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahroodi, O.; Nouri, M.; Sanian, M.V.; Sahebi, A.; Dastgheib, D.; Asgari, E.; Baghshah, M.S.; Rohban, M.H. Khayyam Challenge (PersianMMLU): Is Your LLM Truly Wise to The Persian Language? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.06644. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, P.; Salemi, A.; Dousti, M.J. PersianMind: A Cross-Lingual Persian–English Large Language Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.06466. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Gonen, H.; Mao, Y.; Hou, R.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Khabsa, M. Xlm-v: Overcoming the vocabulary bottleneck in multilingual masked language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10472. [Google Scholar]
- Mollanorozy, S.; Tanti, M.; Nissim, M. Cross-lingual transfer learning with Persian. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Research in Computational Linguistic Typology and Multilingual NLP, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 6 May 2023; pp. 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Aliramezani, M.; Doostmohammadi, E.; Bokaei, M.H.; Sameti, H. Persian sentiment analysis without training data using cross-lingual word embeddings. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th International Symposium onTelecommunications (IST), Tehran, Iran, 15–17 December 2020; pp. 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Torrance, E.P. Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 1966. Available online: https://psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037%2Ft05532-000 (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Huang, D.; Guo, J.; Peng, S.; Hao, Y.; Wen, Y.; Hu, X.; Du, Z.; et al. Assessing and understanding creativity in large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.12491. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.C.; Amini, M.H.; Wu, Y. Security and privacy challenges of large language models: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.00888. [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzellis, F.; Testolin, A.; Sperduti, A. Assessing the Emergent Symbolic Reasoning Abilities of Llama Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.06588. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).