Can PSMA-Targeting Radiopharmaceuticals Be Useful for Detecting Brain Metastasis of Various Tumors Using Positron Emission Tomography?
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Patients
2.2. 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging
2.3. 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT Imaging
2.4. IHC Staining with PSMA
Scoring System
- SP was visually quantified using a four-tiered system:
- 0: SP <20% (no expression).
- 1: SP 20–50% (low expression).
- 2: SP 50–80% (moderate expression).
- 3: SP >80% (high expression).
- SI was also evaluated on a four-tiered scale:
- 0: No staining.
- 1: Weak.
- 2: Moderate.
- 3: Strong.
- The final IHC score was calculated by multiplying the staining percentage score by the staining intensity score. Both membranous and cytoplasmic PSMA expression were recorded (Table 2).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
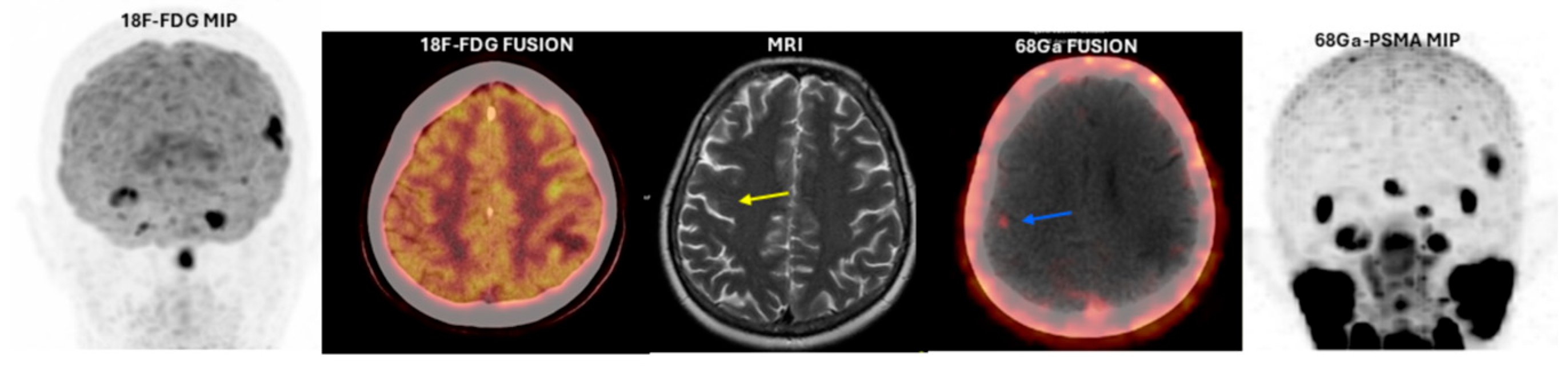
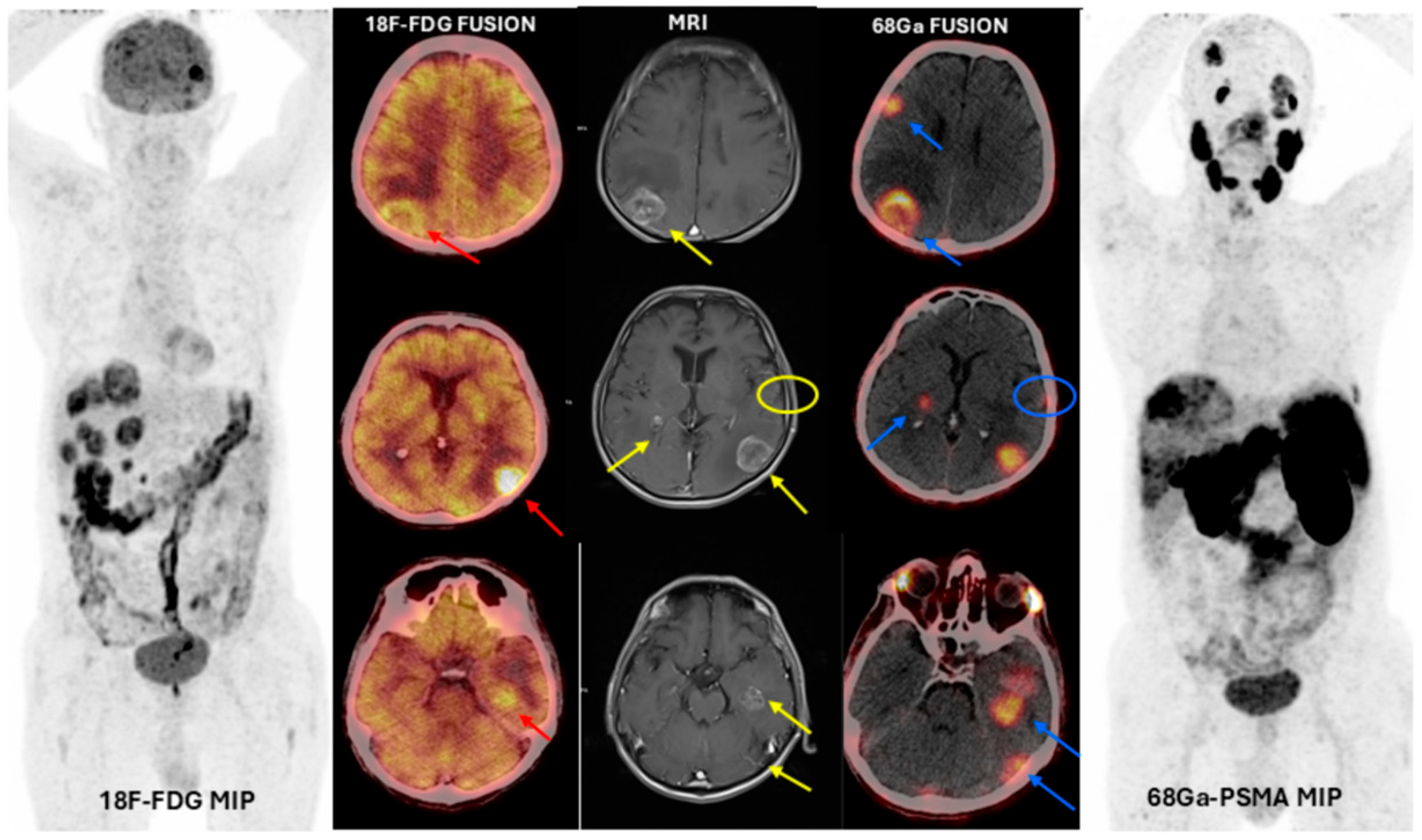
3. Results
| No | Age | Gender | Primary Histopathological Diagnosis | Number of Metastatic Lesions | Axial Diameter of the Most Prominent Metastatic Lesion (cm) | 18F- FDG SUV Max of the Most Prominent Metastatic Lesion | 68Ga-PSMA-11 SUVmax of the Most Prominent Metastatic Lesion | Smallest Axial Diameter of the Lesion Detected with 68Ga-PSMA-11 (cm) | Lesions Observed in 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT not Observed in 18F- FDG PET/CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 47 | Female | Triple-negative ID Breast Carcinoma | 1 | 4.34 | 11.97 | 6.58 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| 2 | 51 | Female | Triple-negative ID Breast Carcinoma | Multiple | 1.13 | 23.98 | 5.55 | 0.71 | Not applicable |
| 3 | 53 | Female | HER2 Positive ID Breast Carcinoma | Multiple | 2.41 | 15.69 | 13.83 | 0.40 | Not applicable |
| 4 | 65 | Female | Luminal B ID Breast Carcinoma | 3 | 2.30 | 17.41 | 7.72 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| 5 | 34 | Female | Luminal B ID Breast Carcinoma | 1 | 2.77 | 20.19 | 10.77 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| 6 | 41 | Female | HER2 Positive ID Breast Carcinoma | 1 | 1.20 | 21.79 | 14.50 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| 7 | 43 | Female | Luminal B ID Breast Carcinoma | Multiple | 2.08 | 30.67 | 4.49 | 0.22 | + |
| 8 | 47 | Female | Luminal B ID Breast Carcinoma | Multiple | 0.57 | No uptake | 2.11 | 0.26 | + |
| 9 | 61 | Male | Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma | Multiple | 1.45 | 11.80 | 4.38 | 0.46 | + |
| 10 | 56 | Female | Lung Adenocarcinoma | 1 | 2.34 | No uptake | 2.19 | 0.39 | + |
| 11 | 71 | Male | Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma | 1 | 3.19 | 10.55 | 4.35 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| 12 | 67 | Male | Small Cell Lung Carcinoma | Multiple | 1.27 | 9.33 | 3.59 | 0.31 | Not applicable |
| 13 | 72 | Male | Colorectal Adenocarcinoma | 1 | 2.00 | 5.60 | 3.80 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| 14 | 51 | Male | Colorectal Adenocarcinoma | 1 | 1.60 | No uptake | 2.80 | 1.60 | + |
| 15 | 67 | Male | Colorectal Adenocarcinoma | Multiple | 2.46 | 11.72 | 6.51 | 0.35 | + |
| 16 | 74 | Male | Colorectal Adenocarcinoma | 4 | 1.39 | 34.87 | 8.29 | 0.54 | Not applicable |
| 17 | 68 | Male | Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Grade 3 | Multiple | 3.02 | 20.29 | 12.44 | 1.32 | + |
| 18 | 47 | Male | Signet Ring Cell Gastric Carcinoma | 3 | 2.28 | 32.00 | 3.77 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| 19 | 64 | Male | Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma | 1 | 1.16 | No uptake | 24.95 | 1.16 | + |
| 20 | 63 | Male | Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma | 1 | 1.76 | 29.37 | 6.89 | 1.76 | Not applicable |
| 21 | 56 | Male | Lung Adenocarcinoma | 1 | 2.81 | No uptake | 2.7 | 2.81 | + |
| 22 | 60 | Male | Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma + Squamous Cell Nasopharnygeal Carcinoma | 1 | 3.73 | 12.27 | 2.23 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| 23 | 51 | Female | Triple-negative ID Breast Carcinoma | 2 | 1.6 | 9.55 | 4.3 | 0.76 | + |
| 24 | 81 | Female | Luminal B ID Breast Carcinoma | 1 | 2.05 | 19.68 | 4.18 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| 25 | 71 | Male | Malignant Melanoma | Multiple | 3.23 | 9.72 | 7.08 | 0.48 | + |
| 26 | 63 | Male | Squamous Cell Larynx Carcinoma + Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma | 1 | 2.18 | No uptake | 2.9 | 2.18 | + |
| 27 | 82 | Male | Squamous Cell Larynx Carcinoma | 1 | 1.7 | No uptake | No uptake | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| N | Primary Histopathological Diagnosis | Primary Tumor PSMA Staining Score | Metastatic Tumor PSMA Staining Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Triple-negative ID Breast Carcinoma | SP:1 | 1 × 1:1 | SP:1 | 1 × 1:1 |
| SI:1 | SI:1 | ||||
| 2. | Triple-negative ID Breast Carcinoma | SP:0 | 0 | SP:0 | 0 |
| SI:0 | SI:0 | ||||
| 13. | Colorectal Adenocarcinoma | SP:1 | 1 × 1:1 | SP:1 | 1 × 1:1 |
| SI:1 | SI:1 | ||||
| 16. | HER2 Positive ID Breast Carcinoma | SP:1 | 1 × 1:1 | SP:2 | 2 × 1:2 |
| SI:1 | SI:1 | ||||
| 18. | Luminal B ID Breast Carcinoma | SP:1 | 1 × 1:1 | SP:0 | 0 |
| SI:1 | SI:0 | ||||
| 10. | Lung Adenocarcinoma | SP:0 | 0 | SP:0 | 0 |
| SI:0 | SI:0 | ||||
| 12. | Small Cell Lung Carcinoma | SP:0 | 0 | SP:0 | 0 |
| SI:0 | SI:0 | ||||
| 3. | HER2 Positive ID Breast Carcinoma | SP:0 | 0 | SP:0 | 0 |
| SI:0 | SI:0 | ||||
| 5. | Luminal B ID Breast Carcinoma | SP:0 | SP:0 | 0 | |
| SI:0 | 0 | SI:0 | |||
| 8. | Luminal B ID Breast Carcinoma | SP:1 | 1 × 1:1 | SP:2 | 2 × 1:2 |
| SI:1 | SI:1 | ||||
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doron, H.; Pukrop, T.; Erez, N. A Blazing Landscape: Neuroinflammation Shapes Brain Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokas, E.; Steinbach, J.P.; Rödel, C. Biology of brain metastases and novel targeted therapies: Time to translate the research. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1835, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xue, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, G. A molecular view of the radioresistance of gliomas. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 100931–100941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, A.; Febvey, O.; Mognetti, T.; Frappaz, D.; Kryza, D. Contribution of Different Positron Emission Tomography Tracers in Glioma Management: Focus on Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, M.; Collins, V.P.; Ehrin, E.; Ericson, K.; Eriksson, L.; Greitz, T.; Halldin, C.; von Hoist, H.; Långström, B.; Lilja, A.; et al. Discrepancies in Brain Tumor Extent as Shown by Computed Tomography and Positron Emission Tomography Using [68Ga]EDTA, [11C]Glucose, and [11C]Methionine. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1983, 7, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herholz, K.; Langen, K.-J.; Schiepers, C.; Mountz, J.M. Brain tumors. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 42, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galldiks, N.; Langen, K.-J.; Pope, W.B. From the clinician’s point of view—What is the status quo of positron emission tomography in patients with brain tumors? Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galldiks, N.; Langen, K.-J.; Albert, N.L.; Chamberlain, M.; Soffietti, R.; Kim, M.M.; Law, I.; Le Rhun, E.; Chang, S.; Schwarting, J.; et al. PET imaging in patients with brain metastasis—Report of the RANO/PET group. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, F.d.G.; Queiroz, M.A.; Nunes, R.F.; Costa, L.B.; Zaniboni, E.C.; Marin, J.F.G.; Cerri, G.G.; Buchpiguel, C.A. Nonprostatic diseases on PSMA PET imaging: A spectrum of benign and malignant findings. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiess, A.P.; Banerjee, S.R.; Mease, R.C.; Rowe, S.P.; Rao, A.; Foss, C.A.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Cho, S.Y.; Nimmagadda, S.; et al. Pros-tate-specific membrane antigen as a target for cancer imaging and therapy. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 59, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demirci, E.; Ocak, M.; Kabasakal, L.; Decristoforo, C.; Talat, Z.; Halaç, M.; Kanmaz, B. 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT imaging of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 41, 1461–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragomeni, R.A.S.; Amir, T.; Sheikhbahaei, S.; Harvey, S.C.; Javadi, M.S.; Solnes, L.B.; Kiess, A.P.; Allaf, M.E.; Pomper, M.G.; Gorin, M.A.; et al. Imaging of Nonprostate Cancers Using PSMA-Targeted Radiotracers: Rationale, Current State of the Field, and a Call to Arms. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathekge, M.; Modiselle, M.; Vorster, M.; Mokgoro, N.; Nyakale, N.; Mokaleng, B.; Ebenhan, T. 68Ga-PSMA imaging of metastatic breast cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 42, 1482–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgun, E.; Akgun, M.Y.; Selçuk, H.H.; Uzan, M.; Sayman, H.B. 68Ga PSMA PET/MR in the differentiation of low and high grade gliomas: Is 68Ga PSMA PET/MRI useful to detect brain gliomas? Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 130, 109199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosonaga, M.; Saya, H.; Arima, Y. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying brain metastasis of breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, A.G.; Edgar, M.A.; Lavi, E.; Liu, H.; Salerno, P.; Bander, N.H.; Gutin, P.H. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen as a Potential Novel Vascular Target for Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011, 135, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, J.T.; Lehtipuro, S.; Sihto, H.; Tóvári, J.; Reiniger, L.; Téglási, V.; Moldvay, J.; Nykter, M.; Haapasalo, H.; Le Joncour, V.; et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in the vasculature of primary lung carcinomas associates with faster metastatic dissemination to the brain. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6916–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habbous, S.; Forster, K.; Darling, G.; Jerzak, K.; Holloway, C.M.B.; Sahgal, A.; Das, S. Incidence and real-world burden of brain metastases from solid tumors and hematologic malignancies in Ontario: A population-based study. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 3, vdaa178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rkosy, P.; Tóth, J.; Béres, E.; Tóth, D.; Szivos, L.; Nagy, J.; Klekner, A.; Virga, J. Prognosis and Treatment Outcomes of Patients Undergoing Resection of Brain Metastases from Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, A.G.; Varma, S.; Greenwood, E.A.; Christos, P.J.; Chao, K.S.C.; Liu, H.; Bander, N.H.; Shin, S.J. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in tumor-associated vasculature of breast cancers. APMIS 2013, 122, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, N.; Pastorino, S.; Jiang, P.; Lambert, G.; Crawford, J.R.; Gymnopoulos, M.; Piccioni, D.; Juarez, T.; Pingle, S.C.; Ma-kale, M.; et al. Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) expression in primary gliomas and breast cancer brain metastases. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hod, N.M.; Lantsberg, S.; Benkovich, E.; Kazap, D.E.; Preiskel, M.; Levin, D. Incidental Detection of Malignant Melanoma Brain Recurrence on 68Ga–Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 45, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo-Armenta, P.; Soto-Andonaegui, J.; Villanueva-Pérez, R.M.; González-Díaz, J.I.; Contreras-Contreras, K.; Bautista-Wong, C.G.; Sandoval-Bonilla, B.; Nettel-Rueda, B.; Santos-Cuevas, C.; Ferro-Flores, G. [99mTc]Tc-iPSMA SPECT brain imaging as a potential specific diagnosis of metastatic brain tumors and high-grade gliomas. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 96–97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, E.; Ergül, N.; Karagöz, Y.; Gedik, A.A.; Çermik, T.F. Recurrent Brain Metastasis of Triple Negative Breast Cancer With High Uptake in 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 46, e106–e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Schlenkhoff, C.; Schwarz, B.; Essler, M.; Ahmadzadehfar, H. Combination of 177Lu-PSMA-617 and Exter-nal Radiotherapy for the Treatment of Cerebral Metastases in Patients with Castration-Resistant Metastatic Pros-tate Cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 42, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armellina, S.D.; Aghakhanyan, G.; Rizzo, A.; Fanni, S.C.; Aringhieri, G.; Faggioni, L.; Cioni, D.; Neri, E.; Volterrani, D.; Morbelli, S. PSMA-targeted PET imaging for brain metastases from non-prostatic solid tumors: A systematic review. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1553505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, B.; Vrachimis, A.; Schäfers, M.; Stegger, L.; Rahbar, K. Subacute Stroke Mimicking Cerebral Metastasis in 68Ga-PSMA-HBED-CC PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 41, e449–e451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, G.; Miles, K. Subacute Cerebellar Infarction With Uptake on 68Ga–Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 43, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; McIntosh, L. Subacute Cerebral Infarct: An Unusual Cause of Radiotracer Uptake at 18 F-PSMA PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2024, 49, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yue, D. 68 Ga-PSMA Uptake of Brain Abscesses in a Patient With Prostate Cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2025, 50, e283–e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arslan, E.; Ergül, N.; Şahin, R.; Beyhan, E.; Erol Fenercioğlu, Ö.; Karagöz, Y.; Algün Gedik, A.; Bozkaya, Y.; Çermik, T.F. Can PSMA-Targeting Radiopharmaceuticals Be Useful for Detecting Brain Metastasis of Various Tumors Using Positron Emission Tomography? Cancers 2025, 17, 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183088
Arslan E, Ergül N, Şahin R, Beyhan E, Erol Fenercioğlu Ö, Karagöz Y, Algün Gedik A, Bozkaya Y, Çermik TF. Can PSMA-Targeting Radiopharmaceuticals Be Useful for Detecting Brain Metastasis of Various Tumors Using Positron Emission Tomography? Cancers. 2025; 17(18):3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183088
Chicago/Turabian StyleArslan, Esra, Nurhan Ergül, Rahime Şahin, Ediz Beyhan, Özge Erol Fenercioğlu, Yeşim Karagöz, Arzu Algün Gedik, Yakup Bozkaya, and Tevfik Fikret Çermik. 2025. "Can PSMA-Targeting Radiopharmaceuticals Be Useful for Detecting Brain Metastasis of Various Tumors Using Positron Emission Tomography?" Cancers 17, no. 18: 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183088
APA StyleArslan, E., Ergül, N., Şahin, R., Beyhan, E., Erol Fenercioğlu, Ö., Karagöz, Y., Algün Gedik, A., Bozkaya, Y., & Çermik, T. F. (2025). Can PSMA-Targeting Radiopharmaceuticals Be Useful for Detecting Brain Metastasis of Various Tumors Using Positron Emission Tomography? Cancers, 17(18), 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183088






