A Multi-Dimensional Framework for Data Quality Assurance in Cancer Imaging Repositories
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
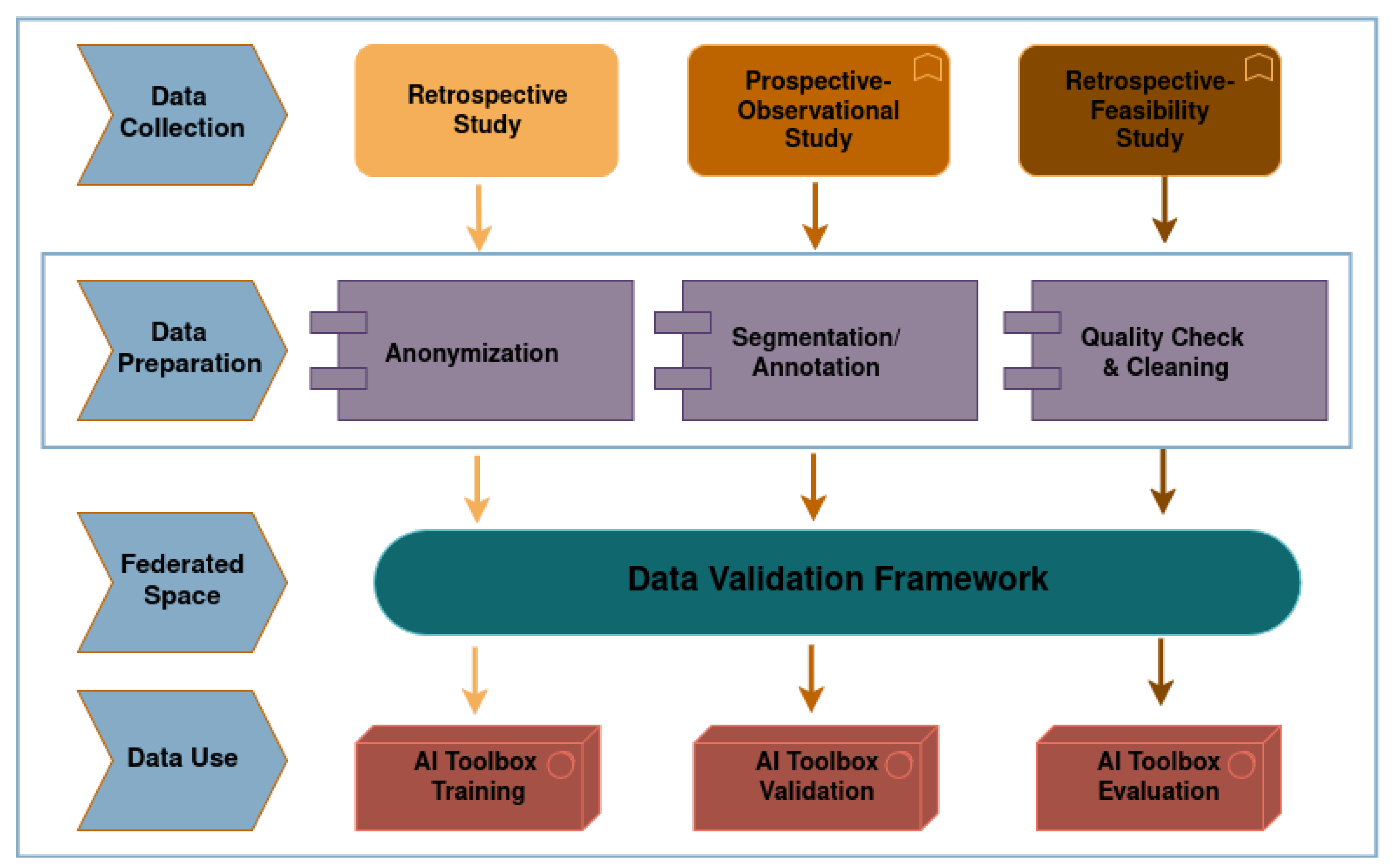
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Background on INCISIVE Repository Data
2.2. The Data Validation Framework
- Data duplication
- Incompleteness
- Internal inconsistency
- Inaccuracies in recorded values
- Lack of standardized definitions
- Disorganized formatting or structure
- Deficiencies in data security
2.2.1. Clinical Metadata Quality Assessment
2.2.2. Image Data Quality Assessment
Image Deduplication and Similarity Identification
Evaluation of Image Annotations
DICOM Attributes/Tags Analysis for Imaging Data Sampling Bias
DICOM Reports Detection
DICOM Anonymization Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Clinical Data Validation
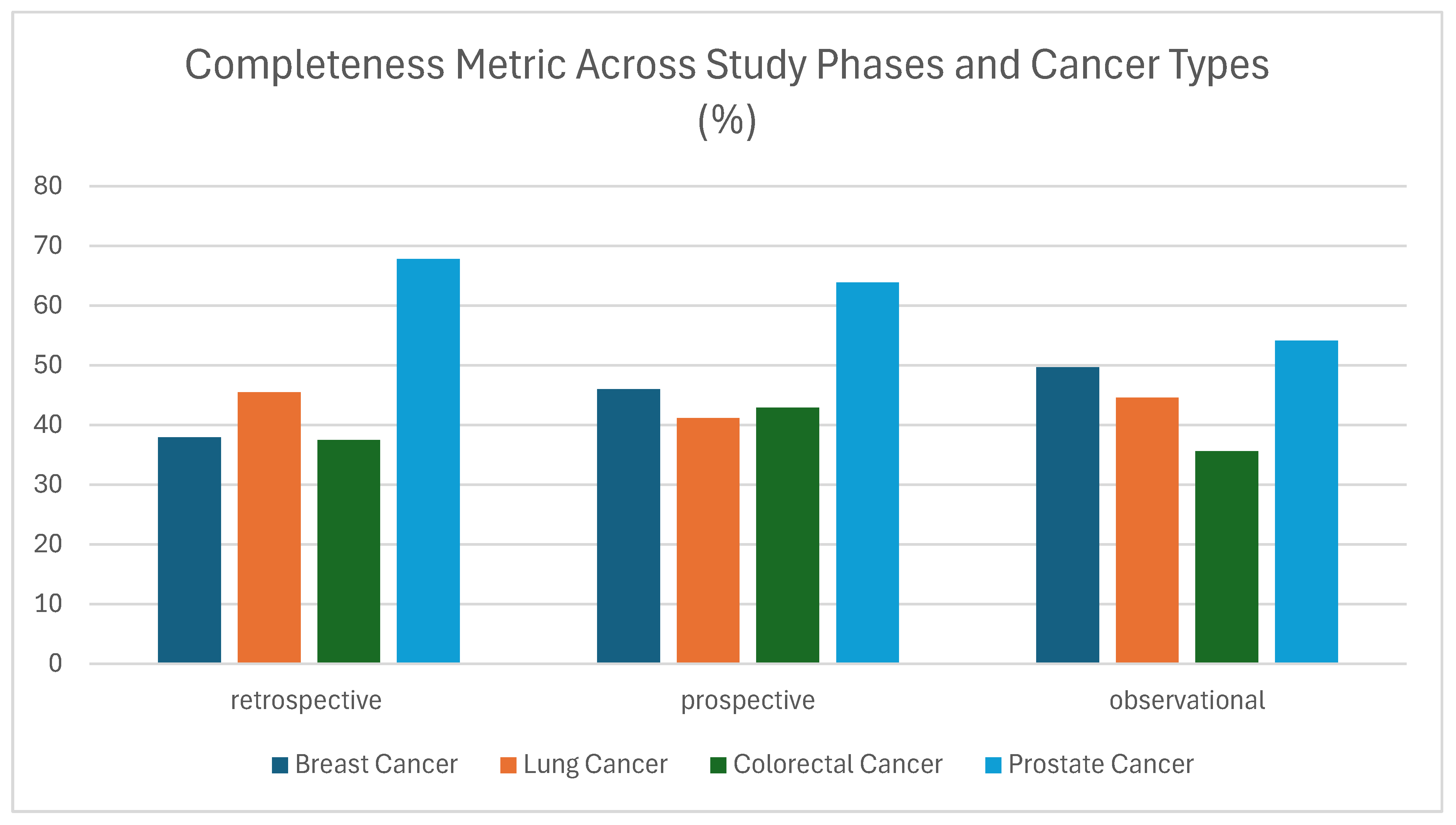
3.1.1. Completeness
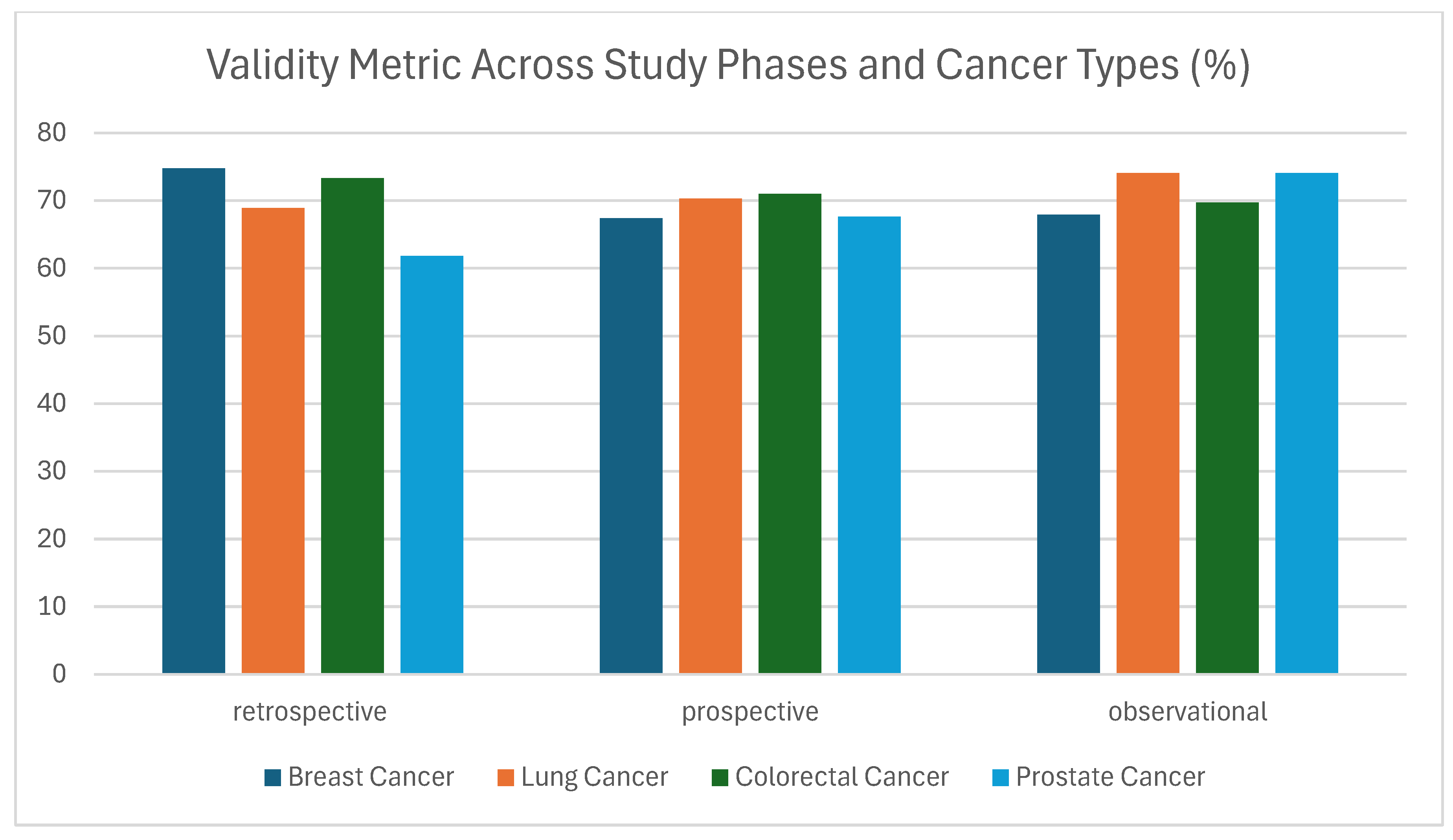
3.1.2. Validity
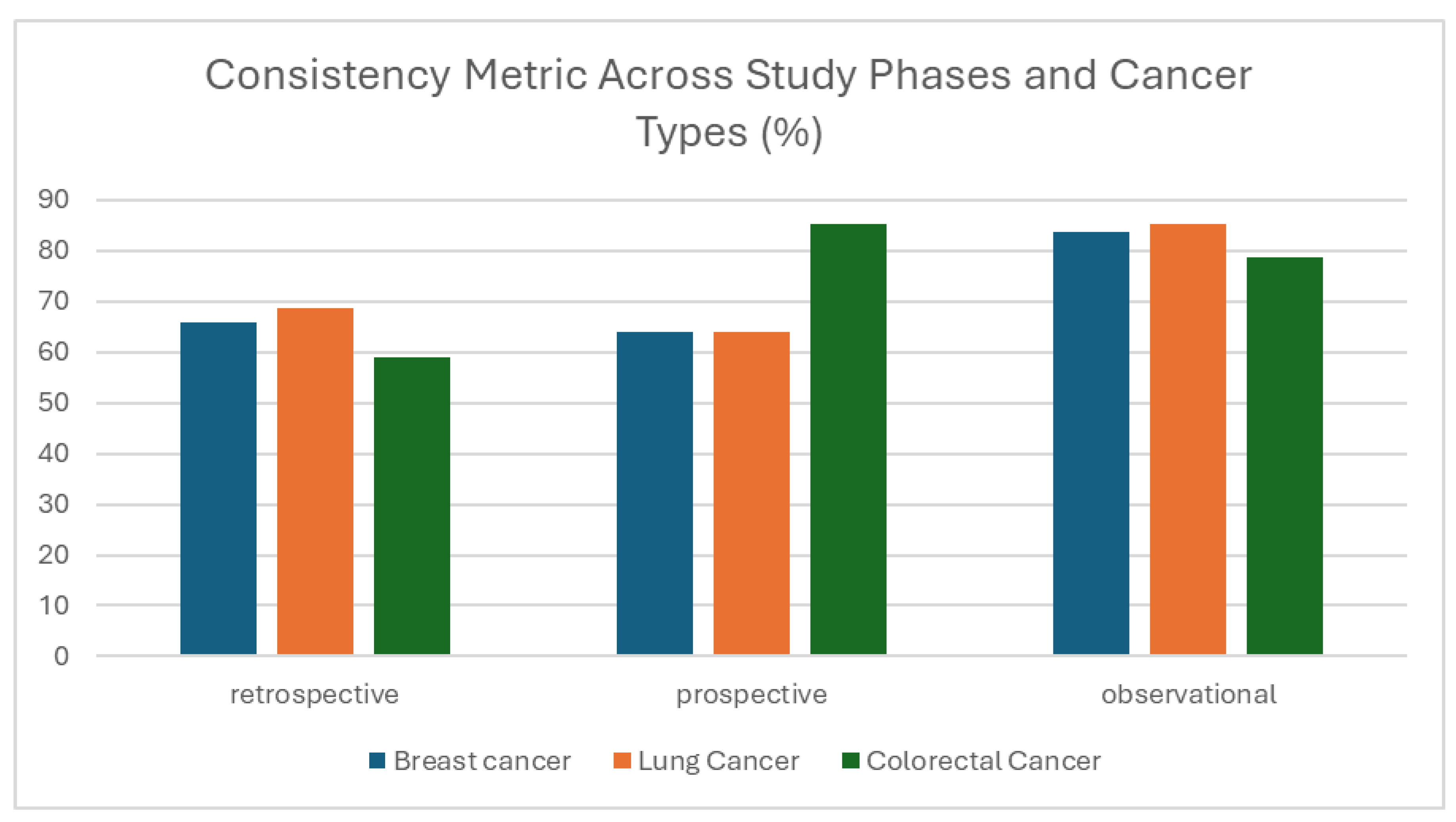
3.1.3. Consistency
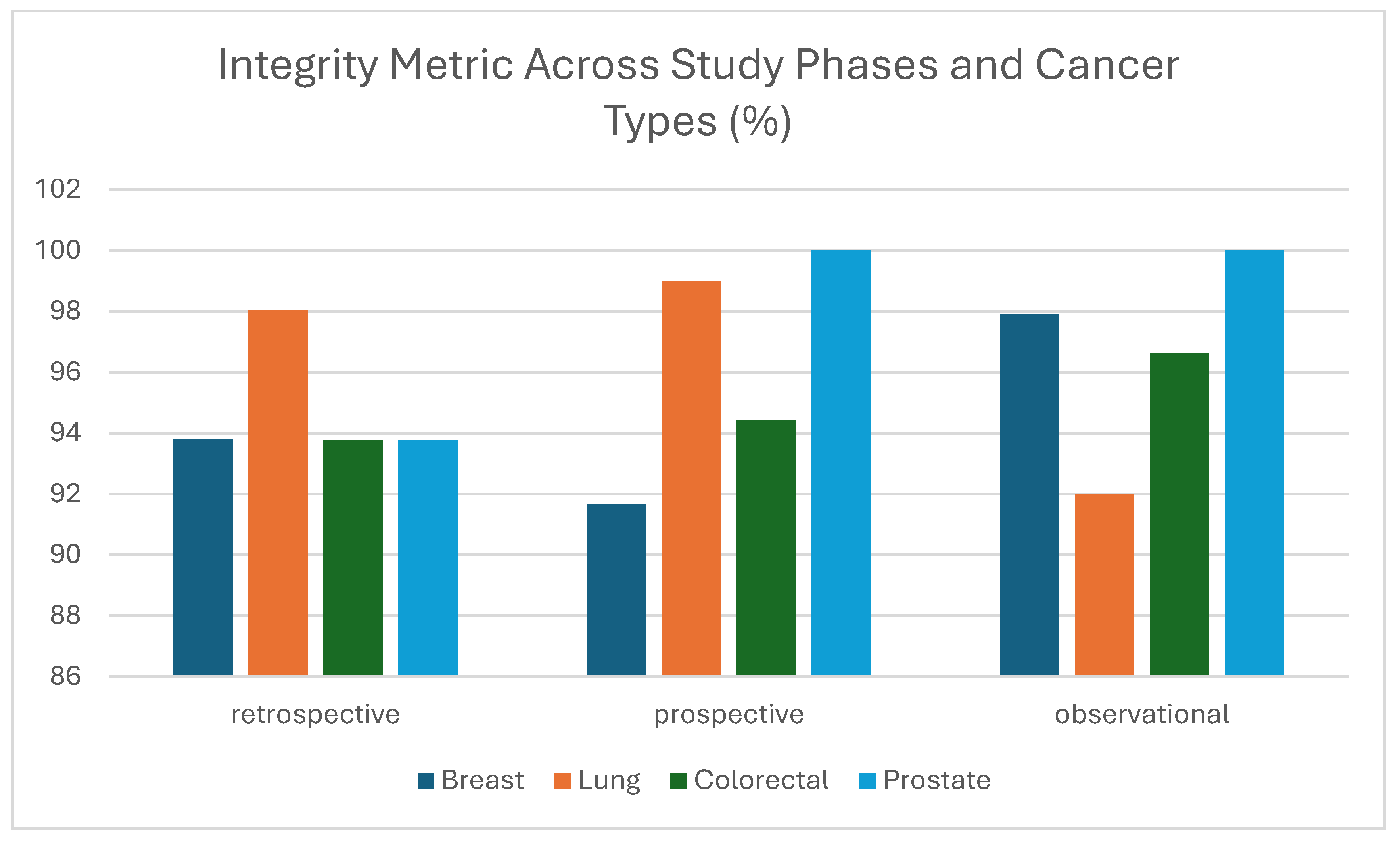
3.1.4. Integrity
3.1.5. Fairness
3.2. Imaging Data Validation
3.2.1. Annotations Results
| Imaging Modality | 1 Timepoint | 2 Timepoints | 3 Timepoints | 4 Timepoints | 5 Timepoints | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast | CT | 43 | 19 | 8 | 2 | 0 |
| FUSCT | 125 | 11 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| FUSPT | 127 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| MG | 94 | 22 | 3 | 42 | 0 | |
| MR | 47 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| US | 44 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Lung | CT | 78 | 39 | 27 | 13 | 1 |
| FUSCT | 283 | 21 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| FUSPT | 242 | 16 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| Xray | 1899 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |
| Colorectal | CT | 66 | 16 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| FUSCT | 98 | 12 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| FUSPT | 91 | 15 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| MR | 28 | 16 | 4 | 23 | 0 | |
| Prostate | MR | 420 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
3.2.2. Imaging Data Sampling Bias Analysis
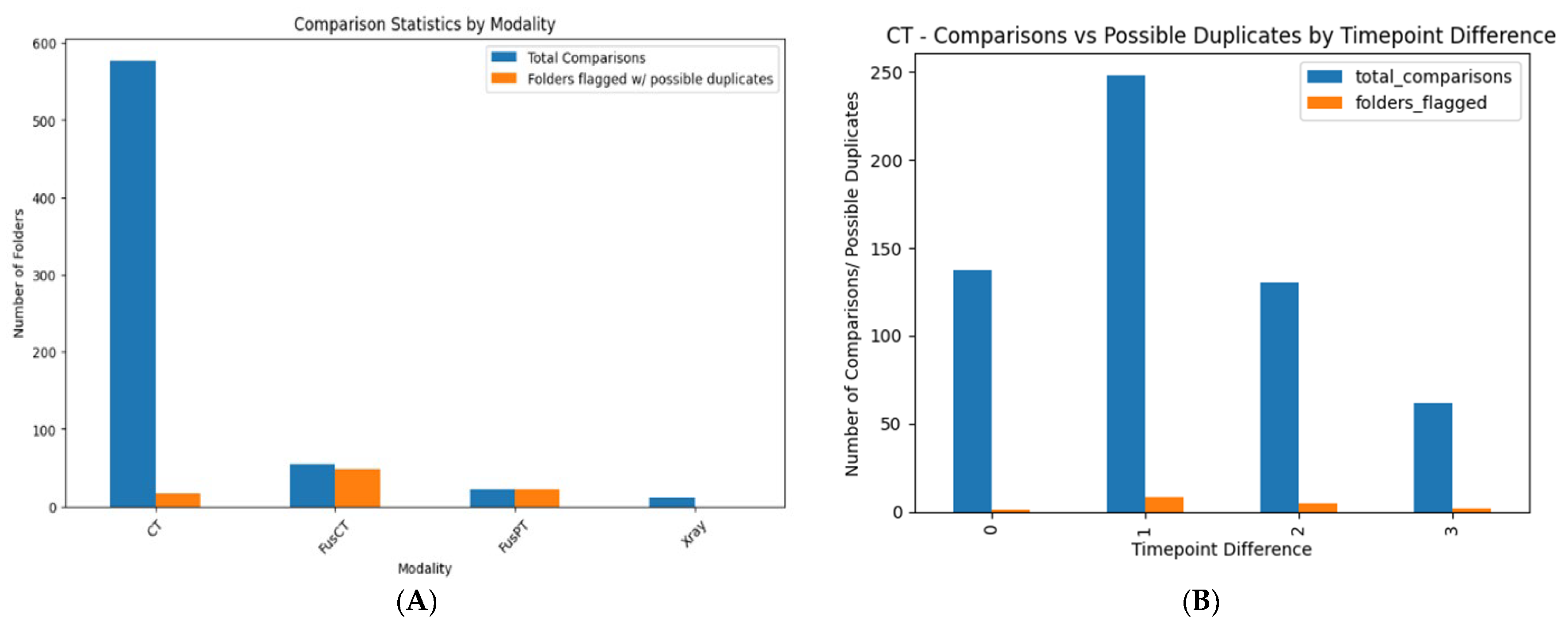
3.2.3. Duplication-Image Similarity Detection
Intra-Directory Analysis
Inter-Directory Analysis
3.2.4. Anonymization
3.2.5. Identification of DICOM Reports
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| DIQCT | Data Integration Quality Check Tool |
| DP | Data Provider |
| HER | Electronic Health Record |
| FNs | Federated Nodes |
| HCP | Healthcare Professional |
| IDC | Invasive Ductal Carcinoma |
| INCISIVE | A European Project on AI in Cancer Imaging |
| ITK-SNAP | Interactive Toolkit for Segmentation of 3D Medical Images |
| MG | Mammography |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NIfTI | Neuroimaging Informatics Technology Initiative |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication System |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| SOP | Standard Operating Procedure |
| UID | Unique Identifier |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| X-ray | X-radiation |
References
- Available online: https://www.who.int/ (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, D.A.; Lennerz, J.K. Technology and Future of Multi-Cancer Early Detection. Life 2024, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhinder, B.; Gilvary, C.; Madhukar, N.S.; Elemento, O. Artificial Intelligence in Cancer Research and Precision Medicine. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 900–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, M.; Zare, Z.; Mojtabaeian, S.M.; Izadi, R. Artificial Intelligence and Decision-Making in Healthcare: A Thematic Analysis of a Systematic Review of Reviews. Health Serv. Res. Manag. Epidemiol. 2024, 11, 23333928241234863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.O.; Struckmann, S.; Enzenbach, C.; Reineke, A.; Stausberg, J.; Damerow, S.; Huebner, M.; Schmidt, B.; Sauerbrei, W.; Richter, A. Facilitating harmonized data quality assessments. A data quality framework for observational health research data collections with software implementations in R. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Cortes, A.; Didonè, F.; Botta, L.; Hjalgrim, L.L.; Jakab, Z.; Nieto, A.C.; Stiller, C.; Zeller, B.; Gatta, G.; Pritchard-Jones, K. Cancer Data Quality and Harmonization in Europe: The Experience of the BENCHISTA Project—International Benchmarking of Childhood Cancer Survival by Stage. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1232451, Erratum in Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1397101. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1397101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Warzel, D.; Eftekhari, A.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.; Knable, J.; Sharma, A.; Jacobs, P. Call for Data Standardization: Lessons Learned and Recommendations in an Imaging Study. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2019, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessach, D.; Shmueli, E. A review on fairness in machine learning. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2022, 55, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.L.; Hosny, A.; Schabath, M.B.; Giger, M.L.; Birkbak, N.J.; Mehrtash, A.; Allison, T.; Arnaout, O.; Abbosh, C.; Dunn, I.F.; et al. Artificial intelligence in cancer imaging: Clinical challenges and applications. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High Level Expert Group on Artificial Intelligence. Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; Available online: https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/ethics-guidelines-trustworthy-ai (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Brancato, V.; Esposito, G.; Coppola, L.; Cavaliere, C.; Mirabelli, P.; Scapicchio, C.; Borgheresi, R.; Neri, E.; Salvatore, M.; Aiello, M. Standardizing digital biobanks: Integrating imaging, genomic, and clinical data for precision medicine. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, R. Chapter 12—Data Integration Processes. In Business Intelligence Guidebook; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 301–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woznicki, P.; Laqua, F.C.; Al-Haj, A.; Bley, T.; Baeßler, B. Addressing challenges in radiomics research: Systematic review and repository of open-access cancer imaging datasets. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylolypavan, A.; Sleeman, D.; Wu, H.; Sim, M. The impact of inconsistent human annotations on AI driven clinical decision making. npj Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazic, I.; Agullo, F.; Ausso, S.; Alves, B.; Barelle, C.; Berral, J.L.; Bizopoulos, P.; Bunduc, O.; Chouvarda, I.; Dominguez, D.; et al. The Holistic Perspective of the INCISIVE Project—Artificial Intelligence in Screening Mammography. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsave, O.; Kosvyra, A.; Filos, D.; Lazic, I.; Loncar-Turukalo, T.; Jakovljevic, N.; Xinou, E.; Fotopoulos, D.; Zacharias, L.; Nabhani-Gebara, S.; et al. Data Validation in Cancer Imaging Repositories: The INCISIVE Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE EMBS Special Topic Conference on Data Science and Engineering in Healthcare, Medicine and Biology, St. Julians, Malta, 7–9 December 2023; pp. 75–76. [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe, D.; Becker, K.; Seyferth, M.; Klaß, A.; Schaeffter, T. The METRIC-framework for assessing data quality for trustworthy AI in medicine: A systematic review. npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Del Ser, J.; Walsh, S.; Schönlieb, C.; Roberts, M.; Selby, I.; Howard, K.; Owen, J.; Neville, J.; Guiot, J.; et al. Data harmonisation for information fusion in digital healthcare: A state-of-the-art systematic review, meta-analysis and future research directions. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sourlos, N.; Vliegenthart, R.; Santinha, J.; Klontzas, M.E.; Cuocolo, R.; Huisman, M.; van Ooijen, P. Recommendations for the creation of benchmark datasets for reproducible artificial intelligence in radiology. Insights Into Imaging 2024, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouten, D.; Nicoletti, G.; Dille, B.; Chia, C.; Vendittelli, P.; Schuurmans, M.; Litjens, G.; Khalili, N. Navigating the landscape of multimodal AI in medicine: A scoping review on technical challenges and clinical applications. Med. Image Anal. 2025, 105, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mortanges, A.P.; Luo, H.; Shu, S.Z.; Kamath, A.; Suter, Y.; Shelan, M.; Pöllinger, A.; Reyes, M. Orchestrating explainable artificial intelligence for multimodal and longitudinal data in medical imaging. npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandoubi, B.; Akhloufi, M.A. Multimodal Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnostics. Information 2025, 16, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Yao, Q.; Li, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, S.K. Addressing fairness issues in deep learning-based medical image analysis: A systematic review. npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drukker, K.; Chen, W.; Gichoya, J.W.; Gruszauskas, N.P.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Koyejo, S.; Myers, K.J.; Sá, R.C.; Sahiner, B.; Whitney, H.M.; et al. Toward fairness in artificial intelligence for medical image analysis: Identification and mitigation of potential biases in the roadmap from data collection to model deployment. J. Med. Imaging 2023, 10, 061104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Yao, Q.; Qi, D.; Zhou, S.K.; Li, X. FairMedFM: Fairness benchmarking for medical imaging foundation models. NeurIPS Datasets & Benchmarks Track. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 111318–111357. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, J.A.; Morgan, K.R.; Konkel, B.; Abdullah, K.; Martin, M.; Ennis, C.; Lo, J.Y.; Stroo, M.; Snyder, D.C.; Bashir, M.R. A Method for Efficient De-identification of DICOM Metadata and Burned-in Pixel Text. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vcelak, P.; Kryl, M.; Kratochvil, M.; Kleckova, J. Identification and classification of DICOM files with burned-in text content. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 126, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheibner, J.; Raisaro, J.L.; Troncoso-Pastoriza, J.R.; Ienca, M.; Fellay, J.; Vayena, E.; Hubaux, J.P. Revolutionizing Medical Data Sharing Using Advanced Privacy-Enhancing Technologies: Technical, Legal, and Ethical Synthesis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e25120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choplin, R.H.; Boehme, J.M.; Maynard, C.D. Picture archiving and communication systems: An overview. RadioGraphics 1992, 12, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fass, L. Imaging and cancer: A review. Mol. Oncol. 2008, 2, 115–152, Erratum in Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 2896. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.13283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITK-Snap, version 3.8.0. 2019. Available online: http://www.itksnap.org/pmwiki/pmwiki.php?n=Downloads.SNAP3 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Kosvyra, A.; Filos, D.T.; Fotopoulos, D.T.; Tsave, O.; Chouvarda, I. Toward Ensuring Data Quality in Multi-Site Cancer Imaging Repositories. Information 2024, 15, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosvyra, A.; Filos, D.; Fotopoulos, D.; Tsave, O.; Chouvarda, I. Data Quality Check in Cancer Imaging Research: Deploying and Evaluating the DIQCT Tool. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 1053–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, M.G.; Callahan, T.J.; Barnard, J.; Bauck, A.E.; Brown, J.; Davidson, B.N.; Estiri, H.; Goerg, C.; Holve, E.; Johnson, S.G.; et al. A Harmonized Data Quality Assessment Terminology and Framework for the Secondary Use of Electronic Health Record Data. eGEMs 2016, 4, 18–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, F. Methods for Data Quality Studies. In Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-Based Approach; Lau, F., Kuziemsky, C., Eds.; University of Victoria: Victoria, BC, USA, 2016; pp. 277–291. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/doceo/document/TA-9-2024-0331-FNL-COR01_EN.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- QUANTUM: Developing A Data Quality and Utility Label for the European Health Data Space. Available online: https://quantumproject.eu/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Available online: https://www.dama-nl.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/DDQ-Dimensions-of-Data-Quality-Research-Paper-version-1.2-d.d.-3-Sept-2020.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Landman, E. difPy: Duplicate Image Finder in Python, version 4.2.0; Python Package Index: Wilmington, DW, USA, 2025. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/difPy/ (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Yang, F.; Zamzmi, G.; Angara, S.; Rajaraman, S.; Aquilina, A.; Xue, Z.; Jaeger, S.; Papagiannakis, E.; Antani, S.K. Assessing Inter-Annotator Agreement for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 21300–21312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, A.; Lewis, E.; Loveland, J. Successes and challenges in extracting information from DICOM image databases for audit and research. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20230104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, D.; Page, C.-E.; Reinartz, S.; Krüger, T.; Deserno, T.M. DICOM for Clinical Research: PACS-Integrated Electronic Data Capture in Multi-Center Trials. J. Digit. Imaging 2015, 28, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pydicom Deid, version 0.3.1; Python Software: Wilmington, DW, USA, 2025. Available online: https://pydicom.github.io/deid/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Weiskopf, N.G.; Weng, C. Methods and dimensions of electronic health record data quality assessment: Enabling reuse for clinical research. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2013, 20, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, D.G.T.; De Keizer, N.F.; Scheffer, G.-J. Defining and Improving Data Quality in Medical Registries: A Literature Review, Case Study, and Generic Framework. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2002, 9, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palis, B.E.; Janczewski, L.M.; Browner, A.E.; Cotler, J.; Nogueira, L.; Richardson, L.C.; Benard, V.; Wilson, R.J.; Walker, N.; McCabe, R.M.; et al. The National Cancer Database Conforms to the Standardized Framework for Registry and Data Quality. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 31, 5546–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, E. Fairness and Bias in Artificial Intelligence: A Brief Survey of Sources, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies. Sci 2024, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulos, D.; Filos, D.; Chouvarda, I. Towards explainable and trustworthy AI for decision support in medicine: An overview of methods and good practices. Aristotle Biomed. J. 2021, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dimension | Definition | Aim | Rule | Record | Metric | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completeness | Wholeness of the data | Identification of gaps or missing information | Mandatory Information & Imaging modalities in diagnosis and one timepoint | Each patient | The percentage of records that are complete | No follow-up information, lack of information availability in EHR |
| Validity | Clinical data conformity to required value attributes | Identification of entries that do not follow predefined rules | Data format, allowable types & value ranges | Each value inserted in the dataset | The percentage of records in which all values are valid | Not confrontation with the defined rules (e.g., Stage: 3 instead of III) |
| Anonymization | Identification of images that do not follow the de-identification protocol | DICOM metadata compared with the de-identification protocol | Each DICOM file | Percentage of DICOM files that do not follow the de-identification profile | DICOM metadata that should have been removed appear in the DICOM file | |
| Consistency | Logical agreement of data across variables and records | Identification of inconsistencies within entries | Sets of entries (longitudinal, cross-linked) | Each value inserted in the dataset | The percentage of the matching values across the dataset | Erroneous cross-linked information (e.g., biological markers inserted, while the ‘Biopsy’ field is marked as ‘No Biopsy’) |
| Annotation | Identification of annotation files that are consistent with the respective imaging data | Annotation ROI and number of slices coincide with the imaging data | Each annotation file | Percentage of annotation files that are consistent with imaging data | ROI in the annotation file and the number of slices are different from the respective imaging series data | |
| Integrity | Accurately joined data references | Identification of inconsistencies in data references | Link between images and clinical metadata | Imaging modalities | The percentage of records properly integrated | Imaging examinations provided do not match insertions in clinical metadata template (e.g., MG was inserted while CT was provided, or 3 modalities were inserted while 4 were provided) |
| Uniqueness | No duplications or overlapping of values across all data sets | Identification of duplicate image files or series. | No duplicate images or series should be provided. | Images | The total number of identified duplicate image files or series within the dataset | Imaging examination series provided multiple times, Same patient imaging examinations provided as different timepoints. |
| Fairness | Balanced representation of subgroups relevant to trustworthy AI | Identification of classes balance | - | Target fields entries | The percentage of each class representation. | Comparable distribution across sex, age groups, cancer subtypes, etc. |
| DICOM bias | Identification of imaging characteristics | - | Target imaging characteristics | Percentage of images that were acquired with specific imaging characteristic | Comparable slice thickness, pixel spacing, ROI or manufacturer scanner. |
| Age Group | DP1 (%) | DP2 (%) | DP3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (20, 25] | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| (25, 30] | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| (30, 35] | 3.57% | 5.0% | 0.0% |
| (35, 40] | 7.14% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| (40, 45] | 0.0% | 10.0% | 8.7% |
| (45, 50] | 14.29% | 15.0% | 4.35% |
| (50, 55] | 7.14% | 20.0% | 0.0% |
| (55, 60] | 10.71% | 5.0% | 8.7% |
| (60, 65] | 14.29% | 20.0% | 21.74% |
| (65, 70] | 10.71% | 15.0% | 21.74% |
| (70, 75] | 10.71% | 5.0% | 17.39% |
| (75, 80] | 17.86% | 5.0% | 0.0% |
| (80, 85] | 3.57% | 0.0% | 13.04% |
| (85, 90] | 0.0% | 0.0% | 4.35% |
| (90, 95] | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Data Provider | Grade 1 (%) | Grade 2 (%) | Grade 3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP1 | 0.0% | 25.0% | 75.0% |
| DP2 | 0.0% | 37.5% | 62.5% |
| DP3 | 0.0% | 77.27% | 22.73% |
| Data Provider | IDC (%) | ILC (%) | IPLC (%) | IMC (%) | IUC (%) | IBC (%) | MPT (%) | SPC (%) | HBOCS (%) | UMN (%) | DCIS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP1 | 90.0% | 10.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| DP2 | 1.96% | 9.8% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 78.43% | 9.8% |
| DP3 | 40.0% | 20.0% | 0.0% | 20.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 20.0% |
| Data Provider | Male (%) | Female (%) |
|---|---|---|
| DP1 | 0.0% | 100.0% |
| DP2 | 0.0% | 100.0% |
| DP3 | 0.0% | 100.0% |
| Age Group | DP1 (%) | DP2 (%) | DP3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (20, 25] | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| (25, 30] | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| (30, 35] | 6.25% | 7.14% | 2.7% |
| (35, 40] | 2.08% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| (40, 45] | 4.17% | 7.14% | 5.41% |
| (45, 50] | 8.33% | 0.0% | 5.41% |
| (50, 55] | 10.42% | 0.0% | 8.11% |
| (55, 60] | 10.42% | 0.0% | 10.81% |
| (60, 65] | 10.42% | 7.14% | 10.81% |
| (65, 70] | 10.42% | 14.29% | 13.51% |
| (70, 75] | 10.42% | 21.43% | 10.81% |
| (75, 80] | 10.42% | 28.57% | 13.51% |
| (80, 85] | 8.33% | 14.29% | 8.11% |
| (85, 90] | 6.25% | 0.0% | 10.81% |
| (90, 95] | 2.08% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Data Provider | Grade 1 (%) | Grade 2 (%) | Grade 3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP1 | 57.14% | 35.71% | 7.14% |
| DP2 | 41.67% | 50.0% | 8.33% |
| Data Provider | Male (%) | Female (%) |
|---|---|---|
| DP1 | 57.5% | 42.5% |
| DP2 | 50.0% | 50.0% |
| DP3 | 58.75% | 41.25% |
| Data Provider | Adenocarcinoma (%) | Squamous (%) | Small-Cell (%) | Large-Cell (%) | Other (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP1 | 88.24% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 11.76% |
| DP2 | 74.36% | 25.64% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Age Group | DP1 (%) | DP2 (%) | DP3 (%) | DP4 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (20, 25] | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| (25, 30] | 0.0% | 4.44% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| (30, 35] | 0.0% | 2.22% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| (35, 40] | 0.0% | 2.22% | 5.26% | 0.0% |
| (40, 45] | 0.0% | 4.44% | 7.89% | 0.0% |
| (45, 50] | 0.0% | 4.44% | 7.89% | 10.0% |
| (50, 55] | 11.11% | 6.67% | 10.53% | 0.0% |
| (55, 60] | 22.22% | 11.11% | 10.53% | 10.0% |
| (60, 65] | 11.11% | 11.11% | 10.53% | 0.0% |
| (65, 70] | 0.0% | 11.11% | 13.16% | 30.0% |
| (70, 75] | 22.22% | 11.11% | 10.53% | 30.0% |
| (75, 80] | 33.33% | 11.11% | 10.53% | 20.0% |
| (80, 85] | 0.0% | 11.11% | 7.89% | 0.0% |
| (85, 90] | 0.0% | 8.89% | 5.26% | 0.0% |
| (90, 95] | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Data Provider | Grade 1 (%) | Grade 2 (%) | Grade 3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP1 | 0.0% | 100.0% | 0.0% |
| DP2 | 0.0% | 57.14% | 42.86% |
| Data Provider | Adenocarcinoma (%) | Squamous (%) | Small-Cell (%) | Large-Cell (%) | Other (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP1 | 40.0% | 40.0% | 20.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| DP2 | 12.5% | 25.0% | 0.0% | 12.5% | 50.0% |
| DP3 | 50.0% | 30.0% | 20.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Data Provider | Male (Normalized %) | Female (Normalized %) |
|---|---|---|
| DP1 | 100.0% | 0.0% |
| DP2 | 60.0% | 40.0% |
| DP3 | 28.57% | 71.43% |
| DP4 | 62.67% | 37.33% |
| Age Group | DP2_1 (Normalized %) | DP2_2 (Normalized %) |
|---|---|---|
| (20, 25] | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| (25, 30] | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| (30, 35] | 4.17 | 0.0 |
| (35, 40] | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| (40, 45] | 4.17 | 0.0 |
| (45, 50] | 4.17 | 4.0 |
| (50, 55] | 8.33 | 16.0 |
| (55, 60] | 12.5 | 16.0 |
| (60, 65] | 20.83 | 20.0 |
| (65, 70] | 16.67 | 20.0 |
| (70, 75] | 12.5 | 16.0 |
| (75, 80] | 12.5 | 8.0 |
| (80, 85] | 4.17 | 0.0 |
| (85, 90] | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| (90, 95] | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Cancer Grade | DP (Normalized %) |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | 32.08 |
| 2.0 | 27.36 |
| 3.0 | 18.87 |
| 4.0 | 16.98 |
| 5.0 | 4.72 |
| Breast | Lung | Colorectal | Prostate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | M: 29.6—B: 35.6 (n = 135) | M: 98.4—B: 1.6 (n = 310) | M: 73.8—B: 26.2 (n = 141) | |
| MR | M: 52.1—B: 22.8 (n = 215) | M: 68.2—B: 31.8 (n = 110) | M: 85.7—B:14.3 (n = 21) | |
| FusCT | M: 77.1—B: 17.4 (n = 144) | M: 94.4—B: 5.6 (n = 339) | M: 97.5—B: 2.5 (n = 121) | |
| FusPT | M: 77.7—B: 17.8 (n = 146) | M: 94.4—B: 5.6 (n = 287) | M: 99.1—B: 0.9 (n = 110) | |
| XRAY | M: 24.4—B: 0 (n = 123) | |||
| MG | M: 7.7—B: 22.9 (n = 1128) | |||
| US | M: 46.6—B: 26.4 (n = 178) |
| Slice Thickness | Pixel Spacing | ROI | Manufacturer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | Breast | 3 [2 3.75] | 0.98 [0.79 1.37] | 512 [512 512] 512 [512 512] | GE: 46.6% Siemens: 46% Other: 7.4% |
| Lung | 2 [1.5 3.75] | 0.98 [0.75 1.37] | 512 [512 512] 512 [512 512] | GE: 45.3% Philips: 13.7% Siemens: 34.7% Other: 6.3% | |
| Colorectal | 3 [1.5 5] | 0.81 [0.73 0.98] | 512 [512 512] 512 [512 512] | GE: 50.2% Siemens: 42.1% Philips: 6.2% Other: 1.5% | |
| PT | Breast | 3.27 [3.26 3.27] | 2.74 [2.74 4.69] | 256 [128 256] 256 [128 256] | GE:87.3% Siemens:12.7% |
| Lung | 3.26 [3.26 3.27] | 2.74 [2.74 2.74] | 256 [256 256] 256 [256 256] | GE: 81.6% Philips: 18.4% | |
| Colorectal | 3.27 [3.27 5.00] | 4 [2.74 4.1] | 168 [144 256] 168 [144 256] | GE: 55% Siemens: 30% Philips: 15% | |
| MR | Breast | 7.5 [5.5 7.5] | 0.68 [0.65 0.78] | 512 [320 512] 512 [448 512] | GE: 1% Siemens: 98.5% Other: 0.5% |
| Colorectal | 6.6 [5 7.7] | 1 [0.78 1.4] | 288 [216 448] 320 [256 448] | GE: 1.8% Philips: 7.2% Siemens: 91% | |
| Prostate | 3 [3 3.3] | 1.63 [0.59 2.36] | 136 [110 512] 160 [110 512] | GE: 20.8% Philips: 9% Siemens: 64.3% Other: 5.9% |
| Total number of directories (patients) examined | 60 | |
| Total number of individual folders compared | 436 | |
| Instances similar images were found | 186 | |
| Comparisons count grouped by modality: (total number of examinations/number of folders similar images found) | ||
| CT | 237 | 35 |
| FusCT | 85 | 82 |
| FusPT | 69 | 69 |
| X-ray | 45 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsave, O.; Kosvyra, A.; Filos, D.T.; Fotopoulos, D.T.; Chouvarda, I. A Multi-Dimensional Framework for Data Quality Assurance in Cancer Imaging Repositories. Cancers 2025, 17, 3213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193213
Tsave O, Kosvyra A, Filos DT, Fotopoulos DT, Chouvarda I. A Multi-Dimensional Framework for Data Quality Assurance in Cancer Imaging Repositories. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193213
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsave, Olga, Alexandra Kosvyra, Dimitrios T. Filos, Dimitris Th. Fotopoulos, and Ioanna Chouvarda. 2025. "A Multi-Dimensional Framework for Data Quality Assurance in Cancer Imaging Repositories" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193213
APA StyleTsave, O., Kosvyra, A., Filos, D. T., Fotopoulos, D. T., & Chouvarda, I. (2025). A Multi-Dimensional Framework for Data Quality Assurance in Cancer Imaging Repositories. Cancers, 17(19), 3213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193213






