Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of microRNA-7-5p Expression and Biological Significance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PICO Framework
- P (Population/Problem): Patients with HNSCC
- I (Intervention/Exposure): Analysis of miR-7-5p expression in patient samples
- C (Comparison): Expression levels of miR-7-5p in matched normal samples
- (Outcome): Determination of miR-7-5p’s biological role (tumour suppressor vs. oncomiR) and potential as a therapeutic target in HNSCC
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Selection Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.5. The Cancer Genome Atlas Data Validation
2.6. miRNA and Target Gene Quantitations in Patient Samples
2.7. Bioinformatic Analyses
2.8. Cell Culture and Drug Treatment
2.9. Animal Study and microRNA In-Situ Hybridisation (ISH)
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
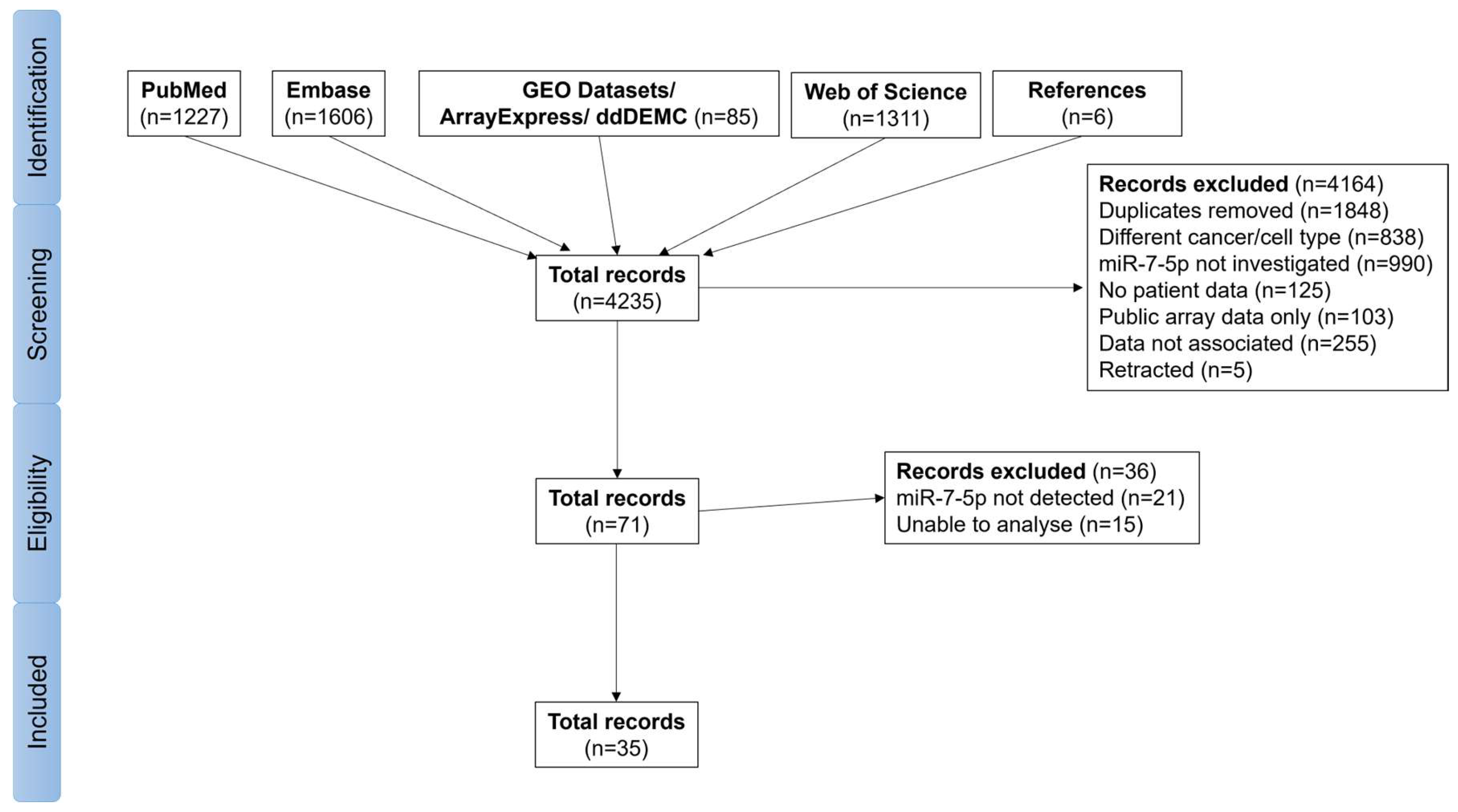
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Meta-Anlysis of miR-7-5p Expression in HNSCC
3.3. Meta-Regression Analyses
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis: Excluding Quantile-Normalised Studies
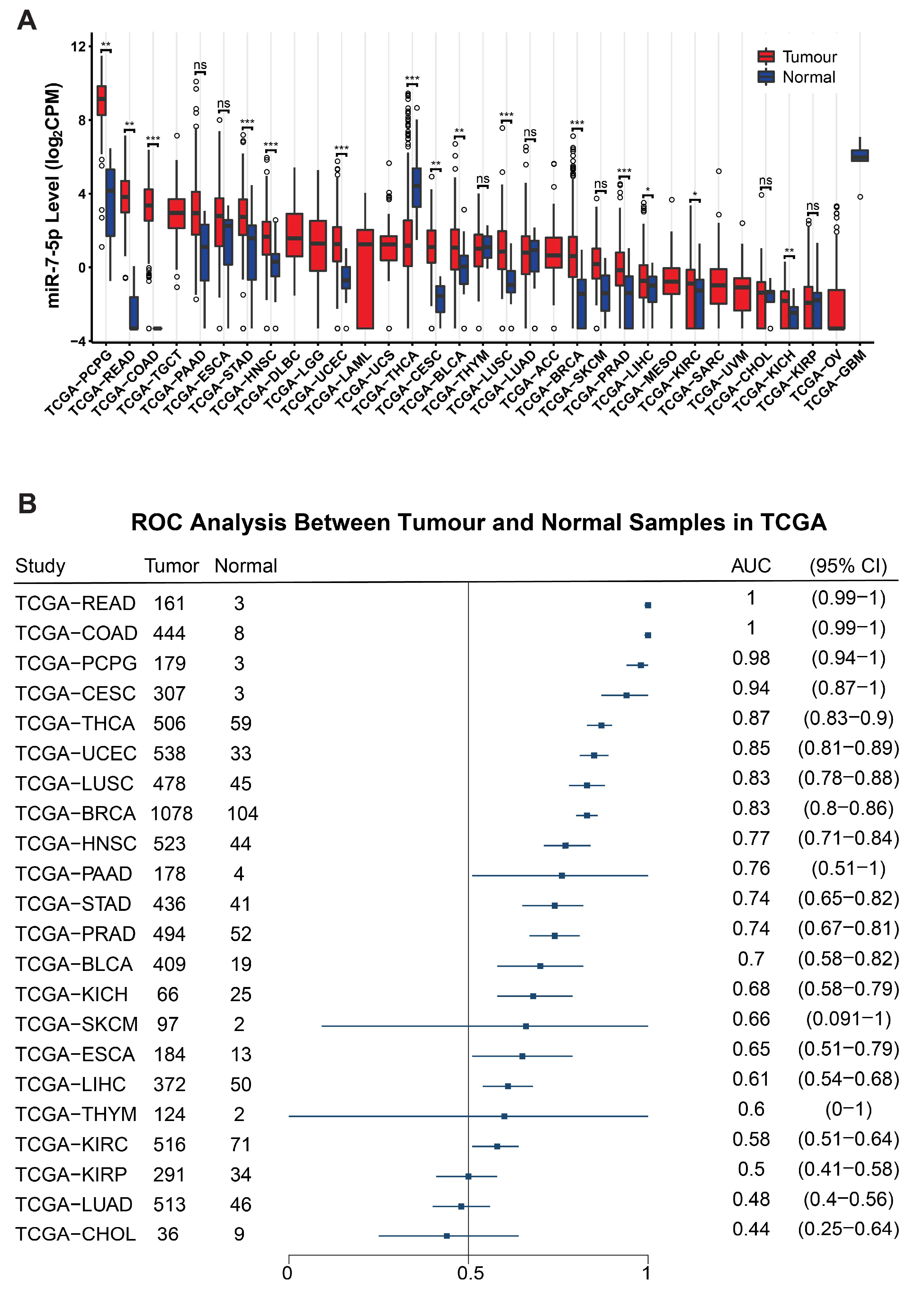
3.5. Analysis of miR-7-5p Expression and Clinical Characteristics Based on TCGA Data
3.6. Meta-Analysis of Clinical Subgroups and Dichotomous Variables
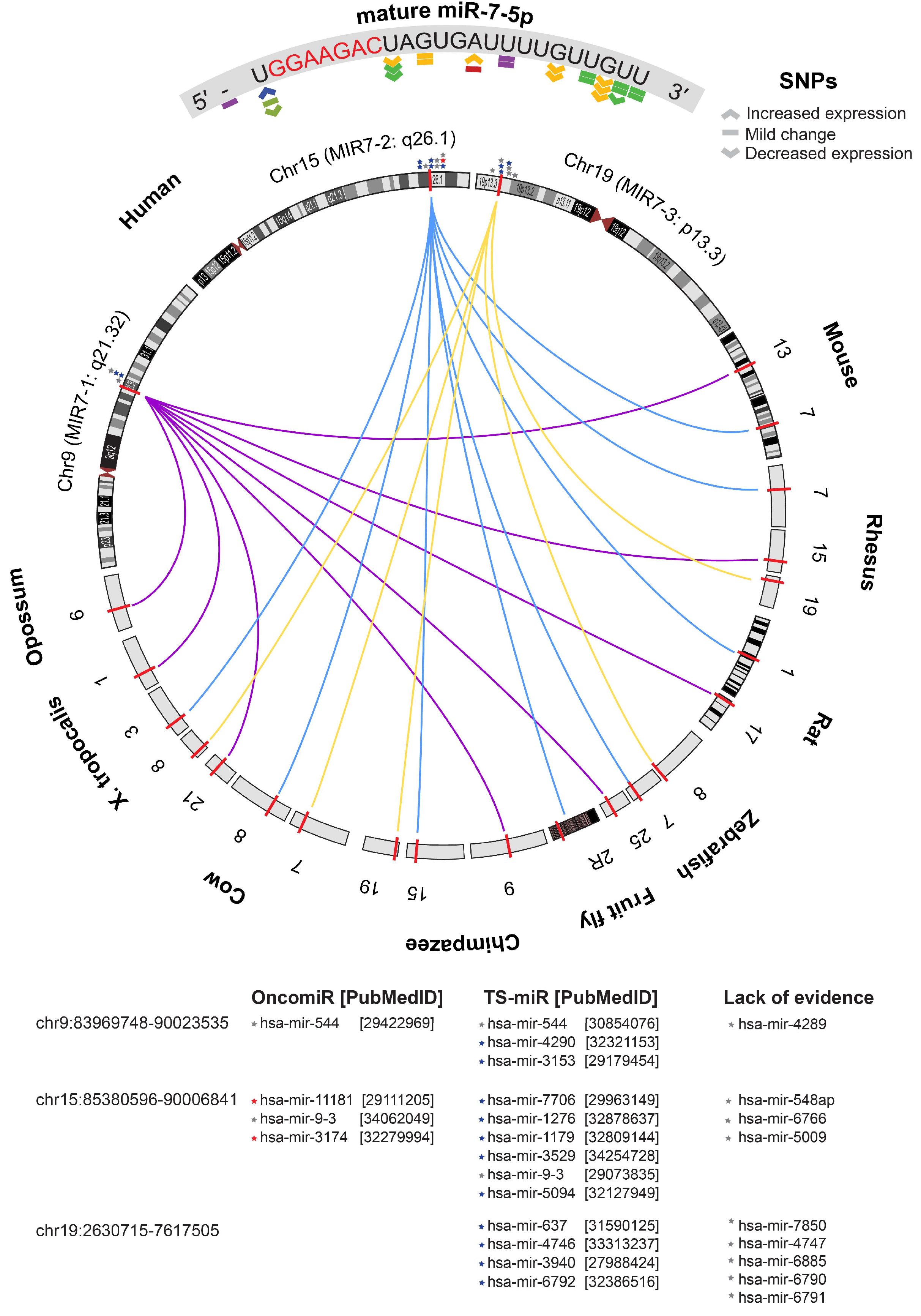
3.7. Bioinformatics Analyses of miR-7-5p in HNSCC
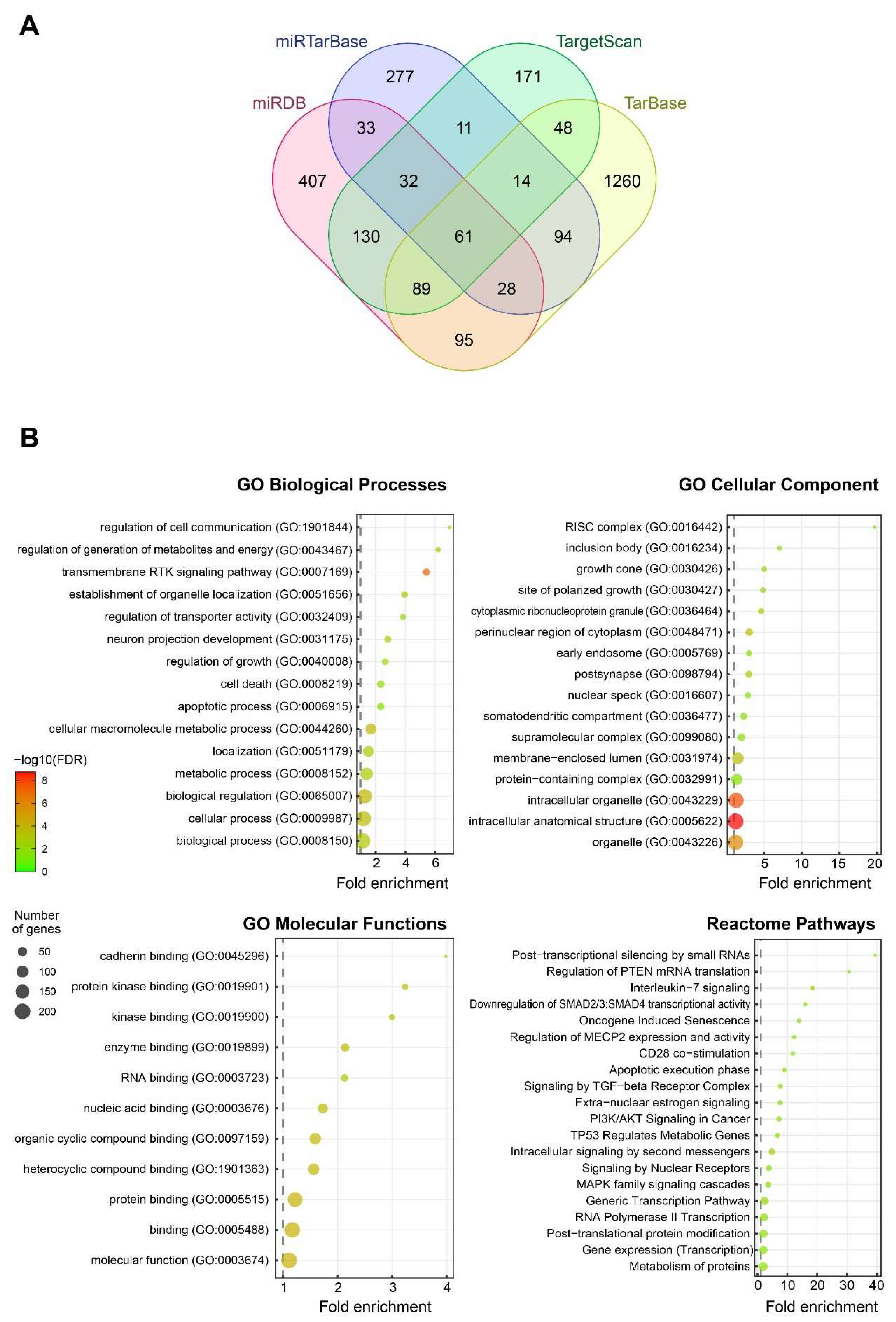
3.8. Functional Annotation of Candidate Target Genes of miR-7-5p and Construction of a Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
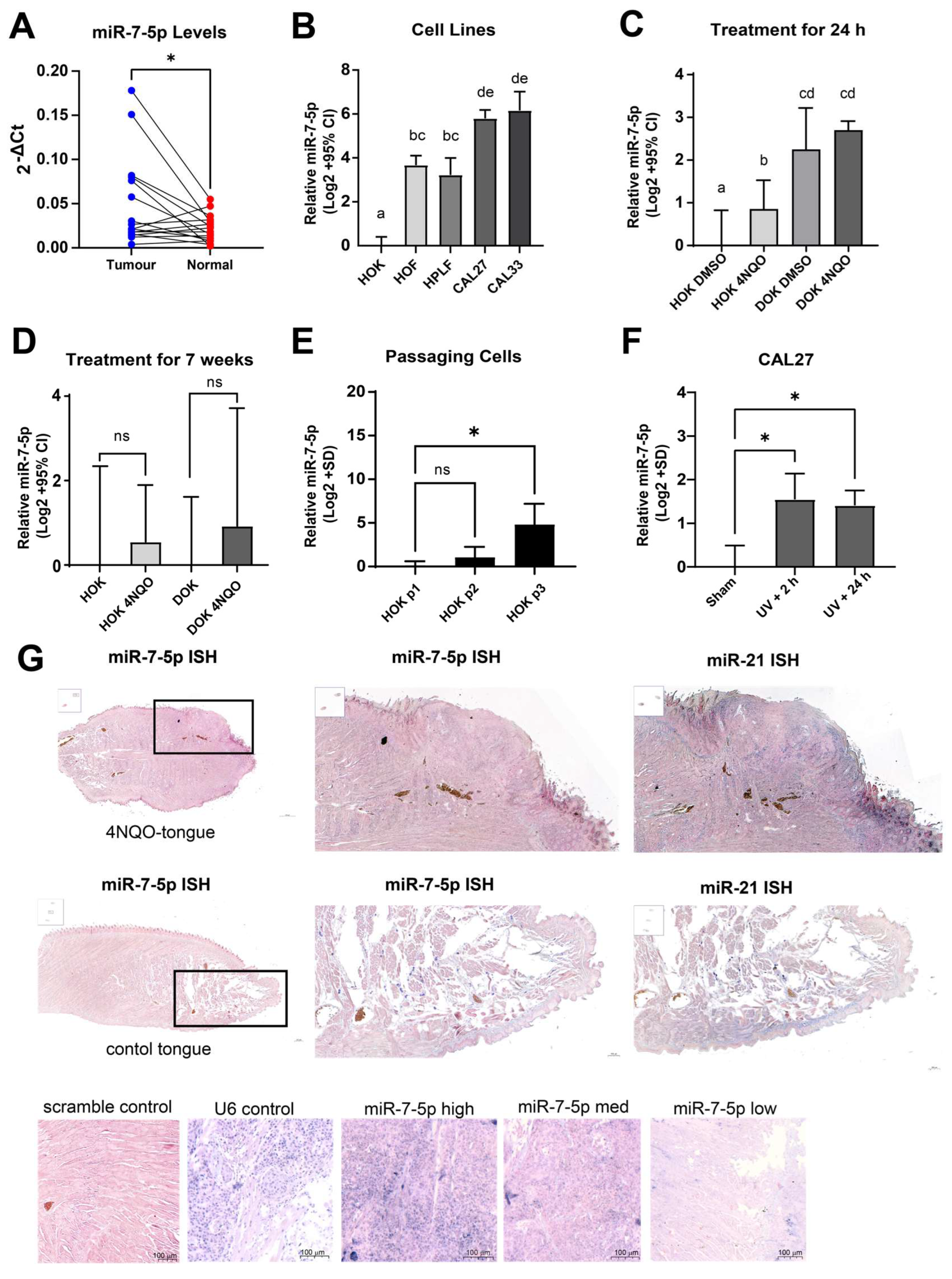
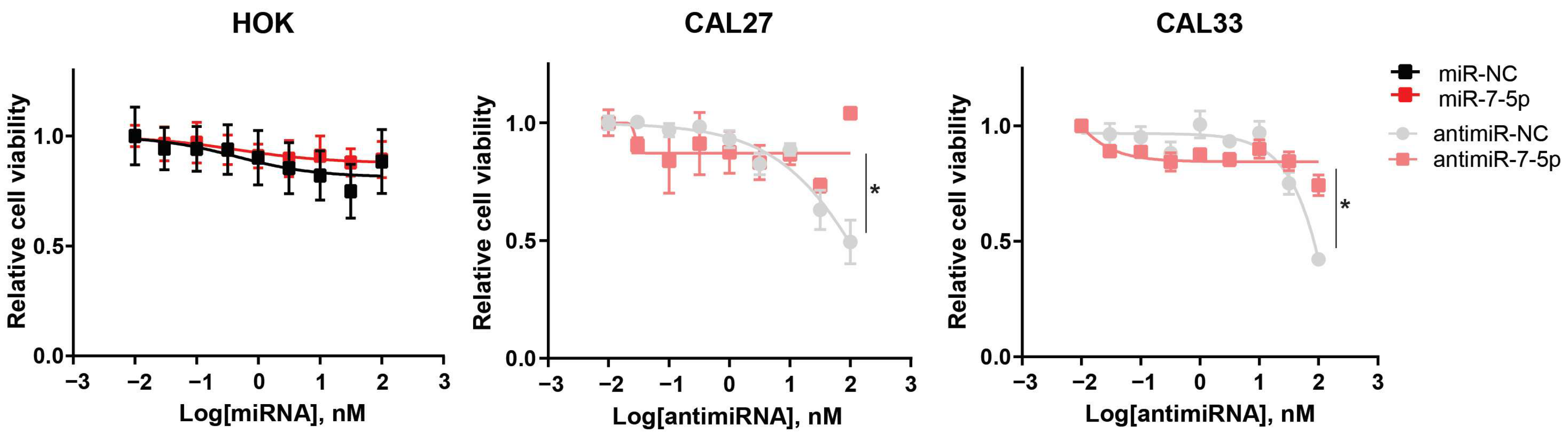
3.9. Validation of Meta-Analysis and Biological Investigation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujan, O. Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Dent. Clin. 2025, 69, 327–346. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, I.; Tan, J.; Alam, A.; Idrees, M.; Brenan, P.A.; Coletta, R.D.; Kujan, O. Epigenetics in the diagnosis and prognosis of head and neck cancer: A systematic review. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2024, 53, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchelor, C.J.J.; Flukes, S.P. Tracheostomy dependence following “organ preservation” (chemo)radiation protocol for laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers. Head Neck 2022, 44, 2779–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Jafari, R.; Marashi, S.A.; Farazmand, A. Indirect role of microRNAs and transcription factors in the regulation of important cancer genes: A network biology approach. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2015, 61, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Gattuso, G.; Crimi, S.; Lavoro, A.; Rizzo, R.; Musumarra, G.; Gallo, S.; Facciponte, F.; Paratore, S.; Russo, A.; Bordonaro, R.; et al. Liquid Biopsy and Circulating Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Precancerous and Cancerous Oral Lesions. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, F.C.; Brown, R.A.M.; Ganda, C.; Giles, K.M.; Epis, M.R.; Horsham, J.; Leedman, P.J. microRNA-7: A tumor suppressor miRNA with therapeutic potential. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 54, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsham, J.L.; Kalinowski, F.C.; Epis, M.R.; Ganda, C.; Brown, R.A.M.; Leedman, P.J. Clinical potential of microRNA-7 in cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 1668–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, F.C.; Giles, K.M.; Candy, P.A.; Ali, A.; Ganda, C.; Epis, M.R.; Webster, R.J.; Leedman, P.J. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and erlotinib sensitivity in head and neck cancer cells by miR-7. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.J.; Giles, K.M.; Price, K.J.; Zhang, P.M.; Mattick, J.S.; Leedman, P.J. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in human cancer cells by microRNA-7. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5731–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, K.M.; Brown, R.A.; Epis, M.R.; Kalinowski, F.C.; Leedman, P.J. miRNA-7-5p inhibits melanoma cell migration and invasion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, K.M.; Brown, R.A.; Ganda, C.; Podgorny, M.J.; Candy, P.A.; Wintle, L.C.; Richardson, K.L.; Kalinowski, F.C.; Stuart, L.M.; Epis, M.R.; et al. microRNA-7-5p inhibits melanoma cell proliferation and metastasis by suppressing RelA/NF-κB. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 31663–31680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, T.D.; Ganda, C.; Brown, R.M.; Beveridge, D.J.; Richardson, K.L.; Chaturvedi, V.; Candy, P.; Epis, M.; Wintle, L.; Kalinowski, F. A microRNA-7/growth arrest specific 6/TYRO3 axis regulates the growth and invasiveness of sorafenib-resistant cells in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, T.D.; Beck, S.; Stuart, L.M.; Li, J.; Hou, R.; Margolis, S.; Kim, C.; Choi, Y.S.; Bastow, E.R.; Beveridge, D.J.; et al. Inhibition of the Caveolin-1 pathway promotes apoptosis and overcomes pan-tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.M.; Phillips, B.L.; Patel, R.S.; Cohen, D.M.; Jakymiw, A.; Kong, W.W.; Cheng, J.Q.; Chan, E.K. Keratinization-associated miR-7 and miR-21 regulate tumor suppressor reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK) in oral cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29261–29272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Victoria, B.; Lopez, Y.N.; Suchorska, W.; Barczak, W.; Sobecka, A.; Golusinski, W.; Masternak, M.M.; Golusinski, P. Tissue and serum microRNA profile of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Z.; Jiang, C.; Wu, Q.; Liu, L.; Yan, X.; Shi, R. A feed-forward regulatory loop between HuR and the long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression and metastasis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Gao, L.; Ren, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Kong, X.; Chi, P.; Zhi, K. CiRS-7 functions as a ceRNA of RAF-1/PIK3CD to promote metastatic progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via MAPK/AKT signaling pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 396, 112290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Heidbreder, C.E.; Kolokythas, A.; Wang, A.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, X. MicroRNA-7 targets IGF1R (insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Biochem. J. 2010, 432, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Nguyen, H.; Lai, T.; Kim, D.R. miRCancerdb: A database for correlation analysis between microRNA and gene expression in cancer. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Qu, H.; Wang, S.; Chater, J.M.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhou, R.; Jia, Q.; Traband, R.; et al. CancerMIRNome: An interactive analysis and visualization database for miRNome profiles of human cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D1139–D1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Hong, W.Y.; Cho, M.; Sim, M.; Lee, D.; Ko, Y.; Kim, J. Synteny Portal: A web-based application portal for synteny block analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W35–W40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-J.; Fu, X.; Xia, M.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, Z.; Guo, A.-Y. miRNASNP-v3: A comprehensive database for SNPs and disease-related variations in miRNAs and miRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D1276–D1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.-D.; Li, J.; Huang, K.-Y.; Shrestha, S.; Hong, H.-C.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.-G.; Jin, C.-N.; Yu, Y. miRTarBase 2020: Updates to the experimentally validated microRNA–target interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D148–D154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.-W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagkouni, D.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Chatzopoulos, S.; Vlachos, I.S.; Tastsoglou, S.; Kanellos, I.; Papadimitriou, D.; Kavakiotis, I.; Maniou, S.; Skoufos, G.; et al. DIANA-TarBase v8: A decade-long collection of experimentally supported miRNA–gene interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D239–D245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Ontology, C. The Gene Ontology resource: Enriching a GOld mine. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, D325–D334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supek, F.; Bošnjak, M.; Škunca, N.; Šmuc, T. REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of Gene Ontology terms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnot, T.; Gillard, M.B.; Nagel, D.H. A simple protocol for informative visualization of enriched Gene Ontology terms. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitturi Suryaprakash, R.T.; Shearston, K.; Farah, C.S.; Fox, S.A.; Iqbal, M.M.; Kadolsky, U.; Zhong, X.; Saxena, A.; Kujan, O. A novel preclinical In vitro 3D model of oral carcinogenesis for biomarker discovery and drug testing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, D.J. Two-stage individual participant data meta-analysis and generalized forest plots. Stata J. 2015, 15, 369–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, E.; Singh, R.; Ray, A.; Roy, R.; De Sarkar, N.; Paul, R.R.; Pal, M.; Aich, R.; Roy, B. Expression deregulation of mir31 and CXCL12 in two types of oral precancers and cancer: Importance in progression of precancer and cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sarkar, N.; Roy, R.; Mitra, J.K.; Ghose, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Paul, R.R.; Mukhopadhyay, I.; Roy, B. A quest for miRNA bio-marker: A track back approach from gingivo buccal cancer to two different types of precancers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganci, F.; Sacconi, A.; Bossel Ben-Moshe, N.; Manciocco, V.; Sperduti, I.; Strigari, L.; Covello, R.; Benevolo, M.; Pescarmona, E.; Domany, E.; et al. Expression of TP53 mutation-associated microRNAs predicts clinical outcome in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 3082–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganci, F.; Sacconi, A.; Manciocco, V.; Covello, R.; Benevolo, M.; Rollo, F.; Strano, S.; Valsoni, S.; Bicciato, S.; Spriano, G.; et al. Altered peritumoral microRNA expression predicts head and neck cancer patients with a high risk of recurrence. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 1387–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganci, F.; Sacconi, A.; Manciocco, V.; Sperduti, I.; Battaglia, P.; Covello, R.; Muti, P.; Strano, S.; Spriano, G.; Fontemaggi, G.; et al. MicroRNA expression as predictor of local recurrence risk in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. S1), E189–E197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Guo, H.; Niu, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, X.; Bo, Y.; Guan, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; et al. circPARD3 drives malignant progression and chemoresistance of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting autophagy through the PRKCI-Akt-mTOR pathway. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikkawa, N.; Hanazawa, T.; Fujimura, L.; Nohata, N.; Suzuki, H.; Chazono, H.; Sakurai, D.; Horiguchi, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Seki, N. miR-489 is a tumour-suppressive miRNA target PTPN11 in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC). Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshizuka, K.; Nohata, N.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Fukumoto, I.; Katada, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Seki, N. Deep sequencing-based microRNA expression signatures in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Dual strands of pre-miR-150 as antitumor miRNAs. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30288–30304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdas, L.; Giri, U.; Ashorn, C.L.; Coombes, K.R.; El-Naggar, A.; Ang, K.K.; Story, M.D. miRNA expression profiles in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and adjacent normal tissue. Head Neck 2009, 31, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, M.; Cao, Y. New insight into microRNA functions in cancer: Oncogene–microRNA–tumor suppressor gene network. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2017, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avissar, M.; McClean, M.D.; Kelsey, K.T.; Marsit, C.J. MicroRNA expression in head and neck cancer associates with alcohol consumption and survival. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, J.P.; Hui, A.B.Y.; Shi, W.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Xu, W.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Waggott, D.M.; Boutros, P.C.; O’Sullivan, B.; et al. Identification of a microRNA signature associated with risk of distant metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4537–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervigne, N.K.; Reis, P.P.; Machado, J.; Sadikovic, B.; Bradley, G.; Galloni, N.N.; Pintilie, M.; Jurisica, I.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Gilbert, R.; et al. Identification of a microRNA signature associated with progression of leukoplakia to oral carcinoma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4818–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro-Petronacci, C.; Perez-Sayáns, M.; Padín-Iruegas, M.E.; Marichalar-Mendia, X.; Gallas-Torreira, M.; García García, A. Differential expression of snoRNAs in oral squamous cell carcinomas: New potential diagnostic markers. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, C.S.; Fox, S.A.; Dalley, A.J. Integrated miRNA-mRNA spatial signature for oral squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective profiling study of Narrow Band Imaging guided resection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, I.; Kinoshita, T.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Chiyomaru, T.; Enokida, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Goto, Y.; Nishikawa, R.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Identification of tumour suppressive microRNA-451a in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma based on microRNA expression signature. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapa, R.M.L.; Barros-Filho, M.C.; Marchi, F.A.; Domingues, M.A.C.; de Carvalho, G.B.; Drigo, S.A.; Kowalski, L.P.; Rogatto, S.R. Integrated miRNA and mRNA expression analysis uncovers drug targets in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma patients. Oral Oncol. 2019, 93, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chen, J.X.; Fu, X.P.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen Kh, H.; Li, Y. microRNA expression profiling of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Chen, N.Y.; Cui, R.X.; Li, W.F.; Li, Y.; Wei, R.R.; Zhang, M.Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, B.J.; Chen, M.; et al. Prognostic value of a microRNA signature in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, X.; Fang, W.; Cai, L.; Zheng, H.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Peng, H.; Cho, W.C.; Wang, E.; et al. TGFβR2 is a major target of miR-93 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma aggressiveness. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, K.X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yue, H.J.; Wen, Y.H.; Liu, T.S.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, Q.H.; Yang, W.Q.; Zhu, X.L.; et al. Using RNA sequencing to identify a putative lncRNA-associated ceRNA network in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Feng, Y.; Rinaldi, G.; Levine, P.; Easley, S.; Martinez, E.; Hashmi, S.; Sadeghi, N.; Brindley, P.J.; Mulvenna, J.P.; et al. Profiling miRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma FFPE tissue by microarray and Next Generation Sequencing. Genom. Data 2014, 2, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Inagaki, K.; Kamimoto, T.; Ito, Y.; Sugita, T.; Nakajo, S.; Hirasawa, A.; Iwamaru, A.; Ishikura, T.; Hanaoka, H.; et al. MicroRNA-196a is a putative diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for laryngeal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Brüggemann, H.; Andreghetto, F.M.; Camps, C.; Klingbeil Mde, F.; de Pereira, W.O.; Soares, R.M.; Moyses, R.; Wünsch-Filho, V.; Mathor, M.B.; et al. MicroRNA expression profile in head and neck cancer: HOX-cluster embedded microRNA-196a and microRNA-10b dysregulation implicated in cell proliferation. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhou, Z.T.; Ma, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Z.X.; Jiang, W.W. MicroRNA-155 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Overexpression, localization, and prognostic potential. Head Neck 2015, 37, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiah, S.G.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chang, W.M.; Chen, Y.W.; Jin, Y.T.; Wong, T.Y.; Huang, J.S.; Tsai, S.T.; Hsu, Y.M.; Chou, S.T.; et al. Downregulated miR329 and miR410 promote the proliferation and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Wnt-7b. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7560–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansfield, J.C.; Rusay, M.; Shan, R.; Kelton, C.; Gaykalova, D.A.; Fertig, E.J.; Califano, J.A.; Ochs, M.F. Toward Signaling-Driven Biomarkers Immune to Normal Tissue Contamination. Cancer Inform. 2016, 15, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Dai, F.; Lu, Y.; Dai, L.; Niu, M.; Guo, H.; Li, W.; Xue, X.; et al. Circular RNA circCORO1C promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression by modulating the let-7c-5p/PBX3 axis. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lian, M.; Feng, L.; Wang, R.; Shi, Q.; Zhai, J.; Liu, X.; Fang, J. Array profiling identified dysregulated miRNAs and target genes and pathways in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 11, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Li, F.-Q.; Tian, L.-L.; Shang, D.-S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.-R.; Liu, M. Comprehensive analysis of the whole coding and non-coding RNA transcriptome expression profiles and construction of the circRNA–lncRNA co-regulated ceRNA network in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2019, 19, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, K.; Liao, S.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. MicroRNA-transcription factor network analysis reveals miRNAs cooperatively suppress RORA in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Yu, P.; Xie, N.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Tao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yin, H.; Zou, B.; et al. MicroRNA-204-5p is a tumor suppressor and potential therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1433–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron, F.; Armenia, J.; Franchin, G.; Polesel, J.; Talamini, R.; D’Andrea, S.; Sulfaro, S.; Croce, C.M.; Klement, W.; Otasek, D.; et al. An integrated approach identifies mediators of local recurrence in head and neck squamous carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3769–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cecco, L.; Giannoccaro, M.; Marchesi, E.; Bossi, P.; Favales, F.; Locati, L.D.; Licitra, L.; Pilotti, S.; Canevari, S. Integrative miRNA-Gene Expression Analysis Enables Refinement of Associated Biology and Prediction of Response to Cetuximab in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer. Genes 2017, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, A.K.; Muer, A.; Mairinger, F.D.; Weichert, W.; Stenzinger, A.; Hummel, M.; Budach, V.; Tinhofer, I. MiR-200b and miR-155 as predictive biomarkers for the efficacy of chemoradiation in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 77, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.; Unger, K.; Maihoefer, C.; Schüttrumpf, L.; Wintergerst, L.; Heider, T.; Weber, P.; Marschner, S.; Braselmann, H.; Samaga, D.; et al. A five-microRNA signature predicts survival and disease control of patients with head and neck cancer negative for HPV infection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, J.; Walter, V.; Yin, X.; Marron, D.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Choi, H.Y.; Zhao, X.; Jo, H.; Hayes, D.N.; Ko, Y.H. Integrative Analysis of miRNAs Identifies Clinically Relevant Epithelial and Stromal Subtypes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S. MicroRNAs Related with the Metastasis of Human Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 2016. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE81821 (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Lian, M.; Tao, Y.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Hou, L.; Cao, S.; Fang, J. Variation of PPARG expression in chemotherapy-sensitive patients of hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. PPAR Res. 2021, 2021, 5525091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, M.C.; Ten Hoeve, J.J.; Grénman, R.; Wessels, L.F.; Kerkhoven, R.; Te Riele, H.; van den Brekel, M.W.; Verheij, M.; Begg, A.C. Pretreatment microRNA Expression Impacting on Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Predicts Intrinsic Radiosensitivity in Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines and Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 5630–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, A.C.; Job, S.; Ledrappier, S.; Macabre, C.; Abecassis, J.; de Reyniès, A.; Wasylyk, B. A poor prognosis subtype of HNSCC is consistently observed across methylome, transcriptome, and miRNome analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4174–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, A.J.; Wang, S.; Kutler, D.I.; Carvajal, R.D.; Philipone, E.; Wang, T.; Peters, S.M.; LaRoche, D.; Hernandez, B.Y.; McDowell, B.D.; et al. MicroRNA-based risk scoring system to identify early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma patients at high-risk for cancer-specific mortality. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, A.J.; Wang, S.; Shen, J.; Robine, N.; Philipone, E.; Oster, M.W.; Nam, A.; Santella, R.M. Prognostic value of miR-375 and miR-214-3p in early stage oral squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2014, 6, 580–592. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Cui, Q.; Yin, Y. Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show significantly different biological patterns: From functions to targets. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Hou, G.; Han, X.; Song, W. MicroRNA-4290 suppresses PDK1-mediated glycolysis to enhance the sensitivity of gastric cancer cell to cisplatin. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, e9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cao, J.; Peng, X. LINC01234 facilitates growth and invasiveness of oral squamous cell carcinoma through regulating the miR-637/NUPR1 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Han, X. miR-3940-5p Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Targeting Cyclin D1 and Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase-28. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, G.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G. Curcumin exerts its antitumor activity through regulation of miR-7/Skp2/p21 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Liu, F.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Q.; Liu, S. IncRNA ZFAS1 contributes to the radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by sponging hsa-miR-7-5p to upregulate ENO2. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y. CDR1as is overexpressed in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma to promote the tumour’s progression via miR-7 signals. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Huang, J.; Wei, J.; Wu, R. Circular RNA CDR1as sponges miR-7-5p to enhance E2F3 stability and promote the growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, I.A. microRNA-7 increases radiosensitivity of human cancer cells with activated EGFR-associated signaling. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 101, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Zheng, L.; Yuan, T.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Xue, X.; Huang, S.; He, W.; Jin, M.; Zhang, Y. The circRNA hsa-circ-0013561 regulates head and neck squamous cell carcinoma development via the miR-7-5p/PDK3 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mockly, S.; Houbron, É.; Seitz, H. A rationalized definition of general tumor suppressor microRNAs excludes miR-34a. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 4703–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron, F.; Segatto, I.; Musco, L.; Pellarin, I.; Rampioni Vinciguerra, G.L.; Franchin, G.; Fanetti, G.; Miccichè, F.; Giacomarra, V.; Lupato, V.; et al. miR-9 modulates and predicts the response to radiotherapy and EGFR inhibition in HNSCC. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Fu, H.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Y. Association of decreased expression of serum miR-9 with poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, M.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Ye, X.; Yu, J. Upregulating the Expression of LncRNA ANRIL Promotes Osteogenesis via the miR-7-5p/IGF-1R Axis in the Inflamed Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 604400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Hu, Q.; Feng, N.; Liu, C.; Shi, N.; Chen, S.; Chen, M.; Guan, H.; You, Z.; et al. Transgenic construction and functional miRNA analysis identify the role of miR-7 in prostate cancer suppression. Oncogene 2022, 41, 4645–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Yue, P.; Miao, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, B.; Leng, S.X.; Meng, X.; Zhang, H. The lncRNA MEG3/miR-16-5p/VGLL4 regulatory axis is involved in etoposide-induced senescence of tumor cells. J. Gene Med. 2021, 23, e3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.-Q.; Chen, H.-B.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Chen, Z.; Tian, L.; Gu, D.-N. MicroRNA-7 modulates cellular senescence to relieve gemcitabine resistance by targeting PARP1/NF-κB signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.; Yang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Ruan, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q. MiR-7-5p-mediated downregulation of PARP1 impacts DNA homologous recombination repair and resistance to doxorubicin in small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Shang, Z.-F.; Liu, X.-D.; Xie, D.-F.; Wang, Q.; Guan, H.; Zhou, P.-K. Bystander autophagy mediated by radiation-induced exosomal miR-7-5p in non-targeted human bronchial epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Shi, G.S.; Cheng, H.Y.; Zeng, Y.N.; Li, G.; Zhang, M.; Song, M.; Zhou, P.K.; Tian, Y.; Cui, F.M.; et al. Exosomal miR-7 Mediates Bystander Autophagy in Lung after Focal Brain Irradiation in Mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakami, F.; Darda, L.; Stafford, P.; Woll, P.; Lambert, D.W.; Hunter, K.D. The roles of HOXD10 in the development and progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsham, J.L.; Ganda, C.; Kalinowski, F.C.; Brown, R.A.; Epis, M.R.; Leedman, P.J. MicroRNA-7: A miRNA with expanding roles in development and disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 69, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.D.N.; Ohshiro, K.; Rayala, S.K.; Kumar, R. MicroRNA-7, a Homeobox D10 Target, Inhibits p21-Activated Kinase 1 and Regulates Its Functions. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8195–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.-T.; Lin, H.-H.; Lien, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Hong, C.-F.; Kao, Y.-R.; Lin, S.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; et al. EGFR promotes lung tumorigenesis by activating miR-7 through a Ras/ERK/Myc pathway that targets the Ets2 transcriptional repressor ERF. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8822–8831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Qin, X.; Yan, M.; Li, R.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote cancer cell growth through a miR-7-RASSF2-PAR-4 axis in the tumor microenvironment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1290–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajthala, S.; Min, A.; Parajuli, H.; Debnath, K.C.; Ljøkjel, B.; Hoven, K.M.; Kvalheim, A.; Lybak, S.; Neppelberg, E.; Vintermyr, O.K.; et al. Profiling and functional analysis of microRNA deregulation in cancer-associated fibroblasts in oral squamous cell carcinoma depicts an anti-invasive role of microRNA-204 via regulation of their motility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 21, 11960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, T. Essential gene expression pattern of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma revealed by tumor-specific expression rule based on single-cell RNA sequencing. BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 7, 165791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakittnen, J.; Ekanayake Weeramange, C.; Wallace, D.F.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Cristino, A.S.; Hartel, G.; Barrero, R.A.; Taheri, T.; Kenny, L.; Vasani, S.; et al. A novel saliva-based miRNA profile to diagnose and predict oral cancer. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2024, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclellan, S.A.; Lawson, J.; Baik, J.; Guillaud, M.; Poh, C.F.; Garnis, C. Differential expression of miRNAs in the serum of patients with high-risk oral lesions. Cancer Med. 2012, 1, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Author | Country | Tumour Site | Age (Median) | Tumour/Normal | Tumour (Average) | Normal (Average) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avissar, 2009 [46] | America | Oral cavity | N.R. | 1.18 | 5.85 | 4.94 |
| Bruce, 2015 [47] | Canada | Pharynx | 51 | 8.23 | 5.17 | 0.629 |
| Cervigne, 2009 [48] | Canada | Oral cavity | N.R. | −1.95 | 2.96 | −1.52 |
| Chamorro, 2018 [49] | Spain | Oral cavity | 54 | 1.11 | 12.4 | 11.2 |
| Farah, 2018 [50] | Australia | Oral cavity | 64 | 1.18 | 6.18 | 5.22 |
| Fukumoto, 2014 [51] | Japan | Pharynx | 64 | 5.34 | 80 | 14.97 |
| Jung, 2012 [16] | America | Mixed | 61 | 1.67 | 672 | 402 |
| Lapa, 2019 [52] | Brazil | Larynx | 62 | 3.37 | 3914 | 1162 |
| Li, 2011 [53] | China | Pharynx | 46 | 1.40 | 2.21 | 1.58 |
| Liu, 2012 [54] | China | Pharynx | 46 | 0.98 | 318 | 326 |
| Lyu, 2014 [55] | China | Pharynx | N.R. | 1.01 | −2.37 | −2.34 |
| Lyu, 2020 [56] | China | Larynx | N.R. | 3.79 | 0.379 | 0.100 |
| Peng, 2014 [57] | America | Pharynx | 48 | 1.31 | 0.567 | 0.432 |
| Saito, 2013 [58] | Japan | Larynx | N.R. | 0.98 | 8.54 | 8.67 |
| Severino, 2013 [59] | Brazil | Oral cavity | 56 | −2.20 | 2.91 | −1.32 |
| Shi, 2015 [60] | China | Oral cavity | N.R. | 0.94 | −3.29 | −3.52 |
| Shiah, 2014 [61] | Taiwan | Oral cavity | 49 | 2.80 | 769 | 275 |
| Stansfield, 2016 [62] | America | Mixed | 58 | 1.34 | 3.22 | 2.41 |
| TCGA | America | Mixed | 61 | 3.68 | 36.9 | 10.0 |
| Wu, 2020 [63] | China | Larynx | N.R. | 3.30 | 8479 | 2569 |
| Yang, 2018 [64] | China | Larynx | 56 | 3.64 | 75.5 | 20.7 |
| Zhao, 2019 [65] | China | Larynx | N.R. | 1.08 | 1.47 | 1.35 |
| Zheng, 2018 [66] | China | Oral cavity | N.R. | 1.91 | 2.11 | 1.11 |
| Zhuang, 2020 [67] | China | Oral cavity | 50 | 1.94 | 5.15 | 2.65 |
| Clinicopathological Parameters | Features | n | Mean ± SD | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unmatched tissue | HNSCC | 514 | 2.113 ± 1.019 | <0.0001 |
| Normal | 40 | 1.107 ± 0.522 | ||
| Matched tissue | HNSCC | 40 | 2.443 ± 1.173 | <0.0001 |
| Normal | 40 | 1.107 ± 0.522 | ||
| Sex | Male | 376 | 2.111 ± 1.034 | 0.9435 |
| Female | 138 | 2.119 ± 0.980 | ||
| Age | ≤50 years | 83 | 1.980 ± 0.867 | 0.1932 |
| >50 years | 431 | 2.139 ± 1.044 | ||
| T stage | T1 or T2 | 182 | 1.986 ± 0.975 | 0.0469 |
| T3 or T4 | 316 | 2.175 ± 1.049 | ||
| N Stage | N0 | 236 | 2.106 ± 1.034 | 0.8749 |
| N1–N3 | 274 | 2.120 ± 1.014 | ||
| M Stage | M0 | 483 | 2.103 ± 1.023 | 0.2772 |
| M1 | 6 | 2.560 ± 1.011 | ||
| Clinical Stage | I–II | 114 | 2.086 ± 0.932 | 0.8222 |
| III–IV | 386 | 2.110 ± 1.051 | ||
| Histological Grade | G1–G2 | 365 | 2.133 ± 0.988 | 0.8491 |
| G3–G4 | 129 | 2.113 ± 1.073 | ||
| Alcohol | Yes | 343 | 2.134 ± 1.034 | 0.592 |
| No | 162 | 2.082 ± 1.004 | ||
| Tobacco | Yes | 381 | 2.152 ± 1.029 | 0.3022 |
| No | 120 | 2.042 ± 0.970 | ||
| HPV Status | Positive | 95 | 1.796 ± 0.999 | 0.0007 |
| Negative | 417 | 2.188 ± 1.010 | ||
| TP53 Status | Mutant | 361 | 2.258 ± 1.017 | 0.0017 |
| Wild-Type | 146 | 1.927 ± 1.025 | ||
| Perineural invasion | Yes | 170 | 2.170 ± 1.078 | 0.7071 |
| No | 193 | 2.130 ± 0.970 | ||
| Lymphovascular invasion | Yes | 122 | 2.162 ± 1.002 | 0.8121 |
| No | 227 | 2.134 ± 1.050 |
| Comparisons | Studies | Participants | I2 | p(Q) | Effect Estimate | p(Z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male vs. Female | 20 | 1421 | 0% | 0.76 | 0.80 [0.62, 1.01] | 0.07 |
| >50 years vs. <50 years | 21 | 149 | 0% | 0.69 | 1.02 [0.80, 1.30] | 0.88 |
| Stage III-IV vs. Stage I-II | 19 | 1187 | 0% | 0.56 | 1.05 [0.81, 1.36] | 0.73 |
| G3–G4 vs. G2–G1 | 5 | 622 | 7% | 0.37 | 0.79 [0.55, 1.13] | 0.19 |
| Drinker vs. Non-drinker | 6 | 697 | 0% | 0.66 | 1.09 [0.79, 1.50] | 0.60 |
| Smoker vs. Non-smoker | 7 | 706 | 0% | 0.48 | 1.25 [0.90, 1.74] | 0.18 |
| HPV+ vs. HPV− | 7 | 721 | 0% | 0.72 | 0.58 [0.39, 0.85] | 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brown, R.A.M.; Phillips, M.; Woo, A.J.; Kujan, O.; Flukes, S.; Winteringham, L.N.; Dymond, L.C.; Wheeler, F.; Pollock, B.; Beveridge, D.J.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of microRNA-7-5p Expression and Biological Significance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193232
Brown RAM, Phillips M, Woo AJ, Kujan O, Flukes S, Winteringham LN, Dymond LC, Wheeler F, Pollock B, Beveridge DJ, et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of microRNA-7-5p Expression and Biological Significance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193232
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrown, Rikki A. M., Michael Phillips, Andrew J. Woo, Omar Kujan, Stephanie Flukes, Louise N. Winteringham, Larissa C. Dymond, Fiona Wheeler, Brianna Pollock, Dianne J. Beveridge, and et al. 2025. "Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of microRNA-7-5p Expression and Biological Significance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193232
APA StyleBrown, R. A. M., Phillips, M., Woo, A. J., Kujan, O., Flukes, S., Winteringham, L. N., Dymond, L. C., Wheeler, F., Pollock, B., Beveridge, D. J., Denisenko, E., & Leedman, P. J. (2025). Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of microRNA-7-5p Expression and Biological Significance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(19), 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193232









