Long-Term Oncological Outcomes of Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) Treatment in Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Selection Process and Data Management
2.4. Eligibility Criteria
2.5. Prognostic Outcomes and Safety
2.6. Data Extraction
2.7. Data Synthesis and Subgroups
2.8. Study Quality Assessment and Risk of Bias
2.9. Confidence in Cumulative Evidence
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Study Characteristics
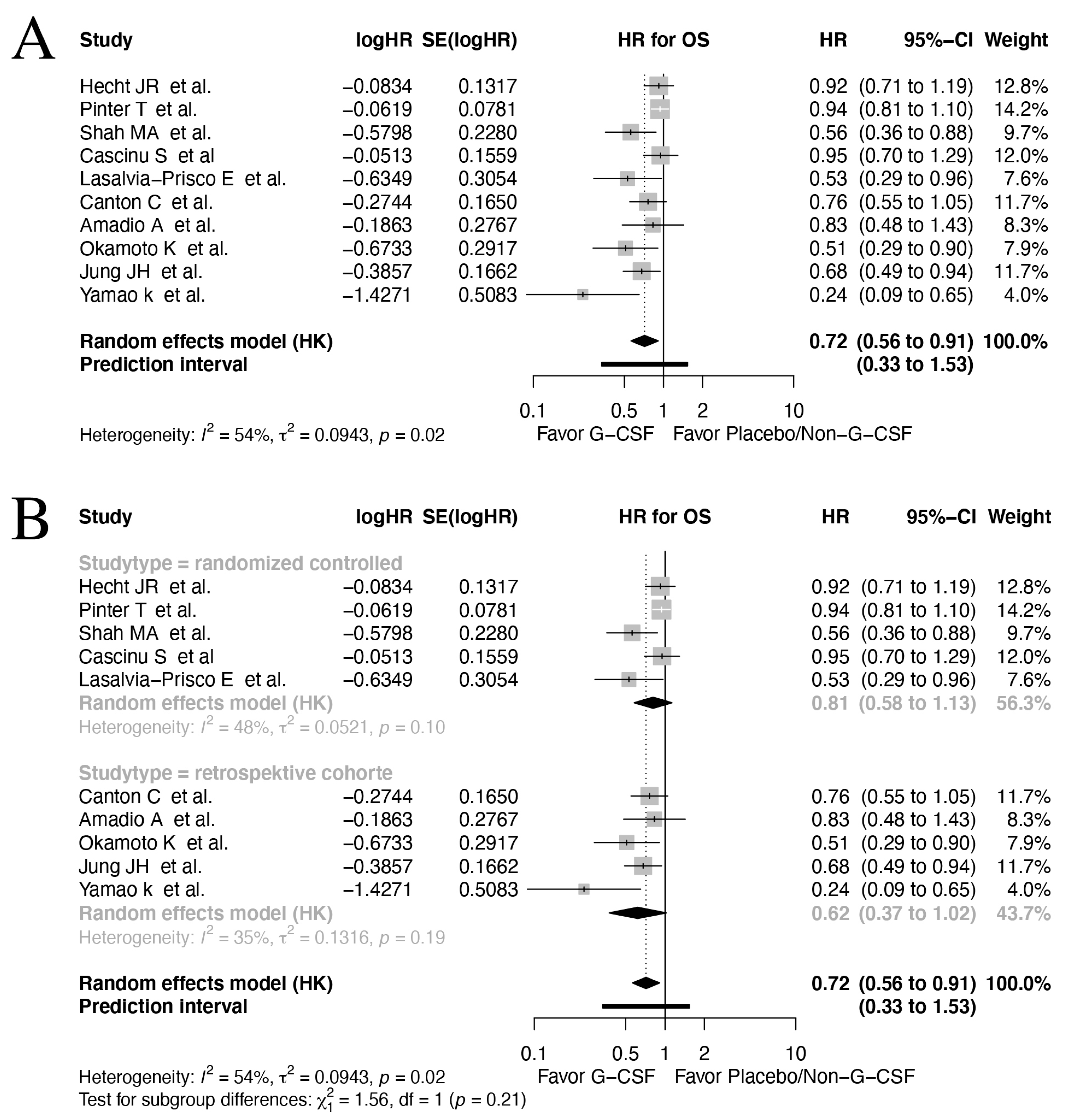
3.3. Overall Survival
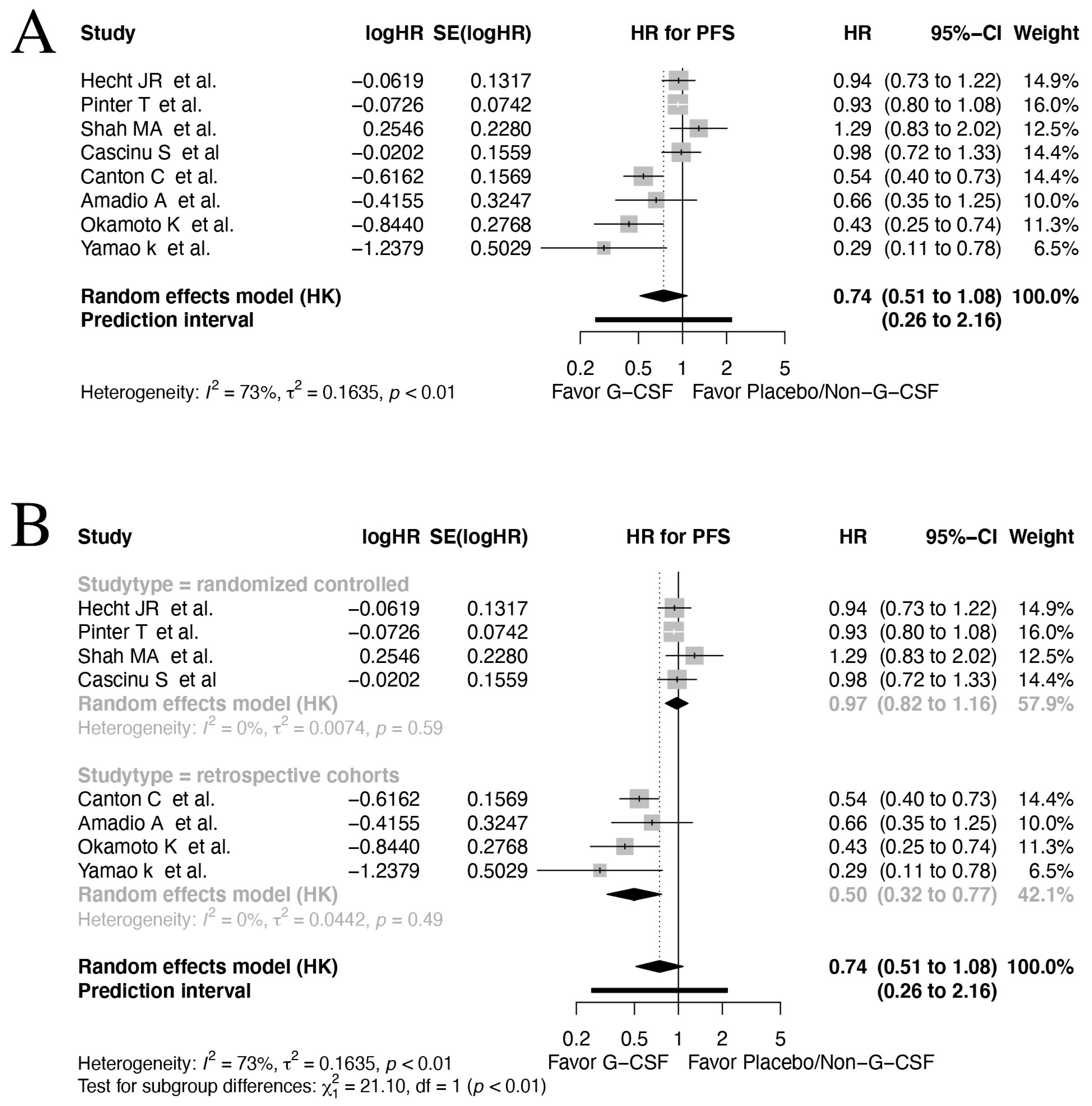
3.4. Progression-Free Survival
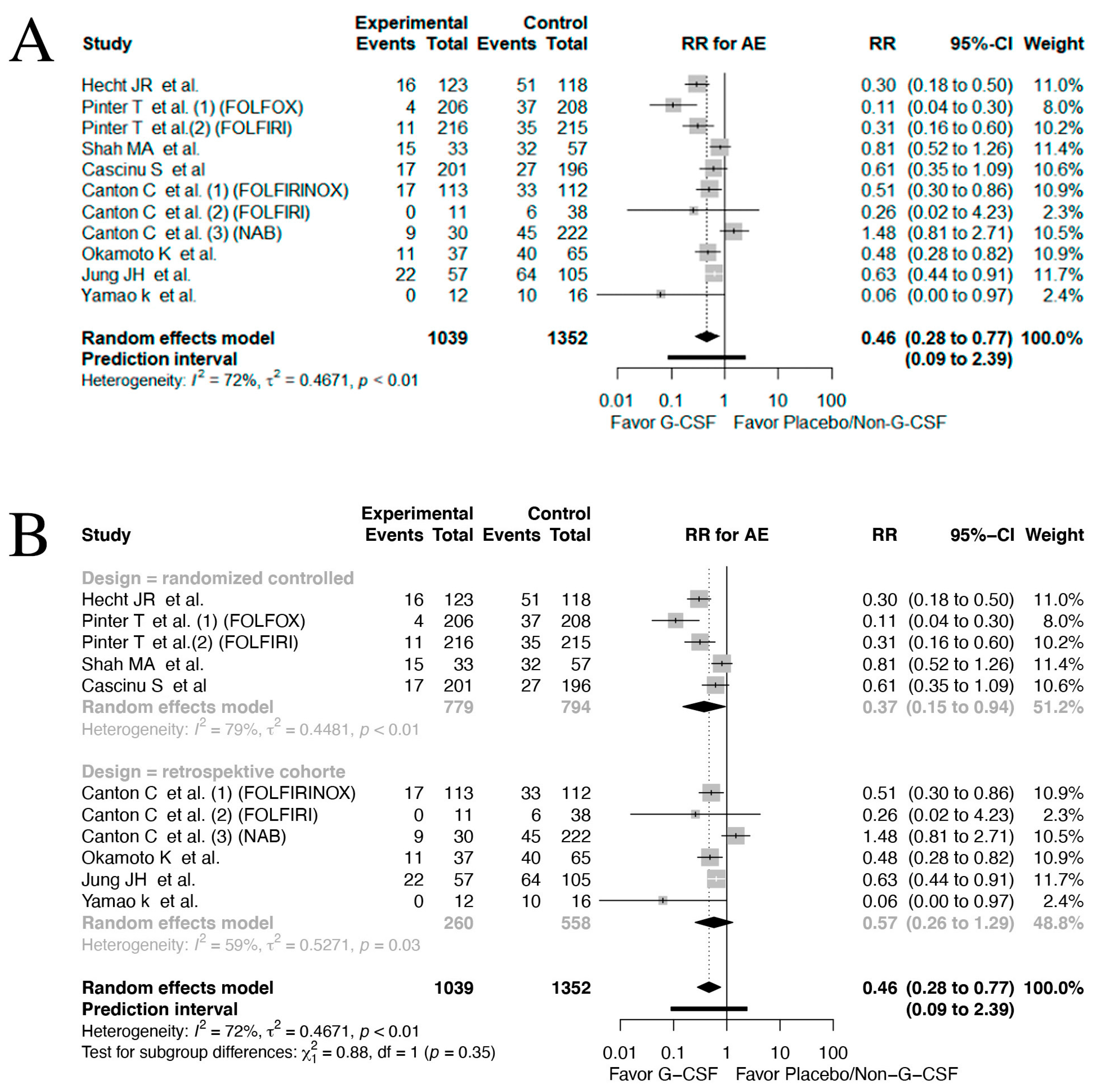
3.5. Adverse Events
3.6. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs)
3.7. Study Quality and Risk of Bias
3.8. Certainty in Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trotta, F.; Mayer, F.; Mecozzi, A.; Amato, L.; Addis, A. Impact of Guidance on the Prescription Patterns of G-CSFs for the Prevention of Febrile Neutropenia Following Anticancer Chemotherapy: A Population-Based Utilization Study in the Lazio Region. BioDrugs 2017, 31, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, K.L.; Madan, J.; Whyte, S.; Stevenson, M.D.; Akehurst, R.L. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factors for febrile neutropenia prophylaxis following chemotherapy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, O.A.C.; Lyman, G.H.; Castro, A.A.; Clark, L.G.O.; Djulbegovic, B. Colony-stimulating factors for chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4198–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuderer, N.M.; Dale, D.C.; Crawford, J.; Lyman, G.H. Impact of Primary Prophylaxis With Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor on Febrile Neutropenia and Mortality in Adult Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3158–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Fan, L.; Tan, B.; Zuo, J.; Hua, K.; Ji, Q. Highly Expressed Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) and Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Receptor (G-CSFR) in Human Gastric Cancer Leads to Poor Survival. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannidis, I.; Salataj, E.; Said, E.; Egal, A.; Beswick, E.J. G-CSF in tumors: Aggressiveness, tumor microenvironment and immune cell regulation. Cytokine 2021, 142, 155479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Guo, P.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Ge, C.; Wang, S. GCSF as a Potential Molecular Target for Overall Survival of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2022, 25, 1005–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskov, H.; Orhan, A.; Gaggar, S.; Gögenur, I. Neutrophils and polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells: An emerging battleground in cancer therapy. Oncogenesis 2022, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, V.T.; Wu, X.; Cheng, J.H.; Sheng, R.X.; Chung, A.S.; Zhuang, G.; Tran, C.; Song, Q.; Kowanetz, M.; Sambrone, A.; et al. Oncogenic RAS pathway activation promotes resistance to anti-VEGF therapy through G-CSF-induced neutrophil recruitment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6079–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, F.; Wu, X.; Qu, X.; Kowanetz, M.; Yu, L.; Tan, M.; Meng, Y.G.; Ferrara, N. G-CSF-initiated myeloid cell mobilization and angiogenesis mediate tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF therapy in mouse models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6742–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.G.; Dasilva, G.; Wexner, S.D. Neutropenic enterocolitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms—NCI. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0. 2017. Available online: https://www.meddra.org (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- Tierney, J.F.; Stewart, L.A.; Ghersi, D.; Burdett, S.; Sydes, M.R. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 2007, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inthout, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Borm, G.F. The Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method for random effects meta-analysis is straightforward and considerably outperforms the standard DerSimonian-Laird method. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Spiegelhalter, D.J. A re-evaluation of random-effects meta-analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2009, 172, 137–159. Available online: https://www.blackwell-synergy.com (accessed on 3 October 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inthout, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Rovers, M.M.; Goeman, J.J. Plea for routinely presenting prediction intervals in meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2016, 6, 10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Hayden, J.A.; Stinson, J.; McGrath, P.J.; Chambers, C.T.; Tougas, M.E.; Wozney, L. Judging the quality of evidence in reviews of prognostic factor research: Adapting the GRADE framework. Syst. Rev. 2013, 2, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowinsky, E.K.; Baker, S.D.; Burks, K.; O’Reilly, S.; Donehower, R.C.; Grochow, L.B. High-dose topotecan with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in fluoropyrimidine-refractory colorectal cancer: A phase II and pharmacodynamic study. Ann. Oncol. 1998, 9, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltz, L.B.; Kemeny, N.E.; Tong, W.; Harrison, J.; Berkery, R.; Kelsen, D.P. 9-Aminocamptothecin by 72-hour continuous intravenous infusion is inactive in the treatment of patients with 5-fluorouracil-refractory colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 1997, 80, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajani, J.A.; Ilson, D.H.; Daugherty, K.; Pazdur, R.; Lynch, P.M.; Kelsen, D.P. Activity of taxol in patients with squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1994, 86, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlon, N.E.; Kammili, A.; Roopnarinesingh, R.; Davern, M.; Power, R.; King, S.; Chmelo, J.; Phillips, A.W.; Donohoe, C.L.; Ravi, N.; et al. FLOT-regimen Chemotherapy and Transthoracic en bloc Resection for Esophageal and Junctional Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2021, 274, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, A.; Boku, N.; Muro, K.; Chin, K.; Muto, M.; Yoshida, S.; Satake, M.; Ishikura, S.; Ogino, T.; Miyata, Y.; et al. Definitive chemoradiotherapy for T4 and/or M1 lymph node squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 2915–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Pramanik, R.; Kumar, A.; Pathy, S.; Kumar, S.; Bhoriwal, S.; Thulkar, S.; Dash, N.R.; Pal, S.; Choudhary, P.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Modified FOLFIRINOX in Unresectable or Metastatic Gallbladder Cancer: A Phase II Pilot Study. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2021, 7, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenacci, D.V.T.; Chase, L.; Lomnicki, S.; Karrison, T.; de Wilton Marsh, R.; Rampurwala, M.M.; Narula, S.; Alpert, L.; Setia, N.; Xiao, S.Y.; et al. Evaluation of the Association of Perioperative UGT1A1 Genotype-Dosed gFOLFIRINOX with Margin-Negative Resection Rates and Pathologic Response Grades Among Patients With Locally Advanced Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1921290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalla Chiesa, M.; Tomasello, G.; Buti, S.; Rovere, R.K.; Brighenti, M.; Lazzarelli, S.; Donati, G.; Passalacqua, R. Sequential chemotherapy with dose-dense docetaxel, cisplatin, folinic acid and 5-fluorouracil (TCF-dd) followed by combination of oxaliplatin, folinic acid, 5-fluorouracil and irinotecan (COFFI) in metastatic gastric cancer: Results of a phase II trial. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lauro, L.; Belli, F.; Arena, M.G.; Carpano, S.; Paoletti, G.; Giannarelli, D.; Lopez, M. Epirubicin, cisplatin and docetaxel combination therapy for metastatic gastric cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 1498–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felici, A.; Carlini, P.; Ruggeri, E.M.; Gamucci, T.; Pollera, C.F.; Marco, S.M.; Fariello, A.M.; Moscetti, L.; Gelibter, A.; Adami, E.; et al. Bi-weekly chemotherapy with cisplatin, epirubicin, folinic acid and 5-fluororacil continuous infusion plus g-csf in advanced gastric cancer: A multicentric phase II study. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, M.; Raderer, M.; Zacherl, J.; Ba-Ssalamah, A.; Püspök, A.; Schmidinger, M.; Pluschnig, U.; Brodowicz, T.; Zielinski, C.C. Phase II study of docetaxel in combination with oxaliplatin in patients with metastatic or locally advanced esophagogastric cancer previously untreated with chemotherapy for advanced disease: Results of the Central European Cooperative Oncology Group Study ESGAS.1.2.001. Anticancer Drugs 2008, 19, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makatsoris, T.; Papakostas, P.; Kalofonos, H.P.; Xanthakis, I.; Tsavdaridis, D.; Aravantinos, G.; Gogas, H.; Klouvas, G.; Kosmidis, P.; Pectasides, D.; et al. Intensive weekly chemotherapy with docetaxel, epirubicin and carboplatin with G-CSF support in patients with advanced gastric cancer: A Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG) phase II study. Med. Oncol. 2007, 24, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroudis, D.; Kourousis, C.; Androulakis, N.; Kalbakis, K.; Agelaki, S.; Kakolyris, S.; Souglakos, J.; Sarra, E.; Vardakis, N.; Hatzidaki, D.; et al. Frontline treatment of advanced gastric cancer with docetaxel and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF): A phase II trial. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 23, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.J.; Jeung, H.C.; Ahn, J.B.; Rha, S.Y.; Yoo, N.C.; Roh, J.K.; Noh, S.H.; Chung, H.C. Mobilized CD34+ cells as a biomarker candidate for the efficacy of combined maximal tolerance dose and continuous infusional chemotherapy and G-CSF surge in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2008, 270, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojic, M.; Pluschnig, U.; Zacherl, J.; Thallinger, C.M.; Ba-Ssalamah, A.; Maresch, J.; Datler, P.; Schoppmann, S.F.; Hejna, M. Docetaxel, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil plus granulocyte colony-stimulating factor prophylaxis in patients with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the stomach and gastroesophageal junction: Experience at the Medical University of Vienna. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 2379–2382. [Google Scholar]
- Dirican, A.; Küçükzeybek, Y.; Tarhan, M.O.; Somali, I.; Erten, C.; Demir, L.; Can, A.; Bayoglu, I.V.; Akyol, M.; Ekinci, N.; et al. One-day DCF regimen in patients with metastatic gastric cancer. Tumori J. 2013, 99, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguigli, W.; Tomasello, G.; Toppo, L.; Poli, R.; Lazzarelli, S.; Negri, F.; Perrucci, B.; Curti, A.; Brighenti, M.; Donati, G.; et al. Safety and efficacy of dose-dense chemotherapy with TCF regimen in elderly patients with locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer. Tumori J. 2017, 103, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, N.; Abali, H.; Vural, M.; Yalcin, S.; Oksuzoglu, B.; Civelek, B.; Oguz, D.; Bostanci, B.; Yalcin, B.; Zengin, N. Docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil combination in neoadjuvant setting in the treatment of locally advanced gastric adenocarcinoma: Phase II NEOTAX study. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 1139–1147, Erratum in Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 76, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, G.; Chiesa, M.D.; Buti, S.; Brighenti, M.; Negri, F.; Rovere, R.K.; Martinotti, M.; Buononato, M.; Brunelli, A.; Lazzarelli, S.; et al. Dose-dense chemotherapy in metastatic gastric cancer with a modified docetaxel-cisplatin-5-fluorouracil regimen. Tumori J. 2010, 96, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, G.; Liguigli, W.; Poli, R.; Lazzarelli, S.; Brighenti, M.; Negri, F.; Curti, A.; Martinotti, M.; Olivetti, L.; Rovatti, M.; et al. Efficacy and tolerability of chemotherapy with modified dose-dense TCF regimen (TCF-dd) in locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer: Final results of a phase II trial. Gastric Cancer 2014, 17, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Gong, J.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, Y.; Wang, L.; Ren, D.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; et al. Dose-dense biweekly docetaxel combined with 5-fluorouracil as first-line treatment in advanced gastric cancer: A phase II trial. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, G.; Valeri, N.; Ghidini, M.; Smyth, E.C.; Liguigli, W.; Toppo, L.; Mattioli, R.; Curti, A.; Hahne, J.C.; Negri, F.M.; et al. First-line dose-dense chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, folinic acid and 5-fluorouracil (DCF) plus panitumumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic cancer of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction: Final results and biomarker analysis from an Italian oncology group for clinical research (GOIRC) phase II study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 111795–111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhai, L.; Xing, L. Study of local three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for patients with stage III hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 26, e92–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamias, A.; Syrigos, K.; Fountzilas, G.; Tzamakou, E.; Soulti, K.; Karavasilis, V.; Alamanos, Y.; Christodoulou, C.; Pavlidis, N. Intensified bimonthly cisplatin with bolus 5-fluorouracil, continuous 5-fluorouracil and high-dose leucovorin (LV5FU2) in Patients with advanced gastrointestinal carcinomas: A phase I dose-finding and pharmacokinetic study. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 27, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androulakis, N.; Kourousis, C.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Samelis, G.; Kakolyris, S.; Tsavaris, N.; Genatas, K.; Aravantinos, G.; Papadimitriou, C.; Karabekios, S.; et al. Treatment of pancreatic cancer with docetaxel and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: A multicenter phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, F.; Formisano, L.; Giardino, A.; Girelli, R.; Servetto, A.; Santaniello, A.; Foschini, F.; Marciano, R.; Mozzillo, E.; Carratù, A.C.; et al. Neoadjuvant Treatment in Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer (LAPC) Patients with FOLFIRINOX or Gemcitabine NabPaclitaxel: A Single-Center Experience and a Literature Review. Cancers 2019, 11, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de W Marsh, R.; Talamonti, M.S.; Baker, M.S.; Posner, M.; Roggin, K.; Matthews, J.; Catenacci, D.; Kozloff, M.; Polite, B.; Britto, M.; et al. Primary systemic therapy in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using mFOLFIRINOX: A pilot study. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Ueno, H.; Mitsunaga, S.; Ohba, A.; Hosoi, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Ueno, M.; Terazawa, T.; Goto, M.; Inoue, D.; et al. A phase II study of FOLFIRINOX with primary prophylactic pegfilgrastim for chemotherapy-naïve Japanese patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 26, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheithauer, W.; Kornek, G.V.; Raderer, M.; Hejna, M.; Valencak, J.; Miholic, J.; Kovats, E.; Lang, F.; Funovics, J.; Bareck, E.; et al. Phase II trial of gemcitabine, epirubicin and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorani, E.; Wong, H.H.; Hewitt, C.; Calder, J.; Corrie, P.; Basu, B. Safety and Efficacy of Modified FOLFIRINOX for Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A UK Single-Centre Experience. Oncology 2015, 89, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sijde, F.; van Dam, J.L.; Groot Koerkamp, B.; Haberkorn, B.C.M.; Homs, M.Y.V.; Mathijssen, D.; Besselink, M.G.; Wilmink, J.W.; van Eijck, C.H.J. Treatment Response and Conditional Survival in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Patients Treated with FOLFIRINOX: A Multicenter Cohort Study. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 8549487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, B.; Reimund, J.M.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Sondag, D.; Noirclerc, M.; Duclos, B.; Kurtz, J.E.; Nguimpi-Tambou, M. Survival and Predictive Factors of Chemotherapy With FOLFIRINOX as First-Line Therapy in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Multicentric Analysis. Pancreas 2021, 50, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.S.; Jacobson, J.L.; Modiano, M.; Moore, D.F.; Gandara, D.R.; Schroder, L.E.; Chapman, R.A. A phase II trial of etoposide, leucovorin, 5-FU, and interferon alpha 2b (ELFI) + G-CSF for patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A Southwest Oncology Group study (SWOG 9413). Investig. New Drugs 2000, 18, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaseth, H.; Brutcher, E.; Kauh, J.; Hawk, N.; Kim, S.; Chen, Z.; Kooby, D.A.; Maithel, S.K.; Landry, J.; El-Rayes, B.F. Modified FOLFIRINOX regimen with improved safety and maintained efficacy in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2013, 42, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathopoulos, G.P.; Mavroudis, D.; Tsavaris, N.; Kouroussis, C.; Aravantinos, G.; Agelaki, S.; Kakolyris, S.; Rigatos, S.K.; Karabekios, S.; Georgoulias, V. Treatment of pancreatic cancer with a combination of docetaxel, gemcitabine and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: A phase II study of the Greek Cooperative Group for Pancreatic Cancer. Ann Oncol. 2001, 12, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combination Chemotherapy with Itraconazole for Treating Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer in the Second-Line or Additional Setting—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26124377 (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Stein, S.M.; James, E.S.; Deng, Y.; Cong, X.; Kortmansky, J.S.; Li, J.; Staugaard, C.; Indukala, D.; Boustani, A.M.; Patel, V.; et al. Final analysis of a phase II study of modified FOLFIRINOX in locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamao, K.; Takenaka, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ishikawa, R.; Okamoto, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Nakai, A.; Omoto, S.; Kamata, K.; Minaga, K.; et al. Clinical Safety and Efficacy of Secondary Prophylactic Pegylated G-CSF in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Patients Treated with mFOLFIRINOX: A Single-center Retrospective Study. Intern. Med. 2019, 58, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitot, H.C.; Knost, J.A.; Mahoney, M.R.; Kugler, J.; Krook, J.E.; Hatfield, A.K.; Sargent, D.J.; Goldberg, R.M. A North Central Cancer Treatment Group Phase II trial of 9-aminocamptothecin in previously untreated patients with measurable metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 89, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canton, C.; Boussari, O.; Boulin, M.; Le Malicot, K.; Taieb, J.; Dahan, L.; Lopez, A.; Lepage, C.; Bachet, J.B. Impact of G-CSF Prophylaxis on Chemotherapy Dose-Intensity, Link Between Dose-Intensity and Survival in Patients with Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Oncologist 2022, 27, e571–e579, Erratum in Oncologist 2022, 27, e536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasalvia-Prisco, E.; Goldschmidt, P.; Galmarini, F.; Cucchi, S.; Vázquez, J.; Aghazarian, M.; Lasalvia-Galante, E.; Golomar, W.; Gordon, W. Addition of an induction regimen of antiangiogenesis and antitumor immunity to standard chemotherapy improves survival in advanced malignancies. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 3626–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascinu, S.; Labianca, R.; Barone, C.; Santoro, A.; Carnaghi, C.; Cassano, A.; Beretta, G.D.; Catalano, V.; Bertetto, O.; Barni, S.; et al. Adjuvant treatment of high-risk, radically resected gastric cancer patients with 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, cisplatin, and epidoxorubicin in a randomized controlled trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Stoller, R.; Shibata, S.; Kemeny, M.; Krishnamurthi, S.; Su, Y.B.; Ocean, A.; Capanu, M.; Mehrotra, B.; et al. Randomized Multicenter Phase II Study of Modified Docetaxel, Cisplatin, and Fluorouracil (DCF) Versus DCF Plus Growth Factor Support in Patients With Metastatic Gastric Adenocarcinoma: A Study of the US Gastric Cancer Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3874–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadler, S.; York, N.; Brain, C.; Catalano, P.; Einzig, A.I. Randomized Phase II Trial of Either Fluorouracil, Parenteral Hydroxyurea, Interferon-a-2a, and Filgrastim or Doxorubicin/Docetaxel in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer with Quality-of-Life Assessment: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E6296. Cancer J. 2002, 8, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, T.; Klippel, Z.; Cesas, A.; Croitoru, A.; Decaestecker, J.; Gibbs, P.; Hotko, Y.; Jassem, J.; Kurteva, G.; Novotny, J.; et al. A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pegfilgrastim in Patients Receiving First-Line FOLFOX/Bevacizumab or FOLFIRI/Bevacizumab for Locally Advanced or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Final Results of the Pegfilgrastim and Anti-VEGF Evaluation Study (PAVES). Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2017, 16, 103–114.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, J.R.; Pillai, M.; Gollard, R.; Heim, W.; Swan, F.; Patel, R.; Dreiling, L.; Mo, M.; Malik, I. A randomized, placebo-controlled phase ii study evaluating the reduction of neutropenia and febrile neutropenia in patients with colorectal cancer receiving pegfilgrastim with every-2-week chemotherapy. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2010, 9, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Pan, Y. The safety and clinical efficacy of recombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor injection for colon cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2017, 63, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, K.; Ninomiya, I.; Saito, H.; Shimada, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Terai, S.; Moriyama, H.; Kinoshita, J.; Nakamura, K.; Inaki, N. Usefulness of Prophylactic Administration of Pegfilgrastim for Esophageal Cancer Chemotherapy: A Single-center Retrospective Study. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.C.; Hwang, J.H. Primary Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Prophylaxis in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients Treated with FOLFIRINOX as the First-Line Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadio, A.; Burkes, R.; Bailie, T.; McLean, M.; Coleman, B. Impact of granulocyte colony-stimulating factors in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Curr. Oncol. 2014, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrador, E.; Salvador, R.; Villaescusa, J.I.; Soriano, J.M.; Estrela, J.M.; Montoro, A. Radioprotection and Radiomitigation: From the Bench to Clinical Practice. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klastersky, J.; de Naurois, J.; Rolston, K.; Rapoport, B.; Maschmeyer, G.; Aapro, M.; Herrstedt, J.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Management of febrile neutropaenia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, v111–v118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orji, C.C.; Brown, C.M.; Hoverman, J.R.; Richards, K.M.; Garey, J.; He, B. Impact of a G-CSF Policy to Reduce Low-Value Care on Guideline Adherence and Mortality. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2022, 17, e1830–e1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, B.; Redfern, A.D.; Mouchemore, K.A.; Hamilton, J.A.; Anderson, R.L. The dark side of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor: A supportive therapy with potential to promote tumour progression. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2018, 35, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, G.H.; Dale, D.C.; Culakova, E.; Poniewierski, M.S.; Wolff, D.A.; Kuderer, N.M.; Huang, M.; Crawford, J. The impact of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on chemotherapy dose intensity and cancer survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, K.T.; Khan, H.; Ahmad, A.; Weston, L.L.; Nofchissey, R.A.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J. G-CSF and G-CSFR are highly expressed in human gastric and colon cancers and promote carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.F.; Song, S.Y.; Wang, T.J.; Ji, W.J.; Li, S.W.; Liu, N.; Yan, C.X. Prognostic role of pretreatment circulating MDSCs in patients with solid malignancies: A meta-analysis of 40 studies. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1494113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Country | Study Design | Cancer | n | Chemotherapy | G-CSF | Outcomes | Follow-Up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wadler S et al. 2002 [63] | US | RCT | Gastric | 23 | FHIG a/AD b | Filgrastim | OS, PFS | Not specified |
| Cascinu S et al. 2007 [61] | Italy | RCT | Gastric | 400 | Cis+5-FU+epi c/5-FU/LV d | Filgrastim | OS, PFS, AE | 60 |
| Hecht JR et al. 2010 [65] | US | RCT | Colorectal | 252 | FOLFOX e/FOLFIRI f/FOIL g | Pegfilgrastim | OS, PFS, AE | 24 |
| Lasalvia-Prisco E et al. 2012 [60] | Uruguay | RCT | Pancreatic | 60 | GCD h/GCD + various support i | Not specified | OS, | 24 |
| Shah MA et al. 2015 [62] | US | RCT | Gastric | 90 | DCF j | Filgrastim | PFS, OS, AE | 42 |
| Chen J et al. 2017 [66] | China | RCT | Colorectal | 100 | Mixed k | Not specified | AE | Not specified |
| Pinter T et al. 2017 [64] | US | RCT | Colorectal | 845 | FOLFOX e/FOLFIRI f | Pegfilgrastim | PFS, OS, AE | 58 |
| Pitot HC et al. 2000 [58] | US | Cohort | Colorectal | 48 | 9AC l | Not specified | PFS, OS, AE | 30 |
| Amadio A et al. 2014 [69] | Canada | Non-RCT | Colorectal | 62 | FOLFIRI f | Filgrastim/ Pegfilgrastim | OS, PFS | 60 |
| Yamao k et al. 2019 [57] | Japan | Cohort | Pancreatic | 28 | FOLFIRINOX m | Pegfilgrastim | PFS, OS | 20 |
| Jung JH et al. 2020 [68] | South Korea | Cohort | Pancreatic | 165 | FOLFIRINOX m | Filgrastim/ Pegfilgrastim | OS, AE | 84 |
| Okamoto K et al. 2022 [67] | Japan | Cohort | Oesophageal | 102 | DCF j | Pegfilgrastim | PFS | 72 |
| Canton C et al. 2022 [59] | France | Cohort | Pancreatic | 498 | Mixed k | Not specified | OS, PFS | Not specified |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fischer, O.W.; Justesen, T.F.; Gögenur, D.S.; Madsen, M.T.; Mortensen, M.B.; Gögenur, I.; Orhan, A. Long-Term Oncological Outcomes of Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) Treatment in Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081313
Fischer OW, Justesen TF, Gögenur DS, Madsen MT, Mortensen MB, Gögenur I, Orhan A. Long-Term Oncological Outcomes of Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) Treatment in Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2025; 17(8):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081313
Chicago/Turabian StyleFischer, Oliver Wedel, Tobias Freyberg Justesen, Dilara Seyma Gögenur, Michael Tvilling Madsen, Michael Bau Mortensen, Ismail Gögenur, and Adile Orhan. 2025. "Long-Term Oncological Outcomes of Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) Treatment in Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 17, no. 8: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081313
APA StyleFischer, O. W., Justesen, T. F., Gögenur, D. S., Madsen, M. T., Mortensen, M. B., Gögenur, I., & Orhan, A. (2025). Long-Term Oncological Outcomes of Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) Treatment in Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 17(8), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081313






