Diagnostic Models for Predicting Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas Using Circulating Plasma MicroRNAs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Selection of MicroRNA
2.3. Microarray
2.4. Microarray Raw Data Preparation and Statistical Analysis
2.5. RNA Isolation
2.6. Reverse Transcription Reaction
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Statistics Analysis
3. Result
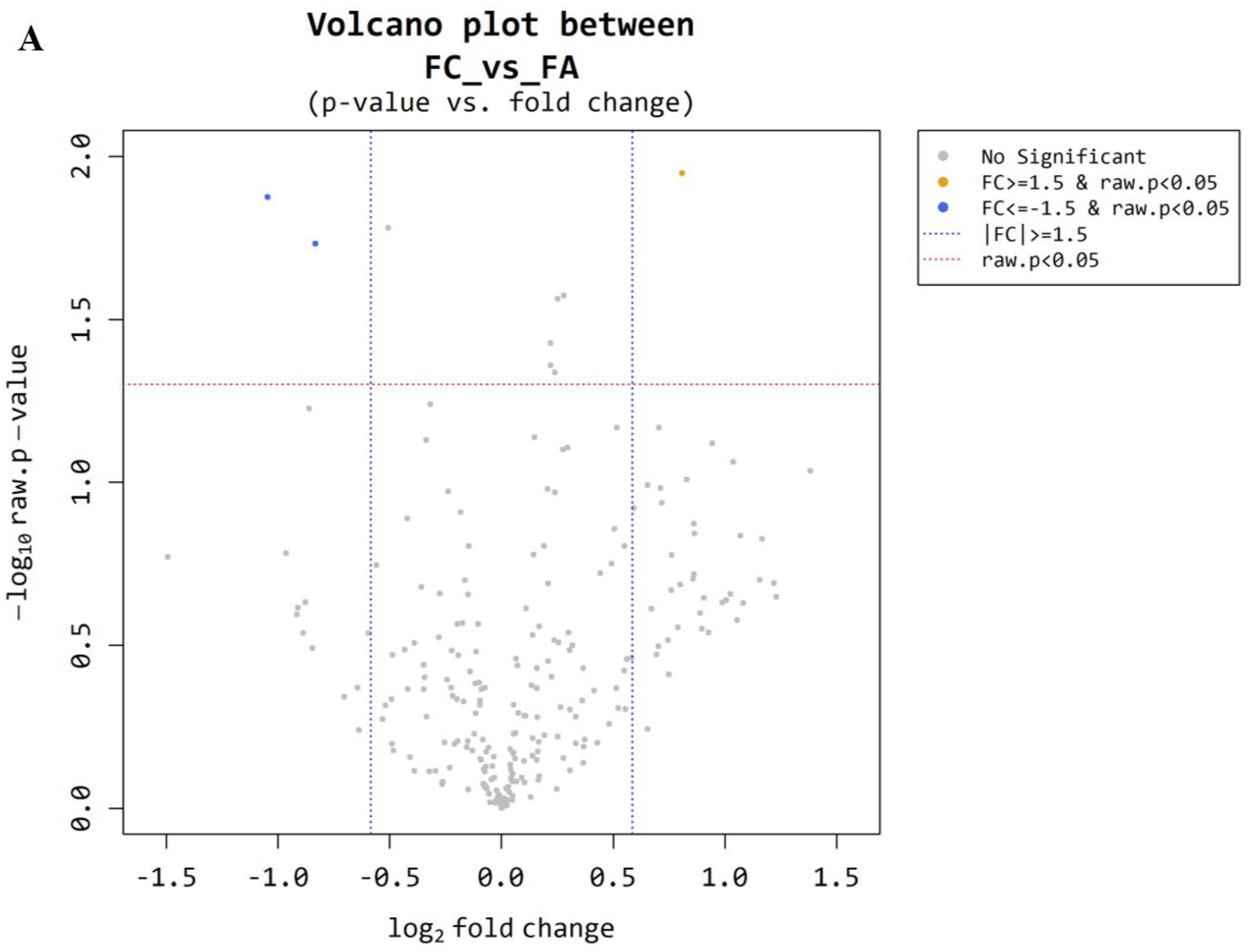
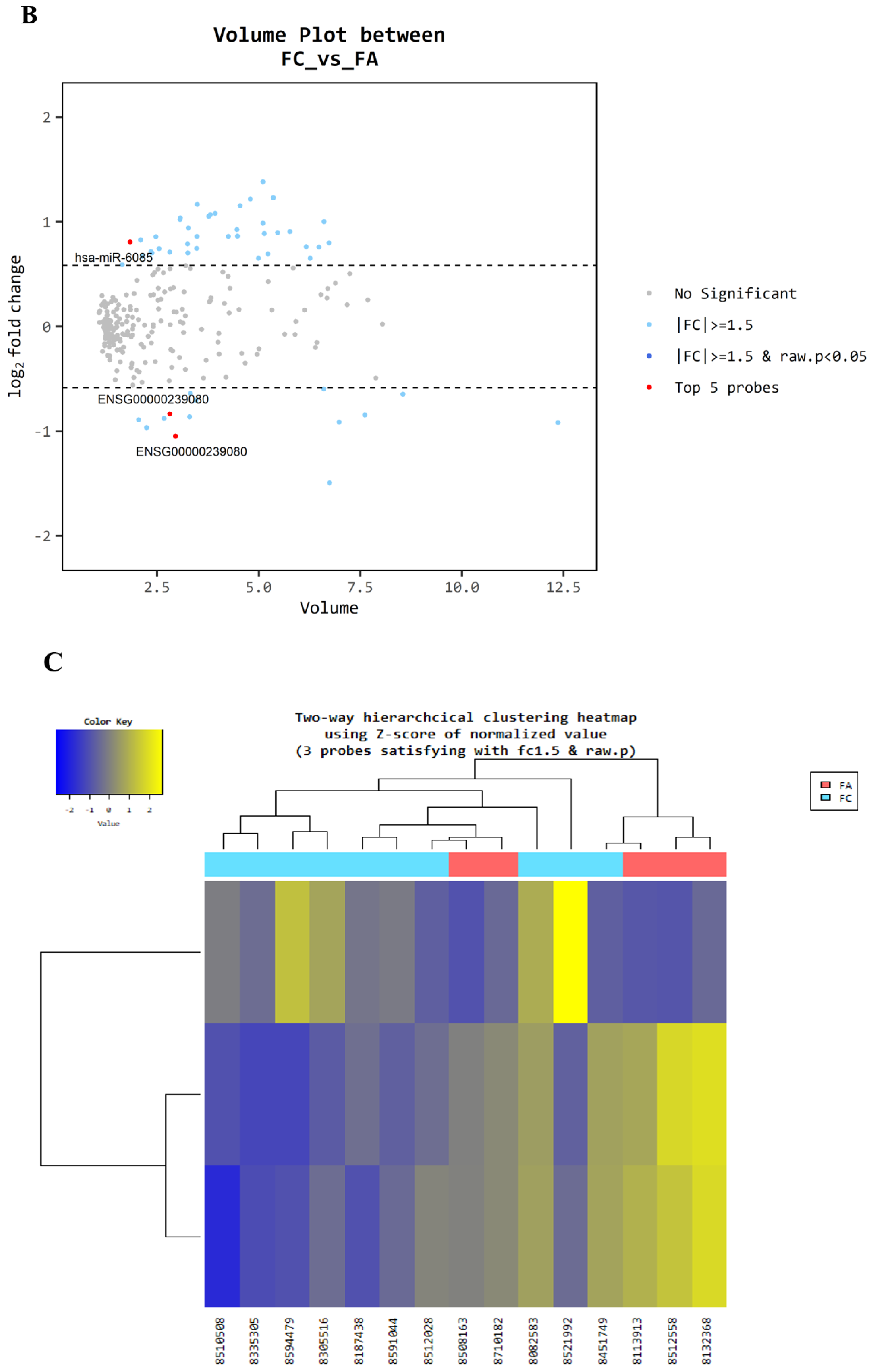
3.1. Microarray Between FC and FA
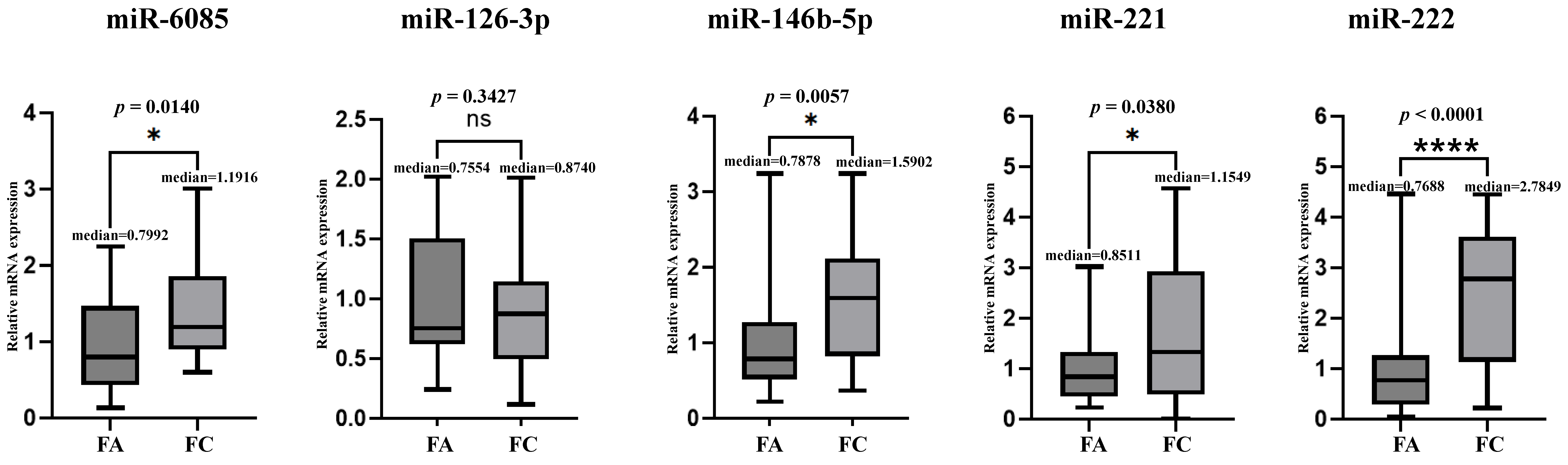
3.2. Plasma miRNAs TaqMan (qRT-PCR) Assay Between FC and FA (Utility Assessment)
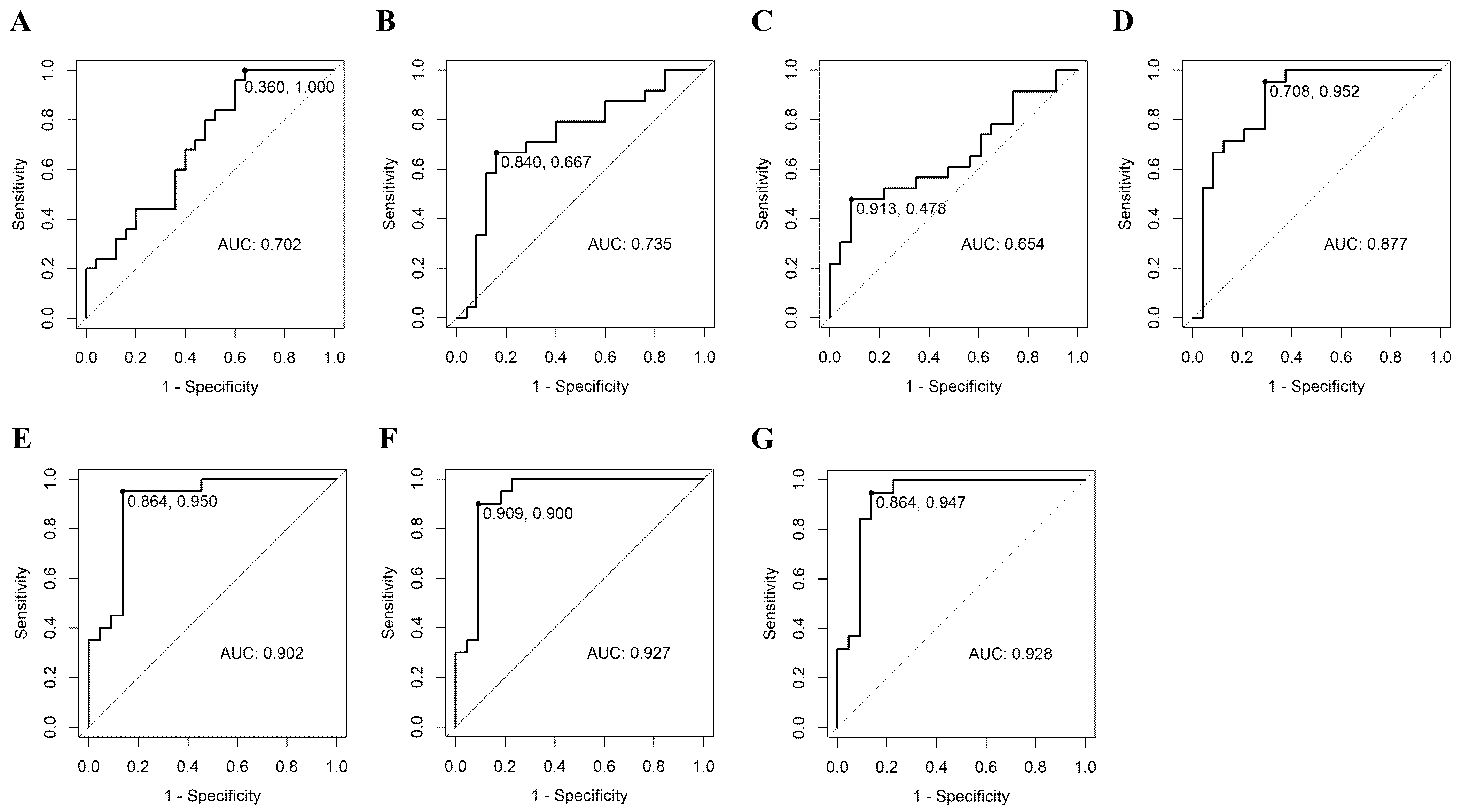
3.3. Prediction of Malignancy of FC by ROC Curve of Plasma MicroRNA
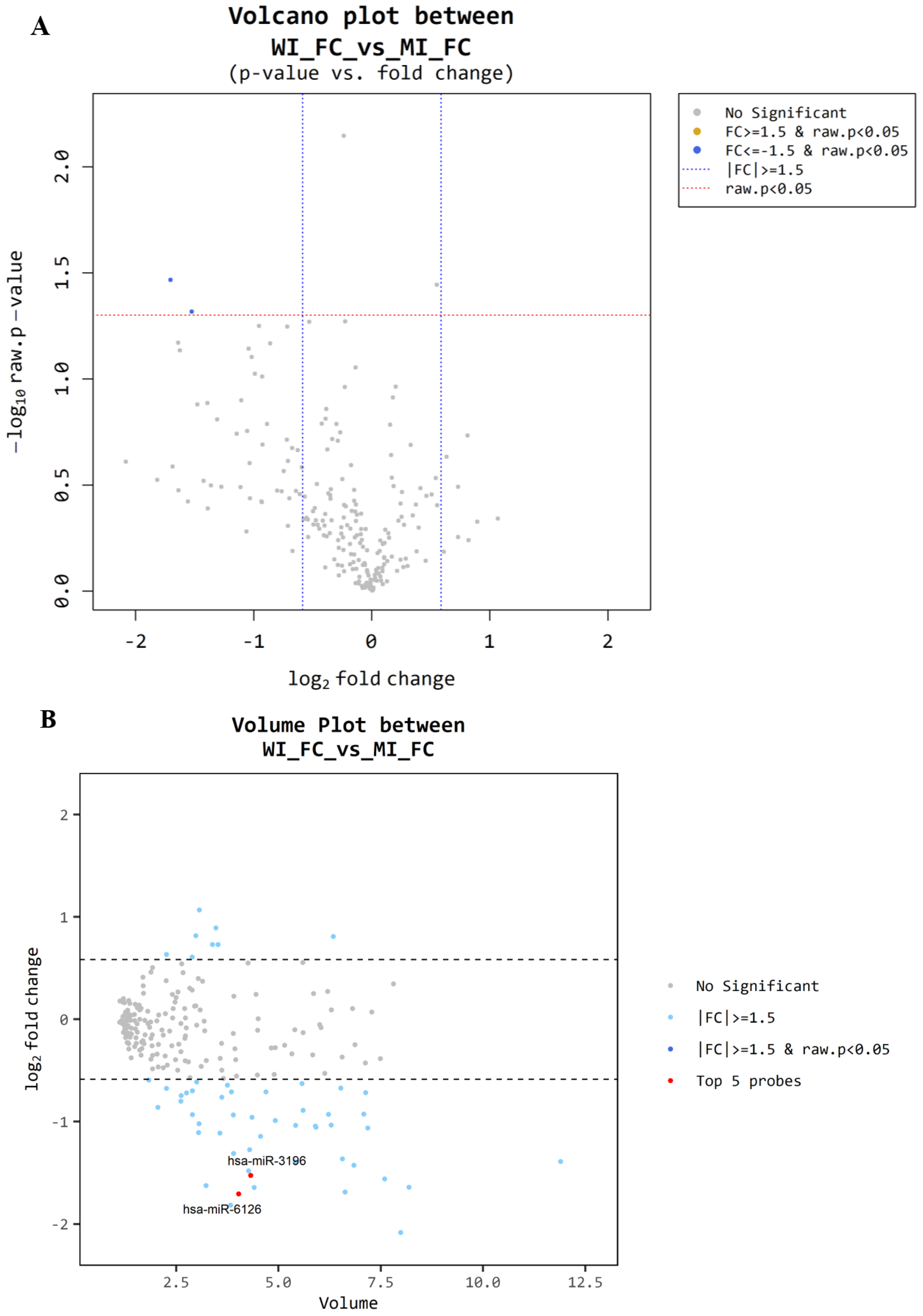
3.4. Microarray Between MI-FC and WI-FC
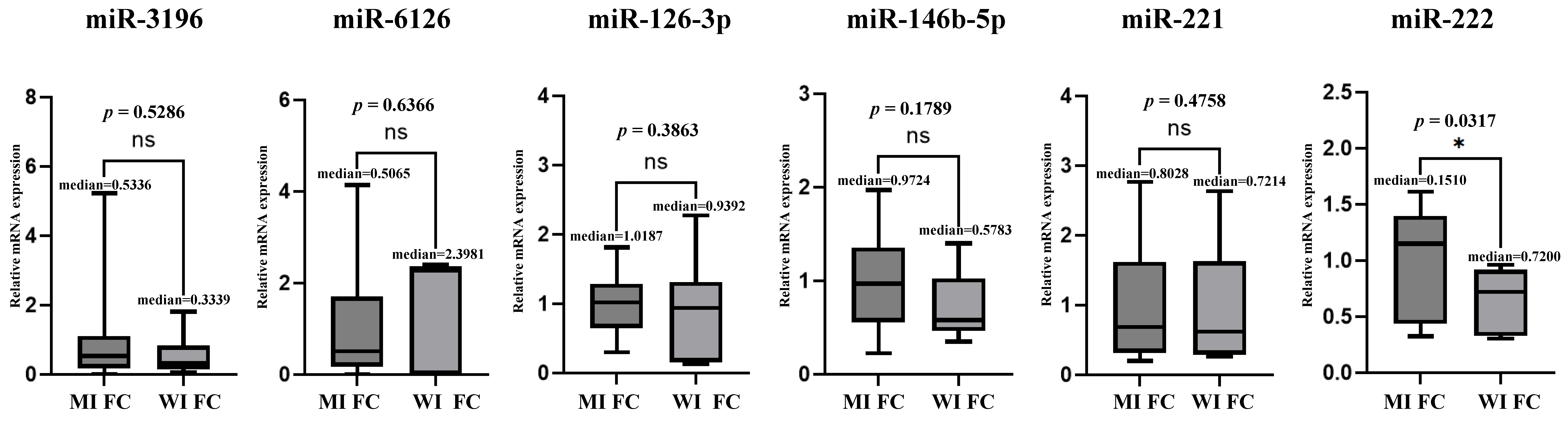
3.5. Microarray and TaqMan (qRT-PCR) Assay Between MI-FC and WI-FC
3.6. Validation Test of Predictive Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Bray, F.; Cao, B.; Franceschi, S.; Vaccarella, S.; Dal Maso, L.; McMahon, M.; Stiller, C.; Ferlay, J.; et al. Thyroid cancer incidence trends by histology in 25 countries: A population-based study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzato, M.; Li, M.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; Singh, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Vaccarella, S.; Dal Maso, L.; McMahon, M.; Stiller, C.; et al. The epidemiological landscape of thyroid cancer worldwide: GLOBOCAN estimates for incidence and mortality rates in 2020. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Devesa, S.S.; Sosa, J.A.; Check, D.; Kitahara, C.M. Trends in Thyroid Cancer Incidence and Mortality in the United States, 1974–2013. JAMA 2017, 317, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; He, L.; Wang, Z.; Dong, W.; Sun, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H. Risk factors for death of follicular thyroid carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine 2023, 82, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.Z.; Baloch, Z.W.; Cochand-Priollet, B.; Schmitt, F.C.; Vielh, P.; VanderLaan, P.A. The 2023 Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Thyroid 2023, 33, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussen, B.M.; Hidayat, H.J.; Salihi, A.; Sabir, D.K.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. MicroRNA: A signature for cancer progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Dutta, A. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Kong, H.; Hou, Y.; Ge, D.; Huang, W.; Ou, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L.; Wu, G.; Song, Y.; et al. Two plasma microRNA panels for diagnosis and subtype discrimination of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 123, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Hu, J.; Lu, B.; Pan, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, L.; et al. Plasma-derived exosomal miR-15a-5p as a promising diagnostic biomarker for early detection of endometrial carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lu, C.; Lai, Y. A serum miRNAs signature for early diagnosis of bladder cancer. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Xu, D.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Sun, L.; Wu, Y.; Qiao, H. Combination of serum microRNAs and ultrasound profile as predictive biomarkers of diagnosis and prognosis for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3611–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, Y.E.; Nikiforova, M.N. Molecular genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewijk, L.; Prins, A.M.; Kist, J.W.; Valk, G.D.; Kranenburg, O.; Rinkes, I.H.; Vriens, M.R. The value of miRNA in diagnosing thyroid cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Biomark. 2012, 11, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Teresi, R.E.; Broelsch, C.E.; Frilling, A.; Eng, C. A limited set of human MicroRNA is deregulated in follicular thyroid carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3584–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, S.; Shabani, N.; Shivaee, S.; Tavangar, S.M.; Yeganeh, M.; Hedayati, M.; Lotfi, J.; Gholami, H. Overexpression of mir-129-1, miR-146b, mir-183, and mir-197 in follicular thyroid carcinoma and adenoma tissues. Mol. Cell Probes. 2020, 51, 101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Kotian, S.; Zeiger, M.A.; Zhang, L.; Kebebew, E. miR-126-3p Inhibits Thyroid Cancer Cell Growth and Metastasis, and Is Associated with Aggressive Thyroid Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Randolph, G.W.; Sawka, A.M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Lee, E.; Song, Y.S.; Chung, E.J.; Kwon, H.; Kim, K.U.; Kim, M.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, W.B.; Kim, W.B.; et al. Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines on the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers; Overview and Summary 2024. Int. J. Thyroidol. 2024, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celano, M.; Rosignolo, F.; Maggisano, V.; Pecce, V.; Iannone, M.; Russo, D.; Bulotta, S. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Thyroid Carcinoma. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 6496570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, R.; Burdakov, V.; Shtam, T.; Radzhabova, Z.; Vasilyev, D.; Tsyrlina, E.; Titov, S.; Ivanov, M.; Berstein, L.; Filatov, M.; et al. Plasma exosomal miR-21 and miR-181a differentiates follicular from papillary thyroid cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 12011–12021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yin, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, D.; Lu, X. Differential expression profiling and functional analysis of microRNAs through stage I-III papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallante, P.; Visone, R.; Croce, C.M.; Fusco, A. Deregulation of microRNA expression in follicular-cell-derived human thyroid carcinomas. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, F91–F104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.R.; Jiang, B.H.; Feng, W.J.; He, Z.L.; Jiang, Y.L.; Xun, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H. Circ0060467 sponges miR-6805 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulating AIFM2 and GPX4 expression. Aging 2024, 16, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Gu, J.; Yu, Y. Celastrol assuages oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced damage in human brain microvascular endothelial cells through the circDLGAP4/miR-6085/GDF11 pathway. Metab. Brain Dis. 2023, 38, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.T.B.; Clark, I.M.; Le, L.T.T. MicroRNA-Based Diagnosis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, A.M.; Mott, J.L. Overview of microRNA biology. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geropoulos, G.; Psarras, K.; Papaioannou, M.; Giannis, D.; Meitanidou, M.; Kapriniotis, K.; Symeonidis, N.; Pavlidis, E.T.; Pavlidis, T.E.; Sapalidis, K.; et al. Circulating microRNAs and Clinicopathological Findings of Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review. In Vivo 2022, 36, 1551–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforova, M.N.; Tseng, G.C.; Steward, D.; Diorio, D.; Nikiforov, Y.E. MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid tumors: Biological significance and diagnostic utility. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macerola, E.; Poma, A.M.; Vignali, P.; Proietti, A.; Torregrossa, L.; Ugolini, C.; Basolo, A.; Matrone, A.; Elisei, R.; Santini, F.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of RAS-mutant thyroid tumors with follicular architecture: MicroRNA signatures to discriminate benign from malignant lesions. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2023, 46, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
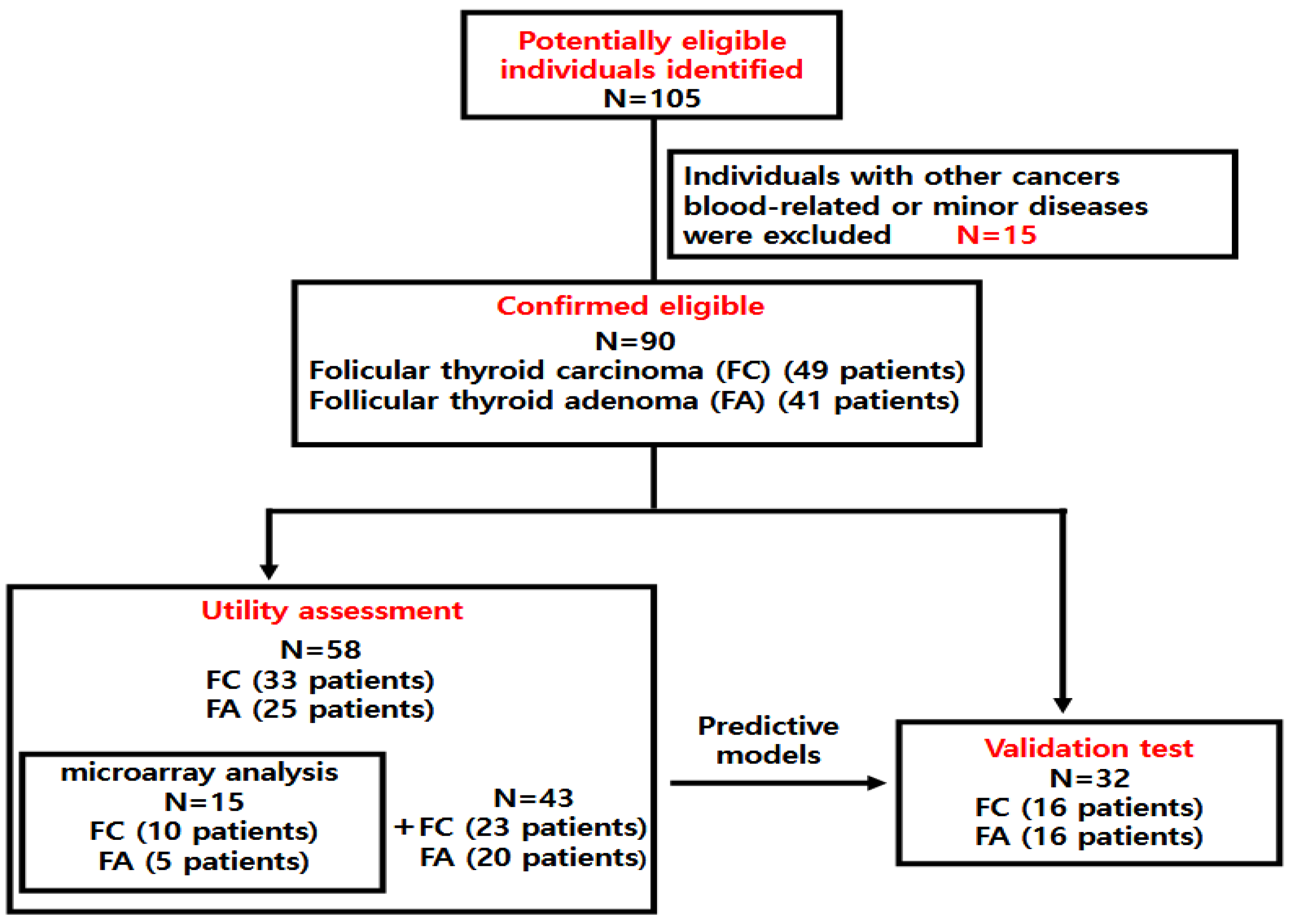

| Characteristics | Utility Assessment (n = 58) | Validation Test (n = 32) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA | FC | Overall | FA | FC | Overall | |
| (n = 25) | (n = 33) | (n = 58) | (n = 16) | (n = 16) | (n = 32) | |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 5 (20.0%) | 5 (17.25) | 10 (17.2%) | 3 (18.8%) | 5 (31.2%) | 8 (25.0%) |
| Female | 20 (80.0%) | 28 (84.8%) | 48 (82.3%) | 13 (81.2%) | 11 (68.8%) | 24 (75.0%) |
| Age (years, Median, IQR) | 52.00 (41.00–64.00) | 57.00 (44.00–65.00) | 54.00 (44.00–64.00) | 46.50 (44.00–63.00) | 53.50 (41.75–62.75) | 51.50 (43.25–63.25) |
| Tumor size (cm, Median, IQR) | 2.50 (1.40–4.00) | 3.30 (2.60–4.00) | 3.00 (2.00–3.78) | 2.05 (1.00–2.85) | 3.00 (1.80–3.60) | 2.45 (1.78–3.25) |
| Multifocality | 0 | 2 | ||||
| Lymph node metastasis | 2 | 0 | ||||
| Distant metastasis | 1 | 0 | ||||
| Aggressiveness | ||||||
| Minimally invasive FC | 25 (75.8%) | 14 (87.5%) | ||||
| Widely invasive FC | 8 (24.2%) | 2 (12.5%) | ||||
| Characteristics | FA (n = 5) | FC (n = 10) | Overall (n = 15) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 1 (20%) | 2 (20%) | 3 (20%) |
| Female | 4 (80%) | 8 (80%) | 12 (80%) |
| Age (years, Median, IQR) | 48.00 (36.00–51.00) | 48.50 (36.00–63.00) | 48.00 (40.50–57.00) |
| Tumor size (cm, Median, IQR) | 2.70 (2.10–3.50) | 3.35 (2.60–3.90) | 3.10 (2.60–3.75) |
| Multifocality | 0 | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | 2 | ||
| Distant metastasis | 0 | ||
| Aggressiveness | |||
| Minimally invasive FC | - | 5 (50%) | |
| Widely invasive FC | - | 5 (50%) |
| miRNA Base | FC/FA Fold Change | FC/FA Raw p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| miR-6085 | 1.75 | 0.011 |
| ENSG00000239080 (probe ID; 20533711) | −2.07 | 0.013 |
| ENSG00000239080 (probe ID; 20533712) | −1.78 | 0.019 |
| Model | miRNA | AUC (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Cut-Off Value | BIC | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | miR-6085 | 0.702 (0.557, 0.848) | 1.000 (1.000, 1.000) | 0.360 (0.200, 0.560) | ≥−0.267 | 69.07 | Logit(P) = −0.384 + 1.335 × mRNA.6085_log |
| 1-2 | miR-146b-5p | 0.735 (0.587, 0.883) | 0.667 (0.458, 0.833) | 0.840 (0.680, 0.960) | ≥0.593 | 67.77 | Logit(P) = −0.475 + 1.289 × mRNA.146b-5p_log |
| 1-3 | miR-221 | 0.654 (0.491, 0.817) | 0.478 (0.261, 0.696) | 0.913 (0.783, 1.000) | ≥0.888 | 67.44 | Logit(P) = −0.176 + 0.77 × mRNA.221_log |
| 1-4 | miR-222 | 0.877 (0.771, 0.983) | 0.952 (0.857, 1.000) | 0.708 (0.500, 0.875) | ≥0.608 | 44.86 | Logit(P) = −2.073 + 2.232 × mRNA.222_log |
| 2-1 | miR-221 + miR-222 | 0.902 (0.804, 1.000) | 0.950 (0.850, 1.000) | 0.864 (0.727, 1.000) | ≥0.575 | 41.12 | Logit(P) = −2.928 + 1.229 × mRNA.221_log + 2.676 × mRNA.222_log |
| 2-2 | miR-6085 + miR-222 | 0.901 (0.806, 0.996) | 0.905 (0.762, 1.000) | 0.792 (0.625, 0.958) | ≥0.362 | 46.74 | Logit(P) = −2.304 + 0.946 × mRNA.6085_log + 2.219 × mRNA.222_log |
| 2-3 | miR-146b-5p + miR-222 | 0.885 (0.787, 0.984) | 0.900 (0.750, 1.000) | 0.792 (0.625, 0.917) | ≥0.382 | 47.33 | Logit(P) = −2.118 + 0.524 × mRNA.146b-5p_log + 2.043 × mRNA.222_log |
| 3-1 | miR-6085 + miR-221 + miR-222 | 0.927 (0.840, 1.000) | 0.900 (0.750, 1.000) | 0.909 (0.773, 1.000) | ≥0.59 | 42.18 | Logit(P) = −3.579 + 1.474 × mRNA.6085_log + 1.4 × mRNA.221_log + 2.808 × mRNA.222_log |
| 3-2 | miR-146b-5p + miR-221 + miR-222 | 0.911 (0.823, 1.000) | 0.947 (0.842, 1.000) | 0.818 (0.636, 0.955) | ≥0.487 | 43 | Logit(P) = −3.091 + 0.827 × mRNA.146b-5p_log + 1.417 × mRNA.221_log + 2.443 × mRNA.222_log |
| 3-3 | miR-6085 + miR-146b-5p + miR-222 | 0.900 (0.806, 0.994) | 0.900 (0.750, 1.000) | 0.792 (0.625, 0.958) | ≥0.366 | 49.74 | Logit(P) = −2.314 + 1.042 × mRNA.6085_log + −0.049 × mRNA.146b-5p_log + 2.164 × mRNA.222_log |
| 4 | miR-6085 + miR-146b-5p + miR-221 + miR-222 | 0.928 (0.843, 1.000) | 0.947 (0.842, 1.000) | 0.864 (0.682, 1.000) | ≥0.432 | 44.77 | Logit(P) = −3.682 + 1.582 × mRNA.6085_log + 0.103 × mRNA.146b-5p_log + 1.468 × mRNA.221_log + 2.723 × mRNA.222_log |
| Model | miRNA | Accuracy (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | miR-6085 | 0.586 (0.389, 0.765) | 0.500 (0.247, 0.753) | 0.692 (0.386, 0.909) |
| 1-2 | miR-146b-5p | 0.593 (0.388, 0.776) | 0.643 (0.351, 0.872) | 0.538 (0.251, 0.808) |
| 1-3 | miR-221 | 0.643 (0.441, 0.814) | 0.857 (0.572, 0.982) | 0.429 (0.177, 0.711) |
| 1-4 | miR-222 | 0.679 (0.476, 0.841) | 0.769 (0.462, 0.950) | 0.600 (0.323, 0.837) |
| 2-1 | miR-221 + miR-222 | 0.600 (0.387, 0.789) | 0.727 (0.390, 0.940) | 0.500 (0.230, 0.770) |
| 2-2 | miR-6085 + miR-222 | 0.538 (0.334, 0.734) | 0.538 (0.251, 0.808) | 0.538 (0.251, 0.808) |
| 2-3 | miR-146b-5p + miR-222 | 0.609 (0.385, 0.803) | 0.545 (0.234, 0.833) | 0.667 (0.349, 0.901) |
| 3-1 | miR-6085 + miR-221 + miR-222 | 0.739 (0.516, 0.898) | 0.727 (0.390, 0.940) | 0.750 (0.428, 0.945) |
| 3-2 | miR-146b-5p + miR-221 + miR-222 | 0.714 (0.478, 0.887) | 0.700 (0.348, 0.933) | 0.727 (0.390, 0.940) |
| 3-3 | miR-6085 + miR-146b-5p + miR-222 | 0.522 (0.306, 0.732) | 0.455 (0.167, 0.766) | 0.583 (0.277, 0.848) |
| 4 | miR-6085 + miR-146b-5p + miR-221 + miR-222 | 0.762 (0.528, 0.918) | 0.700 (0.348, 0.933) | 0.818 (0.482, 0.977) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.W.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.-C.; Cheon, Y.-I.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, B.-J. Diagnostic Models for Predicting Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas Using Circulating Plasma MicroRNAs. Cancers 2025, 17, 3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213401
Kang SW, Kim JM, Shin S-C, Cheon Y-I, Kim BH, Kim M, Kim SS, Lee B-J. Diagnostic Models for Predicting Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas Using Circulating Plasma MicroRNAs. Cancers. 2025; 17(21):3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213401
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Sin Woo, Ji Min Kim, Sung-Chan Shin, Yong-Il Cheon, Bo Hyun Kim, Mijin Kim, Sang Soo Kim, and Byung-Joo Lee. 2025. "Diagnostic Models for Predicting Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas Using Circulating Plasma MicroRNAs" Cancers 17, no. 21: 3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213401
APA StyleKang, S. W., Kim, J. M., Shin, S.-C., Cheon, Y.-I., Kim, B. H., Kim, M., Kim, S. S., & Lee, B.-J. (2025). Diagnostic Models for Predicting Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas Using Circulating Plasma MicroRNAs. Cancers, 17(21), 3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213401






