Development and Validation of Monte Carlo Methods for Converay: A Proof-of-Concept Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
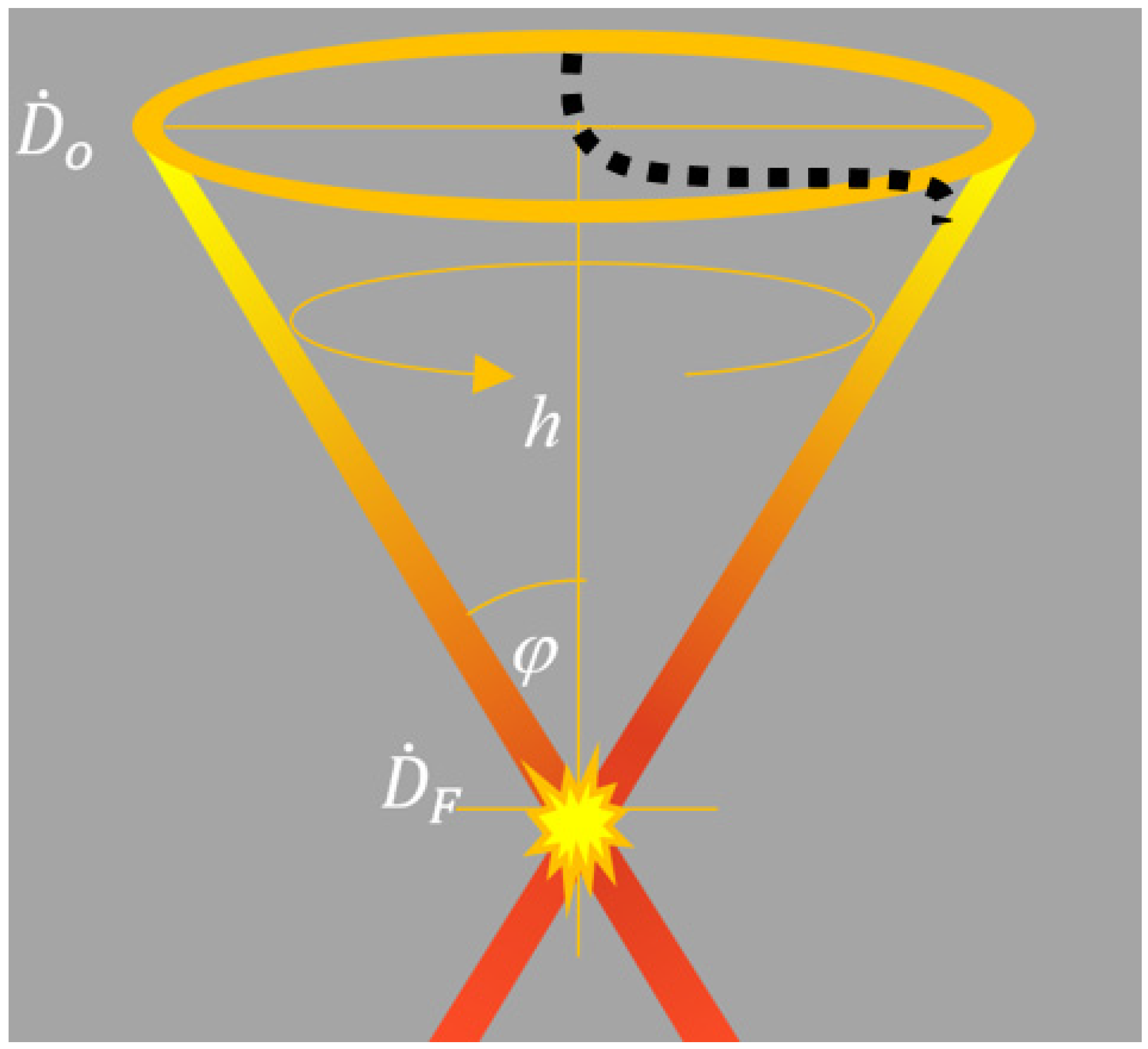
2.1. Analytic Approach to the CONVERAY System
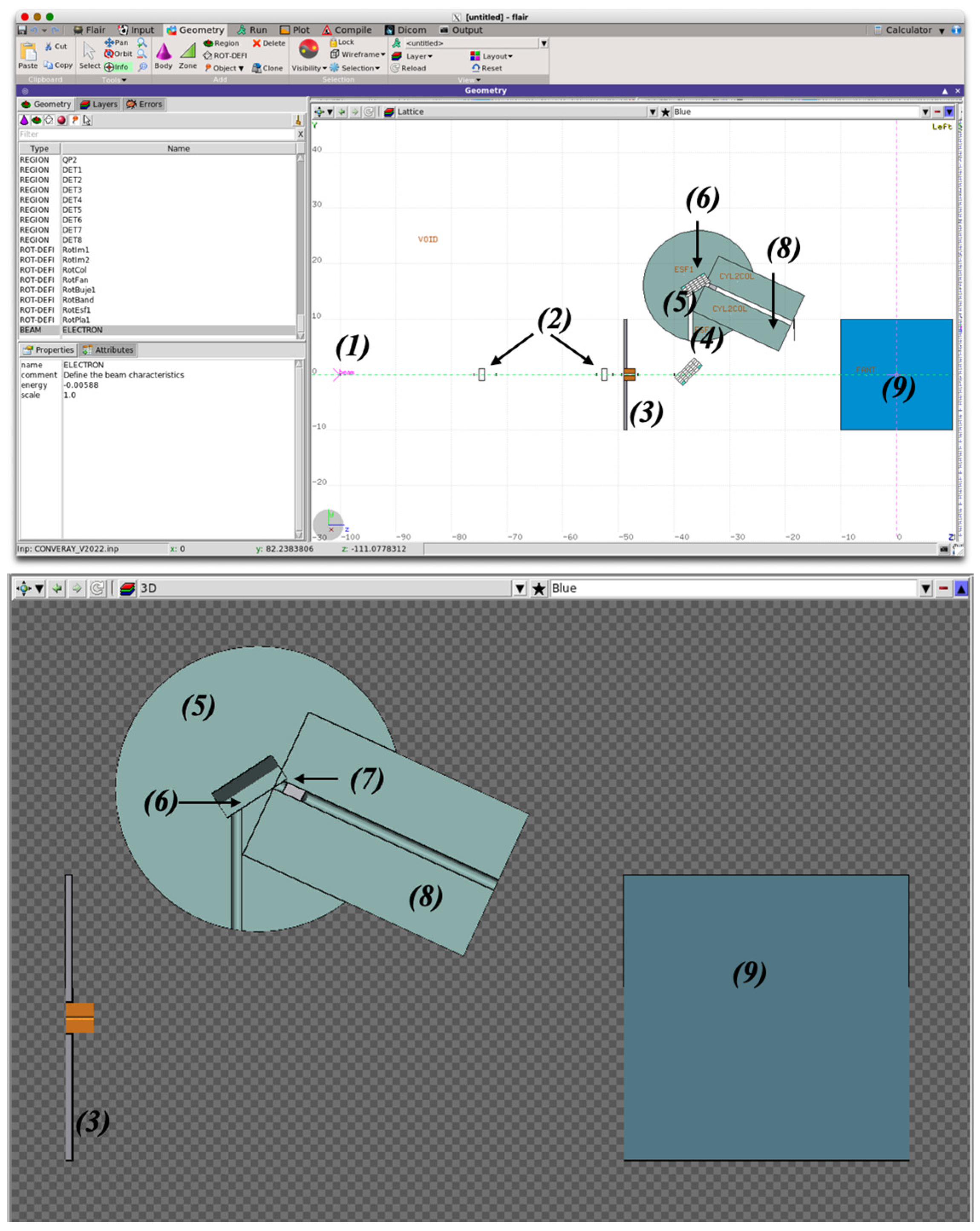
2.2. Monte Carlo Modeling of the CONVERAY System
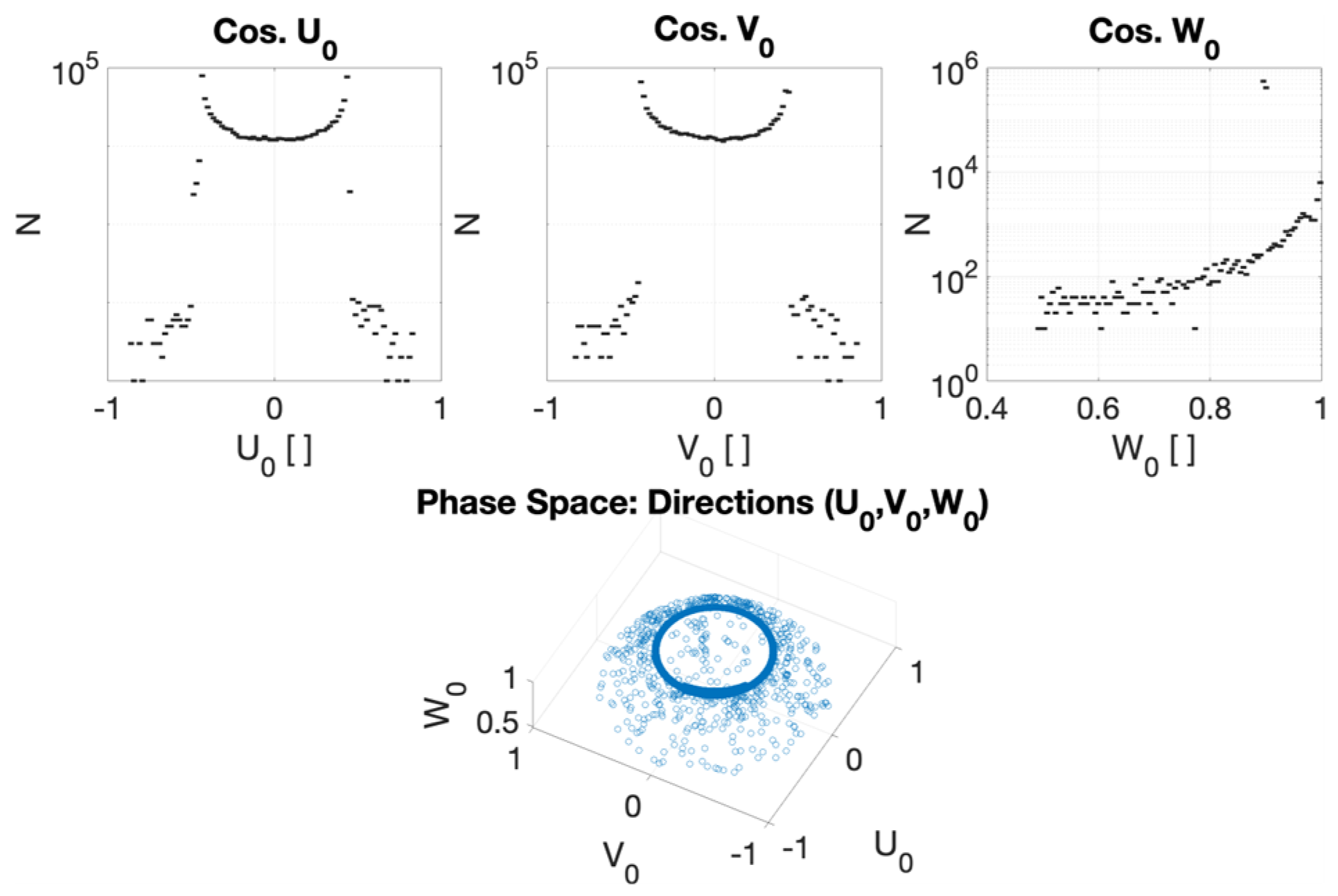
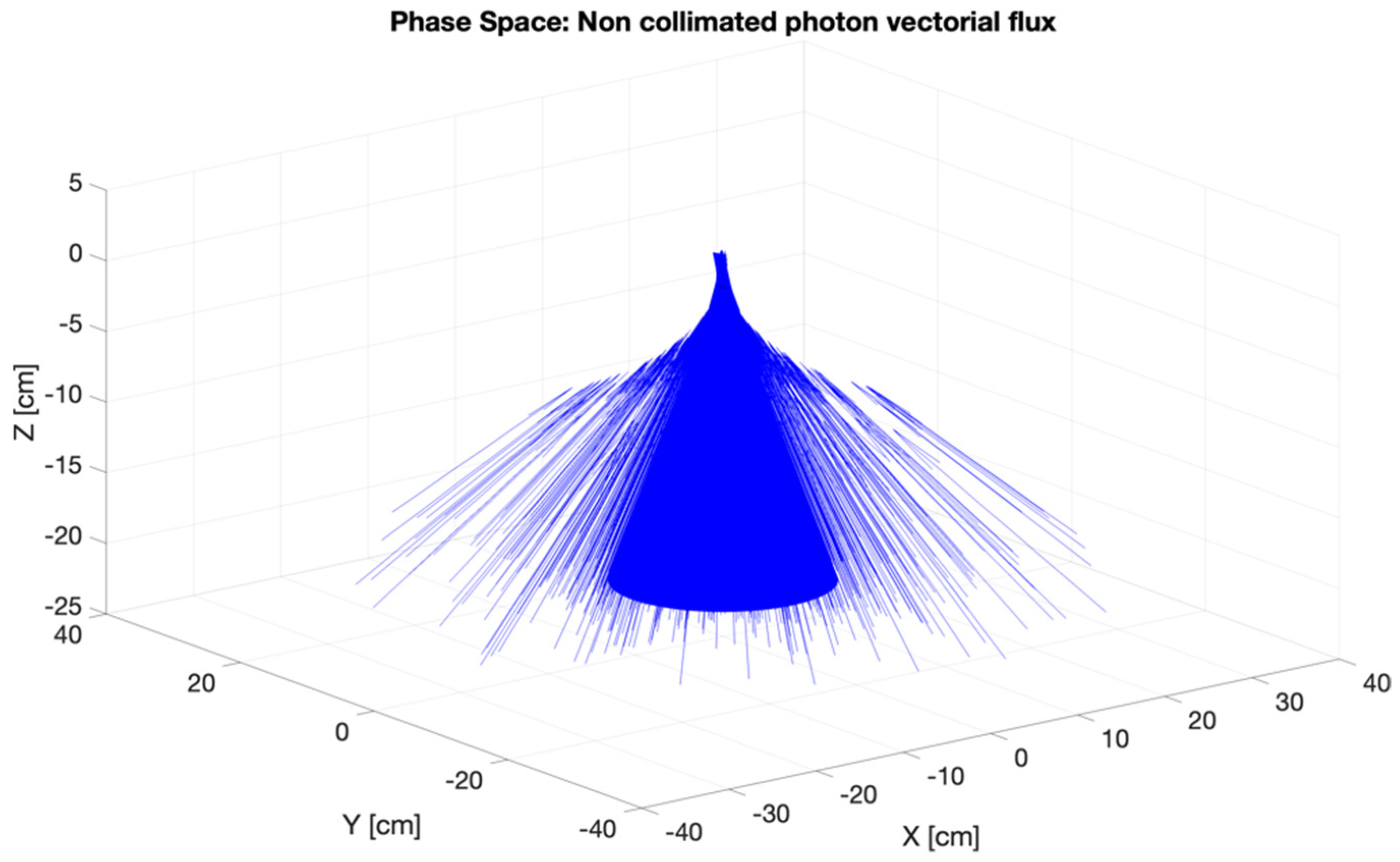
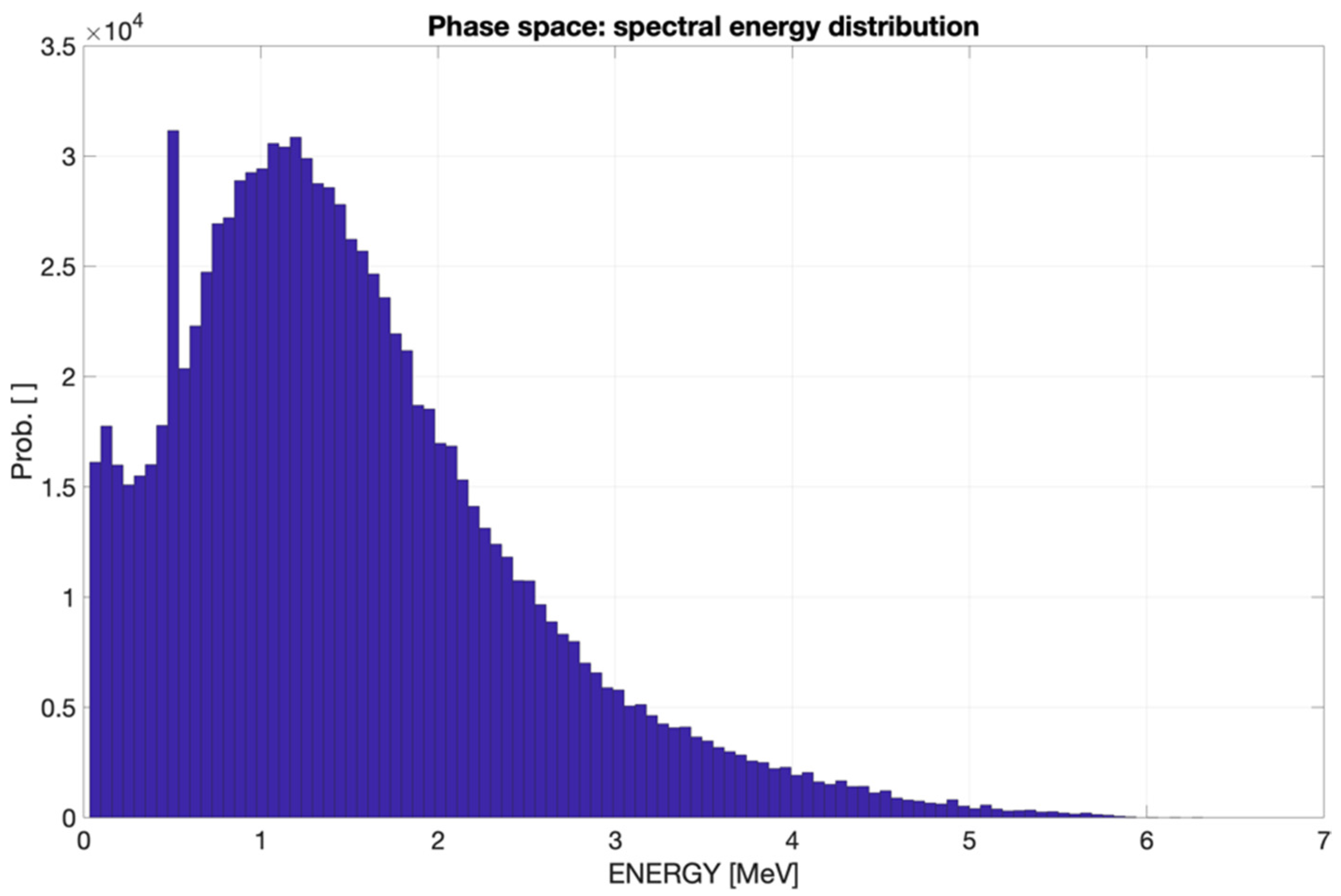
2.2.1. Phase Space for the CONVERAY Prototype
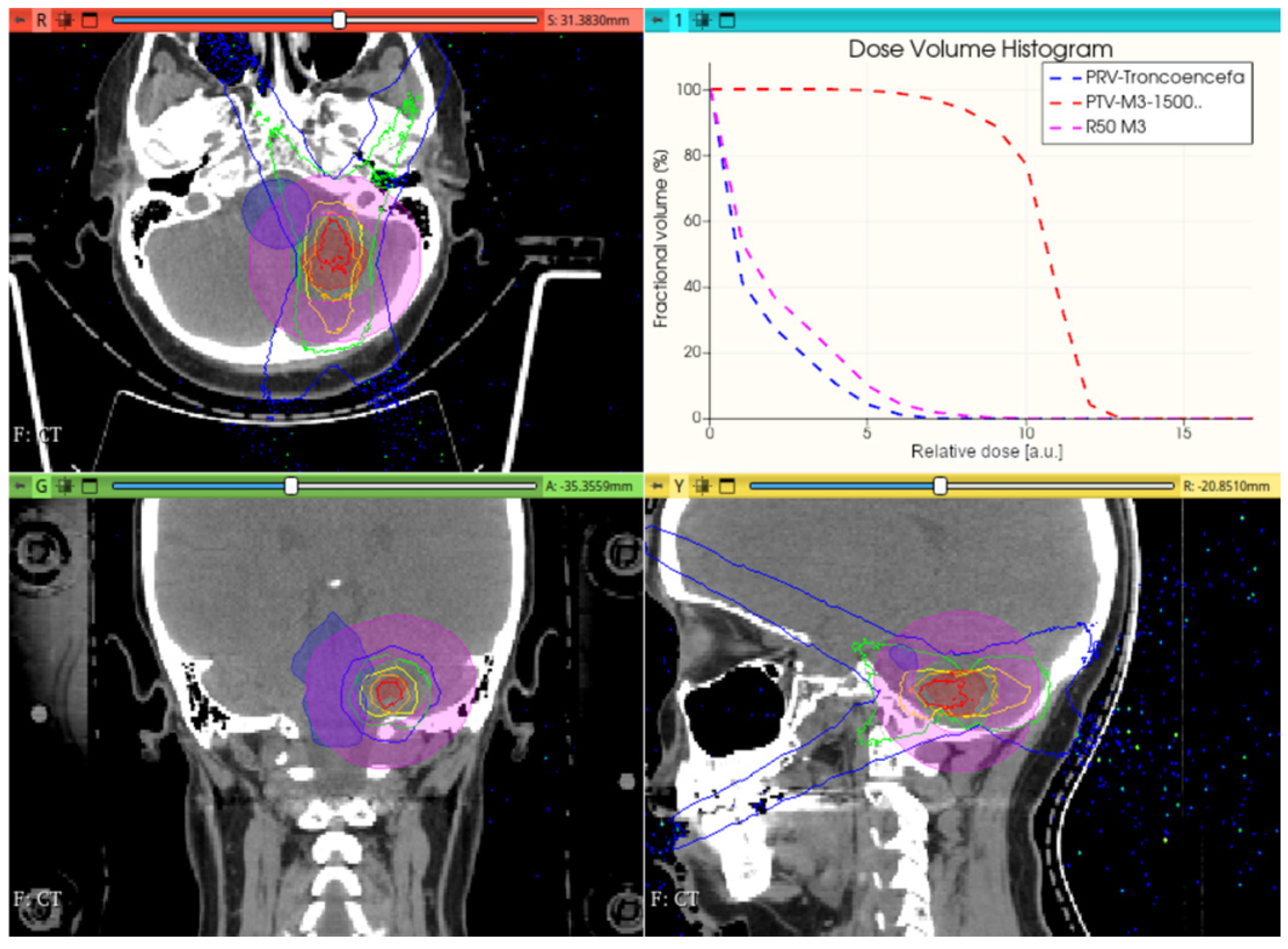
2.2.2. In-Phantom Dosimetry and Dose Concentration Assessment for CONVERAY
2.3. Uncertainties of the CONVERAY Monte Carlo Modeling
3. Results
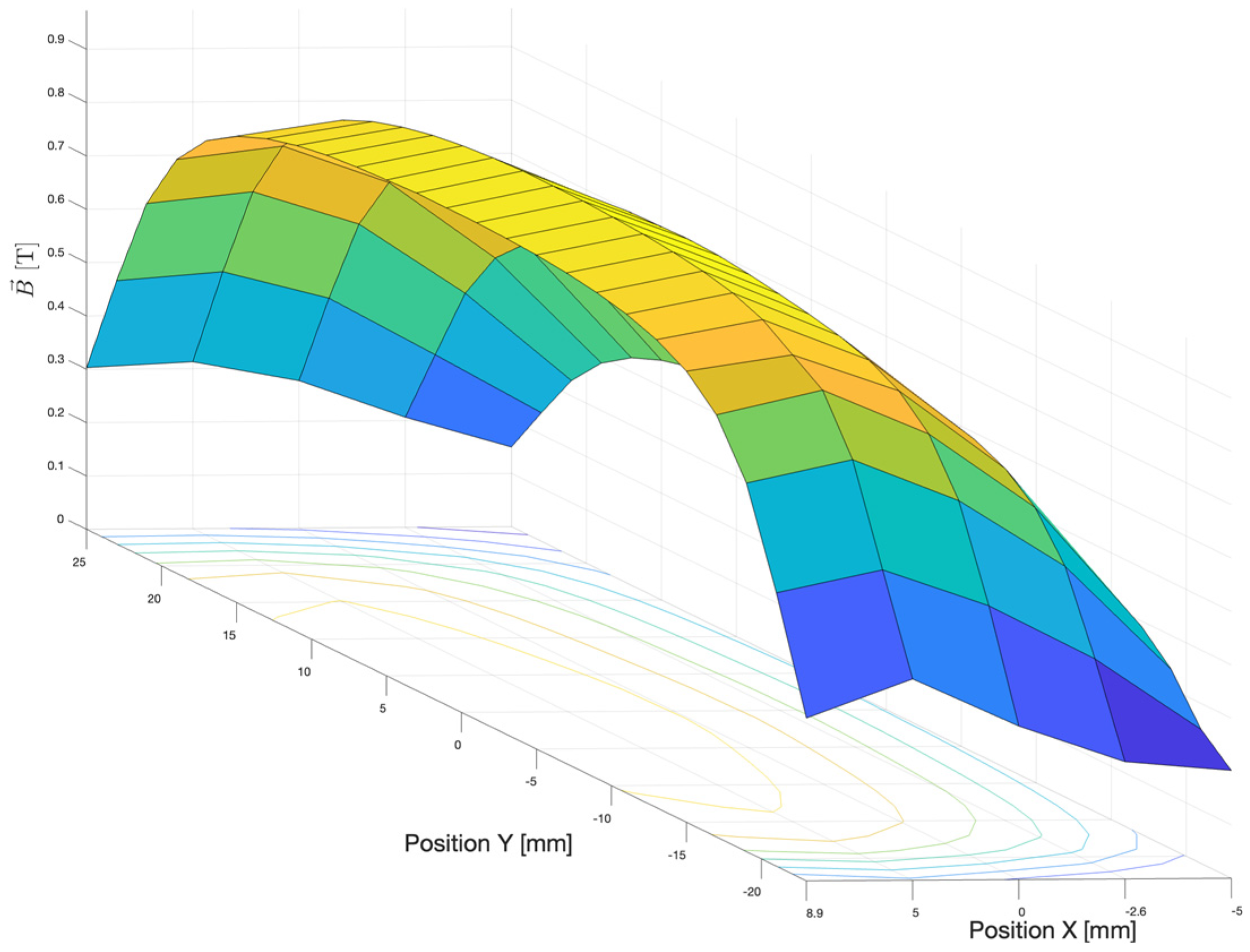
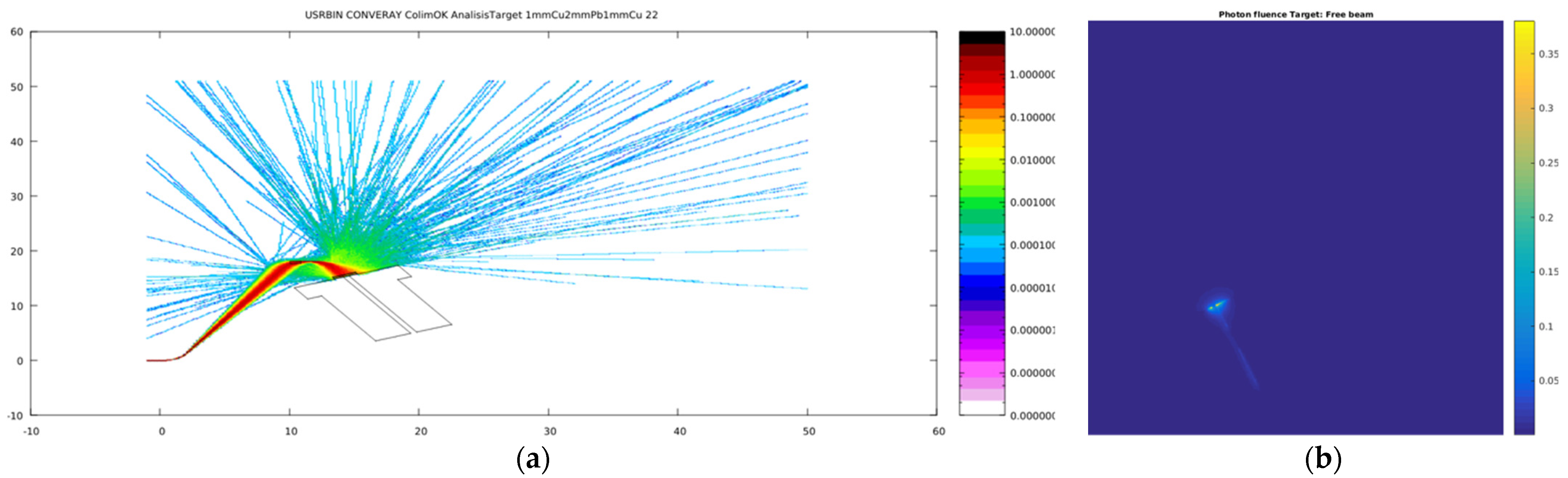
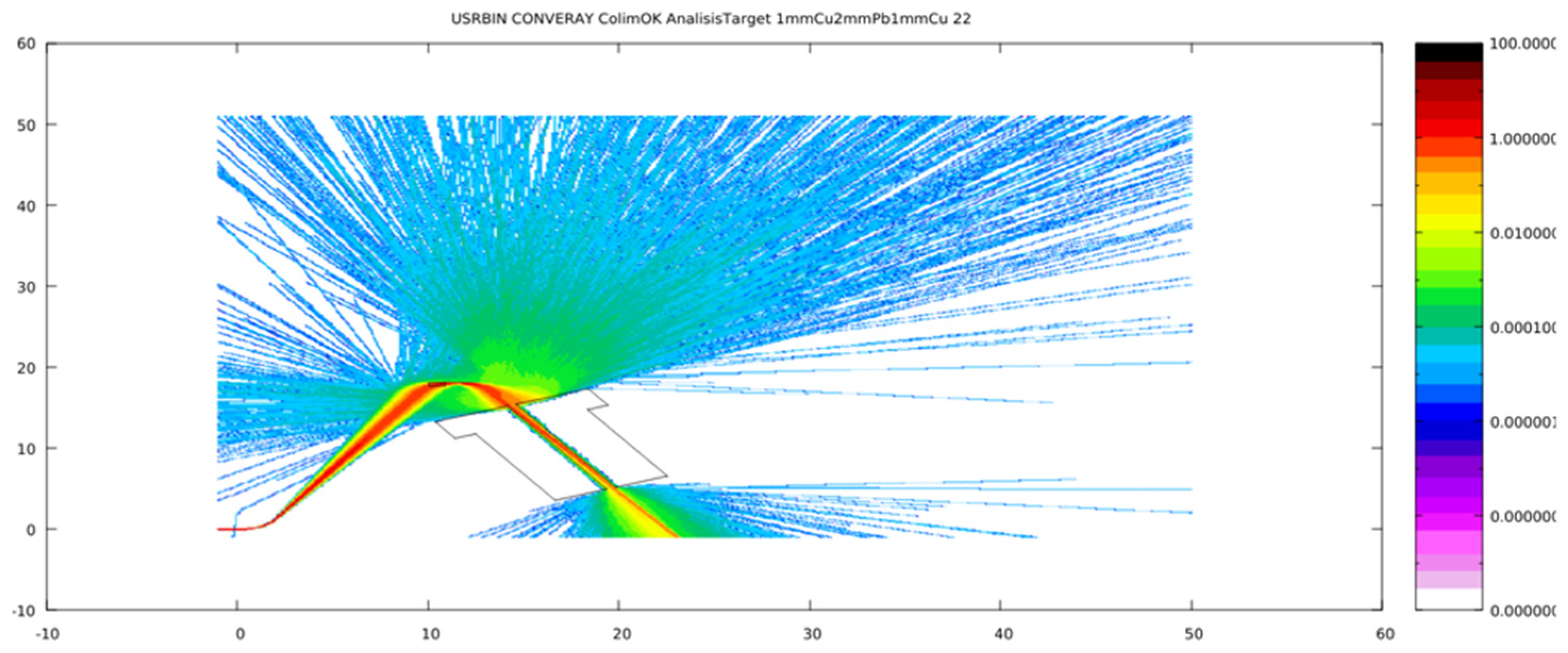
3.1. Primary Particle Fluence in the CONVERAY Prototype
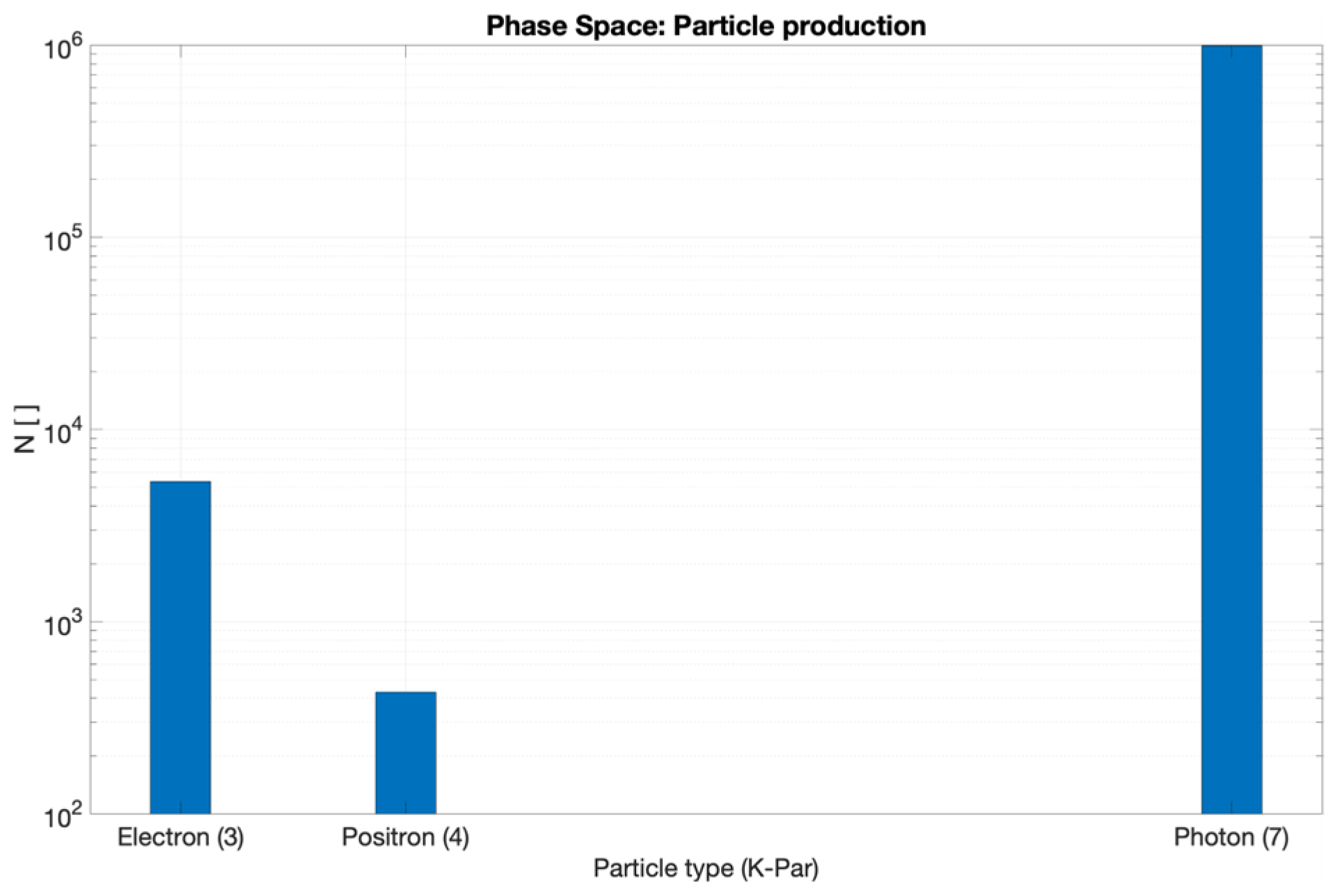
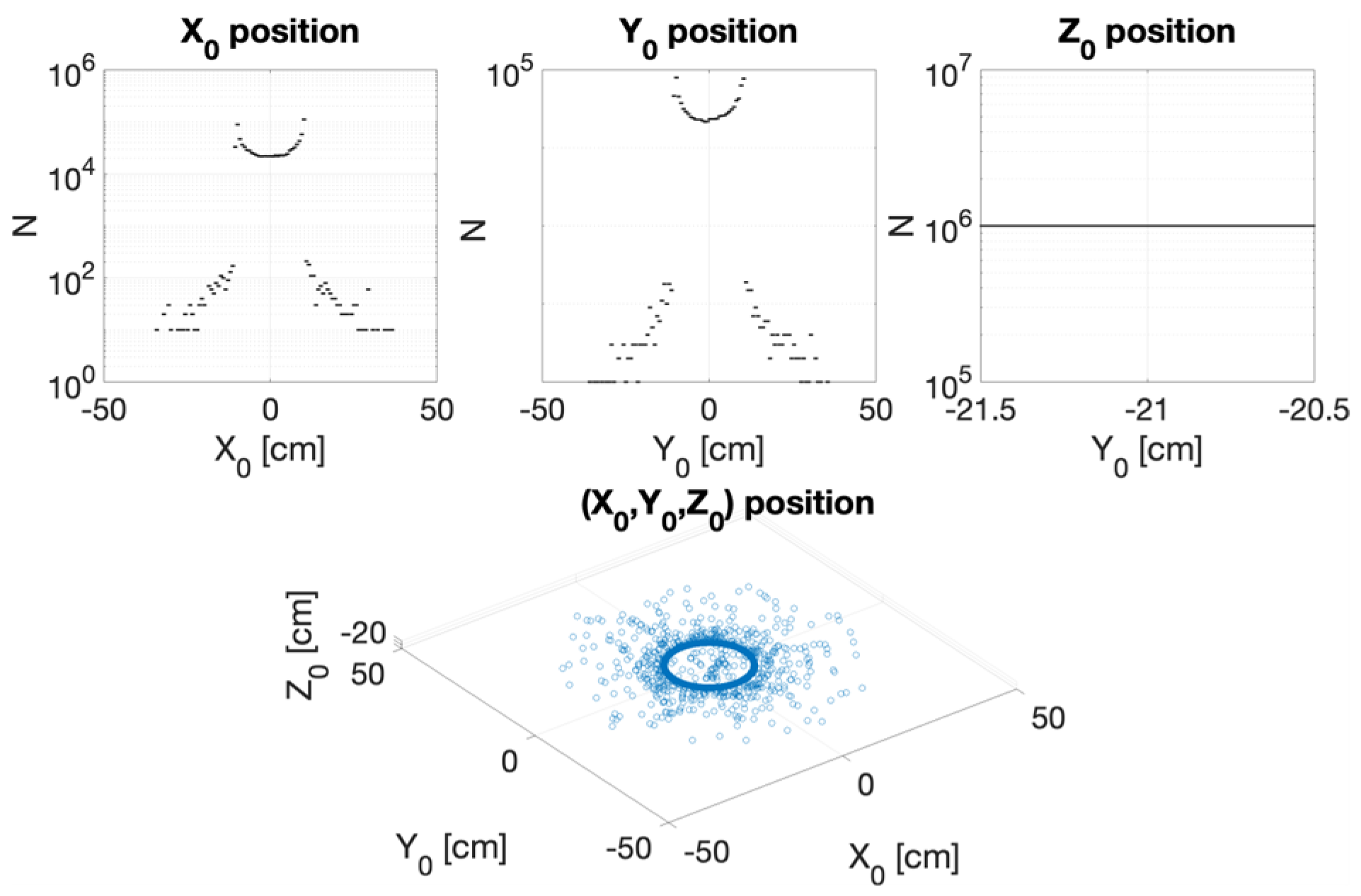
3.2. CONVERAY Phase Space and Photon Beam Production
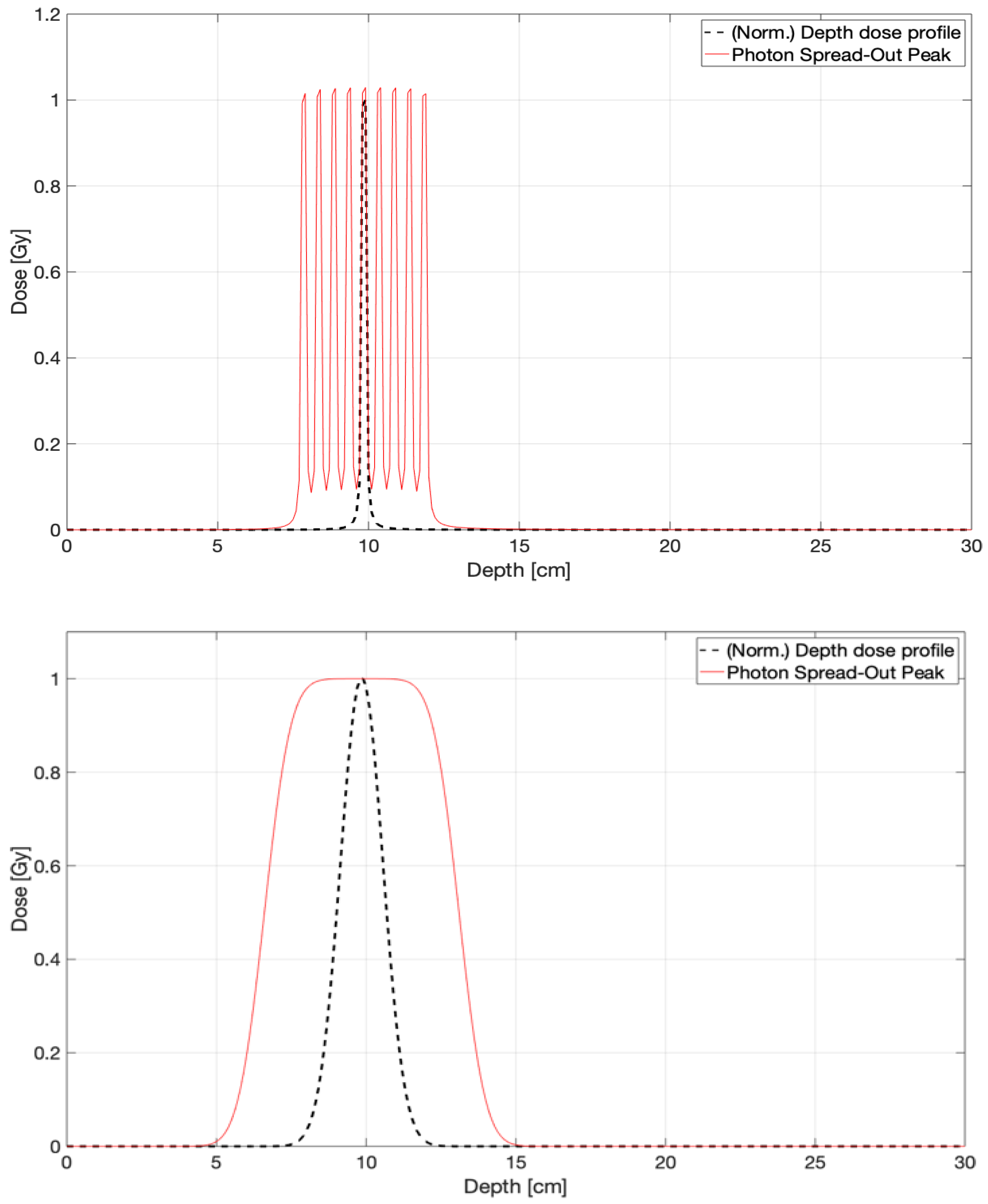
3.3. CONVERAY Dosimetry Performance
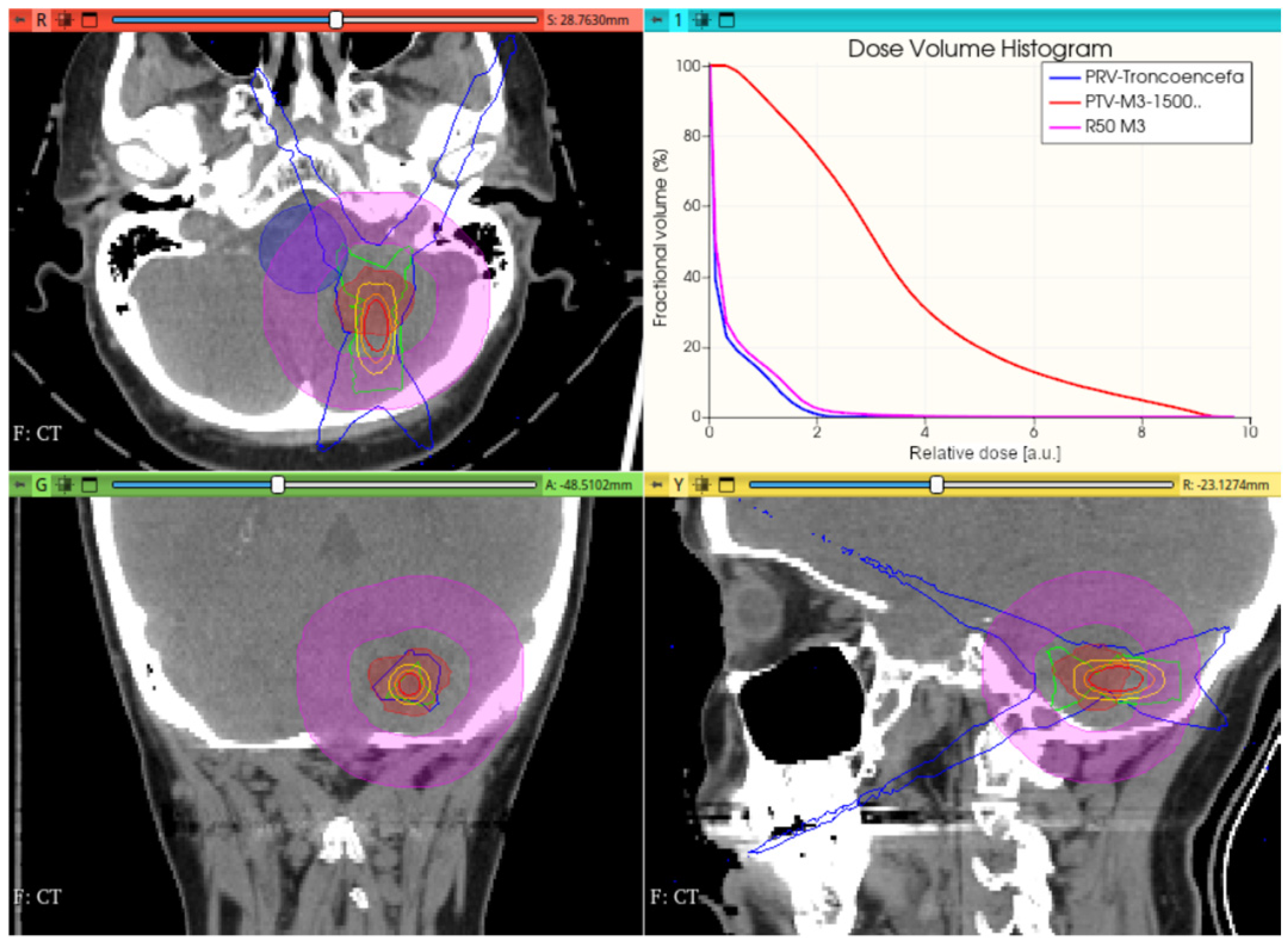
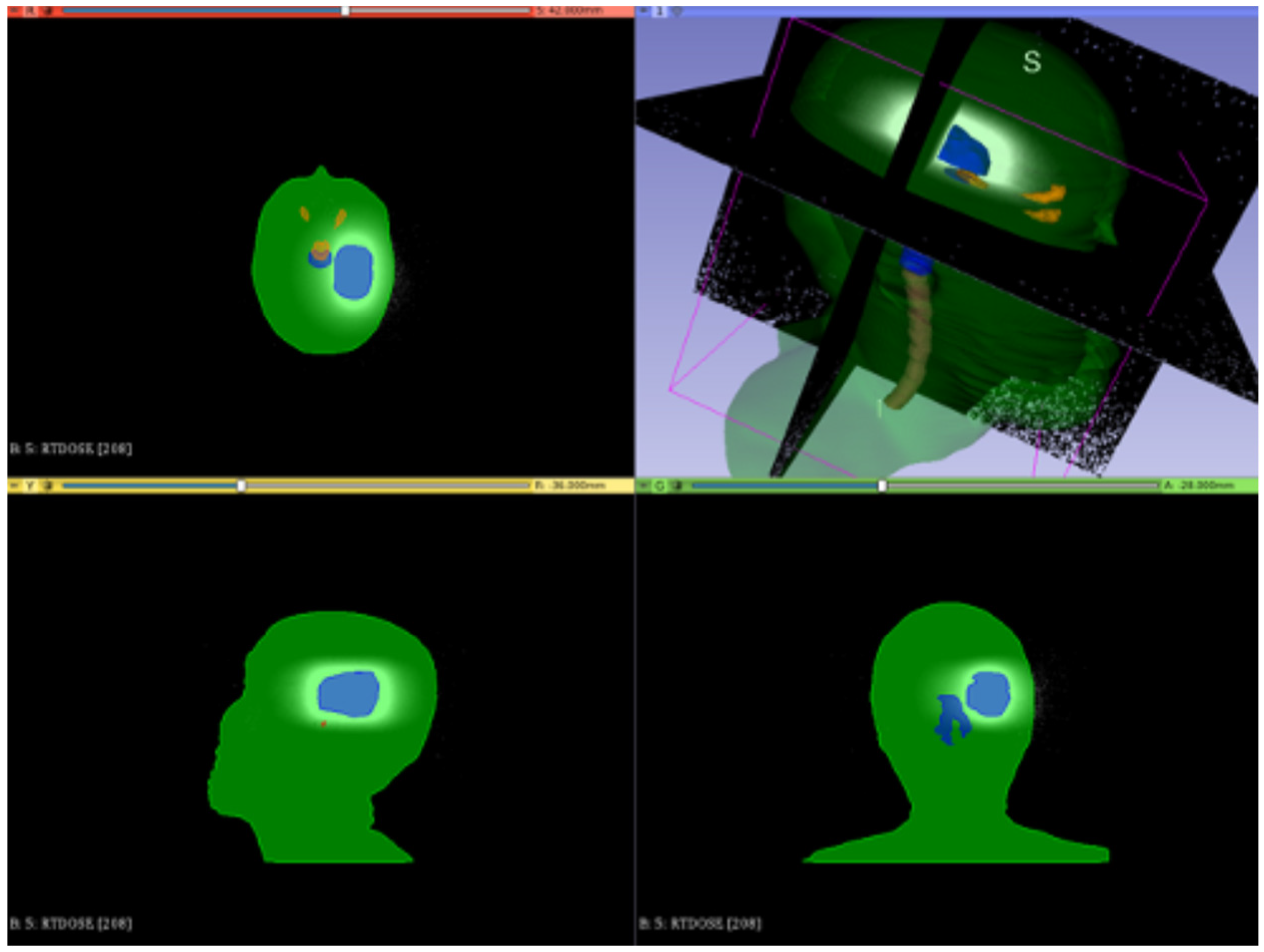
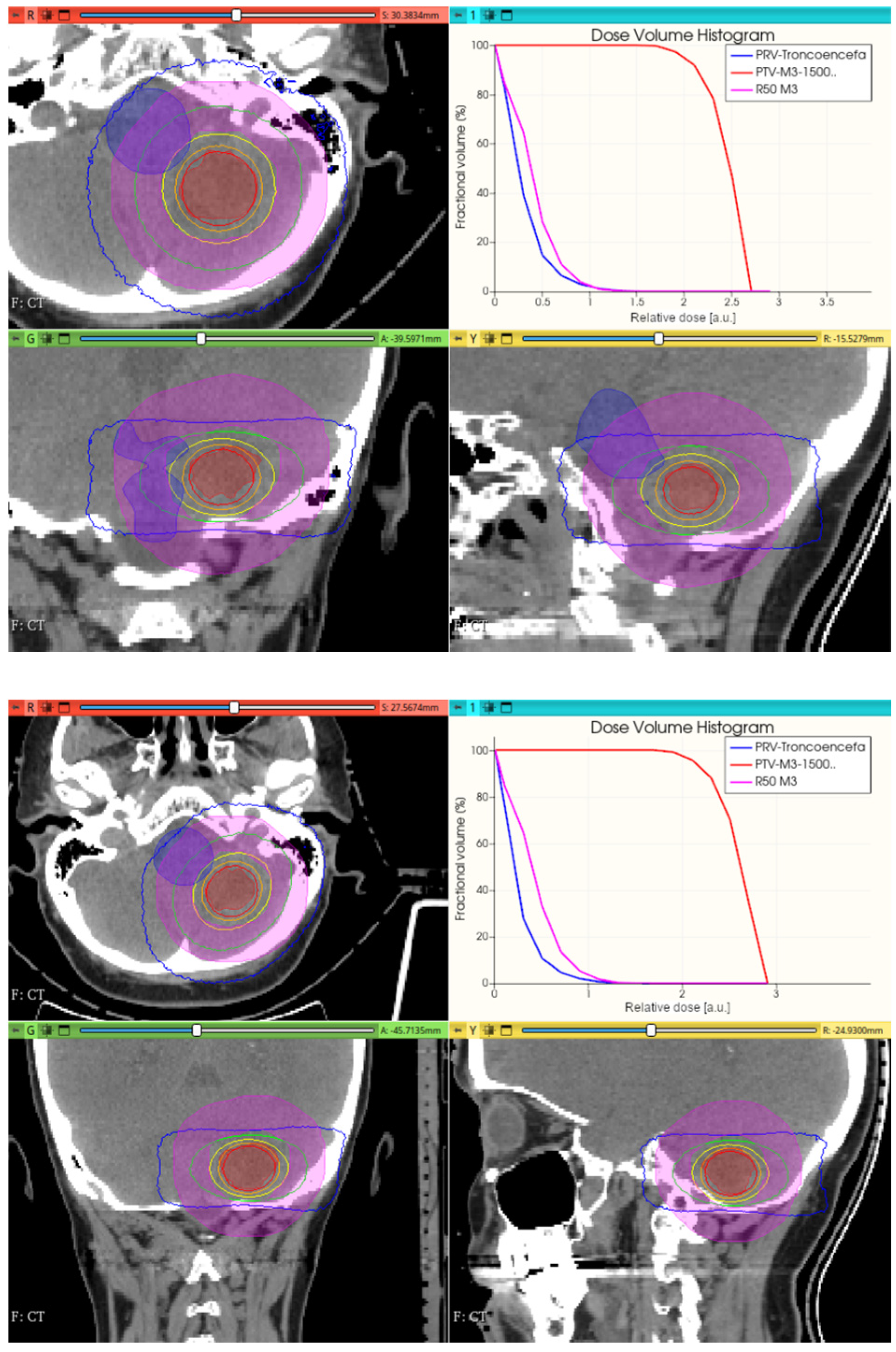
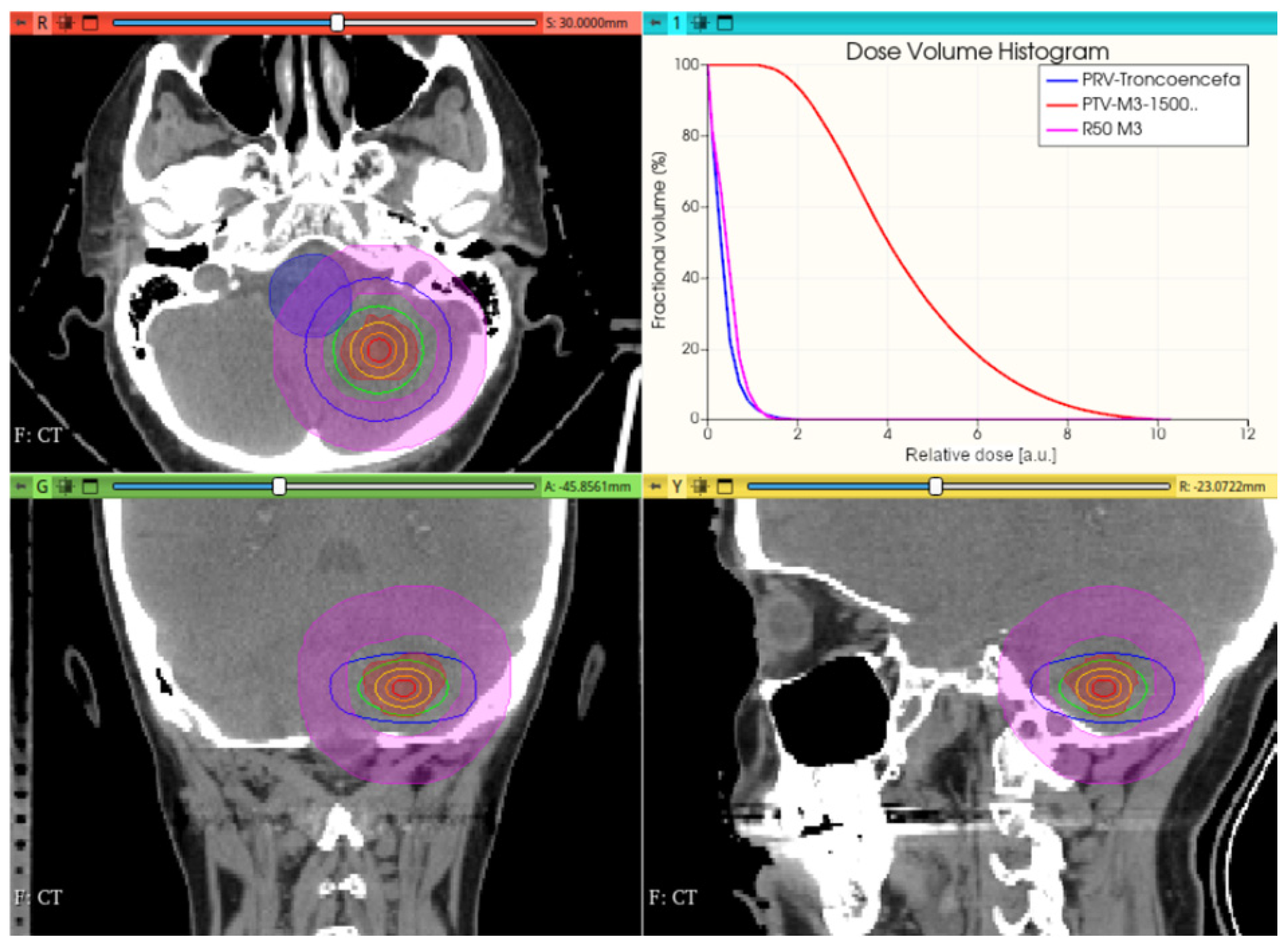
3.3.1. Preliminary CONVERAY Dosimetry Performance for Intracranial Irradiations
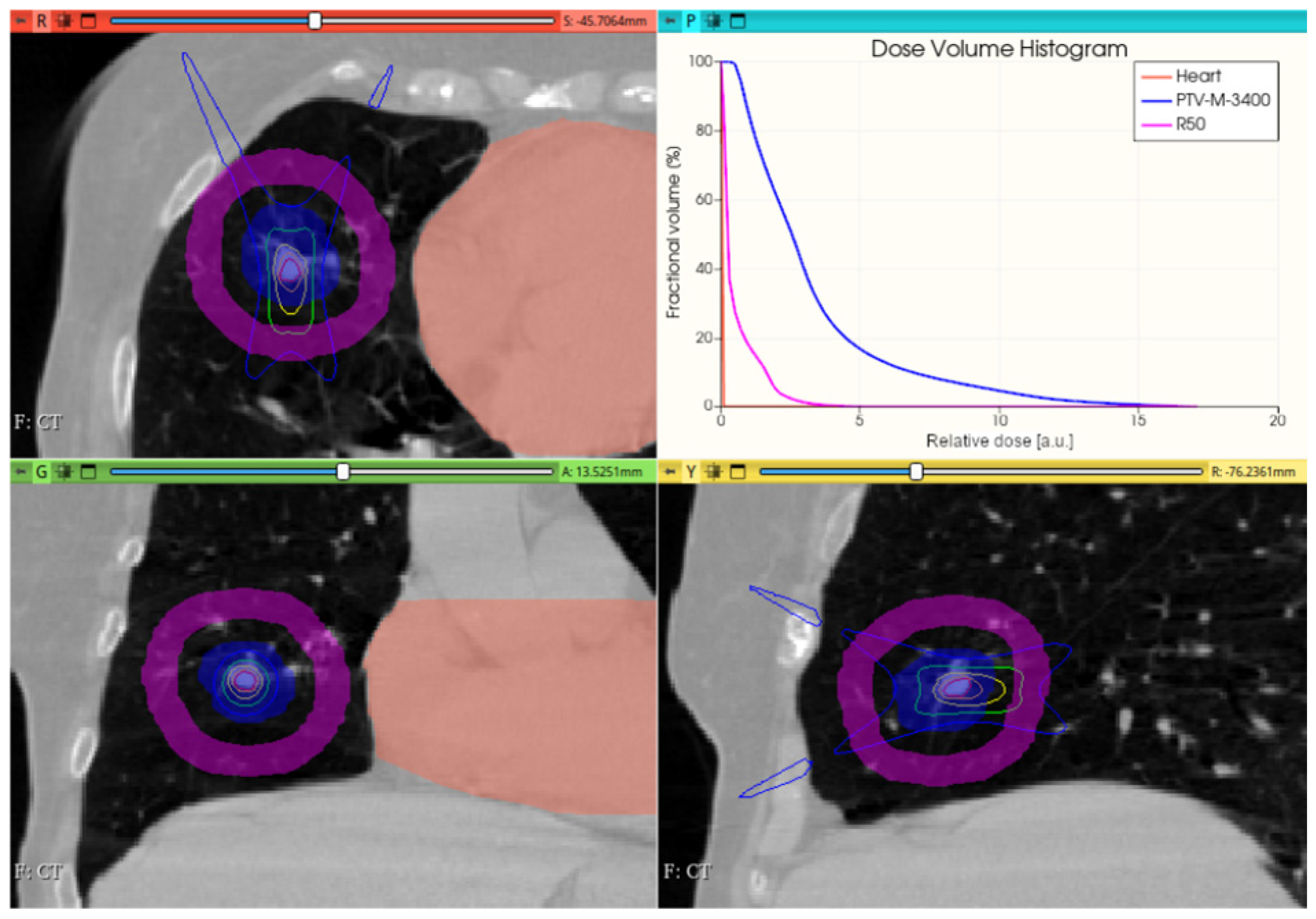
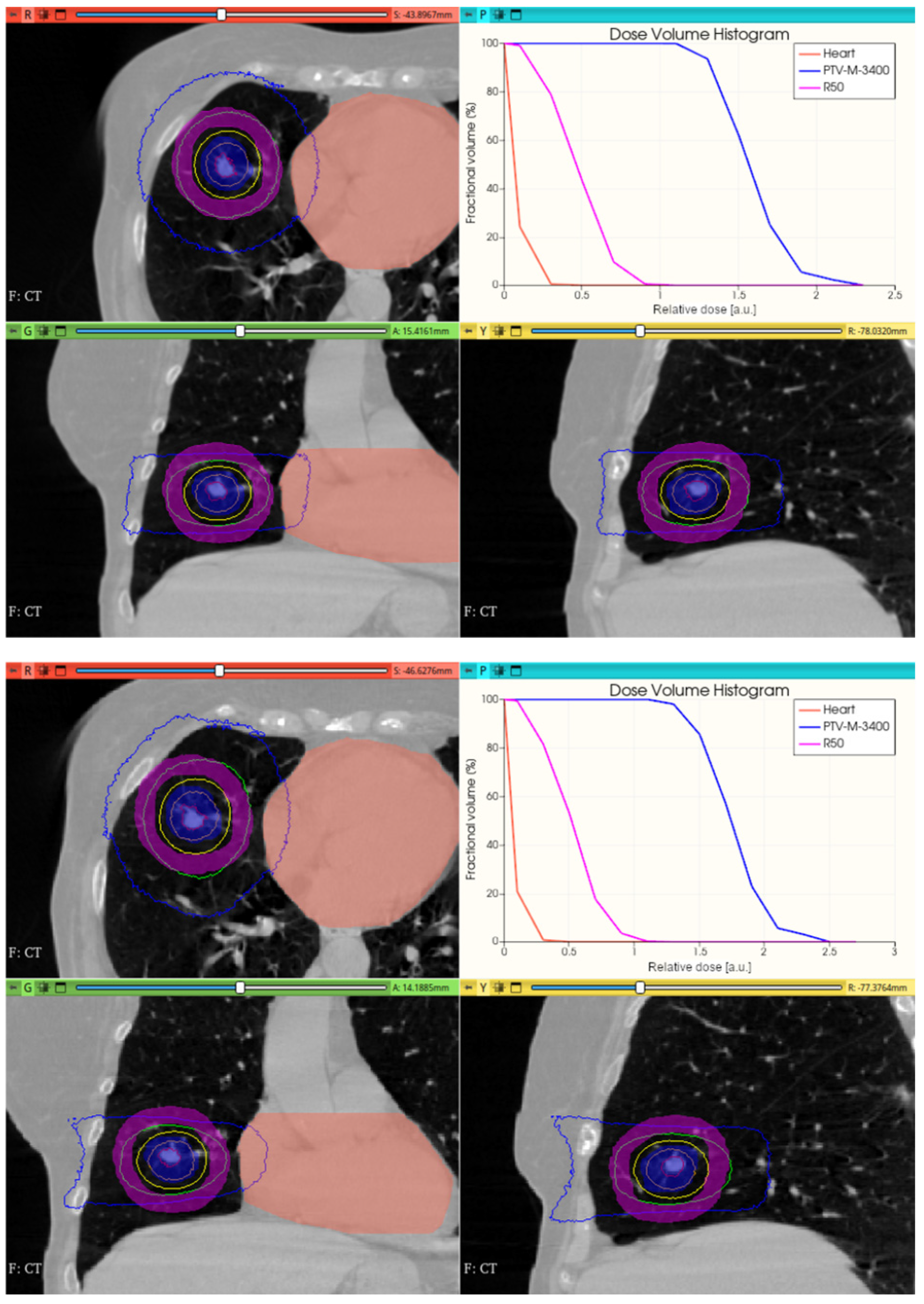
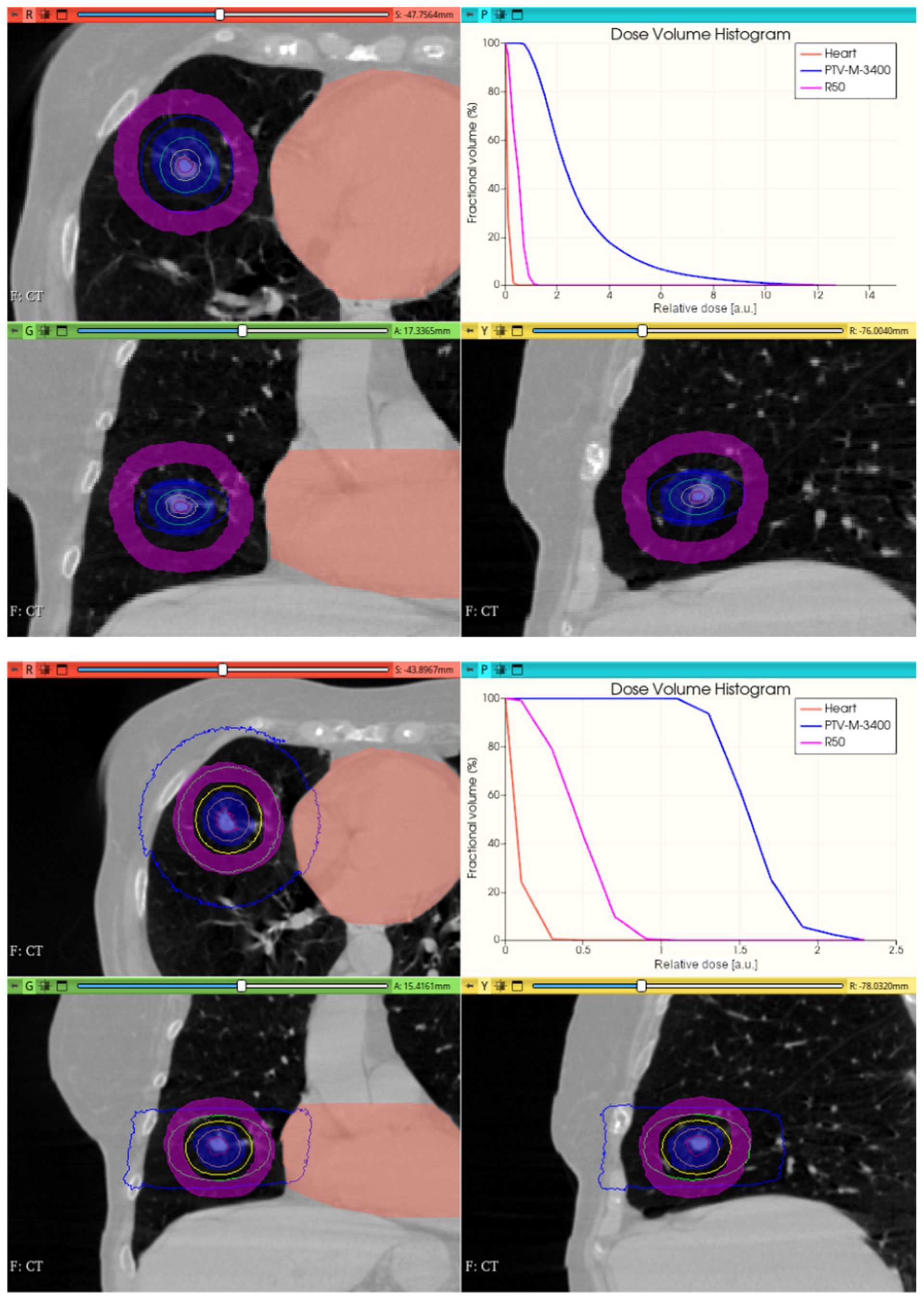
3.3.2. Preliminary CONVERAY Dosimetry Performance for Thoracic Irradiations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirai, K.; Aoki, S.; Endo, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Fukuda, Y.; Akahane, K.; Musha, A.; Sato, H.; Wakatsuki, M.; Ishikawa, H.; et al. Recent developments in the field of radiotherapy for the management of lung cancer. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2025, 43, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, L.; Stephans, K.L. Advances in external beam radiation for hepatocellular carcinoma, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and particle therapy. Hepat. Res. 2024, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.-S. Current perspectives on radiotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma management: A comprehensive review. J. Liver Cancer 2024, 24, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H. Range uncertainties in proton therapy and the role of Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, R99–R117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Mishra, M.; Mehta, M.P. A systematic review of the cost and cost-effectiveness studies of proton radiotherapy. Cancer 2015, 122, 1483–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkoski, D.A.; Bar-David, A.; Kleckner, M.; Mirkovic, M.; Tailor, R.; Moradi-Kurdestany, J.; Borukhin, S.; Harel, Z.; Burshtein, Z.; Zuck, A.; et al. Analysis of a novel X-ray lens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, R.G.; Valente, M. Physical characterization of single convergent beam device for teletherapy: Theoretical and Monte Carlo approach. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 7191–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, R.G.; Valente, M. Convergent Photon and Electron Beam Generator Device. U.S. patent US20140112451A1, 19 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bodensohn, R.; Maier, S.H.; Belka, C.; Minniti, G.; Niyazi, M. Stereotactic Radiosurgery of Multiple Brain Metastases: A Review of Treatment Techniques. Cancers 2023, 15, 5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendee, W.R. Monte Carlo Techniques in Radiation Therapy; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Andreo, P. Monte Carlo techniques in medical radiation physics. Phys. Med. Biol. 1991, 36, 861–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreo, P.; Burns, D.T.; Nahum, A.E.; Seuntjens, J.; Attix, F.H. Fundamentals of Ionizing Radiation Dosimetry, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Andreo, P. Monte Carlo simulations in radiotherapy dosimetry. Rad. Oncol. 2018, 13, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, G. CyberKnife: A new paradigm in radiotherapy. J. Med. Phys. 2010, 35, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez Doblado, F.; Leal, A.; Perucha, M.; Arráns, S.; Núñez, L.; Roselló, J.V.; Sánchez-Nieto, B.; Carrasco, E.; Gonzalez, A.; Medrano, J.C.; et al. Monte carlo clinical dosimetry. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiot. 2002, 7, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Botta, F.; Mairani, A.; Hobbs, R.F.; Vergara Gil, A.; Pacilio, M.; Parodi, K.; Cremonesi, M.; Coca Pérez, M.A.; Di Dia, A.; Ferrari, M. Use of the FLUKA Monte Carlo code for 3D patient-specific dosimetry on PET-CT and SPECT-CT images. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 58, 7191–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhlen, T.T.; Cerutti, F.; Chin, M.P.W.; Fassò, A.; Ferrari, A.; Ortega, P.G.; Mairani, A.; Sala, P.R.; Smirnov, G.; Vlachoudis, V. The FLUKA Code: Developments and Challenges for High Energy and Medical Applications. Nucl. Data Sheets 2014, 120, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempau, J.; Acosta, E.; Baro, J.; Fernández-Varea, J.M.; Salvat, F. An algorithm for Monte Carlo simulation of coupled elec-tron-photon transport. Nucl. Instum. Meth. B 1997, 132, 377–390. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, R.G.; Rojas, L.; Valente, M. Trajectory control of electron beams using high intensity permanent magnets for linac-adaptable convergent beam radiotherapy. Appl. Rad. Isot. 2019, 151, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, R.G.; Leiva, J.; Moncada, R.; Rojas, L.; Santibáñez, M.; Valente, A.; Velásquez, J.; Young, H.; Zelada, G.; Yáñez, R.; et al. Theory, simulation and experiments for precise deflection control of radiotherapy electron beams. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2018, 141, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Baskar, R.; Lee, R.A.; Yeo, R.; Yeoh, K.-W. Cancer and radiation therapy: Current advances and future directions. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, S.F.; Yenice, K.M.; Followill, D.; Galvin, J.M.; Hinson, W.; Kavanagh, B.; Keall, P.; Lovelock, M.; Meeks, S.; Papiez, L.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy: The report of AAPM Task Group 101. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 4078–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.J.; Daly, M.E.; Kennedy, E.B.; Antonoff, M.B.; Broderick, S.; Feldman, J.; Jolly, S.; Meyers, B.; Rocco, G.; Rusthoven, C.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation Oncology Evidence-Based Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 36, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortfeld, T. IMRT: A review and preview. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, R363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygogianni, A.; Koukourakis, I.M.; Georgakopoulos, J.; Armpilia, C.; Liakouli, Z.; Desse, D.; Ntoumas, G.; Simopoulou, F.; Nikoloudi, M.; Kouloulias, V. Robotic Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Patients with Early-Stage Lung Cancer: Results of an Interim Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.; Heijmen, B.J.M.; Verellen, D.; Nisbet, A. Automation in intensity modulated radiotherapy treatment planning-a review of recent innovations. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 2018027010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedenberg, M.; Beltran, C.; Mairani, A.; Alber, M. Advanced Treatment Planning. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, e1011–e1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flickinger, J.D.; Kondziolka, D.; Lunsford, L.D.; Pollock, B.E.; Yamamoto, M.; Gorman, D.A.; Schomberg, P.J.; Sneed, P.; Larson, D.; Smith, V.; et al. A multi-institutional analysis of complication outcomes after arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1999, 44, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Takahashi, W.; Haga, A.; Kida, S.; Saotome, N.; Nakagawa, K. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Small Lung Tumors in the University of Tokyo Hospital. BioMed Res. Intern. 2014, 2014, 136513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusthoven, K.E.; Kavanagh, B.D.; Cardenes, H.; Stieber, V.W.; Burri, S.H.; Feigenberg, S.J.; Chidel, M.A.; Pugh, T.J.; Franklin, W.; Kane, M.; et al. Multi-institutional phase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Bishop, A.J.; Brownlee, Z.; Allen, P.K.; Settle, S.H.; Chang, E.L.; Wang, X.; Amini, B.; Tannir, N.M.; Tatsui, C.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Spinal Metastases in the Postoperative Setting: A Secondary Analysis of Mature Phase 1-2 Trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 2957, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable/Stage | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | Final Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <Eel>/FWHM (Eel) [MeV] | 6.0/0.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/0 |
| 5.9/0.1 | 1.7/0 | 1.7/0 | 1.7/0 | 1.7/0 | 1.7/0 | 2.5/2.9 | 2.5/2.9 | 3.2/3.4 | |
| 6.1/0.1 | 1.6/0 | 1.6/0 | 1.6/0 | 1.6/0 | 1.6/0 | 2.4/2.8 | 2.4/2.8 | 3.1/3.3 | |
| 6.0/0.3 | 0/200 | 0/200 | 0/200 | 0/200 | 0/200 | 0/200 | 4.1/272 | 15.7/488 | |
| αβεαμ/ΦΩHΜα [δεγ] | 0.0/0.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/0 |
| 0.0/0.1 | 0/0.9 | 0/1.4 | 0/3.6 | 0/0.9 | 6.3/14.1 | 10.2/38.1 | 11.1/49.2 | 16.3/64.6 | |
| 0.0/1.0 | 0/95.9 | 0/148 | 0/206 | 341/565 | 1735/7912 | - | - | - | |
| 1.0/0.0 | 2.4/1.2 | 2.6/1.6 | 3.3/59.7 | 11.9/241 | 73/618 | 269/6431 | - | - |
| Simulation Setup | Eabs [eV] | NTot | ft | ∆D [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (6.0 ± 0.1) MeV αbeam = FWHMα = 0 | (1 × 104, 1 × 104) | 2 × 109 | - | - |
| (6.0 ± 0.1) MeV αbeam = FWHMα = 0 | (1 × 104, 1 × 104) | 2 × 108 | 0.12 | 3.1% |
| (6.0 ± 0.1) MeVαbeam = FWHMα = 0 | (1 × 104, 1 × 104) | 2 × 107 | 0.0118 | 8.6% |
| (6.0 ± 0.1) MeV αbeam = FWHMα = 0 | (1 × 104, 1 × 104) | 2 × 106 | 0.001059 | 27.1% |
| (6.0 ± 0.1) MeV αbeam = FWHMα = 0 | (1 × 104, 1 × 104) | 2 × 105 | 0.00011471 | 68.4% |
| (6.0 ± 0.1) MeV αbeam = FWHMα = 0 | (1 × 105, 1 × 104) | 2 × 109 | 0.00001673 | 2.8% |
| (6.0 ± 0.1) MeV αbeam = FWHMα = 0 | (1 × 103, 1 × 104) | 2 × 109 | 1.0748 | 2.1% |
| (6.0 ± 0.1) MeV αbeam = FWHMα = 0 | (1 × 104, 1 × 103) | 2 × 109 | 1.00311 | 1.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Figueroa, R.; Malano, F.; Cuadra, A.; Guarda, J.; Leiva, J.; Leyton, F.; López, A.; Solé, C.; Valente, M. Development and Validation of Monte Carlo Methods for Converay: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071189
Figueroa R, Malano F, Cuadra A, Guarda J, Leiva J, Leyton F, López A, Solé C, Valente M. Development and Validation of Monte Carlo Methods for Converay: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071189
Chicago/Turabian StyleFigueroa, Rodolfo, Francisco Malano, Alejandro Cuadra, Jaime Guarda, Jorge Leiva, Fernando Leyton, Adlin López, Claudio Solé, and Mauro Valente. 2025. "Development and Validation of Monte Carlo Methods for Converay: A Proof-of-Concept Study" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071189
APA StyleFigueroa, R., Malano, F., Cuadra, A., Guarda, J., Leiva, J., Leyton, F., López, A., Solé, C., & Valente, M. (2025). Development and Validation of Monte Carlo Methods for Converay: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Cancers, 17(7), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071189






