A Novel Allosteric Inhibitor Targeting IMPDH at Y233 Overcomes Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Lymphoma
Simple Summary
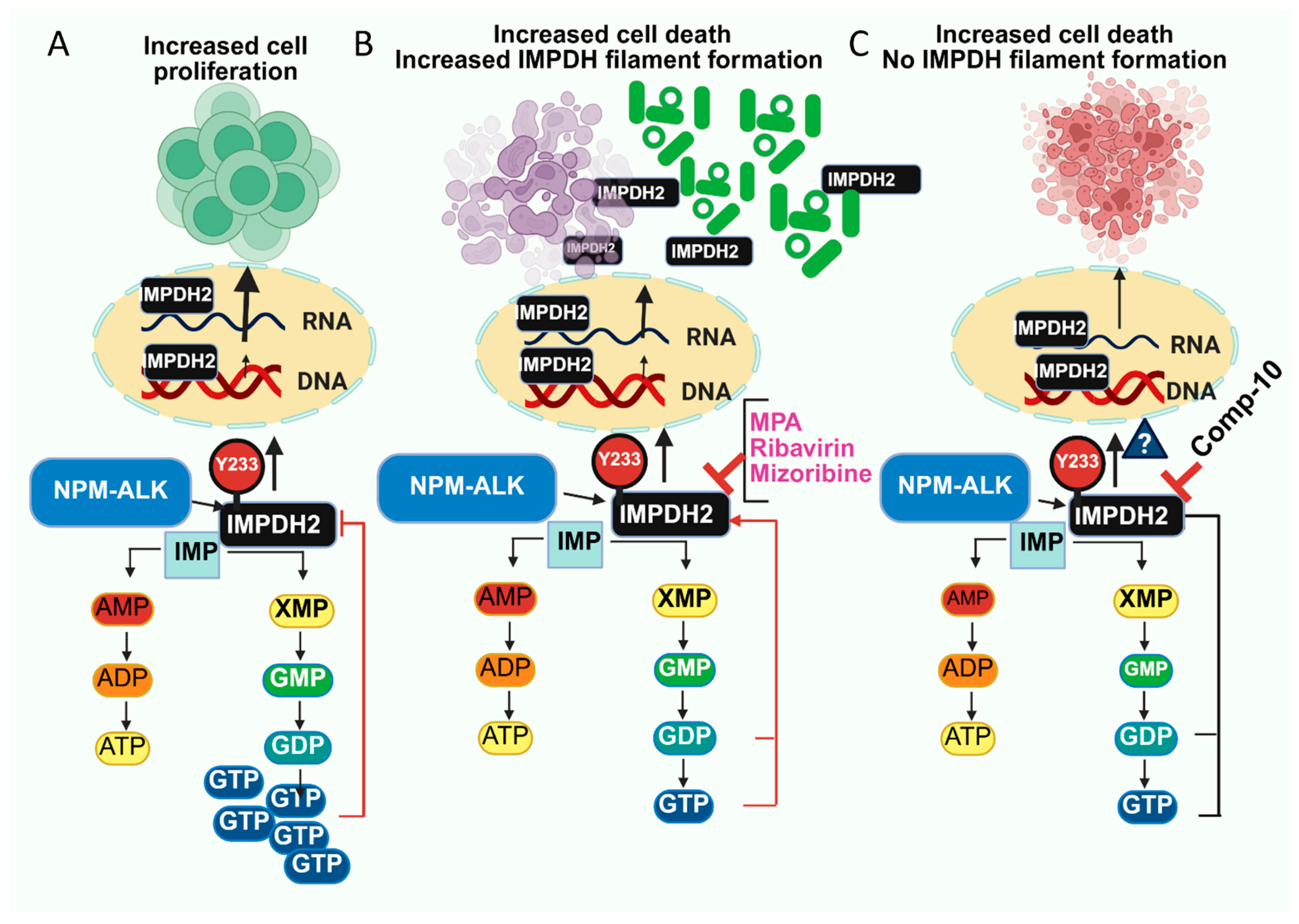
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Plasmids and Lentivirus Products
2.3. MCL, DLBCL, and ALCL Cell Lines
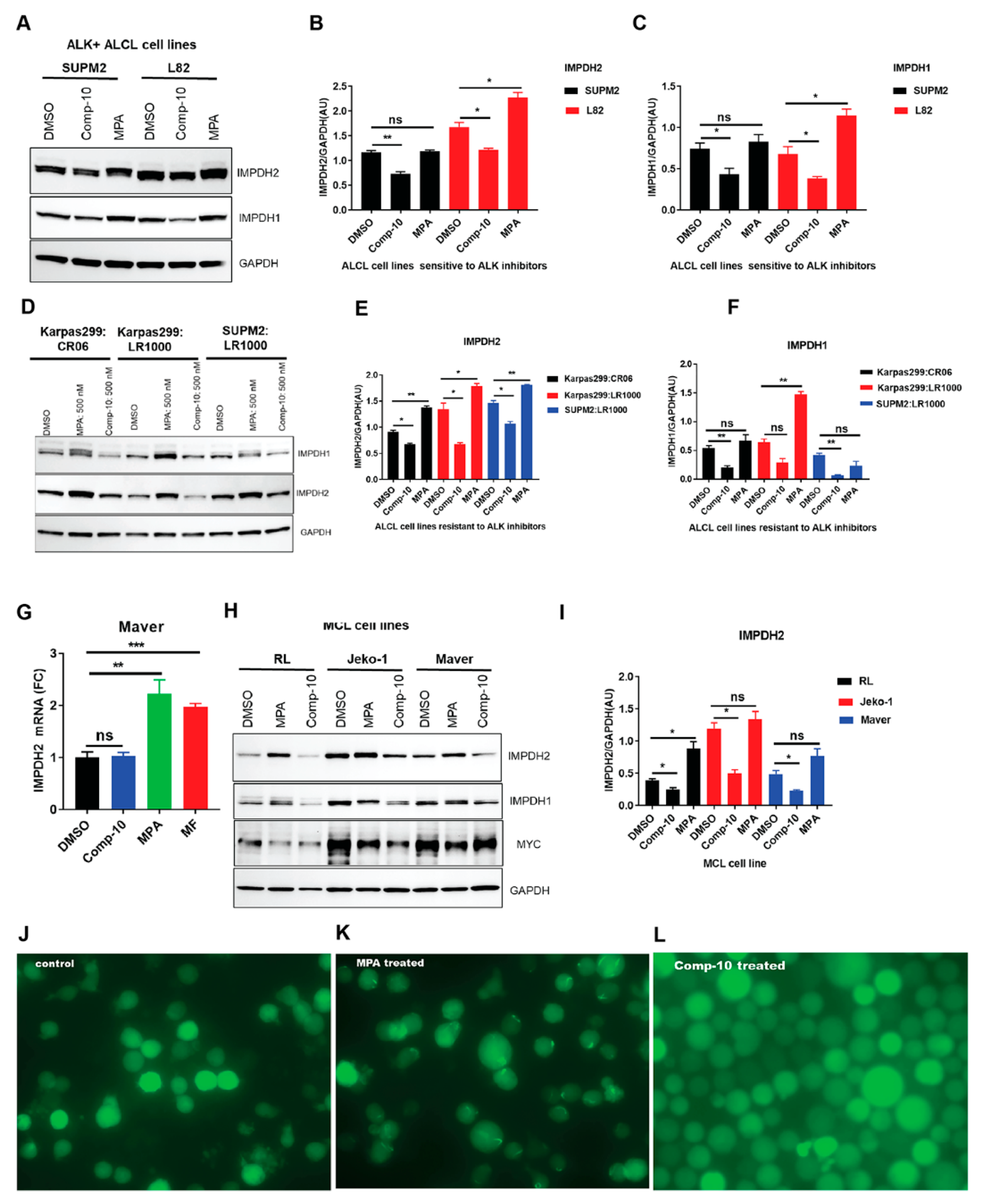
2.4. ALK Inhibitor (ALKi)-Resistant ALCL Cell Lines
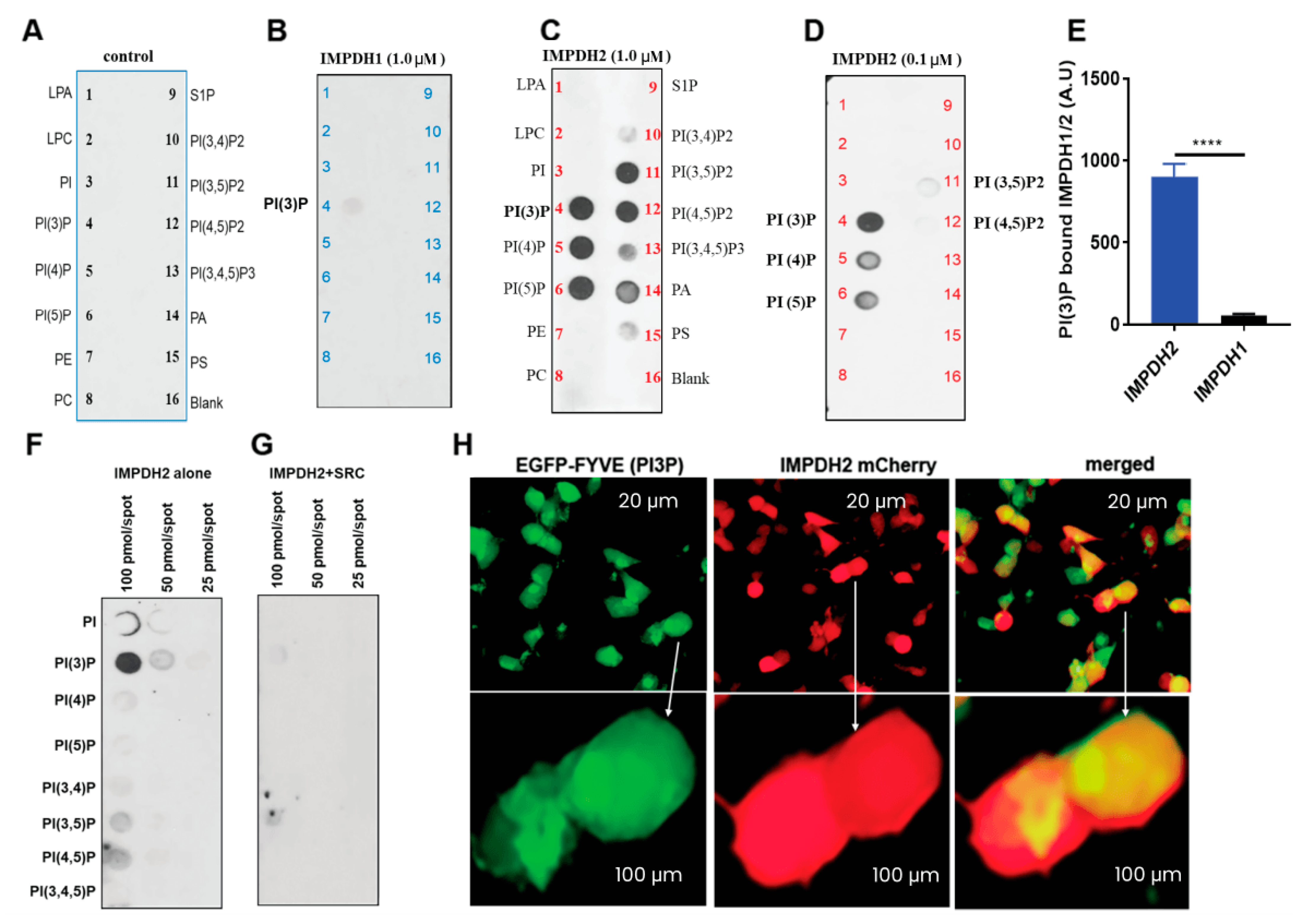
2.5. IMPDH1 and IMPDH2 PIP Strip and PIP Array Binding Assay
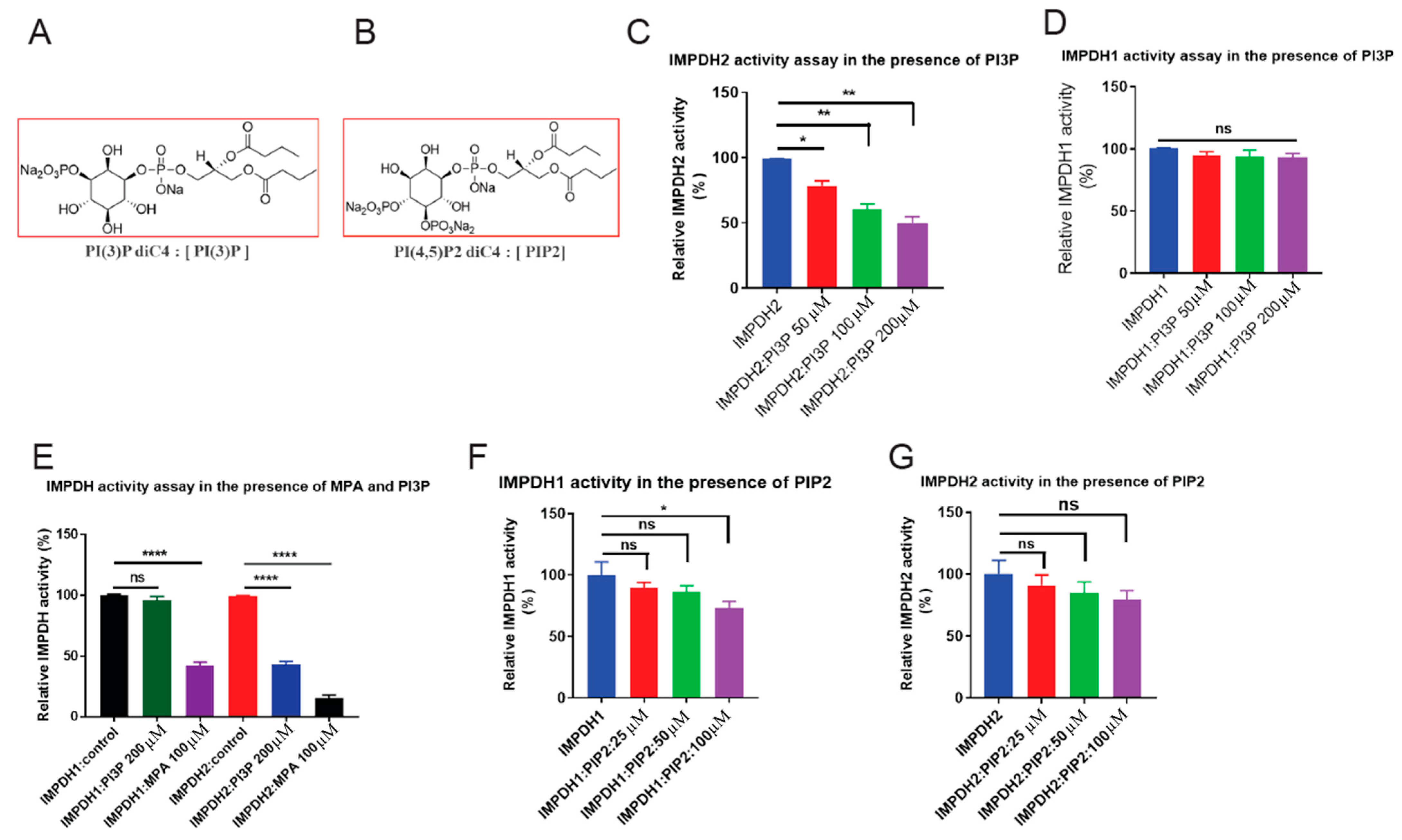
2.6. IMPDH1 and IMPDH2 Activity Assay in the Presence of PIP2 (PI(4,5)P2) and PI3P (PI(3)P diC8)
2.7. In Vitro Kinase Assay and LC-MS/MS Phosphoproteomics Analysis
2.8. Structure-Based In Silico Screening of IMPDH Inhibitors
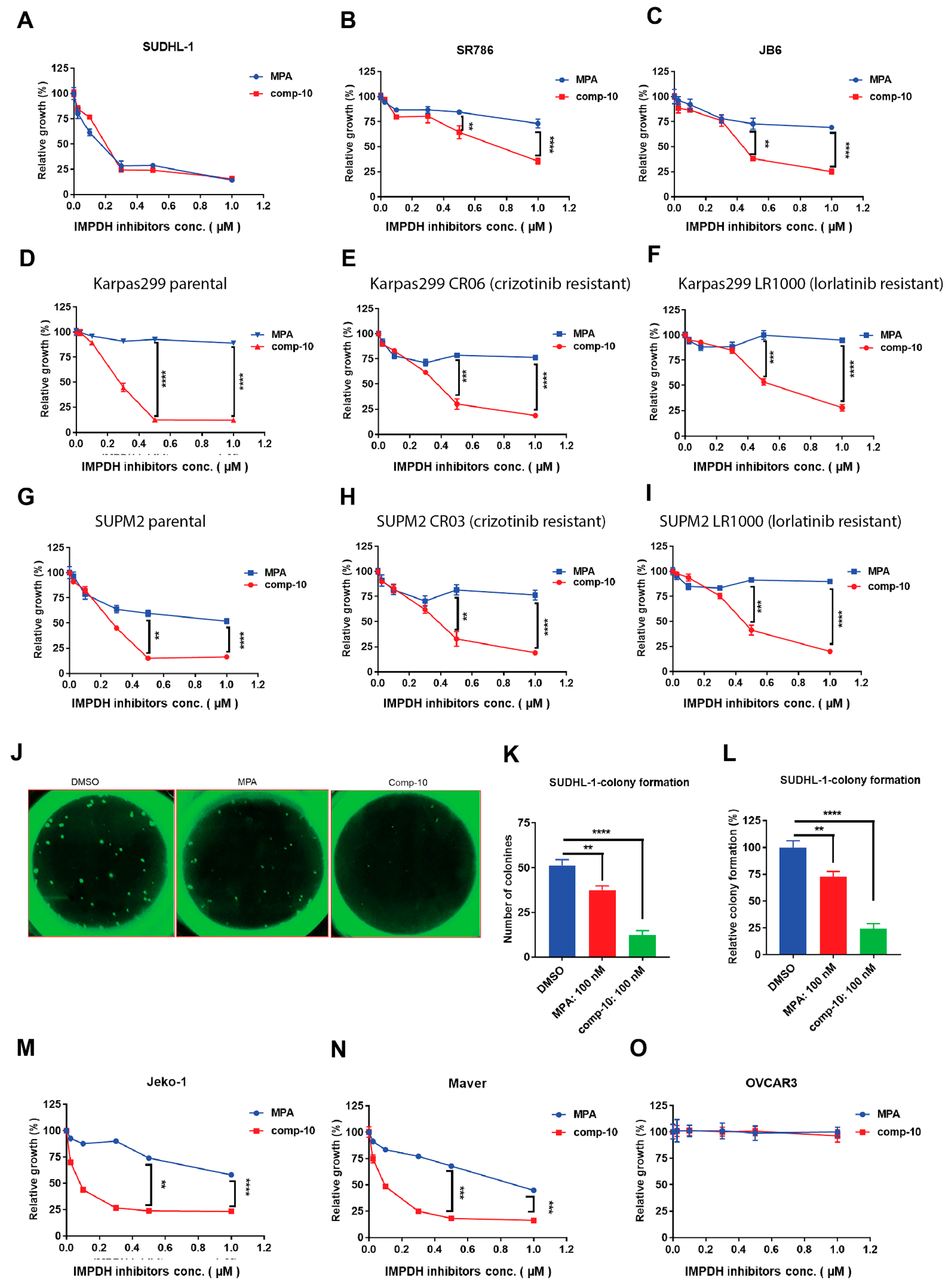
2.9. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.10. Colony Formation Assay
2.11. Statistics and Reproducibility
2.12. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. IMPDH2 Is Significantly Overexpressed in Hematological Malignancies
3.2. In Vitro Kinase and Phosphoproteomic Analyses Reveal Tyrosine Phosphorylation of IMPDH2 in the Allosteric Domain
3.3. IMPDH2 Y233 Phosphorylation Regulates PI3P Binding
3.4. PI3P Binding Inhibits IMPDH2 Activity
3.5. Structure-Based in Silico Screening and Discovery of a Novel Allosteric Inhibitor Targeting IMPDH2
3.6. Comp-10 Downregulates IMPDH1/2 and Prevent Rod/Ring Formation
3.7. Comp-10 Inhibits Growth and Colony Formation of ALK-Positive Malignant Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, L.-X.; Song, X.-M.; Wang, L.-C.; Lv, H.-N.; Chen, J.-F.; Liu, D.; Fu, G.; Zhao, M.-B.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, K.-W.; et al. Highly selective inhibition of IMPDH2 provides the basis of antineuroinflammation therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5986–E5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, A.L.; Kollman, J.M. IMPDH dysregulation in disease: A mini review. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Ni, M.; Chalishazar, M.D.; Huffman, K.E.; Kim, J.; Cai, L.; Shi, X.; Cai, F.; Zacharias, L.G.; Ireland, A.S.; et al. Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase Dependence in a Subset of Small Cell Lung Cancers. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 369–382.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.G.; Boosalis, M.; Malek, K.; Waraska, K. Effects of the IMP-dehydrogenase inhibitor, Tiazofurin, in bcr-abl positive acute myelogenous leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2004, 28, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.J.; Santiago, L.; Mitchell, B.S. Synergy between imatinib and mycophenolic acid in inducing apoptosis in cell lines expressing Bcr-Abl. Blood 2005, 105, 3270–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinar, L.; Garcia-Cao, M.; Schmidt, A.; Kourtis, S.; Zapater, A.G.; Aranda-Vallejo, C.; Ghose, R.; Garcia-Lopez, L.; Sheraj, I.; Pardo-Lorente, N.; et al. Nuclear IMPDH2 controls the DNA damage response by modulating PARP1 activity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xia, D.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, G.; Mo, R.; Zeng, Y.; Dai, Q.; He, H.; Liang, Y.; et al. Enhanced expression of IMPDH2 promotes metastasis and advanced tumor progression in patients with prostate cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 16, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.C.; Wang, G.; Li, C.F.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Z.; Chen, T.; Pan, B.S.; Manne, R.K.; Deep, G.; Gu, H.; et al. IMPA1-derived inositol maintains stemness in castration-resistant prostate cancer via IMPDH2 activation. J. Exp. Med. 2024, 221, e20231832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Han, Z.; Zhou, L.; Cai, C.; Luo, H.; Huang, Y.; Liang, Y.; He, H.; Jiang, F.; Wang, C.; et al. Elevated expression of IMPDH2 is associated with progression of kidney and bladder cancer. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, Y.; Duan, S.; Chen, C.; Rong, J.; Wang, K.; Yun, M.; Weng, H.; Ye, S.; et al. High expression of IMPDH2 is associated with aggressive features and poor prognosis of primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Huffman, K.E.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, K.; Cai, F.; Yang, C.; Cai, L.; Shih, T.S.; Zacharias, L.G.; et al. Guanosine tri-phosphate links MYC-dependent metabolic and ribosome programs in small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, H.; Zha, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, G.; Pan, H.; Fei, X.; Xu, X.; Xing, C.; Zhang, L. IMPDH2 promotes cell proliferation and epithe-lial-mesenchymal transition of non-small cell lung cancer by activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofuji, S.; Hirayama, A.; Eberhardt, A.O.; Kawaguchi, R.; Sugiura, Y.; Sampetrean, O.; Ikeda, Y.; Warren, M.; Sakamoto, N.; Kitahara, S.; et al. IMP dehydrogenase-2 drives aberrant nucleolar activity and promotes tumorigenesis in glioblastoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Iyer, S.V.; Hsieh, D.C.; Li, B.; Elias, H.K.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Ganbold, M.; Lien, M.C.; Peng, Y.C.; et al. Gliocidin is a nico-tinamide-mimetic prodrug that targets glioblastoma. Nature 2024, 636, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, A.M.; Mobilio, D.; Bassey-Archibong, B.I.; Johnson, J.W.; Piotrowski, M.L.; de Araujo, E.D.; Sedighi, A.; Aghaei, N.; Escudero, L.; Ang, P.; et al. De novo GTP synthesis is a metabolic vulnerability for the interception of brain metastases. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, W.; Ma, F.; Zou, J.; Li, K.; Tan, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z.; et al. Longitudinal plasma proteome profiling reveals the diversity of biomarkers for diagnosis and cetuximab therapy response of colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T. Tyrosine phosphorylation: Thirty years and counting. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basappa, J.; Citir, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, X.; Melnikov, O.; Yahya, H.; Stein, F.; Muller, R.; Traynor-Kaplan, A.; et al. ACLY is the novel signaling target of PIP2/PIP3 and Lyn in acute myeloid leukemia. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basappa, J.; ElAzzouny, M.A.; Rolland, D.C.M.; Velusamy, T.; Hwang, S.; Basrur, V.; Conlon, K.; Zhao, L.; Bailey, N.G.; Burant, C.F.; et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation is critical for ACLY activity in lipid metabolism and cancer. bioRxiv 2020. bioRxiv:20.910752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Miller, G.J.; Hurley, J.H. Recognizing Phosphatidylinositol 3-Phosphate. Cell 2001, 107, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremel, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Morado, D.R.; Bertram, J.; Perisic, O.; Brandt, L.T.L.; von Wrisberg, M.-K.; Chen, Z.A.; Maslen, S.L.; Kovtun, O.; et al. Structural basis for VPS34 kinase activation by Rab1 and Rab5 on membranes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valvezan, A.J.; McNamara, M.C.; Miller, S.K.; Torrence, M.E.; Asara, J.M.; Henske, E.P.; Manning, B.D. IMPDH inhibitors for antitumor therapy in tuberous sclerosis complex. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 5, e135071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calise, S.J.; Purich, D.L.; Nguyen, T.; Saleem, D.A.; Krueger, C.; Yin, J.D.; Chan, E.K. ‘Rod and ring’ formation from IMP dehy-drogenase is regulated through the one-carbon metabolic pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3042–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppeke, G.D.; Calise, S.J.; Chan, E.K.L.; Andrade, L.E.C. Ribavirin induces widespread accumulation of IMP dehydrogenase into rods/rings structures in multiple major mouse organs. Antiviral Res. 2019, 162, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcamo, W.C.; Satoh, M.; Kasahara, H.; Terada, N.; Hamazaki, T.; Chan, J.Y.F.; Yao, B.; Tamayo, S.; Covini, G.; A Von Mühlen, C.; et al. Induction of Cytoplasmic Rods and Rings Structures by Inhibition of the CTP and GTP Synthetic Pathway in Mammalian Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Basappa, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Nunez-Cruz, S.; Lobello, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Chekol, S.; Guo, L.; Ziober, A.; et al. Chimeric kinase ALK induces expression of NAMPT and selectively depends on this metabolic enzyme to sustain its own oncogenic function. Leukemia 2023, 37, 2436–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wei, F.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, X.; Roy, D.; Xiong, Q.B.; Jaing, S.; Medvec, A.; Danet-Desnoyers, G.; Watt, C.; et al. The potent oncogene NPM-ALK mediates malignant transformation of normal human CD4(+) T lymphocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1971–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccon, M.; Mologni, L.; Bisson, W.; Scapozza, L.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. Crizotinib-Resistant NPM-ALK Mutants Confer Differential Sensitivity to Unrelated Alk Inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.C.; Kollman, J.M. Cryo-EM structures demonstrate human IMPDH2 filament assembly tunes allosteric regulation. eLife 2020, 9, e53243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pattabiraman, N.; Lobello, C.; Rushmore, D.; Mologni, L.; Wasik, M.; Basappa, J. A Novel Allosteric Inhibitor Targeting IMPDH at Y233 Overcomes Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Lymphoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203389
Pattabiraman N, Lobello C, Rushmore D, Mologni L, Wasik M, Basappa J. A Novel Allosteric Inhibitor Targeting IMPDH at Y233 Overcomes Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Lymphoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(20):3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203389
Chicago/Turabian StylePattabiraman, Nagarajan, Cosimo Lobello, David Rushmore, Luca Mologni, Mariusz Wasik, and Johnvesly Basappa. 2025. "A Novel Allosteric Inhibitor Targeting IMPDH at Y233 Overcomes Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Lymphoma" Cancers 17, no. 20: 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203389
APA StylePattabiraman, N., Lobello, C., Rushmore, D., Mologni, L., Wasik, M., & Basappa, J. (2025). A Novel Allosteric Inhibitor Targeting IMPDH at Y233 Overcomes Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Lymphoma. Cancers, 17(20), 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203389







