Evaluation of an IDH1/2 Mutation FastTrack Assay for Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collective of Patients
2.2. NGS Diagnostics
2.3. IdyllaTM IDH1-2 Mutation Testing
- i.
- IDH1: p.Arg132His, p.Arg132Cyc, p.Arg132Gly, p.Arg132Ser, p.Arg132Leu;
- ii.
- IDH2: p.Arg140Gln, p.Arg140Trp, p.Arg140Leu, p.Arg140Gly, p.Arg172Lys, p.Arg172Met, p.Arg172Gly, p.Arg172Ser, p.Arg172Trp.
- i.
- Mutation status (positive/negative for IDH1/2 mutations);
- ii.
- Cycle threshold (Cq) values from the real-time PCR analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Results Obtained by NGS as a Comparative Method
3.2. Overall Performance of the IdyllaTM IDH1-2 Mutation Assay Kit
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krebs in Deutschland—Gallenblase Gallenwege, Zentrum für Krebsregisterdaten. Available online: https://www.krebsdaten.de/Krebs/DE/Content/Publikationen/Krebs_in_Deutschland/kid_2023/kid_2023_c23_c24_gallenblase.pdf?__blob=publicationFile (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Tyson, G.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2011, 54, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeOliveira, M.L.; Cunningham, S.C.; Cameron, J.L.M.; Kamangar, F.; Winter, J.M.; Lillemoe, K.D.M.; Choti, M.A.M.; Yeo, C.J.M.; Schulick, R.D.M. Cholangiocarcinoma: Thirty-one-year experience with 564 patients at a single institution. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, D.; Ferstl, P.; Waidmann, O.; Trojan, J.; Hartmann, S.; Schnitzbauer, A.A.; Zeuzem, S.; Kraywinkel, K. Cholangiocarcinoma in Germany: Epidemiologic trends and impact of misclassification. Liver Int. 2018, 39, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, T.; Verheij, J.; Gaudio, E.; Evert, M.; Guido, M.; Goeppert, B.; Carpino, G. Anatomical, histomorphological and molecular classification of cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39 (Suppl. S1), 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishima, S.; Oda, Y. Pathogenesis and classification of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Different characters of perihilar large duct type versus peripheral small duct type. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2015, 22, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liau, J.-Y.; Tsai, J.-H.; Yuan, R.-H.; Chang, C.-N.; Lee, H.-J.; Jeng, Y.-M. Morphological subclassification of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Etiological, clinicopathological, and molecular features. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, A.; Misumi, K.; Shibahara, J.; Arita, J.; Sakamoto, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Kokudo, N.; Fukayama, M. Distinct Clinicopathologic and Genetic Features of 2 Histologic Subtypes of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Bridgewater, J.; Edeline, J.; Kelley, R.; Klümpen, H.; Malka, D.; Primrose, J.; Rimassa, L.; Stenzinger, A.; Valle, J.; et al. Biliary tract cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koerkamp, B.G.; Fong, Y. Outcomes in biliary malignancy. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 110, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitler, E. The journal of CardioVascular and Interventional Radiology. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 1990, 13, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kwong, L.N. IDH1 Inhibition Reawakens the Immune Response against Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 604–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshidfar, F.; Zheng, S.; Gingras, M.-C.; Newton, Y.; Shih, J.; Robertson, A.G.; Hinoue, T.; Hoadley, K.A.; Gibb, E.A.; Roszik, J.; et al. Integrative Genomic Analysis of Cholangiocarcinoma Identifies Distinct IDH-Mutant Molecular Profiles. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 2780–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, L.; White, D.W.; Gross, S.; Bennett, B.D.; Bittinger, M.A.; Driggers, E.M.; Fantin, V.R.; Jang, H.G.; Jin, S.; Keenan, M.C.; et al. Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nature 2009, 462, 739–744, Erratum in Nature 2010, 465, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Q.; Cheng, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; et al. IDH Mutation Subgroup Status Associates with Intratumor Heterogeneity and the Tumor Microenvironment in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzler, M.N.; Jeroch, J.; Klasen, C.; Himmelsbach, V.; Koch, C.; Finkelmeier, F.; Trojan, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Pession, U.; Reis, H.; et al. Impact of IDH1 mutation on clinical course of patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A retrospective analysis from a German tertiary center. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 6391–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel-Jimenez, L.; Frezza, C. Fumarate hydratase (FH) and cancer: A paradigm of oncometabolism. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 129, 1546–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biocartis—The Idylla Platform. Available online: https://www.biocartis.com/en/meet-idylla (accessed on 26 April 2024).
- Delgado-García, M.; Weynand, B.; Gómez-Izquierdo, L.; Hernández, M.J.; Blanco, Á.M.; Varela, M.; Matias-Guiu, X.; Nadal, E.; Márquez-Lobo, B.; Alarcão, A.; et al. Clinical performance evaluation of the Idylla™ EGFR Mutation Test on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Villalba, A.; Ruijter, J.M.; Hoff, M.J.B.v.D. Use and Misuse of Cq in qPCR Data Analysis and Reporting. Life 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion GeneStudioTM S5 Prime System, ThermoFisher Scientifc. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/A38196?SID=srch-srp-A38196 (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Ion Chef Instrument, ThermoFisher Scientific. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/4484177 (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle. Available online: https://www.dakks.de/de/home.html (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Landrum, M.J.; Chitipiralla, S.; Brown, G.R.; Chen, C.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; Kaur, K.; Liu, C.; et al. ClinVar: Improvements to accessing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D835–D844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondka, Z.; Dhir, N.B.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Jupe, S.; Madhumita; McLaren, K.; Starkey, M.; Ward, S.; Wilding, J.; Ahmed, M.; et al. COSMIC: A curated database of somatic variants and clinical data for cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1210–D1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Francioli, L.C.; Goodrich, J.K.; Collins, R.L.; Kanai, M.; Wang, Q.; Alföldi, J.; Watts, N.A.; Vittal, C.; Gauthier, L.D.; et al. A genomic mutational constraint map using variation in 76,156 human genomes. Nature 2024, 625, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehnholz, S.P.; Nissan, M.H.; Zhang, H.; Kundra, R.; Nandakumar, S.; Lu, C.; Carrero, S.; Dhaneshwar, A.; Fernandez, N.; Xu, B.W.; et al. Quantifying the Expanding Landscape of Clinical Actionability for Patients with Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitts, A.; Sherry, S. The Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Database (dbSNP) of Nucleotide Sequence Variation. In The NCBI Handbook; McEntyre, J., Ostell, J., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21088/ (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Dunnen, J.T.; Dalgleish, R.; Maglott, D.R.; Hart, R.K.; Greenblatt, M.S.; McGowan-Jordan, J.; Roux, A.-F.; Smith, T.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Taschner, P.E.; et al. HGVS Recommendations for the Description of Sequence Variants: 2016 Update. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, T. Cholangiocarcinoma—Controversies and challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowery, M.A.; Ptashkin, R.; Jordan, E.; Berger, M.F.; Zehir, A.; Capanu, M.; Kemeny, N.E.; O’Reilly, E.M.; El-Dika, I.; Jarnagin, W.R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Intrahepatic and Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinomas: Potential Targets for Intervention. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4154–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscoe, A.N.; Rolland, C.; Kelley, R.K. Frequency and prognostic significance of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutations in cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic literature review. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 10, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, J.P.; Munoz-Zuluaga, C.; Slocum, C.; Dillard, A.; Cong, L.; Wang, J.; Lindeman, N.; Kluk, M.; Liechty, B.; Pisapia, D.; et al. Evaluation of the rapid Idylla IDH1-2 mutation assay in FFPE glioma samples. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
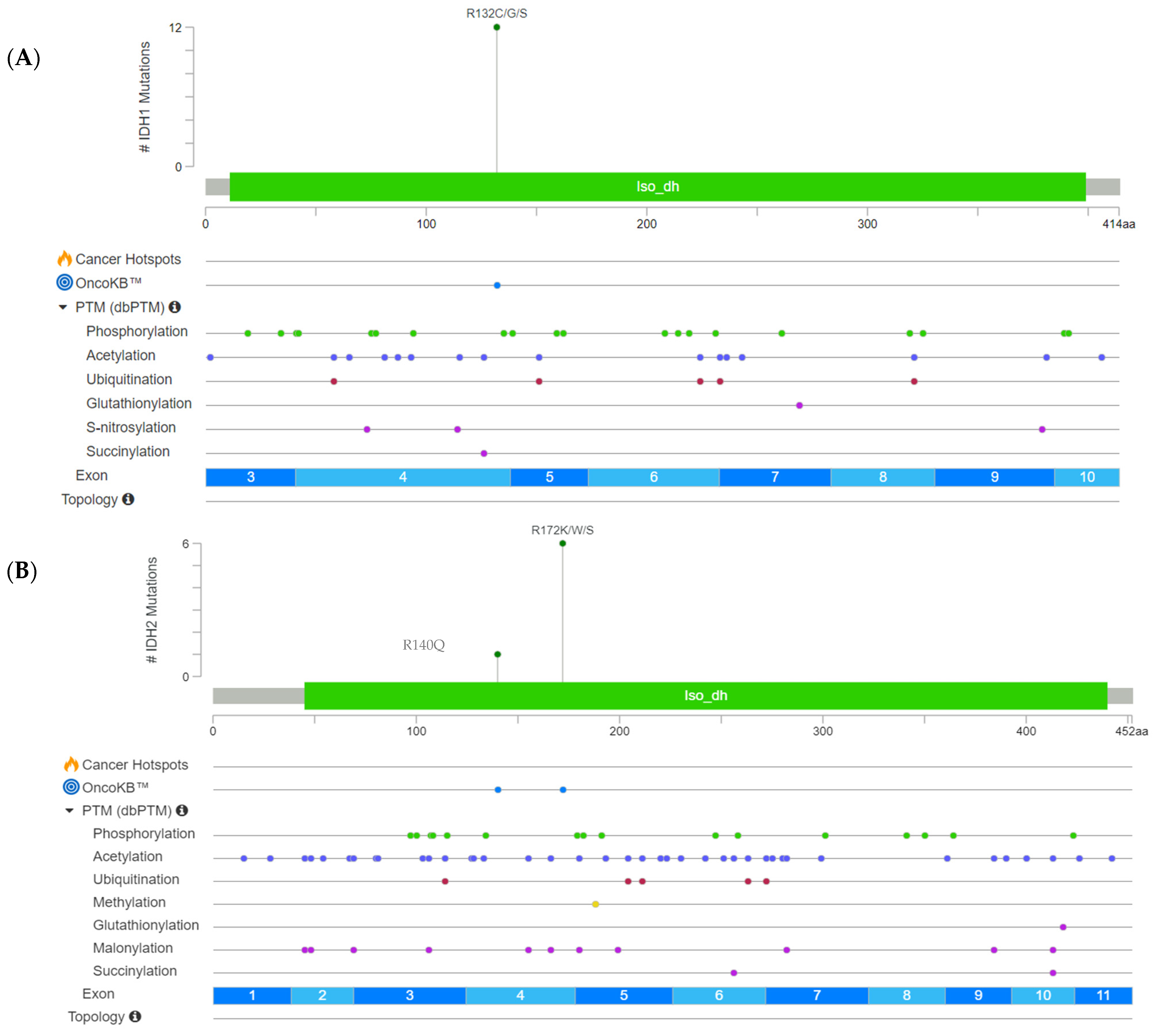
| Study-No. | Gender | Age | TCC [%] | IDH1/2 Status | Nucleotide Substitution | AA Substitution | AF [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 57 | 15 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 15.40 |
| 2 | M | 74 | 15–20 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 15.95 |
| 3 | F | 58 | 20–25 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 17.70 |
| 4 | F | 58 | 40 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 33.03 |
| 5 | M | 40 | 30 | IDH1 | c.394C>G | p.Arg132Gly | 6.00 |
| 6 | M | 60 | 60 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 17.68 |
| 7 | M | 58 | 20 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 9.79 |
| 8 | M | 69 | 70 | IDH1 | c.394C>A | p.Arg132Ser | 54.10 |
| 9 | M | 58 | 30 | IDH2 | c.514A>T | p.Arg172Trp | 66.00 |
| 10 | M | 63 | 50 | IDH2 | c.514A>T | p.Arg172Trp | 21.40 |
| 11 | M | 53 | 60 | IDH2 | c.515G>A | p.Arg172Lys | 32.10 |
| 12 | M | 76 | 15 | Negative | -- | -- | -- |
| 13 | M | 82 | 50 | Negative | -- | -- | -- |
| 14 | M | 60 | 80 | Negative | -- | -- | -- |
| 15 | F | 58 | 80 | Negative | -- | -- | -- |
| 16 | M | 71 | 30 | Negative | -- | -- | -- |
| 17 | M | 83 | 70 | Negative | -- | -- | -- |
| 18 | M | 67 | 70 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 30.50 |
| 19 | M | 75 | 40 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 22.22 |
| 20 | M | 63 | 20 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 19.61 |
| 21 | F | 57 | 20 | IDH1 | c.394C>T | p.Arg132Cys | 32.99 |
| 22 | M | 53 | 75 | IDH2 | c.515G>A | p.Arg172Lys | 52.03 |
| 23 | F | 63 | 45 | IDH2 | c.516G>C | p.Arg172Ser | 20.26 |
| 24 | M | 78 | 60 | IDH2 | c.515G>A | p.Arg172Lys | 36.85 |
| 25 | M | 66 | 40 | IDH2 | c.419G>A | p.Arg140Gln | 8.17 |
| Study-No. | DNA (ng/μL) | NGS | IdyllaTM Biocartis | Codon | Median Cq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.114 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 32.4 |
| 2 | 0.406 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 33.9 |
| 3 | 0.233 | IDH1 | negative | -- | 35.2 * |
| 4 | 1.629 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 31.6 |
| 5 | 1.125 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 33.4 |
| 6 | 0.464 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 34.0 |
| 7 | 0.442 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 34.1 |
| 8 | 8.426 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 31.2 |
| 9 | 1.278 | IDH2 | IDH2 | 172 | 32.9 |
| 10 | 35.490 | IDH2 | IDH2 | 172 | 30.0 |
| 11 | 21.500 | IDH2 | negative | -- | 31.2 |
| 12 | 2.145 | negative | negative | -- | 34.8 |
| 13 | 2.336 | negative | negative | -- | 32.5 |
| 14 | 1.804 | negative | negative | -- | 34.6 |
| 15 | 9.804 | negative | negative | -- | 32.1 |
| 16 | 2.801 | negative | negative | -- | 33.3 |
| 17 | 14.586 | negative | negative | -- | 30.5 |
| 18 | 0.663 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 35.0 |
| 19 | 3.503 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 32.2 |
| 20 | 0.519 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 34.1 |
| 21 | 0.493 | IDH1 | IDH1 | 132 | 35.2 * |
| 22 | 26.660 | IDH2 | IDH2 IDH2 | 140 172 | 29.7 |
| 23 | 0.486 | IDH2 | IDH2 | 172 | 35.1 * |
| 24 | 8.540 | IDH2 | IDH2 | 172 | 32.0 |
| 25 | 2.212 | IDH2 | IDH2 | 140 | 32.7 |
| IdyllaTM vs. NGS | IDH1 | IDH2 |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 91.7% | 83.3% |
| Specificity | 100% | 100% |
| Accuracy | 94.4% | 95.7% |
| Correlation coefficient r(Phi) | 0.8186 | 0.887 |
| Concordance | ||
| Right positive | 91.7% | 85.7% |
| Right negative | 100% | 100% |
| IdyllaTM Biocartis | NGS | |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | quantitaive real-time PCR | sequencing |
| Gene coverage | limited | 95% |
| Time required | <2 h | several days |
| Automation | fully automated | depending on the platform |
| Risk of cross contamination | low, closed system | medium to high |
| Cost/sample | low | high |
| User-friendliness | high, easy to use | technical expertise required |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Winter, M.; Ebner, S.; Scheuber, N.; Schulze, F.; Kinzler, M.N.; Walter, D.; Wild, P.J. Evaluation of an IDH1/2 Mutation FastTrack Assay for Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050820
Winter M, Ebner S, Scheuber N, Schulze F, Kinzler MN, Walter D, Wild PJ. Evaluation of an IDH1/2 Mutation FastTrack Assay for Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(5):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050820
Chicago/Turabian StyleWinter, Melanie, Silvana Ebner, Nina Scheuber, Falko Schulze, Maximilian N. Kinzler, Dirk Walter, and Peter J. Wild. 2025. "Evaluation of an IDH1/2 Mutation FastTrack Assay for Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 5: 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050820
APA StyleWinter, M., Ebner, S., Scheuber, N., Schulze, F., Kinzler, M. N., Walter, D., & Wild, P. J. (2025). Evaluation of an IDH1/2 Mutation FastTrack Assay for Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers, 17(5), 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050820






