Molecular Remodeling of Peritumoral Tissue in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Insights into Inflammaging and Prognostic Markers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Sample Collection
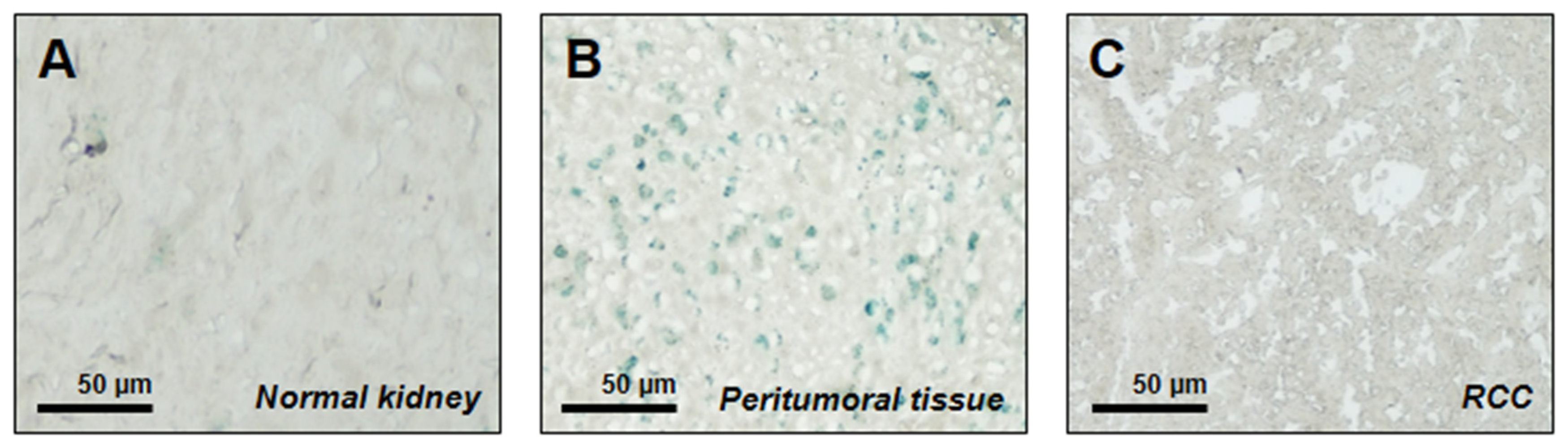
2.2. Senescence-Associated SA-β-Gal Staining
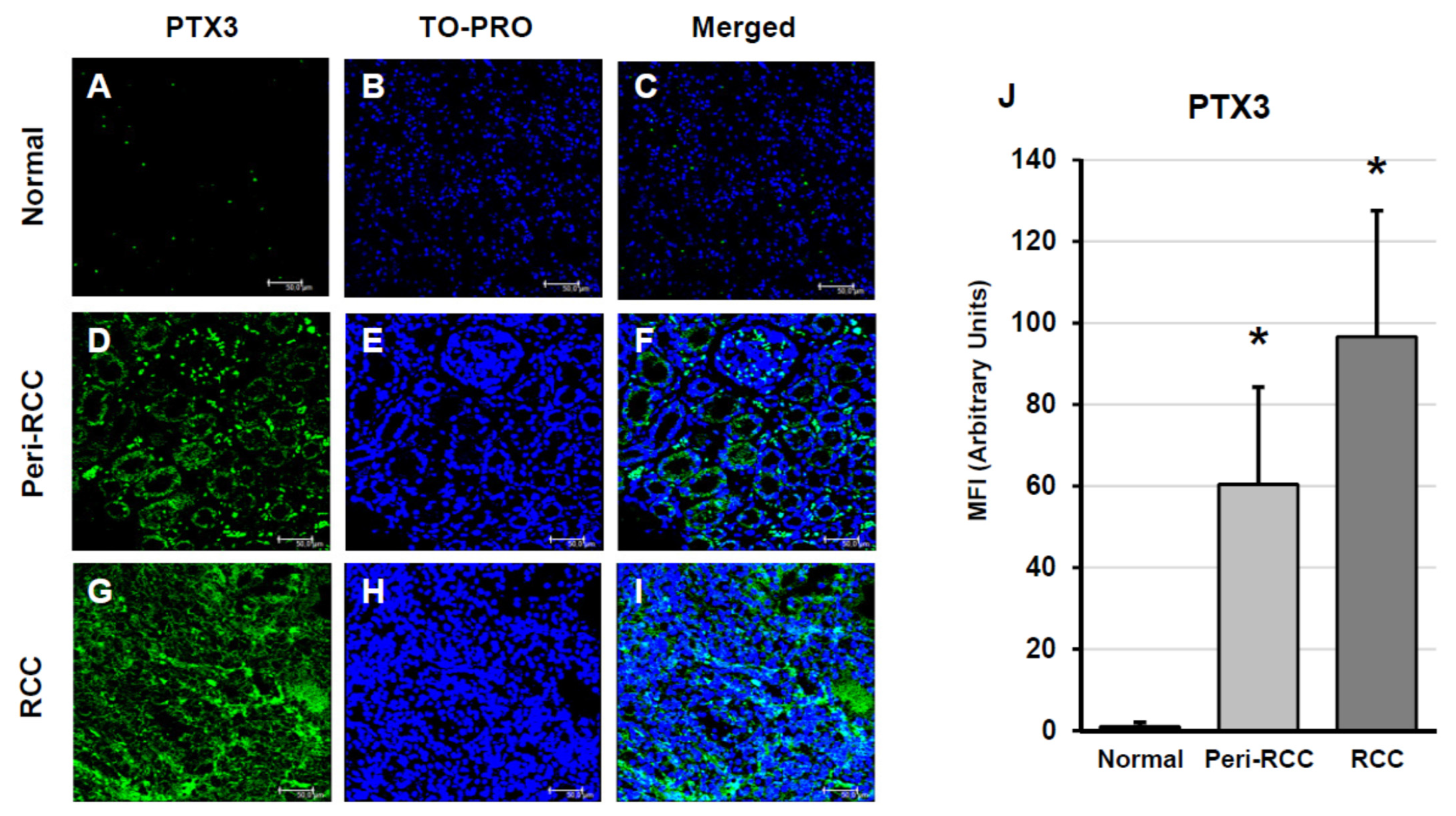
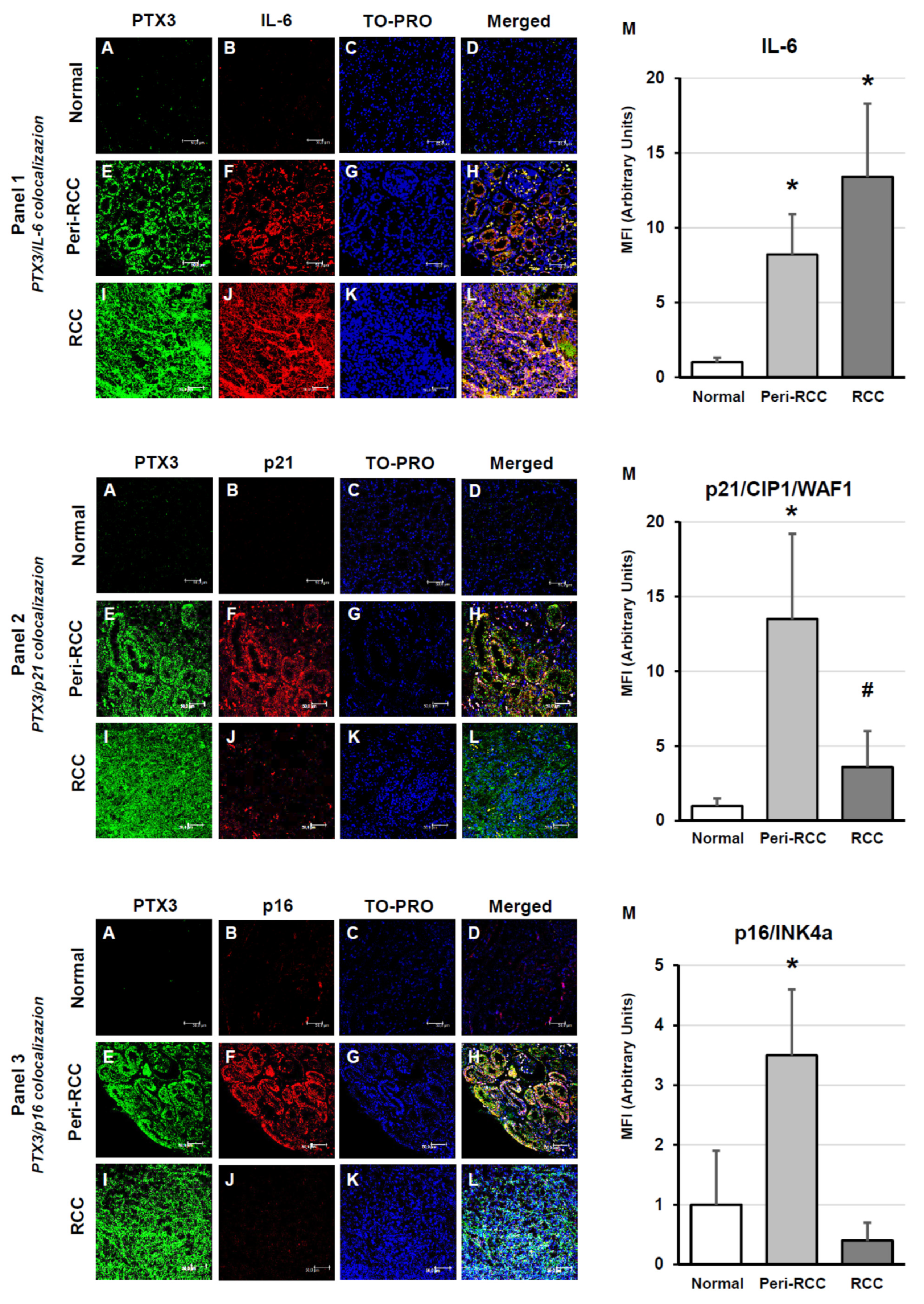
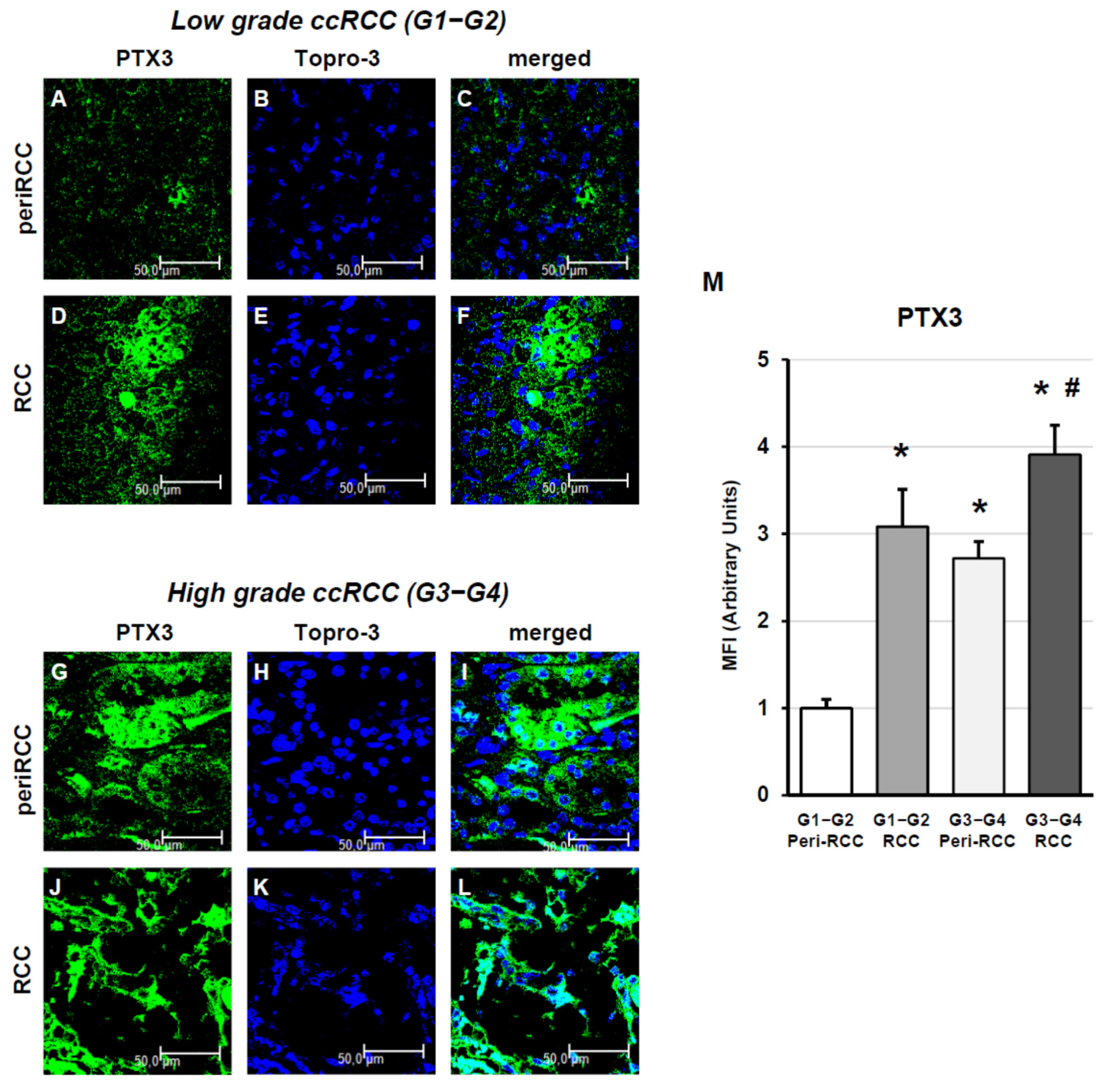
2.3. Indirect Immunofluorescence and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.4. IL-6 Serum Level Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
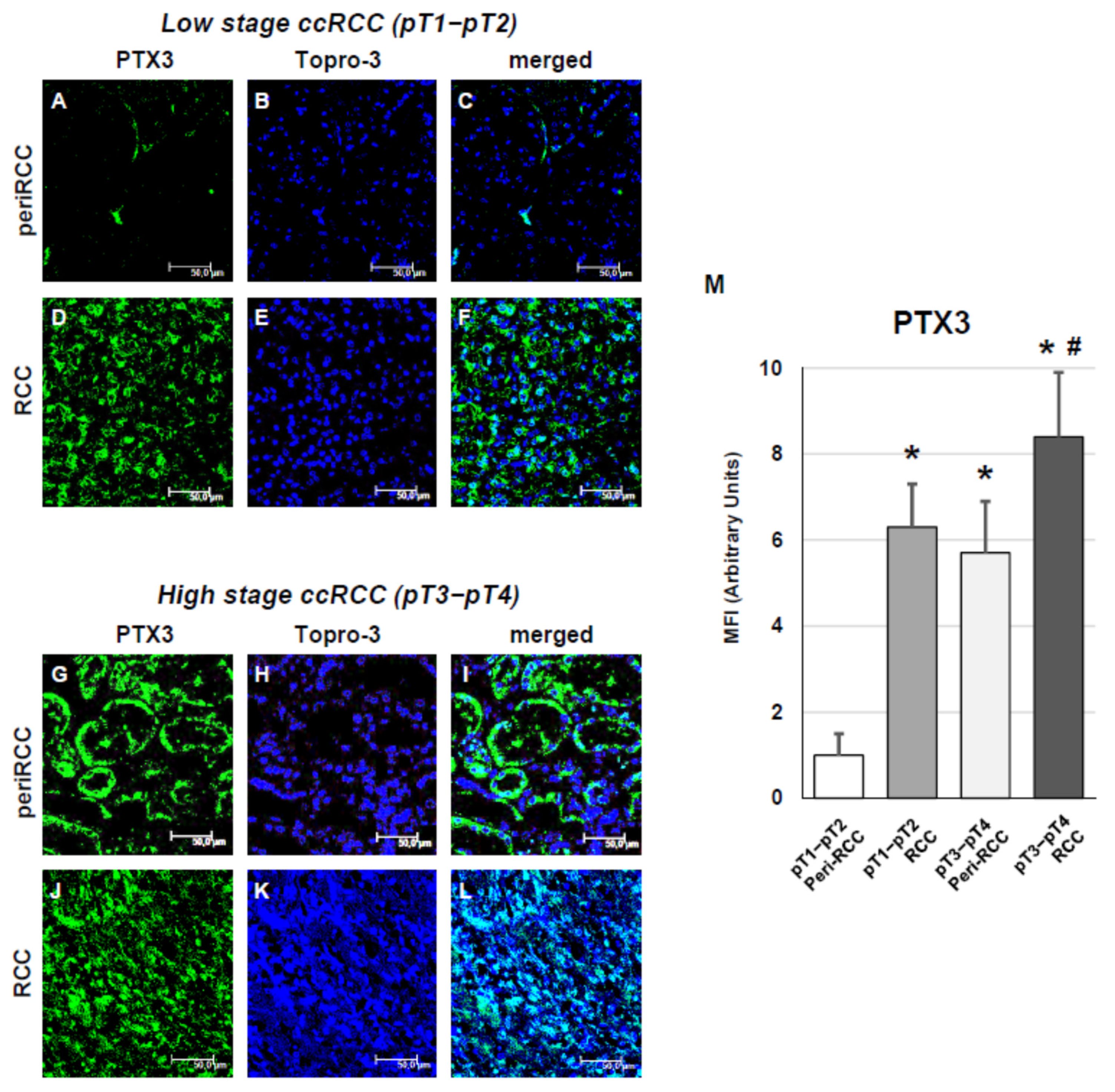
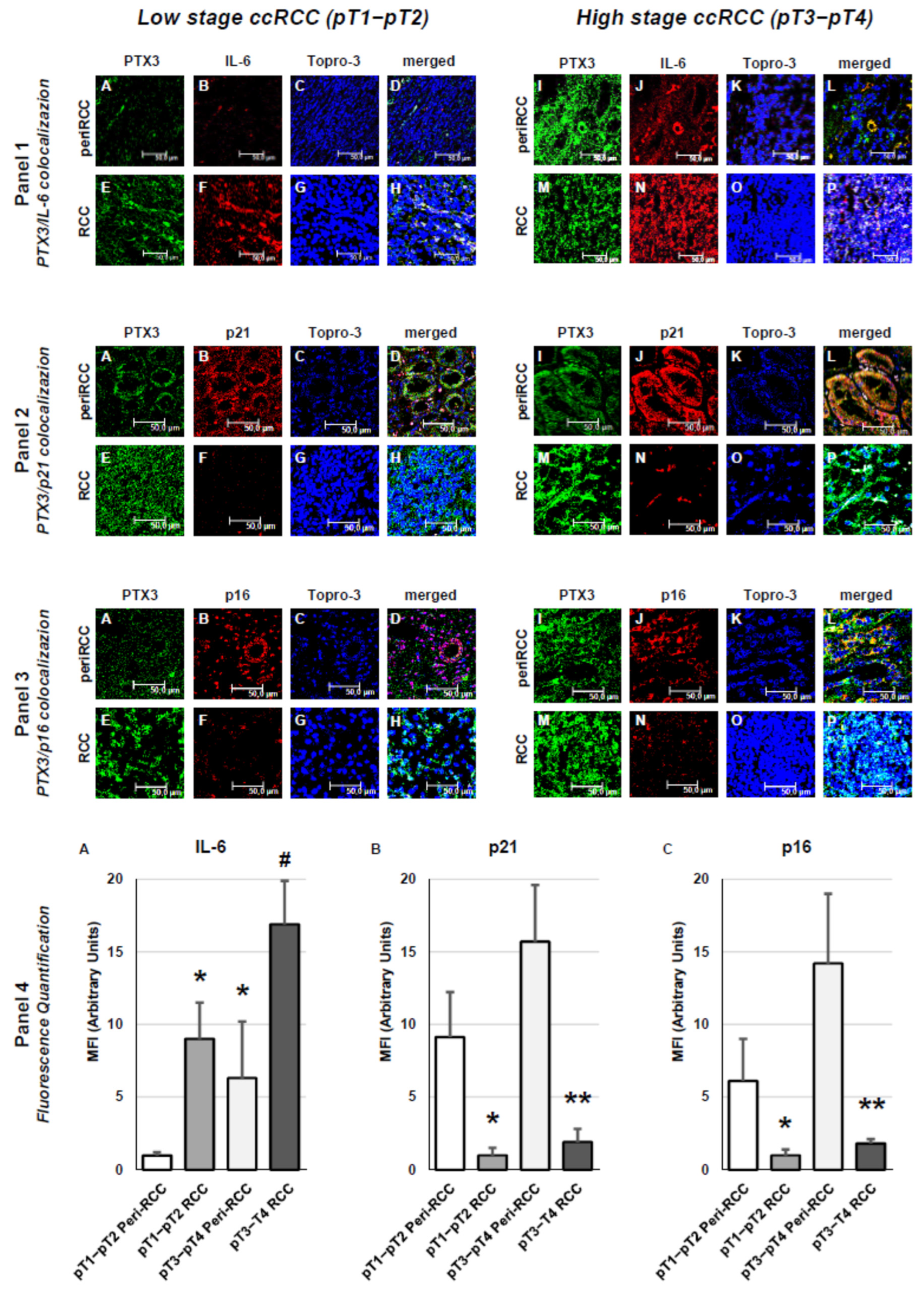
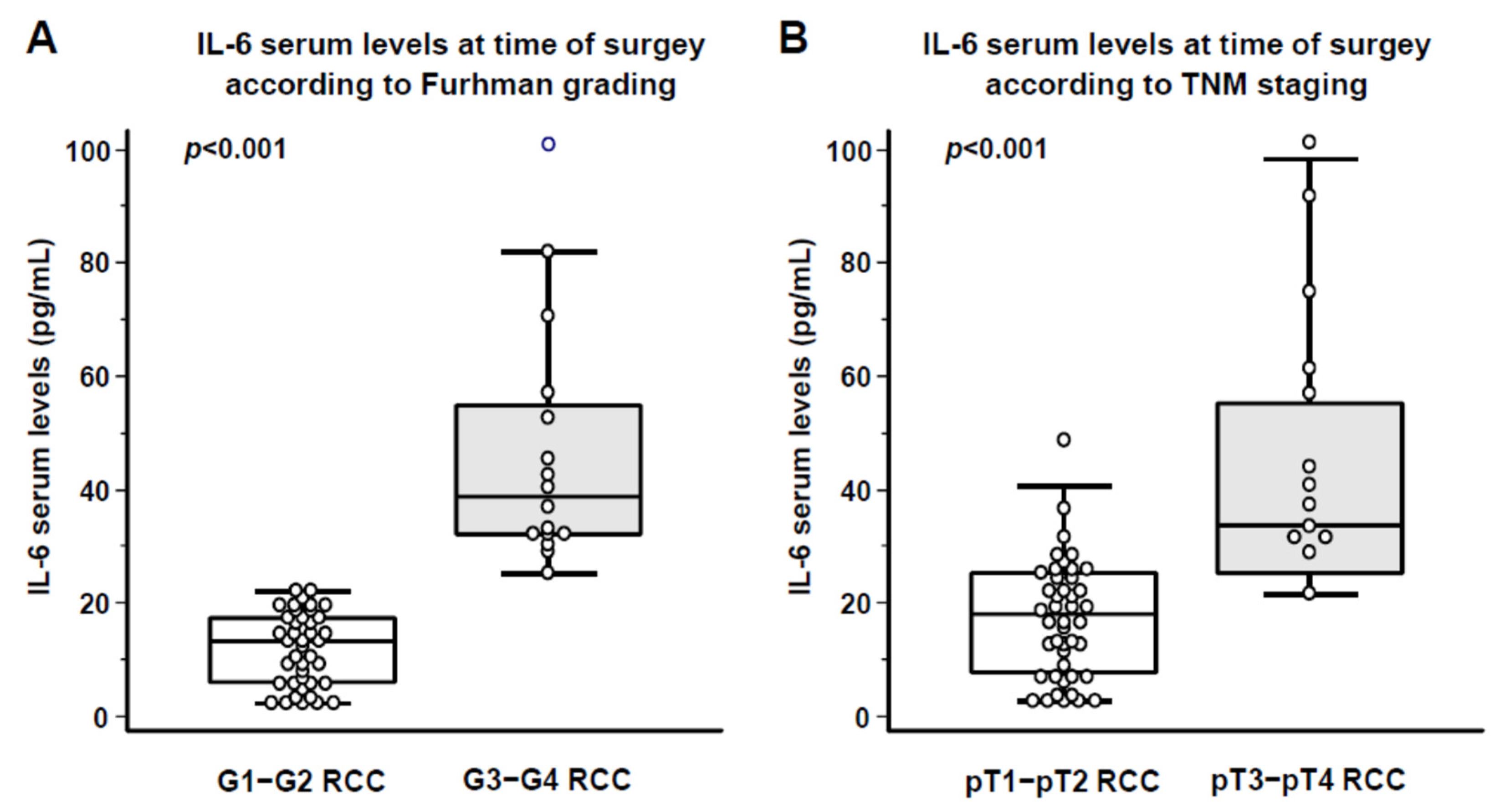
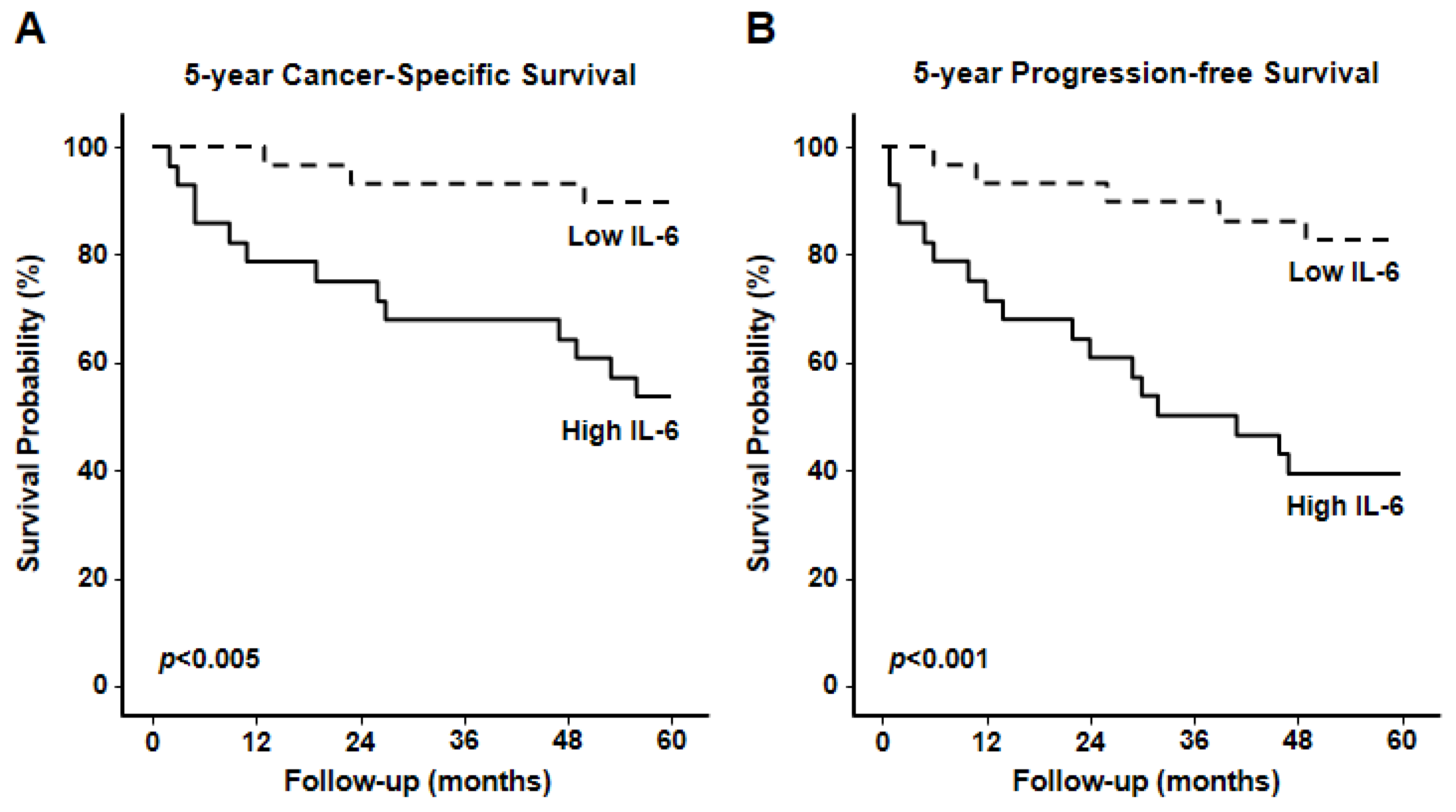
3. Results
| Clinical Characteristics of RCC Patients | ||
| Patients, n | 57 | |
| Age, median (range) | 61 (25–87) | |
| Female Gender, n (%) | 18 (31.6%) | |
| Diabetes Mellitus, n (%) | 14 (24.6%) | |
| high sensitive C reactive protein (hs-CRP); mg/dL | 4.8 ± 1.2 | |
| CKD-EPI eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 89.5 ± 11.5 | |
| Histologic Characterization of RCC Patients | ||
| Fuhrman grading | G 1 | 8 (14.0%) |
| G 2 | 33 (57.9%) | |
| G 3 | 9 (15.8%) | |
| G 4 | 7 (12.3%) | |
| TNM/AJCC Staging | pT1a | 9 (15.8%) |
| pT1b | 24 (42.1%) | |
| pT2a | 6 (10.5%) | |
| pT2b | 5 (8.8%) | |
| pT3a | 12 (21.1%) | |
| pT3b-c | 1 (1.8%) | |
| pT4 | 0 (0.0%) | |
| pN+ | 8 (10.5%) | |
| cM+ | 1 (1.8%) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| CKD-EPI | Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition |
| PTX3 | Pentraxin 3 |
| RCC | Renal Cell Carcinoma |
| SASP | Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype |
| TNM | Tumor, Node, Metastasis |
References
- Rini, B.I.; Campbell, S.C.; Escudier, B. Renal Cell Carcinoma. Lancet 2009, 373, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCastro, G.J.; McKiernan, J.M. Epidemiology, Clinical Staging, and Presentation of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 35, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydlo, J.H. Growth Factors and Renal Cancer: Characterization and Therapeutic Implications. World J. Urol. 1995, 13, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.T.; McGovern, F.J. Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2477–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, R.P.; Montie, J.E.; Correa, R.J.; Mason, J.T. Manifestations of Renal Cell Carcinom. Urology 1976, 8, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.-H.; Dong, L.M.; Devesa, S.S. Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, T.E. Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Clinical Evidence. Oncologist 2011, 16, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, K.; Xiong, Z.; Yuan, C.; Wang, C.; Cao, Q.; Yu, H.; Meng, X.; Xie, K.; Cheng, Z.; et al. Impact of Inflammation and Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, L.; Kotecha, R.R.; Voss, M.H.; Hakimi, A.A. Tumor Microenvironment Dynamics in Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leon, A.D.; Pirasteh, A.; Costa, D.N.; Kapur, P.; Hammers, H.; Brugarolas, J.; Pedrosa, I. Current Challenges in Diagnosis and Assessment of the Response of Locally Advanced and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Radiographics 2019, 39, 998–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottazzi, B.; Inforzato, A.; Messa, M.; Barbagallo, M.; Magrini, E.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. The Pentraxins PTX3 and SAP in Innate Immunity, Regulation of Inflammation and Tissue Remodelling. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zou, H.; Dai, Z.; Feng, S.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, G.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Q. The Basic Characteristics of the Pentraxin Family and Their Functions in Tumor Progression. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doni, A.; Stravalaci, M.; Inforzato, A.; Magrini, E.; Mantovani, A.; Garlanda, C.; Bottazzi, B. The Long Pentraxin PTX3 as a Link Between Innate Immunity, Tissue Remodeling, and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigo, K.; Inforzato, A.; Barajon, I.; Garlanda, C.; Bottazzi, B.; Meri, S.; Mantovani, A. Pentraxins in the Activation and Regulation of Innate Immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inforzato, A.; Reading, P.C.; Barbati, E.; Bottazzi, B.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. The “Sweet” Side of a Long Pentraxin: How Glycosylation Affects PTX3 Functions in Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2013, 3, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, A.; Ghedini, G.C.; Presta, M.; Ronca, R. Long Pentraxin 3: A Novel Multifaceted Player in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2018, 1869, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-C.; Wu, S.-L.; Huang, W.-C.; Hsu, J.-Y.; Chan, S.-H.; Wang, J.-M.; Tsai, J.-P.; Chen, B.-K. PTX3 Gene Activation in EGF-Induced Head and Neck Cancer Cell Metastasis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7741–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.-H.; Tsai, J.-P.; Shen, C.-J.; Liao, Y.-H.; Chen, B.-K. Oleate-Induced PTX3 Promotes Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis through the up-Regulation of Vimentin. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41364–41378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Wang, C.; Guo, C.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, X. Pentraxin 3 Overexpression Accelerated Tumor Metastasis and Indicated Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Driving Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Henry, W.; Cuiffo, B.G.; Collmann, A.Y.; Marangoni, E.; Benhamo, V.; Bhasin, M.K.; Fan, C.; Fuhrmann, L.; Baldwin, A.S.; et al. Pentraxin-3 Is a PI3K Signaling Target That Promotes Stem Cell-like Traits in Basal-like Breast Cancers. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaah4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.; Lee, E.-J.; Shin, M.-K.; Park, Y.S.; Ryu, M.-H.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, E.-Y.; Lee, H.K.; Chang, E.-J. Upregulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Advanced Gastric Cancer Contributes to Bone Metastatic Osteolysis by Inducing Long Pentraxin 3. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55506–55517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rascio, F.; Spadaccino, F.; Rocchetti, M.T.; Castellano, G.; Stallone, G.; Netti, G.S.; Ranieri, E. The Pathogenic Role of PI3K/AKT Pathway in Cancer Onset and Drug Resistance: An Updated Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallone, G.; Netti, G.S.G.S.; Cormio, L.; Castellano, G.; Infante, B.; Pontrelli, P.; Divella, C.; Selvaggio, O.; Spadaccino, F.; Ranieri, E.; et al. Modulation of Complement Activation by Pentraxin-3 in Prostate Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallone, G.; Cormio, L.; Netti, G.S.G.S.; Infante, B.; Selvaggio, O.; Fino, G.D.; Ranieri, E.; Bruno, F.; Prattichizzo, C.; Sanguedolce, F.; et al. Pentraxin 3: A Novel Biomarker for Predicting Progression from Prostatic Inflammation to Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4230–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, M.L.; Williams, S.A.; Jelinek, C.A.; Kostova, M.B.; Denmeade, S.R. Proteolysis of Complement Factors iC3b and C5 by the Serine Protease Prostate-Specific Antigen in Prostatic Fluid and Seminal Plasma. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2567–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loberg, R.D.; Day, L.L.; Dunn, R.; Kalikin, L.M.; Pienta, K.J. Inhibition of Decay-Accelerating Factor (CD55) Attenuates Prostate Cancer Growth and Survival in Vivo. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Jung, M.; Burkhardt, M.; Stephan, C.; Schnorr, D.; Loening, S.; Jung, K.; Dietel, M.; Kristiansen, G. Increased CD59 Protein Expression Predicts a PSA Relapse in Patients after Radical Prostatectomy. Prostate 2004, 62, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, B.; Silwal, A.; Daugherity, E.; Daugherity, M.; Arabi, M.; Daly, P.; Paterson, Y.; Woolford, L.; Christie, A.; Elias, R.; et al. Complement as Prognostic Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target in Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 3218–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tang, S.; Sheerin, N.S.; Vaughan, R.W.; Sacks, S.H. Contribution of Renal Secreted Complement C3 to the Circulating Pool in Humans. Mol. Immunol. 1998, 35, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Marsh, J.E.; Sacks, S.H. Intrarenal Synthesis of Complement. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, L.; Ajona, D.; Rafail, S.; Lasarte, J.J.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Lambris, J.D.; Rouzaut, A.; Pajares, M.J.; Montuenga, L.M.; Pio, R. Anaphylatoxin C5a Creates a Favorable Microenvironment for Lung Cancer Progression. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4674–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezmee, M.N.M.; Kyaw-Tanner, M.; Lee, J.Y.P.; Shiels, I.A.; Rolfe, B.; Woodruff, T.; Mills, P.C. Increased Expression of C5a Receptor (CD88) mRNA in Canine Mammary Tumors. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 139, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, V.T.; Daha, M.R.; Tijsma, O.M.H.; Weissglas, M.G.; van den Broek, L.J.C.M.; Gorter, A. A Possible Role of CD46 for the Protection In Vivo of Human Renal Tumor Cells from Complement-Mediated Damage. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netti, G.S.G.S.; Lucarelli, G.; Spadaccino, F.; Castellano, G.; Gigante, M.; Divella, C.; Rocchetti, M.T.M.T.; Rascio, F.; Mancini, V.; Stallone, G.; et al. PTX3 Modulates the Immunoflogosis in Tumor Microenvironment and Is a Prognostic Factor for Patients with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Aging 2020, 12, 7585–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, J. Aging, Cellular Senescence, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, N.S.M.; Safuan, S.; Shamsuddin, S.; Foroozandeh, P. Aging of the Cells: Insight into Cellular Senescence and Detection Methods. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 99, 151108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.; Blasco, M.A.; Serrano, M. Cellular Senescence in Cancer and Aging. Cell 2007, 130, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, B.G.; Baker, D.J.; Kirkland, J.L.; Campisi, J.; Deursen, J.M. van Senescence and Apoptosis: Dueling or Complementary Cell Fates? EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1139–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.Y.; Han, J.A.; Im, J.S.; Morrone, A.; Johung, K.; Goodwin, E.C.; Kleijer, W.J.; DiMaio, D.; Hwang, E.S. Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase Is Lysosomal β-Galactosidase. Aging Cell 2006, 5, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzin, R.; Stasi, A.; Ranieri, E.; Netti, G.S.G.S.; Cantaluppi, V.; Gesualdo, L.; Stallone, G.; Castellano, G. Targeting Premature Renal Aging: From Molecular Mechanisms of Cellular Senescence to Senolytic Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 630419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, J.; Gil, J. Senescence and the SASP: Many Therapeutic Avenues. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppé, J.-P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Muñoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Campisi, J. Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotypes Reveal Cell-Nonautonomous Functions of Oncogenic RAS and the P53 Tumor Suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 2853–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuilman, T.; Michaloglou, C.; Vredeveld, L.C.W.; Douma, S.; van Doorn, R.; Desmet, C.J.; Aarden, L.A.; Mooi, W.J.; Peeper, D.S. Oncogene-Induced Senescence Relayed by an Interleukin-Dependent Inflammatory Network. Cell 2008, 133, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, S.; Brown, S.; Wessendorf, J.H.; Maciag, T. Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Interleukin 1 Alpha in Various Strains of Young and Senescent Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritschka, B.; Storer, M.; Mas, A.; Heinzmann, F.; Ortells, M.C.; Morton, J.P.; Sansom, O.J.; Zender, L.; Keyes, W.M. The Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype Induces Cellular Plasticity and Tissue Regeneration. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canino, C.; Mori, F.; Cambria, A.; Diamantini, A.; Germoni, S.; Alessandrini, G.; Borsellino, G.; Galati, R.; Battistini, L.; Blandino, R.; et al. SASP Mediates Chemoresistance and Tumor-Initiating-Activity of Mesothelioma Cells. Oncogene 2011, 31, 3148–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tato-Costa, J.; Casimiro, S.; Pacheco, T.; Pires, R.; Fernandes, A.; Alho, I.; Pereira, P.; Costa, P.; Castelo, H.B.; Ferreira, J.; et al. Therapy-Induced Cellular Senescence Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Increases Invasiveness in Rectal Cancer. Clin. Color. Cancer 2016, 15, 170–178.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, J.C.; Banito, A.; Wuestefeld, T.; Georgilis, A.; Janich, P.; Morton, J.P.; Athineos, D.; Kang, T.-W.; Lasitschka, F.; Andrulis, M.; et al. A Complex Secretory Program Orchestrated by the Inflammasome Controls Paracrine Senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosteiro, L.; Pantoja, C.; Alcazar, N.; Marión, R.M.; Chondronasiou, D.; Rovira, M.; Fernandez-Marcos, P.J.; Muñoz-Martin, M.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Pastor, J.; et al. Tissue Damage and Senescence Provide Critical Signals for Cellular Reprogramming in Vivo. Science 2016, 354, aaf4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosteiro, L.; Pantoja, C.; de Martino, A.; Serrano, M. Senescence Promotes in Vivo Reprogramming through P16(INK)(4a) and IL-6. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Tokunaga, H.; Zhou, J.; Kim, J.; Ayala, G.E.; Benedict, W.F.; Lerner, S.P. P53, P21, pRB, and P16 Expression Predict Clinical Outcome in Cystectomy with Bladder Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M. The Tumor Suppressor Protein p16INK4a. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 237, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeesy, N.; Aguirre, A.J.; Chu, G.C.; Cheng, K.-H.; Lopez, L.V.; Hezel, A.F.; Feng, B.; Brennan, C.; Weissleder, R.; Mahmood, U.; et al. Both P16(Ink4a) and the P19(Arf)-P53 Pathway Constrain Progression of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma in the Mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5947–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, D.L.; Sanchez, C.A.; Galipeau, P.C.; Blount, P.L.; Paulson, T.G.; Cowan, D.S.; Ayub, K.; Odze, R.D.; Rabinovitch, P.S.; Reid, B.J. Cell Proliferation, Cell Cycle Abnormalities, and Cancer Outcome in Patients with Barrett’s Esophagus: A Long-Term Prospective Study. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6988–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.H.; Borowsky, A.D.; Seligson, D.; Lin, P.-Y.; Dillard-Telm, L.; Belldegrun, A.S.; Figlin, R.A.; Pantuck, A.D. P21 Is a Prognostic Marker for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Approaches. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuerowo, S.O.; Kuczyk, M.A.; von Wasielewski, R.; Shittu, O.B.; Jonas, U.; Machtens, S.; Serth, J. p16INK4a Expression and Clinicopathologic Parameters in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, B.; Rossini, M.; Leo, S.; Troise, D.; Netti, G.S.; Ranieri, E.; Gesualdo, L.; Castellano, G.; Stallone, G. Recurrent Glomerulonephritis after Renal Transplantation: The Clinical Problem. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netti, G.S.G.S.; Franzin, R.; Stasi, A.; Spadaccino, F.; Strologo, A.D.; Infante, B.; Gesualdo, L.; Castellano, G.; Ranieri, E.; Stallone, G. Role of Complement in Regulating Inflammation Processes in Renal and Prostate Cancers. Cells 2021, 10, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelardi, M.; Netti, G.S.; Giancaspro, R.; Spadaccino, F.; Pennella, A.; Fiore, V.; Gatta, E.L.; Grilli, G.M.; Cassano, M.; Ranieri, E. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis (CRSwNP): The Correlation between Expression of Galectin-10 and Clinical-Cytological Grading (CCG). Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2022, 36, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondi, M.; Netti, G.S.; Rosati, A.; Mazzinghi, B.; Magri, F.; Ronconi, E.; Becherucci, F.; Pradella, F.; Salvadori, M.; Serio, M.; et al. Pretransplant Serum FT3 Levels in Kidney Graft Recipients Are Useful for Identifying Patients with Higher Risk for Graft Failure. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 68, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netti, G.S.; Infante, B.; Spadaccino, F.; Godeas, G.; Corallo, M.G.; Prisciandaro, C.; Croce, L.; Rotondi, M.; Gesualdo, L.; Stallone, G.; et al. Serum Levels of BAFF and APRIL Predict Clinical Response in Anti-PLA2R-Positive Primary Membranous Nephropathy. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 8483650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormio, L.; Lucarelli, G.; Netti, G.S.; Stallone, G.; Selvaggio, O.; Troiano, F.; Fino, G.D.; Sanguedolce, F.; Bufo, P.; Grandaliano, G.; et al. Post-Void Residual Urinary Volume Is an Independent Predictor of Biopsy Results in Men at Risk for Prostate Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar]
- Netti, G.S.; Rotondi, M.; Lorenzo, A.D.; Papantonio, D.; Teri, A.; Schirone, M.; Spadaccino, F.; Croce, L.; Infante, B.; Perulli, R.; et al. Nocturnal Haemodialysis Is Associated with a Reduced Occurrence of Low Triiodothyronine Serum Levels in Haemodialysed Patients. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netti, G.S.; Soccio, P.; Catalano, V.; De Luca, F.; Khalid, J.; Camporeale, V.; Moriondo, G.; Papale, M.; Scioscia, G.; Corso, G.; et al. The Onset of Antinuclear Antibodies (ANAs) as a Potential Risk Factor for Mortality and Morbidity in COVID-19 Patients: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netti, G.S.; Prattichizzo, C.; Montemurno, E.; Simone, S.; Cafiero, C.; Rascio, F.; Stallone, G.; Ranieri, E.; Grandaliano, G.; Gesualdo, L. Exposure to Low- vs Iso-Osmolar Contrast Agents Reduces NADPH-Dependent Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in a Cellular Model of Renal Injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 68, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppé, J.-P.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. The Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype: The Dark Side of Tumor Suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2010, 5, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, Y.; Ueki, K.; Joseph, J.T.; Louis, D.N. Homozygous Deletions of the CDKN2/P16 Gene in Dural Hemangiopericytomas. Acta Neuropathol. 1996, 91, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaelin, W.G. The von Hippel-Lindau Tumor Suppressor Protein and Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 680s–684s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.P.; Schlisio, S.; Minamishima, Y.A.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Grisanzio, C.; Signoretti, S.; Kaelin, W.G. VHL Loss Actuates a HIF-Independent Senescence Programme Mediated by Rb and P400. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Nature 2013, 499, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, J.; d’Adda Di Fagagna, F. Cellular Senescence: When Bad Things Happen to Good Cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in Cancer Inflammation and Immunity: A Leading Role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, B.; Franzin, R.; Madio, D.; Calvaruso, M.; Maiorano, A.; Sangregorio, F.; Netti, G.S.; Ranieri, E.; Gesualdo, L.; Castellano, G.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of AKI in the Elderly: From Animal Models to Therapeutic Intervention. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.H.; Ahmed, A.T.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Bokov, D.O.; Shafie, A.; Al-Hetty, H.R.A.K.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Alissa, M.; Nazir, S.; Jamali, M.C.; et al. Interleukin-6 Serves as a Critical Factor in Various Cancer Progression and Therapy. Med. Oncol. 2024, 41, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Lang, X.; Li, X. The Role of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1023177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 Signalling Axis in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Priceman, S.J.; Xin, H.; Zhang, W.; Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, W.; Chen, M.; Hu, W.; et al. Icaritin Inhibits JAK/STAT3 Signaling and Growth of Renal Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstroem, R.B.; Nielsen, O.H.; Jacobsen, S.; Riis, L.B.; Theile, S.; Bjerrum, J.T.; Vilmann, P.; Johansen, J.S.; Boisen, M.K.; Eefsen, R.H.L.; et al. COLAR: Open-Label Clinical Study of IL-6 Blockade with Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis and Arthritis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serzan, M. Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2024, 22, e245011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| (A) Cancer-Specific Survival | |||||
| 95% CI | |||||
| Variables | Adjustment Variable | HR | Lower | Higher | p Value |
| Serum IL-6 (≥ vs. <16.5 pg/dL) | Fuhrman Grade | 6.821 | 1.724 | 27.054 | 0.006 |
| Serum IL-6 (≥ vs. <16.5 pg/dL) | TNM stage | 6.143 | 1.517 | 24.961 | 0.011 |
| (B) Progression-Free Survival | |||||
| 95% CI | |||||
| Variables | Adjustment Variable | HR | Lower | Higher | p Value |
| Serum IL-6 (≥ vs. <16.5 pg/dL) | Fuhrman Grade | 4.378 | 1.516 | 12.6324 | 0.007 |
| Serum IL-6 (≥ vs. <16.5 pg/dL) | TNM stage | 3.981 | 1.394 | 11.384 | 0.010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Netti, G.S.; Spadaccino, F.; Lucarelli, G.; Catalano, V.; Checchia, A.; Stasi, A.; De Luca, F.; Camporeale, V.; Leccese, G.; Cuttano, R.; et al. Molecular Remodeling of Peritumoral Tissue in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Insights into Inflammaging and Prognostic Markers. Cancers 2026, 18, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers18030414
Netti GS, Spadaccino F, Lucarelli G, Catalano V, Checchia A, Stasi A, De Luca F, Camporeale V, Leccese G, Cuttano R, et al. Molecular Remodeling of Peritumoral Tissue in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Insights into Inflammaging and Prognostic Markers. Cancers. 2026; 18(3):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers18030414
Chicago/Turabian StyleNetti, Giuseppe Stefano, Federica Spadaccino, Giuseppe Lucarelli, Valeria Catalano, Andrea Checchia, Alessandra Stasi, Federica De Luca, Valentina Camporeale, Giorgia Leccese, Roberto Cuttano, and et al. 2026. "Molecular Remodeling of Peritumoral Tissue in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Insights into Inflammaging and Prognostic Markers" Cancers 18, no. 3: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers18030414
APA StyleNetti, G. S., Spadaccino, F., Lucarelli, G., Catalano, V., Checchia, A., Stasi, A., De Luca, F., Camporeale, V., Leccese, G., Cuttano, R., Troise, D., Infante, B., Carrieri, G., Storkus, W. J., Stallone, G., & Ranieri, E. (2026). Molecular Remodeling of Peritumoral Tissue in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Insights into Inflammaging and Prognostic Markers. Cancers, 18(3), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers18030414









