Risk of Esophageal and Gastric Cancer by Histologic Subtype in Steatotic Liver Disease: A UK Biobank Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Definition of Cancer Diagnosis
2.4. Definition of Steatotic Liver Diseases
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Incidence of Upper GI Cancers During Follow-Up According to SLD Subgroups
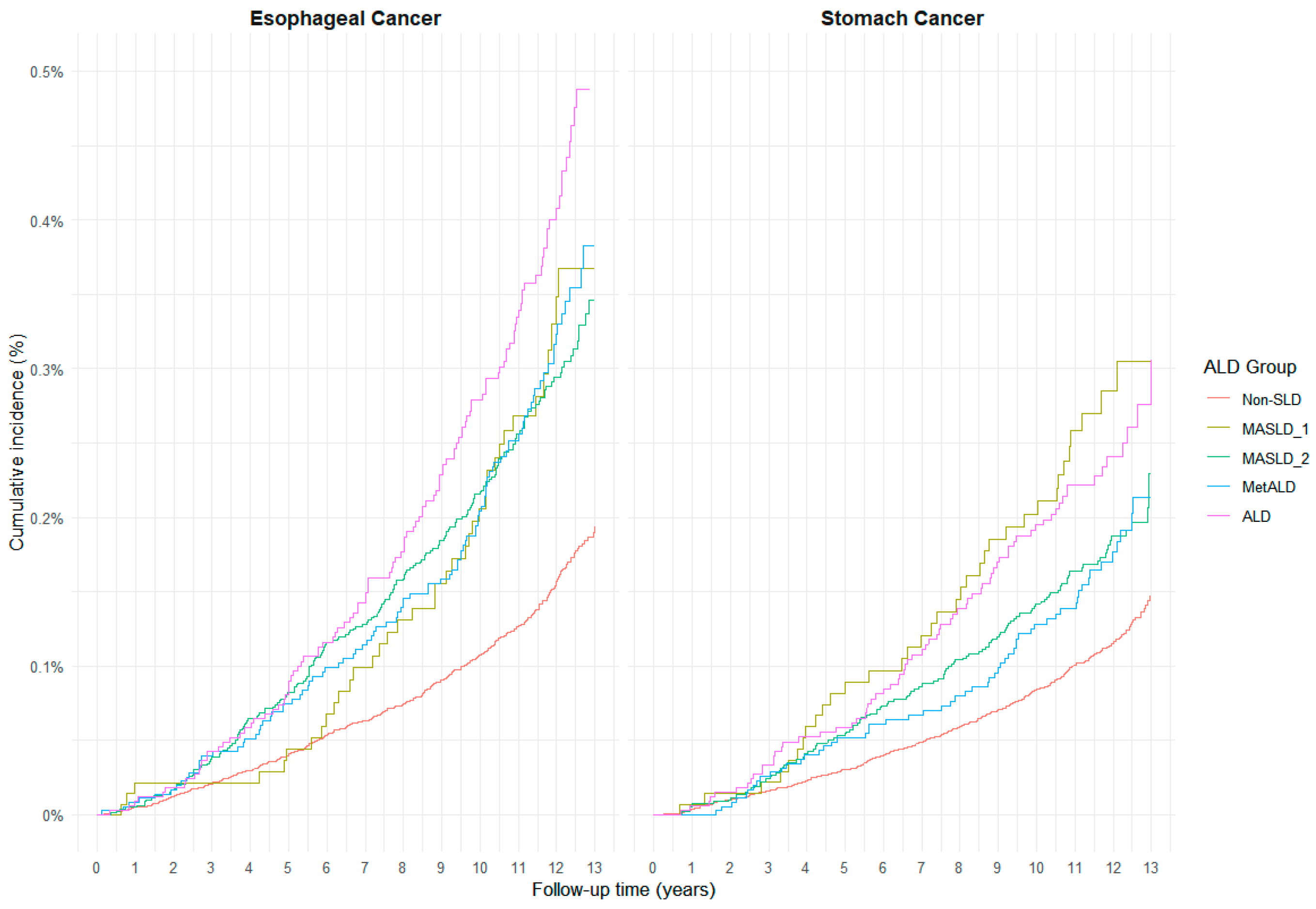
3.3. Cumulative Incidence and Subtype-Specific Risk of Upper GI Cancers by SLD Category
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kanwal, F.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Rinella, M.E. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Update and impact of new nomenclature on the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases practice guidance on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2024, 79, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.H.; Jin, Y.J.; Kim, G.A.; Sung, P.S.; Yoo, J.J.; Chang, Y.; Lee, E.J.; et al. KASL clinical practice guidelines for the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease 2025. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, S1–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Liu, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Temporal relationship between chronic inflammation and insulin resistance and their combined cumulative effect on cancer risk: A longitudinal cohort study. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and increased risk of incident extrahepatic cancers: A meta-analysis of observational cohort studies. Gut 2022, 71, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Si, C.; Gong, J.; Zhou, H.; Gu, J.; Qin, A.; Song, W. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and cancer risk: A cohort study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Jung, J.; Han, S.; Kim, G.A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and MetALD increases the risk of liver cancer and gastrointestinal cancer: A nationwide cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, P.; Palui, R.; Ray, S. Heterogeneity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Implications for clinical practice and research activity. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1584–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.A.; Reynolds, J.V. Visceral Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 627270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; El Hajj, N.; Sittler, S.; Lammert, N.; Barnes, R.; Meloni-Ehrig, A. Gastric cancer: Classification, histology and application of molecular pathology. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2012, 3, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaspuro, M. Key role of local acetaldehyde in upper GI tract carcinogenesis. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherübl, H. Alcohol Use and Gastrointestinal Cancer Risk. Visc. Med. 2020, 36, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Baloch, Z.; He, T.T.; Xia, X. Alcohol Consumption and Gastric Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, N.E.; Lacey, B.; Lawlor, D.A.; Pell, J.P.; Gallacher, J.; Smeeth, L.; Elliott, P.; Matthews, P.M.; Lyons, R.A.; Whetton, A.D. Prospective study design and data analysis in UK Biobank. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eadf4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, G.; Bellentani, S.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Passalacqua, M.; Castiglione, A.; Tiribelli, C. The Fatty Liver Index: A simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Nomenclature Revision Consensus Task Force on behalf of the Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). A new Korean nomenclature for steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 30, S214–S216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Valenti, L.; Byrne, C.D. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 393, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHenry, S.; Zong, X.; Shi, M.; Fritz, C.D.L.; Pedersen, K.S.; Peterson, L.R.; Lee, J.K.; Fields, R.C.; Davidson, N.O.; Cao, Y. Risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and associations with gastrointestinal cancers. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 3299–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa-Allemant, P.; Hubbard, R.A.; Kaplan, D.E.; Serper, M. Adverse Liver Outcomes, Cardiovascular Events, and Mortality in Steatotic Liver Disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2025, 185, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, G.E.; Yu, S.J.; Yoo, J.J.; Cho, Y.; Lee, K.N.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Han, K.; Cho, E.J. Differential risk of 23 site-specific incident cancers and cancer-related mortality among patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: A population-based cohort study with 9.7 million Korean subjects. Cancer Commun. 2023, 43, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustgi, A.K.; El-Serag, H.B. Esophageal carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, T.; Maj, C.; Gehlen, J.; Borisov, O.; Haas, S.L.; Gockel, I.; Vieth, M.; Piessen, G.; Alakus, H.; Vashist, Y. Dissecting the genetic heterogeneity of gastric cancer. eBioMedicine 2023, 92, 104616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, T.L.; Davis, S.; Kristal, A.; Thomas, D.B. Obesity, alcohol, and tobacco as risk factors for cancers of the esophagus and gastric cardia: Adenocarcinoma versus squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1995, 4, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, K.-P. Risk factors of gastric cancer and lifestyle modification for prevention. J. Gastric Cancer 2023, 24, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.J.; Shin, C.M.; Han, K.; Jung, J.H.; Jin, E.H.; Lim, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Yoon, H.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, N.; et al. Impact of Smoking and Alcohol Consumption on Early-Onset Gastric Cancer Development in Young Koreans: A Population-Based Study. J. Gastric Cancer 2024, 24, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, C.; Rosso, C.; Marietti, M.; Bugianesi, E. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Extra-Hepatic Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Obora, A.; Kojima, T.; Fukui, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with obesity as an independent predictor for incident gastric and colorectal cancer: A population-based longitudinal study. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2019, 6, e000295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelucchi, C.; Gallus, S.; Garavello, W.; Bosetti, C.; La Vecchia, C. Cancer risk associated with alcohol and tobacco use: Focus on upper aero-digestive tract and liver. Alcohol Res. Health 2006, 29, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Myung, S.K. Erroneous conclusions about the association between light alcohol drinking and the risk of cancer: Comments on Bagnardi et al.’s meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Deitch, E.A. Dissolution of lipids from mucus: A possible mechanism for prompt disruption of gut barrier function by alcohol. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, J.A.; Patton, G.C.; Cini, K.I.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbas, N.; Abd Al Magied, A.H.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Abdollahi, A.; Abdoun, M. Global, regional, and national prevalence of child and adolescent overweight and obesity, 1990–2021, with forecasts to 2050: A forecasting study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 785–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Han, K.; Yoo, J.; Yeo, Y.; Cho, I.Y.; Cho, B.; Park, J.-H.; Shin, D.W.; Cho, J.H.; Park, Y.-M. Association between metabolic syndrome and risk of esophageal cancer: A nationwide population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2022, 31, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, D.H.; Han, K.-D.; Kim, H.S.; Yoon, H.; Shin, C.M.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, N. The relationship between drinking alcohol and esophageal, gastric or colorectal cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study of South Korea. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holleczek, B.; Schöttker, B.; Brenner, H. Helicobacter pylori infection, chronic atrophic gastritis and risk of stomach and esophagus cancer: Results from the prospective population-based ESTHER cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 2773–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Non-SLD | MASLD1 | MASLD2 | MetALD | ALD | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 293,032) | (N = 13,996) | (N = 79,472) | (N = 35,905) | (N = 33,548) | |||
| Age | 55.82 (8.22) | 57.18 (8.10) | 56.51 (8.01) | 56.88 (7.71) | 58.10 (7.39) | <0.001 | |
| Sex | Male | 107,355 (36.6) | 6520 (46.6) | 45,107 (56.8) | 27,048 (75.3) | 26,874 (80.1) | <0.001 |
| Female | 185,677 (63.4) | 7476 (53.4) | 34,365 (43.2) | 8857 (24.7) | 6674 (19.9) | ||
| Smoking status | Never | 171,299 (58.8) | 8419 (60.6) | 42,175 (53.3) | 16,583 (46.4) | 11,691 (35.0) | <0.001 |
| Previous | 90,585 (31.1) | 3909 (28.2) | 28,040 (35.4) | 15,533 (43.4) | 17,011 (50.9) | ||
| Current | 29,458 (10.1) | 1558 (11.2) | 8890 (11.2) | 3649 (10.2) | 4734 (14.2) | ||
| Weekly alcohol use | Never | 22,749 (7.8) | 13,996 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| <2 | 140,928 (48.3) | 0 (0.0) | 79,472 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| 3–4 | 69,506 (23.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 35,905 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Almost daily | 58,857 (20.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 33,548 (100.0) | ||
| Hypertension | No | 258,708 (88.3) | 11,504 (82.2) | 66,082 (83.2) | 30,258 (84.3) | 27,822 (82.9) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 34,324 (11.7) | 2492 (17.8) | 13,390 (16.8) | 5647 (15.7) | 5726 (17.1) | ||
| Diabetes (all types) | No | 283,144 (96.6) | 11,025 (78.8) | 67,812 (85.3) | 32,171 (89.6) | 30,183 (90.0) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 9888 (3.4) | 2971 (21.2) | 11,660 (14.7) | 3734 (10.4) | 3365 (10.0) | ||
| Dyslipidemia | No | 267,785 (91.4) | 11,788 (84.2) | 68,662 (86.4) | 31,116 (86.7) | 28,750 (85.7) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 25,247 (8.6) | 2208 (15.8) | 10,810 (13.6) | 4789 (13.3) | 4798 (14.3) | ||
| BMI | 25.19 (3.26) | 32.77 (5.14) | 32.16 (4.71) | 30.66 (3.82) | 30.06 (3.67) | <0.001 | |
| WC | 83.58 (9.92) | 103.80 (11.08) | 103.00 (10.44) | 101.82 (9.15) | 101.82 (9.12) | <0.001 | |
| GGT | 26.21 (20.62) | 48.45 (51.10) | 48.30 (46.93) | 57.26 (54.44) | 72.85 (79.11) | <0.001 | |
| Glucose | 89.60 (16.92) | 101.12 (37.94) | 96.62 (30.18) | 94.43 (24.37) | 95.32 (23.81) | <0.001 | |
| Triglyceride | 118.85 (55.44) | 210.63 (108.10) | 212.17 (105.74) | 213.19 (105.62) | 212.68 (108.91) | <0.001 | |
| HDL | 60.53 (14.64) | 45.71 (10.87) | 46.70 (10.65) | 49.34 (11.10) | 52.48 (12.51) | <0.001 |
| Non-SLD | MASLD1 | MASLD2 | MetALD | ALD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| End-point status | Subtype | (N = 293,032, 3,527,433 person-year) | (N = 13,996, 164,360 person-year) | (N = 79,472, 944,540 person-year) | (N = 35,905, 425,466 person-year) | (N = 33,548, 389,545 person-year) |
| Esophageal cancer | Overall | 426 (12.08) | 39 (23.73) | 221 (23.40) | 106 (24.91) | 127 (32.60) |
| Squamous | 159 (4.51) | 9 (5.48) | 20 (2.12) | 17 (4.00) | 30 (7.70) | |
| Adeno | 251 (7.12) | 27 (16.43) | 191 (20.22) | 83 (19.51) | 91 (23.36) | |
| Others | 16 (0.45) | 3 (1.83) | 10 (1.06) | 6 (1.41) | 6 (1.54) | |
| Gastric cancer | Overall | 327 (9.27) | 37 (22.51) | 142 (15.03) | 62 (14.57) | 74 (19.00) |
| Intestinal | 203 (5.75) | 27 (16.43) | 106 (11.22) | 45 (10.58) | 57 (14.63) | |
| Non-intestinal | 124 (3.52) | 10 (6.08) | 36 (3.81) | 17 (4.00) | 17 (4.36) | |
| Death | Overall | 19,385 (549.55) | 2013 (1224.75) | 8096 (857.14) | 3310 (777.97) | 3989 (1024.01) |
| Non-SLD | MASLD1 | MASLD2 | MetALD | ALD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR [95% CI] | HR [95% CI] | HR [95% CI] | HR [95% CI] | |||
| Crude | ||||||
| Esophageal cancer | Overall | (Ref) | 1.99 [1.43–2.76] | 1.97 [1.68–2.32] | 2.11 [1.70–2.61] | 2.75 [2.25–3.35] |
| Squamous | (Ref) | 1.23 [0.63–2.41] | 0.48 [0.30–0.76] | 0.91 [0.55–1.50] | 1.74 [1.18–2.57] | |
| Adeno | (Ref) | 2.34 [1.57–3.49] | 2.90 [2.40–3.50] | 2.81 [2.19–3.60] | 3.35 [2.63–4.26] | |
| Others | (Ref) | 3.98 [1.16–13.66] | 2.31 [1.05–5.09] | 3.08 [1.20–7.86] | 3.36 [1.31–8.58] | |
| Gastric cancer | Overall | (Ref) | 2.45 [1.74–3.44] | 1.65 [1.36–2.01] | 1.61 [1.22–2.11] | 2.08 [1.62–2.68] |
| Intestinal | (Ref) | 2.87 [1.92–4.29] | 1.98 [1.57–2.51] | 1.88 [1.36–2.59] | 2.57 [1.92–3.45] | |
| Non-intestinal | (Ref) | 1.75 [0.92–3.33] | 1.11 [0.76–1.61] | 1.17 [0.70–1.94] | 1.27 [0.76–2.10] | |
| Adjusted | ||||||
| Esophageal cancer | Overall | (Ref) | 1.00 [0.66–1.53] | 1.60 [1.30–1.96] | 1.41 [1.07–1.86] | 1.49 [1.14–1.93] |
| Squamous | (Ref) | 0.51 [0.24–1.09] | 0.76 [0.45–1.30] | 0.84 [0.47–1.50] | 1.22 [0.76–1.97] | |
| Adeno | (Ref) | 1.52 [0.86–2.69] | 1.77 [1.40–2.24] | 1.80 [1.27–2.55] | 1.67 [1.20–2.32] | |
| Others | (Ref) | 3.37 [0.35–32.71] | 1.40 [0.54–3.65] | 1.19 [0.38–3.79] | 6.97 [0.83–58.49] | |
| Gastric cancer | Overall | (Ref) | 1.50 [0.93–2.40] | 1.08 [0.86–1.35] | 1.39 [0.97–1.99] | 1.55 [1.10–2.19] |
| Intestinal | (Ref) | 1.67 [0.94–2.97] | 1.21 [0.92–1.60] | 1.74 [1.10–2.73] | 1.77 [1.17–2.68] | |
| Non-intestinal | (Ref) | 1.16 [0.50–2.70] | 0.80 [0.53–1.23] | 0.95 [0.51–1.76] | 1.11 [0.59–2.11] |
| Non-SLD | MASLD1 | MASLD2 | MetALD | ALD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR [95% CI] | HR [95% CI] | HR [95% CI] | HR [95% CI] | |||
| <60 years old | ||||||
| Esophageal cancer | Overall | (Ref) | 0.97 [0.47–2.00] | 1.51 [1.08–2.11] | 2.19 [1.28–3.75] | 1.72 [1.10–2.67] |
| Squamous | (Ref) | 0.39 [0.08–1.85] | 1.14 [0.50–2.59] | 0.95 [0.32–2.84] | 1.38 [0.66–2.91] | |
| Adeno | (Ref) | 1.30 [0.53–3.21] | 1.49 [1.01–2.18] | 3.11 [1.54–6.25] | 1.96 [1.09–3.51] | |
| Others | (Ref) | - | - | - | - | |
| Gastric cancer | Overall | (Ref) | 1.90 [0.72–5.02] | 1.50 [1.02–2.21] | 1.58 [0.86–2.90] | 2.05 [1.04–4.07] |
| Intestinal | (Ref) | 7.97 [0.96–66.37] | 1.75 [1.09–2.81] | 1.69 [0.79–3.58] | 2.88 [1.17–7.13] | |
| Non-intestinal | (Ref) | 0.87 [0.24–3.13] | 1.05 [0.52–2.11] | 1.38 [0.49–3.89] | 1.21 [0.40–3.65] | |
| ≥60 years old | ||||||
| Esophageal cancer | Overall | (Ref) | 1.00 [0.60–1.68] | 1.63 [1.25–2.12] | 1.16 [0.83–1.62] | 1.36 [0.98–1.88] |
| Squamous | (Ref) | 0.55 [0.23–1.32] | 0.56 [0.27–1.16] | 0.79 [0.40–1.57] | 1.12 [0.61–2.08] | |
| Adeno | (Ref) | 1.65 [0.79–3.46] | 1.94 [1.43–2.62] | 1.43 [0.95–2.16] | 1.52 [1.02–2.26] | |
| Others | (Ref) | 2.18 [0.20–24.39] | 1.02 [0.25–4.20] | 0.84 [0.22–3.21] | 3.23 [0.33–31.52] | |
| Gastric cancer | Overall | (Ref) | 1.39 [0.81–2.38] | 0.89 [0.67–1.19] | 1.31 [0.84–2.04] | 1.40 [0.94–2.09] |
| Intestinal | (Ref) | 1.35 [0.73–2.50] | 1.00 [0.71–1.41] | 1.80 [1.02–3.18] | 1.54 [0.97–2.45] | |
| Non-intestinal | (Ref) | 1.44 [0.46–4.49] | 0.68 [0.39–1.17] | 0.77 [0.35–1.67] | 1.06 [0.48–2.33] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, D.; Han, J.W.; Muir, K.R.; Lophatananon, A.; Lee, J. Risk of Esophageal and Gastric Cancer by Histologic Subtype in Steatotic Liver Disease: A UK Biobank Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213416
Kang D, Han JW, Muir KR, Lophatananon A, Lee J. Risk of Esophageal and Gastric Cancer by Histologic Subtype in Steatotic Liver Disease: A UK Biobank Study. Cancers. 2025; 17(21):3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213416
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Donghoon, Ji Won Han, Kenneth R. Muir, Artitaya Lophatananon, and Jongin Lee. 2025. "Risk of Esophageal and Gastric Cancer by Histologic Subtype in Steatotic Liver Disease: A UK Biobank Study" Cancers 17, no. 21: 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213416
APA StyleKang, D., Han, J. W., Muir, K. R., Lophatananon, A., & Lee, J. (2025). Risk of Esophageal and Gastric Cancer by Histologic Subtype in Steatotic Liver Disease: A UK Biobank Study. Cancers, 17(21), 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213416






