Risk Factors for Unplanned Early Implantable Port Catheter Removal in Adult Leukemia/Lymphoma Patients: Cancer Type or Different Degrees of Cytopenia?
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
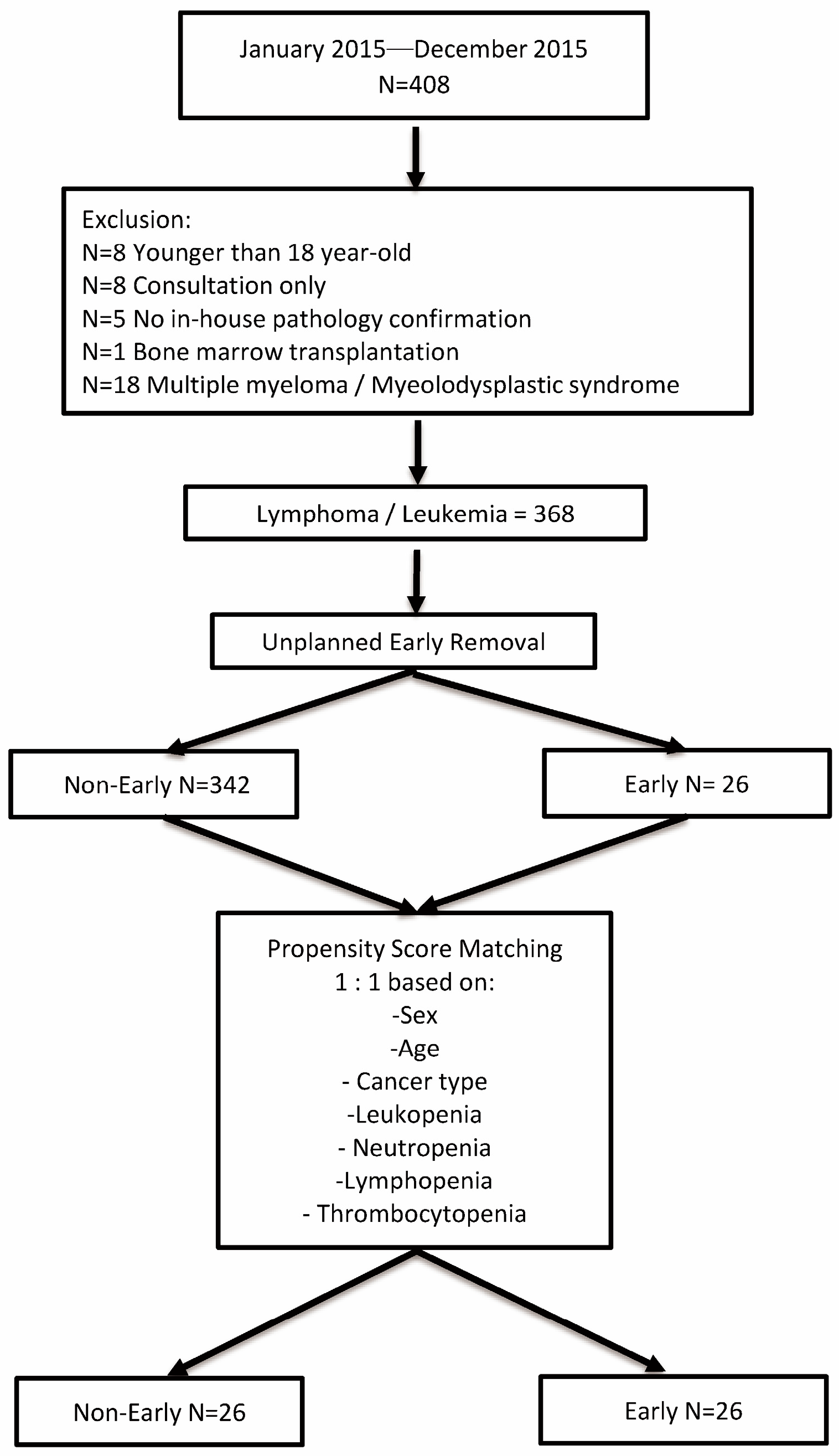
2.1. Study Population
- (i)
- Positive culture of the catheter tip or port reservoir associated with a positive peripheral blood culture with the same microorganism or the difference in time to positivity of blood culture drawn from the catheter versus that from a peripheral vein (positivity of the catheter blood sample was at least 2 h before that of the peripheral blood sample);
- (ii)
- Local or general signs of infection, such as fever and chills, positive culture from the vascular port (catheter tip or the port reservoir), and regression of clinical signs of infection after port removal despite a negative peripheral blood culture [12]. We used clinical local signs such as local heat, erythema, and purulent discharge to diagnose pocket infection. Skin disruption and direct visualization of the port reservoir served for pocket exposure diagnosis.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Surgical Procedure
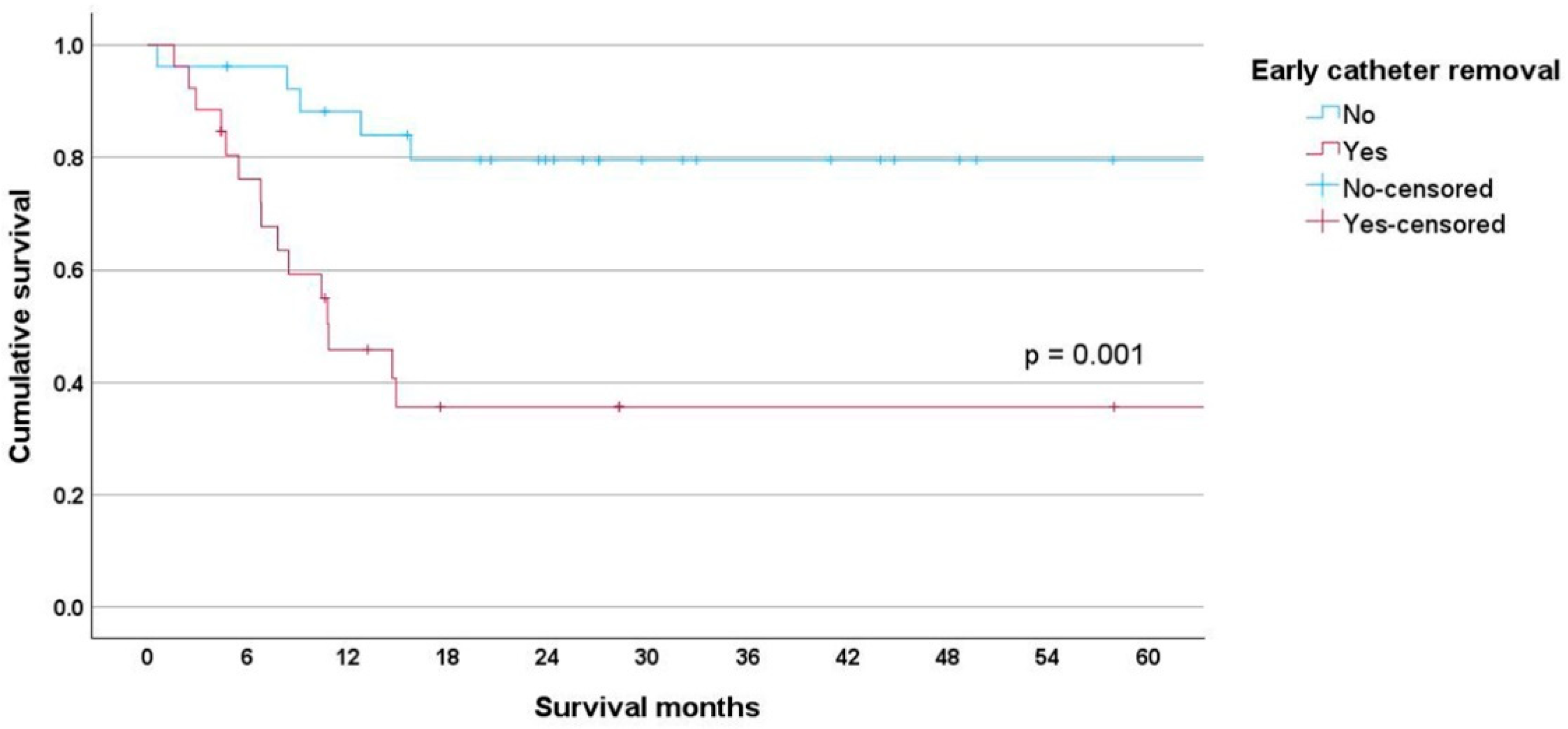
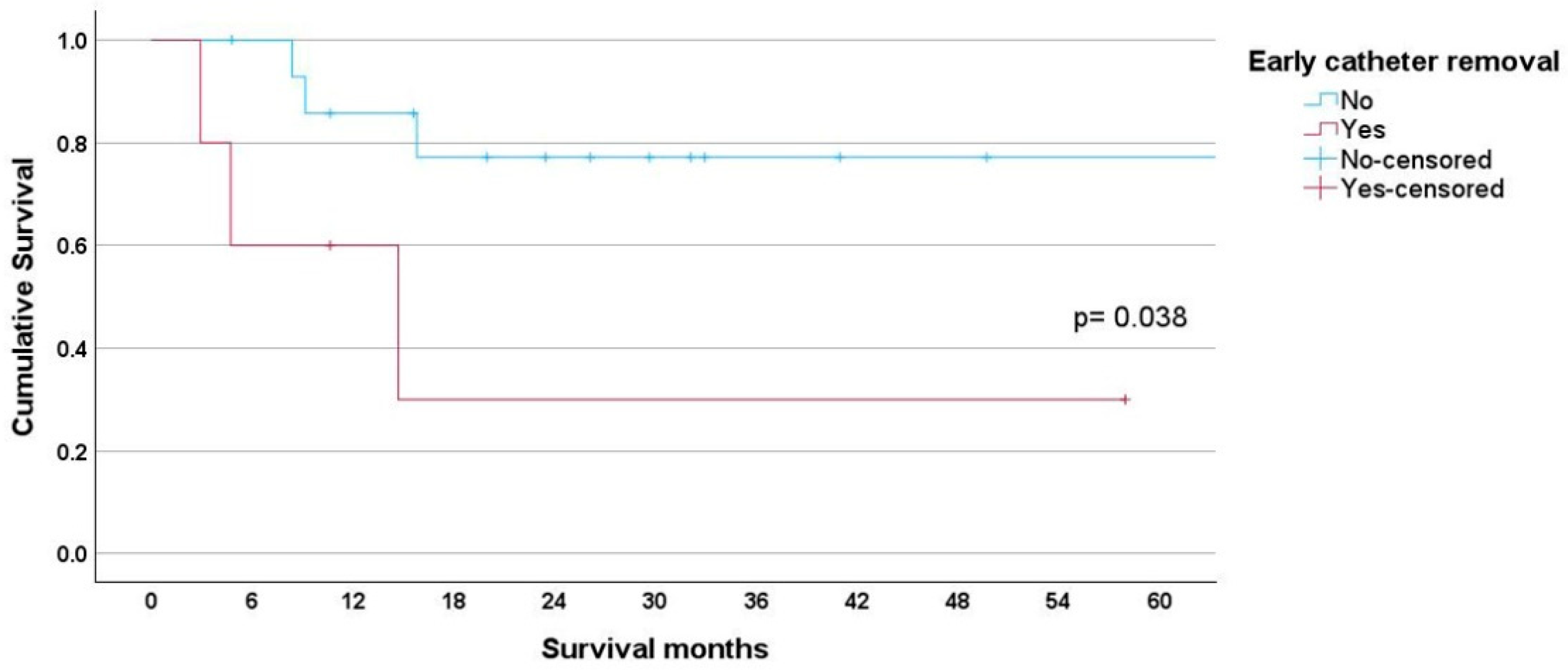
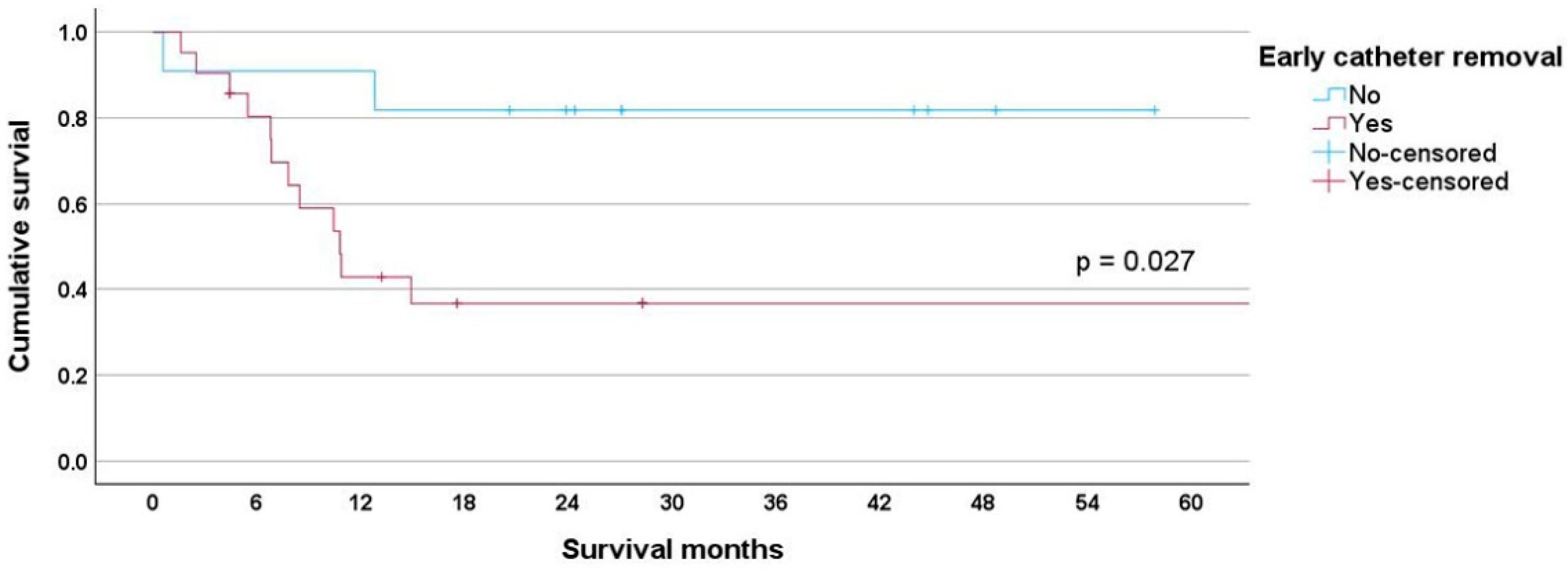
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niederhuber, J.E.; Ensminger, W.; Gyves, J.W.; Liepman, M.; Doan, K.; Cozzi, E. Totally implanted venous and arterial access system to replace external catheters in cancer treatment. Surgery 1982, 92, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fischer, L.; Knebel, P.; Schröder, S.; Bruckner, T.; Diener, M.K.; Hennes, R.; Buhl, K.; Schmied, B.; Seiler, C.M. Reasons for explantation of totally implantable access ports: A multivariate analysis of 385 consecutive patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narducci, F.; Jean-Laurent, M.; Boulanger, L.; El Bédoui, S.; Mallet, Y.; Houpeau, J.L.; Hamdani, A.; Penel, N.; Fournier, C. Totally implantable venous access port systems and risk factors for complications: A one-year prospective study in a cancer centre. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 37, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.; Seo, T.S.; Song, M.G.; Cha, I.H.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, C.W.; Seo, J.H.; Oh, S.C. Incidence and risk factors of infectious complications related to implantable venous-access ports. Korean J. Radiol. 2014, 15, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Faridnia, M.; Skummer, P.; Zhang, D.; Karmel, M.I. Clinical Predictors of Port Infections in Adult Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollee, P.; Jones, M.; Stackelroth, J.; van Kuilenburg, R.; Joubert, W.; Faoagali, J.; Looke, D.; Harper, J.; Clements, A. Catheter-associated bloodstream infection incidence and risk factors in adults with cancer: A prospective cohort study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2011, 78, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skummer, P.; Kobayashi, K.; DeRaddo, J.S.; Blackburn, T.; Schoeneck, M.; Patel, J.; Jawed, M. Risk Factors for Early Port Infections in Adult Oncologic Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana Taveira, M.R.; Lima, L.S.; de Araújo, C.C.; de Mello, M.J. Risk factors for central line-associated bloodstream infection in pediatric oncology patients with a totally implantable venous access port: A cohort study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezami, N.; Xing, M.; Groenwald, M.; Silin, D.; Kokabi, N.; Latich, I. Risk Factors of Infection and Role of Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Totally Implantable Venous Access Port Placement: Propensity Score Matching. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic. Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Ottery, F.D. Assessing nutritional status in cancer: Role of the Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermel, L.A.; Allon, M.; Bouza, E.; Craven, D.E.; Flynn, P.; O’Grady, N.P.; Raad, I.I.; Rijnders, B.J.; Sherertz, R.J.; Warren, D.K. Clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intravascular catheter-related infection: 2009 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2009, 49, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.S.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.C.; Hsieh, C.C. Risk Factors for Unplanned Early Implantable Port Catheter Removal in Adult Hematology Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Propensity Score Matching Study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2024, 16, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, J.G.; Wu, O.; Bodenham, A.R.; Agarwal, R.; Menne, T.F.; Jones, B.L.; Heggie, R.; Hill, S.; Dixon-Hughes, J.; Soulis, E.; et al. Central venous access devices for the delivery of systemic anticancer therapy (CAVA): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, C.L.; Pan, C.Q.; Yu, L. The risk of bloodstream infection associated with totally implantable venous access ports in cancer patient: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, A.W.; Watchmaker, J.M.; Brown, D.B.; Banovac, F. Association between Periprocedural Neutropenia and Early Infection-related Chest Port Removal. Radiology 2019, 291, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, R.; Lorenz, J.M.; Lale, A.J.; Funaki, B.S.; Zangan, S.M. Clinical predictors of port infections within the first 30 days of placement. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yamane, T.; Haruyama, T.; Ishihara, M.; Kazahari, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Tanzawa, S.; Honda, T.; Ichikawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Predictors of central line-associated bloodstream infections in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy through implanted venous access ports: A retrospective, observational study. Transl. Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 3538–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoss, D.R.; Bedros, A.A.; Mesipam, A.; Criddle, J.; Smith, J.C. Severe Neutropenia at the Time of Implantable Subcutaneous Chest Port Insertion Is Not a Risk Factor for Port Removal at a Tertiary Pediatric Center. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanHouwelingen, L.T.; Veras, L.V.; Lu, M.; Wynn, L.; Wu, J.; Prajapati, H.J.; Gold, R.E.; Murphy, A.J.; Fernandez-Pineda, I.; Gosain, A.; et al. Neutropenia at the time of subcutaneous port insertion may not be a risk factor for early infectious complications in pediatric oncology patients. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira, B.L.; Connolly, B.; Abla, O.; Tomlinson, G.; Amaral, J.G. Severe neutropenia at time of port insertion is not a risk factor for catheter-associated infections in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2010, 116, 4368–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, H.G.; Peng, J.; Ni, H.; Hou, M.; Jansen, A.J.G. Low platelet count as risk factor for infections in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia: A retrospective evaluation. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Ni, H. Crosstalk Between Platelets and Microbial Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelborg, K.; Katalin, V.; Erzsébet Horváth, P.; Clouser, M.; Saad, H.A.; Sørensen, H.T. Thrombocytopenia among patients with hematologic malignancies and solid tumors: Risk and prognosis. Blood 2021, 138, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keulers, A.R.; Kiesow, L.; Mahnken, A.H. Port implantation in patients with severe thrombocytopenia is safe with interventional radiology. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2018, 41, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, J.L.; Stanworth, S.J.; Guyatt, G.; Valentine, S.; Dennis, J.; Bakhtary, S.; Cohn, C.S.; Dubon, A.; Grossman, B.J.; Gupta, G.K.; et al. Red Blood Cell Transfusion: 2023 AABB International Guidelines. JAMA 2023, 330, 1892–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitenberg, G.; Raynard, B. Nutritional support of the cancer patient: Issues and dilemmas. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2000, 34, 137–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasco, P. Nutrition in Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shike, M. Nutrition therapy for the cancer patient. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 1996, 10, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Capra, S.; Ferguson, M. Use of the scored patient-generated subjective global assessment (PG-SGA) as a nutrition assessment tool in patients with cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoist, S.; Brouquet, A. Nutritional assessment and screening for malnutrition. J. Visc. Surg. 2015, 152 (Suppl. 1), S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeger, J.S.; Lucas, A.B.; Thaler, H.T.; Friedlander-Klar, H.; Brown, A.E.; Kiehn, T.E.; Armstrong, D. Infectious morbidity associated with long-term use of venous access devices in patients with cancer. Ann. Intern. Med. 1993, 119, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Unmatched Cohort | Matched Cohort | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | All | Non-Early Group | Early Group | p-Value | All | Non-Early Group | Early Group | p-Value |
| Characteristics | ||||||||
| Number of patients n (%) | 368 (100) | 342 (92.90) | 26 (7.10) | 52 (100) | 26 (50.00) | 26 (50.00) | ||
| Age (median + SD in years) | 62.50 ± 15.47 | 63 ± 15.38 | 59.50 ± 16.05 | 0.542 | 57.50 ± 13.93 | 54.00 ± 11.63 | 59.50 ± 16.05 | 0.087 |
| Sex n (%) | 0.447 | 0.397 | ||||||
| Female | 144 (100) | 132 (91.70) | 12 (8.30) | 21 (100) | 9 (42.90) | 12 (57.10) | ||
| Male | 224 (100) | 210 (93.80) | 14 (6.30) | 31 (100) | 17 (54.80) | 14 (45.20) | ||
| Smoking history n (%) | 0.723 | 0.465 | ||||||
| No | 293 (100) | 273 (93.20) | 20 (6.80) | 43 (100) | 23 (53.50) | 20 (46.50) | ||
| Yes | 75 (100) | 69 (92.00) | 6 (8.00) | 9 (100) | 3 (33.33) | 6 (66.67) | ||
| Cancer type | <0.001 | 0.004 | ||||||
| Leukemia | 133 (100) | 112 (84.20) | 21 (15.80) | 32 (100) | 11 (34.40) | 21 (65.60) | ||
| Lymphoma | 235 (100) | 230 (97.90) | 5 (2.10) | 20 (100) | 15 (75.00) | 5 (25.00) | ||
| Body Mass Index n (%) | 0.262 | 0.099 | ||||||
| Underweight | 16 (100) | 15 (93.80) | 1 (6.30) | 2 (100) | 1 (50.00) | 1 (50.00) | ||
| Normal-Overweight | 324 (100) | 303 (93.50) | 21 (6.50) | 46 (100) | 25 (54.30) | 21 (45.70) | ||
| Obese | 28 (100) | 24 (85.70) | 4 (14.30) | 4 (100) | 0 (0) | 4 (100.00) | ||
| Charlson comorbidity score (median + SD) | 3.00 ± 1.96 | 3.00 ± 1.98 | 3.00 ± 1.77 | 0.504 | 2.5 ± 1.54 | 2.00 ± 1.16 | 3.00 ± 1.77 | 0.504 |
| Creatinine (median + SD in mg/dL) | 0.83 ± 0.56 | 0.82 ± 0.56 | 0.90 ± 0.63 | 0.451 | 0.83 ± 0.59 | 0.82 ± 0.56 | 0.90 ± 0.63 | 0.676 |
| Hemoglobin (median + SD in g/dL) | 10.90 ± 2.47 | 11.10 ± 2.47 | 9.15 ± 1.87 | <0.001 | 9.80 ± 2.45 | 10.45 ± 2.68 | 9.15 ± 1.87 | <0.001 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 0.780 | 0.465 | ||||||
| No | 310 (100) | 287 (92.60) | 23 (7.40) | 43 (100) | 20 (46.50) | 23 (53.50) | ||
| Yes | 58 (100) | 55 (94.80) | 3 (5.2) | 9(100) | 6 (66.70) | 3 (33.33) | ||
| Leukopenia n (%) | 0.003 | 0.061 | ||||||
| No | 311 (1000 | 295 (94.90) | 16 (5.10) | 38 (100) | 22 (57.90) | 16 (42.10) | ||
| Yes | 57 (100) | 47 (82.50) | 10 (17.50) | 14 (100) | 4 (28.60) | 10 (71.40) | ||
| Neutropenia n (%) | <0.001 | 0.071 | ||||||
| No | 308 (100) | 293 (95.10) | 15 (4.90) | 36 (100) | 21 (58.30) | 15 (41.70) | ||
| Yes | 60 (100) | 49 (81.70) | 11 (18.30) | 16 (100) | 5 (31.30) | 11 (69.80) | ||
| Lymphopenia n (%) | 0.565 | 0.397 | ||||||
| No | 147 (100) | 138 (93.90) | 9 (6.10) | 21 (100) | 12 (57.10) | 9 (42.90) | ||
| Yes | 221 (100) | 204 (92.30) | 17 (7.70) | 31 (100) | 14 (45.20) | 17 (54.80) | ||
| Thrombocytopenia n (%) | 0.002 | 0.266 | ||||||
| No | 268 (100) | 256 (95.50) | 12 (4.50) | 28 (100) | 16 (57.10) | 12 (42.90) | ||
| Yes | 100 (100) | 86 (86.00) | 14 (14.00) | 24 (100) | 10 (41.70) | 14 (58.30) | ||
| PG-SGA (Scored Patient Generated Subjective Global Assessment) n (%) | ||||||||
| Total PG-SGA Score | 0.162 | 0.001 | ||||||
| Normal nutrition | 111 (100) | 100 (90.10) | 11 (9.90) | 34 (100) | 23 (67.60) | 11 (32.40) | ||
| Malnutrition | 257 (100) | 242 (94.20) | 15 (5.80) | 18 (100) | 3 (16.70) | 15 (83.30) | ||
| Early Unplanned Catheter Removal | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Adjusted Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
| Hemoglobin | 0.831 | 0.773–1.230 | 0.831 |
| Diagnosis | |||
| Lymphoma | Ref | ||
| Leukemia | 4.589 | 1.377–15.299 | 0.013 |
| PG-SGA | |||
| Malnutrition | Ref | ||
| Normal nutrition | 0.258 | 0.116–0.575 | <0.001 |
| PG-SGA: Scored Patient Generated Subjective Global Assessment | |||
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; Ref, reference | |||
| Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | All | Lymphoma | Leukemia | p Value |
| Number of patients n (%) | 52 (100) | 23 (44.20) | 29 (55.80) | |
| Age (median + SD in years) | 57.50 ± 13.93 | 58.00 ± 14.98 | 53.00 ± 113.46 | 0.706 |
| Sex n (%) | 0.964 | |||
| Female | 21 (100) | 8 (38.10) | 13 (61.90) | |
| Male | 31 (100) | 12 (38.70) | 19 (61.30) | |
| Smoking history n (%) | 0.719 | |||
| No | 43 (100) | 16 (37.20) | 27 (62.80) | |
| Yes | 9 (100) | 4 (44.40) | 5 (55.60) | |
| Body Mass Index n (%) | 0.892 | |||
| Underweight | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 2 (100.00) | |
| Normal–Overweight | 46 (100) | 18 (39.10) | 28 (60.90) | |
| Obese | 4 (100) | 0 (0) | 4 (100.00) | |
| Charlson comorbidity score (median + SD) | 2.50 ± 1.54 | 2.50 ± 1.36 | 2.50 ± 1.66 | 0.808 |
| Creatinine (median + SD in mg/dL) | 0.83 ± 0.59 | 0.82 ± 0.90 | 0.88 ± 0.24 | 0.498 |
| Hemoglobin (median + SD in g/dL) | 9.80 ± 2.45 | 12.25 ± 2.10 | 8.65 ± 1.69 | <0.001 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 1.000 | |||
| No | 43 (100) | 17 (39.50) | 26 (60.50) | |
| Yes | 9 (100) | 3 (33.33) | 6 (66.67) | |
| Leukopenia n (%) | 0.005 | |||
| No | 38 (100) | 19 (50.00) | 19 (50.00) | |
| Yes | 14 (100) | 1 (7.10) | 13 (92.90) | |
| Neutropenia n (%) | 0.001 | |||
| No | 36 (100) | 19 (52.80) | 17 (47.20) | |
| Yes | 16 (100) | 1 (6.30) | 15 (93.80) | |
| Lymphopenia n (%) | 0.532 | |||
| No | 21 (100) | 7 (33.30) | 14 (66.70) | |
| Yes | 31 (100) | 13 (41.90) | 18 (58.10) | |
| Thrombocytopenia n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| No | 28 (100) | 18 (64.30) | 10 (35.70) | |
| Yes | 24 (100) | 2 (8.30) | 22 (91.70) | |
| PG-SGA (Scored Patient Generated Subjective Global Assessment) n (%) | 0.580 | |||
| Normal nutrition | 34(100) | 14 (41.20) | 20 (58.80) | |
| Malnutrition | 18 (100) | 6 (33.33) | 12 (66.70) | |
| Early catheter removal n (%) | 0.009 | |||
| No | 26 (100) | 15 (57.70) | 11 (42.30) | |
| Yes | 26 (100) | 5 (19.20) | 21 (80.80) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, M.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Hsieh, C.-C. Risk Factors for Unplanned Early Implantable Port Catheter Removal in Adult Leukemia/Lymphoma Patients: Cancer Type or Different Degrees of Cytopenia? Cancers 2025, 17, 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091505
Lu M-S, Chen C-C, Chang C-C, Lin C-C, Hsieh C-C. Risk Factors for Unplanned Early Implantable Port Catheter Removal in Adult Leukemia/Lymphoma Patients: Cancer Type or Different Degrees of Cytopenia? Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091505
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Ming-Shian, Chih-Chen Chen, Che-Chia Chang, Chien-Chao Lin, and Ching-Chuan Hsieh. 2025. "Risk Factors for Unplanned Early Implantable Port Catheter Removal in Adult Leukemia/Lymphoma Patients: Cancer Type or Different Degrees of Cytopenia?" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091505
APA StyleLu, M.-S., Chen, C.-C., Chang, C.-C., Lin, C.-C., & Hsieh, C.-C. (2025). Risk Factors for Unplanned Early Implantable Port Catheter Removal in Adult Leukemia/Lymphoma Patients: Cancer Type or Different Degrees of Cytopenia? Cancers, 17(9), 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091505





