Pirtobrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Navigating Resistance and the Personalisation of BTK-Targeted Therapy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
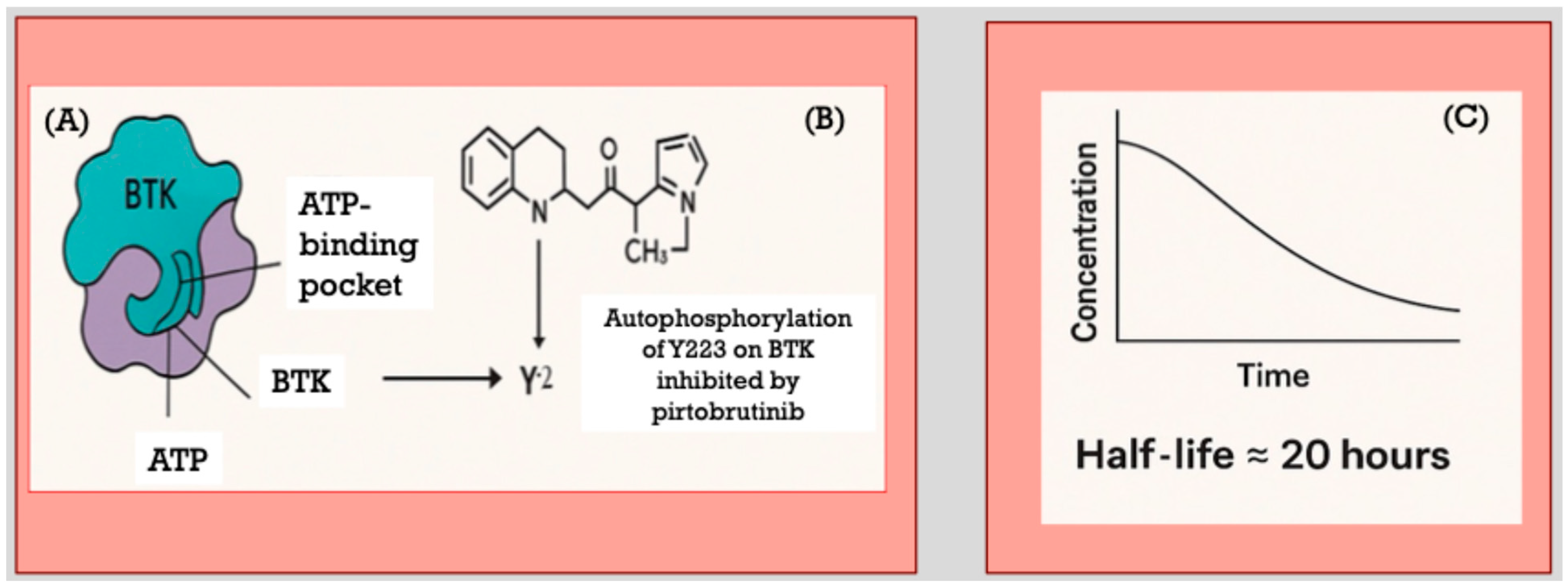
2. Pirtobrutinib Mechanism-of-Action and Pharmacology
3. Early Clinical Studies
4. The Phase 3 Trial BRUIN CLL-321
5. Pirtobrutinib in Patients in Richter Transformation (RT)
6. Pirtobrutinib in Fixed-Duration Regimens
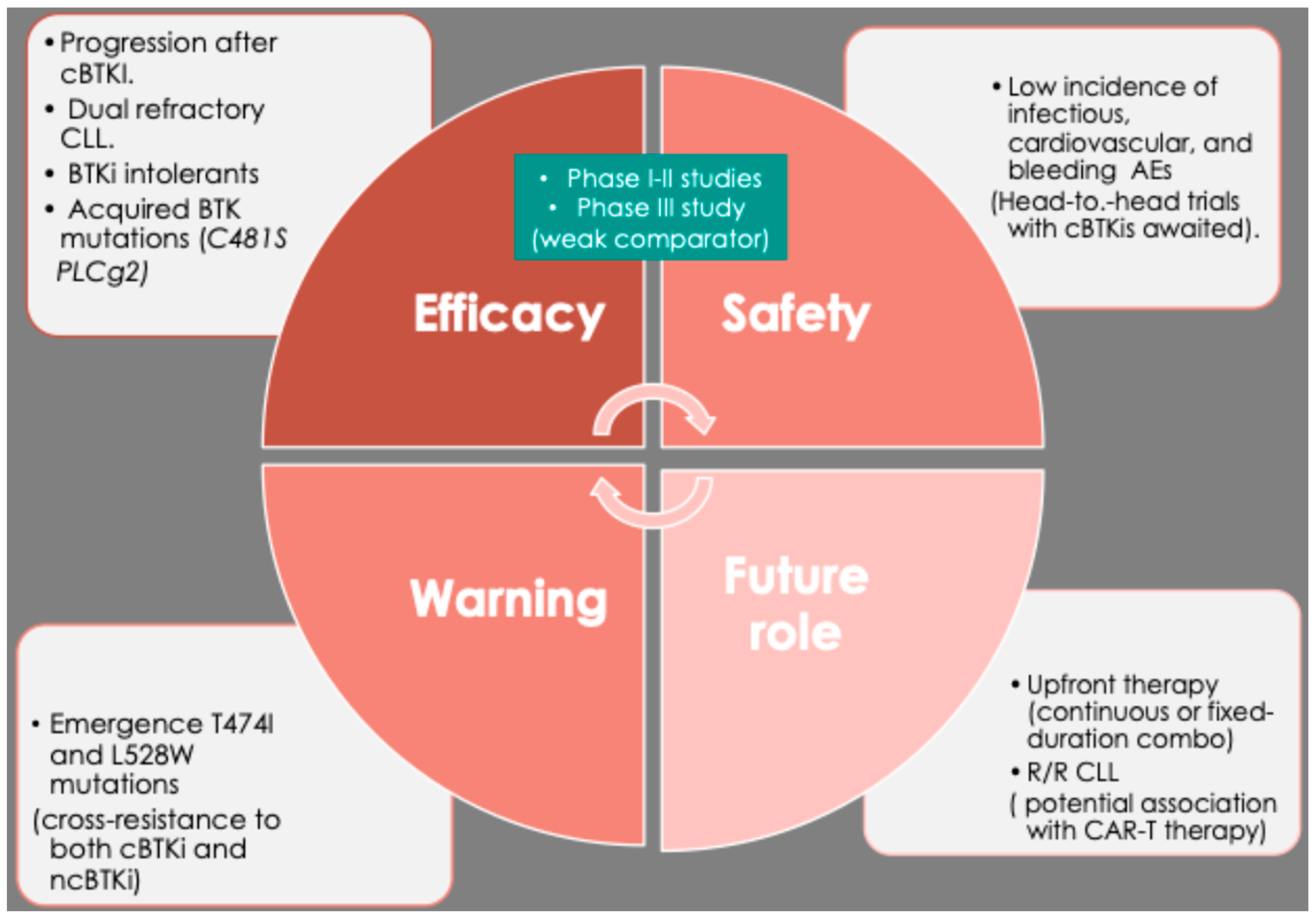
7. Pirtobrutinib Resistance and the Strategic Integration in CLL Management
8. Improving BTKi-Safety with Pirtobrutinib
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, S.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Sharman, J.P.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Richards, D.A.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Ibrutinib as Initial Therapy for Elderly Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia or Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: An Open-Label, Multicentre, Phase 1b/2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Tedeschi, A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Ghia, P.; Bairey, O.; Hillmen, P.; Bartlett, N.L.; Li, J.; et al. Ibrutinib as Initial Therapy for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Tedeschi, A.; Sarma, A.; Patten, P.E.; Grosicki, S.; McCarthy, H.; Offner, F.; et al. Final analysis of the RESONATE-2 study: Up to 10 years of follow-up of first-line ibrutinib treatment for CLL/SLL. Blood 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Kay, N.E.; Hanson, C.A.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; et al. Ibrutinib-Rituximab or Chemoimmunotherapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Booth, A.M.; Ding, W.; Bartlett, N.L.; Brander, D.M.; Barr, P.M.; Rogers, K.A.; et al. Ibrutinib Regimens versus Chemoimmunotherapy in Older Patients with Untreated CLL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, C.; Greil, R.; Demirkan, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Anz, B.; Larratt, L.; Simkovic, M.; Samoilova, O.; Novak, J.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; et al. Ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab in first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (iLLUMINATE): A multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, T.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Barr, P.M.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Final analysis from RESONATE: Up to six years of follow-up on ibrutinib in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzmab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE TN): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman, M.; Munir, T.; Robak, T.; Brown, J.R.; Kahl, B.S.; Ghia, P.; Giannopoulos, K.; Šimkovič, M.; Österborg, A.; Laurenti, L.; et al. Zanubrutinib Versus Bendamustine and Rituximab in Patients with Treatment-Naïve Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: Median 5-Year Follow-Up of SEQUOIA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.; Thompson, P.A. BTK inhibitors in CLL: Second-generation drugs and beyond. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntington, S.F.; de Nigris, E.; Puckett, J.; Kamal-Bahl, S.; Farooqui, M.; Ryland, K.; Sarpong, E.; Leng, S.; Yang, X.; Doshi, J.A. Ibrutinib discontinuation and associated factors in a real-world national sample of elderly Medicare beneficiaries with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2023, 64, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, A.; Lamanna, N. Managing toxicities of Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2020, 2020, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, T.; Wiczer, T.; Waller, A.; Philippon, J.; Porter, K.; Haddad, D.; Guha, A.; Rogers, K.A.; Bhat, S.; Byrd, J.C.; et al. Hypertension and incident cardiovascular events following ibrutinib initiation. Blood 2019, 134, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, S.; Allsup, D.; Giannarelli, D. Prevalence of BTK and PLCG2 Mutations in CLL Patients with Disease Progression on BTK Inhibitor Therapy: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Hematol. 2025, 100, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Hillmen, P.; Ghia, P.; Kater, A.P.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Furman, R.R.; O’Brien, S.; Yenerel, M.N.; Illés, A.; Kay, N.; et al. Acalabrutinib Versus Ibrutinib in Previously Treated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results of the First Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3441–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; Jurczak, W.; Kaźmierczak, M.; Lamanna, N.; O’Brien, S.M.; Tam, C.S.; Qiu, L.; Zhou, K.; et al. Zanubrutinib or Ibrutinib in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Scheerens, H.; Li, S.J.; Schultz, B.E.; Sprengeler, P.A.; Burrill, L.C.; Mendonca, R.V.; Sweeney, M.D.; Scott, K.C.; Grothaus, P.G.; et al. Discovery of selective irreversible inhibitors for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Chem. Med. Chem. 2007, 2, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Sharman, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, N.; Yu, D.; Zhou, C.; Shi, G.; Zhang, B.; Wei, M.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; et al. Discovery of zanubrutinib (BGB-3111), a novel, potent, and selective covalent inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7923–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alu, A.; Lei, H.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. BTK inhibitors in the treatment of hematological malignancies and inflammatory diseases: Mechanisms and clinical studies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruessner, C.; Wiestner, A.; Sun, C. Resistance mechanisms and approach to chronic lymphocytic leukemia after BTK inhibitor therapy. Leuk Lymphoma 2025, 66, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Guinn, D.; Lehman, A.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, A.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Coleman, J.; Jones, D.; et al. BTK(C481S)-mediated resistance to ibrutinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molica, S.; Allsup, D. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): A Clinical View. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2025, 17, e2025053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, E.B.; Ebata, K.; Randeria, H.S.; Rosendahl, M.S.; Cedervall, E.P.; Morales, T.H.; Hanson, L.M.; Brown, N.E.; Gong, X.; Stephens, J.; et al. Preclinical characterization of pirtobrutinib, a highly selective, noncovalent (reversible) BTK inhibitor. Blood 2023, 142, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Gonzalez, A.; Alasfour, M.; Soong, D.; Noy, J.; Pongas, G. Advances in Targeted Therapy: Addressing Resistance to BTK Inhibition in B-Cell Lymphoid Malignancies. Cancers 2024, 16, 3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.A.; Tam, C.S. Pirtobrutinib: A new hope for patients with BTK inhibitor-refractory lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 2023, 141, 3137–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Balendran, S.; Blombery, P. Novel mechanisms of resistance in CLL: Variant BTK mutations in second-generation and noncovalent BTK inhibitors. Blood 2025, 145, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Utro, F.; Wang, Q.; Cha, J.; Vihinen, M.; Martindale, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, Y.; Tyekucheva, S.; Kim, A.S.; et al. Pirtobrutinib targets BTK C481S in ibrutinib-resistant CLL but second-site BTK mutations lead to resistance. Blood. Adv. 2023, 7, 1929–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, B.; Kismali, G.; Iles, L.R.; Manyam, G.C.; Ayres, M.L.; Chen, L.S.; Gagea, M.; Bertilaccio, M.T.S.; Wierda, W.G.; Gandhi, V. Pirtobrutinib inhibits wild-type and mutant Bruton’s tyrosine kinase-mediated signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Shah, N.N.; Jurczak, W.; Cheah, C.Y.; Pagel, J.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Fakhri, B.; Eyre, T.A.; Lamanna, N.; Patel, M.R.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (BRUIN): A phase 1/2 study. Lancet 2021, 397, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Woyach, J.A.; Brown, J.R.; Ghia, P.; Patel, K.; Eyre, T.A.; Munir, T.; Lech-Maranda, E.; Lamanna, N.; Tam, C.S.; et al. Pirtobrutinib after a Covalent BTK Inhibitor in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Wang, M.; Roeker, L.E.; Patel, K.; Woyach, J.A.; Wierda, W.G.; Ujjani, C.S.; Eyre, T.A.; Zinzani, P.L.; Alencar, A.J.; et al. Pirtobrutinib monotherapy in Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor-intolerant patients with B-cell malignancies: Results of the phase I/II BRUIN trial. Haematologica 2025, 110, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Jen, M.H.; Hess, L.M.; Zhang, J.; Goebel, B.; Pagel, J.M.; Abhyankar, S.; Davids, M.S.; Eyre, T.A. Pirtobrutinib versus venetoclax in covalent Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor-pretreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A matching-adjusted indirect comparison. Haematologica 2024, 109, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.A. Choosing between CAR T-cell therapy and pirtobrutinib in double-refractory CLL. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 22, 494–496. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, N.; Eyre, T.A.; Winfree, K.B.; Bhandari, N.R.; Khanal, M.; Sugihara, T.; Chen, Y.; Abada, P.; Patel, K. Real-world outcomes after discontinuation of covalent BTK inhibitor-based therapy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 2025, 66, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kater, A.P.; Harrup, R.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Owen, C.J.; Assouline, S.; Lamanna, N.; Robak, T.; de la Serna, J.; Jaeger, U.; et al. The MURANO study: Final analysis and retreatment/crossover substudy results of VenR for patients with relapsed/refractory CLL. Blood 2025, 145, 2733–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Munir, T.; Grosicki, S.; Roeker, L.E.; Burke, J.M.; Chen, C.I.; Grzasko, N.; Follows, G.; Mátrai, Z.; Sanna, A.; et al. Phase III Trial of Pirtobrutinib Versus Idelalisib/Rituximab or Bendamustine/Rituximab in Covalent Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Pretreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (BRUIN CLL-321). J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 2538–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.; Guddati, A.K. Clinical endpoints in oncology—A primer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Molica, S. Redefining efficacy and safety endpoints for chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the era of targeted therapy. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2023, 16, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.C.; Bhat, S.A.; Jurczak, W.; Patel, K.; Shah, N.N.; Woyach, J.A.; Coombs, C.C.; Eyre, T.A.; Danecki, M.; Dlugosz-Danecka, M.; et al. Outcomes of Therapies Following Discontinuation of Non-Covalent Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Richter Transformation: Results from an International, Multicenter Study. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. S1), 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierda, W.G.; Shah, N.N.; Cheah, C.Y.; Lewis, D.; Hoffmann, M.S.; Coombs, C.C.; Lamanna, N.; Ma, S.; Jagadeesh, D.; Munir, T.; et al. Pirtobrutinib, a highly selective, non-covalent (reversible) BTK inhibitor in patients with B-cell malignancies: Analysis of the Richter transformation subgroup from the multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 BRUIN study. Lancet Haematol 2024, 11, e682–e692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A. Richter transformation-is there light at the end of this tunnel? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2023, 2023, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, S. Navigating the gap between guidelines and practical challenges in selecting first-line therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2025, 18, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.R.; Stephens, D.M. Is there a role for anti-CD20 antibodies in CLL? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2021, 2021, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nhu, N.T.; Tran, V.K.; Viet-Nhi, N.K.; Ho, X.D.; Jhan, M.K.; Chen, Y.P.; Lin, C.F. Efficacy and safety of add-on anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody to Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeker, L.E.; Woyach, J.A.; Cheah, C.Y.Y.; Coombs, C.C.; Shah, N.N.; Wierda, W.G.; Patel, M.R.; Lamanna, N.; Tsai, D.E.; Nair, B.C.; et al. Fixed-duration pirtobrutinib plus venetoclax with or without rituximab in relapsed/refractory CLL: The phase 1b BRUIN trial. Blood 2024, 144, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Endres, S.; Yosifov, D.Y.; Tausch, E.; Dheenadayalan, R.P.; Gao, X.; Müller, A.; Schneider, C.; Mertens, D.; Gierschik, P.; et al. Acquired BTK mutations associated with resistance to noncovalent BTK inhibitors. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 5698–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Desikan, S.P.; Nguyen, B.; Won, H.; Tantawy, S.I.; McNeely, S.; Marella, N.; Ebata, K.; Woyach, J.A.; Patel, K.; et al. Genomic evolution and resistance during pirtobrutinib therapy in covalent BTK-inhibitor (cBTKi) pretreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients: Updated analysis from the BRUIN study [abstract]. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. S1), 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, V.; Tantawy, S.; Aslan, B.; Manyam, G.; Iles, L.; Timofeeva, N.; Singh, N.; Jain, N.; Ferrajoli, A.; Thompson, P.; et al. Pharmacological profiling in CLL patients during pirtobrutinib therapy and disease progression. Res. Sq. 2025, 3, rs-6249480. [Google Scholar]
- Shadman, M.; Davids, M.S. How I treat patients with CLL after prior treatment with a covalent BTK inhibitor and a BCL-2 inhibitor. Blood 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, S.; Allsup, D. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Care and Beyond: Navigating the Needs of Long-Term Survivors. Cancers 2025, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamanna, N.; Tam, C.S.; Woyach, J.A.; Alencar, A.J.; Palomba, M.L.; Zinzani, P.L.; Flinn, I.W.; Fakhri, B.; Cohen, J.B.; Kontos, A.; et al. Evaluation of bleeding risk in patients who received pirtobrutinib in the presence or absence of antithrombotic therapy. EJHaem 2024, 5, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forconi, F.; Moss, P. Perturbation of the normal immune system in patients with CLL. Blood 2015, 126, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.V.; Gladstone, D.E. Covalent and Non-Covalent BTK Inhibition in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treatment. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2025, 26, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, S. Defining treatment success in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Exploring surrogate markers, comorbidities, and patient-centered endpoints. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2024, 17, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Omer, Z.; Collins, G.P.; Forconi, F.; Danilov, A.; Byrd, J.C.; El-Sharkawi, D.; Searle, E.; Alencar, A.J.; Ma, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Degrader NX-5948 in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Updated Results from an Ongoing Phase 1a/b Study. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. S1), 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.C.; Parrondo, R.D.; Frustaci, A.M.; Allan, J.N.; Ghia, P.; Mocanu, I.; Tam, C.S.; Judith Trotman, J.; Ahn, I.E.; Stilgenbauer, S.; et al. Preliminary Efficacy and Safety of the Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Degrader BGB-16673 in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: Results from the Phase 1 CaDAnCe-101 Study. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. S1), 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.; Fakhri, B.; Awan, F.T.; Bentzen, H.H.; Eradat, H.A.; Niemann, C.U.; Offner, F.; Poulsen, C.B.; Hoeyer, T.; Bellido, M.; et al. Epcoritamab Monotherapy in Patients (Pts) with Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Results from CLL Expansion and Optimization Cohorts of Epcore CLL-1. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. S1), 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, S.; Bourcier, J.; Noviski, M.; Lu, H.; Thompson, M.C.; Chirino, A.; Jahn, J.; Sondhi, A.K.; Gajewski, S.; Tan, Y.S.M.; et al. Kinase-impaired BTK mutations are susceptible to clinical-stage BTK and IKZF1/3 degrader NX-2127. Science 2024, 383, eadi5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial | Type of Study | Population | Experimental Arm | Control Arm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05023980 | Phase 3 (BRUIN CLL-313) | Untreated CLL/SLL | Pirtobrutinib | Bendamustine + Rituximab |
| NCT04965493 | Phase 3 (BRUIN CLL-322) | Previously treated CLL/SLL | Pirtobrutinib + Venetoclax + Rituximab | Venetoclax + Rituximab |
| NCT05536349 | Phase 2 | Untreated CLL/Richter Transformation (RT) | Pirtobrutinib, Venetoclax, and Obinutuzumab | |
| NCT06588478 | Phase 3 (CLL18) | Untreated CLL (MRD-guided approach) | Pirtobrutinib plus venetoclax | Venetoclax plus Obinutuzumab |
| NCT05254743 | Phase 3 (BRUIN CLL-314) | Untreated CLL | Pirtobrutinib | Ibrutinib |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molica, S.; Allsup, D. Pirtobrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Navigating Resistance and the Personalisation of BTK-Targeted Therapy. Cancers 2025, 17, 2974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182974
Molica S, Allsup D. Pirtobrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Navigating Resistance and the Personalisation of BTK-Targeted Therapy. Cancers. 2025; 17(18):2974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182974
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolica, Stefano, and David Allsup. 2025. "Pirtobrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Navigating Resistance and the Personalisation of BTK-Targeted Therapy" Cancers 17, no. 18: 2974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182974
APA StyleMolica, S., & Allsup, D. (2025). Pirtobrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Navigating Resistance and the Personalisation of BTK-Targeted Therapy. Cancers, 17(18), 2974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182974







