Novel Urinary Biomarkers for the Detection of Bladder Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
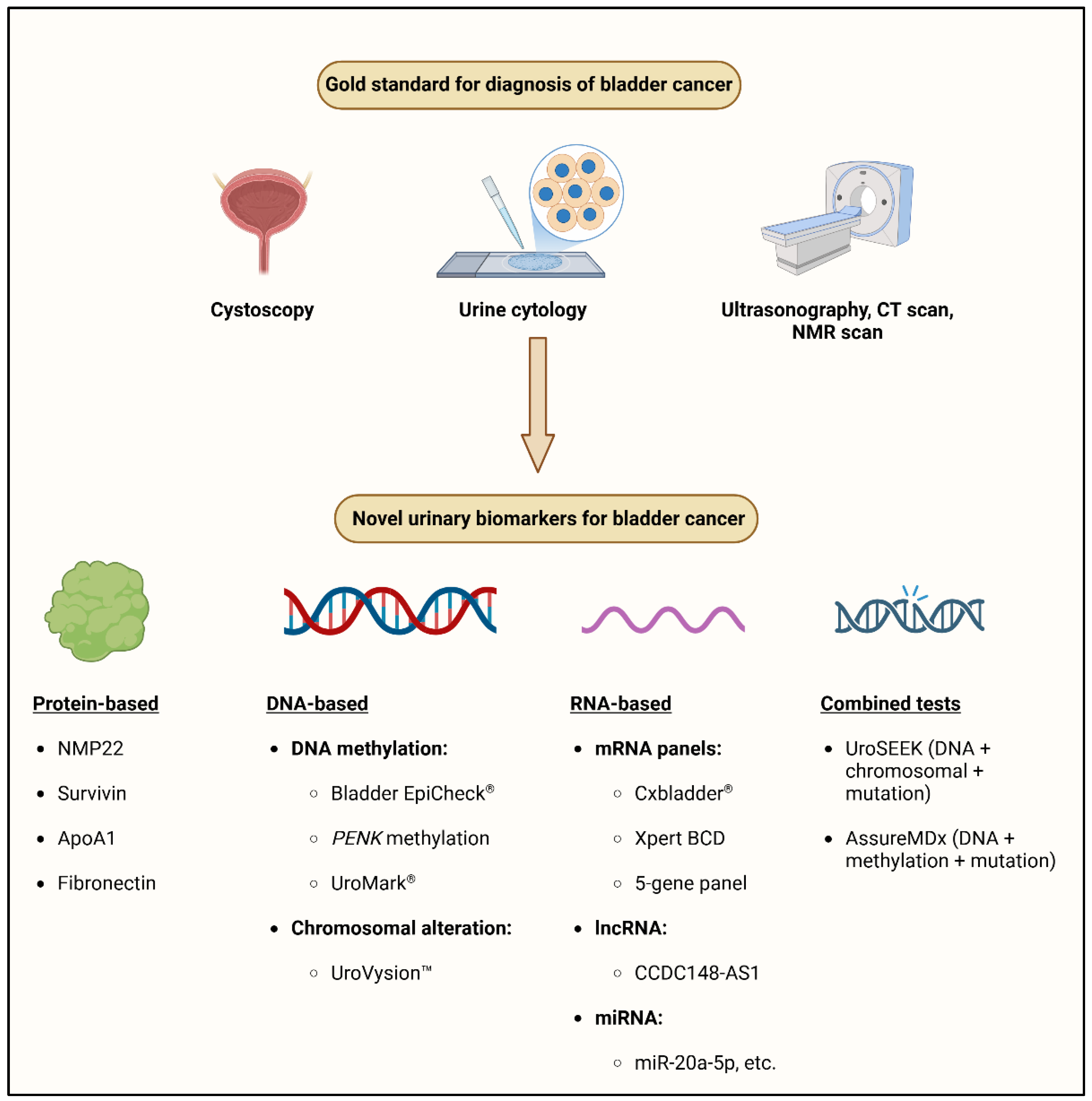
2. Traditional Approaches
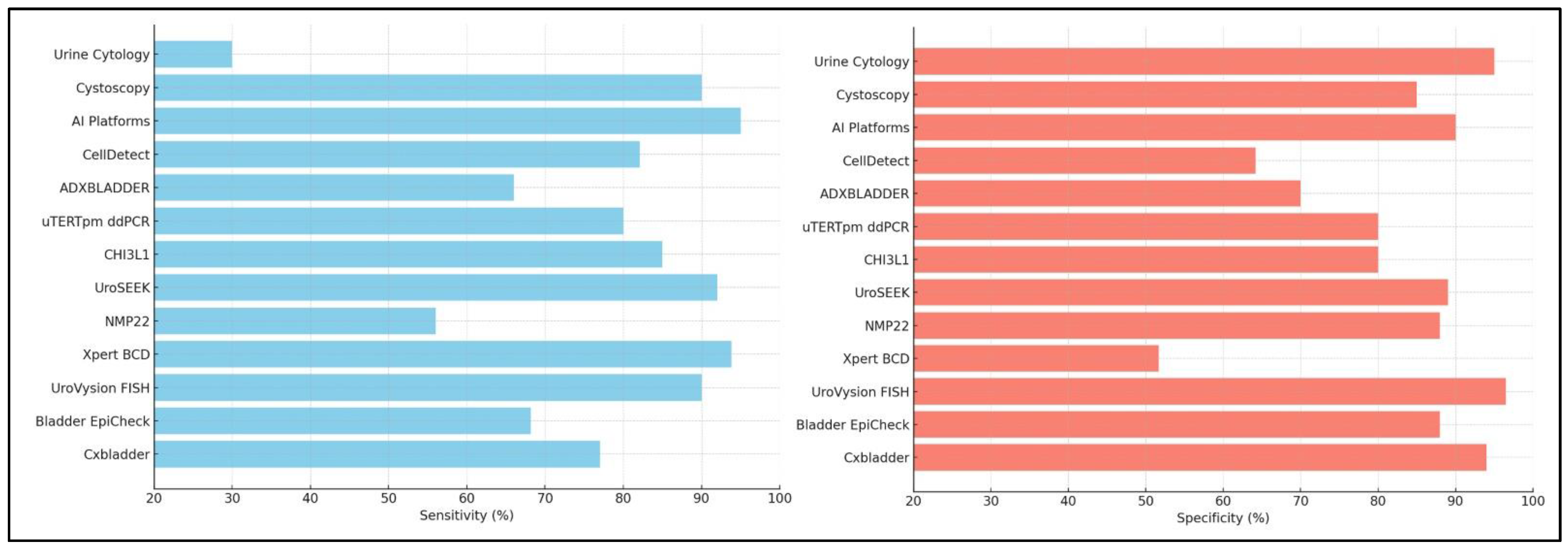
2.1. Cystoscopy
2.2. Urine Cytology
3. Urinary Biomarkers for Bladder Cancer Detection
3.1. Protein Biomarkers
3.2. Molecular Biomarkers and Multi-Gene Panels
3.2.1. Cxbladder®
3.2.2. Bladder EpiCheck®
3.2.3. Xpert Bladder Cancer Detection
3.2.4. Cytokeratin Fragment-19
3.2.5. Uromonitor and TERTpm ddPCR
3.2.6. CellDetect Assay
3.2.7. UroVysionTM
3.2.8. NMP22 BladderChek Test
3.2.9. ADXBLADDER
3.2.10. UroSEEK
3.2.11. AssureMDx
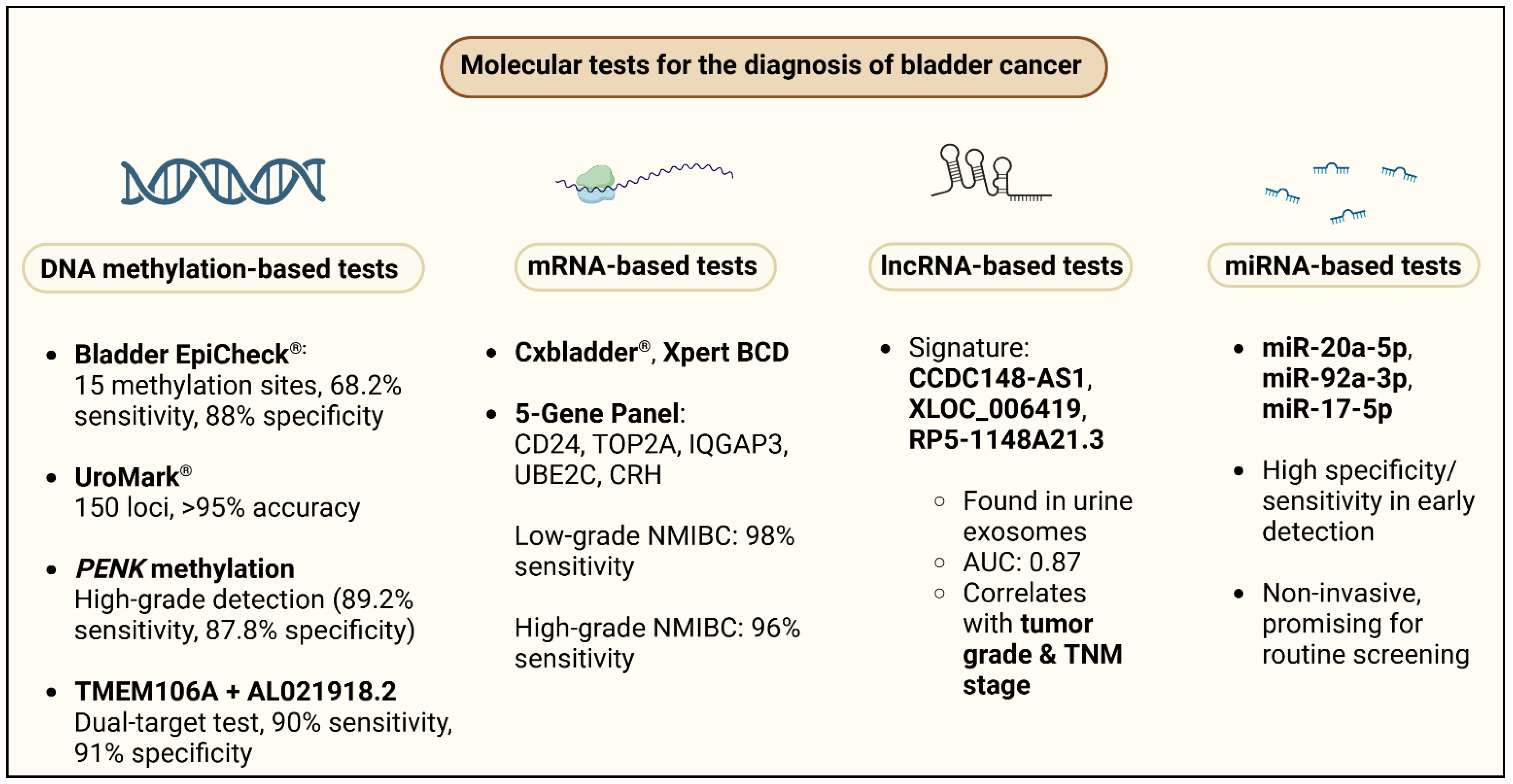
4. Molecular Tests in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer
4.1. DNA Methylation
4.2. mRNA
4.3. LncRNA
4.4. miRNA
Uromonitor
5. Spectroscopy
6. Cell Free DNA
7. Urinary Vesicles
8. Metabolomics
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ALOX5 | Arachidonate 5-Lipoxygenase |
| APC | Adenomatous Polyposis Coli |
| AS1 | Antisense RNA 1 |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BCa | Bladder Cancer |
| BCD | Bladder Cancer Detection |
| BCG | Bacillus Calmette-Guérin |
| BE | Bladder EpiCheck |
| BLCAP | Bladder Cancer Associated Protein |
| BTA | Bladder Tumor Antigen |
| CA9 | Carbonic Anhydrase 9 |
| CD24 | Cluster of Differentiation 24 |
| CDK1 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 |
| CEP55 | Centrosomal Protein 55 |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CIS | Carcinoma In Situ |
| CRH | Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| CXCL16 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 16 |
| CXCR2 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 2 |
| CYFRA21 | Cytokeratin Fragment 21-1 |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| DOR | Diagnostic Odds Ratio |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EMT | Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition |
| ERBB2 | Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 2 |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FGFR | Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor |
| FISH | Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization |
| FLI1 | Friend Leukemia Integration 1 Transcription Factor |
| GALR1 | Galanin Receptor 1 |
| HAND2 | Heart And Neural Crest Derivatives Expressed 2 |
| HG | High Grade |
| HGUC | High-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma |
| HOTAIR | HOX Transcript Antisense RNA |
| HOXA13 | Homeobox A13 |
| HPF | High Power Field |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| HRAS | Harvey Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| IGFBP5 | Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 5 |
| IQGAP3 | IQ Motif Containing GTPase Activating Protein 3 |
| KRAS | Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| LGBC | Low Grade Bladder Cancer |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| MCM5 | Minichromosome Maintenance Complex Component 5 |
| MDK | Midkine |
| MET | Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition Factor |
| MIBC | Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer |
| MLL | Mixed Lineage Leukemia |
| MN | Micronucleus |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| MSP | Methylation-Specific PCR |
| NB | Nuclear Budding |
| NMIBC | Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer |
| NMP22 | Nuclear Matrix Protein 22 |
| NPV | Negative Predictive Value |
| NRN1 | Neuritin 1 |
| OF | Observed Frequency |
| ONECUT2 | One Cut Homeobox 2 |
| OTX1 | Orthodenticle Homeobox 1 |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PENK | Proenkephalin |
| PLR | Positive Likelihood Ratio |
| PLS | Partial Least Squares |
| POC | Point of Care |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
| PTK2 | Protein Tyrosine Kinase 2 |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| RP5 | Reference Sequence 5 |
| RT | Reverse Transcription |
| SERS | Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering |
| SOC | Standard of Care |
| SRGN | Serglycin |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TERT | Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase |
References
- Kirkali, Z.; Chan, T.; Manoharan, M.; Algaba, F.; Busch, C.; Cheng, L.; Kiemeney, L.; Kriegmair, M.; Montironi, R.; Murphy, W.M.; et al. Bladder Cancer: Epidemiology, Staging and Grading, and Diagnosis. Urology 2005, 66, 4–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richters, A.; Aben, K.K.H.; Kiemeney, L.A.L.M. The Global Burden of Urinary Bladder Cancer: An Update. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumberbatch, M.G.K.; Jubber, I.; Black, P.C.; Esperto, F.; Figueroa, J.D.; Kamat, A.M.; Kiemeney, L.; Lotan, Y.; Pang, K.; Silverman, D.T.; et al. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Contemporary Update of Risk Factors in 2018. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobruch, J.; Daneshmand, S.; Fisch, M.; Lotan, Y.; Noon, A.P.; Resnick, M.J.; Shariat, S.F.; Zlotta, A.R.; Boorjian, S.A. Gender and Bladder Cancer: A Collaborative Review of Etiology, Biology, and Outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Milowsky, M.; Droller, M.J. Bladder Cancer in the Elderly. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2009, 27, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and Cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, K.; Hsieh, M.H. Understanding Urogenital Schistosomiasis-Related Bladder Cancer: An Update. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenis, A.T.; Lec, P.M.; Chamie, K.; Mshs, M. Bladder Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldhammer, C.S.; Vásquez, J.L.; Kristensen, V.M.; Norus, T.; Nadler, N.; Jensen, J.B.; Azawi, N. Cystoscopy Accuracy in Detecting Bladder Tumors: A Prospective Video-Confirmed Study. Cancers 2023, 16, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafi, F.A.; Brimo, F.; Steinberg, J.; Aprikian, A.G.; Tanguay, S.; Kassouf, W. Prospective Analysis of Sensitivity and Specificity of Urinary Cytology and Other Urinary Biomarkers for Bladder Cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2015, 33, 66.e25–66.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, E.; Fujita, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Uemura, H.; Nonomura, N. Urinary Markers for Bladder Cancer Diagnosis: A Review of Current Status and Future Challenges. Int. J. Urol. 2024, 31, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, W.; Chen, S.; Wei, Y.; Luo, M. Feasibility of Early Evaluation for the Recurrence of Bladder Cancer after Trans-Urethral Resection: A Comparison between Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Multidetector Computed Tomography. Tomography 2022, 9, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghafer, I.A.; AlAfeshat, N.; Alshomali, L.; Alanee, S.; Qattous, H.; Azzeh, M.; Alkhateeb, A. NMF-Guided Feature Selection and Genetic Algorithm-Driven Framework for Tumor Mutational Burden Classification in Bladder Cancer Using Multi-Omics Data. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinforma 2024, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlies, W.; De Jong, J.J.; Hofmann, F.; Bruins, H.M.; Zuiverloon, T.C.M.; Smith, E.J.; Yuan, Y.; Van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Mostafid, H.; Santesso, N.; et al. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Cystoscopy for Detecting Bladder Cancer in Adults Presenting with Haematuria: A Systematic Review from the European Association of Urology Guidelines Office. Eur. Urol. Focus 2024, 10, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfs, J.R.E.; Hermans, T.J.N.; Koldewijn, E.L.; Van De Kerkhof, D. Novel Urinary Biomarkers ADXBLADDER and Bladder EpiCheck for Diagnostics of Bladder Cancer: A Review. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2021, 39, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.J.; Dickinson, A.J.; Natale, S.; Gosling, J.; Mcgrath, J.S. A Prospective Analysis of the Diagnostic Yield Resulting from the Attendance of 4020 Patients at a Protocol-driven Haematuria Clinic. BJU Int. 2006, 97, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, K.M.; Awad, M.A.; Goldsmith, M.; Hallgarth, L.A.; Raman, J.D. Laboratory Reporting Parameters of Microhematuria: Implications for Interpreting the 2020 AUA Guideline. Urology 2021, 154, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, K.; Svatek, R.S.; Gupta, S.; Ho, R.; Lotan, Y. High-risk Patients with Hematuria Are Not Evaluated According to Guideline Recommendations. Cancer 2010, 116, 2954–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulewicz, R.S.; Rademaker, A.; Meeks, J.J. A Simplified Nomogram to Assess Risk of Bladder Cancer in Patients with a New Diagnosis of Microscopic Hematuria. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeb, R.; Golijanin, D.; Knopf, J.; Davis, M.; Feng, C.; Fender, A.; Stephenson, L.; Messing, E.M. Long-Term Outcome of Patients with a Negative Work-up for Asymptomatic Microhematuria. Urology 2010, 75, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.K.; Gao, T.; Pohl, M.; Jones, J.S. Dipstick Pseudohematuria: Unnecessary Consultation and Evaluation. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanicolaou, G.N.; Marshall, V.F. Urine Sediment Smears as a Diagnostic Procedure in Cancers of the Urinary Tract. Science 1945, 101, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. Diagnostic Value of Urine Cytology in Bladder Cancer. A Meta-Analysis. Anal. Quant. Cytopathol. Histpathol. 2016, 38, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Barkan, G.A.; Wojcik, E.M.; Nayar, R.; Savic-Prince, S.; Quek, M.L.; Kurtycz, D.F.I.; Rosenthal, D.L. The Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology: The Quest to Develop a Standardized Terminology. Acta Cytol. 2016, 60, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtycz, D.F.I.; Wojcik, E.M.; Rosenthal, D.L. Perceptions of Paris: An International Survey in Preparation for The Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology 2.0 (TPS 2.0). J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2023, 12, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kökenek Ünal, T.D.; Aksoy Altınboğa, A. A Pilot Study of the Value of Micronucleus Count in Urinary Cytology Samples in the Follow-up of Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma: Implications for Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cancer Cytopathol. 2025, 133, e22923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaert, M.; Maghari, S.; Speeckaert, M.; Delanghe, J. Improving Clinical Performance of Urine Sediment Analysis by Implementation of Intelligent Verification Criteria. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2022, 60, 1772–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderlini, R.; Manieri, G.; Lucchi, C.; Raisi, O.; Soliera, A.R.; Torricelli, F.; Varani, M.; Trenti, T. Automated Urinalysis with Expert Review for Incidental Identification of Atypical Urothelial Cells: An Anticipated Bladder Carcinoma Diagnosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 451, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, O. Atypical Cells Parameter in an Automated Urine Analyzer: Does It Have a Future? Anal. Biochem. 2020, 600, 113763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, C.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Cao, H. Investigation of Atyp.C Using UF-5000 Flow Cytometer in Patients with a Suspected Diagnosis of Urothelial Carcinoma: A Single-Center Study. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 15, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, O.; Sarikaya, S.; Caglar, E.; Ayas, R.; Ozgurtas, T. Atypical Cells Parameter in Sysmex UN Automated Urine Analyzer: A Single Center Study. Turk. J. Biochem. 2024, 50, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukuya, K.; Morita, Y.; Hisasue, T.; Ono, Y.; Tomiyasu, S.; Kurano, M.; Yatomi, Y.; Tanaka, M. Comparison of the Clinical Performance of the Atyp.C Parameter of the UF-5000 Fully Automated Urine Particle Analyzer with That of Microscopic Urine Sediment Analysis. Pract. Lab. Med. 2023, 36, e00328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Dasari, S.; Long, W.; Mohan, C. Urine Protein Biomarkers for the Detection, Surveillance, and Treatment Response Prediction of Bladder Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1104–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Que, H.; Suo, C.; Han, Z.; Tao, J.; Huang, Z.; Ju, X.; Tan, R.; Gu, M. Evaluation of the NMP22 BladderChek Test for Detecting Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 100648–100656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsü, N.; Ekici, S.; Öge, Ö.; Ergen, A.; Hasçelik, G.; Özen, H. False-Positive Results of the NMP22 Test due to Hematuria. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Diagnostic Accuracy of Urinary Survivin mRNA Expression Detected by RT-PCR Compared with Urine Cytology in the Detection of Bladder Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy in Head-to-head Studies. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 19, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardeer, K.T.; Mohammed, K.A.; Hussein, T.D.; Elsheemy, M.S. Apolipoprotein A1 as a Novel Urinary Biomarker for Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Indian J. Urol. 2021, 37, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Garapati, K.; Ghose, V.; Kandasamy, R.K.; Pandey, A. Recent Progress in Mass Spectrometry-Based Urinary Proteomics. Clin. Proteom. 2024, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavalieris, L.; O’Sullivan, P.; Frampton, C.; Guilford, P.; Darling, D.; Jacobson, E.; Suttie, J.; Raman, J.D.; Shariat, S.F.; Lotan, Y. Performance Characteristics of a Multigene Urine Biomarker Test for Monitoring for Recurrent Urothelial Carcinoma in a Multicenter Study. J. Urol. 2017, 197, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavalieris, L.; O’Sullivan, P.J.; Suttie, J.M.; Pownall, B.K.; Gilling, P.J.; Chemasle, C.; Darling, D.G. A Segregation Index Combining Phenotypic (Clinical Characteristics) and Genotypic (Gene Expression) Biomarkers from a Urine Sample to Triage out Patients Presenting with Hematuria Who Have a Low Probability of Urothelial Carcinoma. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, P.; Sharples, K.; Dalphin, M.; Davidson, P.; Gilling, P.; Cambridge, L.; Harvey, J.; Toro, T.; Giles, N.; Luxmanan, C.; et al. A Multigene Urine Test for the Detection and Stratification of Bladder Cancer in Patients Presenting with Hematuria. J. Urol. 2012, 188, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holyoake, A.; O’Sullivan, P.; Pollock, R.; Best, T.; Watanabe, J.; Kajita, Y.; Matsui, Y.; Ito, M.; Nishiyama, H.; Kerr, N.; et al. Development of a Multiplex RNA Urine Test for the Detection and Stratification of Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konety, B.; Shore, N.; Kader, A.K.; Porten, S.; Daneshmand, S.; Lough, T.; Lotan, Y. Evaluation of Cxbladder and Adjudication of Atypical Cytology and Equivocal Cystoscopy. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotan, Y.; Raman, J.D.; Konety, B.; Daneshmand, S.; Schroeck, F.; Shariat, S.F.; Black, P.; De Lange, M.; Asroff, S.; Goldfischer, E.; et al. Urinary Analysis of FGFR3 and TERT Gene Mutations Enhances Performance of Cxbladder Tests and Improves Patient Risk Stratification. J. Urol. 2023, 209, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, J.D.; Kavalieris, L.; Konety, B.; Porten, S.; Daneshmand, S.; Lotan, Y.; Loo, R. The Diagnostic Performance of Cxbladder Resolve, Alone and in Combination with Other Cxbladder Tests, in the Identification and Priority Evaluation of Patients at Risk for Urothelial Carcinoma. J. Urol. 2021, 206, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.J.; McGeoch, G.; Shand, B. Inclusion of a Molecular Marker of Bladder Cancer in a Clinical Pathway for Investigation of Haematuria May Reduce the Need for Cystoscopy. N. Z. Med. J. 2019, 132, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harvey, J.C.; Cambridge, L.M.; Ellen, C.W.; Colonval, M.; Hazlett, J.A.; Newell, J.; Zhou, X.; Guilford, P.J. Analytical Validation of Cxbladder® Detect, Triage, and Monitor: Assays for Detection and Management of Urothelial Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süzan, S.; Ulus, İ.; Hacıbey, İ.; Müslümanoğlu, A.Y. Predictive Value of Bladder EpiCheck® in Detecting Residual Tumor before Second TUR for Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. World J. Urol. 2025, 43, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caño Velasco, J.; Artero Fullana, S.; Polanco Pujol, L.; Lafuente Puentedura, A.; Subiela, J.D.; Aragón Chamizo, J.; Moralejo Gárate, M.; Hernández Fernández, C. Use of Bladder Epicheck® in the Follow-up of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review. Actas Urológicas Españolas (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 48, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordelli, F.; Desai, A.; Dagnino, F.; Contieri, R.; Giuriolo, S.; Paciotti, M.; Fasulo, V.; Mancon, S.; Maffei, D.; Avolio, P.P.; et al. Xpert Bladder Cancer Detection in Emergency Setting Assessment (XESA Project): A Prospective, Single-Centre Trial. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2025, 71, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Park, Y.; Cho, Y.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, H.-S. Diagnostic Values of Urine CYFRA21-1, NMP22, UBC, and FDP for the Detection of Bladder Cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 414, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, L.I.; Song, W.J.; Qing, H.M.; Yan, S.; Song, F.L. CYFRA21-1 Levels Could Be a Biomarker for Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 3921–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setianingsih, Y.A.; Djatisoesanto, W.; Laksita, T.B.; Aryati, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Urinary Cytokeratin Fragment-19 (CYFRA21-1) for Bladder Cancer. Narra J. 2024, 4, e1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.; Gore, J.L.; Buckley, D.; Fu, R.; Gustafson, K.; Griffin, J.C.; Grusing, S.; Selph, S. Urinary Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabien, A.; Rong, D.; Rabenhorst, S.; Schlomm, T.; Labonté, F.; Hofbauer, S.; Forey, N.; Le Calvez-Kelm, F.; Ecke, T.H. Diagnostic Performance of Uromonitor and TERTpm ddPCR Urine Tests for the Non-Invasive Detection of Bladder Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakmanesh, H.; Anvari, O.; Forey, N.; Weiderpass, E.; Malekpourafshar, R.; Iranpour, M.; Shahesmaeili, A.; Ahmadi, N.; Bazrafshan, A.; Zendehdel, K.; et al. TERT Promoter Mutations as Simple and Non-Invasive Urinary Biomarkers for the Detection of Urothelial Bladder Cancer in a High-Risk Region. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Lou, Z. Single Center Evaluation of Sensitivity and Specificity of CellDetect Assay in Early Bladder Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shefer, H.K.; Masarwe, I.; Bejar, J.; Naamnih, L.H.; Gueta-Milshtein, K.; Shalata, A.; Hadid, Y.; Nativ, O.; Nativ, O. Performance of CellDetect for Detection of Bladder Cancer: Comparison with Urine Cytology and UroVysion. Urol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 296.e1–296.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.; Hu, Z.; Yang, C. UroVysionTM Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization in Urological Cancers: A Narrative Review and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, A.M.; Willis, D.L.; Dickstein, R.J.; Anderson, R.; Nogueras-González, G.; Katz, R.L.; Wu, X.; Barton Grossman, H.; Dinney, C.P. Novel Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization-Based Definition of Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Failure for Use in Enhancing Recruitment into Clinical Trials of Intravesical Therapies. BJU Int. 2016, 117, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, E.I.M.L.; Baard, J.; Cauberg, E.C.C.; Bus, M.T.J.; De Bruin, D.M.; Laguna Pes, M.P.; De La Rosette, J.J.M.C.H.; De Reijke, T.M. Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization as Prognostic Predictor of Tumor Recurrence during Treatment with Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Therapy for Intermediate- and High-Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotan, Y.; Inman, B.A.; Davis, L.G.; Kassouf, W.; Messing, E.; Daneshmand, S.; Canter, D.; Marble, H.T.; Joseph, A.M.; Jewell, S.; et al. Evaluation of the Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Test to Predict Recurrence and/or Progression of Disease after Bacillus Calmette-Guérin for Primary High Grade Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Results from a Prospective Multicenter Trial. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecke, T.H.; Meisl, C.J.; Schlomm, T.; Rabien, A.; Labonté, F.; Rong, D.; Hofbauer, S.; Friedersdorff, F.; Sommerfeldt, L.; Gagel, N.; et al. BTA Stat®, NMP22® BladderChek®, UBC® Rapid Test, and CancerCheck® UBC® Rapid VISUAL as Urinary Marker for Bladder Cancer: Final Results of a German Multicenter Study. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2023, 41, 484.e17–484.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Sharma, A.; Krishna, M.; Ahluwalia, P.; Gautam, G. Diagnostic Performance of Minichromosome Maintenance 5 (MCM5) in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2022, 40, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A.; Morote, J.; Cornel, E.B.; Gakis, G.; Van Valenberg, F.J.P.; Lozano, F.; Sternberg, I.A.; Willemsen, E.; Hegemann, M.L.; Paitan, Y.; et al. Performance of the Bladder EpiCheckTM Methylation Test for Patients Under Surveillance for Non–Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Results of a Multicenter, Prospective, Blinded Clinical Trial. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 1, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białek, Ł.; Czerwińska, K.; Fus, Ł.; Krajewski, W.; Sadowska, A.; Radziszewski, P.; Dobruch, J.; Kryst, P.; Poletajew, S. MCM5 Urine Expression (ADXBLADDER) Is a Reliable Biomarker of High-Risk Non- Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Recurrence: A Prospective Matched Case-Control Study. CBM 2021, 30, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouprêt, M.; Gontero, P.; McCracken, S.R.C.; Dudderidge, T.; Stockley, J.; Kennedy, A.; Rodriguez, O.; Sieverink, C.; Vanié, F.; Allasia, M.; et al. Reducing the Frequency of Follow-up Cystoscopy in Low-Grade pTa Non–Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Using the ADXBLADDER Biomarker. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022, 8, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, F.; Droller, M.J.; Lotan, Y.; Gontero, P.; D’Andrea, D.; Gust, K.M.; Rouprêt, M.; Babjuk, M.; Palou, J.; Shariat, S.F. An Up-to-Date Catalog of Available Urinary Biomarkers for the Surveillance of Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 1981–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.D.; Dudderidge, T.J.; Wollenschlaeger, A.; Okoturo, O.; Burling, K.; Tulloch, F.; Halsall, I.; Prevost, T.; Prevost, A.T.; Vasconcelos, J.C.; et al. Bladder Cancer Diagnosis and Identification of Clinically Significant Disease by Combined Urinary Detection of Mcm5 and Nuclear Matrix Protein 22. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratu, O.; Marcu, D.; Anghel, R.; Spinu, D.; Iorga, L.; Balescu, I.; Bacalbasa, N.; Diaconu, C.; Savu, C.; Savu, C.; et al. Tumoral Markers in Bladder Cancer (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.U.; Chen, C.-H.; Rodriguez Pena, M.D.C.; Li, L.; Douville, C.; Wang, Y.; Cohen, J.D.; Taheri, D.; Silliman, N.; Schaefer, J.; et al. Non-Invasive Detection of Urothelial Cancer through the Analysis of Driver Gene Mutations and Aneuploidy. eLife 2018, 7, e32143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eich, M.-L.; Rodriguez Pena, M.D.C.; Springer, S.U.; Taheri, D.; Tregnago, A.C.; Salles, D.C.; Bezerra, S.M.; Cunha, I.W.; Fujita, K.; Ertoy, D.; et al. Incidence and Distribution of UroSEEK Gene Panel in a Multi-Institutional Cohort of Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Pena, M.D.C.; Springer, S.U.; Taheri, D.; Li, L.; Tregnago, A.C.; Eich, M.-L.; Eltoum, I.-E.A.; VandenBussche, C.J.; Papadopoulos, N.; Kinzler, K.W.; et al. Performance of Novel Non-Invasive Urine Assay UroSEEK in Cohorts of Equivocal Urine Cytology. Virchows Arch. 2020, 476, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kessel, K.E.M.; Beukers, W.; Lurkin, I.; Ziel-van Der Made, A.; Van Der Keur, K.A.; Boormans, J.L.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Márquez, M.; Ørntoft, T.F.; Real, F.X.; et al. Validation of a DNA Methylation-Mutation Urine Assay to Select Patients with Hematuria for Cystoscopy. J. Urol. 2017, 197, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, J.J.; de Jong, F.C.; van der Made, A.C.J.; van Casteren, N.J.; Roshani, H.; Oomens, E.H.G.M.; Pelger, R.C.M.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Boormans, J.L.; Bangma, C.H.; et al. A Molecular Urine Assay to Detect Recurrences During Surveillance of High-Risk Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. Bladder Cancer 2024, 10, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; He, G.; Goh, S.; Low, A.W.X.; Tay, K.J.; Lim, T.K.H.; Yeong, J.; Khor, L.Y.; Lim, T.S. Biomarkers for Precision Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnosis: Current Approaches and the Application of Single-Cell Technologies. Cancers 2021, 13, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallioli, A.; Boissier, R.; Territo, A.; Breda, A. Towards the Future of Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Surveillance: Lessons Learnt from Bladder Cancer Urinary Biomarkers. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1985–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.; Ritch, C.R. Urinary Biomarkers in Bladder Cancer: Where Do We Stand? Curr. Opin. Urol. 2019, 29, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathianathen, N.J.; Butaney, M.; Weight, C.J.; Kumar, R.; Konety, B.R. Urinary Biomarkers in the Evaluation of Primary Hematuria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Bladder Cancer 2018, 4, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, R.K.; Abro, S.; De Ubago, J.M.M.; Pambuccian, S.E.; Quek, M.L.; Wojcik, E.M.; Mehrotra, S.; Chatt, G.U.; Barkan, G.A. The Value of the UroVysion® FISH Assay in the Risk-stratification of Patients with “Atypical Urothelial Cells” in Urinary Cytology Specimens. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2017, 45, 481–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaszek, N.; Bogdanowicz, A.; Siwiec, J.; Starownik, R.; Kwaśniewski, W.; Mlak, R. Epigenetic Biomarkers as a New Diagnostic Tool in Bladder Cancer—From Early Detection to Prognosis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.; Stenzl, A.; Sharma, A.; Vasdev, N. Urinary Biomarkers in Bladder Cancer: A Review of the Current Landscape and Future Directions. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2021, 39, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porten, S.P. Epigenetic Alterations in Bladder Cancer. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2018, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, E.M.; Chihara, Y.; Pan, F.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Siegmund, K.D.; Sugano, K.; Kawashima, K.; Laird, P.W.; Jones, P.A.; Liang, G. Unique DNA Methylation Patterns Distinguish Noninvasive and Invasive Urothelial Cancers and Establish an Epigenetic Field Defect in Premalignant Tissue. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8169–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.; Bondaruk, J.; Jelinek, J.; Lotan, Y.; Liang, S.; Czerniak, B.; Issa, J.-P.J. Detection of Bladder Cancer Using Novel DNA Methylation Biomarkers in Urine Sediments. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.J.; Lim, E.; Bang, B.-R.; Lee, J.J.; Na, Y.G.; Shin, J.H.; Lim, J.S.; Song, K.H.; An, S. Identification and Validation of Methylated PENK Gene for Early Detection of Bladder Cancer Using Urine DNA. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, B.-R.; Zhong, J.; Oh, T.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Seo, Y.; Woo, M.A.; Lim, J.S.; Na, Y.G.; Song, K.H.; Shin, J.H.; et al. EarlyTect BCD, a Streamlined PENK Methylation Test in Urine DNA, Effectively Detects Bladder Cancer in Patients with Hematuria. J. Mol. Diagn. 2024, 26, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Seo, Y.; Woo, M.A.; Lim, J.S.; Na, Y.G.; Song, K.H.; Bang, B.-R.; Lee, J.J.; Shin, J.H.; et al. Evaluation of Sensitive Urine DNA-Based PENK Methylation Test for Detecting Bladder Cancer in Patients with Hematuria. J. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 25, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.G.; Yun, S.-C.; Ha, H.K.; Kang, S.G.; Lee, S.; Park, S.; Sung, H.H.; Kim, S.I.; Hwang, E.C.; Moon, K.C.; et al. Urinary DNA Methylation Test for Bladder Cancer Diagnosis. JAMA Oncol. 2025, 11, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Niu, Y.; Yan, J.; Tian, J.; Yu, W.; Zhang, G.; Li, T.; Wang, Z. Non-Invasive Diagnosis for Urothelial Carcinoma Using a Dual-Target DNA Methylation Biomarker Panel. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 569, 120164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abazari, O.; Shahidi, M.; Dayati, P.; Valizadeh, S.; Vahidi, S.; Tafti, M.A.; Zavarreza, J. Study of Urine-Based mRNA Biomarkers for Early Detection of Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC). Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2025, S1078143924010500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenberg, F.J.P.V.; Hiar, A.M.; Wallace, E.; Bridge, J.A.; Mayne, D.J.; Beqaj, S.; Sexton, W.J.; Lotan, Y.; Weizer, A.Z.; Jansz, G.K.; et al. Prospective Validation of an mRNA-Based Urine Test for Surveillance of Patients with Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abazari, O.; Dayati, P.; Shahidi, M.; ZavarReza, J.; Rahmanian, M.; Naghib, S.M. Exploring a Desirable Quadr-mRNAs Panel for Non-Invasive and Ultrasensitive Bladder Cancer Diagnosis: In-Silico and Clinical Studies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, e080724231721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J. Urine Exosomal lncRNAs as Novel Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer Based on Microarray Differential Expression Profiling. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2025, 40, 03936155251317551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Duan, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Yan, S.; Xie, Y.; Yan, K.; Wang, Q.; et al. Cell-free lncRNA Expression Signatures in Urine Serve as Novel Non-invasive Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Recurrence Prediction of Bladder Cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Medi. 2018, 22, 2838–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wei, X.; Qu, X.; Zhu, Y. Potential Clinical Application of microRNAs in Bladder Cancer. J. Biomed. Res. 2024, 38, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, P.I.; Pinto, V.B.P.; Piancó, E.D.S.; Gomes, M.L.; Monteiro, S.C.M.; Vidal, F.C.B.; Nascimento, M.D.D.S.B.; Pinho, J.D.; Calixto, J.D.R.R.; De Andrade, M.S. The Role of microRNAs in Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review. Einstein 2024, 22, eRW0611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, K.; Köhler, C.U.; Wichert, K.; Deix, T.; Bartsch, G.; Sommer, G.; Lübke, C.; Roghmann, F.; Reike, M.J.; Krentel, H.; et al. Urinary DNA-Methylation and Protein Biomarkers Identify Urothelial Carcinoma among Other Genitourinary Diseases and Cancer-Free Individuals. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqerrout, M.; Mharrach, I.; Anouar Tadlaoui, K.; Laraqui, A.; Tagajdid, M.R.; Ennibi, K.; Ennaji, M.M. Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC) Promoter Gene Methylation in Urine-Derived DNA: A Non-Invasive Biomarker for Early Bladder Cancer Detection and Tumor Aggressiveness. Cureus 2024, 16, e72055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijert, I.J.; Wever, B.M.M.; Hentschel, A.E.; Van Den Burgt, Y.; Kauer, P.C.; Lissenberg-Witte, B.I.; Van Moorselaar, R.J.A.; Steenbergen, R.D.M.; Nieuwenhuijzen, J.A. Bladder Cancer Detection in Urine by Novel Methylation Markers. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, P.; Brás, J.P.; Dias, C.; Bessa-Gonçalves, M.; Botelho, F.; Silva, J.; Silva, C.; Pacheco-Figueiredo, L. Uromonitor: Clinical Validation and Performance Assessment of a Urinary Biomarker Within the Surveillance of Patients with Nonmuscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. J. Urol. 2025, 213, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, R.; Vinagre, J.; Prazeres, H.; Sampaio, C.; Peralta, P.; Conceição, P.; Sismeiro, A.; Leão, R.; Gomes, A.; Furriel, F.; et al. Validation of a Novel, Sensitive, and Specific Urine-Based Test for Recurrence Surveillance of Patients with Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in a Comprehensive Multicenter Study. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Bi, X.; Qian, H.; Pan, J.; Ye, J. Non-Invasive and Rapid Diagnosis of Low-Grade Bladder Cancer via SERSomes of Urine. Nanoscale 2025, 17, 7303–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, S.; Cui, X.; Xu, W.; Kong, C.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, W. Identifying Non-Muscle-Invasive and Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Based on Blood Serum Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, V.; Kasabov, N.; Kamat, A.M.; Jacobson, E.; Suttie, J.M.; O’Sullivan, P.J.; Kavalieris, L.; Darling, D.G. A Holistic Comparative Analysis of Diagnostic Tests for Urothelial Carcinoma: A Study of Cxbladder Detect, UroVysion® FISH, NMP22® and Cytology Based on Imputation of Multiple Datasets. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2015, 15, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jue, M.; Lee, K.; Paulson, B.; Oh, J.; Cho, M.; Kim, J.K. Early-Stage Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning Algorithms in a Rat Model. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 246, 115915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Shao, L.; Yao, Y.; Chen, S.; Lv, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Yan, Z. Urine-Based SERS and Multivariate Statistical Analysis for Identification of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer and Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 6973–6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.A.; Li, R.; Albiges, L.; Choueiri, T.K.; Freedman, M.; Pal, S.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Kamat, A.M. Clinical Utility of Cell-Free and Circulating Tumor DNA in Kidney and Bladder Cancer: A Critical Review of Current Literature. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.M.; Ribeiro, L.C.S.L.; Guidi, R.G.; De Moraes, C.M.T.; Lyra, C.R.; Liebl, B.; Guimarães, V.H.A.; De Lima, R.D.; De Almeida, L.S.; Suartz, C.V.; et al. Cell-Free Tumor DNA: A Promising Technology for Diagnosis, Surveillance and Therapeutic Decision in Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2025, 27, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Zhou, X.-H.; Li, S.; Shi, M.-J.; Li, X.-H.; Yang, B.-Y.; Liu, M.; Yi, K.-Z.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Zhang, H.-Y.; et al. Machine Learning-Based Detection of Bladder Cancer by Urine cfDNA Fragmentation Hotspots That Capture Cancer-Associated Molecular Features. Clin. Chem. 2024, 70, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.S.; Shiang, A.; Alahi, I.; Sundby, R.T.; Feng, W.; Gungoren, B.; Nawaf, C.; Chen, K.; Babbra, R.K.; Harris, P.K.; et al. Urine Cell-Free DNA Multi-Omics to Detect MRD and Predict Survival in Bladder Cancer Patients. npj Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, S.; Passarelli, R.; Biswas, A.; De, S.; Ghodoussipour, S. Plasma-Derived Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker for Early Detection, Prognostication, and Personalized Treatment of Urothelial Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Kang, J.; Wei, Y.; Yu, X.; Du, R.; Hong, X.; et al. Unveiling Urinary Extracellular Vesicle mRNA Signature for Early Diagnosis and Prognosis of Bladder Cancer. Theranostics 2025, 15, 1272–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zheng, W.; He, B.; Huang, L.; Zhong, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Huang, Y. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-Based Urine Metabolomics for the Diagnosis and Staging of Bladder Cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 565, 120022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, H.; Kageyama, S.; Isono, T.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Okada, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Terai, A.; Aral, Y.; Iwamura, H.; Kawakita, M.; et al. Diagnostic Potential in Bladder Cancer of a Panel of Tumor Markers (Calreticulin, Γ-synuclein, and Catechol-o-methyltransferase) Identified by Proteomic Analysis. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, M.; Patschan, O.; Hennenlotter, J.; Senger, E.; Feil, G.; Stenzl, A. Combinations of Urine-Based Tumour Markers in Bladder Cancer Surveillance. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2009, 43, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguedolce, F.; Cormio, A.; Bufo, P.; Carrieri, G.; Cormio, L. Molecular Markers in Bladder Cancer: Novel Research Frontiers. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 52, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Wong, K.-Y.; Yu, X.; Zhao, J.-W.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Yang, T. Multispectral 3D DNA Machine Combined with Multimodal Machine Learning for Noninvasive Precise Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 10046–10055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Automated Particle Analyzer | Patient Population | Reference Measure | Diagnostic Performance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iQ200 Analyzer | Patients with suspicious atypical cells | Urinary cytology and histopathology | Sensitivity: 87.5% | [28] |
| Sysmex UF-5000 | Samples with >1 atypical cell/µL | Manual microscopy | [29] | |
| Sysmex UF-5000 | Specimens (163) from 128 patients | Urinary cytopathology | Sensitivity: 59.0% Specificity: 82.1% PPV: 75.0% NPV: 68.8% | [30] |
| Sysmex UF-5000 | Patients (33) with any indication for a cystoscopy examination | Urine cytology on cystoscopy | Sensitivity: 27.0% Specificity: 78.0% PPV: 50.0% NPV: 56.0% | [31] |
| Sysmex UF-5000 | Patients for which a urinary particle analysis was requested | Histological analysis | Sensitivity: 79.5% Specificity: 85.1% | [32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oyaert, M.; Van Praet, C.; Delrue, C.; Speeckaert, M.M. Novel Urinary Biomarkers for the Detection of Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081283
Oyaert M, Van Praet C, Delrue C, Speeckaert MM. Novel Urinary Biomarkers for the Detection of Bladder Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(8):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081283
Chicago/Turabian StyleOyaert, Matthijs, Charles Van Praet, Charlotte Delrue, and Marijn M. Speeckaert. 2025. "Novel Urinary Biomarkers for the Detection of Bladder Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 8: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081283
APA StyleOyaert, M., Van Praet, C., Delrue, C., & Speeckaert, M. M. (2025). Novel Urinary Biomarkers for the Detection of Bladder Cancer. Cancers, 17(8), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081283







