The Impact of Preoperative Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy on Autologous Breast Reconstruction Outcomes—A Retrospective Single-Center Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
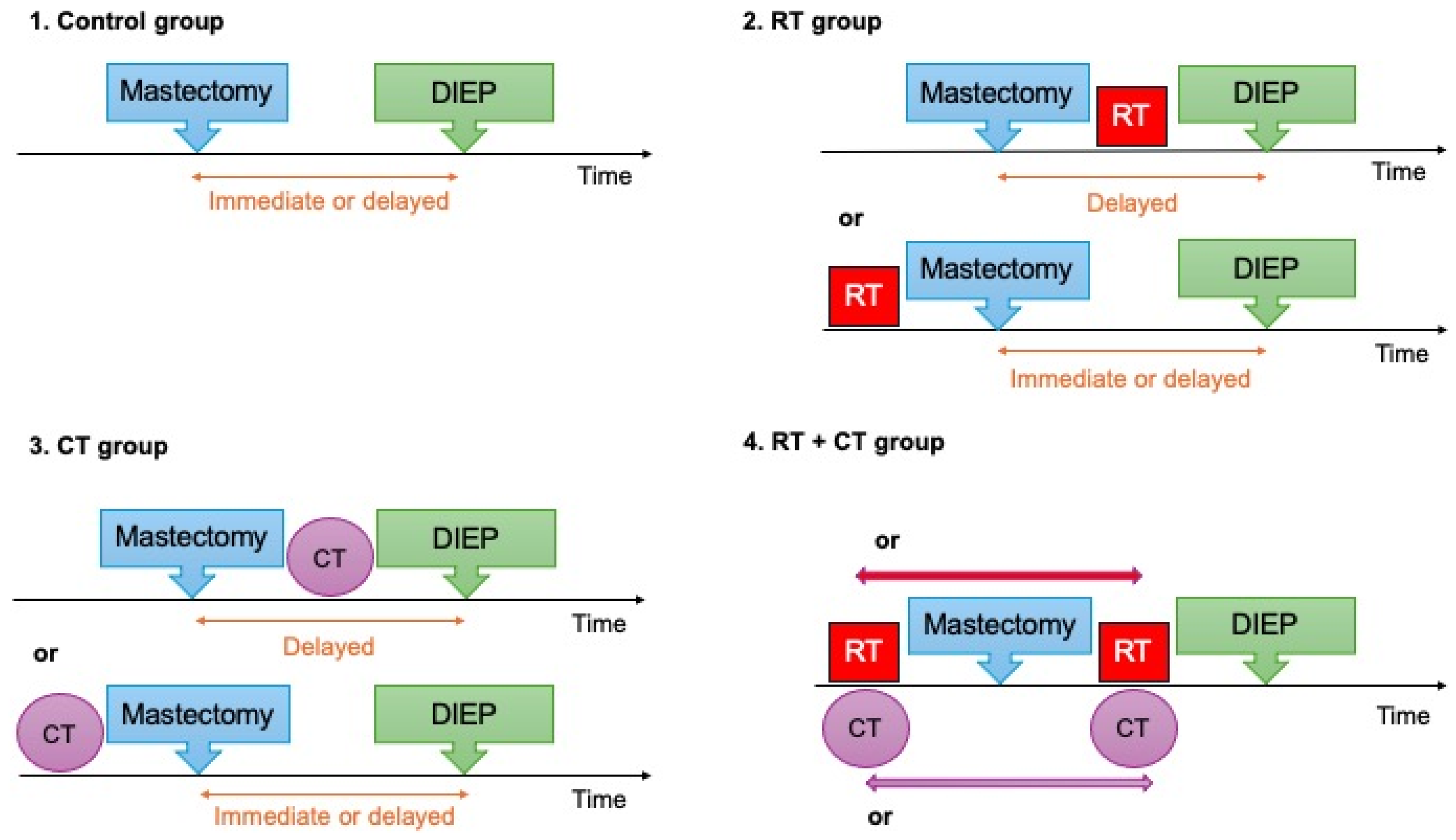
2. Materials and Methods
- Seroma: a collection of serous fluid in the surgical bed detected by imaging and necessitating needle aspiration or surgical reintervention.
- Hematoma: a localized collection of blood within the surgical space, typically requiring drainage or intervention if significant.
- Wound infection: Clinical or laboratory evidence of infection—such as purulent drainage, positive microbial cultures, and/or local/systemic signs of infection (redness, warmth, fever).
- Wound dehiscence: A mechanical separation of the layers of a previously approximated wound (partial or complete), often necessitating additional intervention (negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), re-suturing, local flap)
- Delayed wound healing: A wound that fails to progress through normal phases of healing within the expected postoperative timeframe, without mechanical separation of wound edges (i.e., no dehiscence), and with no other surgical intervention than simple dressings and wound care with topical agents. These cases benefited from ambulatory follow-up at our wound care center.
- A “microvascular complication” was defined as any compromise in flap perfusion necessitating urgent surgical re-exploration, whether or not the arterial or venous anastomoses required revision.
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. Operative Variables
3.3. Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy Characteristics:
3.4. Complications
3.5. Logistic Regression Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| CT | Chemotherapy |
| DIEP | Deep inferior epigastric perforator |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| ASA | Anesthesiologists |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| Gy | Grey |
| NAC | Nipple-areolar-complex |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| HBOT | Hyperbaric oxygen therapy |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégevand, V.; Scampa, M.; McEvoy, H.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Comparison of Outcomes Following Prepectoral and Subpectoral Implants for Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recht, A.; Comen, E.A.; Fine, R.E.; Fleming, G.F.; Hardenbergh, P.H.; Ho, A.Y.; Hudis, C.A.; Hwang, E.S.; Kirshner, J.J.; Morrow, M.; et al. Postmastectomy Radiotherapy: An American Society of Clinical Oncology, American Society for Radiation Oncology, and Society of Surgical Oncology Focused Guideline Update. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, R.; Moustaki, M.; Harris, S.; Roblin, P.; Farhadi, J. Does post-mastectomy radiotherapy affect the outcome and prevalence of complications in immediate DIEP breast reconstruction? A prospective cohort study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2015, 68, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgár, C.; Fodor, J.; Major, T.; Takácsi-Nagy, Z.; Kásler, M.; Hammer, J.; Van Limbergen, E.; Németh, G. Radiotherapy confined to the tumor bed following breast conserving surgery current status, controversies, and future projects. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2002, 178, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, J.; Tekdogan, B.; Lam, G.-T.; Correia, D.; Giordano, S.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Oncological and Surgical Outcomes of Oncoplastic Reduction Mammoplasty: A Single-centre Retrospective Study. In Vivo 2024, 38, 2820–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, G.E.; Oladeru, O.T.; Niemierko, A.; Salama, L.; Winograd, J.; Colwell, A.; Arafat, W.O.; Smith, B.; Ho, A.; Taghian, A.G. Optimal breast reconstruction type for patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, mastectomy followed by radiation therapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 183, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, P.; Zhang, L.; Untch, M.; Mehta, K.; Costantino, J.P.; Wolmark, N.; Bonnefoi, H.; Cameron, D.; Gianni, L.; Valagussa, P.; et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: The CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killelea, B.K.; Yang, V.Q.; Mougalian, S.; Horowitz, N.R.; Pusztai, L.; Chagpar, A.B.; Lannin, D.R. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer increases the rate of breast conservation: Results from the National Cancer Database. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2015, 220, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anampa, J.; Makower, D.; Sparano, J.A. Progress in adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: An overview. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damen, T.H.; Timman, R.; Kunst, E.H.; Gopie, J.P.; Bresser, P.J.; Seynaeve, C.; Menke-Pluijmers, M.B.; Mureau, M.A.; Hofer, S.O.; Tibben, A. High satisfaction rates in women after DIEP flap breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2010, 63, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, J.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Safety and Efficacy of the Superior Gluteal Artery Perforator (SGAP) Flap in Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, J.; Scampa, M.; Viscardi, J.A.; Giordano, S.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Inferior gluteal artery perforator (IGAP) flap in autologous breast reconstruction: A proportional meta-analysis of surgical outcomes. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2023, 84, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekdogan, B.; Martineau, J.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Unilateral Versus Bilateral Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2024, 12, e6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, R.M.; Paik, K.J.; Chung, M.T.; Duscher, D.; Gurtner, G.C.; Longaker, M.T.; Wan, D.C. Studies in fat grafting: Part III. Fat grafting irradiated tissue--improved skin quality and decreased fat graft retention. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.Y.; Hu, Z.I.; Mehrara, B.J.; Wilkins, E.G. Radiotherapy in the setting of breast reconstruction: Types, techniques, and timing. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e742–e753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anavekar, N.S.; Rozen, W.M.; Le Roux, C.M.; Ashton, M.W. Achieving autologous breast reconstruction for breast cancer patients in the setting of post-mastectomy radiotherapy. J. Cancer Surviv. 2011, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Kawamori, J.; Yamauchi, H. Breast reconstruction and postmastectomy radiotherapy: Complications by type and timing and other problems in radiation oncology. Breast Cancer 2017, 24, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, J.; Gohari, S.S.; Rizki, H.; Faheem, M.; Langridge, B.; Kümmel, S.; Johnson, L.; Schmid, P. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on complications following immediate breast reconstruction. Breast 2021, 55, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitovic, A.; Trøstrup, H.; Damsgaard, T.E. The impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on surgical outcomes following autologous and implant-based immediate breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2023, 87, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertsch, S.; Munder, B.; Andree, C.; Witzel, C.; Stambera, P.; Schulz, T.; Hagouan, M.; Gruter, L.; Aufmesser, B.; Staemmler, K.; et al. Risk Factor Analysis for Flap and Donor Site Related Complications in 1274 DIEP Flaps—Retrospective Single Center Study. Chirurgia 2021, 116, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, B.P.; Ahmed, R.; Kidwell, K.M.; Kozlow, J.H.; Chung, K.C.; Momoh, A.O. A systematic review of morbidity associated with autologous breast reconstruction before and after exposure to radiotherapy: Are current practices ideal? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnautovic, A.; Karinja, S.; Olafsson, S.; Carty, M.J.; Erdmann-Sager, J.; Caterson, S.A.; Broyles, J.M. Optimal Timing of Delayed Microvascular Breast Reconstruction after Radiation Therapy. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2023, 39, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Chen, M.; Xiu, B.; Yang, B.; Wu, J. Immediate Breast Reconstruction After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Factors Associated With Surgical Selection and Complications. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2023, 91, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinner, G.; Martineau, J.; Lam, G.-T.; Tremp, M.; Giordano, S.; Dong, E.T.C.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Does prepectoral placement delay adjuvant therapies compared to retropectoral immediate implant-based breast reconstruction? A retrospective analysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2024, 99, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.S.; Tan, V.; Scampa, M.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Complications of Immediate versus Delayed DIEP Reconstruction: A Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. Cancers 2022, 14, 4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.; Ho, K.; Ike, C.; Wood, S.H.; Thiruchelvam, P.T.R.; Khan, A.A.; Leff, D.R. Pre-operative chemoradiotherapy followed by mastectomy and breast reconstruction-A systematic review of clinical, oncological, reconstructive and aesthetic outcomes. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2024, 96, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruchelvam, P.T.R.; Leff, D.R.; Godden, A.R.; Cleator, S.; Wood, S.H.; Kirby, A.M.; Jallali, N.; Somaiah, N.; Hunter, J.E.; Henry, F.P.; et al. Primary radiotherapy and deep inferior epigastric perforator flap reconstruction for patients with breast cancer (PRADA): A multicentre, prospective, non-randomised, feasibility study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, K.; Satake, T.; Muto, M.; Tsunoda, Y.; Koike, T.; Narui, K.; Katsuragi, R.; Onoda, S.; Ishikawa, T. Delayed breast reconstruction with autologous free flap after radiation therapy: Vascular complications and aesthetic outcomes. Breast Cancer 2024, 31, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, A.; Charles, W.N.; Prokopenko, M.; Beswick, A.; Pusic, A.L.; Mosahebi, A.; Dodwell, D.J.; Winters, Z.E. Immediate and delayed autologous abdominal microvascular flap breast reconstruction in patients receiving adjuvant, neoadjuvant or no radiotherapy: A meta-analysis of clinical and quality-of-life outcomes. BJS Open 2020, 4, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, J.A., 3rd; Castaldo, E.T.; Nanney, L.B.; Wu, Y.C.; Donahue, R.; Wendel, J.J.; Hagan, K.F.; Shack, R.B. Autologous breast reconstruction: The Vanderbilt experience (1998 to 2005) of independent predictors of displeasing outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2008, 207, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosnot, J.; Fischer, J.P.; Smartt, J.M., Jr.; Low, D.W.; Kovach, S.J., 3rd; Wu, L.C.; Serletti, J.M. Does previous chest wall irradiation increase vascular complications in free autologous breast reconstruction? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fracol, M.E.; Basta, M.N.; Nelson, J.A.; Fischer, J.P.; Wu, L.C.; Serletti, J.M.; Fosnot, J. Bilateral Free Flap Breast Reconstruction After Unilateral Radiation: Comparing Intraoperative Vascular Complications and Postoperative Outcomes in Radiated Versus Nonradiated Breasts. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaverien, M.V.; Munnoch, D.A. Effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on outcomes of immediate free autologous breast reconstruction. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 39, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, J.; de Romani, S.E.; Masia, J. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer Treatment and the Evidence-Based Interaction with Immediate Autologous and Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2018, 45, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren Peled, A.; Itakura, K.; Foster, R.D.; Hamolsky, D.; Tanaka, J.; Ewing, C.; Alvarado, M.; Esserman, L.J.; Hwang, E.S. Impact of chemotherapy on postoperative complications after mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction. Arch. Surg. 2010, 145, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.; Berlin, L.; Hunter, K.; Bonawitz, S.C. Effects of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Autologous and Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature. Clin. Breast Cancer 2024, 24, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beugels, J.; Meijvogel, J.L.W.; Tuinder, S.M.H.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.G.; Heuts, E.M.; Piatkowski, A.; van der Hulst, R. The influence of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on complications of immediate DIEP flap breast reconstructions. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 176, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słonimska, P.; Sachadyn, P.; Zieliński, J.; Skrzypski, M.; Pikuła, M. Chemotherapy-Mediated Complications of Wound Healing: An Understudied Side Effect. Adv. Wound Care 2024, 13, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, J.A.; Comerci, A.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Alessandri Bonetti, M.; Nguyen, V.T.; Parent, B.; Bailey, E.A.; Moreira, A.A.; Gimbel, M.L.; Egro, F.M. Complications in Prolonged Intraoperative Ischemia Time in Free Flap Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marre, D.; Hontanilla, B. Increments in ischaemia time induces microvascular complications in the DIEP flap for breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2013, 66, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.T.; Lee, J.E.; Nam, S.J.; Mun, G.H. Ischaemic time and fat necrosis in breast reconstruction with a free deep inferior epigastric perforator flap. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2013, 66, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, P.A. Ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Br. J. Surg. 1994, 81, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Heuvel, M.G.W.; Buurman, W.A.; Bast, A.; van der Hulst, R.R.W.J. Review: Ischaemia–reperfusion injury in flap surgery. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2009, 62, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scampa, M.; Martineau, J.; Boet, S.; Pignel, R.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy outcomes in post-irradiated patient undergoing microvascular breast reconstruction: A preliminary retrospective comparative study. JPRAS Open 2024, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.T.; Agarwal, J.P.; Ascherman, J.A.; Caterson, S.A.; Gray, D.D.; Hollenbeck, S.T.; Khan, S.A.; Loeding, L.D.; Mahabir, R.C.; Miller, A.S.; et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline: Autologous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP or Pedicled TRAM Abdominal Flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 651e–664e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, S.O.P.; Damen, T.H.C.; Mureau, M.A.M.; Rakhorst, H.A.; Roche, N.A. A Critical Review of Perioperative Complications in 175 Free Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstructions. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2007, 59, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macadam, S.A.; Zhong, T.; Weichman, K.; Papsdorf, M.; Lennox, P.A.; Hazen, A.; Matros, E.; Disa, J.; Mehrara, B.; Pusic, A.L. Quality of Life and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Multicenter Comparison of Four Abdominally Based Autologous Reconstruction Methods. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann-Sager, J.; Wilkins, E.G.; Pusic, A.L.; Qi, J.; Hamill, J.B.; Kim, H.M.; Guldbrandsen, G.E.; Chun, Y.S. Complications and Patient-Reported Outcomes after Abdominally Based Breast Reconstruction: Results of the Mastectomy Reconstruction Outcomes Consortium Study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahabedian, M.Y.; Patel, K. Autologous flap breast reconstruction: Surgical algorithm and patient selection. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 113, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, J., 3rd; Scheflan, M. The latissimus dorsi musculocutaneous flap: A one-stage breast reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 1980, 7, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Hao, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Shao, Z.; Wu, J. Latissimus dorsi flap—The main force in breast reconstruction for breast tumor in Chinese population. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1159073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldanha, I.J.; Cao, W.; Broyles, J.M.; Adam, G.P.; Bhuma, M.R.; Mehta, S.; Dominici, L.S.; Pusic, A.L.; Balk, E.M. AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. In Breast Reconstruction After Mastectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Steffenssen, M.C.W.; Kristiansen, A.H.; Damsgaard, T.E. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Functional Shoulder Impairment After Latissimus Dorsi Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2019, 82, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mull, A.B.; Qureshi, A.A.; Zubovic, E.; Rao, Y.J.; Zoberi, I.; Sharma, K.; Myckatyn, T.M. Impact of Time Interval between Radiation and Free Autologous Breast Reconstruction. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2017, 33, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, H.N.; Berlin, N.L.; Sugg, K.B.; Chen, J.S.; Chung, K.C.; Momoh, A.O. The Impact of Timing of Delayed Autologous Breast Reconstruction following Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy on Postoperative Morbidity. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2024, 40, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n = 114 Patients | Control Group | RT | CT | RT + CT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 29 | n = 21 | n = 17 | n = 47 | ||
| Age [years], mean (SD) | 49.0 (6.3) | 54.3 (11.1) | 46.0 (9.9) | 49.0 (8.7) | 0.037 |
| BMI [kg/m2], mean (SD) | 25.9 (4.6) | 26.1 (4.7) | 28.3 (3.7) | 27.3 (4.2) | 0.259 |
| ASA score | |||||
| ASA 1, n (%) | 6 (20.7%) | 1 (4.8%) | 5 (29.4%) | 6 (12.8%) | 0.162 |
| ASA 2, n (%) | 23 (79.3%) | 20 (95.2%) | 12 (70.6%) | 41 (87.2%) | |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Active smoker, n (%) | 9 (31.0%) | 4 (19.0%) | 4 (23.5%) | 10 (21.3%) | 0.050 |
| Obesity (BMI > 30 kg/m2), n (%) | 5 (17.2%) | 5 (23.4%) | 6 (35.3%) | 12 (25.5%) | 0.588 |
| HTN, n (%) | 2 (6.9%) | 4 (19.0%) | 3 (17.6%) | 8 (17.0%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 1 (3.4%) | 3 (14.3%) | 1 (5.9%) | 2 (4.3%) | 0.569 |
| Abdominal surgery history, n (%) | 14 (48.3%) | 16 (76.2%) | 7 (41.1%) | 19 (40.4%) | 0.060 |
| n = 114 Patients | Control Group | RT | CT | RT + CT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 29 | n = 21 | n = 17 | n = 47 | ||
| Immediate/Delayed reconstruction | |||||
| Immediate, n (%) | 12 (41.4%) | 5 (23.8%) | 7 (41.2%) | 7 (14.9%) | 0.040 |
| Delayed, n (%) | 17 (58.6%) | 16 (76.2%) | 10 (58.8%) | 40 (85.1%) | |
| Radiotherapy administration | |||||
| Post breast-conserving surgery, n (%) | N.A. | 10 (47.6%) | N.A. | 17 (36.2%) | 0.38 |
| Post mastectomy, n (%) | N.A. | 11 (52.4%) | N.A. | 30 (63.8%) | |
| Unilateral/Bilateral reconstruction | |||||
| Unilateral, n (%) | 25 (86.2%) | 20 (95.2%) | 5 (29.4%) | 37 (78.7%) | <0.001 |
| Bilateral, n (%) | 4 (13.8%) | 1 (4.8%) | 12 (70.5%) | 10 (21.3%) | |
| Operation time [minutes], mean (SD) | 466 (127.1) | 486.6 (133.6) | 601 (144.4) | 506.9 (107) | 0.005 |
| Postoperative length of stay [days], mean (SD) | 9 (2.4) | 9 (2.6) | 10.2 (5.2) | 10 (3.5) | 0.636 |
| Type of flap n = 141 | |||||
| DIEP, n (%) | 33 (100%) | 22 (100%) | 29 (100%) | 57 (100%) | 1.000 |
| Ischemia time [minutes], mean (SD) | 100 (31.3) | 85 (35.5) | 98 (32.7) | 94 (35.6) | 0.512 |
| Number of flap perforators, mean (SD) | 2 (0.8) | 2 (0.92) | 2 (0.6) | 2 (1.1) | 0.947 |
| Target vessel | |||||
| IMA, n (%) | 33 (100%) | 22 (100%) | 29 (100%) | 57 (100%) | 1.000 |
| Venous anastomosis with coupler, n (%) | 14 (42.4%) | 15 (68.2%) | 15 (51.7%) | 34 (59.6%) | 0.233 |
| Surgical indication | |||||
| Prophylactic, n (%) | 2 (6.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 8 (27.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | <0.001 |
| Oncologic, n (%) | 31 (93.9%) | 22 (100%) | 21 (72.4%) | 57 (100%) | |
| Type of previous Mastectomy | |||||
| SSM, n (%) | 23 (69.7%) | 16 (72.7%) | 15 (51.7%) | 33 (57.9%) | 0.309 |
| NSM, n (%) | 9 (27.3%) | 4 (18.2%) | 11 (37.9%) | 7 (12.3%) | 0.043 |
| Simple mastectomy, n (%) | 1 (3.0%) | 2 (9.1%) | 3 (10.4%) | 17 (29.8%) | 0.004 |
| n = 141 DIEPs | Control Group | RT | CT | RT + CT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N of Flaps | n = 33 | n = 22 | n = 29 | n = 57 | |
| Flaps without complications, n (%) | 29 (87.9%) | 18 (81.8%) | 26 (89.7%) | 43 (75.4%) | 0.306 |
| Flaps with ≥1 complication, n (%) | 4 (12.1%) | 4 (18.2%) | 3 (10.3%) | 14 (24.6%) | |
| Seroma, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.141 |
| Hematoma, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (4.5%) | 1 (3.4%) | 2 (1.8%) | 0.333 |
| Wound infection, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.4%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0.638 |
| Wound dehiscence, n (%) | 1 (3.0%) | 1 (4.5%) | 1 (3.4%) | 2 (3.5%) | 0.993 |
| Delayed wound healing, n (%) | 2 (6.1%) | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (3.5%) | 0.627 |
| Partial NAC necrosis, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0.480 |
| Flaps with ≥1 microvascular complication, n (%) | 1 (3.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 8 (14.0%) | 0.021 |
| Venous congestion, n (%) | 1 (3.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.348 |
| Venous thrombosis, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (3.5%) | 0.393 |
| Intraoperative arterial thrombosis, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0.686 |
| Flap loss, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (3.5%) | 0.393 |
| Partial flap loss, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (5.3%) | 0.211 |
| n = 114 Patients | Control Group | RT | CT | RT + CT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 29 | n = 21 | n = 17 | n = 47 | ||
| No complication, n (%) | 22 (75.9%) | 19 (90.5%) | 11 (64.7%) | 26 (55.3%) | 0.025 |
| ≥1 complication, n (%) | 7 (24.1%) | 2 (9.5%) | 6 (35.3%) | 21 (44.7%) | |
| Complication types | |||||
| Seroma, n (%) | 2 (6.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (11.8%) | 2 (4.3%) | 0.414 |
| Hematoma, n (%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (6.4%) | 0.470 |
| Wound infection, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (5.9%) | 2 (4.3%) | 0.469 |
| Wound dehiscence, n (%) | 2 (6.9%) | 1 (4.8%) | 1 (5.9%) | 6 (12.8%) | 0.645 |
| Delayed wound healing, n (%) | 2 (6.9%) | 1 (4.8%) | 2 (11.8%) | 7 (14.9%) | 0.547 |
| Incisional hernia, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0.697 |
| Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval (95%-CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.023 | 0.960–1.090 | 0.475 |
| Smoker | 1.696 | 0.539–5.33 | 0.366 |
| RT | 1.302 | 0.236–7.191 | 0.762 |
| CT | 0.832 | 0.162–4.277 | 0.826 |
| RT + CT | 1.607 | 0.456–5.659 | 0.460 |
| Operation time | 0.999 | 0.995–1.003 | 0.717 |
| Ischemia time | 1.019 | 1.004–1.035 | 0.014 |
| Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval (95%-CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.941 | 0.845–1.047 | 0.262 |
| Smoker | 1.529 | 0.245–9.220 | 0.643 |
| RT | 0.000 | 0.000–N.A. | 0.999 |
| CT | 1.309 | 0.072–23.902 | 0.856 |
| RT + CT | 5.558 | 0.575–53.751 | 0.138 |
| Operation time | 1.000 | 0.993–1.006 | 0.927 |
| Ischemia time | 1.014 | 0.992–1.036 | 0.207 |
| Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval (95%-CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.008 | 0.961–1.056 | 0.752 |
| BMI | 1.001 | 0.908–1.102 | 0.988 |
| Smoker | 1.698 | 0.608–4.238 | 0.257 |
| CT | 0.814 | 0.266–2.492 | 0.718 |
| Operation time | 0.998 | 0.995–1.001 | 0.222 |
| Abdominal surgery history | 1.521 | 0.679–3.407 | 0.308 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nava, C.M.; Martineau, J.; Dong, E.T.C.; Zinner, G.; Oranges, C.M. The Impact of Preoperative Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy on Autologous Breast Reconstruction Outcomes—A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030512
Nava CM, Martineau J, Dong ETC, Zinner G, Oranges CM. The Impact of Preoperative Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy on Autologous Breast Reconstruction Outcomes—A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Cancers. 2025; 17(3):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030512
Chicago/Turabian StyleNava, Caterina M., Jérôme Martineau, Edward T. C. Dong, Gauthier Zinner, and Carlo M. Oranges. 2025. "The Impact of Preoperative Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy on Autologous Breast Reconstruction Outcomes—A Retrospective Single-Center Study" Cancers 17, no. 3: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030512
APA StyleNava, C. M., Martineau, J., Dong, E. T. C., Zinner, G., & Oranges, C. M. (2025). The Impact of Preoperative Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy on Autologous Breast Reconstruction Outcomes—A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Cancers, 17(3), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030512






