A Novel Micro Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device for Glioblastoma Both In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
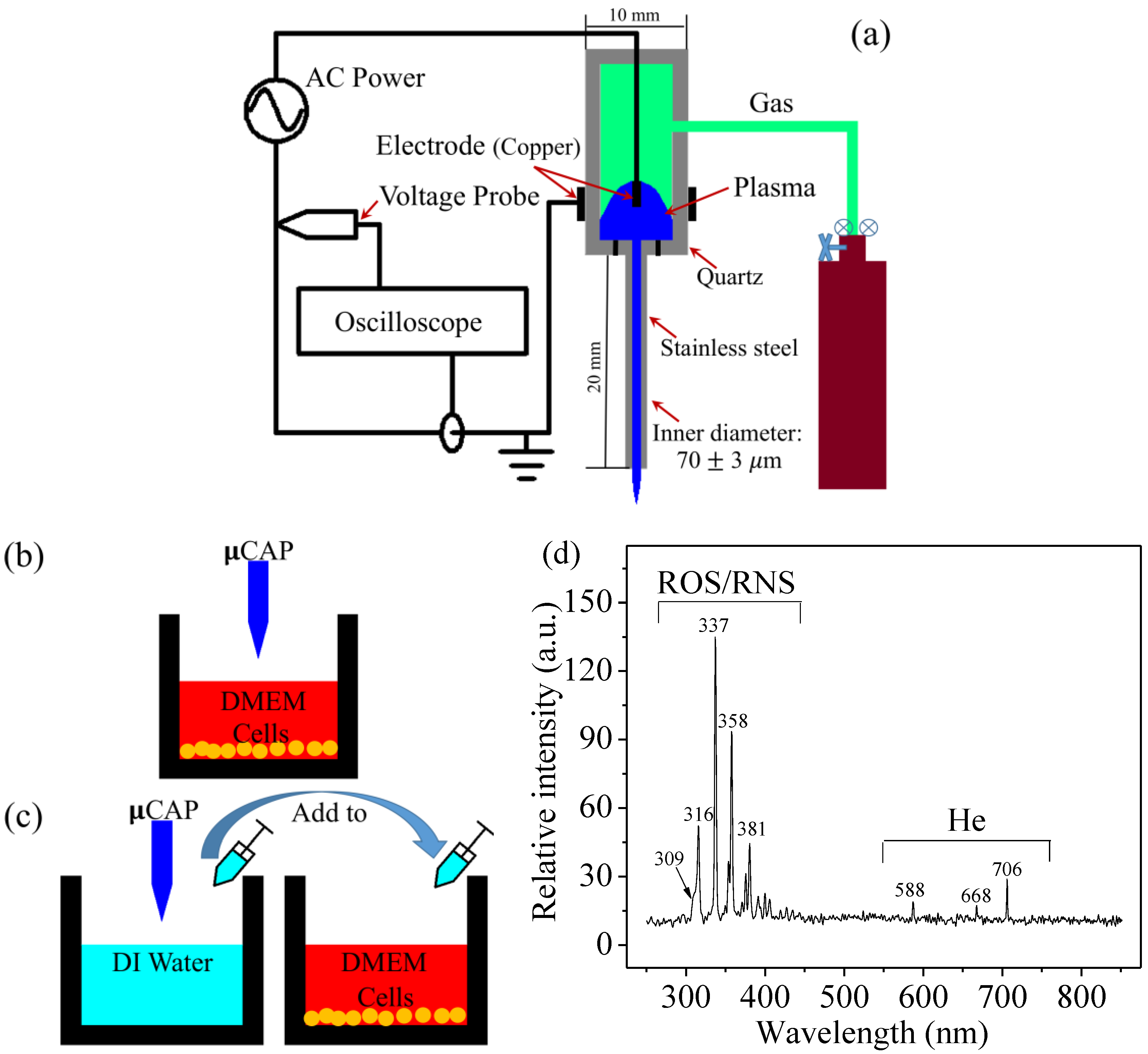
2.1. µCAP and Optical Spectrum
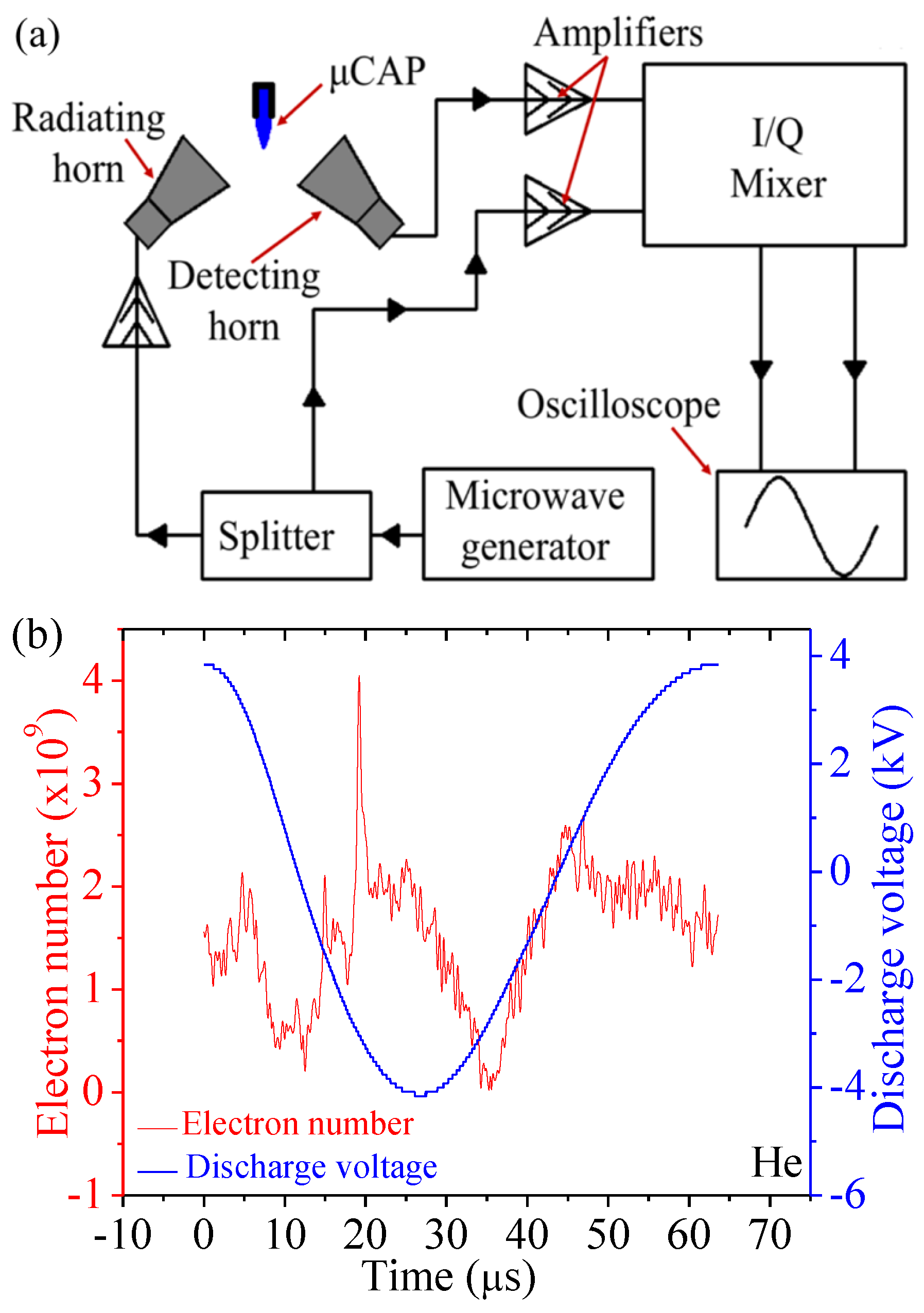
2.2. Electron Density of He µCAP Jet
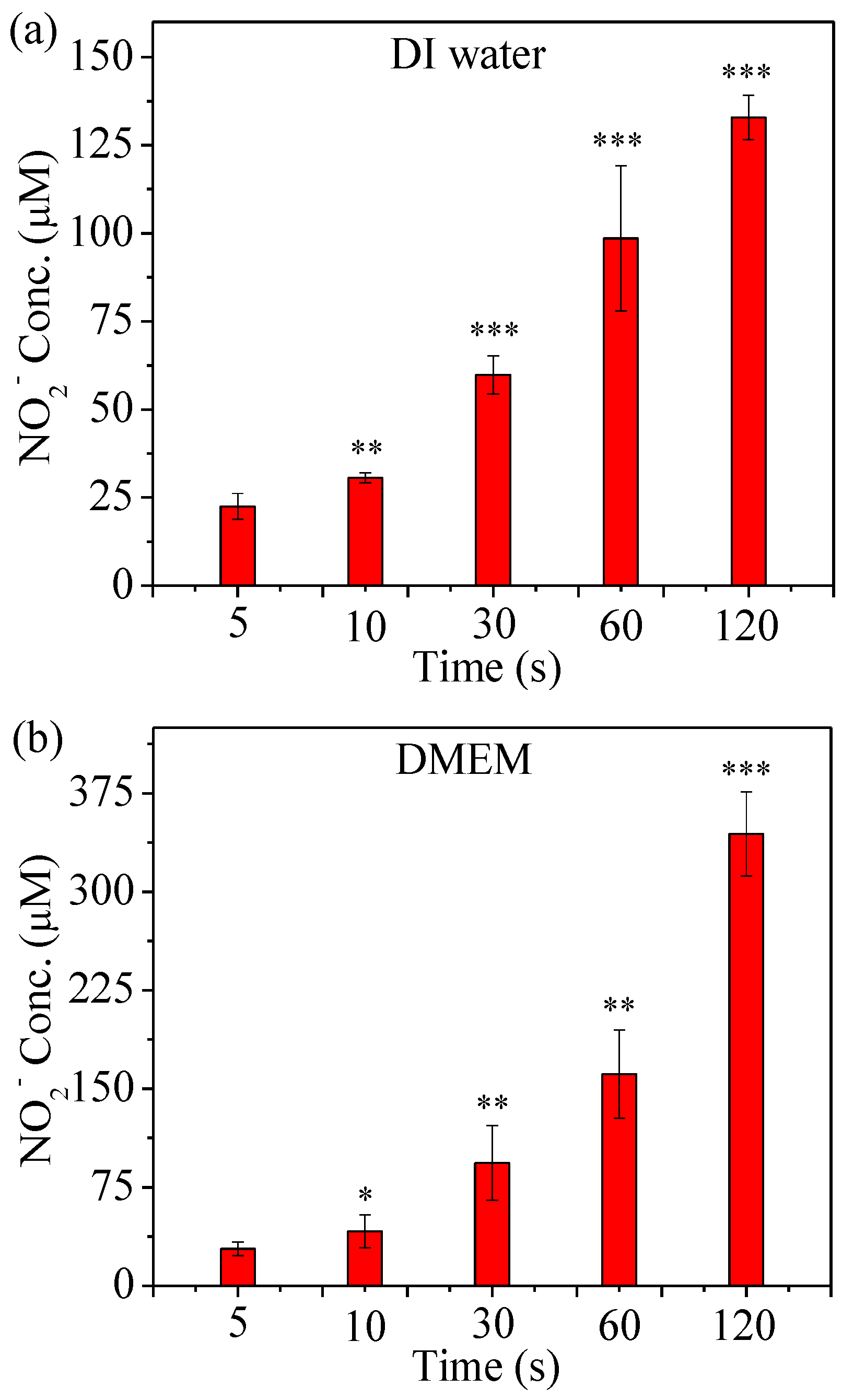
2.3. Detection of RNS Generated by µCAP
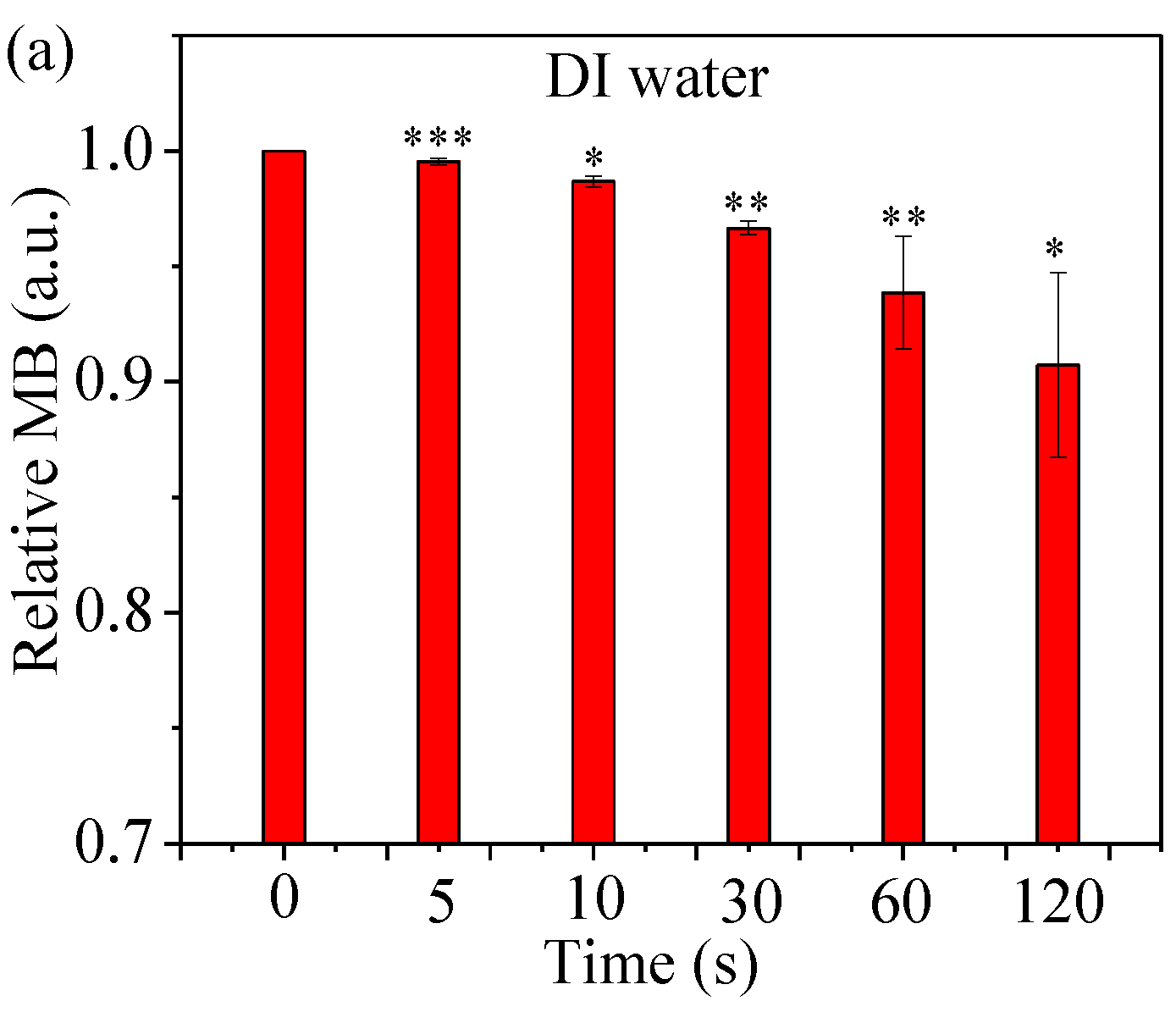
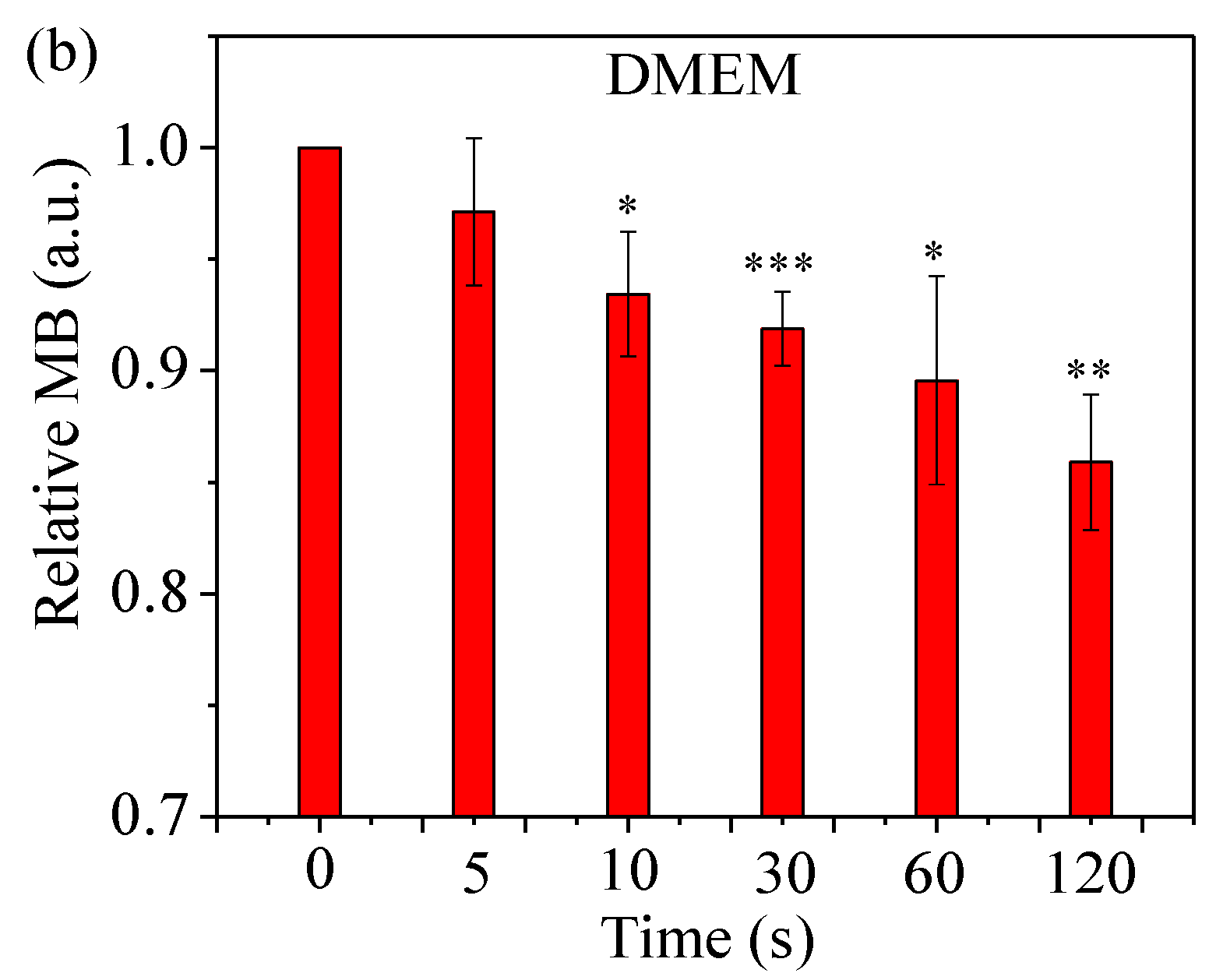
2.4. Assess Relative Concentration of Hydroxyl Radical
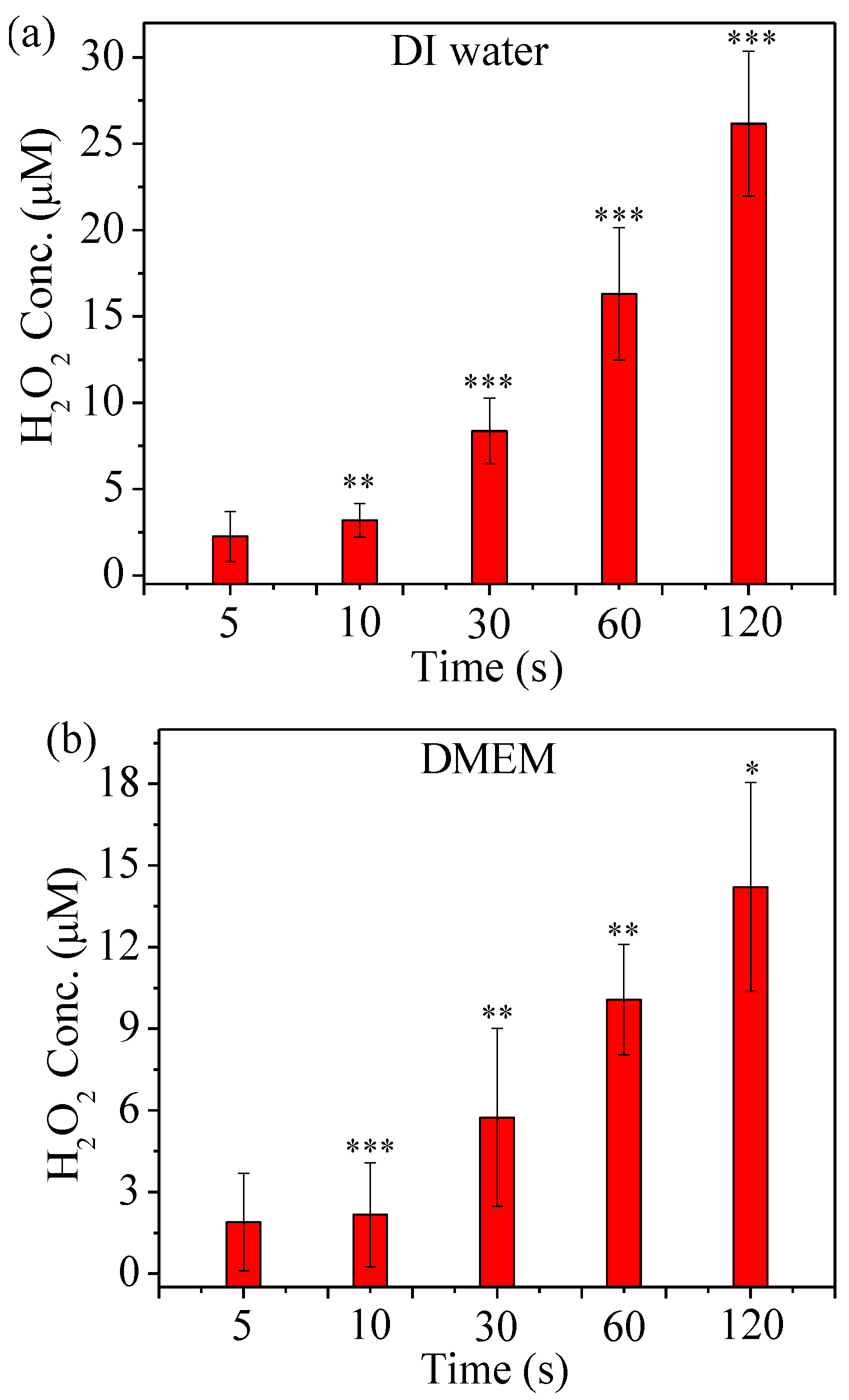
2.5. Detection of ROS Generated by µCAP
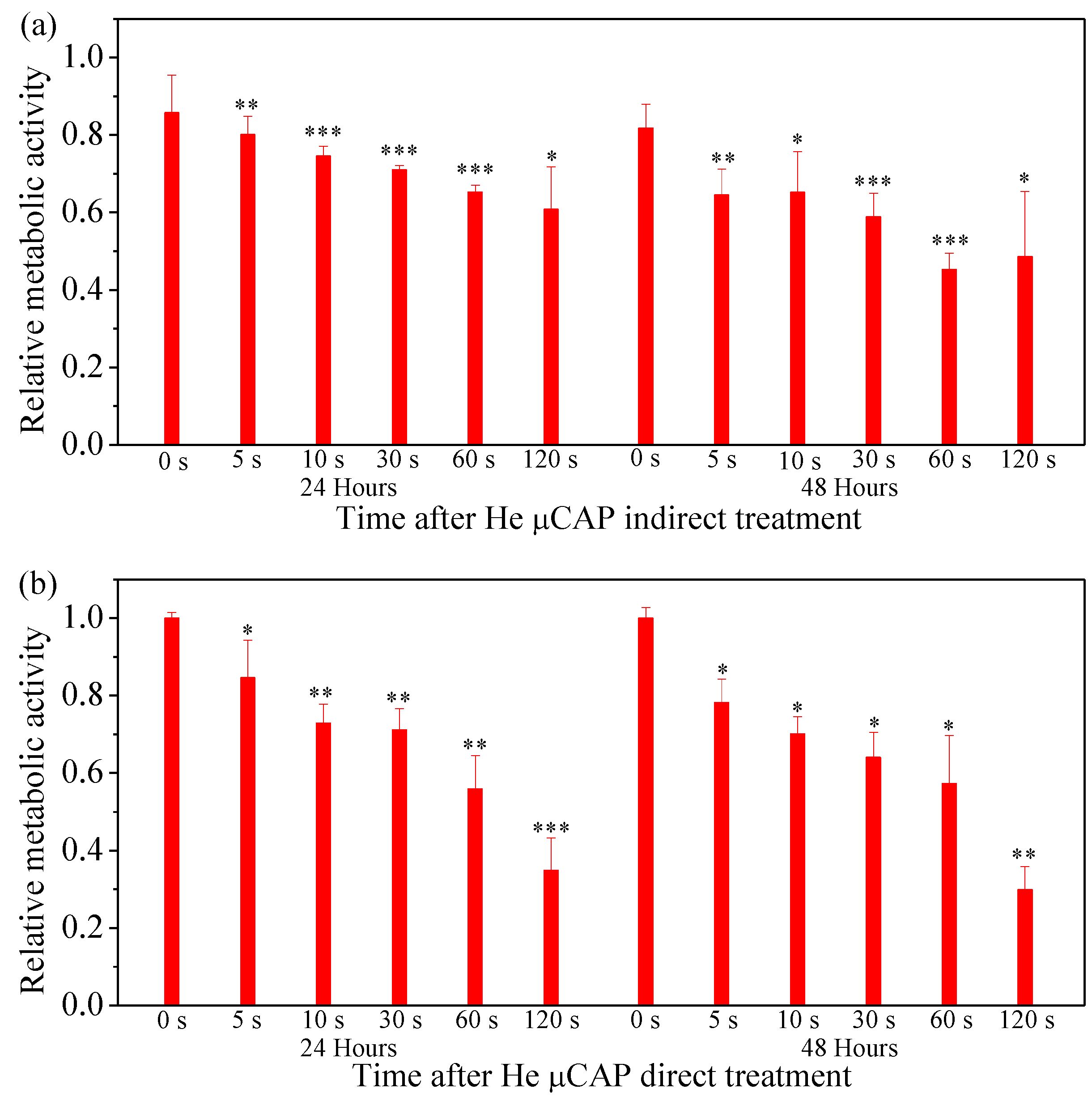
2.6. Cell Viability Follow In Vitro µCAP Treatment Duration
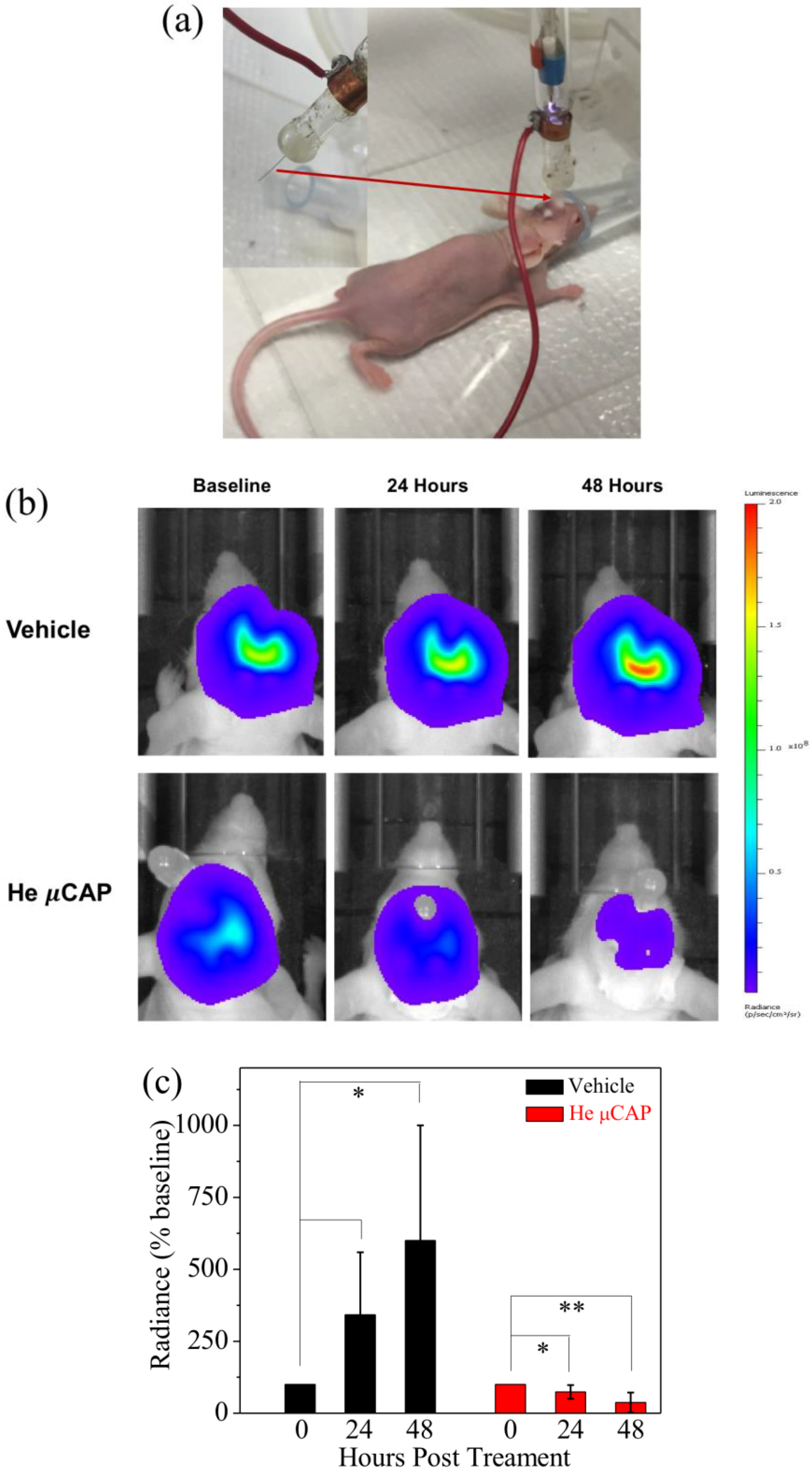
2.7. In Vivo Targeting of Glioblastoma with µCAP
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Device Configuration
4.2. Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) Spectra Measurement
4.3. A Rayleigh Microwave Scattering System (RMS) for Electron Number Measurement
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Determination of H2O2 Concentration
4.6. Determination of NO2− Concentration
4.7. •OH Accumulation in a Methylene Blue (MB) Solution
4.8. Cell Viability Following µCAP Indirect Treatment In Vitro
4.9. Cell Viability Following µCAP Direct Treatment In Vitro
4.10. In Vivo Application of µCAP to Target Intracranial Glioblastoma
4.11. Definition of Control
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attri, P.; Kumar, N.; Park, J.H.; Yadav, D.K.; Choi, S.; Uhm, H.S.; Kim, I.T.; Choi, E.H.; Lee, W. Influence of reactive species on the modification of biomolecules generated from the soft plasma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 08221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratovitski, E.A.; Cheng, X.; Yan, D.; Sherman, J.H.; Canady, J.; Trink, B.; Keidar, M. Anti-cancer therapies of 21st century: Novel approach to treat human cancers using cold atmospheric plasma. Plasma Process. Polym. 2014, 11, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M.; Beilis, I. Plasma Engineering: Applications from Aerospace to Bio and Nanotechnology; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, P.B.; Busetti, A.; Wielogorska, E.; Chevallier, O.P.; Elliott, C.T.; Laverty, G.; Gorman, S.P.; Graham, W.G.; Gilmore, B.F. Non-thermal Plasma Exposure Rapidly Attenuates Bacterial AHL-Dependent Quorum Sensing and Virulence. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keidar, M.; Walk, R.; Shashurin, A.; Srinivasan, P.; Sandler, A.; Dasgupta, S.; Ravi, R.; Guerrero-Preston, R.; Trink, B. Cold plasma selectivity and the possibility of a paradigm shift in cancer therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousfi, M.; Merbahi, N.; Pathak, A.; Eichwald, O. Low-temperature plasmas at atmospheric pressure: Toward new pharmaceutical treatments in medicine. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 28, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Wende, K.; Bekeschus, S.; Bundscherer, L.; Barton, A.; Ottmüller, K.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Masur, K. Non-thermal plasma treatment is associated with changes in transcriptome of human epithelial skin cells. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Kang, S.U.; Kim, Y.E.; Park, J.K.; Yang, S.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, C.-H. Novel Therapeutic Effects of Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma for Muscle Regeneration and Differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daeschlein, G.; Napp, M.; Lutze, S.; Arnold, A.; Podewils, S.; Guembel, D.; Jünger, M. Skin and wound decontamination of multidrug-resistant bacteria by cold atmospheric plasma coagulation. JDDG J. Deutsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2015, 13, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, E.; Vandamme, M.; Brullé, L.; Lerondel, S.; le Pape, A.; Sarron, V.; Riès, D.; Darny, T.; Dozias, S.; Collet, G. Perspectives of endoscopic plasma applications. Clin. Plasma Med. 2013, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M. Plasma for cancer treatment. Plasma Sour. Sci. Technol. 2015, 24, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volotskova, O.; Hawley, T.S.; Stepp, M.A.; Keidar, M. Targeting the cancer cell cycle by cold atmospheric plasma. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 00636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirson, E.D.; Dbalý, V.; Tovaryš, F.; Vymazal, J.; Soustiel, J.F.; Itzhaki, A.; Mordechovich, D.; Steinberg-Shapira, S.; Gurvich, Z.; Schneiderman, R. Alternating electric fields arrest cell proliferation in animal tumor models and human brain tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10152–10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, L.; Cheng, X.; Gjika, E.; Keidar, M. Effects of cold atmospheric plasma generated in deionized water in cell cancer therapy. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M.; Shashurin, A.; Volotskova, O.; Stepp, M.A.; Srinivasan, P.; Sandler, A.; Trink, B. Cold atmospheric plasma in cancer therapya. Phys. Plasmas (1994-present) 2013, 20, 057101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Gutsol, A.; Shekhter, A.B.; Vasilets, V.N.; Fridman, A. Applied plasma medicine. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikalov, S.I.; Harrison, D.G. Methods for detection of mitochondrial and cellular reactive oxygen species. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc, M.; Guay, D.; Coulombe, S.; Leask, R.L. Effects of Non-thermal Plasmas on DNA and Mammalian Cells. Plasma Process. Polym. 2010, 7, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalghatgi, S.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.; Clyne, A.M. Endothelial cell proliferation is enhanced by low dose non-thermal plasma through fibroblast growth factor-2 release. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joh, H.M.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, T.; Leem, S. Reactive oxygen species-related plasma effects on the apoptosis of human bladder cancer cells in atmospheric pressure pulsed plasma jets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 053703. [Google Scholar]
- Shashurin, A.; Keidar, M.; Bronnikov, S.; Jurjus, R.; Stepp, M. Living tissue under treatment of cold plasma atmospheric jet. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 181501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, S.; Nakamura, K.; Hayashi, M.; Tanaka, H.; Kondo, H.; Kajiyama, H.; Kano, H.; Kikkawa, F.; Hori, M. Selective killing of ovarian cancer cells through induction of apoptosis by nonequilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 113702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gweon, B.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.B.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.; Jung, H.; Shin, J.H.; Choe, W. Differential responses of human liver cancer and normal cells to atmospheric pressure plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 063701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, S.N.; Zirnheld, J.; Bagati, A.; DiSanto, T.M.; Soye, B.D.; Wawrzyniak, J.A.; Etemadi, K.; Nikiforov, M.; Berezney, R. Preferential induction of apoptotic cell death in melanoma cells as compared with normal keratinocytes using a non-thermal plasma torch. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2012, 13, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, J.F.; Mohamed, A.-A.H.; Price, R.; Swanson, R.; Bowman, A.; Chiavarini, R.; Stacey, M.; Schoenbach, K. Cold atmospheric pressure air plasma jet for medical applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 241501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalghatgi, S.U.; Fridman, G.; Cooper, M.; Nagaraj, G.; Peddinghaus, M.; Balasubramanian, M.; Vasilets, V.N.; Gutsol, A.F.; Fridman, A.; Friedman, G. Mechanism of blood coagulation by nonthermal atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge plasma. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2007, 35, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussiahn, R.; Brandenburg, R.; Gerling, T.; Kindel, E.; Lange, H.; Lembke, N.; Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T.; Kocher, T. The hairline plasma: An intermittent negative dc-corona discharge at atmospheric pressure for plasma medical applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 143701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutaf-Yardimci, O.; Saveliev, A.V.; Fridman, A.A.; Kennedy, L.A. Thermal and nonthermal regimes of gliding arc discharge in air flow. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirpour, S.; Piroozmand, S.; Soleimani, N.; Faharani, N.J.; Ghomi, H.; Eskandari, H.F.; Sharifi, A.M.; Mirpour, S.; Eftekhari, M.; Nikkhah, M. Utilizing the micron sized non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma inside the animal body for the tumor treatment application. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Foy, P.; Hawkins, T.; Ballato, J.; Kim, S.O. Single-cell-level microplasma cancer therapy. Small 2011, 7, 2291–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Zhao, S.; Lei, Q.; Lu, X.; He, G.; Ostrikov, K. Single-cell-precision microplasma-induced cancer cell apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.A.; Brennan, C.W.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Omuro, A.M. Emerging therapies for glioblastoma. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Fulop, J.; Liu, M.; Blanda, R.; Kromer, C.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012; Neuro-oncology: London, UK, 2015; Volume 17, (Suppl. 4), pp. iv1–iv62. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Q.; Saggar, J.K.; Yu, M.; Wang, M.; Tannock, I.F. Mechanisms of drug resistance related to the microenvironment of solid tumors and possible strategies to inhibit them. Cancer J. 2015, 21, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearse, R.W.B.; Gaydon, A.G.; Pearse, R.W.B.; Gaydon, A.G. The Identification of Molecular Spectra; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Shashurin, A.; Shneider, M.; Dogariu, A.; Miles, R.; Keidar, M. Temporary-resolved measurement of electron density in small atmospheric plasmas. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 171502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Keidar, M. Cold atmospheric plasma jet in an axial DC electric field. Phys. Plasmas (1994-Present) 2016, 23, 083529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, N. Associative ionization reactions involving excited atoms in nitrogen plasma. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2009, 35, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, L.; Cheng, X.; Gjika, E.; Keidar, M. Treatment of gastric cancer cells with nonthermal atmospheric plasma generated in water. Biointerphases 2016, 11, 031010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Cheng, X.; Lin, L.; Keidar, M. Cold atmospheric plasma discharged in water and its potential use in cancer therapy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 015208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.Y.; Trosko, J.E.; Masten, S.J. Methylene blue dye test for rapid qualitative detection of hydroxyl radicals formed in a Fenton’s reaction aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2881–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, B.R.; Thagard, S.M. Analysis and review of chemical reactions and transport processes in pulsed electrical discharge plasma formed directly in liquid water. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2012, 32, 875–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Sarinont, T.; Kim, M.; Amano, T.; Koga, K.; Cho, A.E.; Choi, E.H.; Shiratani, M. Influence of ionic liquid and ionic salt on protein against the reactive species generated using dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirpour, S.; Ghomi, H.; Piroozmand, S.; Nikkhah, M.; Tavassoli, S.H.; Azad, S.Z. The selective characterization of nonthermal atmospheric pressure plasma jet on treatment of human breast cancer and normal cells. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2014, 42, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Talbot, A.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Cheng, X.; Canady, J.; Sherman, J.; Keidar, M. Principles of using cold atmospheric plasma stimulated media for cancer treatment. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, J.; Tresp, H.; Hammer, M.; Iseni, S.; Kupsch, S.; Schmidt-Bleker, A.; Wende, K.; Dünnbier, M.; Masur, K.; Weltmann, K. Tracking plasma generated H2O2 from gas into liquid phase and revealing its dominant impact on human skin cells. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 285401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.B. The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 263001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Kushner, M.J. Atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharges interacting with liquid covered tissue. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 165201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, D.; Heslin, C.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Cytotoxic and mutagenic potential of solutions exposed to cold atmospheric plasma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Chung, T. Cold atmospheric plasma jet-generated RONS and their selective effects on normal and carcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukes, P.; Dolezalova, E.; Sisrova, I.; Clupek, M. Aqueous-phase chemistry and bactericidal effects from an air discharge plasma in contact with water: Evidence for the formation of peroxynitrite through a pseudo-second-order post-discharge reaction of H2O2 and HNO2. Plasma Sour. Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 015019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurake, N.; Tanaka, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Kondo, T.; Sekine, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kajiyama, H.; Kikkawa, F.; Mizuno, M.; Hori, M. Cell survival of glioblastoma grown in medium containing hydrogen peroxide and/or nitrite, or in plasma-activated medium. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 605, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienert, G.P.; Chaumont, F. Aquaporin-facilitated transmembrane diffusion of hydrogen peroxide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, K.; Hara, S.; Kondo, S. Aquaporin water channels in mammals. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2009, 13, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Talbot, A.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Sherman, J.H.; Cheng, X.; Keidar, M. Toward understanding the selective anticancer capacity of cold atmospheric plasma—A model based on aquaporins (Review). Biointerphases 2015, 10, 040801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Saadoun, S. Key roles of aquaporins in tumor biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrynin, D.; Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A. Physical and biological mechanisms of direct plasma interaction with living tissue. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 115020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebicki, S.; Gebicki, J.M. Crosslinking of DNA and proteins induced by protein hydroperoxides. Biochem. J. 1999, 338, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Nonomura, S.; Hara, H.; Kondo, S.; Hori, M. Plasma-activated medium induces A549 cell injury via a spiral apoptotic cascade involving the mitochondrial–nuclear network. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 79, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, A.; Chirokov, A.; Gutsol, A. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure discharges. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, R1–R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, T.; Uehara, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Miyahara, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Iwasawa, A.; Ito, N.; Azuma, T.; Kohno, M.; Okino, A. Investigation of reactive species using various gas plasmas. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 39901–39905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.; Uddin, N.; Sim, G.B.; Hong, Y.J.; Baik, K.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.J.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. Responses of solid tumor cells in DMEM to reactive oxygen species generated by non-thermal plasma and chemically induced ROS systems. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 08587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.L.; Kong, M.G. Contrasting characteristics of linear-field and cross-field atmospheric plasma jets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 111501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, S.; Blagus, T.; Cemazar, M.; Filipic, G.; Sersa, G.; Cvelbar, U. Safety aspects of atmospheric pressure helium plasma jet operation on skin: In vivo study on mouse skin. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174966. [Google Scholar]
- Riedl, S.J.; Shi, Y. Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweitzer, C.; Schmidt, R. Physical mechanisms of generation and deactivation of singlet oxygen. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1685–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, T.J.; Gomer, C.J.; Henderson, B.W.; Jori, G.; Kessel, D.; Korbelik, M.; Moan, J.; Peng, Q. Photodynamic therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 889–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Sherman, J.; Murphy, W.; Ratovitski, E.; Canady, J.; Keidar, M. The effect of tuning cold plasma composition on glioblastoma cell viability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Simonyan, H.; Cheng, X.; Gjika, E.; Lin, L.; Canady, J.; Sherman, J.H.; Young, C.; Keidar, M. A Novel Micro Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device for Glioblastoma Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers 2017, 9, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9060061
Chen Z, Simonyan H, Cheng X, Gjika E, Lin L, Canady J, Sherman JH, Young C, Keidar M. A Novel Micro Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device for Glioblastoma Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers. 2017; 9(6):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9060061
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhitong, Hayk Simonyan, Xiaoqian Cheng, Eda Gjika, Li Lin, Jerome Canady, Jonathan H. Sherman, Colin Young, and Michael Keidar. 2017. "A Novel Micro Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device for Glioblastoma Both In Vitro and In Vivo" Cancers 9, no. 6: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9060061
APA StyleChen, Z., Simonyan, H., Cheng, X., Gjika, E., Lin, L., Canady, J., Sherman, J. H., Young, C., & Keidar, M. (2017). A Novel Micro Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device for Glioblastoma Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers, 9(6), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9060061







