Simple Summary
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most frequent cancer of childhood. Although most children are cured with modern frontline chemoimmunotherapy regimens, those with high-risk genetics and/or relapsed/refractory diseases still face poor outcomes. There is a growing need for more precise and less toxic treatment options than traditional chemotherapy. This comprehensive review focuses upon the investigation of biologically relevant small molecule inhibitors for genetic subtypes of childhood B-ALL or T-ALL. We search a large international clinical trial database (clinicaltrials.gov) to identify studies that tested molecularly targeted drugs in children with ALL. By reviewing the results of all completed trials and presenting an overview of ongoing and upcoming studies, we aim to provide a clear picture of how these therapies have been developed so far and discuss the current direction of precision medicine in pediatric ALL.
Abstract
In the past decades, significant advancements in the biological and genetic characterization of acute leukemias and optimization of risk-adapted multi-agent treatment protocols have dramatically improved cure rates and quality of life for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Despite these optimal results, patients with relapsed or chemotherapy-refractory (R/R) disease or with high-risk genetic features still face unsatisfactory outcomes. Further intensification of conventional chemotherapy has reached its limits in achieving the desired efficacy without undue side effects, necessitating innovative approaches to improve cure rates while continuing to minimize the toxicities associated with chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In the era of precision medicine, two key therapeutic strategies have emerged in hemato-oncology: molecularly targeted therapies and immunotherapies. Antibody-based and cellular immunotherapies have undoubtedly reshaped the landscape of childhood ALL treatment and have significant potential to play leading roles in current and future frontline regimens; these important therapies are well delineated in recent reviews. Molecularly targeted small molecule inhibitor therapies remain a cornerstone of precision medicine, supported by recent advancements in next-generation sequencing, which have enabled the application of transcriptomic and genomic profiling data to risk stratification and therapy optimization. Clinical trials for children with ALL have been instrumental in refining therapies and improving outcomes, a paradigm that remains critical as treatment strategies become increasingly complex. This comprehensive review focuses upon molecularly targeted therapy approaches for childhood ALL and aims to summarize findings from completed clinical trials to highlight the current landscape of ongoing and upcoming trials and to provide insights into future directions for the precision-driven optimization of pediatric B-ALL and T-ALL treatment.
1. Introduction
The cure rates and the quality of life of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) have significantly improved in recent decades due to extraordinary scientific advancements in the characterization of the disease from a biological and genetic perspective and the optimization of risk-stratified multi-agent treatment protocols within the framework of international studies [1,2,3]. The conduction of pediatric-specific ALL therapeutic clinical trials has been a pivotal factor in the dramatic improvement of outcomes observed over the recent decades, offering a structured, evidence-based approach to refining multi-agent chemotherapy protocols. The long-term disease-free survival of children with B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) now exceeds 90% [3], while outcomes for those with T-ALL are approximately 85% [4]. Despite these excellent results, patients with high-risk genetic features and those who experience a relapse or who are refractory to frontline therapy still have a poorer prognosis (long-term survival ∼50% after first relapse) [5]. While treatment options have also improved in the relapsed/refractory setting, patients with B-ALL continue to have more effective therapeutic options than those with T-ALL. The outcomes of children with relapsed/refractory T-ALL are extremely poor (survival rate ∼30% for first relapse T-ALL [6]) and they require successful allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for long-term survival [5,7]. The intensification of conventional treatment based on the use of chemotherapeutic drugs has further reached its maximal limit with minimal gains in improving outcomes for patients with chemo-refractory disease. Innovative treatment approaches based upon disease biology or cell surface antigens are essential to improve the chances of being cured and potentially also to decrease chemotherapy- and HSCT-associated toxicities [8]. In the era of precision medicine in hemato-oncology, two main categories of innovative therapeutic approaches can be distinguished: immunotherapy and molecularly targeted therapy [9,10]. Successful immunotherapeutic modalities, including monoclonal antibodies, antibody–drug conjugates, bispecific antibodies, and chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T), have clearly emerged as extremely effective therapeutic approaches, which have reshaped the scenario for treatment options in relapsed/refractory ALL and more recently also in the frontline setting, and which are reviewed elsewhere [11,12,13,14,15]. As an example, the remarkable results of the recent COG AALL1731 trial [16], which clearly demonstrated the superiority of a blinatumomab-based therapy (two non-sequential blinatumomab cycles added to a standard multi-agent chemotherapy regimen) in newly diagnosed children with Philadelphia chromosome-negative NCI standard risk B-ALL, represent a paradigmatic proof of concept.
Molecularly targeted therapeutic approaches also represent a fundamental paradigm of successful precision medicine in ALL. For instance, the addition of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) to chemotherapy has markedly improved the clinical outcomes for children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) ALL and is now standard in care, and, additionally, clinical trial efforts are ongoing to credit TKI-based therapy for patients with BCR::ABL1-like/Philadelphia-like (Ph-like) ALL [17,18]. The integration of next-generation sequencing (NGS) via transcriptome and genome profiling into the routine diagnostic algorithm for pediatric ALL has further allowed for the identification of new prognostic markers and optimized risk stratification, as well as guiding the selection of appropriately targeted therapies in clinical trials and compassionate use programs, and for off-label applications [19]. Several novel small molecules targeting molecular aberrations or specific molecular pathways are accordingly under preclinical and/or early-phase clinical investigation in children with relapsed leukemias (Figure 1). These agents hold promise for future integration into molecularly guided treatment strategies aimed at optimizing ALL therapy [20]. This paradigm is even more critical in the current context, marked by increasing biological complexity and the rapidly expanding landscape of novel treatment strategies and combinations. At the same time, increasingly, small patient populations with specific high-risk leukemia genetic subtypes call for strong international collaboration to ensure the feasibility of clinical trials and the generation of robust data to further improve outcomes for children with ALL. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the clinical trial investigations into molecularly targeted agents in children with ALL that summarizes and discusses the available results of completed trials and highlights the state-of-the-art of ongoing and registered soon-to-open trials.
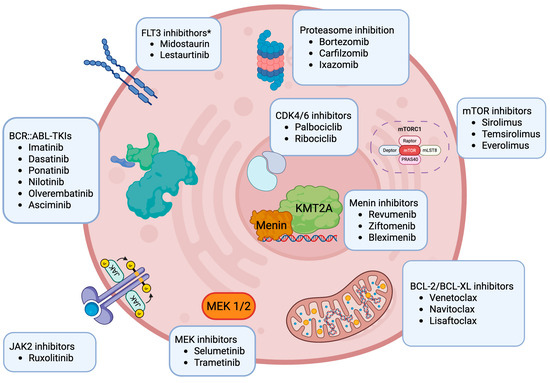
Figure 1.
Overview of current molecularly targeted treatment in development in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Created in https://BioRender.com. Among the drugs listed in Figure 1, only imatinib and dasatinib are currently approved by both the FDA/EMA for pediatric and adult ALL. Revumenib is FDA-approved for R/R KMT2Ar leukemias in patients one year and older. Ponatinib is approved in adults but not in children. The remaining drugs do not yet have a formal approval for ALL. * Though FLT3 inhibitors have been tested in ALL pediatric clinical trials in the past, these agents are not routinely added to chemotherapy for pediatric ALL patients at this time.
2. Materials and Methods
The website https://clinicaltrials.gov was searched to identify clinical trials exploring molecularly targeted agents in pediatric ALL. Immunotherapeutic agents and cellular therapies, including CAR T-cells, were considered to be outside the scope of this review and thus were excluded from the search. Twenty-eight searches were conducted by one investigator (NP) on 15 May 2025, using the advanced search mode with the pre-defined term “acute lymphoblastic leukemia” in the “condition or disease” box. The age-range filter (child, 0–17) was applied. In addition, each search contained one of the following intervention/treatment terms which were pre-determined by the authors as the most relevant agents to be considered in this review: “imatinib”, “dasatinib”, “ponatinib”, “nilotinib”, “asciminib”, “olverembatinib”, “ruxolitinib”, “bortezomib”, “carfilzomib”, “ixazomib”, “venetoclax”, “navitoclax”, “lisaftoclax”, “selumetinib”, “trametinib”, “palbociclib”, “ribociclib”, “sirolimus”, “everolimus”, “temsirolimus”, “vorinostat”, “decitabine”, “azacitidine”, “midostaurin”, “lestaurtinib”, “revumenib”, “ziftomenib”, “bleximenib”. Eligibility criteria were defined a priori, and only interventional clinical trials for children diagnosed with ALL were searched in the period from 1 January 2000 to 1 May 2025. Studies with a status of unknown, withdrawn, terminated early or suspended before recruitment were excluded. The study statuses are reported as of 26 September 2025. The available results from the clinical trials included in this review were retrieved through the PubMed database and from available conference abstracts from the European Hematology Association (EHA) and the American Society of Hematology (ASH).
3. Results
The search strategy at clinicaltrials.gov yielded 274 clinical trials (Table S1). After removing the duplicate records which appeared in the various searches, as mentioned above, 178 studies were assessed for eligibility. Of those, 76 fulfilled the eligibility criteria (Figure 2). Two additional clinical trials were identified through cross-referencing [21,22] for a total number of 78 included clinical trials. The eligible studies were grouped in specific categories according to the molecular target or functional pathway and their results discussed as follows (Table 1). The toxicity profiles of small molecules considered in this review, organized by drug class, are summarized in Table 2.
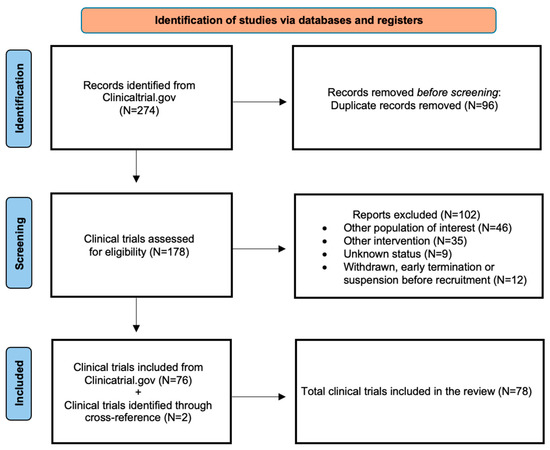
Figure 2.
Flow diagram reporting the results of the searches performed on 15 May 2025 at https://clinicaltrials.gov.

Table 1.
Clinical trials including small molecule inhibitor therapies in pediatric ALL.

Table 2.
Toxicity profiles of small molecule inhibitor therapies organized by drug class.
3.1. BCR::ABL1-Directed Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Ph+ ALL, defined by the canonical BCR::ABL1 fusion from chromosomal translocation t(9;22) (q34;q11), represents the first paradigmatic example of the successful incorporation of a molecularly targeted therapy in the treatment of ALL [80]. This subtype of ALL, accounting for 25% of adults and 3–4% of pediatric patients with B-ALL, was historically considered the most unfavorable ALL subtype. However, starting in the early 2000s, the advent of TKIs directed against BCR::ABL1 has revolutionized its treatment and significantly improved the prognosis of both adult and pediatric patients. In the last 20 years, the North America/Australia/New Zealand-based Children’s Oncology Group (COG) and the European multi-national Ph+ ALL group (EsPhALL) cooperative pediatric study groups have conducted several consecutive clinical trials in children with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL (Table 1). These trials studied first- (imatinib) or second-generation (dasatinib) TKIs with different chemotherapy backbones and clearly demonstrated that this strategy significantly improved outcomes and avoids the need for HSCT in most children and adolescents with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL [81]. More recently, such principles have also been applied to the Ph-like B-ALL subtype, which comprises 15–20% high-risk pediatric ALL cases and is characterized by a gene expression profile very similar to that of Ph+ ALL despite the lack of BCR::ABL1 fusion. Ph-like ALL has proven to be quite genetically heterogeneous with >80 specific fusions identified to date, although the patients can largely be “binned” into one of two subgroups [81,82]. The ABL-class subtype involves fusions of ABL1, ABL2, CSF1R, or PDGFRB. Although genetically distinct from Ph+ ALL, ABL-class ALL has very similar biological, clinical, and prognostic characteristics and, importantly, appears to share with Ph+ ALL excellent sensitivity to TKIs in preclinical studies and clinical case series [18]. For this reason, pediatric patients with ABL-class Ph-like ALL are now also enrolled in international Ph+ ALL protocols for treatment with TKI-based therapies (Table 1). Besides imatinib and dasatinib, in recent years several new-generation BCR::ABL1-directed TKIs have been developed primarily for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), including nilotinib, bosutinib, ponatinib, and olverembatinib, and the specifically targeting ABL myristoyl pocket (STAMP) inhibitor asciminib. Despite testing to date being primarily in adult patients with CML or Ph+ ALL, data are now emerging in the pediatric-specific setting via early-phase clinical trials.
3.1.1. Imatinib
Imatinib mesylate was the first TKI developed to treat Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. It is FDA- and EMA-approved for treating CML and Ph+ ALL in adults and children. Imatinib was first tested in the pediatric population in the COG Phase I study (NCT00004932), which demonstrated the antileukemic activity and the favorable tolerance of daily oral single-agent imatinib at doses ranging from 260 to 570 mg/m2 in children and adolescents with R/R CML and R/R Ph+ ALL [23]. Based on these results, the first pilot study COG AALL0031 (NCT00022737) testing the efficacy of the combination of imatinib 340 mg/m2 and chemotherapy was carried out by the COG group in newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL pediatric patients between 2002 and 2006 [24]. This study tested differential schedules of imatinib (increasing number of chemotherapy blocks including imatinib) in 5 patient cohorts. It demonstrated that higher imatinib dosing in Cohort 5 (continuous exposure from consolidation 1 to maintenance) significantly improved the patient outcomes, with a 3-year event-free survival (EFS), which is more than twice that of historical controls (88 ± 11% vs. 35 ± 4%; p < 0.0001) [24]. No significant toxicities associated with adding imatinib to intensive chemotherapy were reported [24]. These superior results were further confirmed by long-term analysis, with the 5-year EFS of 70 ± 12% for the Cohort 5 patients treated with chemotherapy plus imatinib [83]. Notably, these outcomes were similar to those of patients treated with HSCT in first complete remission (CR1), with 5-year EFS of 65 ± 11% and 59 ± 15% (n = 13, p = 0.60) for related donor HSCT and unrelated donor HSCT, respectively [83].
At the same time as the COG AALL0031, the European EsPhALL group conducted a randomized trial (NCT00287105, EsPhALL 2004) that enrolled children from 2004 to 2009 with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL to test whether outcomes were improved when incorporating discontinuous post-induction imatinib therapy (300 mg/m2) to an intensive Berlin–Frankfurt–Munster (BFM) chemotherapy backbone [25]. Patients stratified as good-risk were randomly assigned to receive chemotherapy alone vs. chemotherapy plus imatinib, while all poor-risk patients received chemotherapy plus imatinib. EsPhALL 2004 results confirmed that the addition of imatinib was beneficial in the treatment of children with Ph+ ALL, with intention-to-treat analysis showing for good-risk patients receiving imatinib a 4-year DFS of 73% vs. that of 62% for those who did not receive imatinib (p = 0.24). Importantly, in this study there was also a high rate (77%) of HSCT in CR1 in the good-risk patient cohort, meaning no conclusions can be drawn regarding the role of HSCT over TKI-containing multi-agent chemotherapy only, for good-risk Ph+ ALL patients. Despite the incorporation of TKI and the extensive use of HSCT, the outcomes for poor-risk patients remained unfavorable, with 4-year EFS of 53.3% [25]. Based upon the COG AALL0031 results published in 2009, which demonstrated the advantage of the earlier and continuous administration of imatinib, the EsPhALL 2004 study was amended in 2010 to test, in a single-arm clinical trial (EsPhALL 2010), continuously dosed imatinib from mid-induction (day 15) in association with the same intensive chemotherapy backbone used in EsPhALL 2004. Furthermore, the allocation of HSCT in CR1 was restricted to MRD-poorly-responding (end of induction 1B MRD > 5 × 10−4) or MRD-non-responding patients, reducing by half the HSCT rate for the overall cohort (38%) and particularly for the good-risk patients (32%). This amended trial (EsPhALL 2010) demonstrated that early and continuous use of imatinib concurrently with intensive chemotherapy can effectively replace HSCT in the majority of good-risk Ph+ ALL patients, resulting in a 5-year EFS of 62.7% [26]. Despite the integration of TKIs, both COG and EsPhALL chemotherapy backbones used to treat Ph+ ALL patients were highly intensive, resulting in high rates of treatment-related toxicities and mortality. Hence, these two major consortia designed a joint international collaborative randomized protocol (NCT03007147, EsPhALL 2017/COG AALL1631) to evaluate whether chemotherapy de-intensification in combination with imatinib could reduce treatment-related morbidity and mortality without adversely impacting the outcomes in standard-risk newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL patients. Conversely, for high-risk patients treated with imatinib in combination with intensive EsPhALL backbone and HSCT, this study aimed to describe the feasibility and outcomes of 1-year post-HSCT imatinib administration. The EsPhALL 2017/COG AALL1631 trial has recently completed its recruitment, representing to date the largest trial performed in pediatric Ph+ ALL, and its results will constitute the benchmark for novel clinical trials in the next years. As aforementioned, ABL-class fusion positive ALL is a high-risk ALL subtype associated with unfavorable outcomes when treated with conventional risk-adapted multi-agent chemotherapy [84], which is likely to benefit from the addition of TKIs such as imatinib and dasatinib as suggested by recent anecdotal evidence and retrospective studies [84,85,86]. Based on this consideration, the EsPhALL 2017/COG AALL1631 was amended in 2021 to also include a cohort of patients with ABL-class fusion positive ALL as eligible to participate in the chemotherapy backbone randomization. The ongoing ALLTogether1 trial (NCT04307576) also treats all patients with ABL-class ALL with non-random experimental intervention, with the addition of imatinib from the induction phase for patients < 25 years and from the consolidation phase for patients ≥ 25 years, with the aim to reduce the risk of disease recurrence.
3.1.2. Dasatinib
Dasatinib is a second-generation TKI with dual ABL/SRC kinase inhibition activity approved by both the FDA and EMA for the treatment of pediatric patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL in combination with chemotherapy. Compared to imatinib, dasatinib has higher in vitro inhibitory potency (>300-fold), and better central nervous system (CNS) penetration capacity and activity against some imatinib-resistant Ph+ clones [87]. The additional effect of dasatinib against SRC family kinases might contribute to higher efficacy in ALL [88]. The safety and efficacy profile of dasatinib (twice daily dosing of 50–110 mg/m2/dose) was firstly assessed in the pediatric population in a phase I study performed by COG (NCT00316953, CA180-038/COG-ADVL0516), which included patients with refractory solid tumors or imatinib-refractory Ph+ leukemias who showed drug disposition of and tolerability to dasatinib similar to that observed in adult patients, and found the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) to be 85 mg/m2/dose administered twice daily [28]. A subsequent European Phase 1 dose-escalation study of dasatinib (NCT00306202, CA180-018/ITCC-005), developed within the framework of the Innovative Therapies for Children and Adolescents with Cancer Consortium (ITCC), was conducted for patients with refractory/intolerant (R/I) CML or R/R Ph+ ALL after prior imatinib therapy, and identified as the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) once daily 60 mg/m2 for CML-CP patients and once daily 80 mg/m2 for children with accelerated or blastic phase CML (CML-AP/BP) and Ph+ ALL [29]. Based on these results and on the hypothesis that substituting dasatinib for imatinib would lead to more rapid clearance of leukemia and better outcomes for pediatric Ph+ ALL patients, the COG group conducted the ALL0622 phase II trial from 2008 to 2012 on a small cohort of patients (n = 60) (NCT00720109) with the aim being to determine the feasibility and safety profile of adding dasatinib (60 mg/m2 continuously from day 15 of induction) to the same chemotherapy backbone previously used in the COG AALL0031 [30]. The results of this trial showed an impressively high rate of end of induction (EOI) complete remission (98%) and end of consolidation (EOC) MRD < 0.01% (89%), which compared favorably with the previous COG study (COG AALL0031) [30]. However, the reported 5-year EFS of 60% was effectively identical to those of both previous imatinib-containing protocols (COG AALL0031 and EsPhALL2004; 5-year EFS 58% and 4-year EFS 61.9%, respectively), not allowing the trial to conclude that dasatinib plus chemotherapy was better than the imatinib plus chemotherapy combination. Notably, this study reinforced the evidence that in the TKI-era the HSCT indication for Ph+ ALL pediatric patients can be limited to high-risk patients. The COG AALL0622 study closed early in order to open the first collaborative Ph+ ALL trial conducted jointly by the COG and EsPhALL trial (NCT01460160, CA180-372/COG AALL1122). This phase II study, the long-term results of which were recently published by Hunger et al. [31], investigated the efficacy of the early and continuous administration of dasatinib in combination with the EsPhALL chemotherapy backbone. The 65.5% 3-year EFS reported was consistent with but not superior to the results of imatinib-containing chemotherapy multi-agent treatment protocols (EsPhALL 2004/2010), despite the very low HSCT rate in CR1 (14%) and the elimination of prophylactic cranial irradiation.
Within the limitation of the small number of patients, the experience of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital (SJCRH) also clearly showed the advantage of early and continuous exposure to TKS in the treatment of patients with Ph+ ALL. The frontline protocols Total XV (NCT00137111) and Total XVI (NCT00549848) integrated, respectively, imatinib 340 mg/m2 and dasatinib 40 mg/m2 twice a day from day 22 of induction, in the treatment of newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL patients. In the 11 patients who received TKIs (5 imatinib and 6 dasatinib) the 5-year EFS was 68.6%, comparing favorably with the outcomes of patients treated at SJCRH pre-TKIs (31.6%, p = 0.022) [27].
Between 2015 and 2018, the first randomized clinical trial in newly diagnosed pediatric Ph+ ALL patients comparing imatinib 300 mg/m2 (n = 97) and dasatinib 80 mg/m2 (n = 92), in combination with a modified SJCRH Total XV/XVI chemotherapy backbone, was conducted by the Chinese Children’s Cancer Group (CCCG) (ChiCTR-IPR-14005706). Shen et al. reported, with a median follow-up of 26.4 months, a significantly better outcome for the dasatinib arm; 4-year EFS of 71% vs. 48.9%, and 4-year OS of 88.4% vs. 69.2% were reported for dasatinib and imatinib, respectively [21]. However, there are some caveats to bear in mind when interpreting these results. Firstly, the follow-up of the study was short, considering the slightly high rate of late relapse in the TKI era for Ph+ ALL. Furthermore, the reported results of the imatinib arm were significantly inferior compared to previous COG and EsPhALL study results, which can be only partially explained by the lower imatinib dosing, higher dasatinib dosing and different backbones administered. Considering the results of all these clinical trials, to date there is no conclusive evidence regarding the superiority of dasatinib or imatinib, and both represent, in combination with chemotherapy, the standard of care for treating Ph+ ALL pediatric patients.
Although the prognosis of Ph+ ALL pediatric patients has markedly improved due to the optimization of TKI-containing multi-agent treatment, the outcomes of Ph+ ALL are still inferior to Ph-negative ALL patients and, thus, novel therapeutic improvements are urgently needed. Recently, very favorable results have been obtained in the treatment of adult patients with Ph+ ALL by combining TKIs such as dasatinib and ponatinib with immunotherapeutic approaches such as blinatumomab or inotuzumab [89,90,91,92,93,94,95], paving the way for a possible chemotherapy-free treatment scenario for this specific acute leukemia subtype, including sparing HSCT as a definitive consolidation.
For ABL-class fusion positive ALL, three major frontline pediatric clinical trials including dasatinib have been conducted in recent years. The COG AALL1131 trial (NCT02883049) for patients with high-risk B-ALL was amended in 2016 to add a post-induction dasatinib non-random treatment arm, including post-induction dasatinib (NCT01406756) for those with ABL-class fusion [96]. The preliminary results of this trial were recently reported [32] with a 4-year EFS of 52.5 ± 18% for the HR ABL-class fusion positive patients treated with the incorporation of dasatinib compared to 86.8 ± 0.7% (p < 0.0001) of all patients on AALL1131 study. Despite the limitation of a small cohort of patients (n = 22) and the high rate of treatment discontinuation of the prescribed protocol therapy (17/22), these are the first available prospective data from a pediatric trial in ABL-class fusion positive ALL. Additionally, the SJCRH Total therapy XVII study (NCT03117751), started in 2017, explored the effect of adding dasatinib from day 15 of induction to all patients with ABL-class fusion positive ALL identified by RNA-seq, regardless of the patient’s MRD level [97]. Notably, in the total XVII study, T-ALL patients who presented ABL-class fusions with partner genes such as NUP214, ETV6, SLC9A3R1 or MBNL1 were also included in the dasatinib sub-arm jointly with B-ALL ABL-class fusion positive patients. The DFCI ALL 16-001 study (NCT03020030) also evaluated the incorporation of dasatinib in the frontline treatment of very high risk B-ALL with ABL-class fusions other than BCR::ABL1. The results of these two former studies have not yet been published.
In pediatrics, the newly opened COG AALL2131/EsPhALL 2022 study (NCT06124157) is exploring an immuno-chemotherapeutic approach with the early introduction of blinatumomab to replace conventional chemotherapy and the combination of fusion-specific TKI therapy for patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ or ABL-class ALL. All patients receive dasatinib with the exception of those with ABL-class ALL harboring PDGFRB treated with imatinib, based upon recent robust data demonstrating differential TKI sensitivity amongst specific ABL-class fusion subgroups [98].
Finally, also the MA-SPORE ALL 2020 study (NCT06336395), ongoing in Malaysa and Singapore, and the NCT06257394 trial, ongoing in South Korea, include dasatinib for the treatment of Ph+ and ABL-class positive ALL pediatric patients.
Although BCR::ABL1 fusions in patients with T-ALL are rare, high in vitro and ex vivo susceptibility to dasatinib in up to 30% of non-BCR::ABL1-rearranged T-ALL cases was recently reported [99,100]. Based on this evidence, T-ALL trials including dasatinib have been designed. The phase I/II trial RAVEN (NCT05192889), evaluating the activity of combination chemotherapy with venetoclax and navitoclax in children with R/R ALL, which included dasatinib for children with R/R ABL-class fusions and non-ETP T-ALL, has recently completed its enrollment. Furthermore, the SJALL23T study (NCT06390319) sponsored by the SJCRH, will test whether the addition of dasatinib to the AALL1231 protocol can improve outcomes for children and young adults with newly diagnosed T-ALL without the near-ETP or ETP phenotype.
Notably, a European-based master protocol sponsored by the Princess Maxima Center for Pediatric Oncology (PMC) in collaboration with major European academic consortia (ITCC, iBFM, IntReALL, and EICNHL) has been recently designed (International Proof of Concept Therapeutic Stratification Trial of Molecular Anomalies in Relapsed or Refractory HEMatological Malignancies in Children, HEM-iSMART), with the aim to investigate multiple investigational medicinal products in children, adolescents and young adults (AYAs) with both R/R B- and T-ALL [101]. The HEM-iSMART sub-protocol B phase I/II trial (NCT05751044) will evaluate the safety and efficacy of dasatinib in combination with venetoclax + dexamethasone + cyclophosphamide and cytarabine in children and AYAs with R/R B- and T-ALL, whose leukemia presents with alterations in the MAPK/SRC pathway.
3.1.3. Ponatinib
Ponatinib is a potent third-generation TKI, also active in patients with T315I mutations in the ABL1 kinase domain, which confer resistance to first- and second-generation TKIs. Currently, ponatinib is approved in adult patients for the second-line treatment of CML and Ph+ ALL and for first-line treatment in the case of a T315I mutation. In the pediatric ALL setting, a phase I/II study exploring the safety and efficacy of ponatinib combined with chemotherapy in pediatric patients with relapsed Ph+ ALL resistant to previous TKI therapies or with the T315I mutation [34], was recently terminated due to dose-limiting toxicities in the phase I (NCT04501614). Ponatinib is currently being tested in an international phase I/II company-sponsored basket trial (INC B 84344) with the aim to assess its safety and efficacy for the treatment of pediatric R/R leukemias (including ALL), lymphomas, and solid tumors (NCT03934372). Additionally, the MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC) has designed a phase II adult/pediatric trial, which will include also children aged ≥ 12 years, for testing the combination of ponatinib with mini-hyper CVD chemotherapy and venetoclax in patients with R/R T-ALL (NCT05268003).
3.1.4. Nilotinib
Nilotinib is a second-generation TKI which is currently approved by the FDA and EMA for the treatment of both CML and Ph+ ALL in adults. In children, conversely, its approval is limited to patients with CML-CP either in first-line treatment or R/I to previous TKI treatment. After the phase I study (NCT01077544), which evaluated nilotinib in pediatric R/I CML patients together with R/R Ph+ ALL [33], no subsequent phase II studies in the Ph+ ALL pediatric population have been conducted.
3.1.5. Olverembatinib
Olverembatinib is a novel third-generation TKI which has recently shown promising results in patients with TKI resistant and/or intolerant CML and R/R Ph+ ALL in adults. A pediatric phase I study is currently ongoing in China for children with R/R Ph+ ALL. This phase I study (NCT05495035) is testing the safety and efficacy of olverembatinib in combination with the second-generation BCL2 inhibitor lisaftoclax, and preliminary promising safety and efficacy data have been reported [35].
No clinical trials in children with ALL are currently available for other TKIs. However, pediatric-specific trials of asciminib are being conducted in CML [102] and are planned for Ph+/ABL-class Ph-like ALL.
3.2. Janus Kinase Inhibitors
Among Ph-like ALL, the largest class of kinase-activating alterations is characterized by the deregulation/activation of JAK/STAT signaling due to different genetic alterations, including CRLF2 rearrangements (CRLF2r) with frequent JAK2 or JAK1 co-mutation, JAK2 rearrangements, EPOR rearrangements, SH2B3 deletions, and IL7R indels [18]. This pathway represents a major potential therapeutic vulnerability. Based upon robust preclinical data, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, such as ruxolitinib, have been investigated in children and adults with this Ph-like ALL subtype (Table 1).
Ruxolitinib
Ruxolitinib is a potent, orally bioavailable inhibitor of the JAK family of kinases with particular efficacy against JAK1 and JAK2. It was first tested as a monotherapy in children with relapsed/refractory solid tumors or hematologic malignancies in the COG ADVL1011 phase 1 study (NCT01164163), which demonstrated a manageable toxicity profile and identified the RP2D as 50 mg/m2/dose BID [36]. Ruxolitinib has been subsequently investigated in combination with intensive multi-agent chemotherapy in children and AYAs with newly diagnosed HR CRLF2r/JAK pathway-mutant Ph-like ALL in the COG AALL1521 phase 2 study (NCT02723994). In part 1 of the study, the safety of adding ruxolitinib to post-induction high-risk B-ALL chemotherapy was explored at six different dose levels, and the RP2D of ruxolitinib was identified as 50 mg/m2/dose × 14 days on/14 days off per cycle of multi-agent chemotherapy [37]. The part 2/efficacy phase of the study involves evaluating whether the addition of ruxolitinib to the standard of care in high-risk B-ALL chemotherapy backbone may improve outcomes for children and AYAs with Ph-like ALL harboring JAK/STAT pathway lesions, with results anticipated in 2026. Additionally, in the total therapy XVII study (NCT03117751), patients with Ph-like ALL with JAK-STAT signaling activation and with day 15 or day 22 MRD ≥ 5% and all the patients with ETP and MPAL received combination therapy with ruxolitinib. These latter two COG and SJCHR trials completed their enrollment in 2022 and 2023, respectively, and their results are pending. Furthermore, the sub-protocol C of the previously mentioned master protocol HEM-iSMART will evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and efficacy of ruxolitinib with venetoclax in combination with dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, and cytarabine in children and AYAs with R/R ALL with alterations in the IL-7R and/or JAK-STAT signaling pathways [50]. Notably, CRLF2/JAK alterations are also very common in ALL patients with Down syndrome, but these children have been excluded from ruxolitinib-based clinical trials to date.
3.3. Proteasome Inhibitors
The ubiquitin–proteasome pathway is essential for the degradation of most proteins and represents, therefore, an actionable pathway, by sensitizing leukemic blasts to apoptosis induced by chemotherapy. Three major proteasome inhibitors, namely bortezomib, carfilzomib, and ixazomib, have been developed and tested in hematological malignant diseases including pediatric ALL (Table 1).
3.3.1. Bortezomib
Bortezomib, as a single agent, was first tested in children with refractory ALL in the phase I study (NCT00077467) sponsored by the COG, which determined the R2PD as 1.3 mg/m2/dose, administered twice weekly for 2 weeks followed by a 1-week rest. Little activity as monotherapy was found in this population [38]. Subsequently the Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia and Lymphoma (TACL) consortium conducted the first phase 1/2 study of bortezomib in combination with chemotherapy (NCT00440726) in R/R pediatric ALL patients [39]. The phase I trial demonstrated that the combination of bortezomib (1.3 mg/m2) with a standard 4-drug chemotherapy reinduction backbone (vincristine, dexamethasone, pegylated L-asparaginase, and doxorubicin) (VPLD) was active with acceptable toxicity in pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory ALL. The phase 2 expansion of this combination (n = 22) in highly pretreated relapsed patients (second or more relapse) showed an overall response rate of 73% [40]. Furthermore, the same combination (Bortezomib + VPLD) was tested in the setting of both B- and T-ALL early and very early first relapse in the COG AALL07P1 phase 2 clinical trial (NCT00873093) [41]. Overall CR2 rates were 68 ± 5% for B-ALL patients, with 63 ± 7% for very early relapse (<18 months from diagnosis) and 72 ± 6% for early relapse (18–36 months from diagnosis). Patients with relapsed T-ALL had a particularly encouraging CR2 rate of 68 ± 10%, suggesting the benefit of adding bortezomib in this group of patients [41]. At the same time, a European pediatric phase II trial explored the efficacy of reinduction chemotherapy including bortezomib in a cohort of heavily pretreated patients. Children were randomized 1:1 to bortezomib (1.3 mg/m2/dose) administered early or late to a dexamethasone and vincristine backbone. The study reported an overall response rate of 60% with no efficacy differences between the two arms [22]. Based on these results, the I-BFM-SG International Study for Children and Adolescents with Relapsed ALL Consortium (lntReALL) designed the IntReALL 2010 high-risk study (IntReALL HR 2010) which is investigating, in a randomized fashion design, the effect of adding bortezomib to the UK ALLR3 reinduction backbone in high-risk ALL patients in their first relapse (NCT03590171). The results of this large international study, which will provide data on larger cohorts of first-relapsed B- and T-ALL are yet to be published, and interim analysis testing did not reach the superiority or futility criteria. Additionally, the CCCG protocol (CCCG-ALL-2017, NCT04224571) tested the addition of bortezomib during reinduction in combination with chemotherapy in relapsed ALL children (results still unpublished). Concomitantly, two international randomized phase III studies have been carried out, which evaluate the effect of combining bortezomib to multi-agent chemotherapy in the frontline setting of pediatric ALL. The European AIEOP-BFM ALL 2017 study, which has recently completed its accrual, investigated in a randomized fashion whether the addition of bortezomib during the extended consolidation treatment can improve outcomes in early HR B-ALL patients (NCT03643276) based on the stratification of flow of MRD at day 15. The COG group conducted, instead, a phase 3 study with the aim to compare outcomes in children with newly diagnosed T-ALL and T-Lymphoblastic (T-LLy), who were randomly assigned to a modified BFM backbone with/without the bortezomib during induction and delayed intensification (AALL1231, NCT02112916). The results of the AALL1231 trial, recently published by Teachey et al. [42], did not show, overall, a statistically significant improvement of outcomes on the bortezomib arm (4-year EFS: 80.1 ± 2.3% (no bortezomib) versus 83.8 ± 2.1% (bortezomib); p = 0.131). Of note, post hoc analyses suggested that bortezomib was effective in T-LLy (4-year EFS: 76.5 ± 5.1% vs. 86.4 ± 4.0%; p = 0.041) and not in T-ALL (4-year EFS: 82.9 ± 2.4% vs. 81.5 ± 2.5%; p = 0.396), although it is not well understood what the biology behind this might be. In light of these results, multiple subsequent trials incorporated bortezomib as a promising experimental treatment for T-ALL and T-LLy, and results in these larger cohorts must be awaited to better interpret its potential added value. The SJCRH total therapy XVII study (NCT03117751) included bortezomib in the early intensification treatment of patients with no targetable lesions and day 15 or day 22 MRD ≥ 5% or LLy patients without EOI complete response, and the future SJALL23T study will include bortezomib for patients with T-LLy (NCT06390319). The incorporation of bortezomib for newly diagnosed T-LLy is currently also being tested by the ongoing CCCG study (NCT05681260). Interestingly, given preclinical data showing bortezomib and vorinostat (histone deacetylase inhibitor) to be novel active agents in primary KMT2A rearranged (KMT2A-r) infant ALL, the SJCHR also carried out the Total Therapy for Infants with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia I study (TINI 1), which incorporated these two agents into an ALL chemotherapy backbone containing dexamethasone, mitoxantrone, and peg-asparaginase during induction and reinduction chemotherapy cycles (NCT02553460). The successor study, TINI 2 (NCT05848687), builds upon the bortezomib/vorinostat backbone by incorporating two cycles of blinatumomab and the menin inhibitor ziftomenib in combination with chemotherapy during reinduction [43].
3.3.2. Carfilzomib
Carfilzomib is a second-generation proteasome inhibitor which demonstrates higher selectivity and potency compared to bortezomib in preclinical ALL models [103]. A global pediatric phase IB/II trial of carfilzomib combined with vincristine, dexamethasone, asparaginase, and daunorubicin (VXLD) as a reinduction therapy for children with R/R ALL has been recently completed (NCT02303821). The dose-escalation phase I study identified 56 mg/m2 as the RP2D of carfilzomib and demonstrated the good tolerance of this combination. Encouraging overall response rates (CR/CRp/CRi) of 50% after induction (12/24) and 58% after consolidation (14/24) in the overall cohort of both relapsed B-ALL and first relapsed, nonrefractory T-ALL patients, were reported [44]. The use of the RP2D of carfilzomib with a modified VLXD as a reinduction therapy in pediatric patients with R/R ALL has further been investigated in the phase 2 part of this trial (NCT02303821) [104], for which results are still pending.
3.3.3. Ixazomib
Ixazomib is a third-generation orally bioavailable proteasome inhibitor, with an improved pharmacokinetic and safety profile compared to bortezomib [105]. The TACL consortium has recently carried out a phase 1 trial of oral ixazomib combined with chemotherapy in children and AYAs with relapsed/refractory ALL or lymphoma, and preliminary results were recently reported (NCT03817320) [45]. Ixazomib at the RP2D of 2 mg/m2/dose showed an acceptable safety profile and an encouraging early efficacy signal in combination with a VXLD backbone chemotherapy. The phase 2/expansion cohort of the study is ongoing.
3.4. BH3 Mimetics
The B-cell lymphoma (BCL-2) family of proteins, including anti-apoptotic (BCL-2, BCL-XL, MCL-1) and pro-apoptotic proteins (BAX, BAK and BH3-only), are essential regulators of programmed cell death and the dysregulation of their interplay has been demonstrated to be a key mechanism of leukemic blast survival in both acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and ALL [106]. This evidence has prompted the development, in the last decade, of BH3 mimetic compounds that inhibit the activity of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 member proteins. Two major BCL-2 inhibitors, venetoclax and navitoclax, have emerged in recent years as effective novel therapeutic approaches across several different hematological malignancies including ALL, and new-generation BCL-2 inhibitors molecules are under preclinical and clinical investigation (Table 1).
3.5. MEK Inhibitors
The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK or MAPK/ERK pathway is a critical signal transduction cascade implicated in the uncontrolled proliferation of many human cancers including ALL. RAS pathway-activating mutations are found in 38% of relapsed pediatric B-ALL patients and additional mutations that activate the RAS signaling cascade (NF1, BRAF, IKZF2, IKZF3, JAK1) have also been found with varying frequencies in relapsed ALL [112]. Preclinical studies showed that RAS pathway mutations confer sensitivity to mitogen-activated extracellular protein kinase (MEK) inhibitors. Two major MEK inhibitors, selumetinib and trametinib, are under clinical investigation for pediatric RAS pathway-mutant ALL (Table 1).
3.5.1. Selumetinib
Based on the preclinical data suggesting the synergistic anticancer effect of the combination of dexamethasone with the MEK 1/2 inhibitor, selumetinib [113], the Cancer Research UK Clinical Trials Unit (University of Birmingham) has sponsored an international, parallel-group, dose-finding with expansion, phase I/II trial (NCT03705507) to assess the selumetinib/dexamethasone combination in adult and pediatric patients with R/R RAS pathway-mutant ALL [114]. The results of this phase I study were recently reported. Although this trial faced various hurdles, including slow recruitment and safety issues concerning severe infections, for which the changing of the dexamethasone dosing and the mandating of antimicrobial prophylaxis were deemed necessary, the preliminary outcome data, with 44% of patients achieving CR (4/9 pts, 3 adults and 1 child), was promising [48].
3.5.2. Trametinib
Trametinib is a reversible and highly selective allosteric MEK1/MEK2 inhibitor, with an indication for the treatment of different solid tumors characterized by MAPK signaling pathway alterations, such as advanced melanoma [115] or low-grade gliomas [116]. Notably, preclinical studies showed that trametinib enhances glucocorticoid responsiveness and is synergistic with the dexamethasone also in T-ALL cell lines [117]. The phase I/II sub-study D of the previously described HEM-iSMART master protocol (NCT05658640), is currently enrolling patients to the test safety and efficacy of trametinib in combination with dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, and cytarabine in children and AYAs with R/R T-ALL and LBL which harbor alterations in the RAS–RAF–MAPK pathway [101].
3.6. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors
The deregulation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) is associated with the uncontrolled proliferation of cancer cells in a wide spectrum of different malignancies including acute leukemias. CDKs inhibition strategy has therefore emerged as a novel molecularly targeted cancer treatment in recent years. In the setting of pediatric acute leukemias, although there is still limited clinical experience with CDK inhibitors treatment, some clinical data is emerging for both palbociclib and ribociclib (Table 1).
3.6.1. Palbociclib
Palbociclib is an oral CDK4/CDK6 inhibitor which showed promising preclinical efficacy when combined with simultaneous chemotherapy in both B- and T-ALL models [118]. Its safety and preliminary activity in combination with a chemotherapy reinduction backbone was recently investigated by the COG AINV18P1 study (NCT03792256) in both relapsed T-ALL/LLy (1st or greater relapse) and multiply relapsed B-ALL/LLy pediatric patients. Despite the limitation of the small numbers (n = 12), this regimen with palbociclib at the RP2D (50 mg/m2/day for 21 days) showed promising efficacy with 42% of ORR in heavily pretreated patients [49]. Another phase I study of palbociclib in combination with chemotherapy was initially started at the SJCRH (RELPALL study, NCT03515200) and is currently sponsored by Standford University (RELPALL2 study, NCT04996160) with the primary objective of confirming the safety of the previously estimated MTD of palbociclib (100 mg/m2/day, days 1–5; 11–15; 21–30) in combination with chemotherapy for pediatric patients with R/R ALL.
3.6.2. Ribociclib
Ribociclib is another selective CDK4/CDK6 inhibitor, and its safety and efficacy in children was firstly tested in a phase I study including patients with malignant rhabdoid tumors, neuroblastoma, and other solid tumors [119], and subsequently in the arms A and B of the AcSé-ESMART Trial (NCT02813135) in combination with topotecan-temozolomide or everolimus, respectively, in children with advanced malignancies [50]. In this last study, one patient with a T-ALL with CDKN2A/CDKN2B deletion and PTEN loss was treated with ribociclib and everolimus, achieving a clinical response with a decrease in the number of blasts but ultimately experiencing the progressing disease. The arm M of the AcSé-ESMART trial is currently enrolling patients with malignant hematological conditions harboring alterations in the cell cycle and mTOR pathway evaluating the ribocliclib in combination with everolimus and dexamethasone. Furthermore, ribociclib with this same combination treatment is currently under investigation in children and AYAs with R/R ALL in a phase I study sponsored by the Dana–Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) (NCT03740334).
3.7. mTOR Inhibitors
The phosphatidylinositiol 3-kinase (PI3K), AKT, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) (PI3K/AKT/mTOR) is a frequently dysregulated signaling pathway in a wide range of hematological conditions including B- and T-cell ALL. The antileukemic activity of rapamycin analogs including everolimus, sirolimus, and temsirolimus have been extensively studied in vitro and in vivo preclinical ALL models providing the rationale for investigating these agents in clinical trials [120,121] (Table 1).
3.7.1. Sirolimus
Sirolimus was first tested as single agent in ≥2nd relapsed pediatric ALL patients in a monocentric phase 1 study (NCT00068302) at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia [52], demonstrating no toxic effects, with three out of seven treated patients showing stable disease as best response. Subsequently, two other institutional studies combining sirolimus with glucocorticoids [53] (NCT00874562) and with methotrexate (NCT01162551), respectively, were conducted. Of note, sirolimus in combination with 5 days of prednisone (window therapy prior to starting multi-agent reinduction chemotherapy) showed to suppress MCL-1 expression in vivo, suggesting that mTOR inhibitors may improve sensitivity to glucocorticoids. Next, a single-institution trial sponsored by the Children’s Hospital Medical Center of Cincinnati, combining sirolimus with the UKALLR3 backbone (NCT01658007) was initiated, but terminated due to slow accrual.
3.7.2. Everolimus
Following the promising evidence of adding mTOR inhibitors to chemotherapy, the DFCI sponsored a multi-institutional phase 1b trial (NCT01523977) in first relapse pediatric ALL patients combining everolimus with a standard 4-drug reinduction regimen. The results of this study proved the safety and tolerability of the applied regimen and the high second CR rate of 86% was reported, with 68% of patients achieving MRD < 10−3 after reinduction. The RP2D of everolimus in combination with a 4-drug reinduction was established as 5 mg/m2/day [54]. Furthermore, a phase I trial (NCT03328104) testing everolimus in combination with a NECTAR regimen (nelarabine, cyclophosphamide, and etoposide) in relapsed T-ALL/LLy was recently completed, and the results are pending. Finally, everolimus is also under investigation in combination with ribociclib and dexamethasone in a phase I study sponsored by the DFCI (NCT03740334).
3.7.3. Temsirolimus
Concomitantly to the everolimus DFCI study, the COG ADVL1114 phase I study (NCT01403415) explored the safety and preliminary activity of the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus (three weekly doses) in combination with an intensive reinduction chemotherapy (UK ALLR3) for 2nd or greater relapse of pediatric ALL. Although 7 of the 15 evaluable patients had a CR or CRi, this treatment combination resulted in excessive toxicity at all dose levels of temsirolimus tested and it was then considered not safe in children with relapsed ALL [55]. The high toxicity shown by the COG ADVL1114 study with 4-drug reinduction therapy prompted the TACL consortium to design a subsequent trial (NCT01523977) of temsirolimus (two weekly doses) in combination with an alternative cyclophosphamide- and etoposide-based chemotherapy backbone in the same patient population. This combination showed an acceptable safety profile and an ORR of 47%. The RP2D of temsirolimus with this chemotherapy was identified at 15 mg/m2 [56].
3.8. Epigenetic Modifying Agents
Epigenetic alterations involving histone modification or DNA methylation are quite frequent in ALL and have been associated with treatment resistance and relapse risk, leading to the development of therapeutic strategies targeting these epigenetic aberrations. Globally, these agents are referred to as “epigenetic modifying agents” and include histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) and DNA methyltransferase inhibitors (DNMTi) or HMAs (Table 1).
3.9. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi)
HDAC inhibitors can be classified into structurally diverse classes, including hydroxamic acids, such as vorinostat and panobinostat, cyclic peptides (e.g., romidepsin) and benzamides (i.e., entinostat). Among these drugs, vorinostat is the one in which clinical development in the context of pediatric ALL is more advanced. The combination of HDACi and DNMTi was shown synergistic in in vitro ALL models [122]; hence, these agents have more frequently been investigated in combination than as single agents.
Vorinostat
Vorinostat was first tested in children with R/R malignancies, including ALL, by the phase I COG study (NCT00217412), which identified the RP2D as 230 mg/m2/d in monotherapy [57]. Next, a monocentric pilot phase II study (NCT00882206), sponsored by the University of Minnesota, investigated the tolerability and efficacy of the combination vorinostat plus decitabine followed by a standard reinduction chemotherapy in pediatric and adults R/R ALL patients [58]. This regimen was tolerable and demonstrated a quite encouraging clinical benefit in a heavily pretreated cohort of patients with 5 out of 13 patients achieving CR and MRD negativity. Based on these results, a subsequent pediatric trial was carried out (NCT01483690) by the TACL consortium to evaluate the effect of an extended schedule of decitabine and vorinostat prior to and concomitantly with an intensive chemotherapy backbone in pediatric and AYA R/R ALL patients. Unfortunately, despite encouraging response rates and pharmacodynamics, this regimen was determined to be not feasible in B-ALL due to the high incidence of significantly infectious toxicities [59]. Furthermore, vorinostat is under clinical evaluation in combination with bortezomib in infants with KMT2A-r ALL, as previously discussed in Section 3.3.1.
3.10. Hypomethylating Agents (HMAs)
DNA methyltransferase inhibitors, azacitidine and decitabine, have been widely investigated in recent years in hematological cancers, mainly in the setting of myeloid malignancies but increasingly also in specific ALL groups such as KMT2A-r ALL and T-ALL, for which there exists a strong biological rationale and preclinical evidence for the use of a hypomethylating treatment strategy [106,123,124].
3.10.1. Azacitidine
The first phase I clinical trial (NCT01861002) testing azacitidine combined with chemotherapy in children with relapsed/refractory acute leukemias (mainly AML) was conducted by the TACL consortium and demonstrated the tolerability of 5 days of azacitidine (75 mg/m2 per day, subcutaneously) followed by chemotherapy [60]. Some years later, the COG conducted the AALL15P1 single-arm groupwide pilot trial (NCT02828358), testing the hypothesis that the addition of 5 days of azacitidine treatment immediately prior to the start of chemotherapy, in 4 post-induction courses, could enhance chemosensitivity of infants with newly diagnosed KMT2A-r ALL. This trial showed that the addition of azacitidine was well-tolerated and led to decreased DNA methylation, but resulted in similar outcomes to similar infants treated with chemotherapy in the prior COG AALL0631 trial (3-year EFS 34.7%) [61].
3.10.2. Decitabine
Decitabine was initially investigated by the COG consortium in a phase I trial in children with relapsed/refractory AML or ALL, which was terminated due to slow accrual (NCT00042796, unpublished). Another phase 1/2 study (NCT00349596) conducted in both children and adults with R/R ALL demonstrated the safety and encouraging clinical activity of decitabine alone and in combination with hyper-CVAD chemotherapy [62]. Subsequently, decitabine has been investigated in combination with vorinostat as an epigenetic modifying strategy plus chemotherapy (NCT00882206, NCT01483690), as previously discussed in Section Vorinostat. Finally, decitabine will be studied in combination with venetoclax and calaspargase pegol-mknl in children with relapsed/refractory T-ALL or LLy via a single-institution trial at MDACC (NCT06561074).
3.11. Molecularly Targeted Treatment in Pediatric KMT2A-r ALL
KMT2A is a central regulator of target genes that drive leukemogenic transformation. KMT2A-r ALL represents one of the more aggressive and unfavorable molecular subtypes of ALL. It typically occurs in infant patients and is associated with dismal outcomes in current chemotherapy-based treatment strategies [125,126].
Different precision medicine approaches have, therefore, been explored to address this large unmet clinical need, including the inhibition of signaling pathways (i.e., FLT3 inhibition) and the modulation of aberrant epigenetic programs (i.e., hypomethylating treatment [61] and DOT1L inhibition [127]); however, these efforts have provided only very limited benefits for these patients. Novel treatment strategies, such as immunotherapy (e.g., blinatumomab [128]), BH3 mimetics agents, and menin inhibitors (as well as their combinations) have recently emerged as promising therapeutic approaches for this very difficult-to-treat ALL subtype (Table 1).
3.12. FLT3 Inhibitors
The use of FLT3 inhibitors (FLT3i) for the treatment of acute leukemias mainly concerns AML, which represents nowadays a treatment paradigm for FLT3-mutated patients [68,129]. Nevertheless, the evidence of the striking overexpression of FLT3 in KMT2A-r infant ALL and the preclinical data of FLT3 inhibition strategy efficacy in KMT2A-r ALL cells [130] has prompted clinical investigation of FLT3i also in KMT2A-r ALL.
3.12.1. Midostaurin
The first-in-child phase I study (NCT00866281) of midostaurin was conducted in both R/R AML and KMT2A-r ALL patients, establishing the recommended dose for expansion as 30 mg/m2 twice daily [63]. Nevertheless, in KMT2A-r patients (n = 14) no clinical efficacy was observed and no further studies with midostaurin have thereby been conducted in ALL.
3.12.2. Lestaurtinib
In 2008, the COG started a phase III study to test the hypothesis that the addition of the FLT3i lestaurtinib to post-induction chemotherapy would improve EFS (AALL0631, NCT00557193) in KMT2Ar ALL infant patients, for which the results were recently published [64]. Though, overall, this randomized study did not show any improvement outcomes in KMT2Ar infants treated with chemotherapy plus lestaurtinib compared to chemotherapy only (3-year EFS 36 ± 6% vs. 39 ± 7%, p = 0.67), it demonstrated that in the subgroup of patients showing potent pharmacodynamic FLT3-inhibition and higher ex vivo sensitivity to FLT3i, the addition of lestaurtinib was beneficial.
3.13. Menin Inhibitors
Recently, the major translational effort for precision medicine in KMT2A-r leukemias has been focusing on a novel molecularly targeted class of small molecules, namely the menin inhibitors. These are oral and selective agents, able to disrupt the interaction between the chromatin adapter menin, and the KMT2A complex. Two different agents, revumenib and ziftomenib, are currently under early clinical-stage investigation in adults and children with both AML and ALL harboring KMT2A rearrangements [131,132] (Table 1).
3.13.1. Revumenib
The AUGMENT-101 study (NCT04065399), opened in 2019, was the first clinical trial testing menin inhibitor revumenib single agents in acute leukemias, and led to the FDA approval of the drug in 2024 for relapsed/refractory acute leukemia with KMT2A rearrangement in patients older than 1 year. This trial included both adult and pediatric patients with R/R KMT2A-r or NPM1-mutated (NPM1m) patients, and the results of the phase I part were recently published [65,133]. In total, 80 patients, including 18 pediatric patients, with R/R KMT2A-r acute leukemias (AML and ALL) were treated across six dose-escalation cohorts, and a RP2D of 276 mg twice a day, without a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, was established (for patients treated with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, i.e., azoles, the RP2D was 163 mg twice a day). Preliminary results of the pivotal phase 2 study were also reported. The interim analysis for the efficacy population (n = 57) of pooled adult and pediatric patients with KMT2A-r acute leukemia showed a combined CR + CRh of 22.8% and ORR of 63.2%, consistent in both adult and pediatric patients, exceeding the protocol-defined null hypothesis of 10% (primary endpoint); therefore, the KMT2A-r cohorts were stopped early for efficacy [66,134,135]. Based on these promising results, the AUGMENT-102 (NCT05326516) study was launched and has recently completed its recruitment. This phase I trial investigated the safety of revumenib in combination with chemotherapy (FLA regimen) in both adults and children with KMT2A-r, NUP98-r, or NPM1-m acute leukemia. Preliminary results of this mostly pediatric population (n = 27, median age 6 years; range 0.8–78) were recently reported, showing preliminary efficacy results similar to that observed with revumenib monotherapy [67]. The publication of the most consolidated results of this trial is expected soon, and together with other ongoing studies—mostly conducted in the context of R/R AML in adult patients (NCT06226571) [136]—will help to highlight the actual benefit of menin inhibitors therapy in combination with intensive chemotherapy for KMT2Ar, NUP98r, and NPM1m leukemias. Currently, the COG consortium is running a phase II study (AALL2121, NCT05761171) to test the safety and efficacy of revumenib in combination with chemotherapy in treating infants and children (aged > 1 month to <6 years) with KMT2A-r relapsed/refractory ALL, which estimates the enrollment of up to 78 patients. Furthermore, a phase I study sponsored by the City of Hope Medical Center is investigating the safety and tolerability of revumenib as a maintenance therapy in patients (>2 years old) with KMT2A-r or NPM1-m acute leukemia after HSCT (NCT06575296).
3.13.2. Ziftomenib
Ziftomenib is currently under clinical investigation in the adult population in the KOMET-001 study. This first-in-human study tested ziftomenib in patients with relapsed/refractory AML and demonstrated a manageable safety profile and preliminary clinical activity in heavily pretreated patients with KMT2A-r or NPM1-m AML, warranting further investigation of this agent as a monotherapy and in combination with rational therapeutic partners [137,138,139]. Notably, the CR rate differed between subgroups, with NPM1-mutant patients showing substantially higher response rates to ziftomenib compared to those with KMT2A rearrangements. In the pediatric setting three different ongoing or planned studies aim to evaluate ziftomenib in patients with KMT2A-r ALL. The TINI 2 study (NCT05848687), sponsored by the Stanford University, includes ziftomenib as part of a multi-agent therapy including chemotherapy, bortezomib, vorinostat, and blinatumomab [43] for the treatment of infant patients. The ITCC-101/APAL2020K (NCT06376162) is a phase 1 trial designed to assess the safety and determine the RP2D of ziftomenib in combination with chemotherapy for children with relapsed/refractory KMT2A-r, NUP98-r, or NPM1-m acute leukemias [68], in the context of a pediatric obligation (Pediatric investigation plan, EMA; Pediatric study plan, FDA). Finally, the MDACC is enrolling patients from 2 to 21 years-old in a phase I study investigating the combination of ziftomenib, venetoclax, and azacitidine in relapsed/refractory KMT2A-r ALL (NCT06397027).
Other menin inhibitors are being tested in adult patients with potential pediatric-specific investigations planned in the future. Bleximenib, for instance, is currently being tested in a pediatric cohort (12 years and older) of the phase 1/2 study (cAMeLot-1) for acute leukemia patients harboring KMT2A, NPM1, NUP98, or NUP214 alterations (NCT04811560).
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
In summary, the clinical development of molecularly targeted therapies for pediatric ALL has achieved notable successes, as well as several setbacks. Its landscape remains rapidly evolving, simultaneously making exciting progress and posing new challenges (Figure 3).
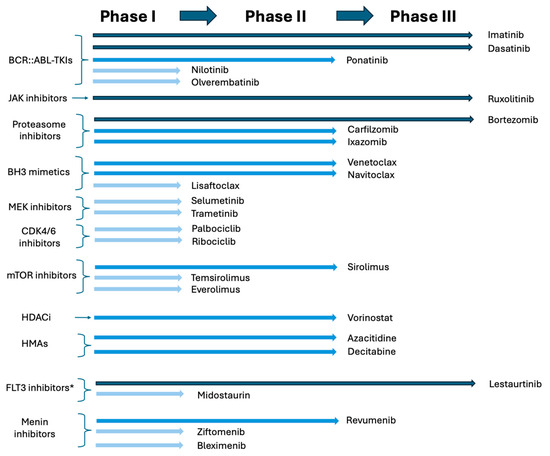
Figure 3.
Current stage of clinical drug development in molecularly targeted agents in pediatric ALL. * Though FLT3 inhibitors have been tested in ALL pediatric clinical trials in the past, these agents are not routinely added to chemotherapy for pediatric ALL patients at this time.
There persists an urgent need to develop more effective frontline and salvage treatments for patients with high-risk genetic subtypes of ALL and/or relapse, and to replace toxic therapy elements with less toxic ones yet retain efficacy. In this context, the integration of molecularly targeted agents combined with immunotherapies may represent the next therapeutic paradigm, as exemplified by the recent outstanding success of adult Ph+ ALL treatment combining dasatinib or ponatinib with blinatumomab [140]. Among the emerging rational combinations of molecularly targeted therapy and immunotherapy in the context of ALL, the integration of a menin inhibitor with blinatumomab in KMT2Ar patients appears particularly intriguing. Furthermore, the combination of venetoclax and inotuzumab showed promising activity in preclinical models [141] and in clinical results in adults with R/R ALL [142]. Importantly, future clinical trials should integrate immune monitoring strategies to assess the immunological impact of small molecules. In this context, careful consideration will be required regarding the potential overlapping toxicities between these two therapeutic approaches.
Equally critical is the continued elucidation of relevant biological biomarkers and in-depth genetic diagnostics refinement to enable patient stratification and guide treatment decisions.
There is a growing recognition of the need to introduce molecularly targeted agents earlier in the frontline setting for high-risk genetic patients rather than restricting their use to relapsed disease, as preventing relapse remains the ultimate therapeutic goal rather than treating it. Accordingly, there is the need to accelerate regulatory pathways to enable more rapid approvals in newly diagnosed pediatric patients, ensuring timely access to potentially transformative treatments. An effective strategy to expedite pediatric drug development could involve lowering the minimum eligible age earlier in phase 1 studies, once a recommended phase 2 dose has been defined in adults. This strategy, as exemplified in the revumenib development program, is particularly justified when the underlying genetic abnormalities are shared across pediatric and adult populations. Subsequently, it needs to be discussed whether a program in relapse is needed, or what the minimum dataset is to move the drug into frontline treatment. This may also imply that Pediatric Study Plans with FDA and EMA should contain placeholders for pivotal trials in newly diagnosed children. Drug development in pediatric oncology continues to face significant hurdles, including limited commercial incentives and smaller patient populations compared to adults. Initiatives, such as ACCELERATE, aiming to strengthen the collaboration and active dialogue amongst pediatric oncologists, pharmaceutical partners, regulators, and patient advocates [143], play a key role in addressing these barriers by fostering collaborative and efficient pediatric trial platforms. In conclusion, it is imperative to accelerate the movement of transformative agents to frontline settings, particularly those with game-changing potential such as the BCR::ABL1-directed TKIs and menin inhibitors reviewed in this review, to improve cure rates and reduce short- and long-term toxicities for children with ALL.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers17203322/s1, Table S1: Clinicaltrial.gov research strategy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.P. and E.B.; writing—original draft preparation, N.P.; writing—review and editing, all authors; supervision, A.B., C.R., S.K.T. and C.M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
S.K.T. is supported by National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute 1U24OD038422 and R01CA293587 awards and a Pennsylvania Department of Health Commonwealth Universal Research Enhancement (CURE) award. S.K.T. is a Scholar of Blood Cancer United (formerly the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society) and holds the Joshua Kahan Endowed Chair in Pediatric Leukemia Research at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
S.K.T. receives research funding from Kura Oncology and Incyte Corporation, serves/d on scientific advisory boards for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Kestrel Therapeutics, Kura Oncology, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Syndax Pharmaceuticals, and has received travel support from Amgen and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. C.M.Z. received institutional funding from Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo, Kura Oncology, AbbVie, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Takeda, and has consulted for Syndax, Beigene, Janssen, Novartis, Incyte, Sanofi, Roche, and Taiho Oncology. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AYAs | Adolescents and young adults |
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| B-ALL | B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| BFM | Berlin–Frankfurt–Münster |
| CAR-T | Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy |
| CCCG | Chinese Children’s Cancer Group |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinases |
| CML | Chronic myeloid leukemia |
| CML-CP | CML chronic phase |
| CML-AP | CML accelerated phase |
| CML-BP | CML blast phase |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| COG | Children’s Oncology Group |
| CR | Complete remission |
| DFCI | Dana–Farber Cancer Institute |
| DNMTi | DNA methyltransferase inhibitor |
| EFS | Event-free survival |
| EsPhALL | European intergroup study Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| EOI | End of induction |
| EOC | End of consolidation |
| ETP | Early T-cell precursor |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| HDACi | Histone deacetylase inhibitor |
| HEM-iSMART | International proof of concept therapeutic Stratification trial of Molecular Anomalies in Relapsed or Refractory HEMatological malignancies in children |
| HMAs | Hypomethylating agents |
| HR | High-risk |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| IntReALL | I-BFM-SG international study for children and adolescents with relapsed ALL |
| LLy | Lymphoblastic lymphoma |
| MDACC | MD Anderson Cancer Center |
| MEK | Mitogen-activated extracellular protein kinase |
| MTD | Maximum tolerated dose |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| ORR | Overall response rate |
| OS | Overall survival |
| Ph+ | Philadelphia chromosome-positive |
| Ph-like | Philadelphia chromosome-like |
| PK | Pharmacokinetics |
| PMC | Princess Máxima Center for Pediatric Oncology |
| RP2D | Recommended phase II dose |
| R/R R/I | Refractory/relapsed Refractory/intolerant |
| SJCRH | St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital |
| STAMP | Specifically targeting ABL myristoyl pocket |
| TACL | Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia and Lymphoma |
| T-ALL | T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| VXLD | Vincristine, dexamethasone, asparaginase, and daunorubicin regimen |
| VPLD | Vincristine, dexamethasone, asparaginase, and doxorubicin regimen |
References
- Inaba, H.; Mullighan, C.G. Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2524–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Pui, C.-H. Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, R.; Mullighan, C.G.; Hunger, S.P. Advancing Diagnostics and Therapy to Reach Universal Cure in Childhood ALL. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5579–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teachey, D.T.; Pui, C.-H. Comparative Features and Outcomes between Paediatric T-Cell and B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e142–e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunger, S.P.; Raetz, E.A. How I Treat Relapsed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the Pediatric Population. Blood 2020, 136, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, C.; Parker, C.; Moorman, A.V.; Irving, J.A.; Kirschner-Schwabe, R.; Groeneveld-Krentz, S.; Révész, T.; Hoogerbrugge, P.; Hancock, J.; Sutton, R.; et al. Risk Factors and Outcomes in Children with High-Risk B-Cell Precursor and T-Cell Relapsed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Combined Analysis of ALLR3 and ALL-REZ BFM 2002 Clinical Trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 151, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.-H.; Yang, J.J.; Hunger, S.P.; Pieters, R.; Schrappe, M.; Biondi, A.; Vora, A.; Baruchel, A.; Silverman, L.B.; Schmiegelow, K.; et al. Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Progress Through Collaboration. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Schrappe, M.; Bernardo, M.E.; Rutella, S. How I Treat Relapsed Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 2807–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Hunger, S.P. The Genomic Landscape of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Precision Medicine Opportunities. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 84, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, E.; Baruchel, A.; Beishuizen, A.; Bourquin, J.-P.; Brown, P.A.; Cooper, T.; Gore, L.; Kolb, E.A.; Locatelli, F.; Maude, S.L.; et al. Targeted Inhibitors and Antibody Immunotherapies: Novel Therapies for Paediatric Leukaemia and Lymphoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 164, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Del Bufalo, F.; Quintarelli, C. Allogeneic Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Children with Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2024, 109, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, E.; Bautista, F.; Zwaan, C.M. Naked Antibodies and Antibody-Drug Conjugates: Targeted Therapy for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2024, 109, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.L.Z.; Vinanica, N.; Wong, D.M.H.; Campana, D. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2024, 109, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, K.U.; Gore, L. Bispecific T-Cell Engagers in Childhood B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2024, 109, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeer, J.L.; Rau, R.E.; Gupta, S.; Maude, S.L.; O’Brien, M.M. Cutting to the Front of the Line: Immunotherapy for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. In American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book; American Society of Clinical Oncology: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2020; pp. e132–e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Rau, R.E.; Kairalla, J.A.; Rabin, K.R.; Wang, C.; Angiolillo, A.L.; Alexander, S.; Carroll, A.J.; Conway, S.; Gore, L.; et al. Blinatumomab in Standard-Risk B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.H.; Loh, M.L. Ph-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hematology 2016, 2016, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Tasian, S.K. Has Ph-like ALL Superseded Ph+ ALL as the Least Favorable Subtype? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2021, 34, 101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobucci, I.; Kimura, S.; Mullighan, C.G. Biologic and Therapeutic Implications of Genomic Alterations in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.-H. Precision Medicine in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Chen, X.; Cai, J.; Yu, J.; Gao, J.; Hu, S.; Zhai, X.; Liang, C.; Ju, X.; Jiang, H.; et al. Effect of Dasatinib vs Imatinib in the Treatment of Pediatric Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspers, G.J.L.; Niewerth, D.; Wilhelm, B.A.J.; Scholte-van Houtem, P.; Lopez-Yurda, M.; Berkhof, J.; Cloos, J.; de Haas, V.; Mathôt, R.A.; Attarbaschi, A.; et al. An Effective Modestly Intensive Re-Induction Regimen with Bortezomib in Relapsed or Refractory Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 181, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, M.A.; Capdeville, R.; Krailo, M.; Qu, W.; Peng, B.; Rosamilia, M.; Therrien, M.; Zoellner, U.; Blaney, S.M.; Bernstein, M. Imatinib Mesylate (STI571) for Treatment of Children with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Leukemia: Results from a Children’s Oncology Group Phase 1 Study. Blood 2004, 104, 2655–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, K.R.; Bowman, W.P.; Aledo, A.; Slayton, W.B.; Sather, H.; Devidas, M.; Wang, C.; Davies, S.M.; Gaynon, P.S.; Trigg, M.; et al. Improved Early Event-Free Survival With Imatinib in Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5175–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, A.; Schrappe, M.; De Lorenzo, P.; Castor, A.; Lucchini, G.; Gandemer, V.; Pieters, R.; Stary, J.; Escherich, G.; Campbell, M.; et al. Imatinib after Induction for Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Philadelphia-Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (EsPhALL): A Randomised, Open-Label, Intergroup Study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, A.; Gandemer, V.; De Lorenzo, P.; Cario, G.; Campbell, M.; Castor, A.; Pieters, R.; Baruchel, A.; Vora, A.; Leoni, V.; et al. Imatinib Treatment of Paediatric Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (EsPhALL2010): A Prospective, Intergroup, Open-Label, Single-Arm Clinical Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2018, 5, e641–e652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeha, S.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Pei, D.; Sandlund, J.T.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Howard, S.C.; Inaba, H.; Bhojwani, D.; Metzger, M.L.; Cheng, C.; et al. Impact of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Minimal Residual Disease and Outcome in Childhood Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer 2014, 120, 1514–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplenc, R.; Blaney, S.M.; Strauss, L.C.; Balis, F.M.; Shusterman, S.; Ingle, A.M.; Agrawal, S.; Sun, J.; Wright, J.J.; Adamson, P.C. Pediatric Phase I Trial and Pharmacokinetic Study of Dasatinib: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group Phase I Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaan, C.M.; Rizzari, C.; Mechinaud, F.; Lancaster, D.L.; Lehrnbecher, T.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Beverloo, B.B.; den Boer, M.L.; Pieters, R.; Reinhardt, D.; et al. Dasatinib in Children and Adolescents with Relapsed or Refractory Leukemia: Results of the CA180-018 Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of the Innovative Therapies for Children with Cancer Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slayton, W.B.; Schultz, K.R.; Kairalla, J.A.; Devidas, M.; Mi, X.; Pulsipher, M.A.; Chang, B.H.; Mullighan, C.; Iacobucci, I.; Silverman, L.B.; et al. Dasatinib Plus Intensive Chemotherapy in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults With Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Results of Children’s Oncology Group Trial AALL0622. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2306–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, S.P.; Tran, T.H.; Saha, V.; Devidas, M.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Cazzaniga, G.; Reshmi, S.C.; Borowitz, M.J.; Moorman, A.V.; et al. Dasatinib with Intensive Chemotherapy in de Novo Paediatric Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (CA180-372/COG AALL1122): A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2023, 10, e510–e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzer, W.L.; Burke, M.J.; Devidas, M.; Chen, Z.; Borowitz, M.J.; Carroll, A.J.; Chen, I.-M.L.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Harvey, R.C.; Heerema, N.A.; et al. Feasibility and Outcome of Post-Induction Therapy Incorporating Dasatinib for Patients with Newly Diagnosed ABL-Class Fusion B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ABL-Class Fusion B-ALL): Children’s Oncology Group AALL1131. Blood 2023, 142, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijiya, N.; Zwaan, C.M.; Rizzari, C.; Foà, R.; Abbink, F.; Lancaster, D.; Landman-Parker, J.; Millot, F.; Moppett, J.; Nelken, B.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of Nilotinib in Pediatric Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Chronic Myeloid Leukemia or Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matloub, Y.; Gore, L.; Loh, M.L.; Pui, C.-H.; Hanley, M.J.; Lu, V.; Leonard, E.J.; Granier, M.; Biondi, A.; Silverman, L.B. A Phase 1/2 Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Ponatinib with Chemotherapy in Pediatric Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive (Ph+) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Blood 2020, 136, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Safety and Efficacy of Olverembatinib (HQP1351) Combined with Lisaftoclax (APG-2575) in Children and Adolescents with Relapsed/Refractory Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (R/R Ph+ ALL): First Report from a Phase 1 Study. In Proceedings of the ASH Meeting 2024, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–10 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, M.L.; Tasian, S.K.; Rabin, K.R.; Brown, P.; Magoon, D.; Reid, J.M.; Chen, X.; Ahern, C.H.; Weigel, B.J.; Blaney, S.M. A Phase 1 Dosing Study of Ruxolitinib in Children with Relapsed or Refractory Solid Tumors, Leukemias, or Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Children’s Oncology Group Phase 1 Consortium Study (ADVL1011). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasian, S.K.; Assad, A.; Hunter, D.S.; Du, Y.; Loh, M.L. A Phase 2 Study of Ruxolitinib with Chemotherapy in Children with Philadelphia Chromosome-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (INCB18424-269/AALL1521): Dose-Finding Results from the Part 1 Safety Phase. Blood 2018, 132, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, T.M.; Pati, D.; Plon, S.E.; Thompson, P.A.; Bomgaars, L.R.; Adamson, P.C.; Ingle, A.M.; Wright, J.; Brockman, A.H.; Paton, M.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of the Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib in Pediatric Patients with Refractory Leukemia: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messinger, Y.; Gaynon, P.; Raetz, E.; Hutchinson, R.; DuBois, S.; Glade-Bender, J.; Sposto, R.; van der Giessen, J.; Eckroth, E.; Bostrom, B.C. Phase I Study of Bortezomib Combined with Chemotherapy in Children with Relapsed Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): A Report from the Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia (TACL) Consortium. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messinger, Y.H.; Gaynon, P.S.; Sposto, R.; van der Giessen, J.; Eckroth, E.; Malvar, J.; Bostrom, B.C. Bortezomib with Chemotherapy Is Highly Active in Advanced B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia & Lymphoma (TACL) Study. Blood 2012, 120, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, T.M.; Whitlock, J.A.; Lu, X.; O’Brien, M.M.; Borowitz, M.J.; Devidas, M.; Raetz, E.A.; Brown, P.A.; Carroll, W.L.; Hunger, S.P. Bortezomib Reinduction Chemotherapy in High-Risk ALL in First Relapse: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teachey, D.T.; Devidas, M.; Wood, B.L.; Chen, Z.; Hayashi, R.J.; Hermiston, M.L.; Annett, R.D.; Archer, J.H.; Asselin, B.L.; August, K.J.; et al. Children’s Oncology Group Trial AALL1231: A Phase III Clinical Trial Testing Bortezomib in Newly Diagnosed T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2106–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, T.A.; Huang, M.; Jeha, S.; Deyell, R.J.; Lewis, V.A.; Chang, B.H.; Lowe, E.J.; Frediani, J.; Vezina, C.; Michon, B.; et al. Outcome of Infants Treated on Total Therapy for Infants with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia I: Results from a Non-Randomized Multi-Center Study. Blood 2023, 142, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.J.; Ziegler, D.S.; Bautista, F.; Attarbaschi, A.; Gore, L.; Locatelli, F.; O’Brien, M.M.; Pauly, M.; Kormany, W.N.; Tian, S.; et al. Phase 1b Study of Carfilzomib with Induction Chemotherapy in Pediatric Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, E.S.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Malvar, J.; Rushing, T.; Doan, A.; Pacenta, H.L.; Schore, R.J.; Sposto, R.; Leong, R.; Gaynon, P.S.; et al. Results from the Phase 1 Portion of a Trial of Oral Ixazomib Combined with Chemotherapy in Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia or Lymphoma in Children, Adolescents and Young Adults: A Report from the Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia and Lymphoma (TACL) Consortium. Blood 2023, 142, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, A.E.; Karol, S.E.; Forlenza, C.J.; Cooper, T.M.; Fraser, C.; Cario, G.; O’Brien, M.M.; Gerber, N.U.; Bourquin, J.-P.; Reinhardt, D.; et al. Venetoclax Combined With Chemotherapy in Pediatric and Adolescent/Young Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2025, 72, e31630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullarkat, V.A.; Lacayo, N.J.; Jabbour, E.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Bajel, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Leonard, J.; Colace, S.I.; Khaw, S.L.; Fleming, S.A.; et al. Venetoclax and Navitoclax in Combination with Chemotherapy in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Lymphoblastic Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vormoor, B.J.; Menne, T.; Savage, J.; Patel, A.; Castleton, A.; Fielding, A.K.; Lancaster, D.; Latif, A.L.; Morley, N.; Shenton, G.; et al. The MEK Inhibitor Selumetinib in Combination with Dexamethasone Leads to Responses in Adult and Pediatric Patients with Relapsed RAS-Pathway Mutated Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Results of a Phase 1/2 Study. Blood 2023, 142, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raetz, E.A.; Teachey, D.T.; Minard, C.; Liu, X.; Norris, R.E.; Denic, K.Z.; Reid, J.; Evensen, N.A.; Gore, L.; Fox, E.; et al. Palbociclib in Combination with Chemotherapy in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Lymphoma: A Children’s Oncology Group Study (AINV18P1). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, F.; Paoletti, X.; Rubino, J.; Brard, C.; Rezai, K.; Nebchi, S.; Andre, N.; Aerts, I.; De Carli, E.; van Eijkelenburg, N.; et al. Phase I or II Study of Ribociclib in Combination With Topotecan-Temozolomide or Everolimus in Children With Advanced Malignancies: Arms A and B of the AcSé-ESMART Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3546–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoerger, B.; Bautista, F.; André, N.; Berlanga, P.; Gatz, S.A.; Marshall, L.V.; Rubino, J.; Archambaud, B.; Marchais, A.; Rubio-San-Simón, A.; et al. Precision Cancer Medicine Platform Trials: Concepts and Design of AcSé-ESMART. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 208, 114201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheingold, S.R.; Sacks, N.; Chang, Y.J.; Brown, V.I.; Teachey, D.T.; Lange, B.J.; Grupp, S.A. A Phase I Trial of Sirolimus (Rapamycin) in Pediatric Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Leukemia. Blood 2007, 110, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlis, K.D.; Stubbs, M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Neuberg, D.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Sallan, S.E.; Armstrong, S.A.; Silverman, L.B. A Pilot Trial of Rapamycin with Glucocorticoids In Children and Adults with Relapsed ALL. Blood 2010, 116, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, A.E.; Pikman, Y.; Stevenson, K.E.; Harris, M.H.; Pauly, M.; Sulis, M.-L.; Hijiya, N.; Gore, L.; Cooper, T.M.; Loh, M.L.; et al. Phase I Trial of the mTOR Inhibitor Everolimus in Combination with Multi-Agent Chemotherapy in Relapsed Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheingold, S.R.; Tasian, S.J.; Whitlock, J.A.; Teachey, D.T.; Borowitz, M.J.; Liu, X.; Minard, C.G.; Fox, E.; Weigel, B.J.; Blaney, S.M. A Phase 1 Trial of Temsirolimus and Intensive Re-Induction Chemotherapy for 2nd or Greater Relapse of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Children’s Oncology Group Study (ADVL1114). Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasian, S.K.; Silverman, L.B.; Whitlock, J.A.; Sposto, R.; Loftus, J.P.; Schafer, E.S.; Schultz, K.R.; Hutchinson, R.J.; Gaynon, P.S.; Orgel, E.; et al. Temsirolimus Combined with Cyclophosphamide and Etoposide for Pediatric Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia Consortium Trial (TACL 2014-001). Haematologica 2022, 107, 2295–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi, M.; Park, J.R.; Stewart, C.F.; Gilbertson, R.J.; Schaiquevich, P.; Sun, J.; Reid, J.M.; Ames, M.M.; Speights, R.; Ingle, A.M.; et al. Pediatric Phase I Trial and Pharmacokinetic Study of Vorinostat: A Children’s Oncology Group Phase I Consortium Report. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3623–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.J.; Lamba, J.K.; Pounds, S.; Cao, X.; Ghodke-Puranaik, Y.; Lindgren, B.R.; Weigel, B.J.; Verneris, M.R.; Miller, J.S. A Therapeutic Trial of Decitabine and Vorinostat in Combination with Chemotherapy for Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.J.; Kostadinov, R.; Sposto, R.; Gore, L.; Kelley, S.; Rabik, C.; Trepel, J.; Lee, M.-J.; Yuno, A.; Lee, S.; et al. Decitabine and Vorinostat with Chemotherapy in Relapsed Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A TACL Pilot Study. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Triche, T.; Malvar, J.; Gaynon, P.; Sposto, R.; Yang, X.; Bittencourt, H.; Place, A.E.; Messinger, Y.; Fraser, C.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of Azacitidine Combined with Chemotherapy in Childhood Leukemia: A Report from the TACL Consortium. Blood 2018, 131, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, E.M.; Kairalla, J.A.; Devidas, M.; Hibbitts, E.; Carroll, A.J.; Heerema, N.A.; Kubaney, H.R.; August, M.A.; Ramesh, S.; Yoo, B.; et al. Azacitidine as Epigenetic Priming for Chemotherapy Is Safe and Well-Tolerated in Infants with Newly Diagnosed KMT2A-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Children’s Oncology Group Trial AALL15P1. Haematologica 2024, 109, 3918–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, C.B.; Thomas, D.A.; Yang, H.; Ravandi, F.; Rytting, M.; O’Brien, S.; Franklin, A.R.; Borthakur, G.; Dara, S.; Kwari, M.; et al. Safety and Clinical Activity of 5-Aza-2’-Deoxycytidine (Decitabine) with or without Hyper-CVAD in Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphocytic Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 167, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaan, C.M.; Söderhäll, S.; Brethon, B.; Luciani, M.; Rizzari, C.; Stam, R.W.; Besse, E.; Dutreix, C.; Fagioli, F.; Ho, P.A.; et al. A Phase 1/2, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Study of Midostaurin in Children with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.A.; Kairalla, J.A.; Hilden, J.M.; Dreyer, Z.E.; Carroll, A.J.; Heerema, N.A.; Wang, C.; Devidas, M.; Gore, L.; Salzer, W.L.; et al. FLT3 Inhibitor Lestaurtinib plus Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed KMT2A-Rearranged Infant Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Children’s Oncology Group Trial AALL0631. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, G.C.; Aldoss, I.; DiPersio, J.; Cuglievan, B.; Stone, R.; Arellano, M.; Thirman, M.J.; Patel, M.R.; Dickens, D.S.; Shenoy, S.; et al. The Menin Inhibitor Revumenib in KMT2A-Rearranged or NPM1-Mutant Leukaemia. Nature 2023, 615, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, G.C.; Aldoss, I.; Thirman, M.J.; DiPersio, J.; Arellano, M.; Blachly, J.S.; Mannis, G.N.; Perl, A.; Dickens, D.S.; McMahon, C.M.; et al. Menin Inhibition With Revumenib for KMT2A-Rearranged Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia (AUGMENT-101). J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, N.; Guest, E.; Tasian, K.; Breese, E.; Schafer, J.; DiPersio, G.; Issa, G.C.; Silverman, B.; Stieglitz, B.; Pollard, J. Safety and Activity of Revumenib in Combination with Fludarabine/Cytarabine (FLA) in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Leukemias [Abstract No. P450 plus Presentation]. In Proceedings of the 29th Congress of the European Haematology Association, Madrid, Spain, 13–16 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Salzer, E.; Stutterheim, J.; Cuglievan, B.; Tomkinson, B.E.; Leoni, M.; Van Tinteren, H.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Willemse, M.; Nichols, G.L.; Bautista, F.; et al. APAL2020K/ITCC-101: A Phase I Trial of the Menin Inhibitor Ziftomenib in Combination with Chemotherapy in Children with Relapsed/Refractory KMT2A-Rearranged, NUP98-Rearranged, or NPM1-Mutant Acute Leukemias. Blood 2024, 144, 4265.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brixey, A.G.; Light, R.W. Pleural Effusions Due to Dasatinib. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2010, 16, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Umbarkar, P.; Tousif, S.; Lal, H. Cardiotoxicity of the BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Emphasis on Ponatinib. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 316, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samis, J.; Lee, P.; Zimmerman, D.; Arceci, R.J.; Suttorp, M.; Hijiya, N. Recognizing Endocrinopathies Associated With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy in Children With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leo, S.; Trevisan, M.; Moneta, C.; Colombo, C. Endocrine-Related Adverse Conditions Induced by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Ann. Endocrinol. 2023, 84, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajayi, S.; Becker, H.; Reinhardt, H.; Engelhardt, M.; Zeiser, R.; von Bubnoff, N.; Wäsch, R. Ruxolitinib. In Small Molecules in Hematology; Recent Results in Cancer Research; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 212, pp. 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, R.; Alberti, P.; Bruna, J.; Psimaras, D.; Argyriou, A.A. Bortezomib and Other Proteosome Inhibitors-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity: From Pathogenesis to Treatment. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2019, 24 (Suppl. 2), S52–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiopoulos, G.; Makris, N.; Laina, A.; Theodorakakou, F.; Briasoulis, A.; Trougakos, I.P.; Dimopoulos, M.-A.; Kastritis, E.; Stamatelopoulos, K. Cardiovascular Toxicity of Proteasome Inhibitors: Underlying Mechanisms and Management Strategies. JACC CardioOncol. 2023, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, H.; Hao, L.; Wang, Q. Ocular Toxicities of MEK Inhibitors in Patients With Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncol. Williston Park N 2023, 37, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivendran, S.; Agarwal, N.; Gartrell, B.; Ying, J.; Boucher, K.M.; Choueiri, T.K.; Sonpavde, G.; Oh, W.K.; Galsky, M.D. Metabolic Complications with the Use of mTOR Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-T.; Chao, C.-M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Hsiao, S.-Y.; Weng, T.-S. Efficacy and Safety of Second-generation FLT3 Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dali, S.A.; Al-Mashdali, A.F.; Kalfah, A.; Mohamed, S.F. Menin Inhibitors in KMT2A-Rearranged and NPM1-Mutated Acute Leukemia: A Scoping Review of Safety and Efficacy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2025, 213, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foà, R.; Chiaretti, S. Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2399–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Leoni, V.; Peccatori, N.; Silverman, L.B.; Biondi, A. Clinical Management of Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive and ABL-Class Fusion-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. In Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children and Adolescents; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 175–187. ISBN 978-3-031-71180-0. [Google Scholar]
- Tasian, S.K.; Loh, M.L.; Hunger, S.P. Philadelphia Chromosome-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2017, 130, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, K.R.; Carroll, A.; Heerema, N.A.; Bowman, W.P.; Aledo, A.; Slayton, W.B.; Sather, H.; Devidas, M.; Zheng, H.W.; Davies, S.M.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of Imatinib in Pediatric Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Children’s Oncology Group Study AALL0031. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cario, G.; Leoni, V.; Conter, V.; Attarbaschi, A.; Zaliova, M.; Sramkova, L.; Cazzaniga, G.; Fazio, G.; Sutton, R.; Elitzur, S.; et al. Relapses and Treatment-Related Events Contributed Equally to Poor Prognosis in Children with ABL-Class Fusion Positive B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated According to AIEOP-BFM Protocols. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V.; Schwab, C.; Winterman, E.; Hancock, J.; Castleton, A.; Cummins, M.; Gibson, B.; Goulden, N.; Kearns, P.; James, B.; et al. Adjuvant Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy Improves Outcome for Children and Adolescents with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Who Have an ABL-Class Fusion. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasi, I.; Ba, I.; Sirvent, N.; Braun, T.; Cuccuini, W.; Ballerini, P.; Duployez, N.; Tanguy-Schmidt, A.; Tamburini, J.; Maury, S.; et al. Efficacy of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Ph-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Harboring ABL-Class Rearrangements. Blood 2019, 134, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerchione, C.; Locatelli, F.; Martinelli, G. Dasatinib in the Management of Pediatric Patients With Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 632231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, M. Dasatinib: A Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Philadelphia Chromosome—Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 2289–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Boissel, N.; Chevallier, P.; Ottmann, O.; Gökbuget, N.; Topp, M.S.; Fielding, A.K.; Rambaldi, A.; Ritchie, E.K.; Papayannidis, C.; et al. Complete Hematologic and Molecular Response in Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Following Treatment With Blinatumomab: Results From a Phase II, Single-Arm, Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Boissel, N.; Chevallier, P.; Ottmann, O.; Gökbuget, N.; Rambaldi, A.; Ritchie, E.K.; Papayannidis, C.; Tuglus, C.A.; Morris, J.D.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of Blinatumomab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Final Analysis of ALCANTARA Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 146, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, W.; Martinelli, G.; Stelljes, M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Gökbuget, N.; Advani, A.S.; O’Brien, S.; Liedtke, M.; Merchant, A.A.; Cassaday, R.D.; et al. Efficacy of Inotuzumab Ozogamicin in Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer 2021, 127, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, E.; Short, N.J.; Jain, N.; Huang, X.; Montalban-Bravo, G.; Banerjee, P.; Rezvani, K.; Jiang, X.; Kim, K.H.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; et al. Ponatinib and Blinatumomab for Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A US, Single-Centre, Single-Arm, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2023, 10, e24–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foà, R.; Bassan, R.; Vitale, A.; Elia, L.; Piciocchi, A.; Puzzolo, M.-C.; Canichella, M.; Viero, P.; Ferrara, F.; Lunghi, M.; et al. Dasatinib–Blinatumomab for Ph-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foà, R.; Bassan, R.; Elia, L.; Piciocchi, A.; Soddu, S.; Messina, M.; Ferrara, F.; Lunghi, M.; Mulè, A.; Bonifacio, M.; et al. Long-Term Results of the Dasatinib-Blinatumomab Protocol for Adult Philadelphia-Positive ALL. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaretti, S.; Leoncin, M.; Elia, L.; Soddu, S.; Piciocchi, A.; Matarazzo, M.; Di Trani, M.; Martelli, M.; Borlenghi, E.; Parisi, M.; et al. Efficacy and Toxicity of Frontline Ponatinib Plus Blinatumomab for Adult Ph+ ALL Patients of All Ages. Intermediate Analysis of the Gimema ALL2820. Blood 2024, 144, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshmi, S.C.; Harvey, R.C.; Roberts, K.G.; Stonerock, E.; Smith, A.; Jenkins, H.; Chen, I.-M.; Valentine, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Targetable Kinase Gene Fusions in High-Risk B-ALL: A Study from the Children’s Oncology Group. Blood 2017, 129, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Azzato, E.M.; Mullighan, C.G. Integration of Next-Generation Sequencing to Treat Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Targetable Lesions: The St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital Approach. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasian, S.K.; Boer, J.M.; den Boer, M.L. From the Bench of Molecular Understanding to the Bedside of Optimal Therapy for BCR::ABL1 and ABL-Class Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children and Adolescents. EJC Paediatr. Oncol. 2025, 6, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frismantas, V.; Dobay, M.P.; Rinaldi, A.; Tchinda, J.; Dunn, S.H.; Kunz, J.; Richter-Pechanska, P.; Marovca, B.; Pail, O.; Jenni, S.; et al. Ex Vivo Drug Response Profiling Detects Recurrent Sensitivity Patterns in Drug-Resistant Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, e26–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocock, R.; Farah, N.; Richardson, S.E.; Mansour, M.R. Current and Emerging Therapeutic Approaches for T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissat, A.; Bautista, F.; Ilan, U.; den Boer, M.; Boer, J.M.; Eckert, C.; Elsinghorst, A.; van Liempt, E.; Bourquin, J.P.; Burkhardt, B.; et al. P428: Hem-ISMART: An International Proof of Concept Therapeutic Stratification Trial of Molecular anomalies in Relapsed or Refractory Hematological Malignancies in Children. In Proceedings of the EHA 2024 Meeting, Madrid, Spain, 13–16 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hijiya, N.; Kapoor, S.; Hoch, M.; Descamps, L.; Dasgupta, K.; Cardoso, A.P.T. PB1980: ASC4KIDS: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase 1B/2 Study to Determine the Dose and Safety of Asciminib in Pediatric Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase. HemaSphere 2023, 7, e1669755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Inukai, T.; Imamura, T.; Yano, M.; Tomoyasu, C.; Lucas, D.M.; Nemoto, A.; Sato, H.; Huang, M.; Abe, M.; et al. Anti-Leukemic Activity of Bortezomib and Carfilzomib on B-Cell Precursor ALL Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.S.; Huynh, V.; Burke, M.J.; Gore, L.; Locatelli, F.; O’Brien, M.M.; Kim, C.; Obreja, M.; Morris, C.L.; Baruchel, A. Phase 2 Study of Carfilzomib in Combination with Induction Chemotherapy in Children with Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Blood 2021, 138, 4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeten, M.S.F.; van Meerloo, J.; Kwidama, Z.J.; ter Huizen, G.; Segerink, W.H.; Zweegman, S.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Jansen, G.; Cloos, J. Pre-Clinical Evaluation of the Proteasome Inhibitor Ixazomib against Bortezomib-Resistant Leukemia Cells and Primary Acute Leukemia Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumann, S.; Shaulov, A.; Haran, A.; Gross Even-Zohar, N.; Vainstein, V.; Nachmias, B. The Emerging Role of Venetoclax-Based Treatments in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaizo Moore, V.; Schlis, K.D.; Sallan, S.E.; Armstrong, S.A.; Letai, A. BCL-2 Dependence and ABT-737 Sensitivity in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, S.E.; Kothari, A.; Loeff, F.C.; Eichhorn, J.M.; Sakurikar, N.; Goselink, H.M.; Saylors, R.L.; Jedema, I.; Falkenburg, J.H.F.; Chambers, T.C. BH3 Inhibitor Sensitivity and Bcl-2 Dependence in Primary Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaw, S.L.; Suryani, S.; Evans, K.; Richmond, J.; Robbins, A.; Kurmasheva, R.T.; Billups, C.A.; Erickson, S.W.; Guo, Y.; Houghton, P.J.; et al. Venetoclax Responses of Pediatric ALL Xenografts Reveal Sensitivity of MLL-Rearranged Leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Place, A.E.; Goldsmith, K.; Bourquin, J.-P.; Loh, M.L.; Gore, L.; Morgenstern, D.A.; Sanzgiri, Y.; Hoffman, D.; Zhou, Y.; Ross, J.A.; et al. Accelerating Drug Development in Pediatric Cancer: A Novel Phase I Study Design of Venetoclax in Relapsed/Refractory Malignancies. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 2115–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meulen, J.; Van Roy, N.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; Speleman, F. The Epigenetic Landscape of T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 53, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, J.; Matheson, E.; Minto, L.; Blair, H.; Case, M.; Halsey, C.; Swidenbank, I.; Ponthan, F.; Kirschner-Schwabe, R.; Groeneveld-Krentz, S.; et al. Ras Pathway Mutations Are Prevalent in Relapsed Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Confer Sensitivity to MEK Inhibition. Blood 2014, 124, 3420–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, E.C.; Thomas, H.; Case, M.; Blair, H.; Jackson, R.K.; Masic, D.; Veal, G.; Halsey, C.; Newell, D.R.; Vormoor, J.; et al. Glucocorticoids and Selumetinib Are Highly Synergistic in RAS Pathway-Mutated Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia through Upregulation of BIM. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menne, T.; Slade, D.; Savage, J.; Johnson, S.; Irving, J.; Kearns, P.; Plummer, R.; Shenton, G.; Veal, G.J.; Vormoor, B.; et al. Selumetinib in Combination with Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory RAS-Pathway Mutated Paediatric and Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (SeluDex): Study Protocol for an International, Parallel-Group, Dose-Finding with Expansion Phase I/II Trial. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Grob, J.J.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Karaszewska, B.; Hauschild, A.; Levchenko, E.; Chiarion Sileni, V.; Schachter, J.; Garbe, C.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes with Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffet, E.; Hansford, J.R.; Garrè, M.L.; Hara, J.; Plant-Fox, A.; Aerts, I.; Locatelli, F.; van der Lugt, J.; Papusha, L.; Sahm, F.; et al. Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Pediatric Glioma with BRAF V600 Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1108–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zwet, J.C.G.; Buijs-Gladdines, J.G.C.A.M.; Cordo’, V.; Debets, D.O.; Smits, W.K.; Chen, Z.; Dylus, J.; Zaman, G.J.R.; Altelaar, M.; Oshima, K.; et al. MAPK-ERK Is a Central Pathway in T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia That Drives Steroid Resistance. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3394–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bride, K.L.; Hu, H.; Tikhonova, A.; Fuller, T.J.; Vincent, T.L.; Shraim, R.; Li, M.M.; Carroll, W.L.; Raetz, E.A.; Aifantis, I.; et al. Rational Drug Combinations with CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2022, 107, 1746–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoerger, B.; Bourdeaut, F.; DuBois, S.G.; Fischer, M.; Geller, J.I.; Gottardo, N.G.; Marabelle, A.; Pearson, A.D.J.; Modak, S.; Cash, T.; et al. A Phase I Study of the CDK4/6 Inhibitor Ribociclib (LEE011) in Pediatric Patients with Malignant Rhabdoid Tumors, Neuroblastoma, and Other Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, D.; Brown, V.I.; Grupp, S.A.; Teachey, D.T. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Axis in Children with Hematologic Malignancies. Paediatr. Drugs 2012, 14, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tasian, S.K.; Teachey, D.T.; Rheingold, S.R. Targeting the PI3K/mTOR Pathway in Pediatric Hematologic Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatla, T.; Wang, J.; Morrison, D.J.; Raetz, E.A.; Burke, M.J.; Brown, P.; Carroll, W.L. Epigenetic Reprogramming Reverses the Relapse-Specific Gene Expression Signature and Restores Chemosensitivity in Childhood B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 5201–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpel, D.J.P.M.; Schotte, D.; Lange-Turenhout, E.a.M.; Schneider, P.; Seslija, L.; de Menezes, R.X.; Marquez, V.E.; Pieters, R.; den Boer, M.L.; Stam, R.W. Hypermethylation of Specific microRNA Genes in MLL-Rearranged Infant Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Major Matters at a Micro Scale. Leukemia 2011, 25, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.J.; Bhatla, T. Epigenetic Modifications in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Pieters, R.; Biondi, A. How I Treat Infant Leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, R.S.; Pieters, R.; Stutterheim, J. KMT2A-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. EJC Paediatr. Oncol. 2024, 4, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, N.; Wetmore, C.; O’Brien, M.M.; Silverman, L.B.; Brown, P.; Cooper, T.M.; Thomson, B.; Blakemore, S.J.; Daigle, S.; Suttle, B.; et al. Final Report of Phase 1 Study of the DOT1L Inhibitor, Pinometostat (EPZ-5676), in Children with Relapsed or Refractory MLL-r Acute Leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sluis, I.M.; de Lorenzo, P.; Kotecha, R.S.; Attarbaschi, A.; Escherich, G.; Nysom, K.; Stary, J.; Ferster, A.; Brethon, B.; Locatelli, F.; et al. Blinatumomab Added to Chemotherapy in Infant Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negotei, C.; Colita, A.; Mitu, I.; Lupu, A.R.; Lapadat, M.-E.; Popovici, C.E.; Crainicu, M.; Stanca, O.; Berbec, N.M. A Review of FLT3 Kinase Inhibitors in AML. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Levis, M.; Shurtleff, S.; Campana, D.; Downing, J.; Small, D. FLT3 Inhibition Selectively Kills Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells with High Levels of FLT3 Expression. Blood 2005, 105, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.Y.; Stein, E.M. Revumenib for Patients with Acute Leukemia: A New Tool for Differentiation Therapy. Haematologica 2024, 109, 3488–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuglievan, B.; Kantarjian, H.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Cooper, T.M.; Zwaan, C.M.; Pollard, J.A.; DiNardo, C.D.; Kadia, T.M.; Guest, E.; Short, N.J.; et al. Menin Inhibitors in Pediatric Acute Leukemia: A Comprehensive Review and Recommendations to Accelerate Progress in Collaboration with Adult Leukemia and the International Community. Leukemia 2024, 38, 2073–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldoss, I.; Issa, G.C.; Thirman, M.J.; DiPersio, J.; Arellano, M.; Blachly, J.S.; Mannis, G.; Perl, A.; Dickens, D.; McMahon, C.M.; et al. Revumenib Monotherapy in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory KMT2Ar Acute Leukemias: Efficacy and Safety Results from the Augment-101 Phase 1/2 Study. Blood 2023, 142, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldoss, I.; Issa, G.C.; Thirman, M.; DiPersio, J.; Arellano, M.; Blachly, J.S.; Mannis, G.N.; Perl, A.; Dickens, D.S.; McMahon, C.M.; et al. Revumenib Monotherapy in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory KMT2Ar Acute Leukemia: Topline Efficacy and Safety Results from the Pivotal Augment-101 Phase 2 Study. Blood 2023, 142, LBA-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaan, C.M.; Shukla, N.; Karras, N.; Chang, B.; Magee, J.; Loeb, D.; DuVall, A.; Whitlock, J.; Schaible, B.; Jha, S.; et al. 2024 ASPHO Conference Papers and Posters. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2024, 71, e30977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldoss, I.; Assouline, S.; DiPersio, J.; Fleming, S.; Grove, C.; Schuh, A.; Taussig, D.; Heidinger, K.; Zhang, J.; Thomas, S.; et al. A Phase 1 Study Of Revumenib + Intensive Chemotherapy in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia Harboring Genetic Alterations In Kmt2a, Npm1, Or Nup98 (Sndx-5613-0708). In Proceedings of the EHA 2025 Meeting, Milan, Italy, 12–15 June 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Erba, H.; Wang, E.; Issa, G.; Altman, J.; Montesinos, P.; DeBotton, S.; Walter, R.; Pettit, K.; Strickland, S.; Patnaik, M.; et al. AML-475 Activity, Tolerability, and Resistance Profile of the Menin Inhibitor Ziftomenib in Adults With Relapsed/Refractory NPM1-Mutated AML. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2023, 23, S304–S305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erba, H.P.; Fathi, A.T.; Issa, G.C.; Altman, J.K.; Montesinos, P.; Patnaik, M.M.; Foran, J.M.; De Botton, S.; Baer, M.R.; Schiller, G.J.; et al. Update on a Phase 1/2 First-in-Human Study of the Menin-KMT2A (MLL) Inhibitor Ziftomenib (KO-539) in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2022, 140, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.S.; Issa, G.C.; Erba, H.P.; Altman, J.K.; Montesinos, P.; DeBotton, S.; Walter, R.B.; Pettit, K.; Savona, M.R.; Shah, M.V.; et al. Ziftomenib in Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (KOMET-001): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Multi-Cohort, Phase 1 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foà, R. Ph-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia—25 Years of Progress. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff, H.; Karsli, U.; Schoenherr, C.; Battmer, K.; Erschow, S.; Talbot, S.R.; Steinemann, D.; Heuser, M.; Heidenreich, O.; Hilfiker-Kleiner, D.; et al. Venetoclax and Dexamethasone Synergize with Inotuzumab Ozogamicin-Induced DNA Damage Signaling in B-Lineage ALL. Blood 2021, 137, 2657–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luskin, M. A Phase I Study of Venetoclax in Combination with Inotuzumab Ozogamicin for Relapsed or Refractory ALL in Adults. In Proceedings of the ASH Meeting 2023, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vassal, G.; Rousseau, R.; Blanc, P.; Moreno, L.; Bode, G.; Schwoch, S.; Schrappe, M.; Skolnik, J.; Bergman, L.; Bradley-Garelik, M.B.; et al. Creating a Unique, Multi-Stakeholder Paediatric Oncology Platform to Improve Drug Development for Children and Adolescents with Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).