Comparative Analysis of Manual ELISA and Ella, an Automated Instrument for ELISA, in Measuring Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Breast Cancer Patient Samples
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
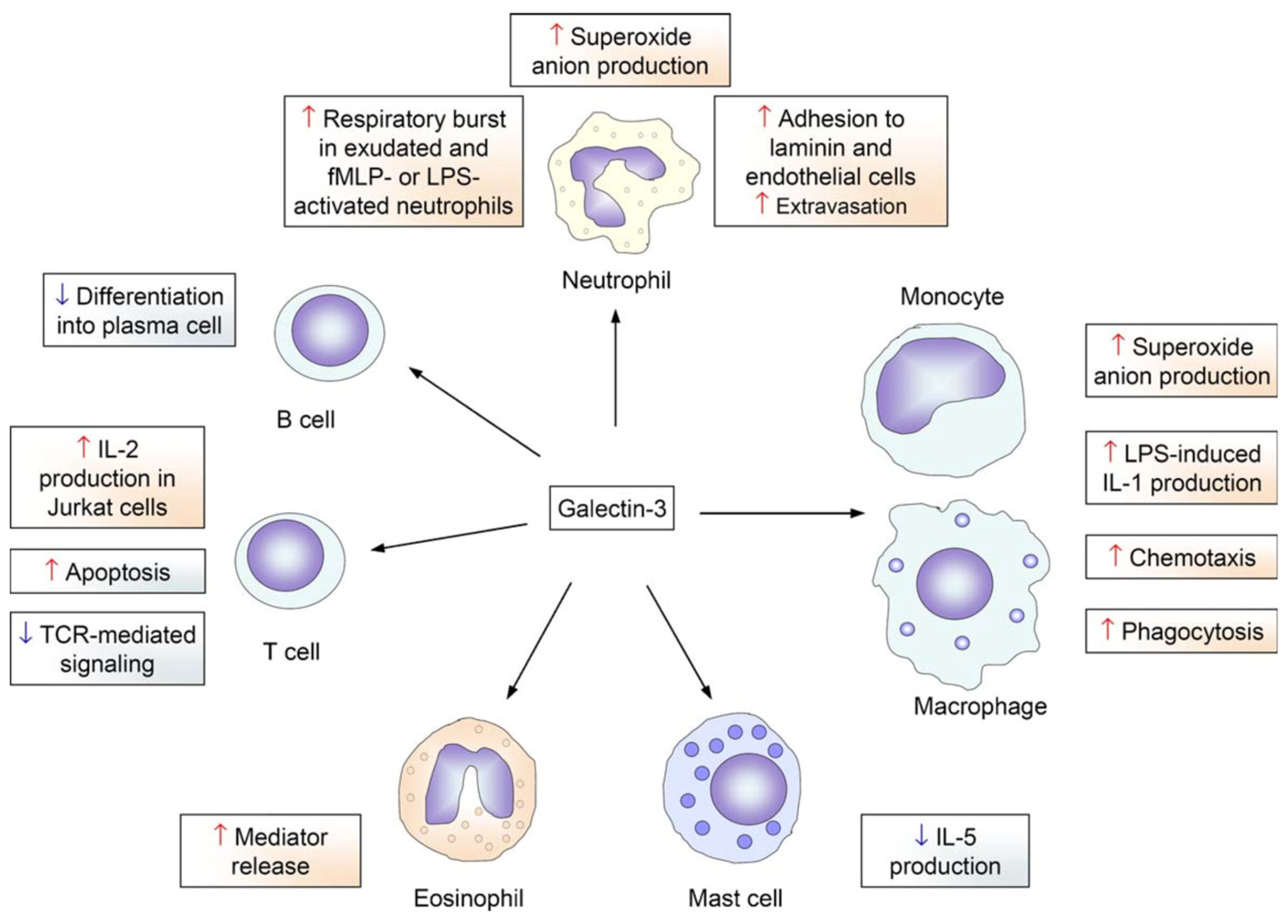
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Sample Collection
2.2. Measurement of Serum Galectin-3 Levels Using ELISA Technology
2.3. Measurement of Serum Galectin-3 Levels Using the Automated Ella System
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Breast Cancer Patient Sample Group
3.2. Measurement Characteristics of Galectin-3 in ELISA and Ella Platforms
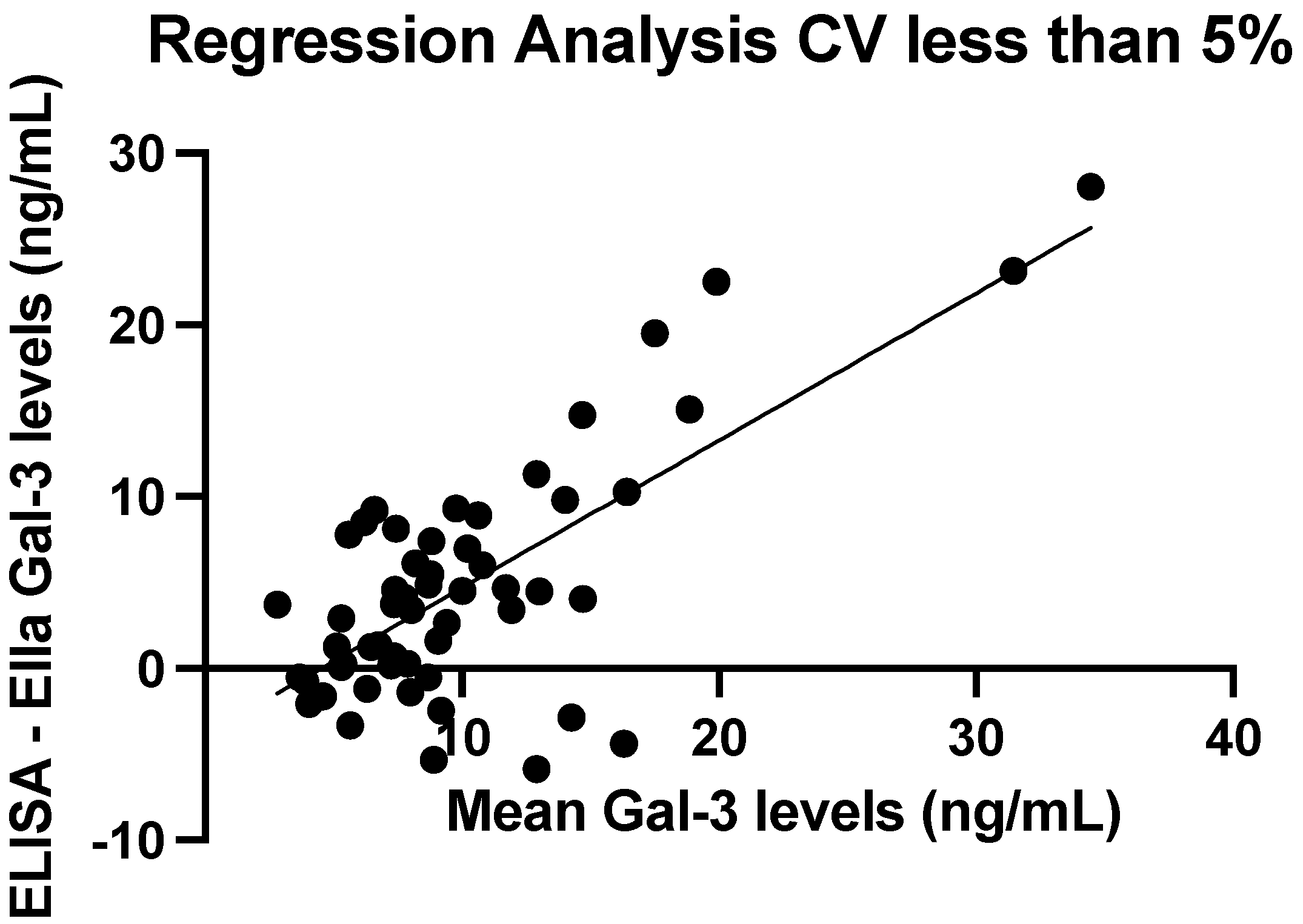
3.3. Quantification of Assay Precision
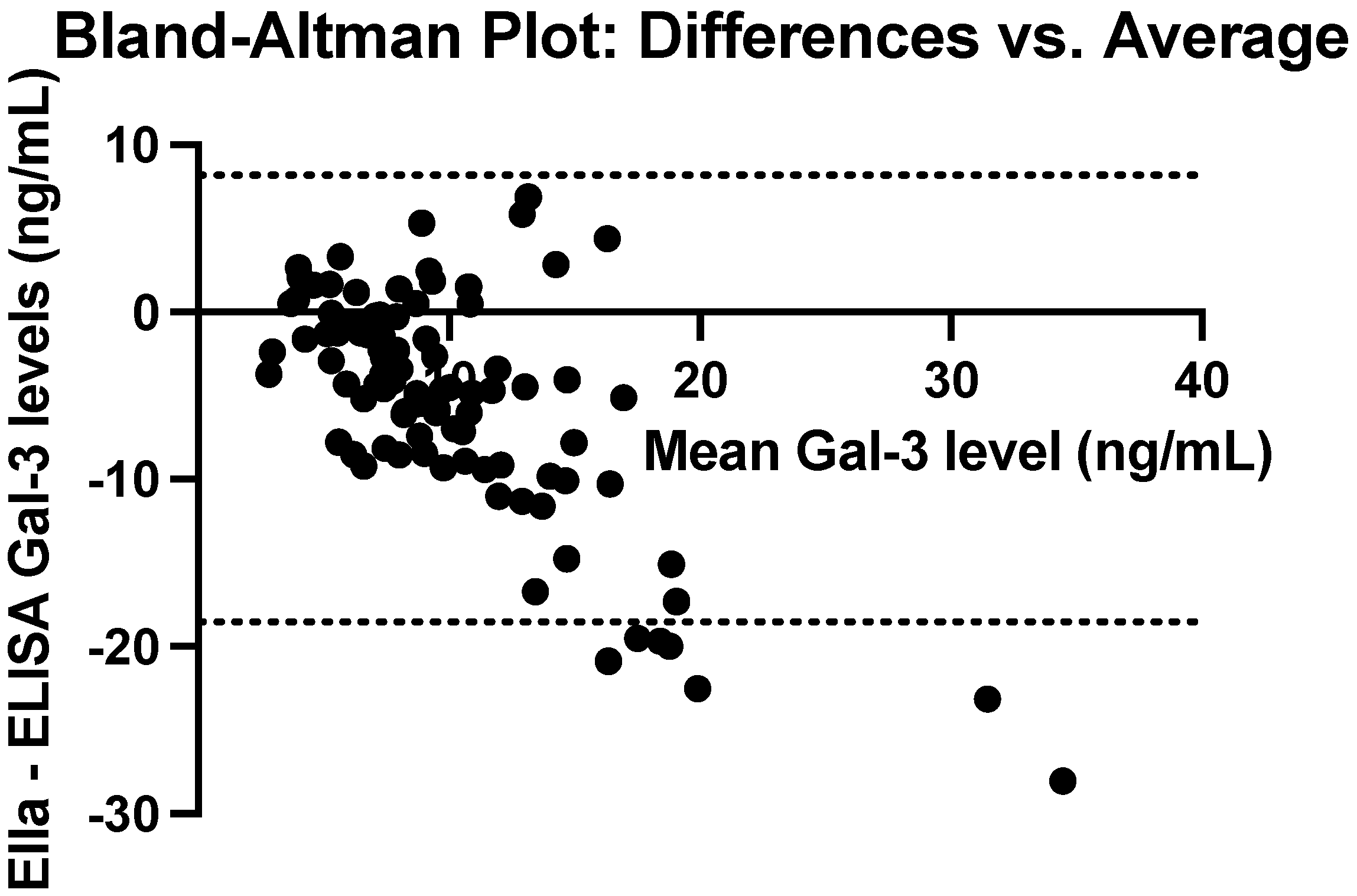
3.4. Comparison of ELISA and Ella Measurements of Galectin-3 Levels
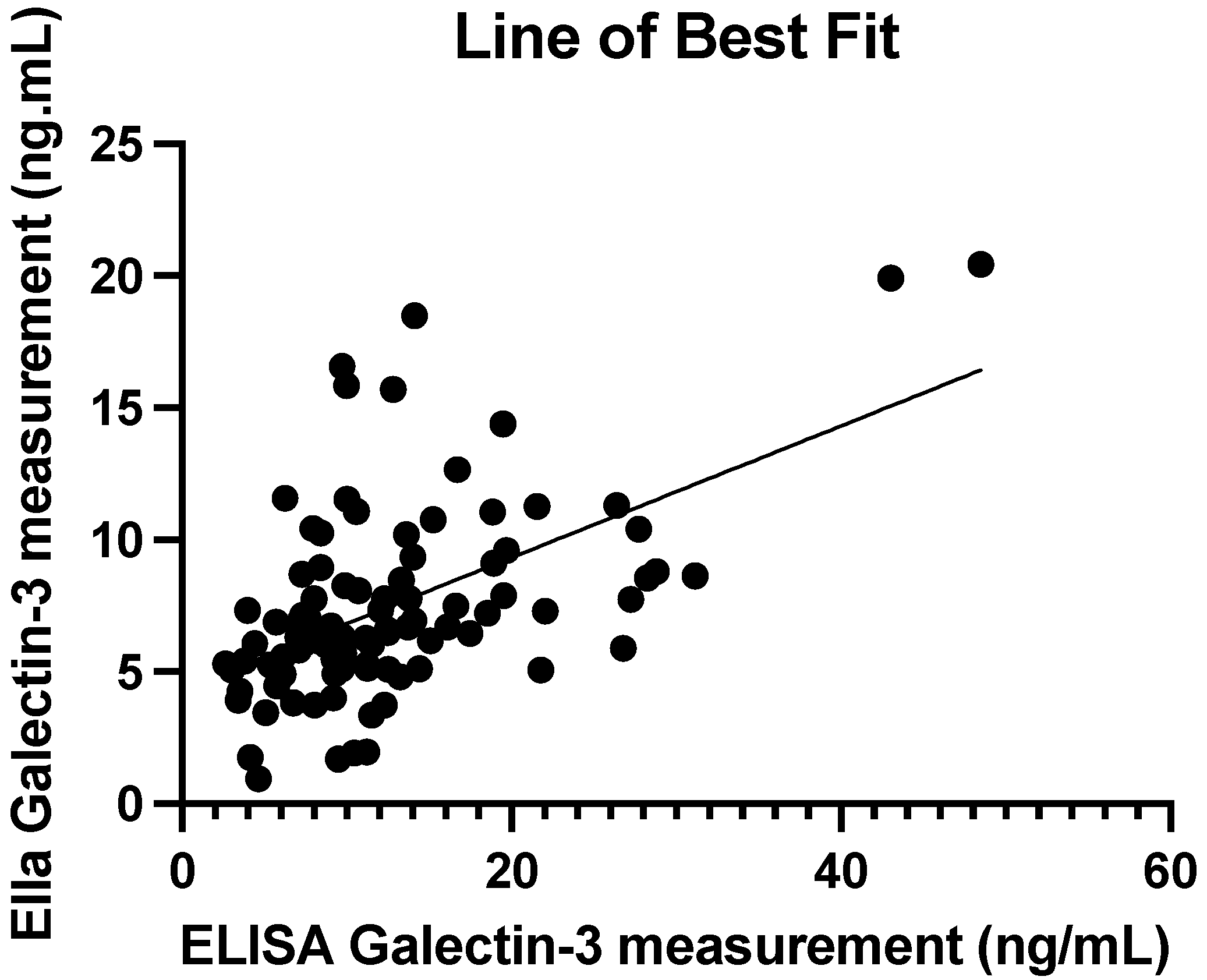
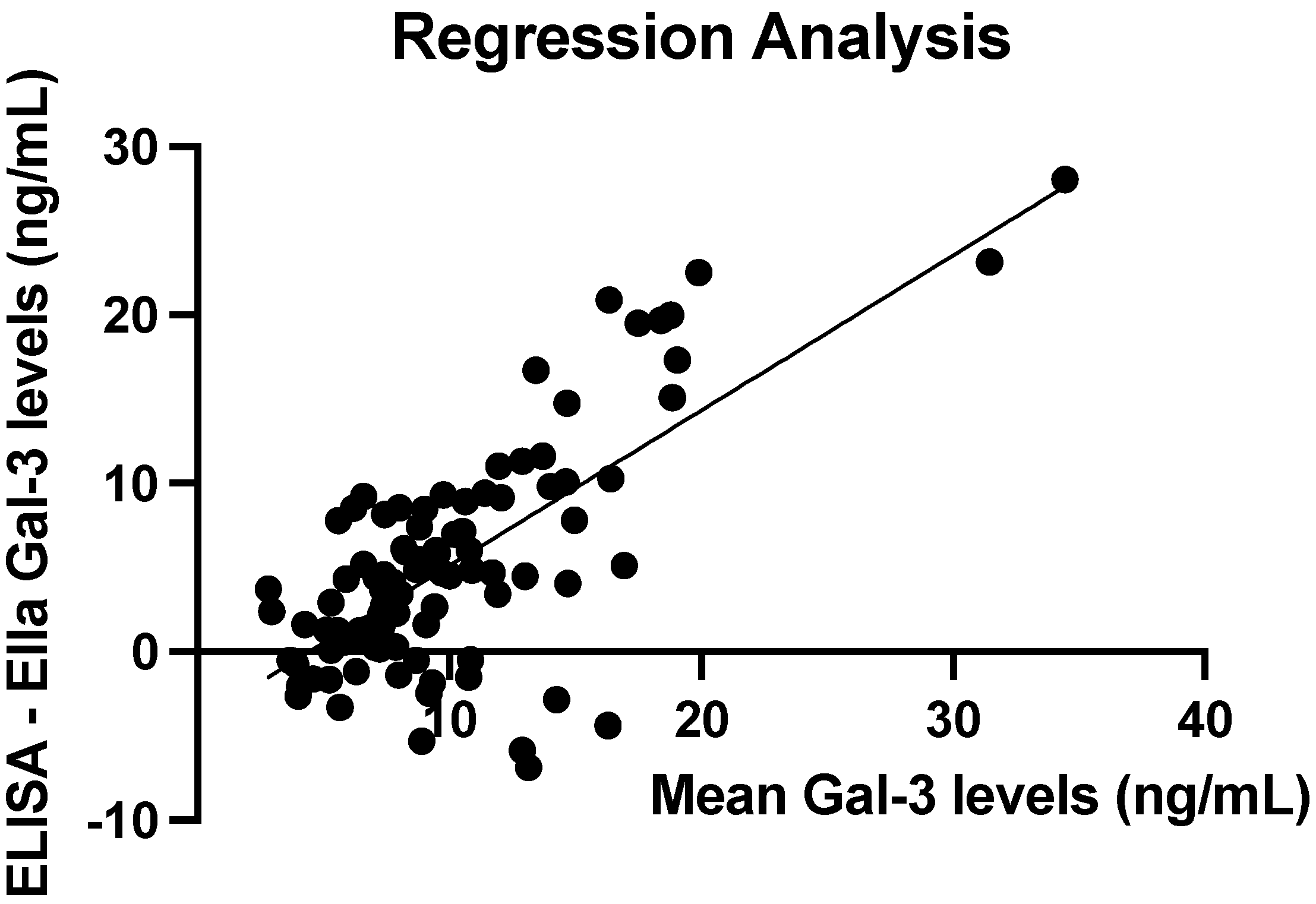
3.5. ELISA vs. Ella Measurements: Regression Line
3.6. Comparison of ELISA and Ella Measurements by Breast Cancer Stage
3.7. Comparison of ELISA and Ella Measurements by Breast Cancer Immunophenotype
3.8. Comparison of ELISA and Ella Measurements by Breast Cancer Histology
4. Discussion
4.1. Study Findings
4.2. Implications
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCL2 | Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand 2 |
| CD45 | Leukocyte Common Antigen |
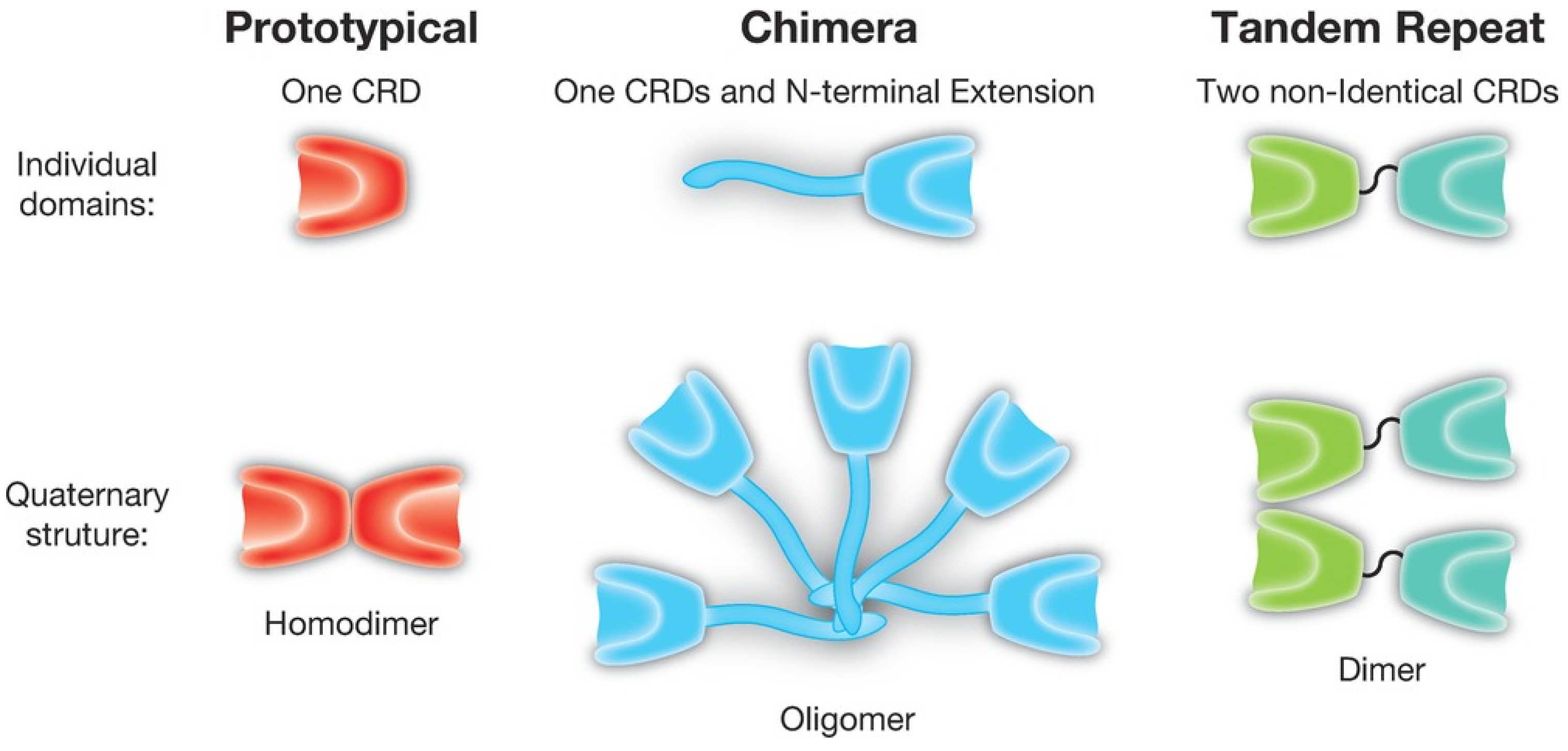
| CRD | Carbohydrate Recognition Domain |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| DCIS | Ductal Carcinoma in Situ |
| ELISA | Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| Gal-3 | Galectin-3 |
| HER2 | Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 |
| MEK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase |
| NOTCH-1 | Neurogenic Locus Notch Homolog Protein 1 |
| PHCI | Prisma Health Cancer Institute |
| Raf | Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma |
| Ras | Rat Sarcoma |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| VEGF-A | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A |
| VEGFR2 | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Receptor 2 |
References
- Liu, F.T.; Patterson, R.J.; Wang, J.L. Intracellular functions of galectins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1572, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nio-Kobayashi, J. Tissue- and cell-specific localization of galectins, β-galactose-binding animal lectins, and their potential functions in health and disease. Anat. Sci. Int. 2017, 92, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamili, N.A.; Arthur, C.M.; Gerner-Smidt, C.; Tafesse, E.; Blenda, A.; Dias-Baruffi, M.; Stowell, S.R. Key regulators of galectin—glycan interactions. Proteomics 2016, 16, 3111–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Alvarez, L.; Ortega, E. The Many Roles of Galectin-3, a Multifaceted Molecule, in Innate Immune Responses against Pathogens. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9247574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Stowell, S.R. The role of galectins in immunity and infection. Nature reviews. Immunology 2023, 23, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadón, A.; Castellano, V.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R. Chapter 55—Biomarkers in drug safety evaluation. In Biomarkers in Toxicology; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 923–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haudek, K.C.; Spronk, K.J.; Voss, P.G.; Patterson, R.J.; Wang, J.L.; Arnoys, E.J. Dynamics of Galectin-3 in the Nucleus and Cytoplasm. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1800, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, Y. Emerging roles of Galectin-3 in diabetes and diabetes complications: A snapshot. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-J.; Yu, G.-F.; Jie, Y.-Q.; Fan, X.-F.; Huang, Q.; Dai, W.-M. Role of galectin-3 in plasma as a predictive biomarker of outcome after acute intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 368, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanda, V.; Bracale, U.M.; Di Taranto, M.D.; Fortunato, G. Galectin-3 in Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, L.; Dépret, F.; Gayat, E.; Legrand, M.; Chadjichristos, C.E. Galectin-3 in Kidney Diseases: From an Old Protein to a New Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aureli, A.; Del Cornò, M.; Marziani, B.; Gessani, S.; Conti, L. Highlights on the Role of Galectin-3 in Colorectal Cancer and the Preventive/Therapeutic Potential of Food-Derived Inhibitors. Cancers 2022, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, B.B.; Funkhouser, A.T.; Goodwin, J.L.; Strigenz, A.M.; Chaballout, B.H.; Martin, J.C.; Arthur, C.M.; Funk, C.R.; Edenfield, W.J.; Blenda, A.V. Increased Circulating Levels of Galectin Proteins in Patients with Breast, Colon, and Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, T.S.; Oshima, C.T.F.; Forones, N.M.; Lima, F.D.O.; Ribeiro, D.A. Expression of galectin-3 in gastric adenocarcinoma. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 140, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.Y.; Hsu, D.K.; Liu, F.T. Expression of galectin-3 modulates T-cell growth and apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6737–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, H.-G.; Goedegebuure, P.S.; Sadanaga, N.; Nagoshi, M.; Von Bernstorff, W.; Eberlein, T.J. Expression and function of galectin-3, a β-galactoside-binding protein in activated T lymphocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigeri, L.G.; Zuberi, R.I.; Liu, F.T. Epsilon BP, a beta-galactoside-binding animal lectin, recognizes IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) and activates mast cells. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 7644–7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, A.-C.D.; Sun, R.; Choi, H.; Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L. Role of Galectin-3 in Classical and Alternative Macrophage Activation in the Liver following Acetaminophen Intoxication. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5934–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, A.; Kuwabara, I.; Frigeri, L.G.; Liu, F.T. A human lectin, galectin-3 (epsilon bp/Mac-2), stimulates superoxide production by neutrophils. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 3479–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagher, S.F.; Wang, J.L.; Patterson, R.J. Identification of galectin-3 as a factor in pre-mRNA splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumic, J.; Dabelic, S.; Flögel, M. Galectin-3: An open-ended story. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2006, 1760, 616–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, A.; Lotan, R. Endogenous galactoside-binding lectins: A new class of functional tumor cell surface molecules related to metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1987, 6, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.C.F.; Andrade, L.N.d.S.; Bustos, S.O.; Chammas, R. Galectin-3 Determines Tumor Cell Adaptive Strategies in Stressed Tumor Microenvironments. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funasaka, T.; Raz, A.; Nangia-Makker, P. Galectin-3 in angiogenesis and metastasis. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, I.; Hu, Z.; AbuSamra, D.B.; Saint-Geniez, M.; Ng, Y.S.E.; Argüeso, P.; D’Amore, P.A. Galectin-3 Enhances Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A Receptor 2 Activity in the Presence of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 734346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, B.-K.; Lee, Y.J.; Battle, P.; Jessup, J.M.; Raz, A.; Kim, H.-R.C. Galectin-3 Protects Human Breast Carcinoma Cells against Nitric Oxide-Induced Apoptosis: Implication of Galectin-3 Function during Metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Nangia-Makker, P.; Balan, V.; Hogan, V.; Raz, A. Calpain activation through galectin-3 inhibition sensitizes prostate cancer cells to cisplatin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, S.; Kim, S.-J.; Shao, F.; Ho, J.W.K.; Wong, K.U.; Miao, Z.; Hao, D.; Zhao, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Cisplatin prevents breast cancer metastasis through blocking early EMT and retards cancer growth together with paclitaxel. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2442–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melief, S.M.; Visser, M.; van der Burg, S.H.; Verdegaal, E.M.E. IDO and galectin-3 hamper the ex vivo generation of clinical grade tumor-specific T cells for adoptive cell therapy in metastatic melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhad, M.; Rolig, A.S.; Redmond, W.L. The role of Galectin-3 in modulating tumor growth and immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1434467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillman, B.N.; Hsu, D.K.; Pang, M.; Brewer, C.F.; Johnson, P.; Liu, F.-T.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-3 and Galectin-1 Bind Distinct Cell Surface Glycoprotein Receptors to Induce T Cell Death1. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangia-Makker, P.; Raz, T.; Tait, L.; Hogan, V.; Fridman, R.; Raz, A. Galectin-3 Cleavage: A Novel Surrogate Marker for Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Growing Breast Cancers. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11760–11768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazier, J.J.; Sylvester, P.W. Role of Galectins in Metastatic Breast Cancer. In Breast Cancer; Mayrovitz, H.N., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022; pp. 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Duan, C.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Z. Galectin-3 as a Marker and Potential Therapeutic Target in Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiter, A.; Barhum, Y.; Lipovetsky, J.; Menachem, C.; Elgavish, S.; Ruppo, S.; Birger, Y.; Izraeli, S.; Steinberg-Shemer, O.; Yerushalmi, R. Galectin-3 secreted by triple-negative breast cancer cells regulates T cell function. Neoplasia 2025, 60, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funkhouser, A.T.; Strigenz, A.M.; Blair, B.B.; Miller, A.P.; Shealy, J.C.; Ewing, J.A.; Martin, J.C.; Funk, C.R.; Edenfield, W.J.; Blenda, A.V. KIT Mutations Correlate with Higher Galectin Levels and Brain Metastasis in Breast and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markalunas, E.G.; Arnold, D.H.; Funkhouser, A.T.; Martin, J.C.; Shtutman, M.; Edenfield, W.J.; Blenda, A.V. Correlation Analysis of Genetic Mutations and Galectin Levels in Breast Cancer Patients. Genes 2024, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çakır, Y.; Talu, C.K.; Mermut, Ö.; Trabulus, D.C.; Arslan, E. The Expression of Galectin-3 in Tumor and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Invasive Micropapillary Breast Carcinomas: Relationship with Clinicopathologic Parameters. Eur. J. Breast Health 2021, 17, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lv, Y.; Niu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Cao, J.; Li, M.; et al. Tumor-secreted galectin-3 suppresses antitumor response by inducing IL-10+ B cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2025, 13, e011445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, C.M.; Leffler, H.; Kahl-Knutsson, B.; Svensson, I.; Jarvis, G.A. Truncated Galectin-3 Inhibits Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Orthotopic Nude Mouse Model of Human Breast Cancer1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar]
- Alhajj, M.; Zubair, M.; Farhana, A. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025; Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555922/ (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Engvall, E. The ELISA, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Maghsoudlou, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): The basics. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2016, 77, C98–C101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S. A short history, principles, and types of ELISA, and our laboratory experience with peptide/protein analyses using ELISA. Peptides 2015, 72, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruson, D.; Mancini, M.; Ahn, S.A.; Rousseau, M.F. Measurement of Galectin-3 with the ARCHITECT assay: Clinical validity and cost-effectiveness in patients with heart failure. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijers, W. Circulating Factors in Heart Failure: Biomarkers, Markers of Co-Morbidities and Disease Factors. Ph.D. Thesis, Rijksuniversiteit Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aldo, P.; Marusov, G.; Svancara, D.; David, J.; Mor, G. Simple PlexTM: A Novel Multi—Analyte, Automated Microfluidic Immunoassay Platform for the Detection of Human and Mouse Cytokines and Chemokines. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 75, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dysinger, M.; Marusov, G.; Fraser, S. Quantitative analysis of four protein biomarkers: An automated microfluidic cartridge-based method and its comparison to colorimetric ELISA. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 451, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, U.; Mackeben, K.; Stubenrauch, K. Use of Ella® to Facilitate drug Quantification and Antidrug Antibody Detection in Preclinical Studies. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macis, D.; Aristarco, V.; Johansson, H.; Guerrieri-Gonzaga, A.; Raimondi, S.; Lazzeroni, M.; Sestak, I.; Cuzick, J.; DeCensi, A.; Bonanni, B.; et al. A Novel Automated Immunoassay Platform to Evaluate the Association of Adiponectin and Leptin Levels with Breast Cancer Risk. Cancers 2021, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Anchondo-Nuñez, P.; Acuña-Aguilar, L.E.; Gómez-Valles, F.O.; Ramírez-Valdespino, C.A. Subtypes of Breast Cancer. In Breast Cancer; Mayrovitz, H.N., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022; Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK583808/ (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Krintus, M.; Kozinski, M.; Fabiszak, T.; Kubica, J.; Panteghini, M.; Sypniewska, G. Establishing reference intervals for galectin-3 concentrations in serum requires careful consideration of its biological determinants. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, R.H.; Duh, S.-H.; Wu, A.H.B.; Smith, A.; Abel, G.; deFilippi, C.R.; Wang, S.; Adourian, A.; Adiletto, C.; Gardiner, P. Multi-center determination of galectin-3 assay performance characteristics: Anatomy of a novel assay for use in heart failure. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (a). Stage | N = 115 | (b). Immunophenotype | N = 79 | (c). Histology | N = 115 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 47 | HER2 Enriched. | 7 | Adenocarcinoma | 6 |
| II | 42 | Luminal A | 20 | Apocrine | 15 |
| III | 17 | Luminal B | 5 | Benign | 4 |
| IV | 9 | Luminal B-like | 25 | Carcinoma | 5 |
| Triple Negative | 22 | Ductal Carcinoma in Situ | 45 | ||
| Invasive Ductal | 25 | ||||
| Invasive Lobular | 1 | ||||
| Invasive Mammary | 5 | ||||
| Invasive Micropapillary | 1 | ||||
| Lobular | 5 | ||||
| Metaplastic | 1 | ||||
| Mucinous | 2 |
| Mean (ng/mL) | SD (ng/mL) | Median (ng/mL) | IQR (ng/mL) | Min–Max (ng/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA (N = 95) | 12.68 | 8.07 | 10.59 | 7.43–15.10 | 2.65–48.48 |
| Ella (N = 95) | 7.49 | 3.71 | 6.70 | 5.20–8.80 | 0.95–20.43 |
| ELISA–Ella (N = 95) | −5.19 | 6.81 | −4.32 | −8.54–−0.30 | −28.06–6.88 |
| Mean (%) | SD (%) | Median (%) | IQR (%) | Min–Max (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA CV (N = 115) | 7.50 | 13.78 | 4.75 | 1.85–7.82 | 0.17–127.84 |
| Ella CV (N = 115) | 2.41 | 1.46 | 2.10 | 1.37–3.27 | 0.19–6.86 |
| Stage | Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient 1 | Wilcoxon Signed Rank (ng/mL) 2 | Regression Line Slope (ng/mL) 3 | of the Regression Line 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage I (N = 39) | 0.39 (p = 0.0145) | −5.34 (p < 0.0001) | 1.03 (p < 0.0001) | 0.5992 |
| Stage II (N = 35) | 0.37 (p = 0.0270) | −5.88 (p < 0.0001) | 0.97 (p < 0.0001) | 0.5346 |
| Stage III (N = 14) | 0.78 (p = 0.0009) | −4.08 (p = 0.0052) | 0.20 (p = 0.5152) | 0.0361 |
| Stage IV (N = 7) | 0.71 (p = 0.0713) | −3.13 (p = 0.0781) | 0.75 (p = 0.0892) | 0.4698 |
| Immunophenotypes | Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient 1 | Wilcoxon Signed Rank (ng/mL) 2 | Regression Line Slope (ng/mL) 3 | of the Regression Line 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HER2 Enriched (N = 7) | 0.54 (p = 0.2152) | −6.98 (p = 0.1094) | 0.98 (p = 0.0018) | 0.8805 |
| Luminal A (N = 17) | 0.59 (p = 0.0130) | −7.58 (p = 0.0007) | 1.24 (p < 0.0001) | 0.6696 |
| Luminal B-like (N = 22) | 0.43 (p = 0.0453) | −4.42 (p = 0.0014) | 0.46 (p = 0.1769) | 0.0892 |
| Triple Negative (N = 20) | 0.04 (p = 0.6970) | −5.49 (p = 0.0056) | 1.25 (p = 0.0028) | 0.4698 |
| Histology | Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient 1 | Wilcoxon Signed Rank (ng/mL) 2 | Regression Line Slope (ng/mL) 3 | of the Regression Line 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apocrine (N = 11) | 0.67 (p = 0.0233) | −8.71 (p = 0.0010) | 0.59 (p = 0.1323) | 0.2333 |
| Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (N = 43) | 0.43 (p = 0.0043) | −4.38 (p = 0.0003) | 0.97 (p < 0.0001) | 0.5301 |
| Invasive Ductal (N = 18) | 0.75 (p = 0.0004) | −2.41 (p = 0.0066) | 0.73 (p = 0.0044) | 0.4074 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markalunas, E.G.; Harold, S.E.; Arnold, D.H.; Martin, J.C.; Edenfield, W.J.; Blenda, A.V. Comparative Analysis of Manual ELISA and Ella, an Automated Instrument for ELISA, in Measuring Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Breast Cancer Patient Samples. Cancers 2025, 17, 3206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193206
Markalunas EG, Harold SE, Arnold DH, Martin JC, Edenfield WJ, Blenda AV. Comparative Analysis of Manual ELISA and Ella, an Automated Instrument for ELISA, in Measuring Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Breast Cancer Patient Samples. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193206
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkalunas, Ella G., Shannon E. Harold, David H. Arnold, Julie C. Martin, W. Jeffery Edenfield, and Anna V. Blenda. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Manual ELISA and Ella, an Automated Instrument for ELISA, in Measuring Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Breast Cancer Patient Samples" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193206
APA StyleMarkalunas, E. G., Harold, S. E., Arnold, D. H., Martin, J. C., Edenfield, W. J., & Blenda, A. V. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Manual ELISA and Ella, an Automated Instrument for ELISA, in Measuring Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Breast Cancer Patient Samples. Cancers, 17(19), 3206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193206








