Prognostic and Immunomodulatory Roles of PAK6 in Colorectal Cancer Through Integrative Transcriptomic and Clinical Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2. Expression Profiling and Diagnostic Evaluation
2.3. Clinical Correlation and Survival Analysis
2.4. Co-Expression Network and Functional Enrichment
2.5. Immune Microenvironment Characterization
2.6. Chemokine Interaction Network
2.7. Tissue Microarray and Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
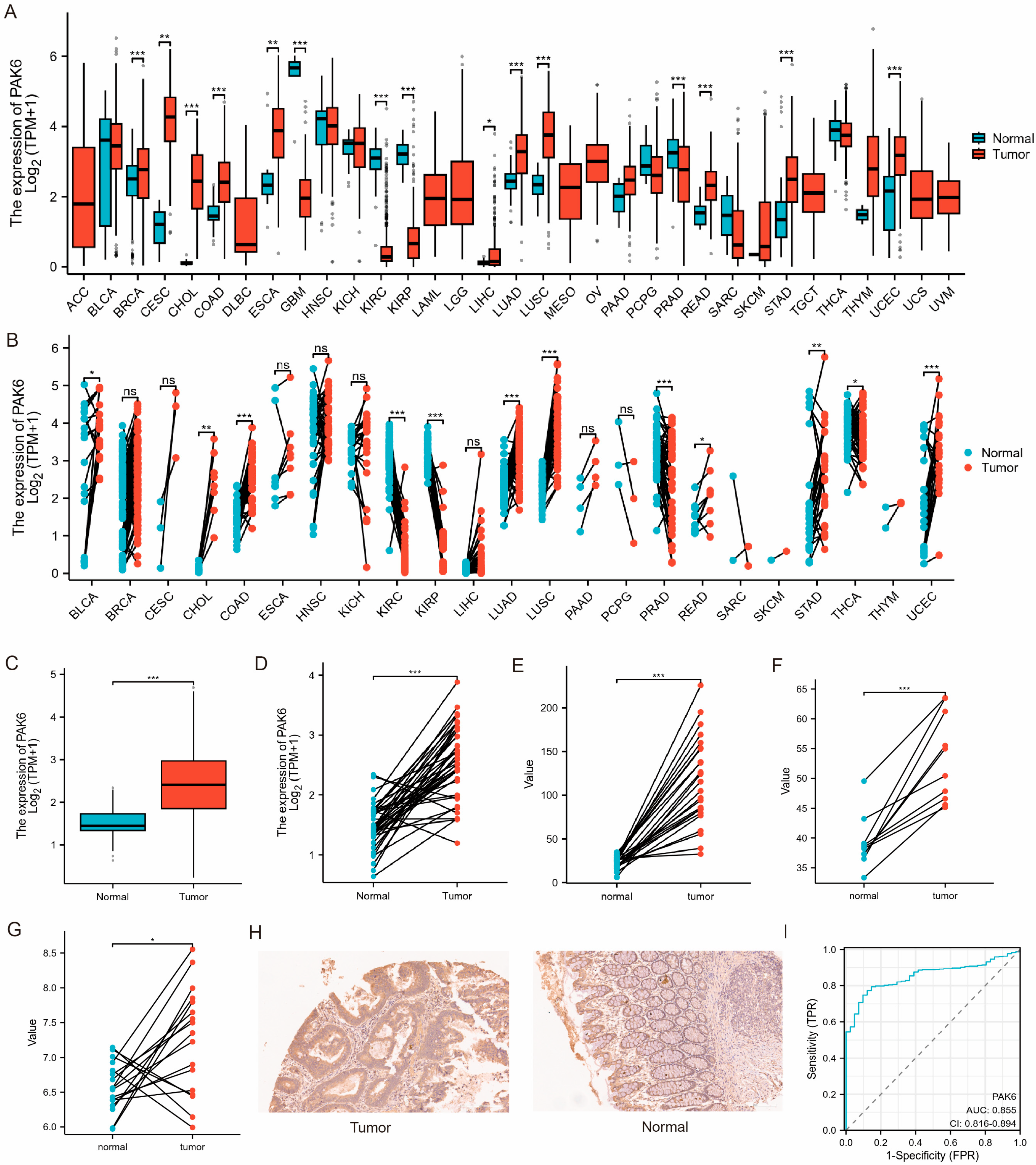
3.1. Aberrant Upregulation of PAK6 mRNA and Protein in Colorectal Cancer
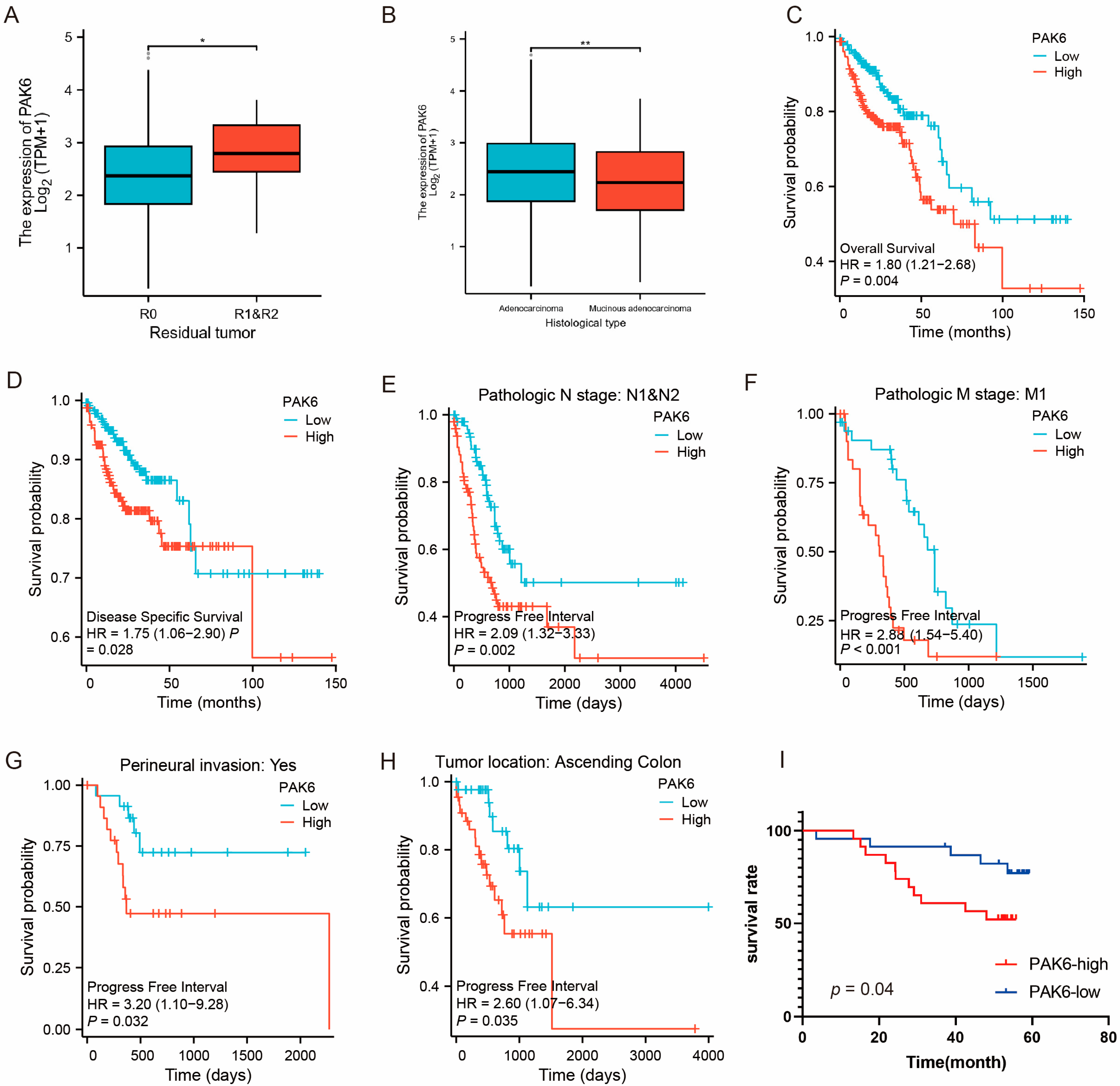
3.2. Association of PAK6 with Aggressive Clinicopathological Features
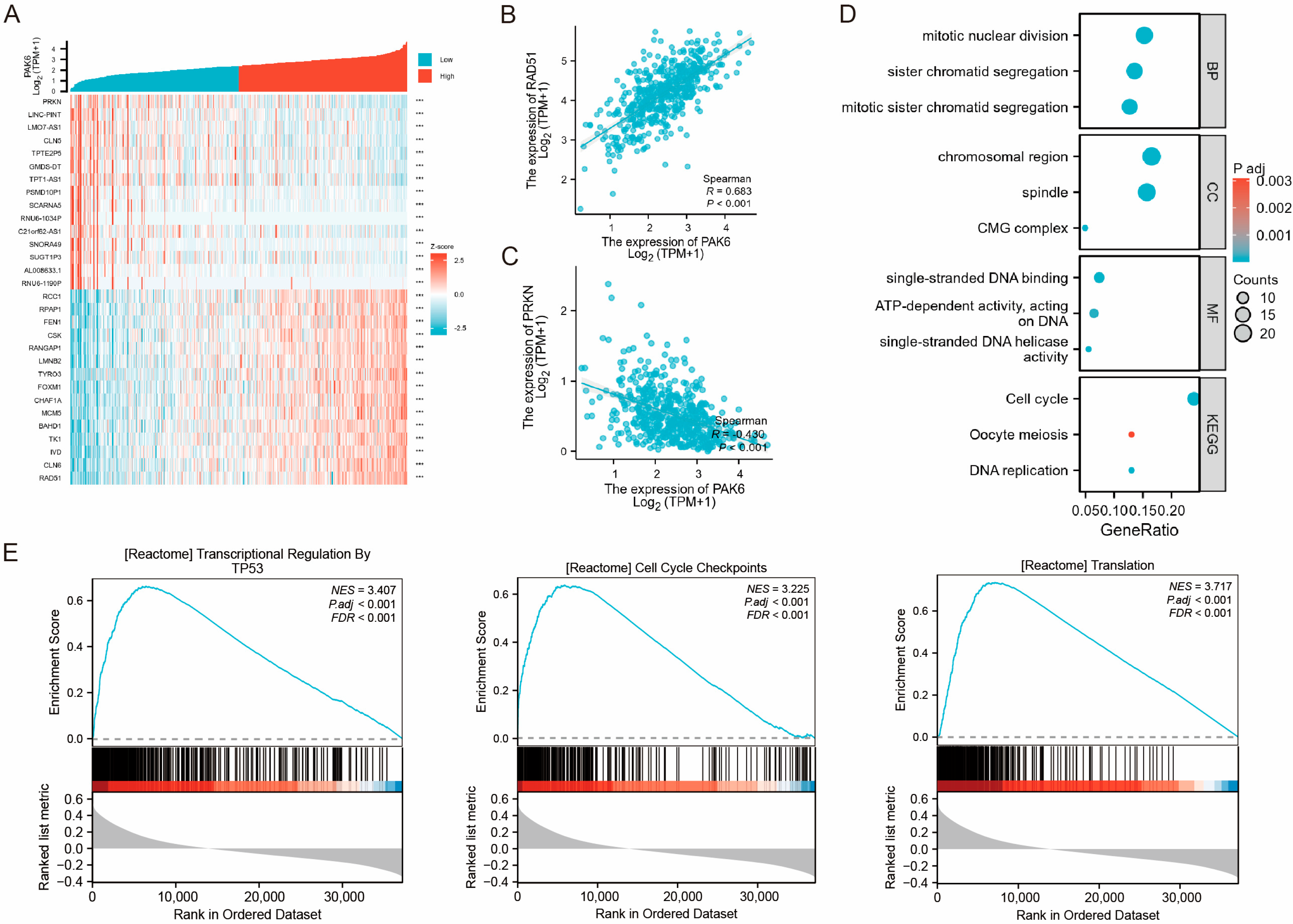
3.3. Functional Enrichment Implicates PAK6 May Be Involved in Malignant Progression of CRC
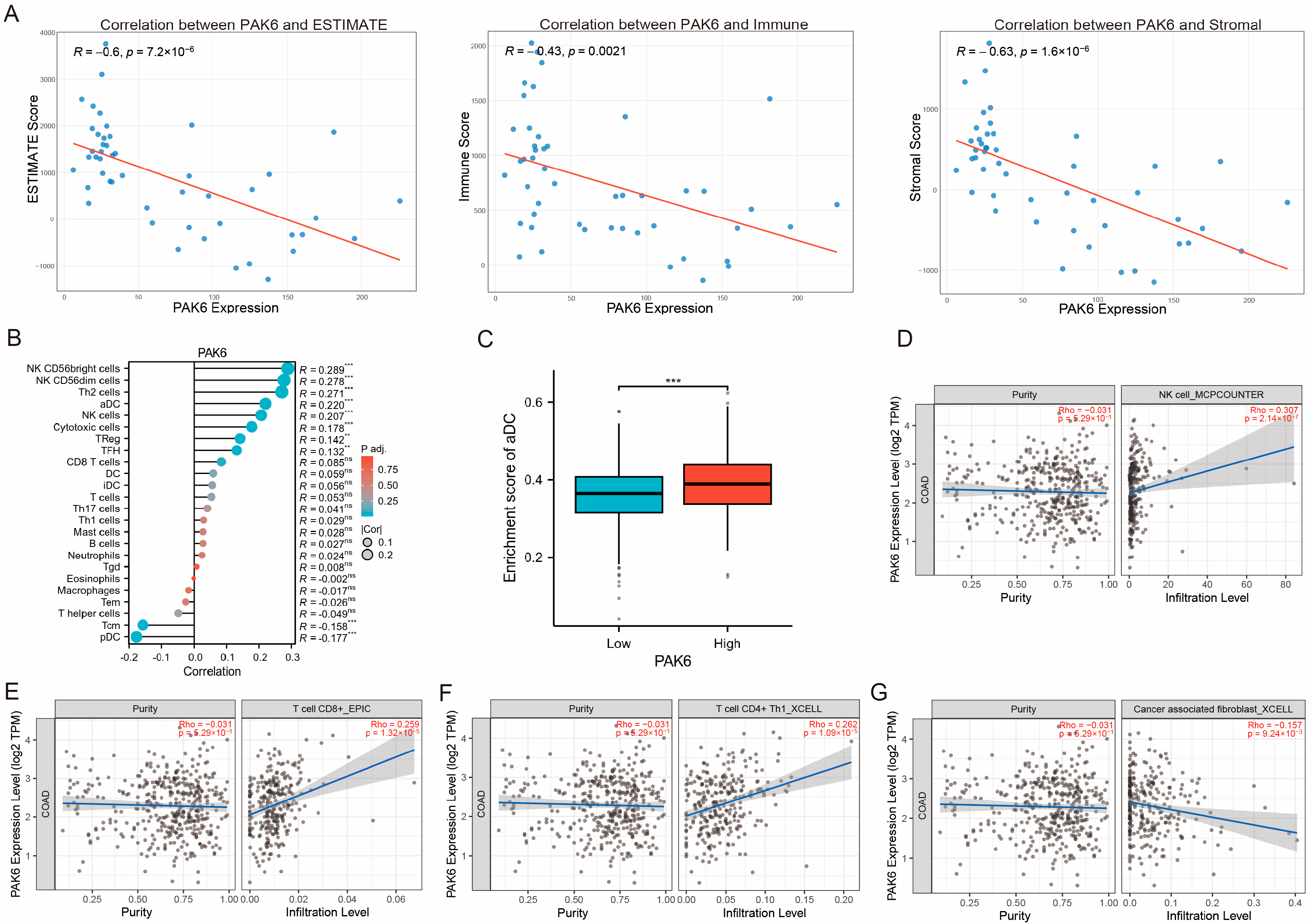
3.4. PAK6 Expression Negatively Correlates with Tumor Microenvironment Scores and Influences Immune Cell Infiltration
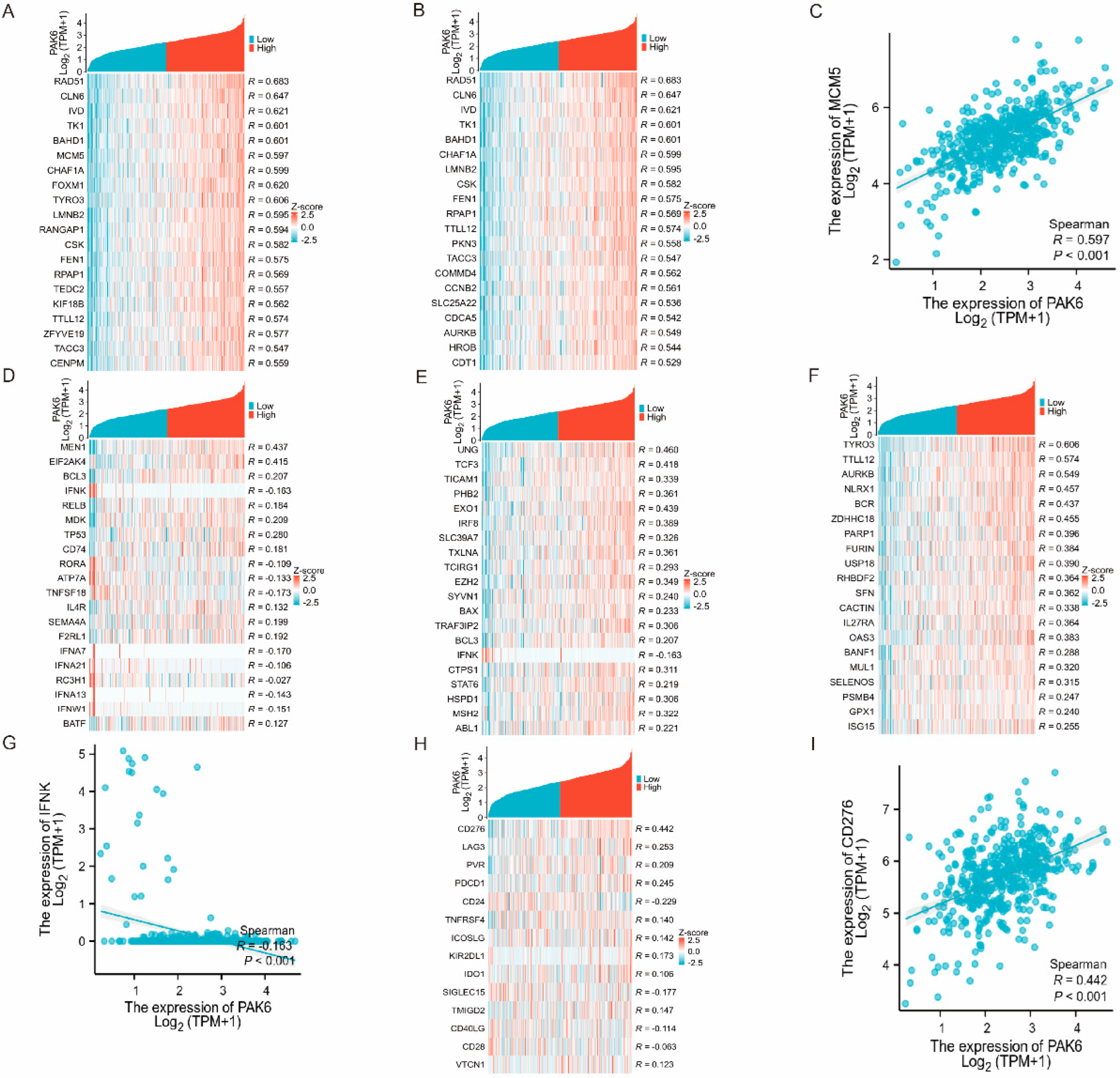
3.5. PAK6 Is Linked to Immune Regulatory Genes and Checkpoint Molecules
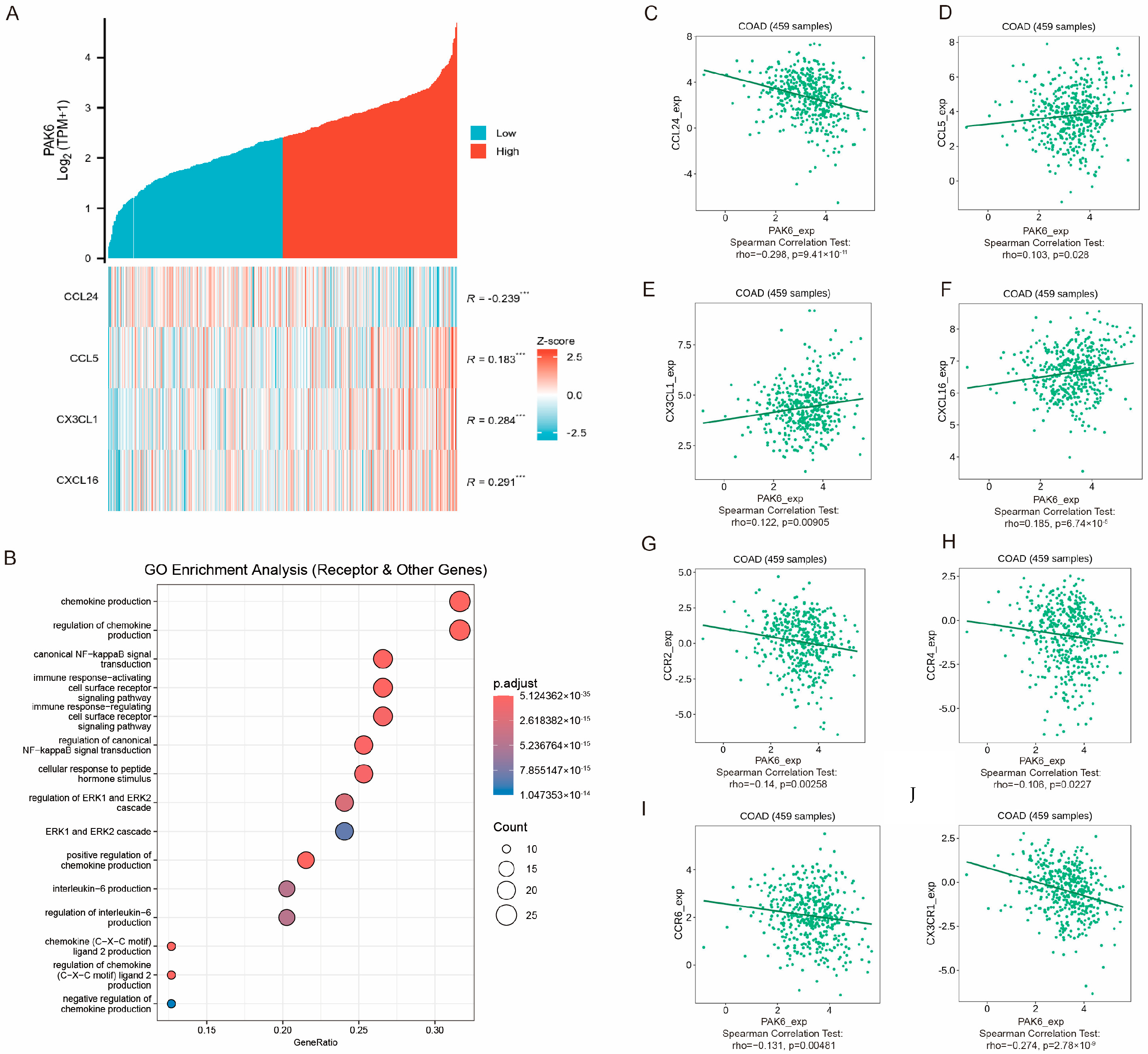
3.6. PAK6 Is Associated with Chemokine Signaling and Immune Cell Migration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunwobi, O.O.; Mahmood, F.; Akingboye, A. Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer: Current Research and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, J.; Shi, W.; Wu, X.; Shao, B.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Ni, L. Upregulation of p21-activated Kinase 6 in rat brain cortex after traumatic brain injury. J. Mol. Histol. 2011, 42, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Sun, M.; Chen, L. miR-3191 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating PAK6. Infect. Agents Cancer 2024, 19, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipili, A.; Babteen, N.A.; Kuwair, L.; Jannet, M.B.; Quist, J.; Ong, K.K.; Pitaluga, R.; Grigoriadis, A.G.; Tutt, A.; Wells, C.M. PAK6 acts downstream of IQGAP3 to promote contractility in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell. Signal 2024, 121, 111233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Lu, K.; Tao, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Guan, H.; Chen, M.; Xu, B. MicroRNA-328 directly targets p21-activated protein kinase 6 inhibiting prostate cancer proliferation and enhancing docetaxel sensitivity. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7389–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chang, Y.; Huang, A.; Xu, T.; Li, G.; Wu, G. PAK6 promotes cervical cancer progression through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabit, H.; Pawlik, T.M.; Abdel-Ghany, S.; Arneth, B. Defensins: Exploring Their Opposing Roles in Colorectal Cancer Progression. Cancers 2024, 16, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Lee, C.-J.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, W.-J.; Jang, T.-Y.; Jeon, S.-E.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, S.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. Dysadherin awakens mechanical forces and promotes colorectal cancer progression. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4399–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, T.; Shiu, K.-K.; Kim, T.W.; Jensen, B.V.; Jensen, L.H.; Punt, C.; Smith, D.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Benavides, M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Microsatellite-Instability–High Advanced Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formica, V.; Sera, F.; Cremolini, C.; Riondino, S.; Morelli, C.; Arkenau, H.-T.; Roselli, M. KRAS and BRAF Mutations in Stage II and III Colon Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Oncology meets immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.P.; Bruce, A.T.; Ikeda, H.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Cancer immunoediting: From immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, M.J.; Thia, K.Y.; Street, S.E.; Cretney, E.; Trapani, J.A.; Taniguchi, M.; Kawano, T.; Pelikan, S.B.; Crowe, N.Y.; Godfrey, D.I. Differential tumor surveillance by natural killer (NK) and NKT cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.-Z.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell 2010, 141, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Ye, D.; Xia, H.; Xu, H.; Tang, W.; Tang, Q.; Bi, F. Sertraline inhibits stress-induced tumor growth through regulating CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2022, 33, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, G.; Wang, M.; Su, T.; Li, H.; et al. Genetically engineered macrophages reverse the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and improve immunotherapeutic efficacy in TNBC. Mol. Ther. 2025, 33, 3339–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, X.; Chao, X.; Wang, F.; Cai, L.; Yan, Z.; Xie, L.; Guo, X. Systemic analysis of the expression and prognostic significance of PAKs in breast cancer. Genomics 2020, 112, 2433–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Han, K.; Chen, Y.; Wei, L.; Sun, X.; Luo, Y.; Wen, L.; Tan, L. P21 activated kinase 6: A promising tool for predicting small cell lung cancer diagnosis and treatment response. PeerJ 2025, 13, e19714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Chen, R.; Li, X.; Cai, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Downregulation of microRNA-23a suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by targeting the PAK6-LIMK1 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3904–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, S.K.; Saji, M.; Zhang, X.; Jarjoura, D.; Fusco, A.; Vasko, V.V.; Ringel, M.D. Group I p21-activated kinases regulate thyroid cancer cell migration and are overexpressed and activated in thyroid cancer invasion. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Miao, J.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Qiao, H. Expression and prognostic significance of p21-activated kinase 6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 189, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Han, Z.; Sun, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, C.; Yu, S.; Hu, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. PAK6 promotes homologous-recombination to enhance chemoresistance to oxaliplatin through ATR/CHK1 signaling in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheurlen, K.M.; Billeter, A.T.; O’Brien, S.J.; Galandiuk, S. Metabolic dysfunction and early-onset colorectal cancer–how macrophages build the bridge. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 6679–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, X. Identification of molecular features correlating with tumor immunity in gastric cancer by multi-omics data analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, C.M.; Rauen, T.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Grammatikos, A.P.; Rodriguez Rodriguez, N.; Ioannidis, C.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Crispin, J.C.; Tsokos, G.C. Stat3 promotes IL-10 expression in lupus T cells through trans-activation and chromatin remodeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13457–13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçin, M.; Malhan, D.; Basti, A.; Peralta, A.R.; Ferreira, J.J.; Relógio, A. A Computational Analysis in a Cohort of Parkinson’s Disease Patients and Clock-Modified Colorectal Cancer Cells Reveals Common Expression Alterations in Clock-Regulated Genes. Cancers 2021, 13, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total (N) | HR(95% CI) Univariate Analysis | p Value Univariate Analysis | HR (95% CI) Multivariate Analysis | p Value Multivariate Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathologic T stage | 476 | ||||
| T1 & T2 | 94 | Reference | Reference | ||
| T3 & T4 | 382 | 3.072 (1.423–6.631) | 0.004 | 279,063.4392 (0.000–Inf) | 0.992 |
| Pathologic N stage | 477 | ||||
| N0 | 283 | Reference | Reference | ||
| N1 & N2 | 194 | 2.592 (1.743–3.855) | <0.001 | 0.003 (0.000–0.078) | <0.001 |
| Pathologic M stage | 414 | ||||
| M0 | 348 | Reference | Reference | ||
| M1 | 66 | 4.193 (2.683–6.554) | <0.001 | 0.956 (0.047–19.598) | 0.977 |
| Pathologic stage | 466 | ||||
| Stage I & Stage II | 267 | Reference | Reference | ||
| Stage III & Stage IV | 199 | 2.947 (1.942–4.471) | <0.001 | 1,085,453,553.6095 (0.000–Inf) | 0.981 |
| PAK6 | 477 | ||||
| Low | 238 | Reference | Reference | ||
| High | 239 | 1.803 (1.211–2.682) | 0.004 | 2.651 (0.251–28.041) | 0.418 |
| Primary therapy outcome | 250 | ||||
| PD&SD | 29 | Reference | Reference | ||
| PR&CR | 221 | 0.094 (0.049–0.182) | <0.001 | 0.020 (0.002–0.168) | <0.001 |
| Gender | 477 | ||||
| Female | 226 | Reference | |||
| Male | 251 | 1.101 (0.746–1.625) | 0.627 | ||
| Age | 477 | ||||
| ≤65 | 194 | Reference | Reference | ||
| >65 | 283 | 1.610 (1.052–2.463) | 0.028 | 2.372 (0.224–25.170) | 0.473 |
| Histological type | 472 | ||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 402 | Reference | |||
| Mucinous adenocarcinoma | 70 | 1.269 (0.753–2.139) | 0.371 | ||
| Residual tumor | 373 | ||||
| R0 | 345 | Reference | Reference | ||
| R1&R2 | 28 | 4.364 (2.401–7.930) | <0.001 | 1.625 (0.081–32.707) | 0.751 |
| Perineural invasion | 181 | ||||
| No | 135 | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes | 46 | 1.940 (0.982–3.832) | 0.056 | 1.147 (0.055–23.782) | 0.93 |
| Lymphatic invasion | 433 | ||||
| No | 265 | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes | 168 | 2.450 (1.614–3.720) | <0.001 | 17.373 (1.959–154.051) | 0.01 |
| Characteristic | Levels | PAK6 Expression | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n = 24) | High (n = 25) | |||
| Gender | Male | 14 (28.6%) | 13 (26.5%) | 0.656 |
| Female | 10 (20.4%) | 12 (24.5%) | ||
| Age | <60 | 8 (16.3%) | 13 (26.5%) | 0.187 |
| ≥60 | 16 (32.7%) | 12 (24.5%) | ||
| Differentiation | Well | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (10.2%) | 0.021 * |
| Moderate | 24 (49.0%) | 20 (40.8%) | ||
| Tumor size | <4 cm | 12 (24.5%) | 16 (32.7%) | 0.322 |
| ≥4 cm | 12 (24.5%) | 9 (18.4%) | ||
| LVI | No | 15 (30.6%) | 13 (26.5%) | 0.458 |
| Yes | 9 (18.4%) | 12 (24.5%) | ||
| PNI | No | 19 (38.8%) | 17 (34.7%) | 0.376 |
| Yes | 5 (10.2%) | 8 (16.3%) | ||
| T stage | T1 + T2 | 4 (8.2%) | 4 (8.2%) | 0.95 |
| T3 + T4 | 20 (40.8%) | 21 (42.9%) | ||
| N stage | Negative | 15 (30.6%) | 14 (28.6%) | 0.644 |
| Positive | 9 (18.4%) | 11 (22.4%) | ||
| M stage | Negative | 20 (40.8%) | 19 (38.8%) | 0.524 |
| Positive | 4 (8.2%) | 6 (12.2%) | ||
| Stage | Early (I + II) | 12 (24.5%) | 12 (24.5%) | 0.889 |
| Late (III + IV) | 12 (24.5%) | 13 (26.5%) | ||
| Immune Cell Type | Coefficient of Correlation | p Value adj.* |
|---|---|---|
| NK CD56bright cells | 0.288948 | 9.9 × 10−9 |
| NK CD56dim cells | 0.277894 | 2.6235 × 10−9 |
| Th2 cells | 0.270829 | 4.89 × 10−9 |
| aDC | 0.220401 | 0.00000243 |
| NK cells | 0.207003 | 0.000008658 |
| Cytotoxic cells | 0.177571 | 0.0001188 |
| pDC | −0.177497 | 0.0001188 |
| Tcm | −0.157958 | 0.0005625 |
| TFH | 0.13176 | 0.0038 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, C.; Yue, G.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Prognostic and Immunomodulatory Roles of PAK6 in Colorectal Cancer Through Integrative Transcriptomic and Clinical Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 3183. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193183
Ye C, Yue G, Yang L, Wang Z. Prognostic and Immunomodulatory Roles of PAK6 in Colorectal Cancer Through Integrative Transcriptomic and Clinical Analysis. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3183. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193183
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Chunxiang, Guanjun Yue, Lei Yang, and Zhenjun Wang. 2025. "Prognostic and Immunomodulatory Roles of PAK6 in Colorectal Cancer Through Integrative Transcriptomic and Clinical Analysis" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3183. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193183
APA StyleYe, C., Yue, G., Yang, L., & Wang, Z. (2025). Prognostic and Immunomodulatory Roles of PAK6 in Colorectal Cancer Through Integrative Transcriptomic and Clinical Analysis. Cancers, 17(19), 3183. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193183





