Targeting NFAT2 for Reversing the P-gp-Mediated Multidrug Resistance to Paclitaxel by Manidipine
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Cell-Cycle Status and Apoptosis Analysis
2.4. Drug Combination Assay
2.5. P-gp ATPase Activity Assay
2.6. Intracellular Uptake and Accumulation Assay
2.7. Animals and Xenograft Model
2.8. Calcium Content Assay Using Fluo-4 AM
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. NFAT2 Knockdown
2.11. Molecular Docking Protocol for Manidipine—NFAT2 Interaction Analysis
2.12. Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS) Experiment
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Manidipine Enhances the Efficacy of PTX and DOX in A549/T and HCT-8/T Cells
3.2. Manidipine Combination with PTX to Induce Apoptosis in Drug-Resistant Cells
3.3. Manidipine Exerts Synergistic Effect with PTX in MDR Cells
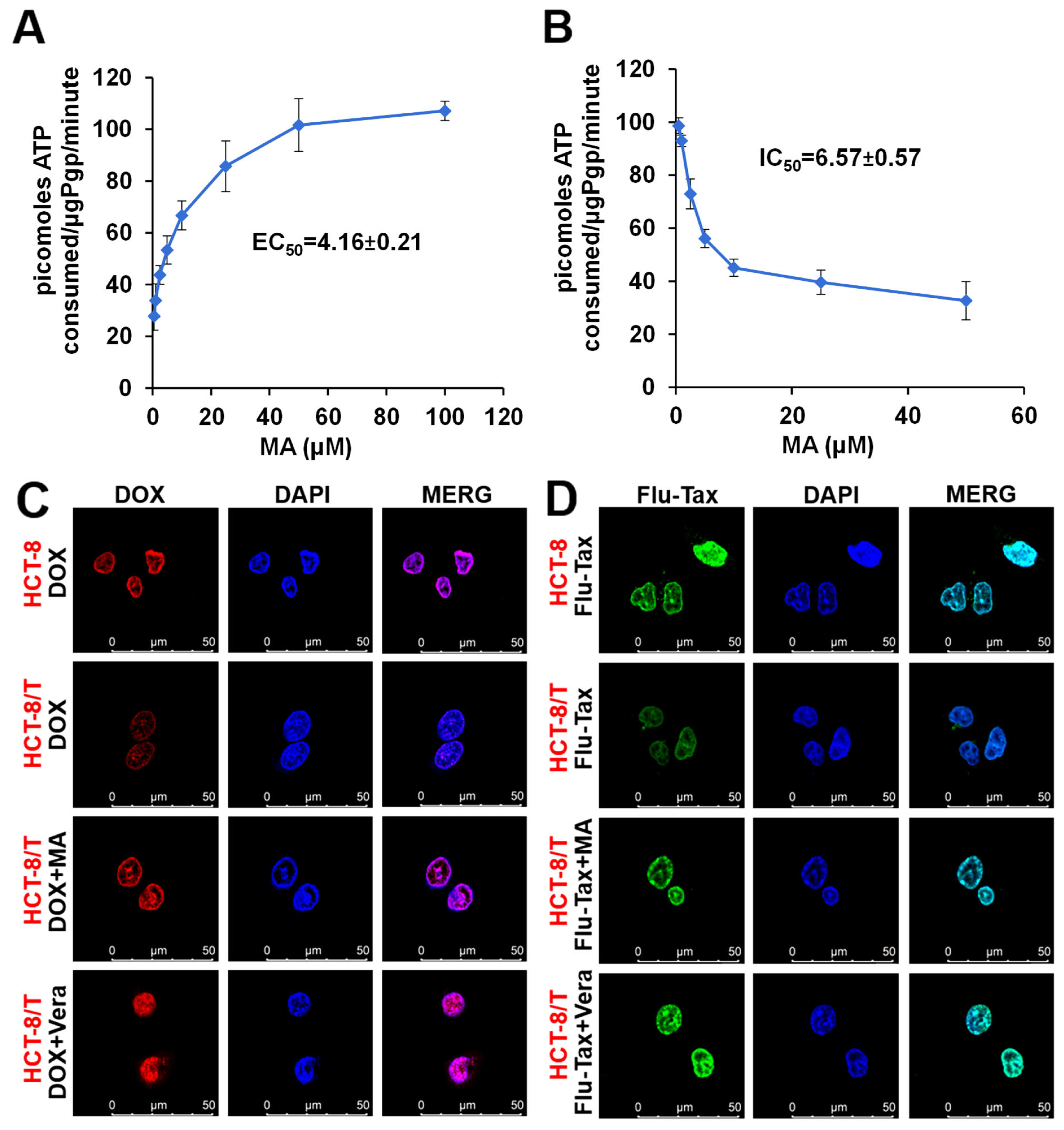
3.4. Manidipine Activates the P-gp ATPase Activity
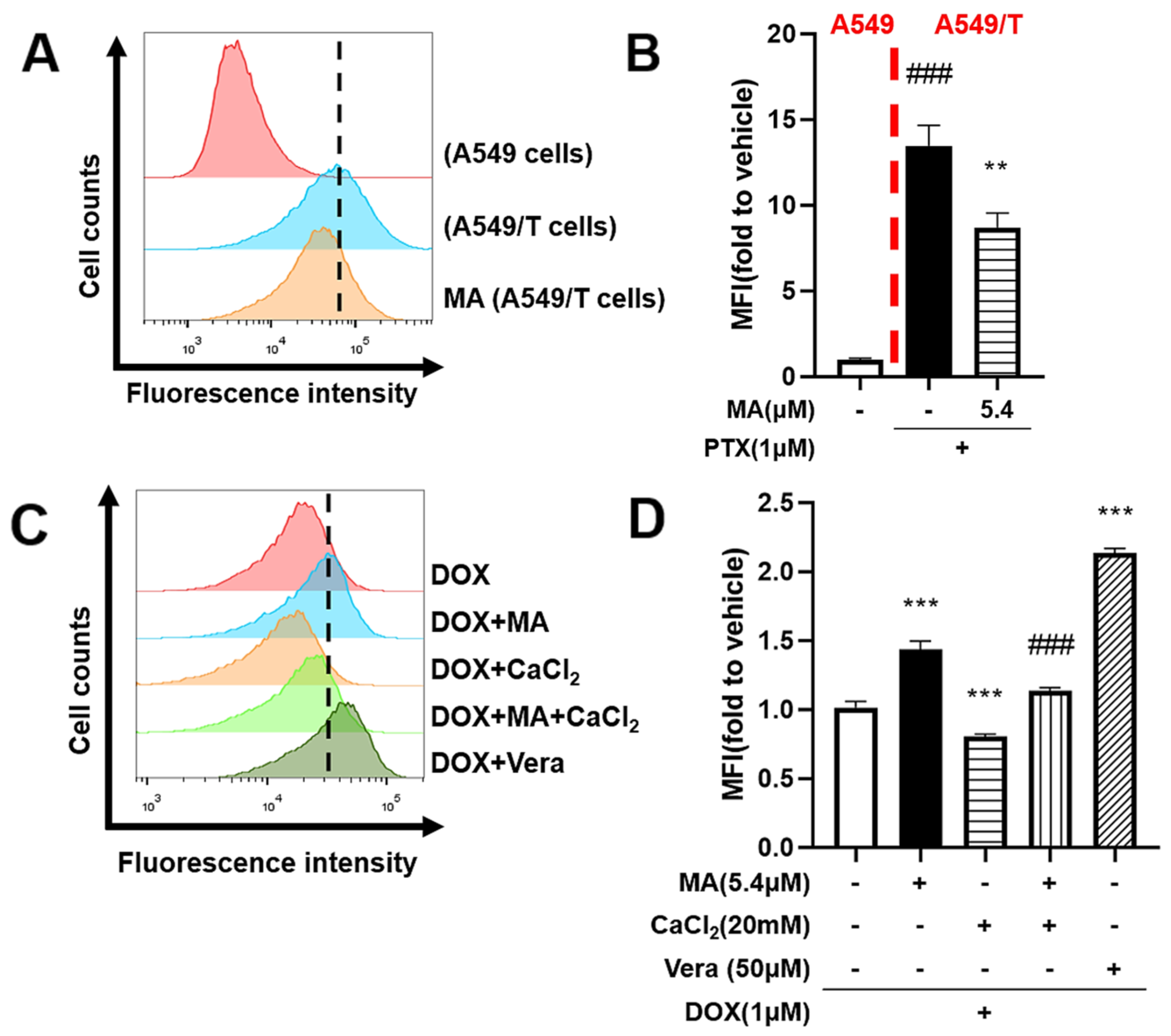
3.5. Manidipine Increases the Intracellular Accumulation of DOX and Flu-Tax
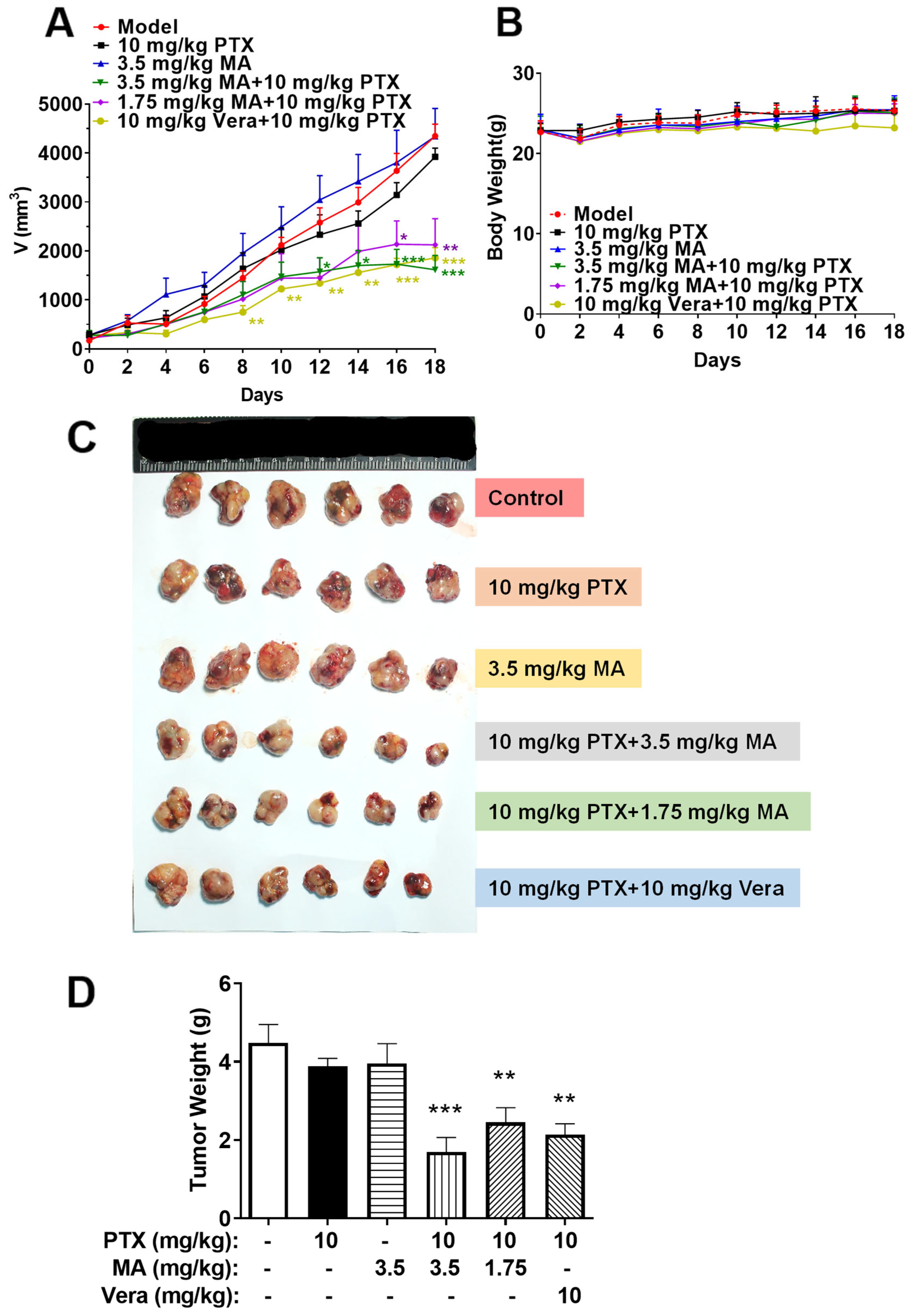
3.6. Manidipine in Combination with PTX Inhibits the Growth of A549/T Xenograft in Nude Mice
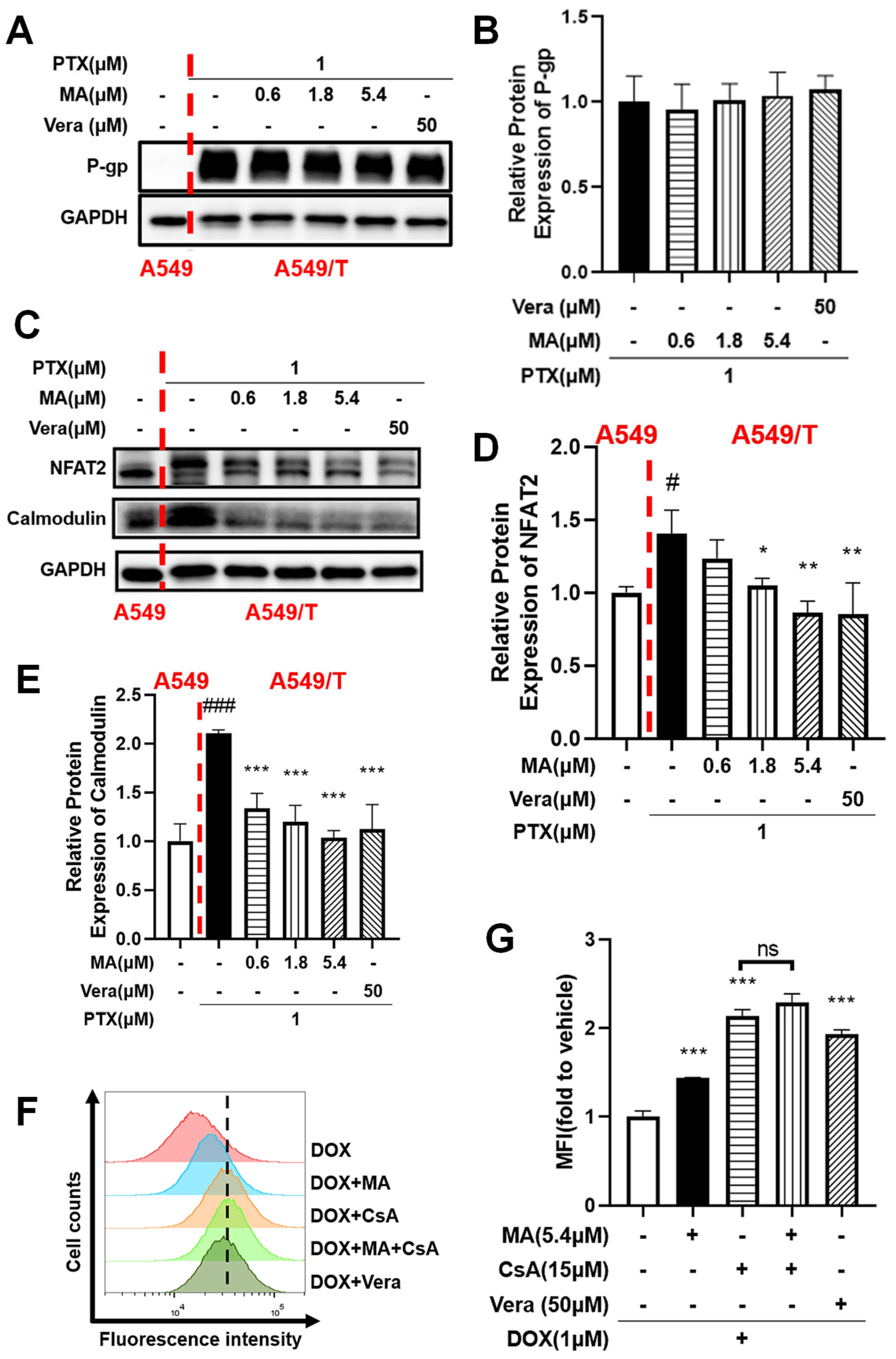
3.7. Manidipine Inhibits Drug Efflux by Mitigating Ca2+ Influx
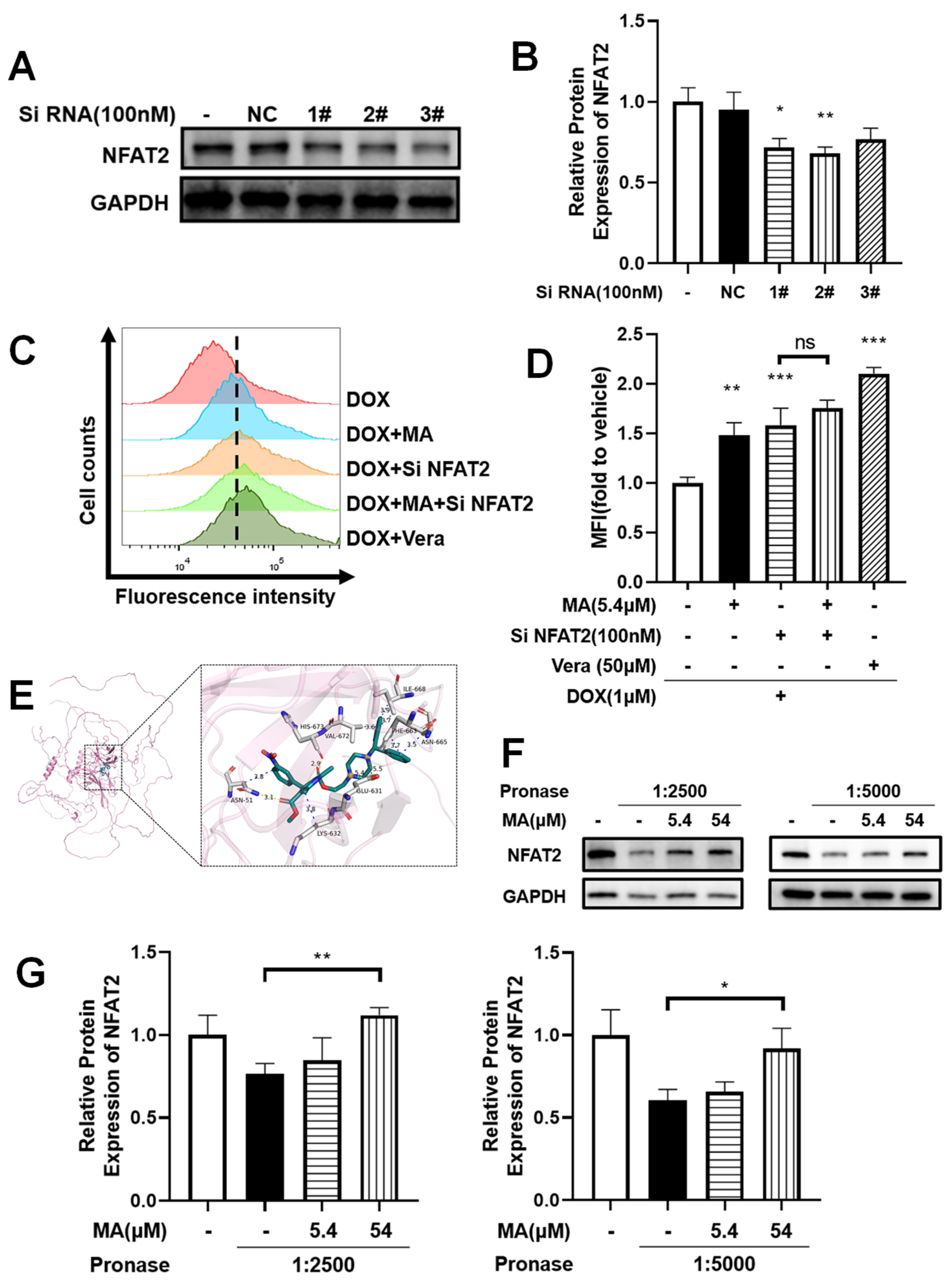
3.8. NFAT2 Was Associated with Drug Resistance
3.9. NFAT2 Silencing Overcomes Drug Efflux
3.10. Manidipine Specifically Targets NFAT2 Through Direct Molecular Interaction
3.11. Protection of NFAT2 from Proteolysis by Manidipine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fan, D. Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.; Coley, H.M. Overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: An update on the clinical strategy of inhibiting p-glycoprotein. Cancer Control 2003, 10, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.E.; Brouwer, K.R.; McNamara, P.J. GF120918, a P-glycoprotein modulator, increases the concentration of unbound amprenavir in the central nervous system in rats. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2284–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Borgne, M.; Falson, P.; Boumendjel, A. Drug candidates targeting multidrug resistance in cancer and infections. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 249, 115173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Wolf, C.R. Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. Biochem. J. 1990, 272, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Yu, M.; Xu, J.; Li, B.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kankala, R.K. Overcoming Cancer Multi-drug Resistance (MDR): Reasons, mechanisms, nanotherapeutic solutions, and challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, J.I.; Haber, M.; Henderson, M.J.; Norris, M.D. ABC transporters in cancer: More than just drug efflux pumps. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I.; Ambudkar, S.V. P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1996, 6, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonessa, F.; Clarke, R. ATP binding cassette transporters and drug resistance in breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2003, 10, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Foley, N.E.; Gleason-Guzman, M.C.; Dalton, W.S. Resistance to the chemosensitizer verapamil in a multi-drug-resistant (MDR) human multiple myeloma cell line. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 66, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Bharate, S.B. Natural alkaloids as P-gp inhibitors for multidrug resistance reversal in cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeage, K.; Scott, L.J. Manidipine: A review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs 2004, 64, 1923–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheer, S.M.; McClellan, K. Manidipine: A review of its use in hypertension. Drugs 2001, 61, 1777–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Cusachs, A.; Triposkiadis, F. Antihypertensive effect of manidipine. Drugs 2005, 65 (Suppl. 2), S11–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Zimetti, F.; Pedrelli, M.; Cremonesi, G.; Bernini, F. Manidipine reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion in human endothelial cells and macrophages. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, N.; Barma, S.; Konwar, N.; Dewanjee, S.; Manna, P. Mechanistic insight of diabetic nephropathy and its pharmacotherapeutic targets: An update. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 791, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, T.; Pan, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Ding, L. The regulatory roles of calcium channels in tumors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 169, 113603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Chatterjee, O.; Roy, L.; Chatterjee, S. Targeting Ca(2+) signaling: A new arsenal against cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colotti, G.; Poser, E.; Fiorillo, A.; Genovese, I.; Chiarini, V.; Ilari, A. Sorcin, a calcium binding protein involved in the multidrug resistance mechanisms in cancer cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 13976–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.Q.; Song, L.L.; Xu, S.W.; Yu, M.S.Y.; Kadioglu, O.; Michelangeli, F.; Law, B.Y.K.; Efferth, T.; Lam, C.W.; Wong, V.K.W. Pomiferin targets SERCA, mTOR, and P-gp to induce autophagic cell death in apoptosis-resistant cancer cells, and reverses the MDR phenotype in cisplatin-resistant tumors in vivo. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 191, 106769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, T.; Zhang, W.; Guo, H.; Pan, X.; Chen, X.; He, Q.; Yang, B.; Ding, L. The regulatory and modulatory roles of TRP family channels in malignant tumors and relevant therapeutic strategies. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1761–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, M.; Hou, A.; Han, S. NFAT signaling dysregulation in cancer: Emerging roles in cancer stem cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, J.; Jing, J.; Xie, J.; You, L.; Jing, Z.; Yao, J.; Han, W.; Pan, H. Nuclear factor of activated T cells in cancer development and treatment. Cancer Lett. 2015, 361, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Sasaki, C.Y.; Hardwick, J.M.; Longo, D.L. Bcl-2-mediated drug resistance: Inhibition of apoptosis by blocking nuclear factor of activated T lymphocytes (NFAT)-induced Fas ligand transcription. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pan, C.G.; Luo, Z.Q. High expression of NFAT2 contributes to carboplatin resistance in lung cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2019, 110, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, E.A.; Kasinski, A.L. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay in Cell Culture to Investigate Cell Proliferation. Bio Protoc. 2016, 6, e1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martínez, S.; Redondo, J.M. Inhibitors of the calcineurin/NFAT pathway. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, T.; Kashiwagi, E.; Ide, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Netto, G.J.; Ishiguro, H.; Miyamoto, H. Cyclosporine A and tacrolimus inhibit bladder cancer growth through down-regulation of NFATc1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomenick, B.; Hao, R.; Jonai, N.; Chin, R.M.; Aghajan, M.; Warburton, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, R.P.; Gomez, F.; Loo, J.A.; et al. Target identification using drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21984–21989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.Y.; Ko, J.L.; Lee, Y.J.; Yang, T.Y.; Tee, Y.T.; Sheu, G.T. L-type calcium channel blockers reverse docetaxel and vincristine-induced multidrug resistance independent of ABCB1 expression in human lung cancer cell lines. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 192, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Ren, W.; Chen, X.; He, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G. Determination and pharmacokinetics of manidipine in human plasma by HPLC/ESIMS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellet, M.; Ahmad, F.; Villanueva, R.; Valdivia, C.; Palomino-Doza, J.; Ruiz, A.; Gonzàlez, X.; Adrover, E.; Azaro, A.; Valls-Margarit, M.; et al. Palbociclib and ribociclib in breast cancer: Consensus workshop on the management of concomitant medication. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919833867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, Y.L.; Saetaew, M.; Chanthawong, S.; Yap, Y.S.; Chan, E.C.; Ho, H.K.; Chan, A. Effect of CYP3A4 inducer dexamethasone on hepatotoxicity of lapatinib: Clinical and in vitro evidence. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, M.A.; Baillie, M.T.; Shen, D.D.; Kunze, K.L.; Thummel, K.E. Persistent inhibition of CYP3A4 by ketoconazole in modified Caco-2 cells. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, R.; Hayashi, R.; Umemori, Y.; Arimatsu, A.; Yuki, A.; Abe, R. Refractory Bullous Pemphigoid Improved by Discontinuation of Phenytoin as an CYP3A4 Inducer. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
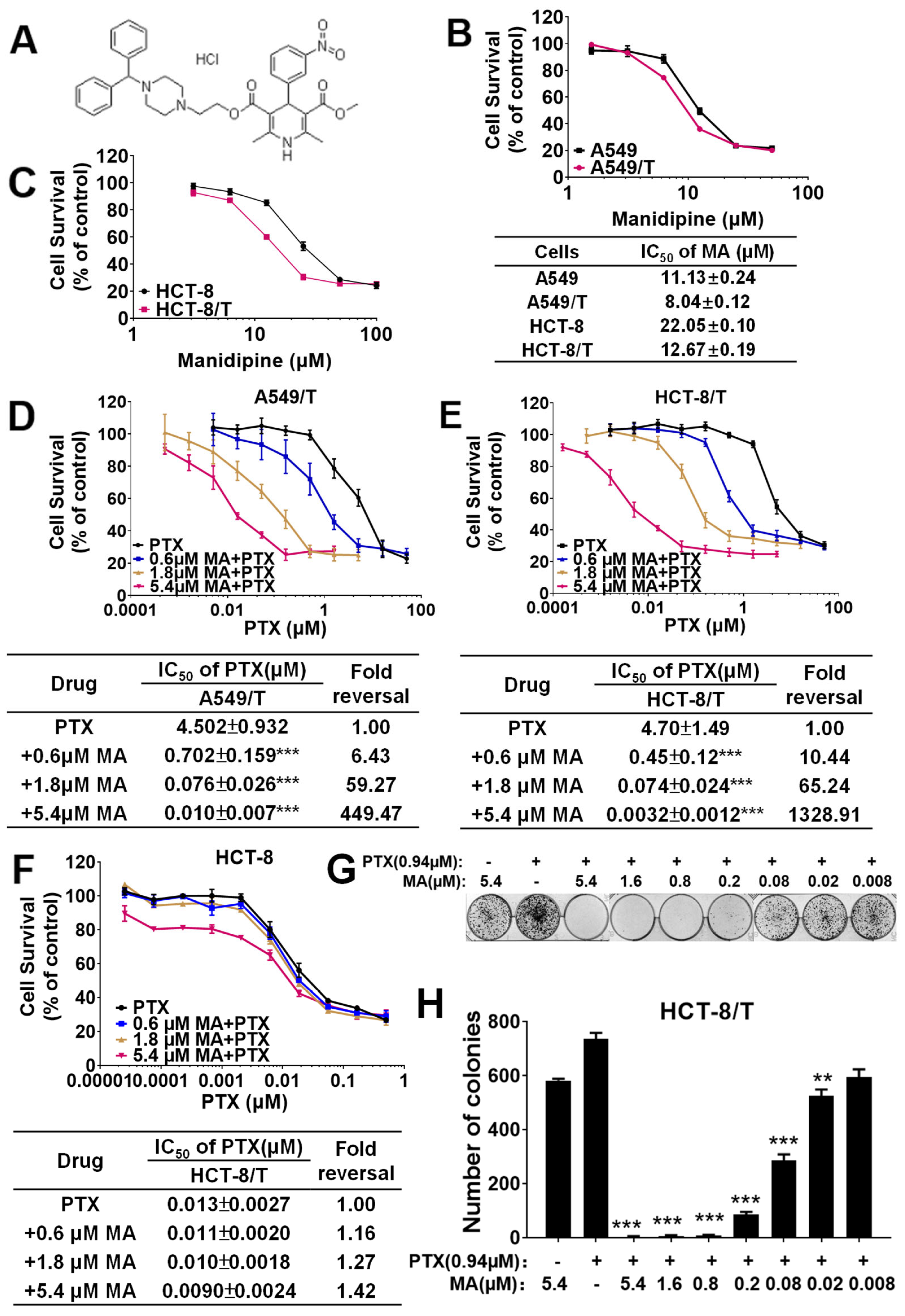

| Drug | IC50 (μM) | Fold Reversal |
|---|---|---|
| HCT-8/T | ||
| PTX | 4.70 ± 1.49 | 1 |
| +0.6 μM MA | 0.45 ± 0.12 *** | 10.44 |
| +1.8 μM MA | 0.074 ± 0.024 *** | 65.24 |
| +5.4 μM MA | 0.0032 ± 0.0012 *** | 1328.91 |
| DOX | 4.26 ± 1.11 | 1.00 |
| +0.6 μM MA | 2.62 ± 1.12 | 1.63 |
| +1.8 μM MA | 0.51 ± 0.16 | 8.40 |
| +5.4 μM MA | 0.24 ± 0.067 *** | 18.05 |
| TXT | 1.21 ± 0.22 | 1.00 |
| +0.6 μM MA | 0.24 ± 0.030 ** | 5.12 |
| +1.8 μM MA | 0.029 ± 0.0053 *** | 41.66 |
| +5.4 μM MA | 0.0023 ± 0.0014 *** | 604 |
| DAU | 2.045 ± 0.43 | 1.00 |
| +0.6 μM MA | 0.210 ± 0.062 *** | 9.74 |
| +1.8 μM MA | 0.053 ± 0.012 *** | 40.94 |
| +5.4 μM MA | 0.015 ± 0.0061 *** | 136.33 |
| 5-FU | 134.62 ± 21.74 | 1.00 |
| +0.6 μM MA | 127.33 ± 28.83 | 1.057 |
| +1.8 μM MA | 204.00 ± 15.62 | 0.66 |
| +5.4 μM MA | 264.73 ± 32 | 0.508 |
| Data for Fa = 0.5 | CI Value | Dose MA (µM) | Dose PTX (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manidipine | / | 14.8226 | / |
| PTX | / | / | 5.36072 |
| Manidipine + PTX | 1.96 × 10−5 | 1.47 × 10−4 | 5.16 × 10−5 |
| Data for Fa = 0.9 | CI value | Dose MA (µM) | Dose PTX (µM) |
| Manidipine | / | 3.30204 | / |
| PTX | / | / | 0.85596 |
| Manidipine + PTX | 6.9 × 10−13 | 9.6 × 10−13 | 3.4 × 10−13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Wang, N.; Lin, Y.-K.; Li, Q.-L.; Liu, R.-M.; Hu, J.-Q.; Zhou, H.; Lan, H.; Xie, Y. Targeting NFAT2 for Reversing the P-gp-Mediated Multidrug Resistance to Paclitaxel by Manidipine. Cancers 2025, 17, 3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203289
Zhou J, Wang N, Lin Y-K, Li Q-L, Liu R-M, Hu J-Q, Zhou H, Lan H, Xie Y. Targeting NFAT2 for Reversing the P-gp-Mediated Multidrug Resistance to Paclitaxel by Manidipine. Cancers. 2025; 17(20):3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203289
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jian, Nan Wang, Yu-Kang Lin, Qi-Lu Li, Rui-Ming Liu, Jia-Qin Hu, Hua Zhou, Hai Lan, and Ying Xie. 2025. "Targeting NFAT2 for Reversing the P-gp-Mediated Multidrug Resistance to Paclitaxel by Manidipine" Cancers 17, no. 20: 3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203289
APA StyleZhou, J., Wang, N., Lin, Y.-K., Li, Q.-L., Liu, R.-M., Hu, J.-Q., Zhou, H., Lan, H., & Xie, Y. (2025). Targeting NFAT2 for Reversing the P-gp-Mediated Multidrug Resistance to Paclitaxel by Manidipine. Cancers, 17(20), 3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203289





