Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Common Mutations: New Strategies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
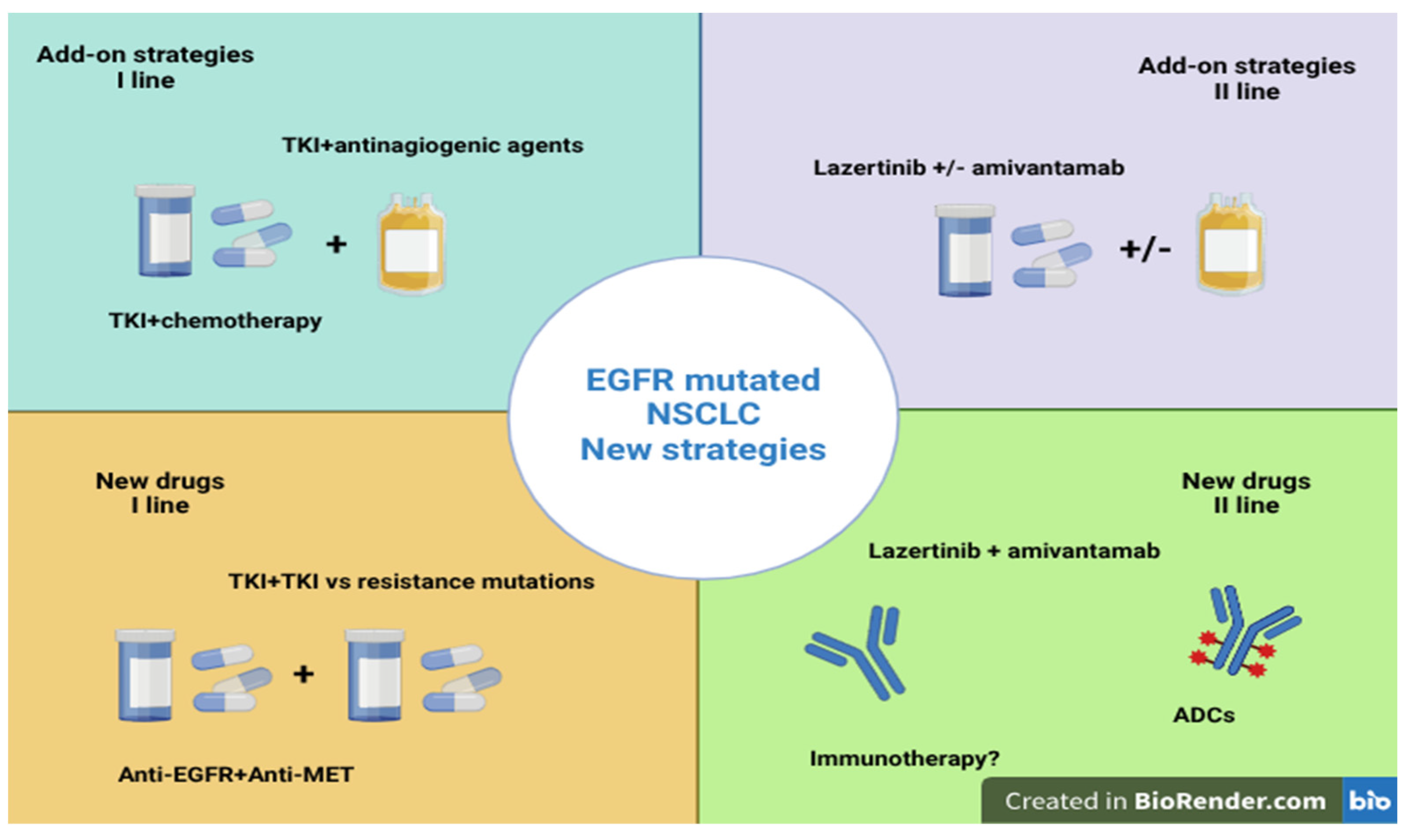
2. Update on Advanced NSCLC with EGFR Common Mutations
2.1. Strengthening the First-Line Treatment
2.1.1. Combination of TKIs with Chemotherapy
2.1.2. Combination of TKIs with Antiangiogenic Agents
| Clinical Trial | Phase | Treatment | Median PFS | Median OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seto et al. [37] | 2 | Erlotinib + bevacizumab vs. Erlotinib | 16 months 9 months | 47 months 47.4 months |
| Stinchcombe et al. [38] | 2 | Erlotinib + bevacizumab vs. Erlotinib | 17.9 months 13.5 months | 32.4 months 50.6 months |
| Saito et al. [39] | 3 | Erlotinib + bevacizumab vs. Erlotinib | 16.9 months 13.3 months | - |
| Nakagawa et al. [40] | 3 | Erlotinib + ramucirunab vs. Erlotinib | 19.4 months 12.4 months | - |
| Zhou et al. [41] | 3 | Erlotinib + bevacizumab vs. Erlotinib | 18 months 11.3 months | - |
2.1.3. New Third-Generation TKIs
2.1.4. Fourth-Generation TKIs
2.1.5. Anti-EGFR and Anti-MET Drugs: Combination of Lazertinib and Amivantamab
2.1.6. Role of Radiotherapy
2.2. Strengthening Second-Line Treatment
2.2.1. Combination of Anti-EGFR and Anti-MET Drugs in the Second-Line Treatment
2.2.2. Combination of Lazertinib and Amivantamab in the Second-Line Treatment
2.2.3. Combination of Anti-EGFR and Other Target Therapies
2.2.4. Role of Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
2.2.5. Role of Immunotherapy
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoPiccolo, J.; Gusev, A.; Christiani, D.C.; Jänne, P.A. Lung cancer in patients who have never smoked—An emerging disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Castellanos, E.; Feld, E.; Horn, L. Driven by Mutations: The Predictive Value of Mutation Subtype in EGFR -Mutated Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, L.; Kerr, K.; Menis, J.; Mok, T.; Nestle, U.; Passaro, A.; Peters, S.; Planchard, D.; Smit, E.; Solomon, B.; et al. Oncogene-addicted metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gristina, V.; Malapelle, U.; Galvano, A.; Pisapia, P.; Pepe, F.; Rolfo, C.; Tortorici, S.; Bazan, V.; Troncone, G.; Russo, A. The significance of epidermal growth factor receptor uncommon mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and critical appraisal. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 85, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Mok, T.; Peters, S.; Popat, S.; Ahn, M.-J.; de Marinis, F. Recent Advances on the Role of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Management of NSCLC with Uncommon, Non Exon 20 Insertions, EGFR Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.Y.; Na Cho, E.; Park, H.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Lim, S.; Youn, J.P.; Hwang, S.Y.; Chang, Y.S. Compound EGFR mutation is frequently detected with co-mutations of actionable genes and associated with poor clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, D.H. Treatments for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): The road to a success, paved with failures. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 174, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Davies, L.; Wu, Y.-L.; Mitsudomi, T.; Inoue, A.; Rosell, R.; Zhou, C.; Nakagawa, K.; Thongprasert, S.; Fukuoka, M.; et al. Gefitinib or Erlotinib vs Chemotherapy for EGFR Mutation-Positive Lung Cancer: Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of Overall Survival. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Tan, E.-H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Boyer, M.; Mok, T.; Hirsh, V.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Tan, E.-H.; O’byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Hirsh, V.; Boyer, M.; Yang, J.-H.; Mok, T.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Overall survival data from the phase IIb LUX-Lung 7 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Mok, T.S.; Zhou, X.; Lu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, J.; Du, Y.; Yu, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of first-line dacomitinib in Asian patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer: Results from a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial (ARCHER 1050). Lung Cancer 2021, 154, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoli, E.; De Carlo, E.; Del Conte, A.; Stanzione, B.; Revelant, A.; Fassetta, K.; Spina, M.; Bearz, A. Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: How Do We Overcome It? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, D.-W.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Su, W.-C.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, J.-H.; Planchard, D.; Felip, E.; et al. Osimertinib in Pretreated T790M-Positive Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: AURA Study Phase II Extension Component. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Fu, L. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Favorito, V.; Ricciotti, I.; De Giglio, A.; Fabbri, L.; Seminerio, R.; Di Federico, A.; Gariazzo, E.; Costabile, S.; Metro, G. Non-small cell lung cancer: An update on emerging EGFR-targeted therapies. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2024, 29, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-F.; Ren, S.-X.; Li, W.; Gao, G.-H. Frequency of the acquired resistant mutation T790 M in non-small cell lung cancer patients with active exon 19Del and exon 21 L858R: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zalaquett, Z.; Hachem, M.C.R.; Kassis, Y.; Hachem, S.; Eid, R.; Kourie, H.R.; Planchard, D. Acquired resistance mechanisms to osimertinib: The constant battle. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 116, 102557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, N.; Hong, L.; Zhang, J.; Heymach, J.; Hong, D.; Le, X. Beyond epidermal growth factor receptor: MET amplification as a general resistance driver to targeted therapy in oncogene-driven non-small-cell lung cancer. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ohashi, K.; Sequist, L.V.; Arcila, M.E.; Moran, T.; Chmielecki, J.; Lin, Y.-L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, L.; de Stanchina, E.; Shien, K.; et al. Lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors occasionally harbor BRAF gene mutations but lack mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or MEK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2127–E2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ware, K.E.; Marshall, M.E.; Heasley, L.R.; Marek, L.; Hinz, T.K.; Hercule, P.; Helfrich, B.A.; Doebele, R.C.; Heasley, L.E. Rapidly Acquired Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in NSCLC Cell Lines through De-Repression of FGFR2 and FGFR3 Expression. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pecci, F.; Cantini, L.; Metro, G.; Ricciuti, B.; Lamberti, G.; Farooqi, A.A.; Berardi, R. Non-small-cell lung cancer: How to manage EGFR-mutated disease. Drugs Context 2022, 11, 2022-4-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Niederst, M.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Poirier, J.T.; Mermel, C.H.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Katayama, R.; Costa, C.; Ross, K.N.; Moran, T.; et al. RB loss in resistant EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Offin, M.; Chan, J.M.; Tenet, M.; Rizvi, H.A.; Shen, R.; Riely, G.J.; Rekhtman, N.; Daneshbod, Y.; Quintanal-Villalonga, A.; Penson, A.; et al. Concurrent RB1 and TP53 Alterations Define a Subset of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers at risk for Histologic Transformation and Inferior Clinical Outcomes. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, J.-K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Youk, J.; Park, S.; An, Y.; Keam, B.; Kim, D.-W.; Heo, D.S.; et al. Clonal History and Genetic Predictors of Transformation Into Small-Cell Carcinomas From Lung Adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Yang, B.; An, Q.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Cao, X.; Xia, J. Acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR-TKIs and emerging next-generation EGFR inhibitors. Innovation 2021, 2, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schmid, S.; Li, J.J.; Leighl, N.B. Mechanisms of osimertinib resistance and emerging treatment options. Lung Cancer 2020, 147, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landre, T.; Assié, J.-B.; Chouahnia, K.; Guetz, G.D.; Auliac, J.-B.; Chouaïd, C. First-line concomitant EGFR-TKI + chemotherapy versus EGFR-TKI alone for advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC: A meta-analysis of randomized phase III trials. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2024, 24, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyauchi, E.; Morita, S.; Nakamura, A.; Hosomi, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ikeda, S.; Seike, M.; Fujita, Y.; Minato, K.; Ko, R.; et al. Updated Analysis of NEJ009: Gefitinib-Alone Versus Gefitinib Plus Chemotherapy for Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Mutated EGFR. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3587–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Noronha, V.; Patil, V.M.; Joshi, A.; Menon, N.; Chougule, A.; Mahajan, A.; Janu, A.; Purandare, N.; Kumar, R.; More, S.; et al. Gefitinib Versus Gefitinib Plus Pemetrexed and Carboplatin Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Li, M.; Wu, G.; Feng, W.; Su, J.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; You, Z.; et al. Gefitinib Plus Chemotherapy vs Gefitinib Alone in Untreated EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Patients with Brain Metastases: The GAP BRAIN Open-Label, Randomized, Multicenter, Phase 3 Study. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2255050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Planchard, D.; Jänne, P.A.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.-W.; Sugawara, S.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Geater, S.L.; et al. Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenberger, B.M.; Tan, P.K.; Niederleithner, H.; Ferrara, N.; Petzelbauer, P.; Sibilia, M. Autocrine VEGF Signaling Synergizes with EGFR in Tumor Cells to Promote Epithelial Cancer Development. Cell 2010, 140, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Bao, H.; Cheng, Y. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of TKIs Alone or in Combination with Antiangiogenic Agents in Advanced EGFR-Mutated NSCLC as the First-Line Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 23, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, T.; Kato, T.; Nishio, M.; Goto, K.; Atagi, S.; Hosomi, Y.; Hida, T.; Maemondo, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Nagase, S.; et al. Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): An open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinchcombe, T.E.; Jänne, P.A.; Wang, X.; Bertino, E.M.; Weiss, J.; Bazhenova, L.; Gu, L.; Lau, C.; Paweletz, C.; Jaslowski, A.; et al. Effect of Erlotinib Plus Bevacizumab vs Erlotinib Alone on Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Advanced EGFR-Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saito, H.; Fukuhara, T.; Furuya, N.; Watanabe, K.; Sugawara, S.; Iwasawa, S.; Tsunezuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okada, M.; Yoshimori, K.; et al. Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): Interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Garon, E.B.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Aix, S.P.; Paz-Ares, L.; Chiu, C.-H.; Park, K.; Novello, S.; Nadal, E.; et al. Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Xu, C.-R.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.-P.; Chen, G.-Y.; Cui, J.-W.; Yang, N.; Song, Y.; Li, X.-L.; Lu, S.; et al. Bevacizumab plus erlotinib in Chinese patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced NSCLC (ARTEMIS-CTONG1509): A multicenter phase 3 study. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1279–1291.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dafni, U.; Peters, S.; Tsourti, Z.; Zygoura, P.; Vervita, K.; Han, J.-Y.; De Castro, J.; Coate, L.; Früh, M.; Hashemi, S.; et al. Impact of smoking status on the relative efficacy of the EGFR TKI/angiogenesis inhibitor combination therapy in advanced NSCLC—A systematic review and meta-analysis. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Han, J.-Y.; Ahn, M.-J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, Y.-G.; Kim, D.-W.; Min, Y.J.; Kim, S.-W.; Cho, E.K.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, G.-W.; et al. Updated overall survival and ctDNA analysis in patients with EGFR T790M-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with lazertinib in the phase 1/2 LASER201 study. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cho, B.C.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kang, J.H.; Soo, R.A.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Cicin, I.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Lu, S.; et al. Lazertinib Versus Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment in Patients with EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From LASER301. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4208–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Dong, X.; Yang, C.-T.; Song, Y.; Chang, G.-C.; Lu, Y.; Pan, H.; Chiu, C.-H.; et al. Efficacy of Aumolertinib (HS-10296) in Patients with Advanced EGFR T790M+ NSCLC: Updated Post-National Medical Products Administration Approval Results From the APOLLO Registrational Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Dong, X.; Jian, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Lu, J.; et al. AENEAS: A Randomized Phase III Trial of Aumolertinib Versus Gefitinib as First-Line Therapy for Locally Advanced or MetastaticNon–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 19 Deletion or L858R Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3162–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, T.; Chang, K.; Qiu, X.; Lai, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Lv, W.; Lin, Z.; Pei, X.; Wu, X.; et al. A pilot study of anlotinib with third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in untreated EGFR-mutant patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Hao, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Furmonertinib (AST2818) versus gefitinib as first-line therapy for Chinese patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (FURLONG): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.-J.; Huang, J.; Ye, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.-C.; Tu, H.-Y.; Han-Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.-L. Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring EGFR T790M and In Trans C797S Responds to Combination Therapy of First- and Third-Generation EGFR TKIs and Shifts Allelic Configuration at Resistance. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederst, M.J.; Hu, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. The Allelic Context of the C797S Mutation Acquired upon Treatment with Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors Impacts Sensitivity to Subsequent Treatment Strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mansour, M.A.; AboulMagd, A.M.; Abbas, S.H.; Abdel-Rahman, H.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M. Insights into fourth generation selective inhibitors of (C797S) EGFR mutation combating non-small cell lung cancer resistance: A critical review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 18825–18853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dempke, W.C.M.; Fenchel, K. Targeting C797S mutations and beyond in non-small cell lung cancer—A mini-review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 6540–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Johnson, M.L.; Henry, J.T.; Spira, A.I.; Battiste, J.; Alnahhas, I.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Barve, M.A.; Edenfield, W.J.; Nam, D.-H.; Eathiraj, S.; et al. A phase 1 study to assess BDTX-1535, an oral EGFR inhibitor, in patients with glioblastoma or non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, TPS9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigley, N. BDTX-1535 Yields Radiographic Responses in Small EGFR+ NSCLC Population. Available online: https://cancernetwork.com (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Wespiser, M.; Swalduz, A.; Pérol, M. Treatment sequences in EGFR mutant advanced NSCLC. Lung Cancer 2024, 194, 107895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Lu, S.; Felip, E.; Spira, A.I.; Girard, N.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Ostapenko, Y.; Danchaivijitr, P.; Liu, B.; et al. Amivantamab plus Lazertinib in Previously Untreated EGFR -Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felip, E.; Cho, B.; Gutiérrez, V.; Alip, A.; Besse, B.; Lu, S.; Spira, A.; Girard, N.; Califano, R.; Gadgeel, S.; et al. Amivantamab plus lazertinib versus osimertinib in first-line EGFR-mutant advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with biomarkers of high-risk disease: A secondary analysis from MARIPOSA. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Liu, B.; Ostapenko, Y.; Lu, S.; Alip, A.; Korbenfeld, E.; Dias, J.; Danchaivijitr, P.; et al. 4O: Amivantamab plus lazertinib vs osimertinib in first-line (1L) EGFR-mutant (EGFRm) advanced NSCLC: Final overall survival (OS) from the phase III MARIPOSA study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2025, 20, S6–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-S.; Bai, Y.-F.; Verma, V.; Yu, R.-L.; Tian, W.; Ao, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Liu, H.; Pan, H.-X.; et al. Randomized Trial of First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor with or Without Radiotherapy for Synchronous Oligometastatic EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 115, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khan, T.M.; Verbus, E.A.; Gandhi, S.; Heymach, J.V.; Hernandez, J.M.; Elamin, Y.Y. Osimertinib, Surgery, and Radiation Therapy in Treating Patients with Stage IIIB or IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Mutations (NORTHSTAR). Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4688–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Yu, C.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; Lin, M.-C.; Sriuranpong, V.; Tsai, C.-M.; Lee, J.-S.; Kang, J.-H.; Chan, K.C.A.; Perez-Moreno, P.; et al. First-Line Erlotinib Therapy Until and Beyond Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors Progression in Asian Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The ASPIRATION Study. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Liao, X.-Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, B.; Duan, Y.; Sun, J. Concurrent EGFR-TKI and Thoracic Radiotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR Active Mutations. Oncologist 2019, 24, 1031–e612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mavrikios, A.; Remon, J.; Quevrin, C.; Mercier, O.; Tselikas, L.; Botticella, A.; Nicolas, E.; Deutsch, E.; Besse, B.; Planchard, D.; et al. Local control strategies for management of NSCLC with oligoprogressive disease. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 120, 102621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, F.; Hanna, G. Oligoprogressive Oncogene-addicted Lung Tumours: Does Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Have a Role? Introducing the HALT Trial. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Leighl, N.; Blackhall, F.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Ahn, M.; Arcila, M.; Arrieta, O.; Planchard, D.; de Marinis, F.; et al. ESMO expert consensus statements on the management of EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 466–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmaier, R.J.; Markovets, A.A.; Ahn, M.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Han, J.-Y.; Cho, B.C.; Yu, H.A.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. Osimertinib + Savolitinib to Overcome Acquired MET-Mediated Resistance in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor–Mutated, MET-Amplified Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: TATTON. Cancer Discov. 2022, 13, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sequist, L.V.; Han, J.-Y.; Ahn, M.-J.; Cho, B.C.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, J.S.; Su, W.-C.; Kowalski, D.; et al. Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Goldberg, S.B.; Le, X.; Piotrowska, Z.; Goldman, J.W.; De Langen, A.J.; Okamoto, I.; Cho, B.C.; Smith, P.; Mensi, I.; et al. Biomarker-Directed Phase II Platform Study in Patients with EGFR Sensitizing Mutation-Positive Advanced/Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Whose Disease Has Progressed on First-Line Osimertinib Therapy (ORCHARD). Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahn, M.J.; Marinis, F.D.; Bonanno, L.; Cho, B.C.; Kim, T.M.; Cheng, S.; Novello, S.; Proto, C.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.S.; et al. EP08.02-140 MET Biomarker-based Preliminary Efficacy Analysis in SAVANNAH: Savolitinib+ osimertinib in EGFRm NSCLC post-Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S469–S470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Guarneri, V.; Voon, P.J.; Lim, B.K.; Yang, J.-J.; Wislez, M.; Huang, C.; Liam, C.K.; Mazieres, J.; Tho, L.M.; et al. Tepotinib plus osimertinib in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer with MET amplification following progression on first-line osimertinib (INSIGHT 2): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 989–1002, Erratum in Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, e472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Kim, D.-W.; Spira, A.I.; Gomez, J.E.; Haura, E.B.; Kim, S.-W.; Sanborn, R.E.; Cho, E.K.; Lee, K.H.; Minchom, A.; et al. Amivantamab plus lazertinib in osimertinib-relapsed EGFR-mutant advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer: A phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Besse, B.; Baik, C.S.; Marmarelis, M.E.; Sabari, J.K.; Goto, K.; Shu, C.A.; Lee, J.-S.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Cho, B.C.; Waqar, S.N.; et al. Predictive biomarkers for treatment with amivantamab plus lazertinib among EGFR-mutated NSCLC in the post-osimertinib setting: Analysis of tissue IHC and ctDNA NGS. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, B.; Goto, K.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Marmarelis, M.E.; Ohe, Y.; Caro, R.B.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; Cousin, S.; et al. Amivantamab Plus Lazertinib in Patients with EGFR-Mutant NSCLC After Progression on Osimertinib and Platinum-Based Chemotherapy: Results From CHRYSALIS-2 Cohort A. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2025; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Melosky, B.; Shih, J.-Y.; Azuma, K.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Cobo, M.; Felip, E.; et al. Amivantamab plus chemotherapy with and without lazertinib in EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC after disease progression on osimertinib: Primary results from the phase III MARIPOSA-2 study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 35, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leighl, N.B.; Akamatsu, H.; Lim, S.M.; Cheng, Y.; Minchom, A.R.; Marmarelis, M.E.; Sanborn, R.E.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Liu, B.; John, T.; et al. Subcutaneous Versus Intravenous Amivantamab, Both in Combination with Lazertinib, in Refractory Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor–Mutated Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Primary Results From the Phase III PALOMA-3 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 3593–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, Y.; Gan, J.; Guo, K.; Deng, Y.; Fang, W. Acquired BRAF V600E Mutation Mediated Resistance to Osimertinib and Responded to Osimertinib, Dabrafenib, and Trametinib Combination Therapy. J. Thoracic Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2019, 14, e236–e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Piotrowska, Z.; Cobb, R.; Banwait, M.; Lennerz, J.K.; Hata, A.N.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Sequist, L.V. Response to the Combination of Osimertinib and Trametinib in a Patient with EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Harboring an Acquired BRAF Fusion. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e226–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Gu, Y.; Xie, X.; Lin, X.; Ouyang, M.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lizaso, A.; Chen, S.; Zhou, C. Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring Concomitant EGFR Mutations and BRAF V600E Responds to a Combination of Osimertinib and Vemurafenib to Overcome Osimertinib Resistance. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, e390–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Gervais, R.; Riely, G.; Hollebecque, A.; Blay, J.-Y.; Felip, E.; Schuler, M.; Gonçalves, A.; Italiano, A.; Keedy, V.; et al. Efficacy of Vemurafenib in Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with BRAF V600 Mutation: An Open-Label, Single-Arm Cohort of the Histology-Independent VE-BASKET Study. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, PO.18.00266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Batra, U.; Sharma, M.; Amrith, B.; Mehta, A.; Jain, P. EML4-ALK Fusion as a Resistance Mechanism to Osimertinib and Its Successful Management with Osimertinib and Alectinib: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, E597–E600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offin, M.; Somwar, R.; Rekhtman, N.; Benayed, R.; Chang, J.C.; Plodkowski, A.; Lui, A.J.; Eng, J.; Rosenblum, M.; Li, B.T.; et al. Acquired ALK and RET Gene Fusions as Mechanisms of Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR -Mutant Lung Cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, PO.18.00126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Y. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired resistance mechanism alternates between EGFR and ALK in a lung adenocarcinoma patient. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Q.; Jia, G.; Zhang, X.; Ma, W. Targeting HER3 to overcome EGFR TKI resistance in NSCLC. Front. Immunol. 2024, 14, 1332057, Erratum in Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1376045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yu, H.A.; Goto, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Felip, E.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Reck, M.; Yoh, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Besse, B.; et al. HERTHENA-Lung01, a Phase II Trial of Patritumab Deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor–Mutated Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer After Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy and Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5363–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mok, T.; Jänne, P.A.; Nishio, M.; Novello, S.; Reck, M.; Steuer, C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Fougeray, R.; Fan, P.-D.; Meng, J.; et al. HERTHENA-Lung02: Phase III study of patritumab deruxtecan in advanced EGFR -mutated NSCLC after a third-generation EGFR TKI. Future Oncol. 2023, 20, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.-J.; Tanaka, K.; Paz-Ares, L.; Cornelissen, R.; Girard, N.; Pons-Tostivint, E.; Baz, D.V.; Sugawara, S.; Cobo, M.; Pérol, M.; et al. Datopotamab Deruxtecan Versus Docetaxel for Previously Treated Advanced or Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Randomized, Open-Label Phase III TROPION-Lung01 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sands, J.; Sands, J.; Sands, J.; Ahn, M.-J.; Ahn, M.-J.; Ahn, M.-J.; Lisberg, A.; Lisberg, A.; Lisberg, A.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Datopotamab Deruxtecan in Advanced or Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer with Actionable Genomic Alterations: Results From the Phase II TROPION-Lung05 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foffano, L.; Bertoli, E.; Bortolot, M.; Torresan, S.; De Carlo, E.; Stanzione, B.; Del Conte, A.; Puglisi, F.; Spina, M.; Bearz, A. Immunotherapy in Oncogene-Addicted NSCLC: Evidence and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Zhan, J.; Hong, S.; Tang, Y.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, T.; Qin, T.; et al. Upregulation of PD-L1 by EGFR Activation Mediates the Immune Escape in EGFR-Driven NSCLC: Implication for Optional Immune Targeted Therapy for NSCLC Patients with EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Cheng, J.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B. EGFR-TKI down-regulates PD-L1 in EGFR mutant NSCLC through inhibiting NF-κB. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 95–101, Erratum in Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 629, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.-Y.; Zhang, J.-T.; Liu, S.-Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Tu, H.-Y.; Xu, C.-R.; Yan, L.-X.; et al. EGFR mutation correlates with uninflamed phenotype and weak immunogenicity, causing impaired response to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. OncoImmunology 2017, 6, e1356145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Toki, M.I.; Mani, N.; Smithy, J.W.; Liu, Y.; Altan, M.; Wasserman, B.; Tuktamyshov, R.; Schalper, K.; Syrigos, K.N.; Rimm, D.L. Immune Marker Profiling and Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression Across NSCLC Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mok, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Park, K.; Ohe, Y.; Girard, N.; Kim, H.R.; Wu, Y.-L.; Gainor, J.; Lee, S.-H.; Chiu, C.-H.; et al. Nivolumab Plus Chemotherapy in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor–Mutated Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer After Disease Progression on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Final Results of CheckMate 722. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.-S.; Fan, Y.; de Marinis, F.; Iwama, E.; Inoue, T.; Rodríguez-Cid, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.-T.; et al. Phase III KEYNOTE-789 Study of Pemetrexed and Platinum with or Without Pembrolizumab for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor–Resistant, EGFR –Mutant, Metastatic Nonsquamous Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 4029–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reck, M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower150): Key subgroup analyses of patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver metastases in a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Ho, C.; Yang, J.C.; Yu, S.; Lin, S.; Liao, B.; Yang, C.; Lin, Y.; Yu, C.; Chuang, Y.; et al. Atezolizumab, bevacizumab, pemetrexed and platinum for EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients after EGFR TKI failure: A phase II study with immune cell profile analysis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 15, e70149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lu, S.; Wu, L.; Jian, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Han, L.; Sun, M.; et al. Sintilimab plus chemotherapy for patients with EGFR-mutated non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer with disease progression after EGFR tyrosine-kinase inhibitor therapy (ORIENT-31): Second interim analysis from a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HARMONi-A Study Investigators; Fang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yang, R.; Huang, Y.; He, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, M.; Li, K.; et al. Ivonescimab Plus Chemotherapy in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Variant: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Clinical Trial | Treat Ments | PTS (n) | ORR | Median icPFS | Median PFS | Median OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAP-Brain [33] | Gefitinib + ChT vs. Gefitinib | 161 | 80.0% (95% CI, 71.0–89.0%) vs. 64.2% (95% CI, 53.5–74.9%) | 15.6 mo (95% CI, 14.3–16.9) vs. 9.1 mo (95% CI, 8.0–10.2) | 16.3 (95% CI, 14.4–18.2) vs. 9.5 mo (95% CI, 8.3–10.8) | 35.0 vs. 28.9 mo; hazard ratio, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.43–0.99 |
| NEJ009 [31] | Gefitinib + ChT vs. Gefitinib | 345 | - | - | 20.9 (95% CI, 18.0–24.0) vs. 18.0 mo (95% CI, 16.3–20.7) | 49.03 (95% CI, 41.77–56.73) vs. 38.47 mo (95% CI, 31.1–47.1) |
| Noronha et al. [32] | Gefitinib + ChT vs. Gefitinib | 350 | - | - | 16 (95% CI, 13.5 to 18.5) vs. 8 mo (95% CI, 7.0–9.0) | not reached vs. 17 mo (95% CI, 13.5–20.5) |
| FLAURA-2 [34] | Osimertinib + ChT vs. Osimertinib | 557 | 83% (95% CI, 78–87) vs. 76% (95% CI, 70–80) | - | 25.5 (95% CI, 24.7–NC) vs. 16.7 mo (95% CI, 14.1–21.3) | - |
| Clinical Trial | Phase | ORR | Median DoR | Median PFS | Median OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TATTON [63] | 1b | 33% | - | 5.5 months | - |
| ORCHARD [64] | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| SAVANNAH [65] | 2b | 49% | - | 7.1 months | - |
| INSIGHT2 [66] | 2 | 50% | 8.5 months | 5.6 months | 17.8 months |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanzione, B.; Del Conte, A.; Bertoli, E.; De Carlo, E.; Bortolot, M.; Torresan, S.; Spina, M.; Bearz, A. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Common Mutations: New Strategies. Cancers 2025, 17, 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091515
Stanzione B, Del Conte A, Bertoli E, De Carlo E, Bortolot M, Torresan S, Spina M, Bearz A. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Common Mutations: New Strategies. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091515
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanzione, Brigida, Alessandro Del Conte, Elisa Bertoli, Elisa De Carlo, Martina Bortolot, Sara Torresan, Michele Spina, and Alessandra Bearz. 2025. "Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Common Mutations: New Strategies" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091515
APA StyleStanzione, B., Del Conte, A., Bertoli, E., De Carlo, E., Bortolot, M., Torresan, S., Spina, M., & Bearz, A. (2025). Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Common Mutations: New Strategies. Cancers, 17(9), 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091515





