Functional Heterogeneity and Context-Dependent Roles of LncRNAs in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. LncRNAs: A Brief Overview
1.1.1. LncRNAs: Biogenesis
1.1.2. LncRNAs: Functions
1.2. Breast Cancer: Pathophysiology
2. Materials and Methods
3. Sources of LncRNA Functional Heterogeneity
3.1. Breast Cancer Subtypes
| BC Subtype(s) | Associated LncRNA | Expression in BC Samples or Cells | BC Prognosis | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All BCs | BCAL8 | Upregulated | Linked to poor prognosis | [37] |
| EMX2OS | Downregulated | Unknown correlation | [38] | |
| MYCNOS | Upregulated | Unknown correlation | [38] | |
| NEAT1 | Frequently overexpressed; some mixed results | Frequently linked to poor prognosis; some mixed results | [41,47,48,49,50] | |
| MALAT1 | Frequently upregulated; some mixed results | Frequently linked to poor prognosis; some mixed results | [41,49,50] | |
| HOTAIR | Frequently upregulated; some mixed results | Frequently linked to poor prognosis; some mixed results | [41,50,51,52] | |
| Luminal A | TSIX | Downregulated | Unknown correlation | [38] |
| Luminal B | PVT1 | Upregulated | Unknown correlation | [38] |
| HER2-enriched | SNHG8 | Downregulated | Unknown correlation | [38] |
| GAS5 | Downregulated | Linked to resistance to trastuzumab and lapatinib | [38,44] | |
| LINC01269 | Upregulated | Linked to poor prognosis | [41] | |
| ER- | HAS2-AS1 | Upregulated | Linked to better prognosis | [42] |
| ER+ | HAS2-AS1 | Downregulated | Weak correlation | [42] |
| ER+ and ER- | LINC00324 | Upregulated | Linked to better prognosis | [44] |
| PTPRG-AS1 | Downregulated | Linked to better prognosis | [44] | |
| SNHG17 | Downregulated | Linked to better prognosis | [44] | |
| Basal-like/TNBC | HCP5 | Upregulated | Linked to better prognosis | [38,39] |
| SNHG3 | Upregulated | Linked to poor prognosis | [38,40] | |
| MIR155H | Upregulated | Unknown correlation | [38] | |
| AL078604 | Upregulated | Linked to poor prognosis | [41] | |
| MNX1-AS1 | Upregulated | Linked to poor prognosis | [46] |
3.2. Isoform Diversity and Alternative Splicing
3.2.1. HOX Antisense Intergenic RNA (HOTAIR)
3.2.2. Nuclear Paraspeckle Assembly Transcript 1 (NEAT1)
3.2.3. Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 (MALAT1)
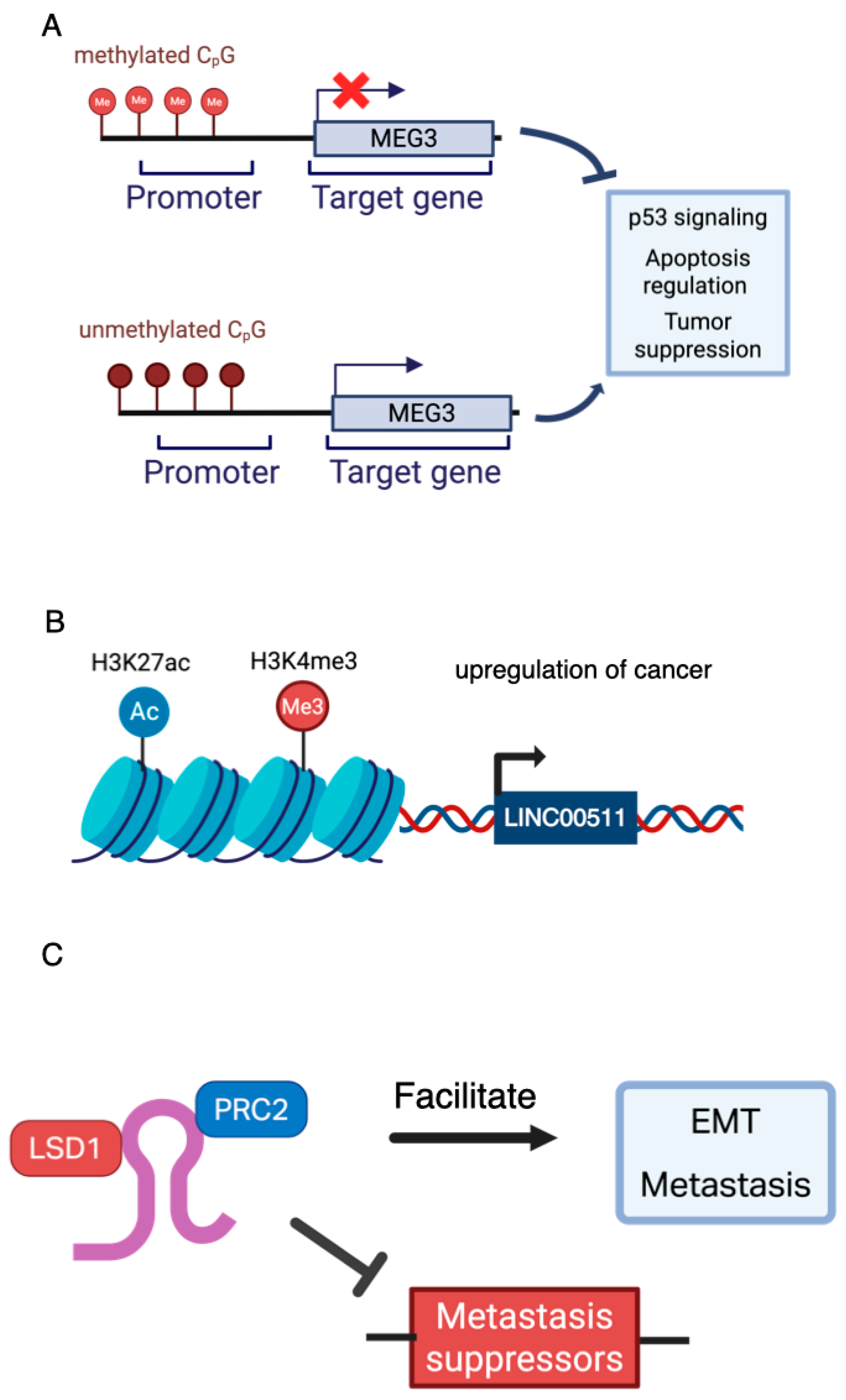
3.3. Epigenetic Regulation as a Driver of Functional Heterogeneity
3.4. Subcellular Localization
3.5. Interactions with Different Molecular Partners
3.5.1. LncRNA–miRNA Interactions
3.5.2. LncRNA–Protein Interactions
3.5.3. Multiplex and Dynamic Behavior
3.6. Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironments
3.7. Hormone Signaling
4. LncRNAs in the Clinic: Biomarker and Therapeutic Development in Breast Cancer
5. Strategies to Address LncRNA Functional Heterogeneity
5.1. Improving LncRNA Classification Systems
5.2. Uncovering LncRNA Functions with CRISPR/Cas Systems
5.3. Use of Single-Cell and Spatial Sequencing in LncRNA Research
5.4. Prioritizing LncRNA Targets
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Alternative splicing |
| ASO | Antisense oligonucleotide |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| BCSC | Breast cancer stem cell |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblast |
| ceRNA | Competing endogenous RNA |
| CLIP-seq | Crosslinking immunoprecipitation with high-throughput sequencing |
| CLS | Capture long-read sequencing |
| c-Myc | Cellular myelocytomatosis oncogene |
| DSB | Double-stranded break |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| EMT-TF | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition transcription factor |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| ER+ | Estrogen receptor-positive |
| ER- | Estrogen receptor-negative |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor 2 |
| HER2+ | Human epidermal growth factor 2-positive |
| H3K27ac | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation |
| H3K4me3 | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation |
| IDElncRNA | Individualized differentially expressed lncRNA |
| LLM | Large language model |
| lncRNA | Long non-coding ribonucleic acid |
| lrECM | Laminin-rich extracellular matrix |
| MFS | Metastasis-free survival |
| miRNA | Micro-ribonucleic acid |
| ML | Machine learning |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| nt | Nucleotide |
| PgR | Progesterone receptor |
| RBP | RNA-binding protein |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
| RNA-FISH | RNA-fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| RNAi | RNA interference |
| scRNA-seq | Single-cell RNA sequencing |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| TANRIC | The Atlas of Noncoding RNAs in Cancer |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
References
- Kim, J.; Harper, A.; McCormack, V.; Sung, H.; Houssami, N.; Morgan, E.; Mutebi, M.; Garvey, G.; Soerjomataram, I.; Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M. Global Patterns and Trends in Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality across 185 Countries. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Definitions, Functions, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Laurent, G.; Wahlestedt, C.; Kapranov, P. The Landscape of Long Noncoding RNA Classification. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojima, T.; Proudfoot, N.J. Mechanisms of lncRNA Biogenesis as Revealed by Nascent Transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 Catalog of Human Long Noncoding RNAs: Analysis of Their Gene Structure, Evolution, and Expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, K.; Dey, A.; Kiran, M. Inefficient Splicing of Long Non-Coding RNAs Is Associated with Higher Transcript Complexity in Human and Mouse. RNA Biol. 2023, 20, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melé, M.; Mattioli, K.; Mallard, W.; Shechner, D.M.; Gerhardinger, C.; Rinn, J.L. Chromatin Environment, Transcriptional Regulation, and Splicing Distinguish lincRNAs and mRNAs. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constanty, F.; Shkumatava, A. lncRNAs in Development and Differentiation: From Sequence Motifs to Functional Characterization. Development 2021, 148, dev182741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Fullwood, M.J. Roles, Functions, and Mechanisms of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome Regulation by Long Noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.L.C.; Eichhorn, P.J.A. Deciphering the Roles of lncRNAs in Breast Development and Disease. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20179–20212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, P.; Meeran, S.M. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Breast Cancer Metastasis. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020, 5, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolvand, M.; Chermahini, Z.M.; Bahaloo, S.; Emami, M.H.; Fahim, A.; Rahimi, H.; Amjadi, E.; Maghool, F.; Rohani, F.; Dadkhah, M.; et al. New Long Noncoding RNA Biomarkers and ceRNA Networks on miR-616-3p in Colorectal Cancer: Bioinformatics-Based Study. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2024, 29, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Morris, K.V.; Weinberg, M.S. Perspectives on the Mechanism of Transcriptional Regulation by Long Non-Coding RNAs. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, T. Long Non-Coding RNAs: The Regulatory Mechanisms, Research Strategies, and Future Directions in Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 598817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNA as Modular Scaffold of Histone Modification Complexes. Science 2010, 329, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.-C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Reprograms Chromatin State to Promote Cancer Metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Li, R.; Meng, F.; Fang, M. NKILA Inhibits NF-κB Signaling and Suppresses Tumor Metastasis. Aging 2018, 10, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The Multilayered Complexity of ceRNA Crosstalk and Competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Maquat, L.E. lncRNAs Transactivate STAU1-Mediated mRNA Decay by Duplexing with 3′ UTRs via Alu Elements. Nature 2011, 470, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, M.C.; Daulagala, A.C.; Kourtidis, A. LNCcation: LncRNA Localization and Function. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202009045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Hai, R. Noncoding RNAs Serve as the Deadliest Universal Regulators of All Cancers. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2021, 18, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, K.; Jia, Q.; Ding, X. Roles of miRNA and lncRNA in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2020, 21, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.-D. Roles and Mechanisms of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, B.; Wapinski, O.L.; Tsai, M.-C.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J.; Carlson, J.C.; Lin, M.; Fang, F.; Gupta, R.A.; et al. Targeted Disruption of Hotair Leads to Homeotic Transformation and Gene Derepression. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amândio, A.R.; Necsulea, A.; Joye, E.; Mascrez, B.; Duboule, D. Hotair Is Dispensible for Mouse Development. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qi, M.; Fei, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, K. Long Non-Coding RNA XIST: A Novel Oncogene in Multiple Cancers. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Weng, X.-D.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.-H.; Zhu, H.-C.; Guo, J.; Ning, J.-Z.; Xiao, C.-C. LncRNA XIST Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Prostate Cancer through Sponging miR-23a to Modulate RKIP Expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 94358–94370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Zheng, L.-W.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Cai, Y.-W.; Wang, L.-P.; Huang, L.; Liu, C.-C.; Shao, Z.-M.; Yu, K.-D. Breast Cancer: Pathogenesis and Treatments. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren, E.; Das, J.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Polyphenols as Immunomodulators and Epigenetic Modulators: An Analysis of Their Role in the Treatment and Prevention of Breast Cancer. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasiewicz, S.; Czeczelewski, M.; Forma, A.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, R.; Stanisławek, A. Breast Cancer-Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies-An Updated Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørklund, S.S.; Aure, M.R.; Hákkinen, J.; Vallon-Christersson, J.; Kumar, S.; Evensen, K.B.; Fleischer, T.; Tost, J.; Sahlberg, K.K.; Mathelier, A.; et al. Subtype and Cell Type Specific Expression of lncRNAs Provide Insight into Breast Cancer. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.-K.; Jung, Y.L.; Cheong, T.-C.; Espejo Valle-Inclan, J.; Chu, C.; Gulhan, D.C.; Ljungström, V.; Jin, H.; Viswanadham, V.V.; Watson, E.V.; et al. ERα-Associated Translocations Underlie Oncogene Amplifications in Breast Cancer. Nature 2023, 618, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic Microenvironment in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thoubaity, F.K. Molecular Classification of Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 49, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Noshokaty, T.M.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Abdelhamid, R.; Mansour, A.; Abdellatif, N.; Alaaeldien, A.; Reda, T.; Gendi, D.; Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; Elshaer, S.S.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Role in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis and Drug Resistance: Navigating the Non-Coding Landscape Review. Exp. Cell Res. 2025, 444, 114365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Hu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Hu, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, S.D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Shan, W.; He, Q.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization of Long Non-Coding RNAs across Human Cancers. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cava, C.; Armaos, A.; Lang, B.; Tartaglia, G.G.; Castiglioni, I. Identification of Long Non-Coding RNAs and RNA Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer Subtypes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, C.; Liu, C.; Zhou, C.; Ma, X.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Qi, L.; Yao, Y.; et al. Four lncRNAs Associated with Breast Cancer Prognosis Identified by Coexpression Network Analysis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14019–14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Le, L. Overexpression of lncRNA SNGH3 Predicts Unfavorable Prognosis and Clinical Outcomes in Human Cancers: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7974034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasson, M.-C.D.; Venkatesh, J.; Cahill, H.F.; McLean, M.E.; Dean, C.A.; Marcato, P. LncRNAs Exhibit Subtype-Specific Expression, Survival Associations, and Cancer-Promoting Effects in Breast Cancer. Gene 2024, 901, 148165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnigoni, A.; Caon, I.; Teo, W.X.; Hua, S.H.; Moretto, P.; Bartolini, B.; Viola, M.; Karousou, E.; Yip, G.W.; Götte, M.; et al. The Natural Antisense Transcript HAS2-AS1 Regulates Breast Cancer Cells Aggressiveness Independently from Hyaluronan Metabolism. Matrix Biol. 2022, 109, 140–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnigoni, A.; Caon, I.; Moretto, P.; Viola, M.; Karousou, E.; Passi, A.; Vigetti, D. The Role of the Multifaceted Long Non-Coding RNAs: A Nuclear-Cytosolic Interplay to Regulate Hyaluronan Metabolism. Matrix Biol. Plus 2021, 11, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Luo, J.; Jiao, S. Comprehensive Characterization of Cancer Subtype Associated Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Clinical Implications. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrando, L.; Cirmena, G.; Garuti, A.; Scabini, S.; Grillo, F.; Mastracci, L.; Isnaldi, E.; Marrone, C.; Gonella, R.; Murialdo, R.; et al. Development of a Long Non-Coding RNA Signature for Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, K.; Bi, Z.; Li, Y. Long Non-Coding RNA MNX1-AS1 Promotes Progression of Triple Negative Breast Cancer by Enhancing Phosphorylation of Stat3. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, K. Pan-Cancer Analysis of Long Non-Coding RNA NEAT1 in Various Cancers. Genes Dis. 2018, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, V.Y.; Chen, J.; Cheuk, I.W.-Y.; Siu, M.-T.; Ho, C.-W.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Kwong, A. Long Non-Coding RNA NEAT1 Confers Oncogenic Role in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer through Modulating Chemoresistance and Cancer Stemness. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaens, C.; Rambow, F.; Bervoets, G.; Silla, T.; Mito, M.; Chiba, T.; Asahara, H.; Hirose, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Jensen, T.H.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1_1 Is Seemingly Dispensable for Normal Tissue Homeostasis and Cancer Cell Growth. RNA 2019, 25, 1681–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Wang, M.; Lin, S.; Guo, Y.; Dai, Z.; Liu, K.; Yang, P.; Dai, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. The Impact of lncRNA Dysregulation on Clinicopathology and Survival of Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2018, 12, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozdarani, H.; Ezzatizadeh, V.; Rahbar Parvaneh, R. The Emerging Role of the Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR in Breast Cancer Development and Treatment. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylerli, O.; Gareev, I.; Sufianov, A.; Ilyasova, T.; Guang, Y. Long Noncoding RNAs as Promising Biomarkers in Cancer. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022, 7, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krchňáková, Z.; Thakur, P.K.; Krausová, M.; Bieberstein, N.; Haberman, N.; Müller-McNicoll, M.; Staněk, D. Splicing of Long Non-Coding RNAs Primarily Depends on Polypyrimidine Tract and 5′ Splice-Site Sequences Due to Weak Interactions with SR Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 911–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, C.; Esposito, G.; Iaiza, A.; Goeman, F.; Benedetti, A.; Gallo, E.; Daralioti, T.; Perracchio, L.; Sacconi, A.; Pasanisi, P.; et al. MALAT1-Dependent Hsa_circ_0076611 Regulates Translation Rate in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Han, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Han, M.; Wang, W. LncRNA ZNF649-AS1 Promotes Trastuzumab Resistance and TAM-Dependent PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer by Regulating EXOC7 Alternative Splicing. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 761, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grelet, S.; Link, L.A.; Howley, B.; Obellianne, C.; Palanisamy, V.; Gangaraju, V.K.; Diehl, J.A.; Howe, P.H. A Regulated PNUTS mRNA to lncRNA Splice Switch Mediates EMT and Tumor Progression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Feng, Y.C.; Guo, S.T.; Wang, P.L.; Qi, T.F.; Yue, Y.M.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, S.N.; Tang, C.X.; La, T.; et al. The Pan-Cancer lncRNA PLANE Regulates an Alternative Splicing Program to Promote Cancer Pathogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Li, Q.; Fang, J.; Zhao, T. LncRNA HOTAIR: A Potential Prognostic Factor and Therapeutic Target in Human Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 679244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Alsager, S.; Zhuo, Y.; Shan, B. HOX Transcript Antisense RNA (HOTAIR) in Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 454, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Lin, Z.; Jayawickramarajah, J.; Alsager, J.S.; Schmidt, E.; Nephew, K.P.; Fang, F.; Balasubramanian, S.; Shan, B. G-Quadruplex Is Critical to Epigenetic Activation of the lncRNA HOTAIR in Cancer Cells. iScience 2023, 26, 108559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Flemington, E.K.; Lin, Z.; Shan, B. Induction of a Novel Isoform of the lncRNA HOTAIR in Claudin-low Breast Cancer Cells Attached to Extracellular Matrix. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1698–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemson, C.M.; Hutchinson, J.N.; Sara, S.A.; Ensminger, A.W.; Fox, A.H.; Chess, A.; Lawrence, J.B. An Architectural Role for a Nuclear Non-Coding RNA: NEAT1 RNA Is Essential for the Structure of Paraspeckles. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.H.; Lamond, A.I. Paraspeckles. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Zheng, H.; Chan, M.T.V.; Wu, W.K.K. NEAT1: A Novel Cancer-related Long Non-coding RNA. Cell Prolif. 2017, 50, e12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Virnicchi, G.; Tanigawa, A.; Naganuma, T.; Li, R.; Kimura, H.; Yokoi, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Bénard, M.; Fox, A.H.; et al. NEAT1 Long Noncoding RNA Regulates Transcription via Protein Sequestration within Subnuclear Bodies. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, M.; Toya, H.; Mito, M.; Chiba, T.; Asahara, H.; Hirose, T.; Nakagawa, S. Forced Isoform Switching of Neat1_1 to Neat1_2 Leads to the Loss of Neat1_1 and the Hyperformation of Paraspeckles but Does Not Affect the Development and Growth of Mice. RNA 2020, 26, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, E.; Lellahi, S.M.; Aure, M.R.; Nord, S.; Fismen, S.; Larsen, K.B.; Gabriel, M.T.; Hedberg, A.; Bjørklund, S.S.; Bofin, A.M.; et al. The Expression of the Long NEAT1_2 Isoform Is Associated with Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.K.; Zhang, L.; Min, K.-W.; Cho, J.-H.; Yeh, C.-C.; Moon, H.; Hormaechea-Agulla, D.; Mun, H.; Ko, S.; Lee, J.W.; et al. NEAT1 Is Essential for Metabolic Changes That Promote Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2380–2397.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyganov, M.M.; Ibragimova, M.K. MALAT1 Long Non-Coding RNA and Its Role in Breast Carcinogenesis. Acta Naturae 2023, 15, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseure, D.; Vacher, S.; Lallemand, F.; Alsibai, K.D.; Hatem, R.; Chemlali, W.; Nicolas, A.; De Koning, L.; Pasmant, E.; Callens, C.; et al. Prognostic Value of a Newly Identified MALAT1 Alternatively Spliced Transcript in Breast Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, C.D.; Lukowski, Z.L.; Min, J.; Martorana, G.M.; Wilson, M.-K.; Schaefer, J.L.; Levine, M.A.; Meyers, C.A.; Blake, C.R.; Schultz, G.S.; et al. Modulating Ocular Scarring in Glaucoma Filtration Surgery Using the Epigenetic Adjunct Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid. J. Curr. Glaucoma Pract. 2019, 13, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Role of Epigenetic Regulation in Plasticity of Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 640369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, L.; Zeng, W.; Huang, P.; Chen, H.; Jia, Z.; Wang, P.; Huang, D.; Chen, J.; Nie, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. CD8+ T Cell–Dependent Remodeling of the Tumor Microenvironment Overcomes Chemoresistance. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 11, 320–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Ma, M.; Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Zuo, X.; Gu, X.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y. LncRNA MEG3 Regulates Breast Cancer Proliferation and Apoptosis through miR-141-3p/RBMS3 Axis. Genomics 2021, 113, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Li, C.; Xing, Z.; Hu, Q.; Liang, K.; Han, L.; Wang, C.; Hawke, D.H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The LINK-A lncRNA Activates Normoxic HIF1\alpha Signalling in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amicone, L.; Marchetti, A.; Cicchini, C. The lncRNA HOTAIR: A Pleiotropic Regulator of Epithelial Cell Plasticity. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Li, R.; Xiao, X.; Saw, P.E.; Xu, X. Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer: From Subcellular Localization to Nanoparticle-Mediated Targeted Regulation. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2023, 33, 774–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Shen, H.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Xiong, S.; Chi, H.; Xu, W. A Nuclear lncRNA Linc00839 as a Myc Target to Promote Breast Cancer Chemoresistance via PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3279–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Li, T.-T.; Wang, K.-L.; Xiao, G.-Q.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhao, H.-D.; Kang, Z.-J.; Fan, W.-J.; Zhu, L.-L.; Li, M.; et al. H19/Let-7/LIN28 Reciprocal Negative Regulatory Circuit Promotes Breast Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 8, e2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Luo, Z.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA LINC00511 Contributes to Breast Cancer Tumourigenesis and Stemness by Inducing the miR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog Axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, F.; Fiscon, G.; Chiara, M.; Colombo, T.; Farina, L.; Paci, P. Role of the Long Non-Coding RNA PVT1 in the Dysregulation of the ceRNA-ceRNA Network in Human Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horman, S.R.; Janas, M.M.; Litterst, C.; Wang, B.; MacRae, I.J.; Sever, M.J.; Morrissey, D.V.; Graves, P.; Luo, B.; Umesalma, S.; et al. Akt-Mediated Phosphorylation of Argonaute 2 Downregulates Cleavage and Upregulates Translational Repression of MicroRNA Targets. Mol. Cell 2013, 50, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Long Noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Imamachi, N.; Akizuki, G.; Kumakura, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nagata, K.; Kato, A.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Sato, H.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1-Dependent SFPQ Relocation from Promoter Region to Paraspeckle Mediates IL8 Expression upon Immune Stimuli. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.A.; Ahmad, S.M.; Mumtaz, P.T.; Malik, A.A.; Dar, M.A.; Urwat, U.; Shah, R.A.; Ganai, N.A. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Mechanism of Action and Functional Utility. Noncoding RNA Res. 2016, 1, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, H. Biomolecules Interacting with Long Noncoding RNAs. Biology 2025, 14, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Zhang, Q.C.; da Rocha, S.T.; Flynn, R.A.; Bharadwaj, M.; Calabrese, J.M.; Magnuson, T.; Heard, E.; Chang, H.Y. Systematic Discovery of Xist RNA Binding Proteins. Cell 2015, 161, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallen, A.N.; Zhou, X.-B.; Xu, J.; Qiao, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, L.; Lu, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, J.-S.; Zhang, H.; et al. The Imprinted H19 lncRNA Antagonizes Let-7 microRNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, W.; Zhang, X.; Yue, B.; Qi, A.; Shen, X.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Chen, H. Insight into m6A Methylation from Occurrence to Functions. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-D.; Shan, B.-J.; Wang, L.; Gao, S.; Hao, L.; Yu, H.-Y.; Pan, Y.-Y. The m6A Modification of LINC01133 Suppresses ER+ Breast Cancer Progression by Modulating IGF2BP2 Protein Stability via a Ubiquitination-Dependent Mechanism. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1608574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, V.; Melendez-Zajgla, J. The Role of Hypoxia-Associated Long Non-Coding RNAs in Breast Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, W.; Xiao, S.; Lin, K. Identification of a Hypoxia-Suppressed lncRNA RAMP2-AS1 in Breast Cancer. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-C.; Yeh, C.-C.; Chao, L.-Y.; Tsai, M.-H.; Chen, H.-H.; Chuang, E.Y.; Lai, L.-C. The Hypoxia-Responsive lncRNA NDRG-OT1 Promotes NDRG1 Degradation via Ubiquitin-Mediated Proteolysis in Breast Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 10470–10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Ni, R.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Song, H.; Jin, L.; Pan, Y. Hypoxia-Induced lncRNA RBM5-AS1 Promotes Tumorigenesis via Activating Wnt/\beta-Catenin Signaling in Breast Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W.; Yang, J.; Ni, R.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, M.; Jin, L.; et al. Hypoxia Induced Cellular and Exosomal RPPH1 Promotes Breast Cancer Angiogenesis and Metastasis through Stabilizing the IGF2BP2/FGFR2 Axis. Oncogene 2025, 44, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Bessone, M.I.; Gattas, M.J.; Laporte, T.; Tanaka, M.; Simian, M. The Tumor Microenvironment as a Regulator of Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Yang, Y.A.; Zhang, A.; Fong, K.; Kim, J.; Song, B.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.C.; Yu, J. LncRNA HOTAIR Enhances ER Signaling and Confers Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Katsaros, D.; Biglia, N.; Shen, Y.; Loo, L.; Yu, X.; Lin, H.; Fu, Y.; Chu, W.-M.; Fei, P.; et al. ER\alpha Upregulates the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNA LINC00472 Which Suppresses the Phosphorylation of NF-\kappaB in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 175, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, M. The Multiple Functions and Mechanisms of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Regulating Breast Cancer Progression. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1559408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriaga-Canon, C.; Contreras-Espinosa, L.; Aguilar-Villanueva, S.; Bargalló-Rocha, E.; García-Gordillo, J.A.; Cabrera-Galeana, P.; Castro-Hernández, C.; Jiménez-Trejo, F.; Herrera, L.A. The Clinical Utility of lncRNAs and Their Application as Molecular Biomarkers in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, Q.; et al. Individualized lncRNA Differential Expression Profile Reveals Heterogeneity of Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4604–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhai, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Wei, Q. Downregulation of LncRNA GAS5 Causes Trastuzumab Resistance in Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27778–27786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-Z.; Liu, Y.-R.; Xu, X.-E.; Jin, X.; Hu, X.; Yu, K.-D.; Shao, Z.-M. Transcriptome Analysis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Reveals an Integrated mRNA-lncRNA Signature with Predictive and Prognostic Value. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Gong, Y.; Fan, L.; Liu, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.-C.; Mo, M.; Hou, Y.-F.; Di, G.-H.; et al. Intensive Chemotherapy versus Standard Chemotherapy among Patients with High Risk, Operable, Triple Negative Breast Cancer Based on Integrated mRNA-lncRNA Signature (BCTOP-T-A01): Randomised, Multicentre, Phase 3 Trial. BMJ 2024, 387, e079603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GENCODE—Human Release Statistics. Available online: https://www.gencodegenes.org/human/stats.html (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Volders, P.-J.; Anckaert, J.; Verheggen, K.; Nuytens, J.; Martens, L.; Mestdagh, P.; Vandesompele, J. LNCipedia 5: Towards a Reference Set of Human Long Non-Coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D135–D139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Song, T.; Wu, Y.; Fang, S.; Bu, D.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Pei, D.; et al. NONCODEV6: An Updated Database Dedicated to Long Non-Coding RNA Annotation in Both Animals and Plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D165–D171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Feng, C.; Qin, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, L. LncBook 2.0: Integrating Human Long Non-Coding RNAs with Multi-Omics Annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D186–D191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, S.; Gandhi, S.; Scaria, V. Navigating the Dynamic Landscape of Long Noncoding RNA and Protein-Coding Gene Annotations in GENCODE. Hum. Genom. 2016, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, J.; Uszczynska-Ratajczak, B.; Carbonell, S.; Pérez-Lluch, S.; Abad, A.; Davis, C.; Gingeras, T.R.; Frankish, A.; Harrow, J.; Guigó, R.; et al. High-Throughput Annotation of Full-Length Long Noncoding RNAs with Capture Long-Read Sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Perteghella, T.; Carbonell-Sala, S.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Hunt, T.; Mądry, T.; Jungreis, I.; Arnan, C.; Lagarde, J.; Borsari, B.; et al. GENCODE: Massively Expanding the lncRNA Catalog through Capture Long-Read RNA Sequencing. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadbakht, N.; Doosti, A.; Jami, M.-S. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated LINC00511 Knockout Strategies, Increased Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via Suppressing Antiapoptotic Genes. Biol. Proced. Online 2022, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardia, T.; Zhang, Y.; Thompson, K.N.; Lee, S.J.; Martin, S.S.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos, A. OBSCN Restoration via OBSCN-AS1 Long-Noncoding RNA CRISPR-Targeting Suppresses Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2215553120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Bitar, M.; Lu, X.; Jacquelin, S.; Nair, S.; Sivakumaran, H.; Hillman, K.M.; Kaufmann, S.; Ziegman, R.; Casciello, F.; et al. CRISPR-Cas13d Screens Identify KILR, a Breast Cancer Risk-Associated lncRNA That Regulates DNA Replication and Repair. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkney, H.R.; Black, M.A.; Diermeier, S.D. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals Heterogeneous lncRNA Expression in Xenografted Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Biology 2021, 10, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakrithi, P.; Vo, T.; Vu, H.; Xiong, A.; Nguyen, L.; Newman, A.; Whitehall, V.; Gonzalez Cruz, J.L.; Gupta, I.; Nguyen, Q. Unraveling lncRNA Diversity at a Single Cell Resolution and in a Spatial Context across Different Cancer Types. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hou, Z.; Liu, X.; Peng, X. Exploring the Potentials and Challenges of Using Large Language Models for the Analysis of Transcriptional Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNAs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.03522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-W.; Nam, J.-W. TERIUS: Accurate Prediction of lncRNA via High-Throughput Sequencing Data Representing RNA-Binding Protein Association. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeijn, L.; Cats, D.; Wolstencroft, K.; Mei, H. LncRNA-BERT: An RNA Language Model for Classifying Coding and Long Non-Coding RNA. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Ghoshal, T.; Wilkins, D.; Mo, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y. lncRNA Gene Signatures for Prediction of Breast Cancer Intrinsic Subtypes and Prognosis. Genes 2018, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, R.C.-D.; Wei, H.; Kim, D.H.; Wu, J.Q. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Important Regulators in the Development, Function, and Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2019, 45, 538–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibitt, S.; Hartford, C.C.R.; Lal, A. Interrogating lncRNA Functions via CRISPR/Cas Systems. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojic, L.; Lun, A.T.L.; Mangei, J.; Mascalchi, P.; Quarantotti, V.; Barr, A.R.; Bakal, C.; Marioni, J.C.; Gergely, F.; Odom, D.T. Specificity of RNAi, LNA and CRISPRi as Loss-of-Function Methods in Transcriptional Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 5950–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.-W.; Müller, S.; Hart, S.K.; Wessels, H.-H.; Méndez-Mancilla, A.; Sookdeo, A.; Choi, O.; Caragine, C.M.; Corman, A.; Lu, L.; et al. Transcriptome-Scale RNA-Targeting CRISPR Screens Reveal Essential lncRNAs in Human Cells. Cell 2024, 187, 7637–7654.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Jin, X.; Luo, Y.; Zou, H.; Lv, D.; Wang, L.; Fu, L.; Cai, Y.; Shao, T.; Li, Y.; et al. Spatial Transcriptome Analysis of Long Non-Coding RNAs Reveals Tissue Specificity and Functional Roles in Cancer. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2023, 24, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponting, C.P.; Haerty, W. Genome-Wide Analysis of Human Long Noncoding RNAs: A Provocative Review. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2022, 23, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
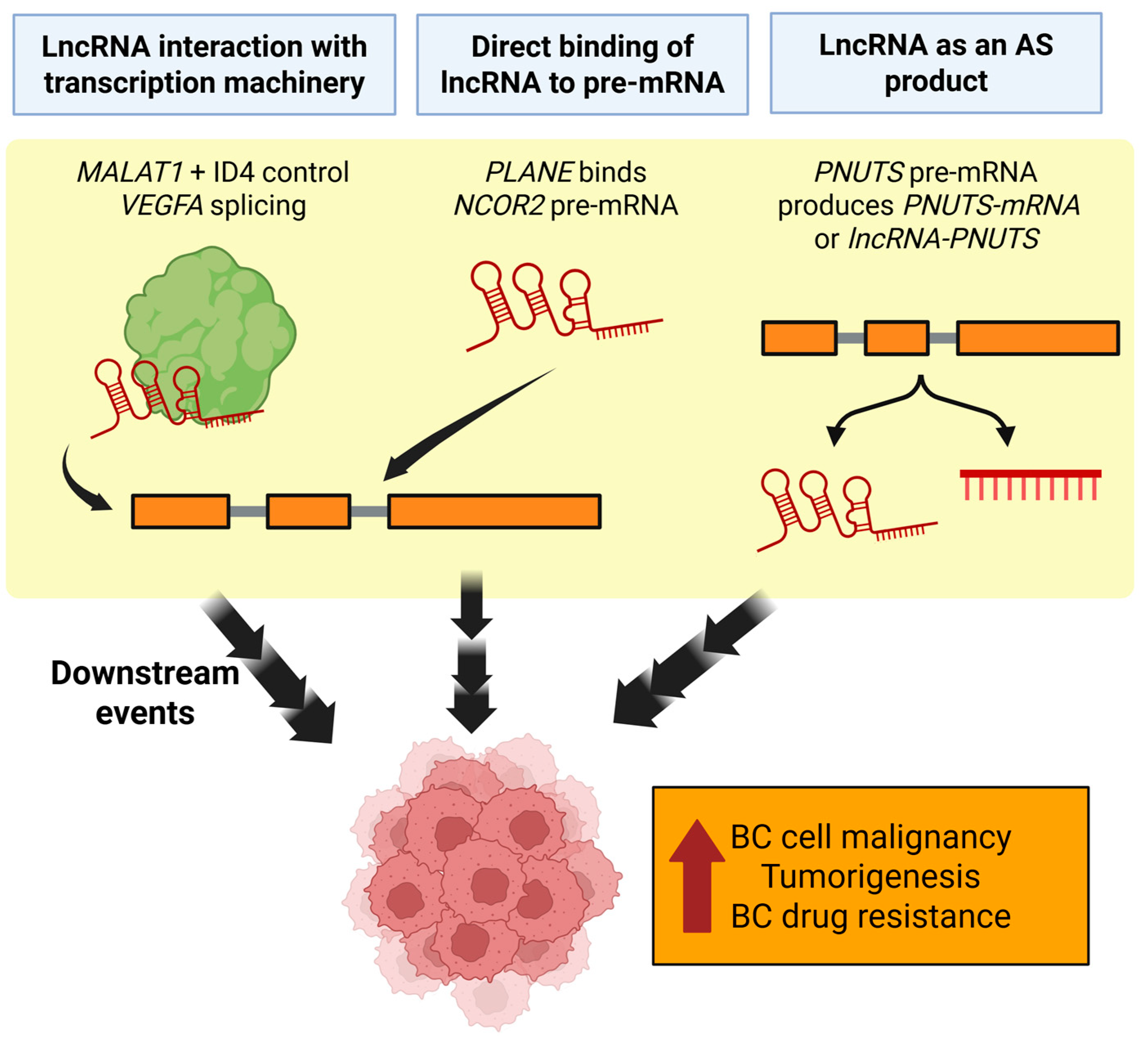

| LncRNA | Function | BC Prognosis | Therapeutic Potential | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOTAIR | Scaffolds PRC2/LSD1, drives chromatin remodeling, EMT, and metastasis | Upregulation frequently linked to poor prognosis; some mixed results | ASOs/siRNA to disrupt PRC2/LSD1 interaction; HOTAIR-N upregulation as a candidate biomarker | [61,76] |
| NEAT1 | Maintains paraspeckle integrity, promotes stress survival | Upregulation frequently linked to poor prognosis; some mixed results | Isoform-specific targeting; RNA-FISH for patient stratification | [63,66,67] |
| MALAT1 | Regulates EMT, metastasis, alternative splicing, PI3K-Akt signaling | Upregulation frequently linked to poor prognosis; some mixed results | Δsv-MALAT1 as decoy; Δsv-MALAT1 downregulation as a candidate biomarker | [49,69,70] |
| H19 | Sponges let-7; supports stemness; confers tamoxifen resistance via autophagy regulation | Upregulation frequently linked to poor prognosis | H19 upregulation as a candidate biomarker | [79,88] |
| GAS5 | Tumor suppressor, modulates drug sensitivity (trastuzumab, lapatinib) | Downregulation linked to drug resistance in HER2+ BC | Restoration strategies to enhance HER2-targeted therapy | [38,102] |
| Tool/Technique | Overview | Example Use Case in BC | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personalized lncRNA expression profiling | Generates of sample-specific lncRNA (IDElncRNAs). | LncRIndiv constructs a IDElncRNA profile for BRCA to characterize subtype-specfic lncRNAs. | [101] |
| Capture Long-Read Sequencing (CLS) | Probes targeting lncRNAs are created, from which cDNA libraries enriching for complete 5′ to 3′ RNA molecules are then made. Long-read sequencing is then carried out on the libraries. | Improve lncRNA annotation quality. | [111] |
| CRISPR/Cas9 | DSB induced by Cas9 is repaired by sgRNA, which can be customized to make specific edits to DNA. | Suppression of LINC00511 transcription, which decreases BC cell proliferation rate. | [112] |
| CRISPRa | CRISPR system to activate genes by using catalytically inactive Cas9 to recruit transcriptional activators. | Activate OBSCN-AS1 to restore OBSCN expression, thus suppressing TNBC cell migration. | [113] |
| CRISPRi | CRISPR system to repress gene expression by using catalytically inactive Cas9 to recruit transcriptional repressors. | ||
| CRISPR/Cas13d | Knock-down lncRNA via cleavage by Cas13. | Used in a screen for lncRNAs that can upregulate BC cell proliferation. The tumor suppressor KILR was identified via this method. | [114] |
| scRNA-seq | Analyses of transcriptional profiles at the resolution of individual cells. | Together with spatial transcriptomics, TINCR expression was found to be highly expressed in BC samples. | [115,116] |
| Spatial transcriptomics | Preserves the spatial context of gene expression within samples with heterogenous cell populations. | Together with scRNA-seq, TINCR expression was found to be highly expressed in BC samples. | [116] |
| Machine learning (ML) methods | The use of computational models and statistical algorithms to automatically analyze and draw inferences from patterns. | Uncover patterns overlooked by traditional annotation. TERIUS distinguishes lncRNAs from false positives by focusing on 3′ UTR fragments. | [117,118] |
| Large Language Models (LLMs) | Artificial intelligence system that automatically analyzes and generates human-like language and text based on patterns from large text datasets that it is trained on. | Uncover patterns overlooked by traditional annotation. LncRNA-BERT uses a model trained on existing sequence databases to distinguish mRNA from lncRNA. | [117,119] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lye, S.H.; Polycarp, N.; Durojaye, T.J.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Functional Heterogeneity and Context-Dependent Roles of LncRNAs in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193191
Lye SH, Polycarp N, Durojaye TJ, Tollefsbol TO. Functional Heterogeneity and Context-Dependent Roles of LncRNAs in Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193191
Chicago/Turabian StyleLye, Shu Hui, Nunaya Polycarp, Titilayomi Juliet Durojaye, and Trygve O. Tollefsbol. 2025. "Functional Heterogeneity and Context-Dependent Roles of LncRNAs in Breast Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193191
APA StyleLye, S. H., Polycarp, N., Durojaye, T. J., & Tollefsbol, T. O. (2025). Functional Heterogeneity and Context-Dependent Roles of LncRNAs in Breast Cancer. Cancers, 17(19), 3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193191






