Systemic Treatment of Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
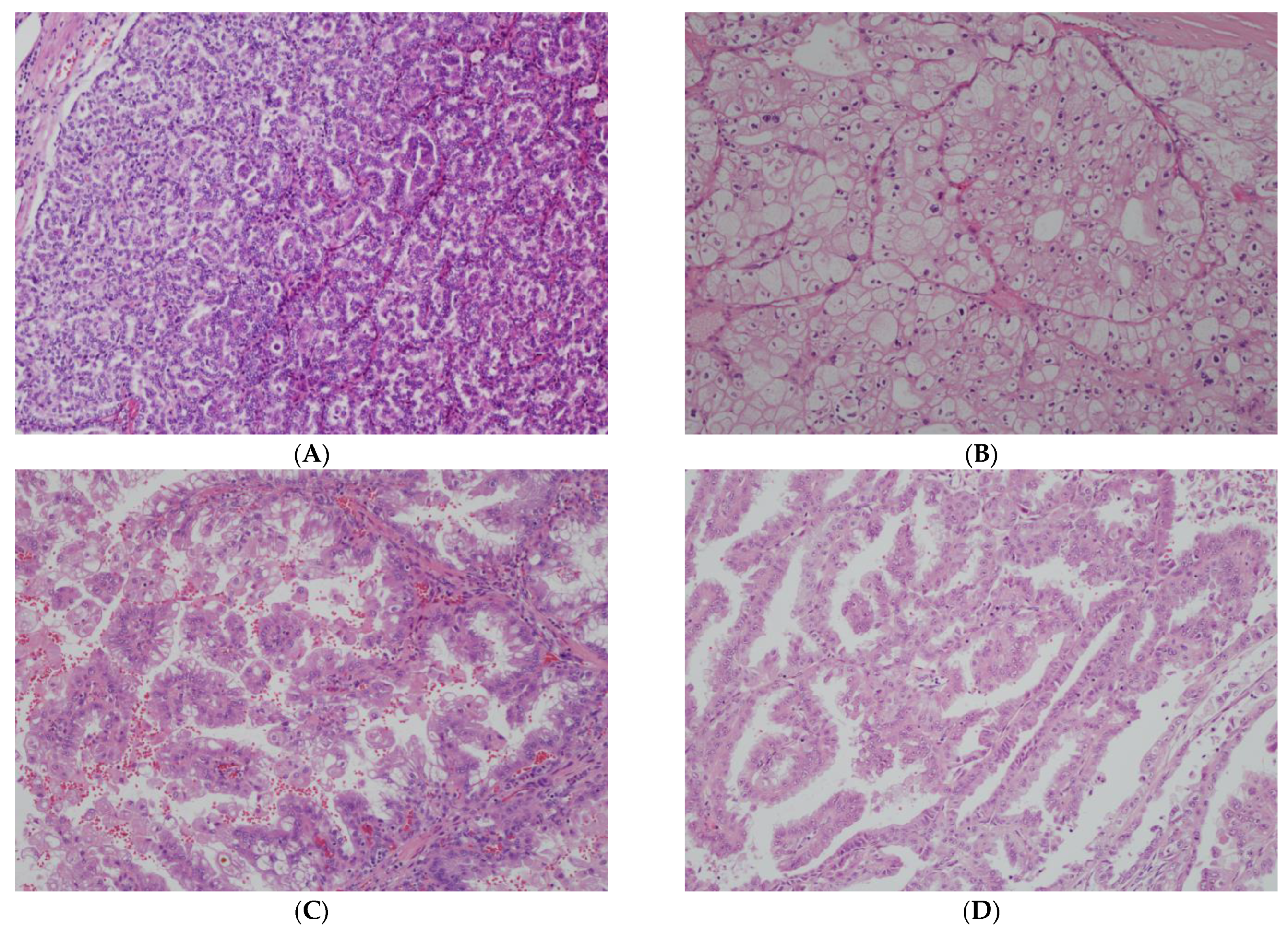
2.1. Updates in nccRCC Classification
2.2. Papillary RCC
2.2.1. VEGFR TKI Monotherapy
2.2.2. mTOR Inhibitors
2.2.3. ICI Monotherapy
2.2.4. ICI Combination Therapies
2.2.5. Papillary RCC Summary
2.3. Chromophobe RCC
2.4. Not Otherwise Specified (Also Referred to in the Literature as Unclassified) RCC
2.5. Translocation RCC
2.6. Collecting Duct Carcinoma
| Study | Study Drug(s) | n | nccRCC Subtype (s) | ORR (95% CI) | mPFS (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prospective Clinical Trials | |||||
| BEVABEL-GETUG/ AFU24 [68] | Gemcitabine + platinum chemo + bevacizumab | 34 | Collecting Duct Renal Medullary | 41.2% (25–57%) | 5.9 mo (5.3–9.3 mo) |
| GETUG 2007 [67] | Gemcitabine + platinum chemo | 23 | Collecting Duct | 26% (8–44%) | 7.1 mo (3–11.3 mo) |
| BONSAI [69] | Cabozantinib | 22 | Collecting Duct | 35% (16–57%) | 4 mo (3–31 mo) |
| BONSAI-2 [70] | Nivolumab (Post-cabo) | 4 | 25% | PFS 2.8–19.9 mo | |
| NCT02721732 [71] | Pembrolizumab (1 front-line) | 5 | Renal Medullary | 0/5 (0%) | 8.7 weeks |
| Retrospective Reviews | |||||
| Shah et al. [72] (at any line of therapy) | Carboplatin/ paclitaxel (±bev) | 21 | Renal Medullary | 7/21 33% | N/A |
| Gemcitabine/ cisplatin (±bev) | 12 | 4/12 33% | N/A | ||
| Gemcitabine/ doxorubicin (±paclitaxel/bev) | 11 | 3/11 27.3% | N/A | ||
| Gemcitabine/ carboplatin/ paclitaxel | 2 | 1/2 50% | N/A | ||
| Gemcitabine/ cisplatin/ paclitaxel | 1 | 1/1 100% | N/A | ||
| Wilson et al. [73] | Gemcitabine + doxorubicin (second-line) | 16 | Renal Medullary | 18.8% | 2.8 mo (0–6 mo) |
2.7. Renal Medullary Carcinoma
2.8. Fumarate-Hydratase-Deficient RCC and Other Molecularly Defined nccRCC Subtypes
2.9. Sarcomatoid Differentiation and PD-L1 Status
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| ccRCC | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| FH | Fumarate hydratase |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| mOS | Median overall survival |
| mPFS | Median progression-free survival |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| nccRCC | Non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma |
| ORR | Overall response rate |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PARPi | Poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibitor |
| RCC | Renal cell carcinoma |
| SDH | Succinate Dehydrogenase |
| SOC | Standard of Care |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| VEGFR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Rose, T.L.; Kim, W.Y. Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Review. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2024, 332, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, P.R.; Singh, G.; Patel, T.; Dave, R. The WHO 2022 Classification of Renal Neoplasms (5th Edition): Salient Updates. Cureus 2022, 16, e58470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Wang, L.; Panian, J.; Dhanji, S.; Derweesh, I.; Rose, B.; Bagrodia, A.; McKay, R.R. Treatment Landscape of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 1889–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrier, S.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Ferlay, C.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Gravis, G.; Geoffrois, L.; Chevreau, C.; Boyle, H.; Rolland, F.; Blanc, E.; et al. Axitinib in first-line for patients with metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma: Results of the multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase II AXIPAP trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 129, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Tangen, C.; Thompson, I.M.; Balzer-Haas, N.; George, D.J.; Heng, D.Y.C.; Shuch, B.; Stein, M.; Tretiakova, M.; Humphrey, P.; et al. A comparison of sunitinib with cabozantinib, crizotinib, and savolitinib for treatment of advanced papillary renal cell carcinoma: A randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannir, N.M.; Jonasch, E.; Albiges, L.; Altinmakas, E.; Ng, C.S.; Matin, S.F.; Wang, X.; Qiao, W.; Dubauskas Lim, Z.; Tamboli, P.; et al. Everolimus Versus Sunitinib Prospective Evaluation in Metastatic Non–Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ESPN): A Randomized Multicenter Phase 2 Trial. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Halabi, S.; Eisen, T.; Broderick, S.; Stadler, W.M.; Jones, R.J.; Garcia, J.A.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Picus, J.; Hawkins, R.E.; et al. Everolimus versus sunitinib for patients with metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ASPEN): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, T.E.; Michaelson, M.D.; Kuzel, T.M.; Agarwal, N.; Molina, A.M.; Hsieh, J.J.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Xie, R.; Bapat, U.; Ye, W.; et al. A Single-arm, Multicenter, Phase 2 Study of Lenvatinib Plus Everolimus in Patients with Advanced Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, M.H.; Molina, A.M.; Chen, Y.B.; Woo, K.M.; Chaim, J.L.; Coskey, D.T.; Redzematovic, A.; Wang, P.; Lee, W.; Selcuklu, S.D.; et al. Phase II Trial and Correlative Genomic Analysis of Everolimus Plus Bevacizumab in Advanced Non–Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3846–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazopanib for the Treatment of Non-clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase II Study. Available online: https://www.e-crt.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.4143/crt.2016.584 (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Barata, P.C.; Chehrazi-Raffle, A.; Allman, K.D.; Asnis-Alibozek, A.; Kasturi, V.; Pal, S.K. Activity of Tivozanib in Non-clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Subgroup Analysis from a Phase II Randomized Discontinuation Trial. Oncologist 2023, 28, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, D.F.; Lee, J.L.; Ziobro, M.; Suarez, C.; Langiewicz, P.; Matveev, V.B.; Wiechno, P.; Gafanov, R.A.; Tomczak, P.; Pouliot, F.; et al. Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase II Study of Pembrolizumab Monotherapy as First-Line Therapy in Patients with Advanced Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Olsen, M.R.; McFarlane, J.J.; Arrowsmith, E.; Bauer, T.M.; Jain, R.K.; Somer, B.; Lam, E.T.; Kochenderfer, M.D.; Molina, A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced Non–Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Results from the Phase IIIb/IV CheckMate 374 Study. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2020, 18, 461–468.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conduit, C.; Davis, I.D.; Goh, J.C.; Kichenadasse, G.; Gurney, H.; Harris, C.A.; Pook, D.; Krieger, L.; Parnis, F.; Underhill, C.; et al. A phase II trial of nivolumab followed by ipilimumab and nivolumab in advanced non-clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2024, 133 (Suppl. S3), 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiges, L.; Gurney, H.; Atduev, V.; Suarez, C.; Climent, M.A.; Pook, D.; Tomczak, P.; Barthelemy, P.; Lee, J.L.; Stus, V.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib as first-line therapy for advanced non-clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-B61): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Voss, M.H.; Carlo, M.I.; Chen, Y.B.; Zucker, M.; Knezevic, A.; Lefkowitz, R.A.; Shapnik, N.; Dadoun, C.; Reznik, E.; et al. Phase II Trial of Cabozantinib Plus Nivolumab in Patients with Non-Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Genomic Correlates. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tykodi, S.S.; Gordan, L.N.; Alter, R.S.; Arrowsmith, E.; Harrison, M.R.; Percent, I.; Singal, R.; Veldhuizen, P.V.; George, D.J.; Hutson, T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with advanced non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Results from the phase 3b/4 CheckMate 920 trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, L.; Ahrens, M.; Albiges, L.; Goupil, M.G.; Boleti, E.; Gravis, G.; Flechon, A.; Grimm, M.O.J.; Rausch, S.; Barthelemy, P.; et al. LBA75 Prospective randomised phase-II trial of ipilimumab/nivolumab versus standard of care in non-clear cell renal cell cancer: Results of the SUNNIFORECAST trial. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, S1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, B.A.; Huang, J.; Xie, W.; Xu, W.; Bilen, M.A.; Braun, D.A.; Zhang, T.; McKay, R.R.; McDermott, D.F.; Hammers, H.J.; et al. Phase II study of cabozantinib (Cabo) with nivolumab (Nivo) and ipilimumab (Ipi) in advanced renal cell carcinoma with variant histologies (RCCvh). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S16), 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, C.; Larkin, J.M.G.; Patel, P.; Valderrama, B.P.; Rodriguez-Vida, A.; Glen, H.; Thistlethwaite, F.; Ralph, C.; Srinivasan, G.; Mendez-Vidal, M.J.; et al. Phase II Study Investigating the Safety and Efficacy of Savolitinib and Durvalumab in Metastatic Papillary Renal Cancer (CALYPSO). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2493–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; McGregor, B.; Suárez, C.; Tsao, C.K.; Kelly, W.; Vaishampayan, U.; Pagliaro, L.; Maughan, B.L.; Loriot, Y.; Castellano, D.; et al. Cabozantinib in Combination with Atezolizumab for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Results From the COSMIC-021 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3725–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, B.A.; McKay, R.R.; Braun, D.A.; Werner, L.; Gray, K.; Flaifel, A.; Signoretti, S.; Hirsch, M.S.; Steinharter, J.A.; Bakouny, Z.; et al. Results of a Multicenter Phase II Study of Atezolizumab and Bevacizumab for Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma with Variant Histology and/or Sarcomatoid Features. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franczyk, B.; Rysz, J.; Ławiński, J.; Ciałkowska-Rysz, A.; Gluba-Brzózka, A. Cardiotoxicity of Selected Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Huntington, S.; Gross, C.; Wang, S.Y. Immunotherapy utilization patterns in patients with advanced cancer and autoimmune disease. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.; Porta, C.; Alekseev, B.; Rha, S.Y.; Choueiri, T.K.; Mendez-Vidal, M.J.; Hong, S.H.; Kapoor, A.; Goh, J.C.; Eto, M.; et al. Health-related quality-of-life outcomes in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab or everolimus versus sunitinib (CLEAR): A randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, R.K.; Upadhyay, R.; Wang, S.J.; Singer, E.A.; Dason, S. Incorporating Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy into the Multidisciplinary Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 10283–10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.; Ohashi, R.; Amin, M.B.; Berney, D.M.; Compérat, E.M.; Cree, I.A.; Gill, A.J.; Hartmann, A.; Menon, S.; Netto, G.J.; et al. WHO 2022 landscape of papillary and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2022, 81, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Papillary Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.D.; Uzzo, R.G.; Choueiri, T.K. 2nd Wuof/Siu Icud on Kidney Cancer. In Wiuf/Siu/Icud; World Urologic Oncology Federation: Seville, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khurshid, H. Role of artificial intelligence in cancer diagnosis and treatment: Current trends and future directions. Glob. J. Basic Sci. 2024, 1, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, K.; Xing, Y.; Jiang, S.; Qin, Z.; et al. Single-cell chromatin accessibility landscape in kidney identifies additional cell-of-origin in heterogenous papillary renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). A Phase II Randomized Trial of Cabozantinib (NSC #761968) With or Without Atezolizumab (NSC #783608) in Patients with Advanced Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma (PAPMET2). 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05411081 (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Ravaud, A.; Oudard, S.; De Fromont, M.; Chevreau, C.; Gravis, G.; Zanetta, S.; Theodore, C.; Jimenez, M.; Sevin, E.; Laguerre, B.; et al. First-line treatment with sunitinib for type 1 and type 2 locally advanced or metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma: A phase II study (SUPAP) by the French Genitourinary Group (GETUG)†. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.A.; Link, E.; Goh, J.C.; Parnis, F.; Gurney, H.; Kichenadasse, G.; Underhill, C.; Torres, J.; Roncolato, F.; Inderjeeth, A.J.; et al. UNICAB: Cabozantinib in locally advanced or metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma post immunotherapy or in those unsuitable for immunotherapy (ANZUP 1802). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.; Alekseev, B.; Rha, S.Y.; Porta, C.; Eto, M.; Powles, T.; Grünwald, V.; Hutson, T.E.; Kopyltsov, E.; Méndez-Vidal, M.J.; et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.N.; Lee, C.H.; Voss, M.H.; Carlo, M.I.; Knezevic, A.; Peralta, L.; Chen, Y.; Lefkowitz, R.A.; Shah, N.J.; Owens, C.N.; et al. Cabozantinib Plus Nivolumab in Patients with Non–Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Updated Results from a Phase 2 Trial. Eur. Urol. 2024, 86, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Powles, T.; Burotto, M.; Escudier, B.; Bourlon, M.T.; Zurawski, B.; Juárez, V.M.O.; Hsieh, J.J.; Basso, U.; Shah, A.Y.; et al. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Frontera, O.A.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Xu, W.; Poole, L.; Telaranta-Keerie, A. SAMETA: An open-label, three-arm, multicenter, phase III study of savolitinib + durvalumab versus sunitinib and durvalumab monotherapy in patients with MET-driven, unresectable, locally advanced/metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, B.A.; Paul, M.; Xie, W.; Xu, W.; Bilen, M.A.; Braun, D.A.; Berg, S.; Zhang, T.; McKay, R.R.; McDermott, D.F.; et al. 1702P Updated Results of Phase II Study of Cabozantinib (Cabo) with Nivolumab (Nivo) and Ipilimumab (Ipi) in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma with Divergent Histologies (RCCdh)–Annals of Oncology. Available online: https://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-7534(24)03314-3/fulltext (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). A Phase II Study of Ipilimumab, Cabozantinib, and Nivolumab in Rare Genitourinary Cancers (ICONIC). 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03866382 (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Maughan, B.L.; Plets, M.; Pal, S.K.; Ged, Y.; Tangen, C.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Lerner, S.P.; Thompson, I.M. SWOG S2200 (PAPMET2): A phase II randomized trial of cabozantinib with or without atezolizumab in patients with advanced papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. S4), TPS493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). A Randomized Phase 2 Trial of Axitinib/Nivolumab Combination Therapy vs. Single Agent Nivolumab for the Treatment of TFE/Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma (tRCC) Across All Age Groups. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03595124 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- 44. M.D. Anderson Cancer Center. Phase II Trial of Immunotherapy in Patients with Carcinomas Arising from the Renal Medulla. 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05347212 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). A Phase 1/2 Study of Tiragolumab (NSC# 827799) and Atezolizumab (NSC# 783608) in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory SMARCB1 or SMARCA4 Deficient Tumors. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05286801 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). A Phase 2 Study of Bevacizumab, Erlotinib and Atezolizumab in Subjects with Advanced Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Cancer (HLRCC) Associated or Sporadic Papillary Renal Cell Cancer. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04981509 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Garje, R.; Elhag, D.; Yasin, H.A.; Acharya, L.; Vaena, D.; Dahmoush, L. Comprehensive review of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 160, 103287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henske, E.P.; Cheng, L.; Hakimi, A.A.; Choueiri, T.K.; Braun, D.A. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, P.; Zhong, H.; Le, D.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Miyata, J.; Carrillo, D.; Rakheja, D.; Rajaram, S.; Durinck, S.; Modrusan, Z.; et al. Molecular underpinnings of dedifferentiation and aggressiveness in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e176743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, J.J.; Kochenderfer, M.D.; Olsen, M.R.; Bauer, T.M.; Molina, A.; Hauke, R.J.; Reeves, J.A.; Babu, S.; Veldhuizen, P.V.; Somer, B.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Results from the Phase IIIb/IV CheckMate 374 Study. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2020, 18, 469–476.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conduit, C.; Kichenadasse, G.; Harris, C.A.; Gurney, H.; Ferguson, T.; Parnis, F.; Goh, J.C.; Morris, M.F.; Underhill, C.; Pook, D.W.; et al. Sequential immunotherapy in rare variant renal cell carcinomafinal report of UNISoN (ANZUP 1602): Nivolumab then ipilimumab + nivolumab in advanced nonclear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), 4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, M.J.; Khandelwal, J.; Wilson, N.R.; Malikayil, K.L.; Surasi, D.S.; Bathala, T.K.; Lin, Y.; Rao, P.; Tamboli, P.; Sircar, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with metastatic variant histology (non-clear cell) renal cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2025, 13, e010958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paffenholz, P.; Casuscelli, J.; Zschaebitz, S.; Rinderknecht, E.; Mattigk, A.; Volk, A.L.; Ivanyi, P.; Hilser, T.; Darr, C.; Flegar, L.; et al. Real world evidence from a retrospective multi-center analysis on first-line therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma with chromophobe histology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43 (Suppl. S5), 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Chanzá, N.; Xie, W.; Asim Bilen, M.; Dzimitrowicz, H.; Burkart, J.; Geynisman, D.M.; Balakrishnan, A.; Bowman, I.A.; Jain, R.; Stadler, W.; et al. Cabozantinib in advanced non-clear-cell renal cell carcinoma: A multicentre, retrospective, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.T.; Bilen, M.A.; Shah, A.Y.; Lemke, E.; Jonasch, E.; Venkatesan, A.M.; Altinmakas, E.; Duran, C.; Msaouel, P.; Tannir, N.M. Cabozantinib for the treatment of patients with metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A retrospective analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 104, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalabi, O.; Thouvenin, J.; Négrier, S.; Vano, Y.A.; Campedel, L.; Hasanov, E.; Bakouny, Z.; Hahn, A.W.; Bilen, M.A.; Msaouel, P.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Therapy Combinations in Adult Advanced MiT Family Translocation Renal Cell Carcinomas. Oncologist 2023, 28, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ged, Y.; Touma, A.; Meza Contreras, L.; Elias, R.; Van Galen, J.; Cupo, O.; Baraban, E.; Singla, N.; Lee, C.H.; Pal, S.; et al. Multi-institutional Analysis of Immune-Oncology Combination Therapy for Metastatic MiT Family Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunother. 2025, 48, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgul, M.; Cheng, L. Immunophenotypic and pathologic heterogeneity of unclassified renal cell carcinoma: A study of 300 cases. Hum. Pathol. 2020, 102, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekeduz, E.; Braun, D.A.; El Hajj Chehade, R.; Eid, M.; Labaki, C.; Machaalani, M.; Nassar, A.; Nawfal, R.; Saad, E.; Saliby, R.M.; et al. Applying genomic analysis to refine unclassified renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. S16), 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ged, Y.; Feinaj, A.; Baraban, E.; Singla, N. Management of translocation carcinomas of the kidney. Trans. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durinck, S.; Stawiski, E.W.; Pavía-Jiménez, A.; Modrusan, Z.; Kapur, P.; Jaiswal, B.S.; Zhang, N.; Toffessi-Tcheuyap, V.; Nguyen, T.T.; Pahuja, K.B.; et al. Spectrum of diverse genomic alterations define non–clear cell renal carcinoma subtypes. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Johnson, S.H.; Vasmatzis, G.; Porath, B.; Rustin, J.G.; Rao, P.; Costello, B.A.; Leibovich, B.C.; Thompson, R.H.; Cheville, J.C.; et al. TFEB-VEGFA (6p21.1) co-amplified renal cell carcinoma: A distinct entity with potential implications for clinical management. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 998–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Banchereau, R.; Hamidi, H.; Powles, T.; McDermott, D.; Atkins, M.B.; Escudier, B.; Liu, L.F.; Leng, N.; Abbas, A.R.; et al. Molecular Subsets in Renal Cancer Determine Outcome to Checkpoint and Angiogenesis Blockade. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 803–817.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakasam, G.; Mishra, A.; Christie, A.; Miyata, J.; Carrillo, D.; Tcheuyap, V.T.; Ye, H.; Do, Q.N.; Wang, Y.; Torras, O.R.; et al. Comparative genomics incorporating translocation renal cell carcinoma mouse model reveals molecular mechanisms of tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e170559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, G.; Montoya-Cerrillo, D.; Kryvenko, O.N.; Pal, S.K.; Arias-Stella, J.A. Collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney: Diagnosis and implications for management. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2022, 40, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Choueiri, T.K.; Wang, K.; Khaira, D.; Karam, J.A.; Van Allen, E.; Palma, N.A.; Stein, M.N.; Johnson, A.; Squillace, R.; et al. Characterization of Clinical Cases of Collecting Duct Carcinoma of the Kidney Assessed by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudard, S.; Banu, E.; Vieillefond, A.; Fournier, L.; Priou, F.; Medioni, J.; Banu, A.; Duclos, B.; Rolland, F.; Escudier, B.; et al. Prospective Multicenter Phase II Study of Gemcitabine Plus Platinum Salt for Metastatic Collecting Duct Carcinoma: Results of a GETUG (Groupe d’Etudes des Tumeurs Uro-Génitales) Study. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, C.; Fléchon, A.; Albiges, L.; Joly, C.; Barthelemy, P.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Chevreau, C.; Coquan, E.; Rolland, F.; Laguerre, B.; et al. Gemcitabine plus platinum-based chemotherapy in combination with bevacizumab for kidney metastatic collecting duct and medullary carcinomas: Results of a prospective phase II trial (BEVABEL-GETUG/AFU24). Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 186, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, G.; Sepe, P.; Claps, M.; Buti, S.; Colecchia, M.; Giannatempo, P.; Guadalupi, V.; Mariani, L.; Lalli, L.; Fucà, G.; et al. Cabozantinib as First-line Treatment in Patients with Metastatic Collecting Duct Renal Cell Carcinoma: Results of the BONSAI Trial for the Italian Network for Research in Urologic-Oncology (Meet-URO 2 Study). JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buti, S.; Trentini, F.; Sepe, P.; Claps, M.; Isella, L.; Verzoni, E.; Procopio, G. BONSAI-2 study: Nivolumab as therapeutic option after cabozantinib failure in metastatic collecting duct carcinoma patients. Tumori J. 2023, 109, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nze, C.; Msaouel, P.; Derbala, M.H.; Stephen, B.; Abonofal, A.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Tannir, N.M.; Naing, A. A Phase II Clinical Trial of Pembrolizumab Efficacy and Safety in Advanced Renal Medullary Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.Y.; Karam, J.A.; Malouf, G.G.; Rao, P.; Lim, Z.D.; Jonasch, E.; Xiao, L.; Gao, J.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Heng, D.Y.; et al. Management and outcomes of patients with renal medullary carcinoma: A multicentre collaborative study. BJU Int. 2017, 120, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, N.R.; Wiele, A.J.; Surasi, D.S.; Rao, P.; Sircar, K.; Tamboli, P.; Shah, A.Y.; Genovese, G.; Karam, J.A.; Wood, C.G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of gemcitabine plus doxorubicin in patients with renal medullary carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2021, 19, e401–e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebenthal, J.M.; Kontoyiannis, P.D.; Hahn, A.W.; Lim, Z.D.; Rao, P.; Cheng, J.P.; Chan, B.; Daw, N.C.; Sheth, R.A.; Karam, J.A.; et al. Clinical Characteristics, Management, and Outcomes of Patients with Renal Medullary Carcinoma: A Single-center Retrospective Analysis of 135 Patients. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2024, 8, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.M.; Feldman, D.R.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Kroog, G.; Tickoo, S.K.; Jia, X.; Georges, M.; Patil, S.; Baum, M.S.; Reuter, V.E.; et al. Phase II trial of sunitinib in patients with metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, A.K.; Tulchiner, G.; Seeber, A.; Siska, P.J.; Thurnher, M.; Pichler, R. Targeting strategies in the treatment of fumarate hydratase deficient renal cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Gurram, S.; Al Harthy, M.; Singer, E.A.; Sidana, A.; Shuch, B.M.; Ball, M.W.; Friend, J.C.; Mac, L.; Purcell, E.; et al. Results from a phase II study of bevacizumab and erlotinib in subjects with advanced hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (HLRCC) or sporadic papillary renal cell cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S15), 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, R.R.; Doshi, S.D.; Knezevic, A.; Chaim, J.; Chen, Y.; Jacobi, R.; Zucker, M.; Reznik, E.; McHugh, D.; Shah, N.J.; et al. A Phase 2 Trial of Talazoparib and Avelumab in Genomically Defined Metastatic Kidney Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2024, 7, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Wu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Lenvatinib plus tislelizumab as first-line therapy for advanced fumarate hydratase-deficient renal cell carcinoma: A single-center, single-arm, phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43 (Suppl. S5), 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Bergerot, P.; Dizman, N.; Bergerot, C.; Adashek, J.; Madison, R.; Chung, J.; Ali, S.; Jones, J.; Salgia, R. Responses to Alectinib in ALK-rearranged Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Gouda, M.A.; Ryll, B.; Burris, H.A., III; Kurzrock, R. The evolving landscape of tissue-agnostic therapies in precision oncology. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathmell, W.K.; Rumble, R.B.; Van Veldhuizen, P.J.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Emamekhoo, H.; Hauke, R.J.; Louie, A.V.; Milowsky, M.I.; Molina, A.M.; Rose, T.L.; et al. Management of Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2957–2995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guidelines Detail. NCCN. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1440 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Subbiah, V.; Othus, M.; Palma, J.; Cuglievan, B.; Kurzrock, R. Designing Clinical Trials for Patients with Rare Cancers: Connecting the Zebras. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2025, 45, e100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial Name | Study Drug(s) | n | Efficacy (ORR *, mPFS, mOS with 95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Papillary RCC-Only Trials | ||||||
| AXIPAP [4] | Axitinib | 44 | ORR 12/42, 28.6% (15.7–44.6) mPFS 6.6 mo (5.5–9.2) | |||
| PAPMET [5] | Cabozantinib | 44 | ORR 23% mPFS 9.0 mo (6–12) mOS 21.5 mo (12.0–28.1) | |||
| Sunitinib | 46 | ORR 4% mPFS 5.6 mo (3) mOS 17.3 mo (12.8–21.8) | ||||
| Savolitinib | 29 | ORR 3% | ||||
| Crizotinib | 28 | ORR 0% | ||||
| Trials With Multiple nccRCC Subtypes | ||||||
| Papillary RCC | Chromophobe RCC | Unclassified RCC | Translocation RCC | |||
| ESPN [6] | Sunitinib | 34 | ORR 3/33 (9%) | |||
| mPFS 5.7 mo (1.4–19.8) | mPFS 8.9 mo (2.9–20.1) | mPFS 9.4 mo (3.3–15.4) | mPFS 6.1 mo (6.0–8.8) | |||
| Everolimus | 38 | ORR 1/35 (3%) | ||||
| mPFS 4.1 mo (1.5–7.48) | NA | mPFS 4.7 mo (2.6–NA) | mPFS 3.0 (1.3–NA) | |||
| ASPEN [7] | Sunitinib | 51 | ORR 8/33 24% | ORR 1/10 10% | ORR 0/8 0% | - |
| Everolimus | 57 | ORR 2/37 5% | ORR 2/6 33% | ORR 1/14 7% | - | |
| NCT02915783 [8] | Lenvatinib + everolimus | 31 | ORR 3/20 15% | ORR 4/9 44.4% | ORR 1/2 50% | - |
| NCT01399918 [9] | Everolimus + Bevacizumab | 35 | ORR 7/18 ** 38.9% | ORR 2/5 40% | ORR 1/9 11.1% | - |
| NCT01538238 [10] | Pazopanib | 28 | ORR 7/18 39% | ORR 1/3 33% | ORR 0/2 0% | NA |
| NCT00502307 [11] | Tivozanib | 46 | ORR 7/8 87.5% | ORR 2/2 100% | ORR 18/27 66.7% | - |
| Trial Name | Study Drug(s) | n | Efficacy (ORR *, mPFS with 95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Papillary RCC | Chromophobe RCC | Unclassified RCC | Translocation RCC | |||
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Monotherapy | ||||||
| KEYNOTE-427 [12] | Pembrolizumab | 165 | ORR 34/118 28.8% (20.8–37.9) | ORR 2/21 9.5% (1.2–30.4) | ORR 8/26 30.8% (14.3–51.8) | NA |
| CheckMate 374 [13] | Nivolumab | 44 | ORR 2/24 8.3% | ORR 2/7 28.6% | ORR 1/8 12.5% | NA |
| UNISoN [14] | Nivolumab | 80 | ORR 5/34 14.7% | ORR 1/13 8% | ORR 1/8 13% | ORR 2/5 40% |
| Nivolumab + Ipilimumab (post-nivo) | 41 | ORR 10% (95% CI 3–23) | ||||
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Combination Therapies | ||||||
| KEYNOTE-B61 [15] | Lenvatinib + Pembrolizumab | 158 | ORR 50/93 54% (43–64) mPFS 17.5 mo (15-NR) | ORR 8/29 28% (13–64) mPFS 12.5 mo (3.9-NR) | ORR 11/21 52% (30–74) | ORR 4/6 67% (22–96) |
| CA209–9KU [16] | Cabozantinib + Nivolumab | 47 | ORR 15/32 47% (30–64) mPFS 13 mo (7–16) | ORR 0/7 0% (0–41.0) | ORR 3/6 50% (12–88) mPFS 8 mo (1-NE) | ORR 1/2 50% (1–99) mPFS 14 mo (5–23) |
| CheckMate 920 [17] | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | 46 | Overall ORR 9/46 19.6% (9.4–33.9%) | |||
| 1 CR, 4 PR 18 patients ** | 0 CR, 0 PR 7 patients ** | 1 CR, 3 PR 22 patients ** | 0 CR, 0 PR 2 patients ** | |||
| SUNNIFORECAST [18] (intervention arm) | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | 125 | ORR 21/72 29.2% | ORR 7/27 25.9% | NA | NA |
| NCT04413123 [19] | Cabozantinib + nivolumab + ipilimumab | 40 | ORR 6/19 31.6% | ORR 1/11 9.1% | ORR 1/1 100% | ORR 0/5 0% |
| CALYPSO [20] MET-driven subgroup | Savolitinib + Durvalumab | 41 | ORR 12/41 29% (16–46) | - | - | - |
| 17 | ORR 9/17 53% (28–77) | - | - | - | ||
| COSMIC-021 [21] | Cabozantinib + Atezolizumab | 32 | ORR 7/15 47% | ORR 1/9 11% | - | - |
| NCT02724878 [22] | Bevacizumab + Atezolizumab | 42 | ORR 3/12 25% | ORR 1/10 10% | ORR 3/9 3.3% | ORR 1/5 20% |
| Study | Study Drug(s) | nccRCC Subtype(s) | Primary Outcome | Goal Recruitment (n) | Estimated Completion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICONIC [41] (NCT03866382) | Nivolumab, Ipilimumab, and cabozantinib | Papillary Chromophobe Collecting Duct Sarcomatoid (~50%) Renal Medullary | ORR Secondary: PFS, OS | 314 | February 2026 |
| PAPMET2 [42] (NCT05411081) | Cabozantinib +/- Atezolizumab | Papillary | PFS Secondary: OS, ORR | 200 | July 2027 |
| SAMETA [39] (NCT05043090) | Durvalumab +/- savolitinib vs. sunitinib | MET-driven Papillary | mPFS Secondary: OS, ORR | 147 | June 2026 |
| NCT03595124 [43] | Axitinib +/- Nivolumab | Translocation | mPFS Secondary: toxicities | 15 | January 2026 |
| NCT05347212 [44] | Nivolumab + Relatlimab | Renal Medullary | ORR Secondary: OS, PFS | 30 | July 2027 |
| NCT05286801 [45] | Tiragolumab + atezolizumab | Renal Medullary | ORR Secondary: PFS, OS, PK | 86 | June 2026 |
| NCT04981509 [46] | Bevacizumab + erlotinib + atezolizumab | Papillary HLRCC | CR Secondary: ORR, | 65 | December 2027 |
| Study | Study Drug(s) | n | nccRCC Subtype(s) | ORR | mPFS (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moussa et al. [52] | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | 55 | Papillary Chromophobe Unclassified | 12/25 (48%) 3/12 (25%) 5/18 (27.8%) | 10.6 mo (2.8–22.8) 3.6 mo (0.9–NE) 3 mo (2.1–7) |
| Alhalabi et al. [56] | ICI + TKI | 18 | Translocation | 1/18 (5.5%) | 5.4 mo |
| ICI + ICI | 11 | 4/11(36%) | 2.8 mo | ||
| Ged et al. [57] | ICI + TKI ICI + ICI | 14 8 | Translocation | 1/7 (14%) 6/11 (54%) | TTF 1.2 mo TTF 6.2 mo |
| Paffenholz et al. [53] | ICI + TKI | 10 | Chromophobe | 3/10 (30%) | 8 mo (0–19.2) |
| ICI + ICI | 8 | 1/8 (12.5%) | 3 mo (2.4–3.6) | ||
| TKI | 13 | 2/13 (15%) | 4 mo (0–10.2) | ||
| Chanza et al. [54] | Cabozantinib | 112 | Papillary Chromophobe Unclassified Translocation | 18/66 (27%) 3/10 (30%) 2/15 (13%) 5/17 (29%) | 6.9 mo (4.6–10.1) 5.7 mo (1.1–7.8) 6.0 mo (1.4–9.9) 8.3 mo (4.6–NR) |
| Campbell et al. [55] | Cabozantinib | 30 | Papillary Chromophobe Unclassified Translocation | 1/15 (7%) 1/6 (17%) 1/3 (33%) 0/2 (0%) | 8.6 mo (6.1–14.7) |
| Trial Name | Study Drug(s) | n | Objective Response Rates (ORR) * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | Sarcomatoid Differentiation | PD-L1 ≥ 1% | |||
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Monotherapy | |||||
| KEYNOTE-427 [12] | Pembrolizumab | 165 | 26.7% | 16/38 42.1% (95% CI, 26.3–59.2%) | 36/102 35.3% (26.1–45.4) |
| CheckMate 374 [13] | Nivolumab | 44 | 13.6% | 2/4 50% | NA mOS 16.3 mo |
| UNISoN [14] | Nivolumab | 80 | 16.9% | NA | NA |
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Combination Therapies | |||||
| KEYNOTE-B61 [15] | Lenvatinib + Pembrolizumab | 158 | 49% | 9/18 47% (95% CI 24–71) | 54/93 58% (95% CI 47–68) |
| CA209-9KU [16] | Cabozantinib + Nivolumab | 47 | 47.5% | NA | NA |
| CheckMate 920 [17] | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | 46 | 19.6% | 5/14 35.7% (95% CI 12.8–64.9) | 4/13 30.8% |
| SUNNIFORECAST [18] | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | 125 | 32.8% | NA | NA HR for OS 0.56 (95% CI 0.33–0.95) |
| NCT04413123 [19] | Cabozantinib + nivolumab + ipilimumab | 40 | 21% | 3/9 33.3% | NA |
| CALYPSO [20] | Savolitinib + Durvalumab | 41 | 29% | NA | 9/27 33% (95% CI 17–54) |
| COSMIC-021 [21] | Cabozantinib + Atezolizumab | 32 | 23% | NA | 5/23 22% |
| NCT02724878 [22] | Bevacizumab + Atezolizumab | 42 | 26% | 3/8 38% | 9/23 36% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vento, J.; Zhang, T.; Kapur, P.; Hammers, H.; Brugarolas, J.; Qin, Q. Systemic Treatment of Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091527
Vento J, Zhang T, Kapur P, Hammers H, Brugarolas J, Qin Q. Systemic Treatment of Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091527
Chicago/Turabian StyleVento, Joseph, Tian Zhang, Payal Kapur, Hans Hammers, James Brugarolas, and Qian Qin. 2025. "Systemic Treatment of Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091527
APA StyleVento, J., Zhang, T., Kapur, P., Hammers, H., Brugarolas, J., & Qin, Q. (2025). Systemic Treatment of Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(9), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091527






