Adverse In-Hospital Outcomes Following Robot-Assisted vs. Open Radical Prostatectomy in Quadragenarians
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Outcomes of Interest
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Overall Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Adverse In-Hospital Outcomes Before Propensity Score Matching
3.3. Adverse In-Hospital Outcomes After Propensity Score Matching
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornford, P.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Brunckhorst, O.; Darraugh, J.; Eberli, D.; De Meerleer, G.; De Santis, M.; Farolfi, A.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2024 Update. Part I: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2024, 86, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastham, J.A.; Auffenberg, G.B.; Barocas, D.A.; Chou, R.; Crispino, T.; Davis, J.W.; Eggener, S.; Horwitz, E.M.; Kane, C.J.; Kirkby, E.; et al. Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO Guideline, Part I: Introduction, Risk Assessment, Staging, and Risk-Based Management. J. Urol. 2022, 208, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Prostate Cancer V.1.2025; National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc.: Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Mehring, G.; Tilki, D.; Heinzer, H.; Steuber, T.; Pose, R.M.; Thederan, I.; Budäus, L.; Salomon, G.; Haese, A.; Michl, U.; et al. Histopathological Results of Radical Prostatectomy Specimen of Men Younger than 50 Years of Age at the Time of Surgery: Possible Implications for Prostate Cancer Screening Programs? World J. Urol. 2023, 41, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twiss, C.; Slova, D.; Lepor, H. Outcomes for Men Younger than 50 Years Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy. Urology 2005, 66, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Lee, H.; Lee, M.S.; Hong, S.K. Outcomes of Men Aged ≤50 Years Treated with Radical Prostatectomy: A Retrospective Analysis. Asian J. Androl. 2019, 21, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Tennstedt, P.; Hansen, J.; Trinh, Q.D.; Kluth, L.; Atassi, N.; Schlomm, T.; Salomon, G.; Haese, A.; Budaeus, L.; et al. Functional and Oncological Outcomes of Patients Aged <50 Years Treated with Radical Prostatectomy for Localised Prostate Cancer in a European Population. BJU Int. 2014, 114, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, P.M.; Rice, K.R.; Sterbis, J.R.; Chen, Y.; Cullen, J.; McLeod, D.G.; Brassell, S.A. Prostate Cancer in Men Less than the Age of 50: A Comparison of Race and Outcomes. Urology 2011, 78, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnear, N.J.; Kichenadasse, G.; Plagakis, S.; O’Callaghan, M.E.; Kopsaftis, T.; Walsh, S.; Foreman, D. Prostate Cancer in Men Aged Less than 50 Years at Diagnosis. World J. Urol. 2016, 34, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendeville, S.; Nesbitt, M.E.; Evans, A.J.; Fleshner, N.E.; van der Kwast, T.H. Variant Histology and Clinicopathological Features of Prostate Cancer in Men Younger than 50 Years Treated with Radical Prostatectomy. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labanaris, A.P.; Zugor, V.; Witt, J.H. Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy in Men ≤50 Years of Age. Surgical, Oncological and Functional Outcomes. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 2097–2101. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, K.R.S.; Onol, F.F.; Moschovas, M.C.; Reddy, S.; Noel, J.; Rogers, T.; Coelho, R.; Rocco, B.; Patel, V. Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy in Young Adults: Age-Stratified Oncological and Functional Outcomes. J. Robot. Surg. 2022, 16, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilki, D.; Maurer, V.; Pompe, R.S.; Chun, F.K.; Preisser, F.; Haese, A.; Graefen, M.; Huland, H.; Mandel, P. Tumor Characteristics, Oncological and Functional Outcomes after Radical Prostatectomy in Very Young Men ≤ 45 Years of Age. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosini, F.; Knipper, S.; Tilki, D.; Heinzer, H.; Salomon, G.; Michl, U.; Steuber, T.; Pose, R.M.; Budäus, L.; Maurer, T.; et al. Robot-Assisted vs. Open Retropubic Radical Prostatectomy: A Propensity Score-Matched Comparative Analysis Based on 15 Years and 18,805 Patients. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Rockville, MD HCUP Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS). Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). 2008–2019. Available online: www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/nisoverview.jsp (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Falkenbach, F.; Di Bello, F.; Rodriguez Peñaranda, N.; Longoni, M.; Marmiroli, A.; Le, Q.C.; Tian, Z.; Goyal, J.A.; Longo, N.; Micali, S.; et al. Adverse In-Hospital Outcomes after Radical Prostatectomy in Leukemia History Patients. Cancers 2024, 16, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyo, R.A.; Cherkin, D.C.; Ciol, M.A. Adapting a Clinical Comorbidity Index for Use with ICD-9-CM Administrative Databases. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1992, 45, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Sundararajan, V.; Halfon, P.; Fong, A.; Burnand, B.; Luthi, J.-C.; Saunders, L.D.; Beck, C.A.; Feasby, T.E.; Ghali, W.A. Coding Algorithms for Defining Comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 Administrative Data. Med. Care 2005, 43, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posit Team. Posit Software, PBC RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Available online: http://www.posit.co/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Trinh, Q.-D.; Sammon, J.; Sun, M.; Ravi, P.; Ghani, K.R.; Bianchi, M.; Jeong, W.; Shariat, S.F.; Hansen, J.; Schmitges, J.; et al. Perioperative Outcomes of Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy Compared with Open Radical Prostatectomy: Results from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leow, J.J.; Chang, S.L.; Meyer, C.P.; Wang, Y.; Hanske, J.; Sammon, J.D.; Cole, A.P.; Preston, M.A.; Dasgupta, P.; Menon, M.; et al. Robot-Assisted Versus Open Radical Prostatectomy: A Contemporary Analysis of an All-Payer Discharge Database. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandaglia, G.; Sammon, J.D.; Chang, S.L.; Choueiri, T.K.; Hu, J.C.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Kibel, A.S.; Kim, S.P.; Konijeti, R.; Montorsi, F.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Robot-Assisted and Open Radical Prostatectomy in the Postdissemination Era. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisser, F.; Nazzani, S.; Mazzone, E.; Knipper, S.; Bandini, M.; Tian, Z.; Haese, A.; Saad, F.; Zorn, K.C.; Montorsi, F.; et al. Regional Differences in Total Hospital Charges between Open and Robotically Assisted Radical Prostatectomy in the United States. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, Q.-D.; Sun, M.; Kim, S.P.; Sammon, J.; Kowalczyk, K.J.; Friedman, A.A.; Sukumar, S.; Ravi, P.; Muhletaler, F.; Agarwal, P.K.; et al. The Impact of Hospital Volume, Residency, and Fellowship Training on Perioperative Outcomes after Radical Prostatectomy. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 29.e13–29.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, Q.-D.; Schmitges, J.; Sun, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Sukumar, S.; Bianchi, M.; Tian, Z.; Jeldres, C.; Sammon, J.; Perrotte, P.; et al. Radical Prostatectomy at Academic Versus Nonacademic Institutions: A Population Based Analysis. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciamani, G.E.; Maas, M.; Nassiri, N.; Ortega, D.; Gill, K.; Dell’Oglio, P.; Thalmann, G.N.; Heidenreich, A.; Eastham, J.A.; Evans, C.P.; et al. Impact of Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection and Its Extent on Perioperative Morbidity in Patients Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompe, R.S.; Beyer, B.; Haese, A.; Preisser, F.; Michl, U.; Steuber, T.; Graefen, M.; Huland, H.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Tilki, D. Postoperative Complications of Contemporary Open and Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy Using Standardised Reporting Systems. BJU Int. 2018, 122, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzenburg, J.U.; Kyriazis, I.; Fahlenbrach, C.; Gilfrich, C.; Günster, C.; Jeschke, E.; Popken, G.; Weißbach, L.; von Zastrow, C.; Leicht, H. National Trends and Differences in Morbidity among Surgical Approaches for Radical Prostatectomy in Germany. World J. Urol. 2016, 34, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, G.; Ficarra, V.; Rosen, R.C.; Artibani, W.; Costello, A.; Eastham, J.A.; Graefen, M.; Guazzoni, G.; Shariat, S.F.; Stolzenburg, J.-U.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Perioperative Outcomes and Complications after Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Bao, E.; Wang, J.; Tan, C.; Tang, T. Robot-Assisted versus Open Radical Prostatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. J. Robot. Surg. 2023, 17, 2617–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhawere, K.E.; Shih, I.-F.; Lee, S.-H.; Li, Y.; Wong, J.A.; Badani, K.K. Comparison of 1-Year Health Care Costs and Use Associated With Open vs. Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e212265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
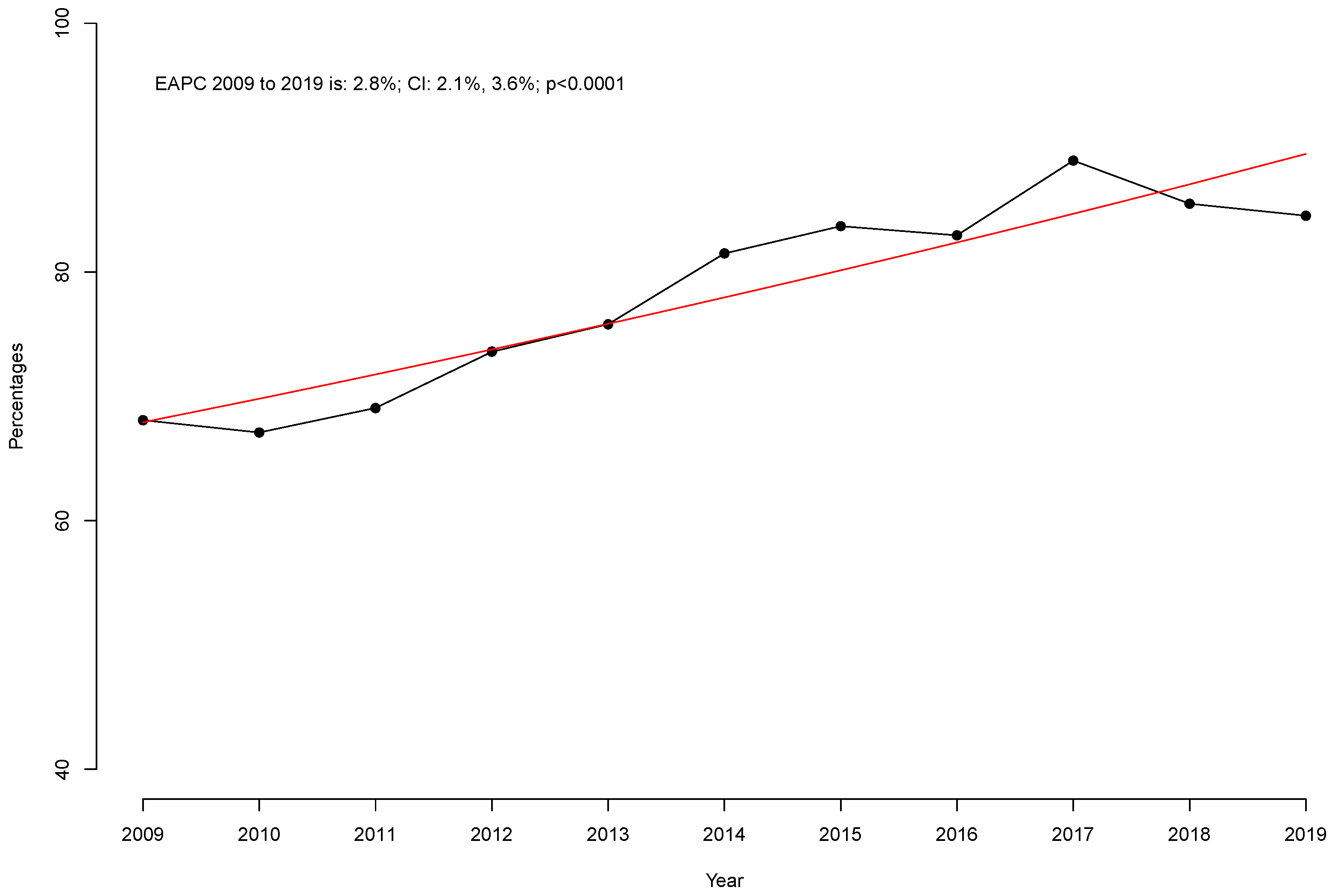
| Prior PSM | After PSM 1:1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORP (n = 1343, 24.8%) | RARP (n = 4083, 75.2%) | p-Value 1 | ORP (n = 1343, 50.0%) | RARP (n = 1343, 50.0%) | p-Value 1 | |
| Age, median (IQR) | 47 (45, 49) | 47 (45, 48) | 0.97 | 47 (45, 49) | 47 (45, 49) | 0.9 |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | 0.7 | 0.6 | ||||
| Caucasian | 737 (54.9%) | 2206 (54.0%) | 737 (54.9%) | 735 (54.7%) | ||
| Afro-American | 304 (22.6%) | 974 (23.9%) | 304 (22.6%) | 287 (21.4%) | ||
| Others | 302 (22.5%) | 903 (22.1%) | 302 (22.5%) | 321 (23.9%) | ||
| CCI, n (%) | 0.6 | 0.3 | ||||
| 0 | 1120 (83.4%) | 3380 (82.8%) | 1120 (83.4%) | 1151 (85.7%) | ||
| 1 | 154 (11.5%) | 508 (12.4%) | 154 (11.5%) | 132 (9.8%) | ||
| ≥2 | 69 (5.1%) | 195 (4.8%) | 69 (5.1%) | 60 (4.5%) | ||
| PLND, n (%) | 601 (44.8%) | 1681 (41.2%) | 0.02 | 601 (44.8%) | 605 (45.0%) | 0.9 |
| Year of surgery, n (%) | <0.001 | 0.5 | ||||
| 2009–2014 | 1106 (82.4%) | 2735 (67.0%) | 1106 (82.4%) | 1121 (83.5%) | ||
| 2015–2019 | 237 (17.6%) | 1348 (33.0%) | 237 (17.6%) | 222 (16.5%) | ||
| Large size hospital, n (%) | 915 (68.1%) | 2566 (62.8%) | <0.001 | 915 (68.1%) | 936 (69.7%) | 0.4 |
| Teaching hospital, n (%) | 903 (67.2%) | 3247 (79.5%) | <0.001 | 903 (67.2%) | 931 (69.3%) | 0.3 |
| Prior PSM | After PSM 1:1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORP (n = 1343, 24.8%) | RARP (n = 4083, 75.2%) | Absolute Difference RARP vs. ORP (Δ) | p-Value 1 | ORP (n = 1343, 50.0%) | RARP (n = 1343, 50.0%) | Absolute Difference RARP vs. ORP (Δ) | p-Value 1 | |
| Overall complications, n (%) | 180 (13.4%) | 318 (7.8%) | −5.6% | <0.001 | 180 (13.4%) | 94 (7.0%) | −6.4% | <0.001 |
| Intraoperative complications, n (%) | 49 (3.6%) | 98 (2.4%) | −1.2% | 0.02 | 49 (3.6%) | 37 (2.8%) | −0.8% | 0.2 |
| Critical care therapy, n (%) | <11 | 15 (0.4%) | −0.1% | 0.9 | <11 | <11 | 0.0% | 0.99 |
| Bleeding complications, n (%) | 16 (1.2%) | 33 (0.8%) | −0.4% | 0.3 | 16 (1.2%) | 13 (1.0%) | −0.2% | 0.7 |
| Blood transfusions, n (%) | 85 (6.3%) | 51 (1.2%) | −5.1% | <0.001 | 85 (6.3%) | 20 (1.5%) | −4.8% | <0.001 |
| Cardiac complications, n (%) | <11 | 30 (0.7%) | +0.4% | 0.1 | <11 | 12 (0.9%) | +0.6% | 0.08 |
| Respiratory complications, n (%) | 25 (1.9%) | 27 (0.7%) | −1.2% | <0.001 | 25 (1.9%) | <11 | −1.2% | 0.02 |
| Genitourinary complications, n (%) | 22 (1.6%) | 30 (0.7%) | −0.9% | 0.005 | 22 (1.6%) | 15 (1.1%) | −0.5% | 0.3 |
| Wound complications, n (%) | <11 | <11 | −0.1% | 0.3 | <11 | <11 | −0.1% | 0.99 |
| Infectious complications, n (%) | <11 | <11 | +0.1% | 0.5 | <11 | <11 | 0.1% | 0.99 |
| Vascular complications, n (%) | <11 | <11 | −0.1% | 0.3 | <11 | <11 | −0.1% | 0.6 |
| Misc. surgical complications, n (%) | <11 | 19 (0.5%) | −0.1% | 0.7 | <11 | <11 | −0.4% | 0.2 |
| Misc. medical complications, n (%) | 28 (2.1%) | 70 (1.7%) | −0.4% | 0.4 | 28 (2.1%) | 15 (1.1%) | −1.0% | 0.07 |
| In-hospital mortality, n (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Prolonged LOS (>2 days) †, n (%) | 385 (28.7%) | 432 (10.6%) | −18.1% | <0.001 | 385 (28.7%) | 146 (10.9%) | −17.8% | <0.001 |
| THC, USD, median (IQR) | 36,840 (24,100, 53,280) | 45,030 (32,850, 63,830) | +8190 | <0.001 | 36,840 (24,100, 53,280) | 43,690 (31,200, 61,940) | +6850 | <0.001 |
| Prior PSM | After PSM 1:1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multivariable OR/IRR (95% CI) * | p-Value | Multivariable OR/IRR (95% CI) * | p-Value | |
| Overall complications | 0.54 (0.44–0.67) | <0.001 | 0.49 (0.38–0.64) | <0.001 |
| Intraoperative complications | 0.77 (0.53–1.11) | 0.2 | 0.77 (0.49–1.20) | 0.2 |
| Critical care therapy | 0.91 (0.32–2.59) | 0.9 | 0.99 (0.32–3.02) | 0.99 |
| Bleeding complications | 0.76 (0.41–1.40) | 0.4 | 0.83 (0.40–1.74) | 0.6 |
| Blood transfusions | 0.21 (0.15–0.31) | <0.001 | 0.23 (0.14–0.37) | <0.001 |
| Cardiac complications | 2.02 (0.68–6.03) | 0.2 | 3.29 (1.02–10.63) | 0.047 |
| Respiratory complications | 0.43 (0.24–0.77) | 0.005 | 0.40 (0.19–0.84) | 0.02 |
| Genitourinary complications | 0.48 (0.27–0.85) | 0.01 | 0.69 (0.37–1.28) | 0.2 |
| Wound complications | 0.30 (0.06–1.49) | 0.1 | 0.68 (0.11–4.39) | 0.7 |
| Infectious complications | 1.98 (0.29–13.32) | 0.5 | 2.34 (0.34–16.00) | 0.4 |
| Vascular complications | 0.29 (0.07–1.22) | 0.09 | 0.36 (0.04–3.29) | 0.4 |
| Misc. surgical complications | 0.94 (0.42–2.10) | 0.9 | 0.38 (0.10–1.43) | 0.2 |
| Misc. medical complications | 0.68 (0.43–1.08) | 0.1 | 0.58 (0.31–1.08) | 0.09 |
| Prolonged LOS (>2 days) † | 0.32 (0.27–0.38) | <0.001 | 0.30 (0.24–0.37) | <0.001 |
| Total hospital charges | 1.20 (1.15–1.25) | <0.001 | 1.18 (1.13–1.24) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falkenbach, F.; Di Bello, F.; Rodriguez Peñaranda, N.; Longoni, M.; Marmiroli, A.; Le, Q.C.; Catanzaro, C.; Nicolazzini, M.; Tian, Z.; Goyal, J.A.; et al. Adverse In-Hospital Outcomes Following Robot-Assisted vs. Open Radical Prostatectomy in Quadragenarians. Cancers 2025, 17, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071193
Falkenbach F, Di Bello F, Rodriguez Peñaranda N, Longoni M, Marmiroli A, Le QC, Catanzaro C, Nicolazzini M, Tian Z, Goyal JA, et al. Adverse In-Hospital Outcomes Following Robot-Assisted vs. Open Radical Prostatectomy in Quadragenarians. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071193
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalkenbach, Fabian, Francesco Di Bello, Natali Rodriguez Peñaranda, Mattia Longoni, Andrea Marmiroli, Quynh Chi Le, Calogero Catanzaro, Michele Nicolazzini, Zhe Tian, Jordan A. Goyal, and et al. 2025. "Adverse In-Hospital Outcomes Following Robot-Assisted vs. Open Radical Prostatectomy in Quadragenarians" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071193
APA StyleFalkenbach, F., Di Bello, F., Rodriguez Peñaranda, N., Longoni, M., Marmiroli, A., Le, Q. C., Catanzaro, C., Nicolazzini, M., Tian, Z., Goyal, J. A., Longo, N., Puliatti, S., Schiavina, R., Palumbo, C., Musi, G., Chun, F. K. H., Briganti, A., Saad, F., Shariat, S. F., ... Karakiewicz, P. I. (2025). Adverse In-Hospital Outcomes Following Robot-Assisted vs. Open Radical Prostatectomy in Quadragenarians. Cancers, 17(7), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071193









