Epigenetic Perspectives and Their Prognostic Value in Early Recurrence After Hepatocellular Carcinoma Resection
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Patients and Clinical Samples
2.2. DNA Methylation Microarray and Functional Analysis
2.3. Combined Bisulfite Restriction Analysis (COBRA)
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative Methylation Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
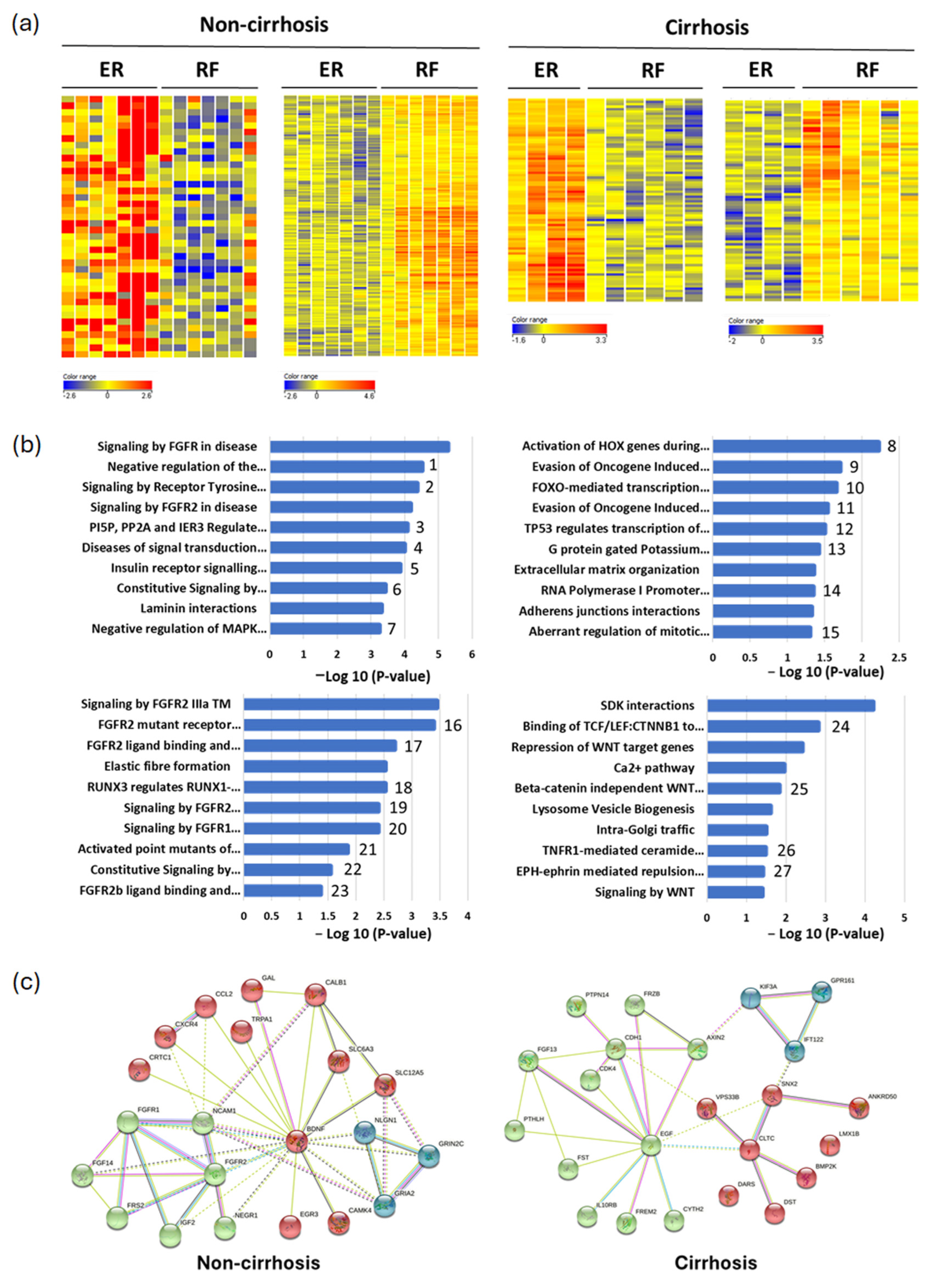
3.1. Identification of Differential Methylation Regions in Early Recurrent HCC Patients
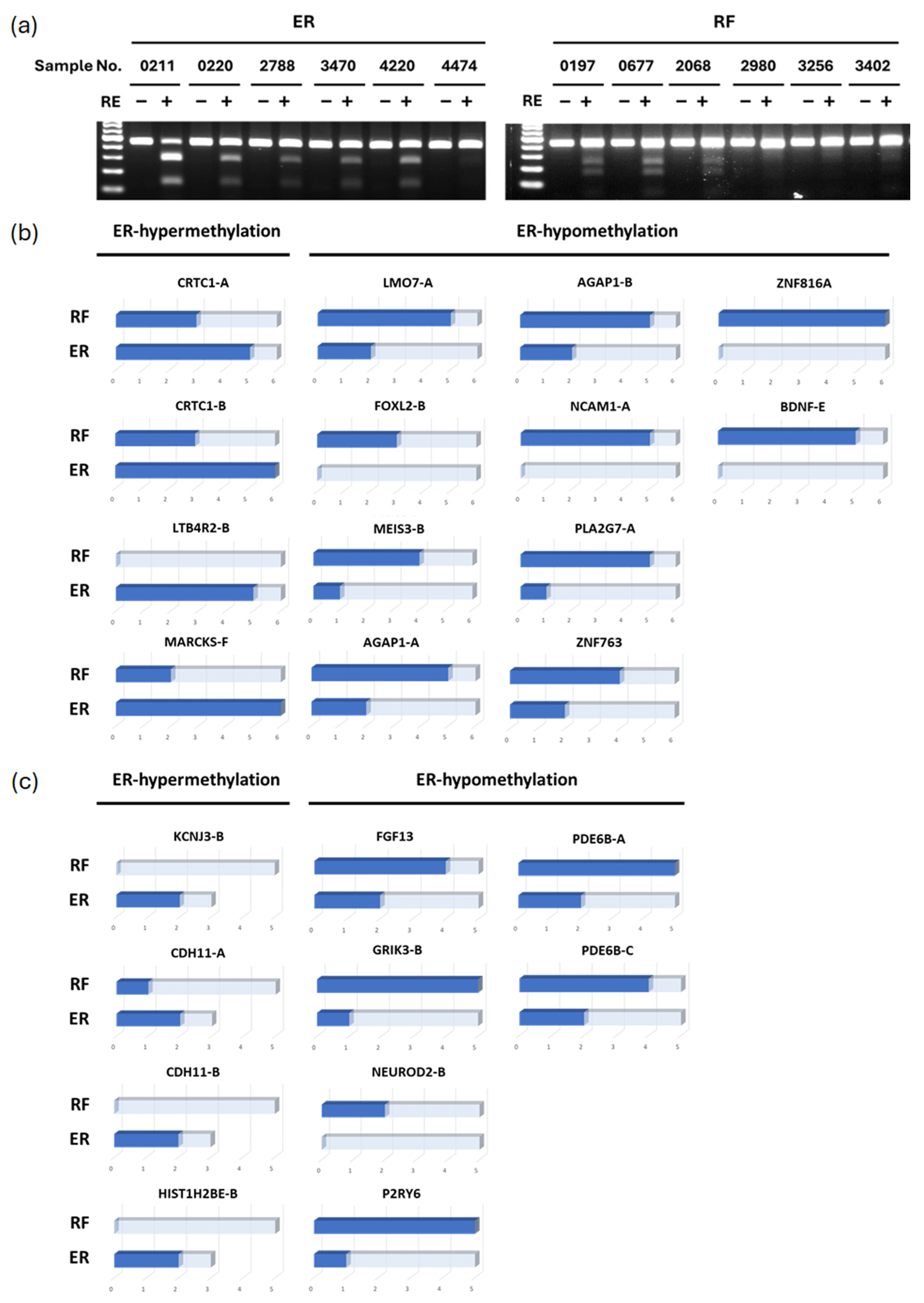
3.2. Validation of Differential Methylated Genes by COBRA (Combined Bisulfite Restriction Analysis)
3.3. Methylation Levels of Candidate Markers in Clinical Samples
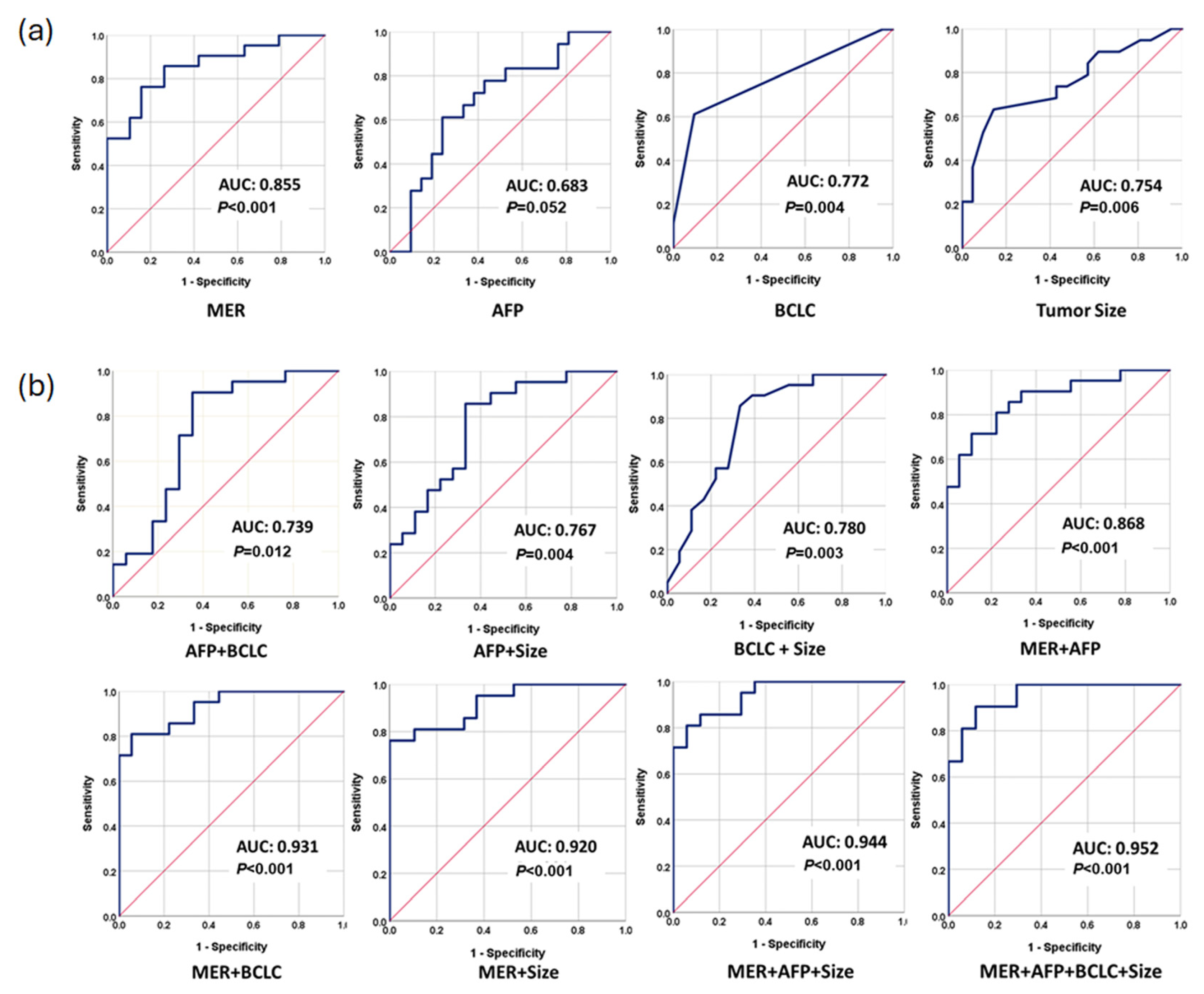
3.4. Performance of Methylation Prediction Model for ER Prediction
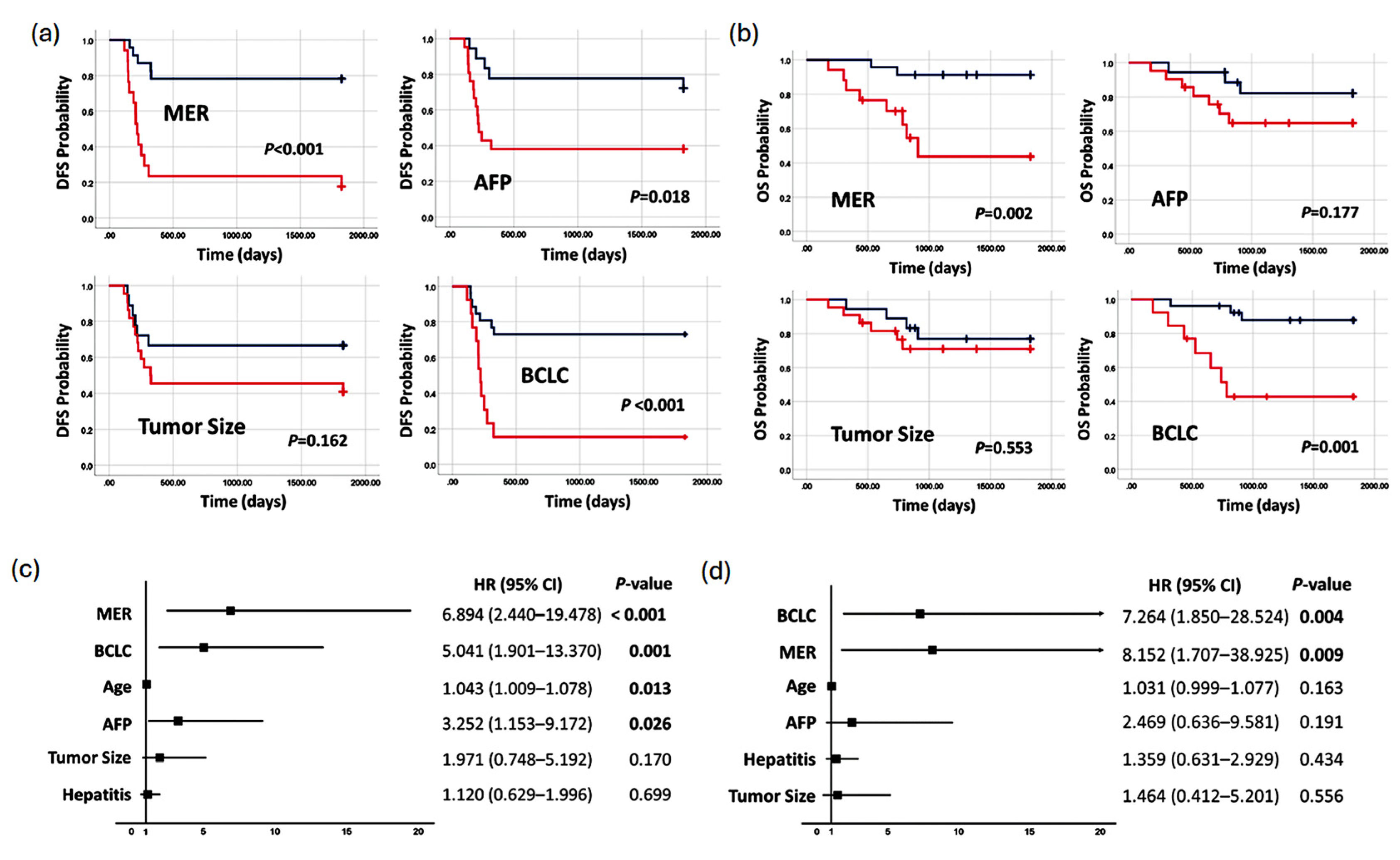
3.5. Methylation Prediction Model in Predicting Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFP | alpha-fetoprotein |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| BCLC | Barcelona clinic liver cancer classification |
| COBRA | combined bisulfite restriction analysis |
| ER | early recurrence |
| FGFR | fibroblast growth factor receptors |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MER | methylation prediction model for ER |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinases |
| qMSP | real-time quantitative methylation-specific PCR |
| RF | recurrence-free |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic curve |
References
- Sherman, M. Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.C.; Cheung, T.T. Strategic Overview on the Best Treatment Option for Intrahepaitc Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2016, 16, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Hsieh, S.; Lu, Y.; Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Lo, S.; Wu, C.; Chou, M.; Huang, T.H.; Chang, Y. Aberrant DNA Methylation Profile and Frequent Methylation of KLK10 and OXGR1 Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2009, 48, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leygo, C.; Williams, M.; Jin, H.C.; Chan, M.W.Y.; Chu, W.K.; Grusch, M.; Cheng, Y.Y. DNA Methylation as a Noninvasive Epigenetic Biomarker for the Detection of Cancer. Dis. Markers 2017, 2017, 3726595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portolani, N.; Coniglio, A.; Ghidoni, S.; Giovanelli, M.; Benetti, A.; Tiberio, G.A.M.; Giulini, S.M. Early and Late Recurrence After Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. Ann. Surg. 2006, 243, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, R.T.; Fan, S.T.; Ng, I.O.; Lo, C.M.; Liu, C.L.; Wong, J. Different Risk Factors and Prognosis for Early and Late Intrahepatic Recurrence after Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 89, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, X.-F.; Bagante, F.; Ratti, F.; Marques, H.P.; Silva, S.; Soubrane, O.; Lam, V.; Poultsides, G.A.; Popescu, I.; et al. Early Versus Late Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgical Resection Based on Post-Recurrence Survival: An International Multi-Institutional Analysis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 25, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, H.; Matsuyama, Y.; Tanaka, E.; Ohkubo, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Miyagawa, S.; Sugawara, Y.; Minagawa, M.; Takayama, T.; Kawasaki, S.; et al. Risk Factors Contributing to Early and Late Phase Intrahepatic Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Hepatectomy. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.-G.; Wei, Y.-G.; Chen, K.-F.; Li, B. Risk Factors Associated with Early and Late Recurrence after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Single Institution’s Experience with 398 Consecutive Patients. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2014, 13, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wu, H.J.; Zhang, H.F.; Fang, S.Q.; Zeng, R. miR-143-3p Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Regulating Its Target Gene FGF1. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harimoto, N.; Taguchi, K.; Shirabe, K.; Adachi, E.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Toh, Y.; Okamura, T.; Kayashima, H.; Taketomi, A.; Maehara, Y. The Significance of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 Expression in Differentiation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncology 2010, 78, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, B.G.; Lee, W.C.; Jang, J.Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Chang, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, S.G.; Cheon, G.J.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Relation of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 Expression to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence after Liver Resection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Duan, S.; Dai, D.; Jiang, D.; Sui, X.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Ding, F.; et al. Meta-Analysis of DNA Methylation Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81255–81267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Zhai, F.; Zhang, L.; Cui, L. RUNX3 Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Metastasis via Targeting miR-186/E-Cadherin/EMT Pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 61475–61486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, H.; Olmeda, D.; Cano, A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH Factors in Tumour Progression: An Alliance against the Epithelial Phenotype? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, M.; Ueno, S.; Sakoda, M.; Iino, S.; Hiwatashi, K.; Minami, K.; Ando, K.; Mataki, Y.; Maemura, K.; Shinchi, H.; et al. Clinical Implication of ZEB-1 and E-Cadherin Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; An, T.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhu, W.; Yang, X. FOXO1 Inhibits the Invasion and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Reversing ZEB2-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Huang, W.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.; Qi, X.; Chen, Z.; Shang, X.; Nie, Y.; Wu, K. Forkhead Box Q1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis by Transactivating ZEB2 and VersicanV1 Expression: Hepatology. Hepatology 2014, 59, 958–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, X.; Lin, C.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L.; Ren, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; et al. AKIP1 Promotes Early Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin/CBP Signaling Pathway. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5516–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pergaris, A.; Danas, E.; Goutas, D.; Sykaras, A.G.; Soranidis, A.; Theocharis, S. The Clinical Impact of the EPH/Ephrin System in Cancer: Unwinding the Thread. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; Xia, J. The Role of EGF—EGFR Signalling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Inflammatory Microenvironment. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.-C.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jeon, B.-N.; Kang, H.-B.; Ko, H. Catechol Inhibits Epidermal Growth Factor-Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Stem Cell-like Properties in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavon, I.R.G. The E-Cadherin–Catenin Complex in Tumour Metastasis. Eur. J. Cancer 2000, 36, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzel, T.; Mech, K.; Wroński, M.; Gerkowicz, K.; Bednarczyk, A.; Adamczyk, W.; Radecka, M.; Słodkowski, M. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Gastroenterology Oncology—Short Review of Current Literature. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2021, 28, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Yang, Z.; Huang, F.; Yin, L.; Yan, G.; Gong, G. microRNA-107 Inhibits Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis by Targeting PI3K/AKT Pathway. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 121, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Hou, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Zhu, L.; Liang, J.; Jiang, X. More Expressions of BDNF and TrkB in Multiple Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Anti-BDNF or K252a Induced Apoptosis, Supressed Invasion of HepG2 and HCCLM3 Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, S. A Signature of 33 Immune-related Gene Pairs Predicts Clinical Outcome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 2868–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, Q.; Shao, Z. Tumor-Suppressive Role of microRNA-202-3p in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through the KDM3A/HOXA1/MEIS3 Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 556004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Wu, L.; Zang, Y. Development and Validation of a Metabolic-Related Prognostic Model for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Zhang, W.G.; Cescon, M.; Liang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, M.D.; Wu, H.; Lau, W.Y.; Zhou, Y.H.; Gu, W.M.; et al. Defining and predicting early recurrence after liver resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A multi-institutional study. HPB 2020, 5, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Del Prete, V.; Antonino, M.; Crucinio, N.; Neve, V.; Di Leo, A.; Carr, B.I.; Barone, M. Post-recurrence survival in hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Arase, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Tsubota, A.; Chayama, K.; Murashima, N.; Kumada, H. Interferon beta prevents recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after complete resection or ablation of the primary tumor-A prospective randomized study of hepatitis C virus-related liver cancer. Hepatology 2000, 32, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.; Das, B.K.; Choudhary, S.; Gupta, D.; Patil, U.K. Diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: A pathophysiological link and pharmacological management. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Testing, n = 24 (%) | Validation, n = 40 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median) | 59 | 56 | |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 20 (83.3) | 28 (70) | |
| Female | 4 (16.7) | 12 (30) | |
| Hepatitis | |||
| HBV−/HCV− | 4 (16.7) | 10 (25) | |
| HBV+ | 17 (70.8) | 20 (50) | |
| HCV+ | 2 (0.08) | 8 (20) | |
| HBV+/HCV+ | 1(0.04) | 2 (5) | |
| AFP value (ng/mL) (median) | 13 | 24 | |
| BCLC staging | |||
| 0-A | 12 (70.6) | 26 (66.8) | |
| B-C | 5 (29.4) | 13 (33.2) | |
| pTNM staging | |||
| Stage 1 | 9 (47.4) | 15 (42.9) | |
| Stage 2 | 4 (21) | 15 (42.9) | |
| Stage 3 | 2 (31.5) | 5 (14.2) | |
| Diameter of largest HCC nodule | |||
| <5 cm | 19 (79.2) | 21 (52.5) | |
| ≥5 cm | 5 (20.8) | 19 (47.5) | |
| Histologic grade | |||
| Well | 4 (23.5) | 5 (12.8) | |
| Moderately | 10 (58.8) | 27 (69.2) | |
| Poorly | 3 (17.6) | 7 (17.9) | |
| Status of non-tumor liver | |||
| Non-cirrhosis | 14 (58.3) | 40 (100) | |
| Cirrhosis | 10 (41.7) | 0 (0) | |
| Early recurrence | |||
| Yes (ER group) | 11 (45.8) | 20 (50) | |
| No (RF group) | 13 (54.2) | 20 (50) | |
| AUC (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Tumor Size | 0.754 (0.600–0.909) | 73.7 (64.1–83.3) | 57.1 (45.8–68.4) | 0.006 |
| BCLC | 0.772 (0.619–0.926) | 61.1 (40.2–81.9) | 90.5 (76.9–100) | 0.004 |
| AFP | 0.683 (0.511–0.854) | 72.7 (53.6–91.7) | 61.9 (39.4–84.3) | 0.052 |
| MER | 0.855 (0.738–0.971) | 85.7 (70.7–100) | 73.7 (53.9–93.4) | <0.001 |
| MER + AFP | 0.868 (0.756–0.979) | 85.7 (70.7–100) | 72.2 (51.5–92.8) | <0.001 |
| AFP + Size | 0.767 (0.616–0.919) | 85.7 (70.7–100) | 66.7 (44.9–88.4) | 0.004 |
| AFP + BCLC | 0.739 (0.569–0.910) | 85.7 (70.7–100) | 73.7 (52.7–94.6) | 0.012 |
| Size + BCLC | 0.780 (0.629–0.932) | 85.7 (70.7–100) | 66.7 (44.9–88.4) | 0.003 |
| MER + Size | 0.920 (0.838–1.000) | 81.0 (64.2–97.7) | 89.5 (76.0–100)) | <0.001 |
| MER + BCLC | 0.931 (0.857–1.000) | 81.0 (64.2–97.7) | 94.4 (84.3–100) | <0.001 |
| MER + AFP + BCLC | 0.944 (0.662–0.951) | 85.7 (70.7–100) | 82.4 (64.2–100) | <0.001 |
| MER + AFP + Size + BCLC | 0.952 (0.893–1.000) | 90.5 (77.9–100) | 88.2 (72.8–100) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-P.; Lee, H.-L.; Peng, P.-J.; Huang, S.-C.; Chuang, M.-R.; Lin, Y.-J. Epigenetic Perspectives and Their Prognostic Value in Early Recurrence After Hepatocellular Carcinoma Resection. Cancers 2025, 17, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050769
Lu C-Y, Lin C-P, Lee H-L, Peng P-J, Huang S-C, Chuang M-R, Lin Y-J. Epigenetic Perspectives and Their Prognostic Value in Early Recurrence After Hepatocellular Carcinoma Resection. Cancers. 2025; 17(5):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050769
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Chang-Yi, Ching-Pin Lin, Hsiang-Lin Lee, Pey-Jey Peng, Shao-Chang Huang, Meng-Rong Chuang, and Yih-Jyh Lin. 2025. "Epigenetic Perspectives and Their Prognostic Value in Early Recurrence After Hepatocellular Carcinoma Resection" Cancers 17, no. 5: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050769
APA StyleLu, C.-Y., Lin, C.-P., Lee, H.-L., Peng, P.-J., Huang, S.-C., Chuang, M.-R., & Lin, Y.-J. (2025). Epigenetic Perspectives and Their Prognostic Value in Early Recurrence After Hepatocellular Carcinoma Resection. Cancers, 17(5), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050769







