Increased EGFR/HER2 Pathway Activation Contributes to Skin Tumorigenesis in Tpl2−/− Mice
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vivo Tumor Experiment
2.2. Primary Keratinocyte Isolation and Treatment
2.3. RT-qPCR
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ErbB Receptor Upregulation in Tpl2−/− Keratinocytes and Compensatory Response to Inhibitor Treatment
3.2. miR205 and miR21 Are Upregulated in Tpl2−/− Keratinocytes
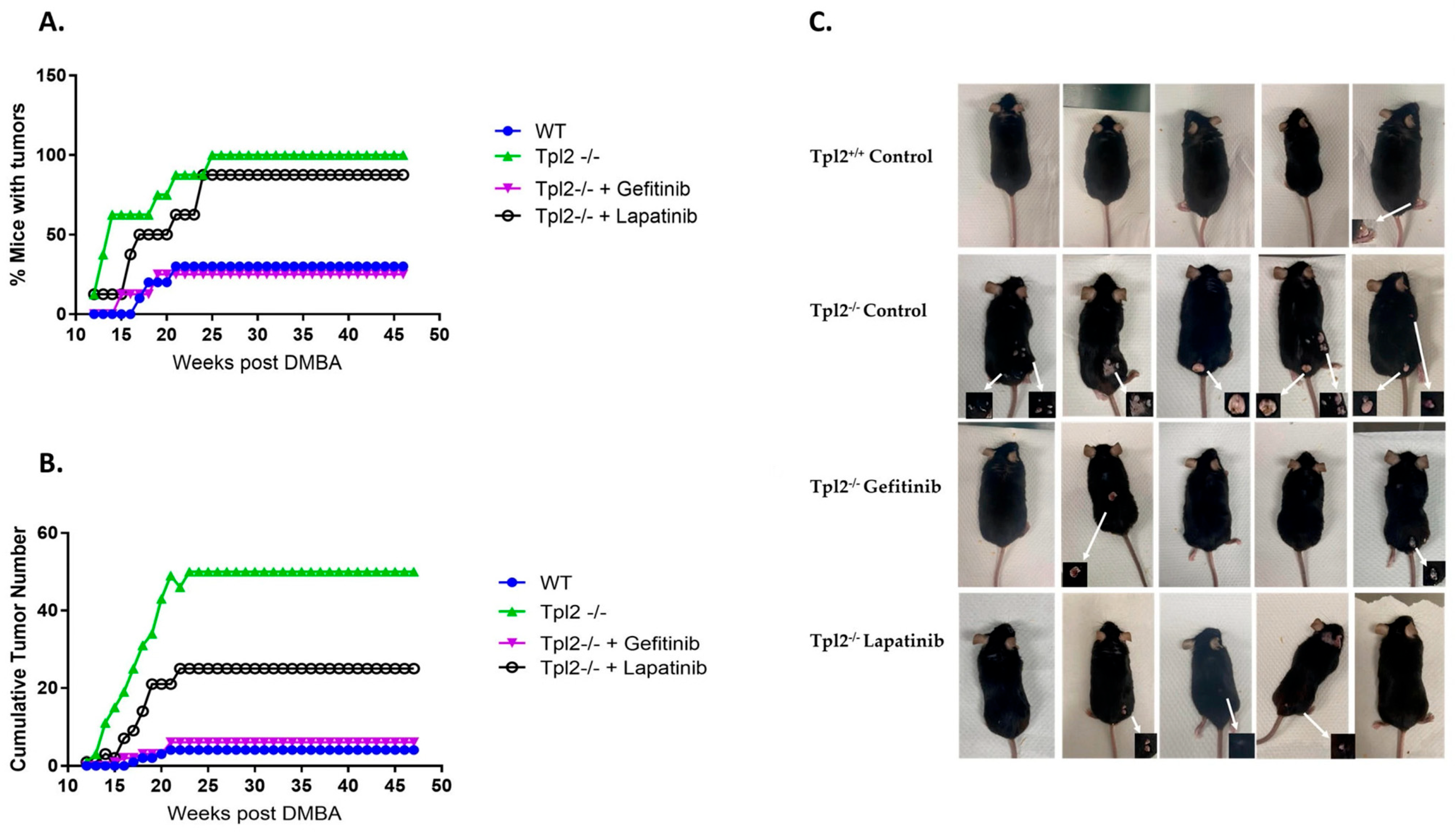
3.3. Pharmacological Inhibition of EGFR or HER2 Decreases Tumorigenesis in Tpl2−/− Mice
3.4. Papillomas from Tpl2−/− Mice Have Increased Expression of EGFR, p-EGFR and HER2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eggermont, C.J.; Eggermont, A.M.M. Shifting landscape in skin cancer incidence: The rising tide of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and potential implications for prevention. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 190, 460–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, K.; Mehrmal, S.; Uppal, P.; Giesey, R.L.; Delost, G.R. The global burden of skin cancer: A longitudinal analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study, 1990–2017. JAAD Int. 2021, 2, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Fritz, M.; Que, S.K.T. Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corchado-Cobos, R.; García-Sancha, N.; González-Sarmiento, R.; Pérez-Losada, J.; Cañueto, J. Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: From Biology to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Shain, A.H. The landscape of driver mutations in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. npj Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braicu, C.; Buse, M.; Busuioc, C.; Drula, R.; Gulei, D.; Raduly, L.; Rusu, A.; Irimie, A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Slaby, O.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on MAPK: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantke, T.; Sriskantharajah, S.; Ley, S.C. Regulation and function of TPL-2, an IκB kinase-regulated MAP kinase kinase kinase. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katie DeCicco-Skinner, M.D.a.J.W. The Role of Tpl2 Protein Kinase in Carcinogenesis and Inflammation; InTech: Houston TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Decicco-Skinner, K.L.; Trovato, E.L.; Simmons, J.K.; Lepage, P.K.; Wiest, J.S. Loss of tumor progression locus 2 (tpl2) enhances tumorigenesis and inflammation in two-stage skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2011, 30, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonan, N.F.; Kowalski, D.; Kudlac, K.; Flaherty, K.; Gwilliam, J.C.; Falkenberg, L.G.; Maradiaga, E.; DeCicco-Skinner, K.L. Inhibition of HGF/MET signaling decreases overall tumor burden and blocks malignant conversion in Tpl2-related skin cancer. Oncogenesis 2019, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.B.; Geddes, T.J.; Ochiai, M.; Lampl, N.M.; Kothmann, W.W.; Fierstein, S.R.; Kent, V.; DeCicco-Skinner, K. Loss of Tpl2 activates compensatory signaling and resistance to EGFR/MET dual inhibition in v-RAS transduced keratinocytes. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañueto, J.; Cardeñoso, E.; García, J.L.; Santos-Briz, Á.; Castellanos-Martín, A.; Fernández-López, E.; Blanco Gómez, A.; Pérez-Losada, J.; Román-Curto, C. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression is associated with poor outcome in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droll, S.; Bao, X. Oh, the Mutations You’ll Acquire! A Systematic Overview of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 55, 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, J.P.; Rodrigues, A.; Goldinger, S.M.; Sim, H.W.; Liu, J. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e14978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghav, K.P.S.; Moasser, M.M. Molecular Pathways and Mechanisms of HER2 in Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 2351–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlhoff, M.; Muzumdar, S.; Schäfer, M.; Schneider, M.R. ERBB2 Is Essential for the Growth of Chemically Induced Skin Tumors in Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Lee, S.; Senavirathne, G.; Lai, E.C. microRNAs in action: Biogenesis, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 816–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sancha, N.; Corchado-Cobos, R.; Pérez-Losada, J.; Cañueto, J. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.E.; Lin, R.J. MicroRNA and HER2-overexpressing cancer. Microrna 2013, 2, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceci, J.D.; Patriotis, C.P.; Tsatsanis, C.; Makris, A.M.; Kovatch, R.; Swing, D.A.; Jenkins, N.A.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Copeland, N.G. Tpl-2 is an oncogenic kinase that is activated by carboxy-terminal truncation. Genes. Dev. 1997, 11, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichti, U.; Anders, J.; Yuspa, S.H. Isolation and short-term culture of primary keratinocytes, hair follicle populations and dermal cells from newborn mice and keratinocytes from adult mice for in vitro analysis and for grafting to immunodeficient mice. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCicco-Skinner, K.; Jung, S.; Tabib, T.; Gwilliam, J.; Alexander, H.; Goodheart, S.; Merchant, A.; Shan, M.; Garber, C.; Wiest, J. Tpl2 knockout keratinocytes have increased biomarkers for invasion and metastasis. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2789–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCicco-Skinner, K.L.; Nolan, S.J.; Deshpande, M.M.; Trovato, E.L.; Dempsey, T.A.; Wiest, J.S. Altered Prostanoid Signaling Contributes to Increased Skin Tumorigenesis in Tpl2 Knockout Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinatha Pillai, M.S.; Aiswarya, S.U.; Keerthana, C.K.; Rayginia, T.P.; Anto, R.J. Targeting receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: Avenues in the management of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. iScience 2023, 26, 106816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberholzer, P.A.; Kee, D.; Dziunycz, P.; Sucker, A.; Kamsukom, N.; Jones, R.; Roden, C.; Chalk, C.J.; Ardlie, K.; Palescandolo, E.; et al. RAS Mutations Are Associated with the Development of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Tumors in Patients Treated with RAF Inhibitors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Martínez, M.; Vega, M.I. Role of MicroRNA-7 (MiR-7) in Cancer Physiopathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojadinovic, O.; Ramirez, H.; Pastar, I.; Gordon, K.A.; Stone, R.; Choudhary, S.; Badiavas, E.; Nouri, K.; Tomic-Canic, M. MiR-21 and miR-205 are induced in invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, A.N.; Fisher, M.D.; Amborski, G.; Allain, D.C.; Klee, V.; Peters, S.B.; Kang, S.; Toland, A.E. MicroRNA Expression Profiling of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinomas Arising in Different Sites. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2020, 163, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañueto, J.; Cardeñoso-Álvarez, E.; García-Hernández, J.L.; Galindo-Villardón, P.; Vicente-Galindo, P.; Vicente-Villardón, J.L.; Alonso-López, D.; De Las Rivas, J.; Valero, J.; Moyano-Sanz, E.; et al. MicroRNA (miR)-203 and miR-205 expression patterns identify subgroups of prognosis in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konicke, K.; López-Luna, A.; Muñoz-Carrillo, J.L.; Servín-González, L.S.; Flores-de la Torre, A.; Olasz, E.; Lazarova, Z. The microRNA landscape of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenni, D.; Karpova, M.B.; Mühleisen, B.; Mangana, J.; Dreier, J.; Hafner, J.; Dummer, R. A prospective clinical trial to assess lapatinib effects on cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and actinic keratosis. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.M.; Glisson, B.S.; Feng, L.; Wan, F.; Tang, X.; Wistuba, I.I.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Chambers, M.S.; Lustig, R.A.; et al. A phase II study of gefitinib for aggressive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name | EGFR | HER2 | HER3 | GAPDH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward Sequence (5′ to 3′) | GCCATCTGGGCCAAAGATACC | ACATGCTTCGCCACCTCTAC | CGGTTCCGGAGGGGATTATG | CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG |
| Reverse Sequence (5′ to 3′) | GTCTTCGCATGAATAGGCC | AGCTGAGTCCCTCTCACGAT | TGCCAGTAATCGGGGTTGTC | ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG |
| miR | miR21 (mmu-miR-21a-3p) | miR205 (mmu-miR-205-3p) | miR7 (mmu-miR-7b-3p) | miR125 (mmu-miR-125b-5p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence (Mature) | CAACACAGUCGAUGGGCUGUC | GAUUUCAGUGGAGUGAAGCUCA | UGGAAGACUUGUGAUUUUGUUGUU | UCCCUGAGACCCUAACUUGUGA |
| Papillomas | Squamous Cell Carcinomas | Other | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tpl2+/+ normal diet | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Tpl2−/− normal diet | 46 | 4 | 0 | 50 |
| Tpl2−/− Gefitinib diet | 4 | 1 | 1 (Atypical verrucous keratosis) | 6 |
| Tpl2−/− Lapatinib diet | 24 | 1 | 0 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Purkey, L.R.; Mehedincu, S.; Irvine, C.; Akdag, R.; Little, M.; Kothmann, W.W.; Rus, K.; Greenberg, E.; Shady, N.; DeCicco-Skinner, K. Increased EGFR/HER2 Pathway Activation Contributes to Skin Tumorigenesis in Tpl2−/− Mice. Cancers 2025, 17, 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203362
Purkey LR, Mehedincu S, Irvine C, Akdag R, Little M, Kothmann WW, Rus K, Greenberg E, Shady N, DeCicco-Skinner K. Increased EGFR/HER2 Pathway Activation Contributes to Skin Tumorigenesis in Tpl2−/− Mice. Cancers. 2025; 17(20):3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203362
Chicago/Turabian StylePurkey, Laura R., Stefania Mehedincu, Charles Irvine, Raelyn Akdag, Megan Little, W. Wade Kothmann, Katharine Rus, Erin Greenberg, Neil Shady, and Kathleen DeCicco-Skinner. 2025. "Increased EGFR/HER2 Pathway Activation Contributes to Skin Tumorigenesis in Tpl2−/− Mice" Cancers 17, no. 20: 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203362
APA StylePurkey, L. R., Mehedincu, S., Irvine, C., Akdag, R., Little, M., Kothmann, W. W., Rus, K., Greenberg, E., Shady, N., & DeCicco-Skinner, K. (2025). Increased EGFR/HER2 Pathway Activation Contributes to Skin Tumorigenesis in Tpl2−/− Mice. Cancers, 17(20), 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203362





