Trends in Efficacy Endpoints in Phase II Glioblastoma Trials: A Regulatory Science Analysis (FY2020–FY2022)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
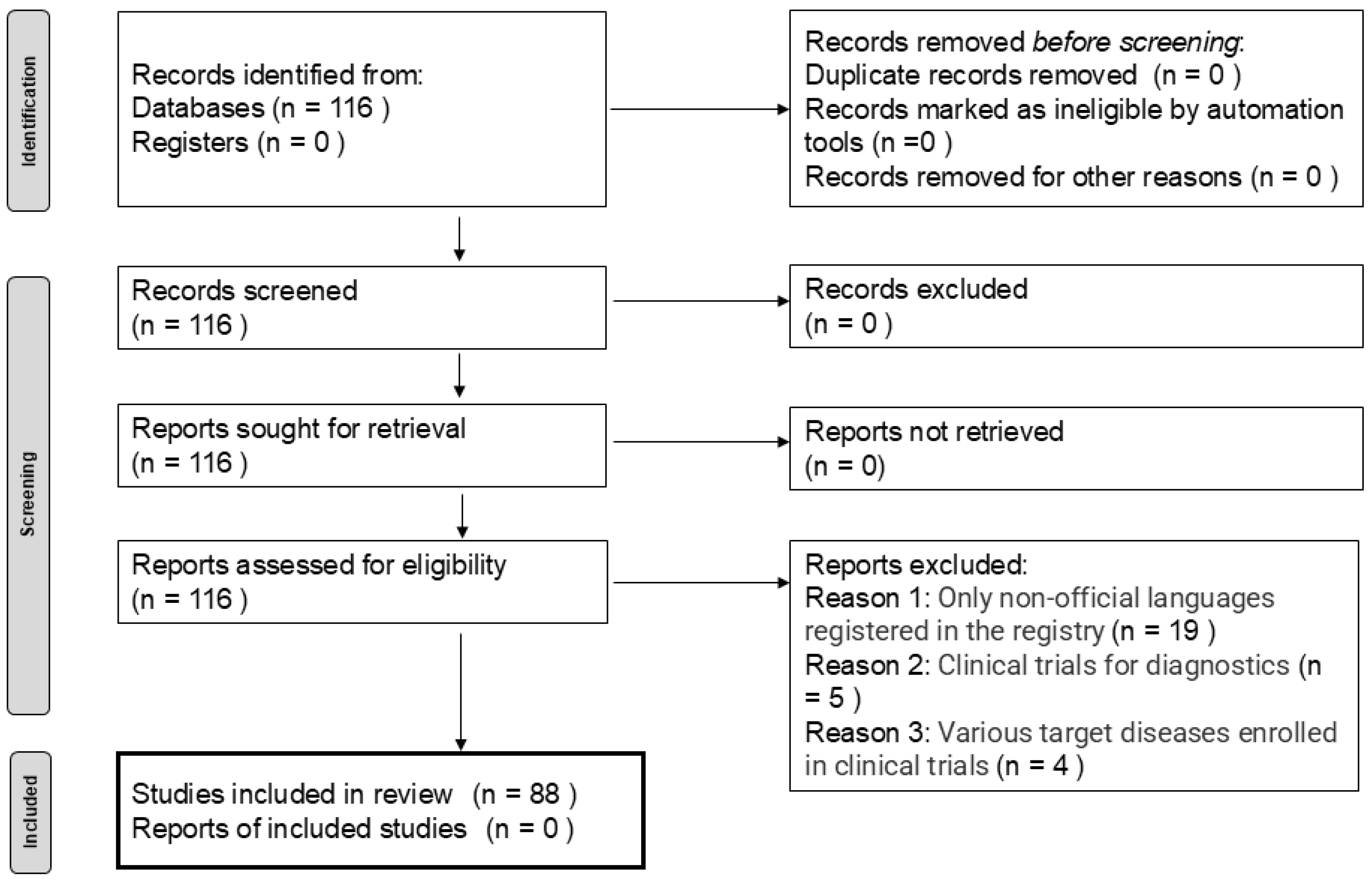
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Primary and Secondary Efficacy Endpoints
3.3. Clinical Trial Settings for Efficacy Endpoints
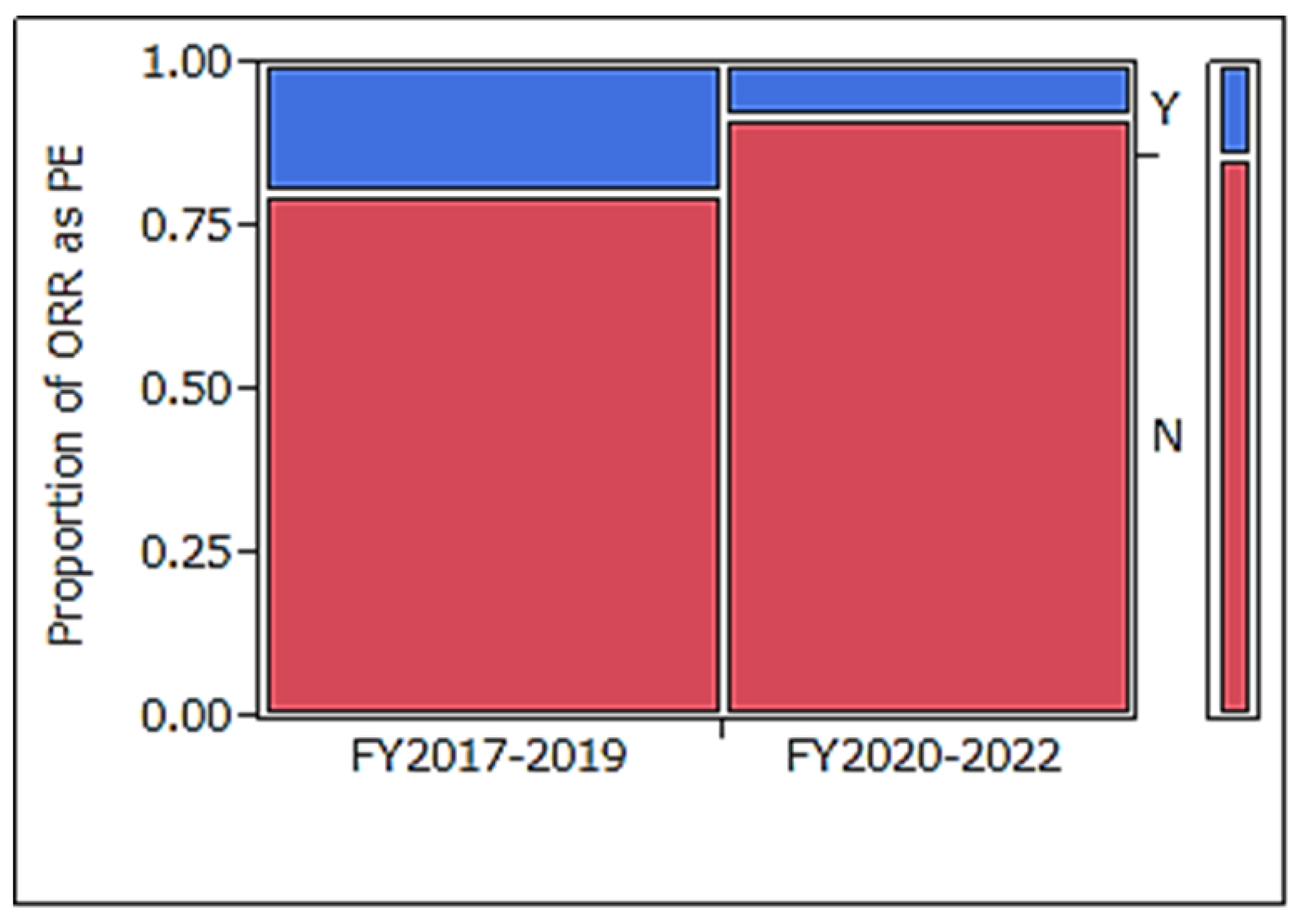
3.4. Comparison of Efficacy Primary Endpoint with Clinical Trials Started in FY2017–2019
4. Discussion
4.1. Were Recent Endpoint Settings Affected by the Study Design of the Trial?
4.1.1. Type of Clinical Trial Item
4.1.2. Target Patient Segment
4.1.3. Trial Design: Randomized Double-Blinded Clinical Trial or Not
4.2. What Are the Reasons for the Changes in Trial Endpoints, and the Pros and Cons of Those Changes?
4.3. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FY | Fiscal Year |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| PE | Primary Endpoint |
| SE | Secondary Endpoint |
| ORR | Objective Response Rate |
| RECIST | Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors |
| RANO | Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology |
| iRANO | Immunotherapy Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology |
| TTE | Time-to-Event |
| JMP | (Software used for statistical analysis, developed by SAS Institute) |
| SAS | Statistical Analysis System |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Minami, H.; Kiyota, N.; Kimbara, S.; Ando, Y.; Shimokata, T.; Ohtsu, A.; Fuse, N.; Kuboki, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Guidelines for clinical evaluation of anti-cancer drugs. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 2563–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therasse, P.; Eisenhauer, E.A.; Verweij, J. RECIST revisited: A review of validation studies on tumour assessment. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Nonaka, T.; Maeda, M. Fact-finding research on efficacy endpoints in recent Phase II clinical trials targeting glioblastoma. Pharm. Dev. Regul. Sci. 2021, 52, 358–367, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, T.R.; Powers, J.H. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints in clinical trials. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 2973–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Nonaka, T.; Maeda, M.; Sugii, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Takano, S.; Koyanagi, T.; Yamada, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Ishikawa, E. Efficacy endpoints in phase II clinical trials for meningioma: An analysis of recent clinical trials. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2023, 57, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Nonaka, T.; Maeda, M.; Yamada, M.; Sugii, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Takano, S.; Koyanagi, T.; Arakawa, Y.; Ishikawa, E. Recent status of Phase I clinical trials for brain tumors: A regulatory science study of exploratory efficacy endpoints. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2024, 58, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shergalis, A.; Bankhead, A.; Luesakul, U.; Muangsin, N.; Neamati, N. Current challenges and opportunities in treating glioblastoma. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 412–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuka, S.; Van Meir, E.G. Overcoming therapeutic resistance in glioblastoma: The way forward. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.C.; Ashley, D.M.; López, G.Y.; Malinzak, M.; Friedman, H.S.; Khasraw, M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; Macdonald, D.R.; Reardon, D.A.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Sorensen, A.G.; Galanis, E.; Degroot, J.; Wick, W.; Gilbert, M.R.; Lassman, A.B.; et al. Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: Response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Weller, M.; Huang, R.; Finocchiaro, G.; Gilbert, M.R.; Wick, W.; Ellingson, B.M.; Hashimoto, N.; Pollack, I.F.; Brandes, A.A.; et al. Immunotherapy response assessment in neuro-oncology: A report of the RANO working group. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e534–e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Brandes, A.A.; Peereboom, D.M.; Galanis, E.; Lin, N.U.; Soffietti, R.; Macdonald, D.R.; Chamberlain, M.; Perry, J.; et al. The Neurologic Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (NANO) scale: A tool to assess neurologic function for integration into the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria. Neuro. Oncol. 2017, 19, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, S.I.; Nonoguchi, N.; Furuse, M.; Yoritsune, E.; Miyata, T.; Kawabata, S.; Kuroiwa, T. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of radiation necrosis in the brain. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2015, 55, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain Tumor Registry of Japan. Report of Brain Tumor Registry of Japan (2005–2008). Neurol. Med. Chir. 2017, 57, 9–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondy, M.L.; Scheurer, M.E.; Malmer, B.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Davis, F.G.; Il’yasova, D.; Kruchko, C.; McCarthy, B.J.; Rajaraman, P.; Schwartzbaum, J.A.; et al. Brain tumor epidemiology: Consensus from the Brain Tumor Epidemiology Consortium. Cancer 2008, 113, 1953–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, W.K.; Albright, R.E.; Olson, J.; Fredericks, R.; Fink, K.; Prados, M.D.; Brada, M.; Spence, A.; Hohl, R.J.; Shapiro, W.; et al. A phase II study of temozolomide vs. procarbazine in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, W.K.; Prados, M.D.; Yaya-Tur, R.; Rosenfeld, S.S.; Brada, M.; Friedman, H.S.; Albright, R.; Olson, J.; Chang, S.M.; O’Neill, A.M.; et al. Multicenter phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with anaplastic astrocytoma or anaplastic oligoastrocytoma at first relapse. Temodal Brain Tumor Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 2762–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brada, M.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Rampling, R.; Dietrich, P.Y.; Dirix, L.Y.; Macdonald, D.; Heimans, J.J.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; Bravo-Marques, J.M.; Henriksson, R.; et al. Multicenter phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todo, T.; Ito, H.; Ino, Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Ota, Y.; Shibahara, J.; Tanaka, M. Intratumoral oncolytic herpes virus G47∆ for residual or recurrent glioblastoma: A phase 2 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Nishikawa, R.; Sugiyama, K.; Nonoguchi, N.; Kawabata, N.; Mishima, K.; Adachi, J.I.; Kurisu, K.; Yamasaki, F.; Tominaga, T.; et al. A multicenter phase I/II study of the BCNU implant (Gliadel® Wafer) for Japanese patients with malignant gliomas. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2014, 54, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Loong, H.H.; Summers, Y.; Thomas, Z.M.; French, P.; Lin, B.K.; Sashegyi, A.; Wolf, J.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Drilon, A. Correlation between treatment effects on response rate and progression-free survival and overall survival in trials of targeted therapies in molecularly enriched populations. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batich, K.A.; Mitchell, D.A.; Healy, P.; Herndon, J.E.; Sampson, J.H. Once, Twice, Three Times a Finding: Reproducibility of Dendritic Cell Vaccine Trials Targeting Cytomegalovirus in Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5297–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; van den Bent, M.; Youssef, G.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Ellingson, B.M.; Weller, M.; Galanis, E.; Barboriak, D.P.; de Groot, J.; Gilbert, M.R.; et al. RANO 2.0: Update to the response assessment in neuro-oncology criteria for high- and low-grade gliomas in adults. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5187–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, B.M.; Bendszus, M.; Boxerman, J.; Barboriak, D.; Erickson, B.J.; Smits, M.; Nelson, S.J.; Gerstner, E.; Alexander, B.; Goldmacher, G.; et al. Consensus recommendations for a standardized Brain Tumor Imaging Protocol in clinical trials. Neuro-Oncol. 2015, 17, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; van den Bent, M.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Chang, S.M. RANO 2.0: The revised Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria for high- and low-grade glial tumors in adults designed for the future. Neuro Oncol. 2024, 26, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickingereder, P.; Isensee, F.; Tursunova, I.; Petersen, J.; Neuberger, U.; Bonekamp, D.; Brugnara, G.; Schell, M.; Kessler, T.; Foltyn, M.; et al. Automated quantitative tumour response assessment of MRI in neuro-oncology with artificial neural networks: A multicentre, retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, A.G.; Louis, D.N.; Poussaint, T.Y.; Linscott, L.L.; Salzman, K.L. The 2021 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: What Neuroradiologists Need to Know. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 43, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Category | Number of Trials (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Patient segmentation | Newly diagnosed | 44 (50) |
| Recurrent | 42 (48) | |
| Both | 2 (2) | |
| Item category | Pharmaceutical | 51 (58) |
| Multiple combinations | 11 (13) | |
| Biological product | 8 (9) | |
| Medical device | 6 (7) | |
| Radiotherapy | 5 (6) | |
| Supplement | 3 (3) | |
| Treatment procedure change | 2 (2) | |
| Others | 2 (2) | |
| Region * | USA | 29 (33) |
| China | 21 (24) | |
| Germany | 4 (5) | |
| Italy | 3 (3) | |
| Japan | 2 (2) | |
| Canada | 2 (2) | |
| France | 2 (2) | |
| Israel | 2 (2) | |
| Switzerland | 2 (2) | |
| Others ** | 18 (20) | |
| Organization(s) | Academia | 48 (55) |
| Academia + company | 21 (24) | |
| Company | 12 (14) | |
| Academia + government | 4 (5) | |
| Government | 3 (3) |
| Category | Numbers (Median, Min–Max) |
|---|---|
| Trial arm numbers (arm) | 1, 1–4 |
| Trial sites (sites) | 1, 1–545 |
| Planned trial duration * (months) | 38, 8–118 |
| Enrolment patients (persons) | 39, 1–640 |
| Category | Numbers of Endpoint (%) |
|---|---|
| PFS | 22 (22) |
| OS | 20 (20) |
| PFS rate | 17 (17) |
| Immunological marker/tumor cell | 13 (13) |
| OS rate | 11 (11) |
| ORR | 7 * (7) |
| DOR | 3 (3) |
| Neurological outcome | 3 (3) |
| Anxiety | 2 (2) |
| RFS | 1 (1) |
| DRR | 1 (1) |
| Others | 1 (1) |
| Category | Numbers of Endpoint (%) |
|---|---|
| OS | 45 (15) |
| PFS | 44 (15) |
| QOL | 43 (14) |
| Immunological marker/tumor cell | 35 (12) |
| ORR | 32 ** (11) |
| Neurological outcome | 15 (5) |
| PFS rate | 13 (4) |
| Cognitive function | 12 (4) |
| DCR | 9 (3) |
| OS rate | 8 (3) |
| DOR | 7 (2) |
| Volume | 5 (2) |
| Anxiety | 2 (1) |
| RFS | 2 (1) |
| EFS | 2 (1) |
| Others | 25 (8) |
| Design Type of Trials | Number of Trials (%) |
|---|---|
| Multiple efficacy endpoints | 28 (32) |
| ORR * | 7 (8) |
| TTE outcome | 63 (72) ** |
| Design Type of Trials | Number of Trials (%) |
|---|---|
| Multiple efficacy endpoints | 77 (99) |
| ORR ** | 35 *** (45) |
| TTE outcome | 72 (92) **** |
| FY2017–2019 | FY2020–2022 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 0.13 ** | ||
| median (Min–Max) | 1, 0–5 | 1, 0–7 | |
| average ± SD | 1.21 ± 0.57 | 1.15 ± 0.93 | |
| Types of endpoints | OS 29% | PFS 22% | 0.022 **** |
| ORR 20% | OS 20% | ||
| PFS 17% | PFS rate 17% | ||
| OS rate 10% | Immunological/tumor marker 13% | ||
| PFS rate 9% | OS rate 11% | ||
| Others 14% | ORR 7% | ||
| DOR 3% | |||
| Neurological outcome 3% | |||
| Anxiety 2% | |||
| RFS 1% | |||
| DRR 1% | |||
| Others 1% | |||
| Proportion of RANO + iRANO in ORR * | 13 **/16 (81%) | 7 ***/7 (100%) | 0.52 ***** |
| Pharmaceuticals Alone | Not | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number median (Min–Max) average ± SD | efficacy PE | 1 (0–7) 1.18 ± 1.03 | 1 (0–4) 1.11 ± 0.77 | 0.053 |
| efficacy SE * | 3 (1–11) 3.50 ± 2.15 | 4 (1–12) 4.41 ± 2.78 | 0.13 | |
| ORR | efficacy PE | 8% (4/51) | 8% (3/37) | 1.00 |
| efficacy PE + SE * | 45% (20/44) | 44% (15/34) | 1.00 | |
| TTE outcome | efficacy PE | 75% (38/51) | 68% (25/37) | 0.48 |
| efficacy PE + SE * | 91% (40/44) | 94% (32/34) | 0.48 | |
| Newly Diagnosed | Recurrent | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number median (Min–Max) average ± SD | efficacy PE | 1 (0–4) 0. 98 ± 0.73 | 1 (0–7) 1.33 ± 1.07 | 0.046 |
| efficacy SE ** | 4 (1–11) 3.90 ± 2.17 | 3 (1–12) 3.81 ± 2.79 | 0.42 | |
| ORR | efficacy PE | 0 | 17% (7/42) | 0.050 |
| efficacy PE + SE ** | 27% (11/41) | 64% (23/36) | 0.0014 | |
| TTE outcome | efficacy PE | 68% (30/44) | 79% (33/42) | 0.33 |
| efficacy PE + SE ** | 88% (36/41) | 97% (35/36) | 0.21 | |
| Randomized Double-Blinded Clinical Trial | Not | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number median (Min–Max) average ± SD | efficacy PE | 1 (1–2) 1.38 ± 0.52 | 1 (0–7) 1.13 ± 0.96 | 0.10 |
| efficacy SE * | 2 (1–4) 2.13 ± 1.13 | 4 (1–12) 4.10 ± 2.50 | 0.016 | |
| ORR | efficacy PE | 0 | 9% (7/80) | 1.00 |
| efficacy PE + SE * | 13% (1/8) | 49% (34/70) | 0.070 | |
| TTE outcome | efficacy PE | 75% (6/8) | 71% (57/80) | 1.00 |
| efficacy PE + SE * | 88% (7/8) | 93% (65/70) | 0.49 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, S.; Maeda, M.; Sugii, N.; Yamada, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Ishikawa, E. Trends in Efficacy Endpoints in Phase II Glioblastoma Trials: A Regulatory Science Analysis (FY2020–FY2022). Cancers 2025, 17, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050855
Watanabe S, Maeda M, Sugii N, Yamada M, Arakawa Y, Nakamura K, Hashimoto K, Ishikawa E. Trends in Efficacy Endpoints in Phase II Glioblastoma Trials: A Regulatory Science Analysis (FY2020–FY2022). Cancers. 2025; 17(5):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050855
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Shinya, Makoto Maeda, Narushi Sugii, Masanobu Yamada, Yoshihiro Arakawa, Kimika Nakamura, Koichi Hashimoto, and Eiichi Ishikawa. 2025. "Trends in Efficacy Endpoints in Phase II Glioblastoma Trials: A Regulatory Science Analysis (FY2020–FY2022)" Cancers 17, no. 5: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050855
APA StyleWatanabe, S., Maeda, M., Sugii, N., Yamada, M., Arakawa, Y., Nakamura, K., Hashimoto, K., & Ishikawa, E. (2025). Trends in Efficacy Endpoints in Phase II Glioblastoma Trials: A Regulatory Science Analysis (FY2020–FY2022). Cancers, 17(5), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050855






