The Impact of Radiotherapy and Attenuated Chemotherapy Regimens in Older Patients with Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Real-Life Study from the ReLLi Network
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Features
3.2. Treatment Approaches and Outcomes
3.2.1. Early-Stage Treatment
3.2.2. Advanced Stage Treatment
3.3. Second-Line Therapies
3.4. Outcomes and Survival Analysis
3.5. Synthetic Data Augmentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| eHL | Elderly Hodgkin Lymphoma |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| CSS | Cancer-Specific Survival |
| EFS | Event-Free Survival |
| DFS | Disease-Free Survival |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| CR | Complete Remission |
| ReLLi | Rete-Linfomi-Lazio |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| HR | Hazard Ratios |
| MV | Multivariate (analyses) |
References
- Wahlin, B.E.; Övergaard, N.; Peterson, S.; Digkas, E.; Glimelius, I.; Lagerlöf, I.; Johansson, A.S.; Palma, M.; Hansson, L.; Linderoth, J.; et al. Real-world data on treatment concepts in classical Hodgkin lymphoma in Sweden 2000–2014, focusing on patients aged >60 years. eJHaem 2021, 2, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, A.A.; Aeppli, S.; Güsewell, S.; Bargetzi, M.; Caspar, C.; Brülisauer, D.; Ebnöther, M.; Fehr, M.; Fischer, N.; Ghilardi, G.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients over 60 years with Hodgkin lymphoma treated in Switzerland. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia, K.; Jørgensen, R.R.K.; LWold, B.; Fluge, Ø.; Fagerli, U.M.; Bersvendsen, H.; Bø, I.B.; Bhargava, S.; Fosså, A. Overall survival and causes of death in elderly patients with Hodgkin lymphoma: A Norwegian population-based case-control study. Haematologica 2024, 109, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Orellana-Noia, V.M.; Isaac, K.; Malecek, M.K.; Bartlett, N.L.; Voorhees, T.J.; Grover, N.S.; Hwang, S.R.; Bennani, N.N.; Hu, R.; Hill, B.T.; et al. Multicenter analysis of geriatric fitness and real-world outcomes in older patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.; Jang, H.; Kim, S.; Halwani, A.S. A comprehensive SEER registry analysis of elderly patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma based on treatment era and race. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Hilden, P.; Coiffier, B.; Hagenbeek, A.; Salles, G.; Wilson, W.; Seymour, J.F.; Kelly, K.; Gribben, J.; Pfreunschuh, M.; et al. International Working Group consensus response evaluation criteria in lymphoma (RECIL 2017). Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D. Staging and response assessment in lymphomas: The new Lugano classification. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.J.; Lu, M.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Mahmood, F. Synthetic data in machine learning for medicine and healthcare. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, S.; Dall’Olio, D.; Sala, C.; Dall’Olio, L.; Sauta, E.; Zampini, M.; Asti, G.; Lanino, L.; Maggioni, G.; Campagna, A.; et al. Synthetic Data Generation by Artificial Intelligence to Accelerate Research and Precision Medicine in Hematology. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2023, 7, e2300021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Obermeyer, Z.; Emanuel, E.J. Predicting the Future—Big Data, Machine Learning, and Clinical Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowok, B.; Raab, G.M.; Dibben, C. synthpop: Bespoke Creation of Synthetic Data in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 74, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T. A Package for Survival Analysis in R. R Package Version 3.7-0. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Terry, M.; Therneau, P.; Grambsch, M. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-387-98784-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Kosinski, M.; Biecek, P. Survminer: Drawing Survival Curves Using ‘ggplot2’. R Package Version 0.4.9. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survminer (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Rajotte, J.F.; Bergen, R.; Buckeridge, D.L.; El Emam, K.; Ng, R.; Strome, E. Synthetic data as an enabler for machine learning applications in medicine. iScience 2022, 25, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, M.P.E.; Girinsky, T.; Federico, M.; Reman, O.; Fortpied, C.; Gotti, M.; Casasnovas, O.; Brice, P.; van der Maazen, R.; Re, A.; et al. Early Positron Emission Tomography Response-Adapted Treatment in Stage I and II Hodgkin Lymphoma: Final Results of the Randomized EORTC/LYSA/FIL H10 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, M.; Fortpied, C.; Stepanishyna, Y.; Gotti, M.; van der Maazen, R.; Cristinelli, C.; Re, A.; Plattel, W.; Lazarovici, J.; Merli, F.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of the Response-Adapted Intergroup EORTC/LYSA/FIL H10 Trial for Localized Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, M.; Jacob, A.S.; Kaul, H.; Kobe, C.; Kuhnert, G.; Pabst, T.; Greil, R.; Bröckelmann, P.J.; Topp, M.S.; Just, M.; et al. Follow-up of the GHSG HD16 trial of PET-guided treatment in early-stage favorable Hodgkin lymphoma. Leukemia 2024, 38, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, J.; Illidge, T.; Counsell, N.; Hancock, B.; Pettengell, R.; Johnson, P.; Wimperis, J.; Culligan, D.; Popova, B.; Smith, P.; et al. Results of a trial of PET-directed therapy for early-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.; Federico, M.; Kirkwood, A.; Fosså, A.; Berkahn, L.; Carella, A.; d’Amore, F.; Enblad, G.; Franceschetto, A.; Fulham, M.; et al. Adapted treatment guided by interim PET-CT scan in advanced Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2419–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böll, B.; Goergen, H.; Behringer, K.; Bröckelmann, P.J.; Hitz, F.; Kerkhoff, A.; Greil, R.; von Tresckow, B.; Eichenauer, D.A.; Bürkle, C.; et al. Bleomycin in older early-stage favorable Hodgkin lymphoma patients: Analysis of the German Hodgkin Study Group (GHSG) HD10 and HD13 trials. Blood 2016, 127, 2189–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchmann, P.; Ferdinandus, J.; Schneider, G.; Moccia, A.; Greil, R.; Hertzberg, M.; Schaub, V.; Hüttmann, A.; Keil, F.; Dierlamm, J.; et al. Assessing the efficacy and tolerability of PET-guided BrECADD versus eBEACOPP in advanced-stage, classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HD21): A randomised, multicentre, parallel, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2024, 404, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröckelmann, P.J. Treatment approaches for older Hodgkin lymphoma patients. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2024, 36, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torka, P.; Feldman, T.; Savage, K.J.; Ganesan, N.; Drill, E.; Hancock, H.; Davey, T.; Perez, L.; Capadona, C.; Subzwari, S.; et al. Phase II Trial of Nivolumab Plus Doxorubicin, Vinblastine, Dacarbazine as Frontline Therapy in Older Adults with Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, JCO2401278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, A.M.; Connors, J.M.; Younes, A.; Ansell, S.M.; Kim, W.S.; Radford, J.; Feldman, T.; Tuscano, J.; Savage, K.J.; Oki, Y.; et al. Older patients (aged 60 years) with previously untreated advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma: A detailed analysis from the phase III ECHELON-1 study. Haematologica 2022, 107, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evens, A.M.; Advani, R.H.; Helenowski, I.B.; Fanale, M.; Smith, S.M.; Jovanovic, B.D.; Bociek, G.R.; Klein, A.K.; Winter, J.N.; Gordon, L.I.; et al. Multicenter Phase II Study of Sequential Brentuximab Vedotin and Doxorubicin, Vinblastine, and Dacarbazine Chemotherapy for Older Patients With Untreated Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3015–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.F.; LeBlanc, M.; Castellino, S.M.; Li, H.; Rutherford, S.C.; Evens, A.M.; Davison, K.; Punnett, A.; Parsons, S.K.; Ahmed, S.; et al. Nivolumab+AVD in Advanced-Stage Classic Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, L.; Carollo, A.; Di Martino, E.; Novara, M.E.; Cutaia, S.; Provenzani, A.; Rizzo, S. Cardiotoxicity associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2025, 206, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, F.; Luminari, S.; Tucci, A.; Arcari, A.; Rigacci, L.; Hawkes, E.; Chiattone, C.S.; Cavallo, F.; Cabras, G.; Alvarez, I.; et al. Simplified Geriatric Assessment in Older Patients With Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: The Prospective Elderly Project of the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehtap, Ö.; Toptas, T.; Dal, M.S.; Karadag, F.K.; Atas, U. A new scoring system to predict survival in elderly advanced stage Hodgkin lymphoma patients. Leuk. Lymphoma 2024, 65, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasenclever, D.; Diehl, V. A prognostic score for advanced Hodgkin’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
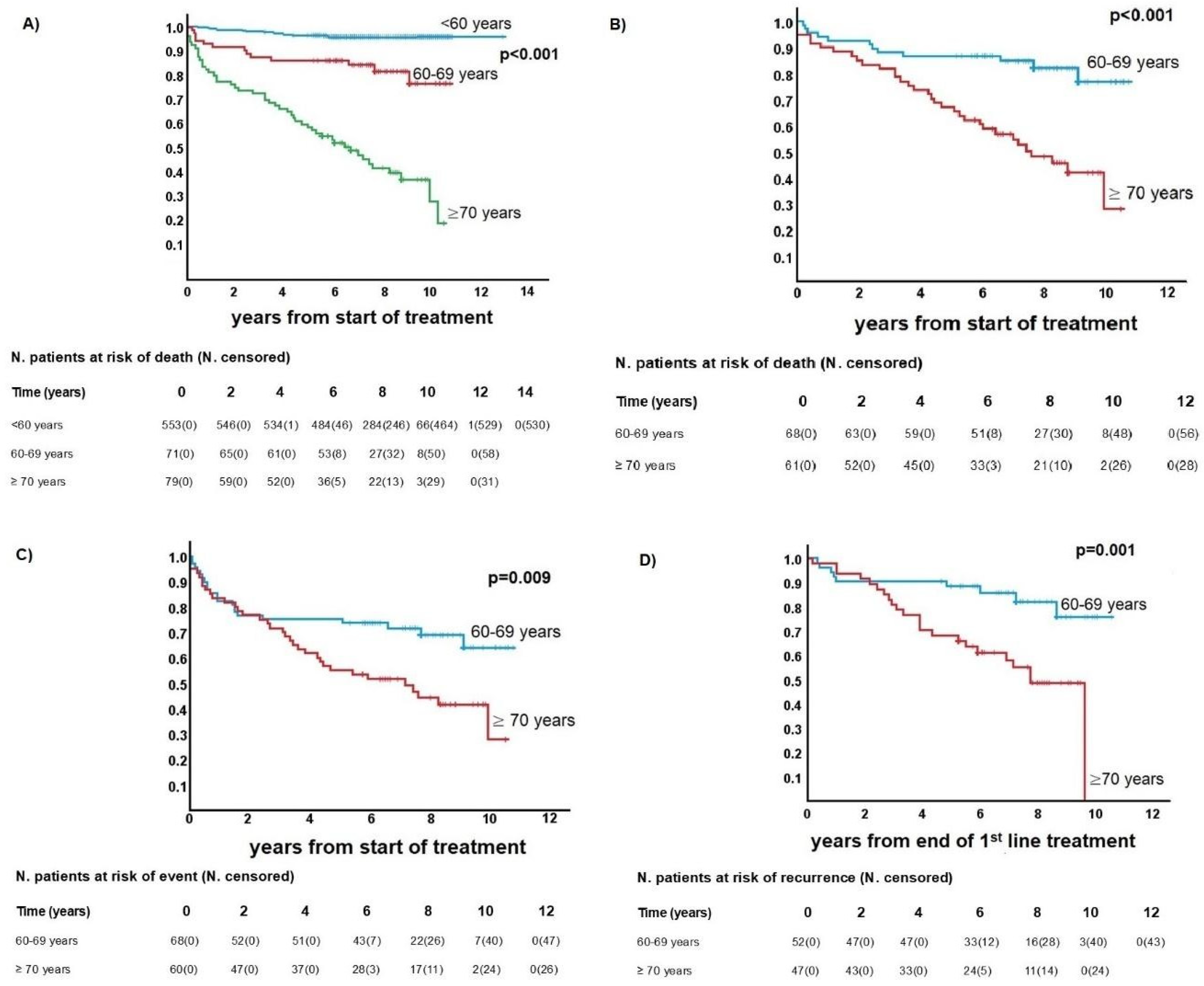
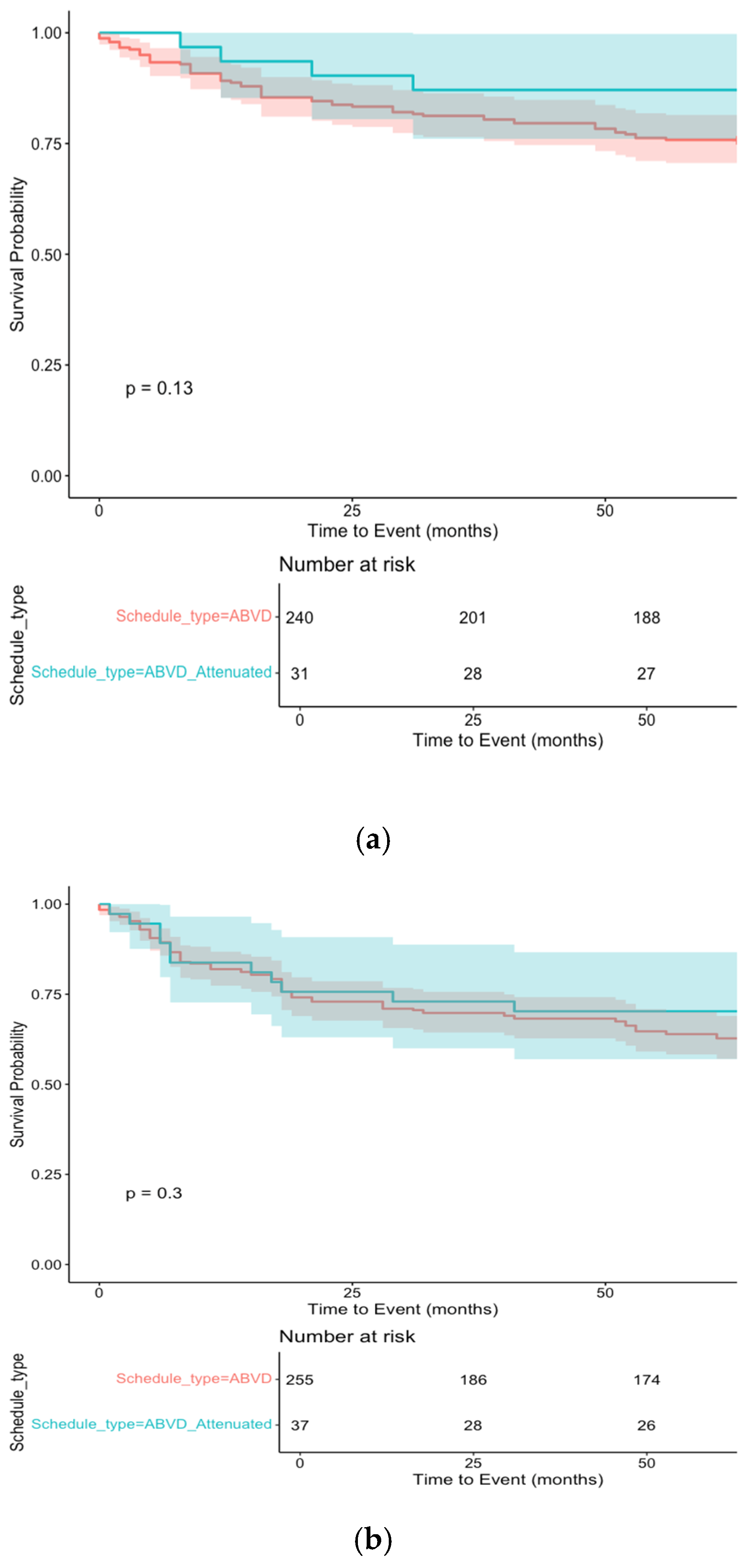
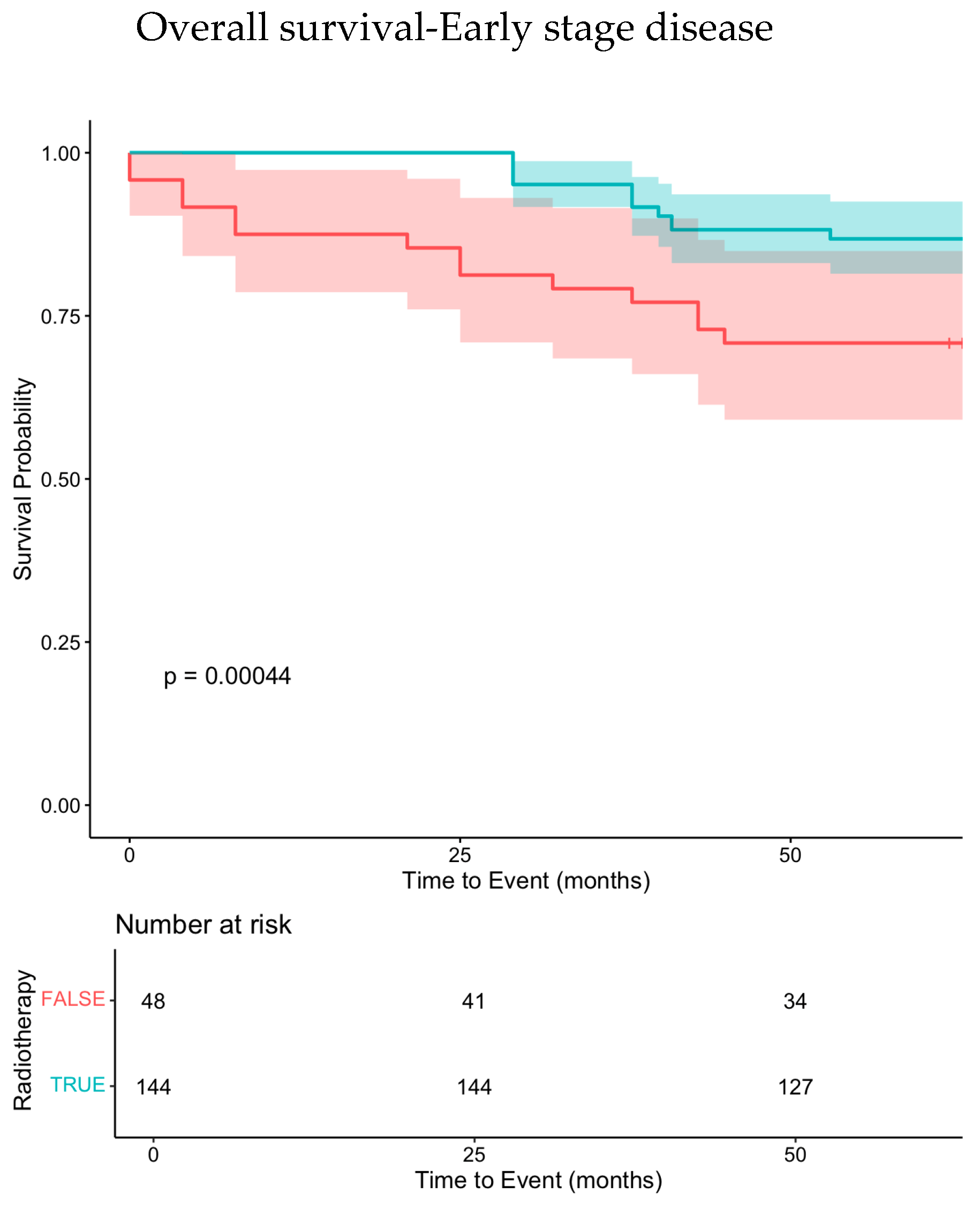
| Variable | <60 Years Old | 60–69 Years Old | ≥70 Years Old | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 556 | 71 | 79 | |
| Male sex | 48% (266/556) | 63% (45/71) | 58% (46/79) | 0.017 |
| Stage I–II | 55% (308/556) | 44% (31/71) | 30% (24/79) | <0.001 |
| Stage III–IV | 45% (248/556) | 54% (40/71) | 71% (55/79) | <0.001 |
| B symptoms | 34% (187/556) | 27% (19/71) | 29% (23/79) | 0.41 |
| ESR > 30 | 61% (207/340) | 66% (27/41) | 55% (26/47) | 0.60 |
| ESR > 50 | 40% (137/340) | 46% (19/41) | 38% (18/47) | 0.71 |
| Alb < 3.5 g/dL | 18% (81/460) | 29% (16/56) | 32% (19/60) | 0.010 |
| Hb < 10.5 g/dL | 16% (75/467) | 19% (11/57) | 26% (16/61) | 0.13 |
| WBCs > 15,000/mmc | 13% (62/469) | 7% (4/56) | 7% (4/61) | 0.16 |
| Low lymphocyte count * | 12% (58/466) | 12% (7/57) | 28% (17/60) | 0.003 |
| Bulky disease (>7.5 cm) | 29% (123/423) | 14% (7/51) | 6% (3/54) | <0.001 |
| Early-stage with > 3 lymph nodes | 37% (114/308) | 29% (9/31) | 21% (5/24) | 0.21 |
| 1st-line curative therapy | 99% (540/543) | 96% (67/70) | 76% (52/68) | <0.001 |
| Radiotherapy (1st line) | ||||
| All | 46% (255/556) | 41% (29/71) | 25% (20/79) | 0.002 |
| Stage I–II | 63% (195/308) | 68% (21/31) | 67% (16/24) | 0.85 |
| Stage III–IV | 24% (60/248) | 20% (8/40) | 7% (4/55) | 0.020 |
| First-line response after chemotherapy | ||||
| CR | 79% (406/518) | 79% (50/63) | 84% (41/49) | 0.30 |
| PR | 9% (49/518) | 15% (9/63) | 4% (2/49) | |
| NR/P | 12% (63/518) | 6% (4/63) | 12% (6/49) |
| Patient No. | Age Class | Schedule Type % (n) | Schedule | n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABVD | 46 | ||||
| 71 | 60–69 | ABVD-like | 81.7% (58) | ABVD/AVD | 5 |
| AVD | 5 | ||||
| MBVD/MVD | 1 | ||||
| BEGEV | 1 | ||||
| Attenuated | 14.1% (10) | ABVD-like/OPP or COPP | 10 | ||
| Palliative | 4.2% (3) | Bendamustine | 1 | ||
| COPP | 2 | ||||
| ABVD | 39 | ||||
| 75 | ≥70 | ABVD-like | 69.3% (52) | AVD | 3 |
| MBVD | 9 | ||||
| MVD | 1 | ||||
| Attenuated | 10.7% (8) | AVD/OPP | 8 | ||
| Palliative | 20% (15) | Bendamustine | 6 | ||
| CHLVPP | 1 | ||||
| COPP | 4 | ||||
| OPP | 1 | ||||
| PROVECIP | 1 | ||||
| Vinblastine | 2 | ||||
| Patient No. | Age | Second-Line Therapy | % (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BEGEV | 13.2 (2) | ||
| 15 | 60–69 | Brentuximab-Bendamustine | 6.7 (1) |
| Bendamustine | 6.7 (1) | ||
| COPP | 6.7 (1) | ||
| CTX | 6.7 (1) | ||
| Bendamustine(3) or IGEV(2) or BEGEV(4) + ASCT | 60 (9) | ||
| 17 | ≥70 | Bendamustine | 29.4 (5) |
| Brentuximab | 11.8 (2) | ||
| Chlorambucil | 5.9 (1) | ||
| COPP; OPP; PROVECIP; VCR-CTX | 23.5 (4) | ||
| DHAOX; IGEV | 11.8 (2) | ||
| GEM-VNR | 17.6 (3) |
| Event-Free Survival | Overall Survival | Cancer-Specific Survival | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate | Univariate | Multivariate | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
| p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (<70 vs. ≥70) years | 0.008 | 1.9 (1.1–3.4) | 0.017 | <0.001 | 3.6 (1.8–7.1) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 4.9 (2.2–10.8) | <0.001 |
| Gender (M vs. F) | 0.96 | - | - | 0.50 | - | - | 0.19 | - | - |
| Stage (I–II vs. III–IV) | 0.008 | 1.1 (0.6–2.1) | 0.76 | 0.028 | 0.9 (0.4–1.8) | 0.72 | 0.046 | 0.7 (0.3–1.6) | 0.42 |
| B symptoms (no vs. yes) | 0.70 | - | - | 0.39 | - | - | 0.53 | - | - |
| Bulky disease (no vs. yes) | 0.95 | - | - | 0.86 | - | - | 0.49 | - | - |
| Hemoglobin (<10.5 vs. ≥10.5) g/dL | 0.23 | - | - | 0.10 | - | - | 0.21 | - | - |
| WBCs (<15,000 vs. ≥15,000) μL−1 | 0.065 | - | - | 0.77 | - | - | 0.52 | - | - |
| Lymphocytes (≤600 vs. >600) μL−1 | 0.17 | - | - | 0.17 | - | - | 0.12 | - | - |
| Radiotherapy (no vs. yes) | 0.001 | 3.3 (1.6–7.1) | 0.002 | <0.001 | 4.9 (1.9–12.5) | 0.001 | 0.001 | 6.9 (2.2–21.2) | 0.001 |
| Complete remission (no vs. yes) | <0.001 | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.2 (0.1–0.4) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.2 (0.1–0.4) | <0.001 |
| PET 2 (no vs. yes) | 0.41 | - | - | 0.90 | - | - | 0.81 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cox, M.C.; Caridi, M.; Patirelis, A.; Del Giudice, I.; Pulsoni, A.; Renzi, D.; Pelliccia, S.; Battistini, R.; Anticoli Borza, P.; Annibali, O.; et al. The Impact of Radiotherapy and Attenuated Chemotherapy Regimens in Older Patients with Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Real-Life Study from the ReLLi Network. Cancers 2025, 17, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050765
Cox MC, Caridi M, Patirelis A, Del Giudice I, Pulsoni A, Renzi D, Pelliccia S, Battistini R, Anticoli Borza P, Annibali O, et al. The Impact of Radiotherapy and Attenuated Chemotherapy Regimens in Older Patients with Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Real-Life Study from the ReLLi Network. Cancers. 2025; 17(5):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050765
Chicago/Turabian StyleCox, Maria Christina, Matteo Caridi, Alexandro Patirelis, Ilaria Del Giudice, Alessandro Pulsoni, Daniela Renzi, Sabrina Pelliccia, Roberta Battistini, Paola Anticoli Borza, Ombretta Annibali, and et al. 2025. "The Impact of Radiotherapy and Attenuated Chemotherapy Regimens in Older Patients with Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Real-Life Study from the ReLLi Network" Cancers 17, no. 5: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050765
APA StyleCox, M. C., Caridi, M., Patirelis, A., Del Giudice, I., Pulsoni, A., Renzi, D., Pelliccia, S., Battistini, R., Anticoli Borza, P., Annibali, O., Rapisarda, V., Alma, E., Messina, N., D’Elia, G. M., Marchesi, F., Cenfra, N., Bianchi, M. P., Natalino, F., Carpaneto, A., ... Rigacci, L. (2025). The Impact of Radiotherapy and Attenuated Chemotherapy Regimens in Older Patients with Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Real-Life Study from the ReLLi Network. Cancers, 17(5), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050765






