Treatment-Related Adverse Events in Extended Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Receiving First-Line Chemoimmunotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
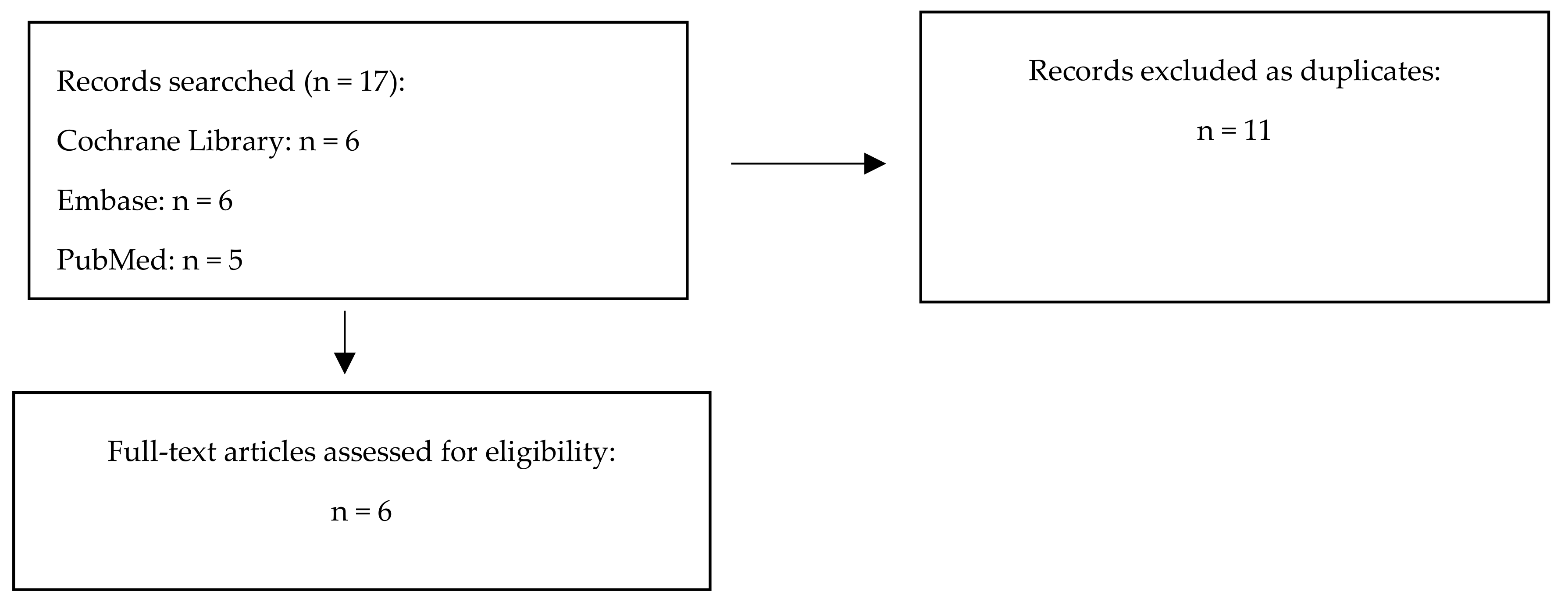
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
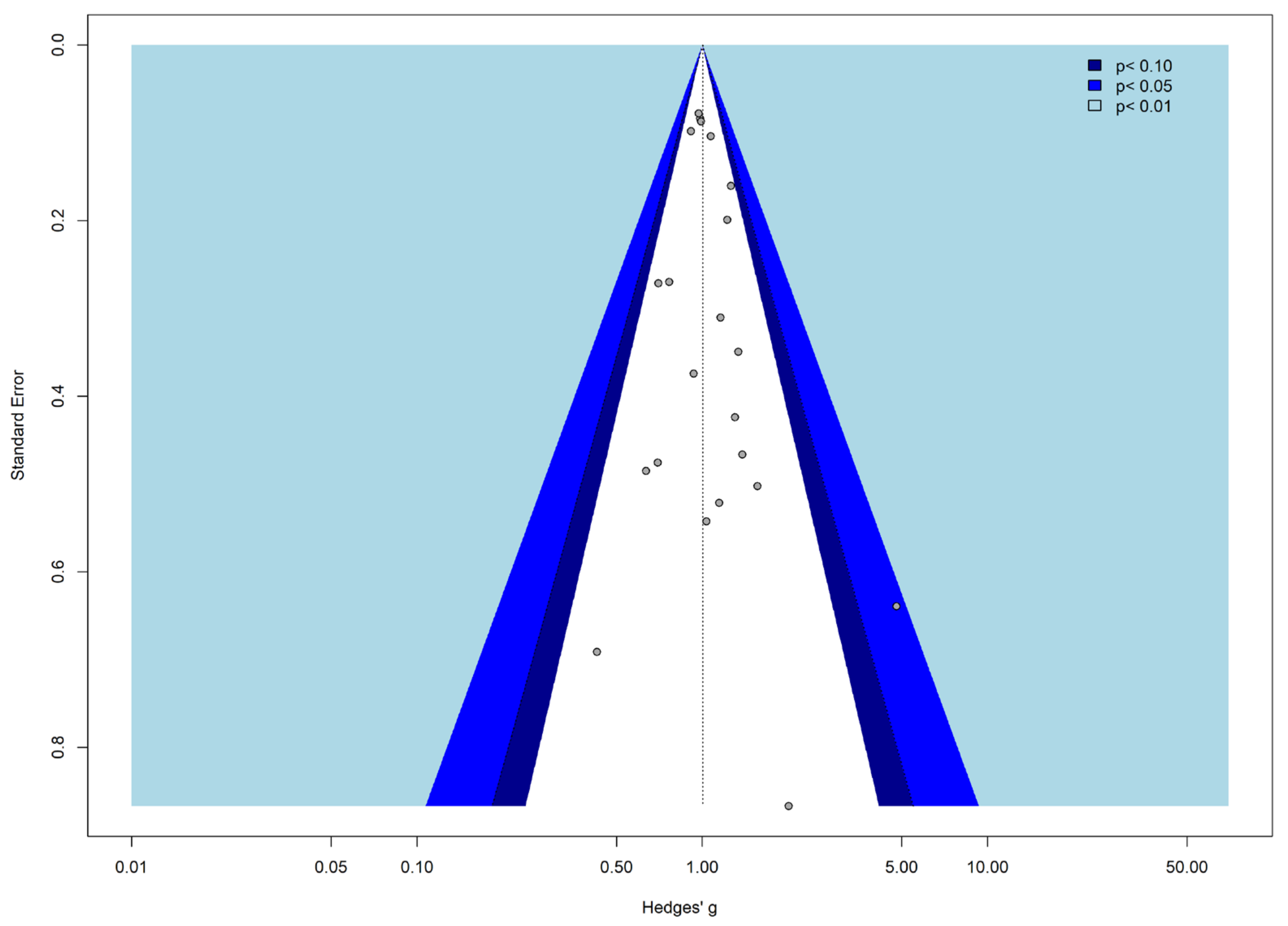
3.1. The Main Features of the Included Any Grade TRAEs
3.2. Meta-Analysis
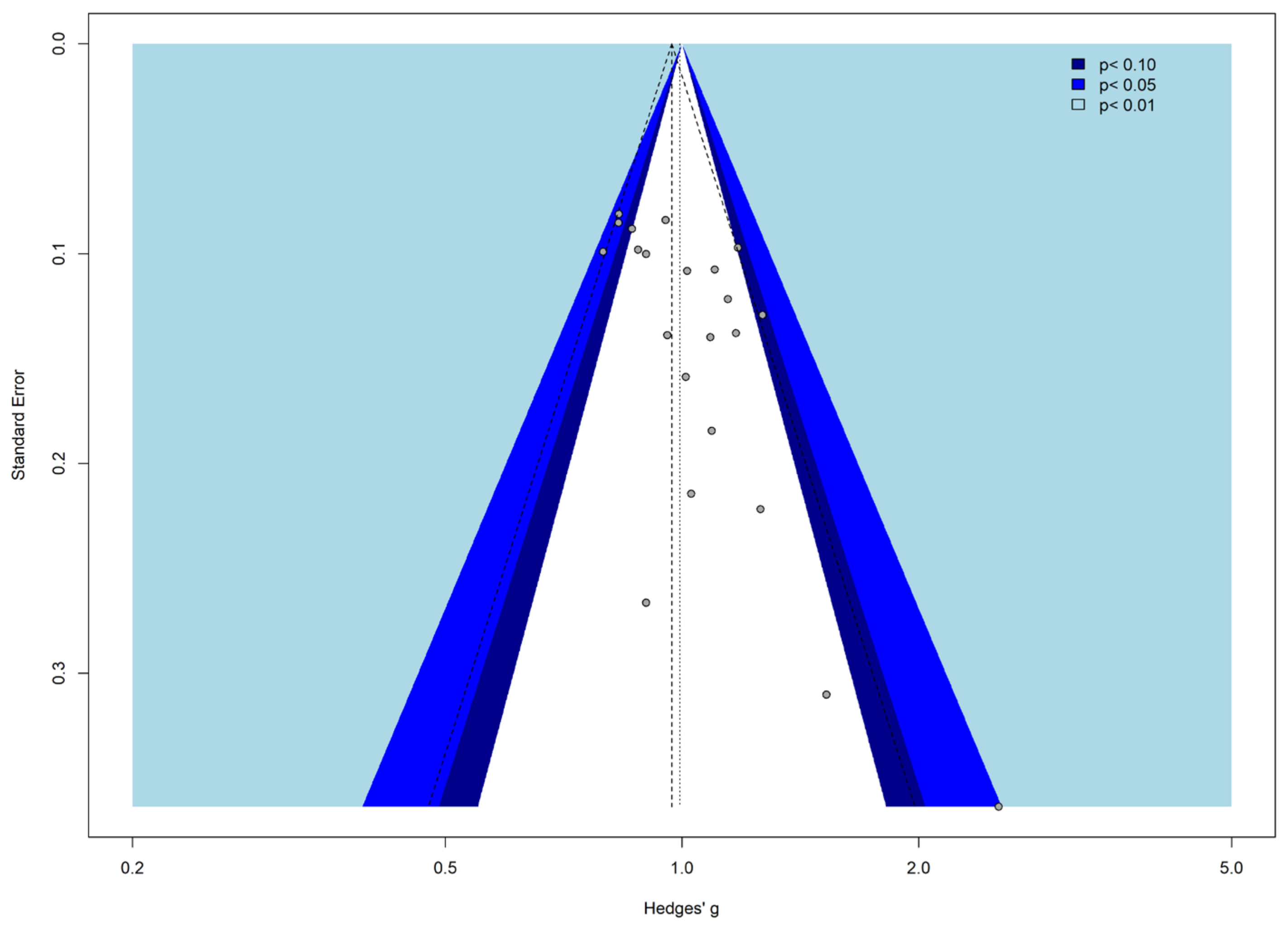
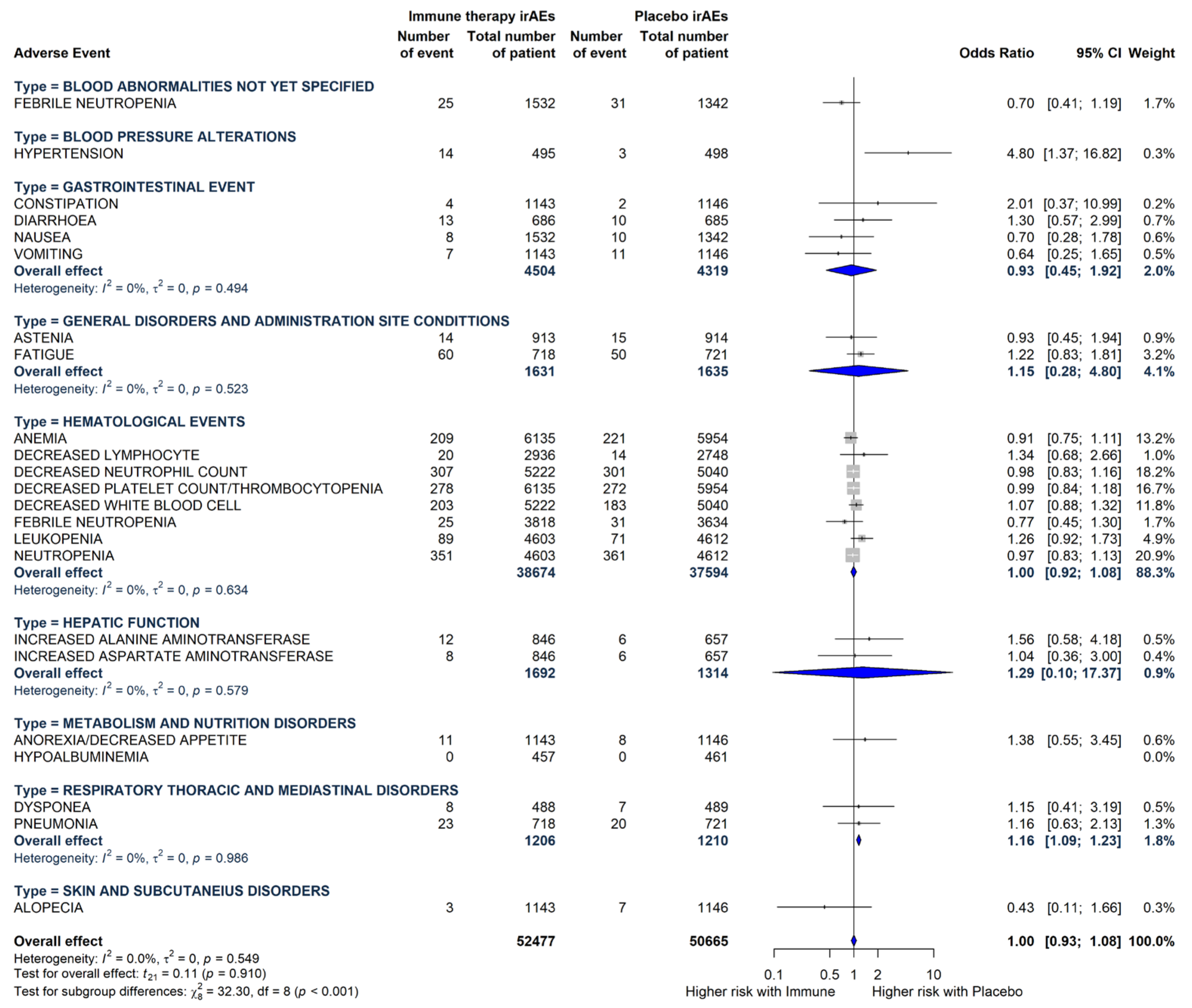
3.3. The Main Features of the Included Grade 3 or More TRAEs
3.4. Meta-Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dingemans, A.C.; Früh, M.; Ardizzoni, A.; Besse, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Hendriks, L.E.; Lantuejoul, S.; Peters, S.; Reguart, N.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, J.T.; George, J.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Berns, A.; Brambilla, E.; Byers, L.A.; Carbone, D.; Chen, H.J.; Christensen, C.L.; Dive, C.; et al. New Approaches to SCLC Therapy: From the Laboratory to the Clinic. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 520–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farago, A.F.; Keane, F.K. Current standards for clinical management of small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Pennell, N.A.; Fidler, M.J.; Halmos, B.; Bonomi, P.; Stevenson, J.; Schneider, B.; Sukari, A.; Ventimiglia, J.; Chen, W.; et al. Phase II Study of Maintenance Pembrolizumab in Patients with Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, P.A.; Elez, E.; Hiret, S.; Kim, D.W.; Morosky, A.; Saraf, S.; Piperdi, B.; Mehnert, J.M. Pembrolizumab in Patients With Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the Phase Ib KEYNOTE-028 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2017, 35, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.V.; Reck, M.; Mansfield, A.S.; Mok, T.; Scherpereel, A.; Reinmuth, N.; Garassino, M.C.; De Castro Carpeno, J.; Califano, R.; Nishio, M.; et al. Updated Overall Survival and PD-L1 Subgroup Analysis of Patients With Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Atezolizumab, Carboplatin, and Etoposide (IMpower133). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczęsna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.W.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide alone in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): Updated results from a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Yao, W.; Wang, Q.; Min, X.; Chen, G.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Fang, Y.; et al. Adebrelimab or placebo plus carboplatin and etoposide as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CAPSTONE-1): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Han, L.; Wu, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Wen, G.; Ji, Y.; Dvorkin, M.; Shi, J.; Pan, Z.; et al. Lung Cancer: The ASTRUM-005 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 328, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Kang, M.; Yang, N.; Zhong, D.; Wang, Z.; et al. Tislelizumab Plus Platinum and Etoposide Versus Placebo Plus Platinum and Etoposide as First-Line Treatment for Extensive-Stage SCLC (RATIONALE-312): A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized, Phase 3 Clinical Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, V.; Catino, A.; Montrone, M.; Pizzutilo, P.; Annese, T.; Pesola, F.; Marech, I.; Cassiano, S.; Ribatti, D.; Galetta, D. What Are the Biomarkers for Immunotherapy in SCLC? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, L.B.; Salama, A.K.S. A review of cancer immunotherapy toxicity. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020, 70, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Awad, M.M.; Navarro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peters, S.; Csőszi, T.; Cheema, P.K.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Wollner, M.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum as First-Line Therapy for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III KEYNOTE-604 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, N.; Haenszel, W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1959, 22, 719–748. [Google Scholar]
- Deeks, J.J.; Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, G.; Hartung, J. Improved Tests for a Random Effects Meta-Regression with a Single Covariate. Stat. Med. 2003, 22, 2693–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W.; Cheung, M.W. Outlier and influence diagnostics for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.; Clarke, M. Forest plots: Trying to see the wood and the trees. Br. Med. J. 2001, 322, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Lacchetti, C.; Schneider, B.J.; Atkins, M.B.; Brassil, K.J.; Caterino, J.M.; Chau, I.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Gardner, J.M.; Ginex, P.; et al. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1714–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Guo, S.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Grossi, F.; Ichiki, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for treatment of small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordo-Bahamonde, C.; Lorenzo-Herrero, S.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, A.P.; Martínez-Pérez, A.; Rodrigo, J.P.; García-Pedrero, J.M.; Gonzalez, S. Chemo-Immunotherapy: A New Trend in Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2023, 15, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanen, J.B.A.G.; Carbonnel, F.; Robert, C.; Kerr, K.M.; Peters, S.; Larkin, J.; Jordan, K.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28 (Suppl. S4), iv119–iv142, Erratum in Ann. Oncol.2018, 29 (Suppl. S4), iv264–iv266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, A.; Maji, A.; Potdar, P.D.; Singh, N.; Parikh, P.; Bisht, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Paul, M.K. Lung cancer immunotherapy: Progress, pitfalls, and promises. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, Y.; Kim, I.Y.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, J.; Cha, H.S.; Koh, E.M.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. Risk factors for immune-related adverse events associated with anti-PD-1 pembrolizumab. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, A.; Toyokawa, G.; Koutake, Y.; Kimura, S.; Kawamata, Y.; Fukuishi, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Takeo, S. Association between pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and immune-related adverse events due to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.Y.; Oen, K.Q.X.; Lim, G.R.S.; Hartono, J.L.; Muthiah, M.; Huang, D.Q.; Teo, F.S.W.; Li, A.Y.; Mak, A.; Chandran, N.S.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts development of immune-related adverse events and outcomes from immune checkpoint blockade: A case-control study. Cancers 2021, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wang, Z.; Tian, P.; Li, W. Safety and tolerability of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, J.; Fernandez, E.; Alwan, H.; Philippe, J. Programmed cell death-1 and programmed cell death ligand-1 antibodies-induced dysthyroidism. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, R196–R211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, C.G.; Giovannucci, E.; Testa, M.; Glass, T.A.; Kawachi, I. The association of treatment-related symptoms with quality-of-life outcomes for localized prostate carcinoma patients. Cancer 2002, 94, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, M.; Chiu, M.N.; Pilkhwal Sah, S. Adverse cutaneous toxicities by PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors: Pathogenesis, treatment, and surveillance. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chang, J.; Mendenhall, M.; Cherry, G.; Goldman, J.W.; Kulkarni, R.P. Diverse cutaneous adverse eruptions caused by anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and anti-programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) immunotherapies: Clinical features and management. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, A.N.; Phillips, G.S.; Barrios, D.M.; Wu, J.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Moy, A.P.; Kern, J.A.; Lacouture, M.E. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related dermatologic adverse events. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Narukawa, M. Immune-related and Common Adverse Events With Programmed Cell Death 1/Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 inhibitors combined with other Anticancer Therapy for Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 37, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, F.C.A.; Lôbo, A.O.M.; Sano, V.K.T.; Kelly, F.A.; Burbano, R.M.R. Treatment-related Adverse Events, Including Fatal Toxicities, in Patients With Extensive-stage Small-cell Lung Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Programmed Cell Death 1/Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 Inhibitors: A Meta-analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 36, e408–e419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaji, N.; Watanabe, N.; Kita, N.; Bandoh, S.; Tadokoro, A.; Ishii, T.; Dobashi, H.; Matsunaga, T. Paraneoplastic syndromes associated with lung cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, M.; Fancelli, S.; Caliman, E.; Mazzoni, F.; Michelet, M.G.; Mancini, S.; Manneschi, C.; Shabani, S.; Napolitano, B.; Pillozzi, S.; et al. Impact of natremia on metastatic non small cell lung cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavdy, T.; Samavedam, J.M.; Mathias, P.; Lee, H.J. Severe Hyponatremia Triggered by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in a Patient With Mulvihill-Smith Syndrome. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2024, 10, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, J.C.; Ni, A.; Chaft, J.E.; Pollina, R.; Kasler, M.K.; Stephens, D.; Rodriguez, C.; Cambridge, L.; Rizvi, H.; Wolchok, J.D.; et al. Antibody-mediated thyroid dysfunction during T-cell checkpoint blockade in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2017, 28, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.-H.; Chien, W.-C.; Liu, C.-C.; Chung, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Kuo, F.-C.; Fang, H.-H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Ding, Y.-X.; Tien, C.-H.; et al. An enigma of hypothyroidism and hyponatremia coexistence: A nationwide population-based retrospective study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liamis, G.; Filippatos, T.D.; Liontos, A.; Elisaf, M.S. Management of endocrine disease: Hypothyroidism-associated hyponatremia: Mechanisms, implications and treatment. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, R15–R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.; Beiglböck, H.; Smaijs, S.; Wrba, T.; Rasoul-Rockenschaub, S.; Marculescu, R.; Gessl, A.; Luger, A.; Winhofer, Y.; Krebs, M. Hypothyroidism and Hyponatremia: Rather Coincidence Than Causality. Thyroid 2017, 27, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.J.; Powers, A.C.; Johnson, D.B. Endocrine toxicities of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Wang, F.; Xie, X.; Liu, T.; Zeng, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, M.; Deng, H.; Yang, Y.; Lin, X.; et al. A retrospective real-world experience of immunotherapy in patients with extensive stage small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 14881–14891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, L.; Calvetti, L.; Dal Maso, A.; Pavan, A.; Bao, L.C.; De Nuzzo, M.; Frega, S.; Sartori, G.; Ferro, A.; Pasello, G.; et al. Real-world impact of the introduction of chemo-immunotherapy in extended small cell lung cancer: A multicentric analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1353889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, E.; Rizzo, A.; Santa, K.; Jirillo, E. Associations between “Cancer Risk”, “Inflammation” and “Metabolic Syndrome”: A Scoping Review. Biology 2024, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, E.; Rizzo, A.; Maistrello, L.; Guven, D.C.; Massafra, R.; Mollica, V.; Monteiro, F.S.M.; Santoni, M.; Massari, F. Sex differences in adverse events among cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: The MOUSEION-07 systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Mizuki, Y.; Kawagoe, T.; Mihara, T.; Yamashiro, T. Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) of Effect Sizes other than Mean Difference. J. Clin. Quest. 2024, 1, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Adverse Events | Immunotherapy | Chemotherapy Alone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events (n) | Patients (n) | Incidence: Events (n)/Patients (n) (%) | Events (n) | Patients (n) | Incidence: Events (n)/Patients (n) (%) | |
| BLOOD ABNORMALITIES NOT YET SPECIFIED | ||||||
| FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA | 28 | 693 | 0.04 | 31 | 694 | 0.04 |
| HYPONATREMIA | 109 | 1217 | 0.09 | 65 | 1060 | 0.06 |
| BLOOD PRESSURE ALTERATIONS | ||||||
| HYPERTENSION | 27 | 489 | 0.06 | 11 | 487 | 0.02 |
| GASTROINTESTINAL EVENT | ||||||
| DIARRHOEA | 92 | 686 | 0.13 | 91 | 685 | 0.13 |
| NAUSEA | 472 | 1415 | 0.33 | 472 | 1256 | 0.38 |
| VOMITING | 210 | 1143 | 0.18 | 208 | 1146 | 0.18 |
| CONSTIPATION | 220 | 1143 | 0.19 | 204 | 1146 | 0.18 |
| GENERAL DISORDERS AND ADMINISTRATION SITE CONDITTIONS | ||||||
| ASTENIA | 123 | 718 | 0.17 | 128 | 721 | 0.18 |
| FATIGUE | 174 | 913 | 0.19 | 156 | 914 | 0.17 |
| HEMATOLOGICAL EVENTS | ||||||
| DECREASED WHITE BLOOD CELL | 325 | 965 | 0.34 | 290 | 804 | 0.36 |
| DECREASED NEUTROPHIL COUNT | 356 | 965 | 0.37 | 321 | 804 | 0.40 |
| NEUTROPENIA | 335 | 958 | 0.35 | 321 | 795 | 0.40 |
| ANEMIA | 566 | 1188 | 0.48 | 537 | 1027 | 0.52 |
| LEUKOPENIA | 136 | 958 | 0.14 | 105 | 795 | 0.13 |
| FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA | 28 | 693 | 0.04 | 31 | 694 | 0.04 |
| DECREASED PLATELET COUNT/THROMBOCYTOPENIA | 422 | 1188 | 0.36 | 400 | 1027 | 0.39 |
| DECREASED LYMPHOCYTE | 35 | 502 | 0.07 | 16 | 342 | 0.05 |
| HEPATIC FUNCTION | ||||||
| INCREASED ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE | 201 | 729 | 0.28 | 132 | 571 | 0.23 |
| INCREASED ASPARTATE AMINOTRANSFERASE | 162 | 729 | 0.22 | 112 | 571 | 0.20 |
| METABOLISM AND NUTRITION DISORDERS | ||||||
| ANOREXIA/DECREASED APPETITE | 299 | 1143 | 0.26 | 265 | 1146 | 0.23 |
| HYPOALBUMINEMIA | 50 | 457 | 0.11 | 41 | 461 | 0.09 |
| RESPIRATORY THORACIC AND MEDIASTINAL DISORDERS | ||||||
| PNEUMONIA | 47 | 718 | 0.07 | 46 | 721 | 0.06 |
| DYSPONEA | 71 | 488 | 0.15 | 66 | 489 | 0.13 |
| SKIN AND SUBCUTANEIUS DISORDERS | ||||||
| ALOPECIA | 506 | 1143 | 0.44 | 521 | 1146 | 0.45 |
| RASH | 58 | 450 | 0.13 | 31 | 452 | 0.07 |
| THYROID DISORDERS | ||||||
| HYPOTHYROIDISM | 138 | 952 | 0.14 | 40 | 794 | 0.05 |
| Adverse Events | Immunotherapy | Chemotherapy Alone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events (n) | Patients (n) | Incidence: Events (n)/Patients (n) (%) | Events (n) | Patients (n) | Incidence: Events (n)/Patients (n) (%) | |
| BLOOD ABNORMALITIES NOT YET SPECIFIED | ||||||
| FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA | 25 | 1532 | 0.02 | 31 | 1342 | 0.02 |
| HYPONATREMIA | 28 | 1532 | 0.02 | 18 | 1342 | 0.01 |
| BLOOD PRESSURE ALTERATIONS | ||||||
| HYPERTENSION | 14 | 495 | 0.03 | 3 | 498 | 0.01 |
| GASTROINTESTINAL EVENT | ||||||
| DIARRHOEA | 13 | 686 | 0.02 | 10 | 685 | 0.01 |
| NAUSEA | 8 | 1532 | 0.01 | 10 | 1342 | 0.01 |
| VOMITING | 7 | 1143 | 0.01 | 11 | 1146 | 0.01 |
| CONSTIPATION | 4 | 1143 | 0 | 2 | 1146 | 0 |
| GENERAL DISORDERS AND ADMINISTRATION SITE CONDITTIONS | ||||||
| ASTENIA | 14 | 913 | 0.02 | 15 | 914 | 0.02 |
| FATIGUE | 60 | 718 | 0.08 | 50 | 721 | 0.07 |
| HEMATOLOGICAL EVENTS | ||||||
| DECREASED WHITE BLOOD CELL | 203 | 5222 | 0.04 | 183 | 5040 | 0.04 |
| DECREASED NEUTROPHIL COUNT | 307 | 5222 | 0.06 | 301 | 5040 | 0.06 |
| NEUTROPENIA | 351 | 4603 | 0.08 | 361 | 4612 | 0.08 |
| ANEMIA | 209 | 6135 | 0.03 | 221 | 5954 | 0.04 |
| LEUKOPENIA | 89 | 4603 | 0.02 | 71 | 4612 | 0.02 |
| FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA | 25 | 3818 | 0.01 | 31 | 3634 | 0.01 |
| DECREASED PLATELET COUNT/THROMBOCYTOPENIA | 278 | 6135 | 0.05 | 272 | 5954 | 0.05 |
| DECREASED LYMPHOCYTE | 20 | 2936 | 0.01 | 14 | 2748 | 0.01 |
| HEPATIC FUNCTION | ||||||
| INCREASED ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE | 12 | 846 | 0.01 | 6 | 657 | 0.01 |
| INCREASED ASPARTATE AMINOTRANSFERASE | 8 | 846 | 0.01 | 6 | 657 | 0.01 |
| METABOLISM AND NUTRITION DISORDERS | ||||||
| ANOREXIA/DECREASED APPETITE | 11 | 1143 | 0.01 | 8 | 1146 | 0.01 |
| HYPOALBUMINEMIA | 0 | 457 | 0 | 0 | 461 | 0 |
| RESPIRATORY THORACIC AND MEDIASTINAL DISORDERS | ||||||
| PNEUMONIA | 23 | 718 | 0.03 | 20 | 721 | 0.03 |
| DYSPONEA | 8 | 488 | 0.02 | 7 | 489 | 0.01 |
| SKIN AND SUBCUTANEIUS DISORDERS | ||||||
| ALOPECIA | 3 | 1143 | 0 | 7 | 1146 | 0.01 |
| RASH | 8 | 450 | 0.02 | 0 | 452 | 0 |
| THYROID DISORDERS | ||||||
| HYPOTHYROIDISM | 2 | 1069 | 0 | 0 | 880 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vitale, E.; Rizzo, A.; Maistrello, L.; Guven, D.C.; Cauli, O.; Galetta, D.; Longo, V. Treatment-Related Adverse Events in Extended Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Receiving First-Line Chemoimmunotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091571
Vitale E, Rizzo A, Maistrello L, Guven DC, Cauli O, Galetta D, Longo V. Treatment-Related Adverse Events in Extended Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Receiving First-Line Chemoimmunotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091571
Chicago/Turabian StyleVitale, Elsa, Alessandro Rizzo, Lorenza Maistrello, Deniz Can Guven, Omar Cauli, Domenico Galetta, and Vito Longo. 2025. "Treatment-Related Adverse Events in Extended Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Receiving First-Line Chemoimmunotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091571
APA StyleVitale, E., Rizzo, A., Maistrello, L., Guven, D. C., Cauli, O., Galetta, D., & Longo, V. (2025). Treatment-Related Adverse Events in Extended Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Receiving First-Line Chemoimmunotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 17(9), 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091571










