Correction: Cloître et al. Spatial Distribution of Recurrence and Long-Term Toxicity Following Dose Escalation to the Dominant Intra-Prostatic Nodule for Intermediate–High-Risk Prostate Cancer: Insights from a Phase I/II Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 2097
Error in Figure
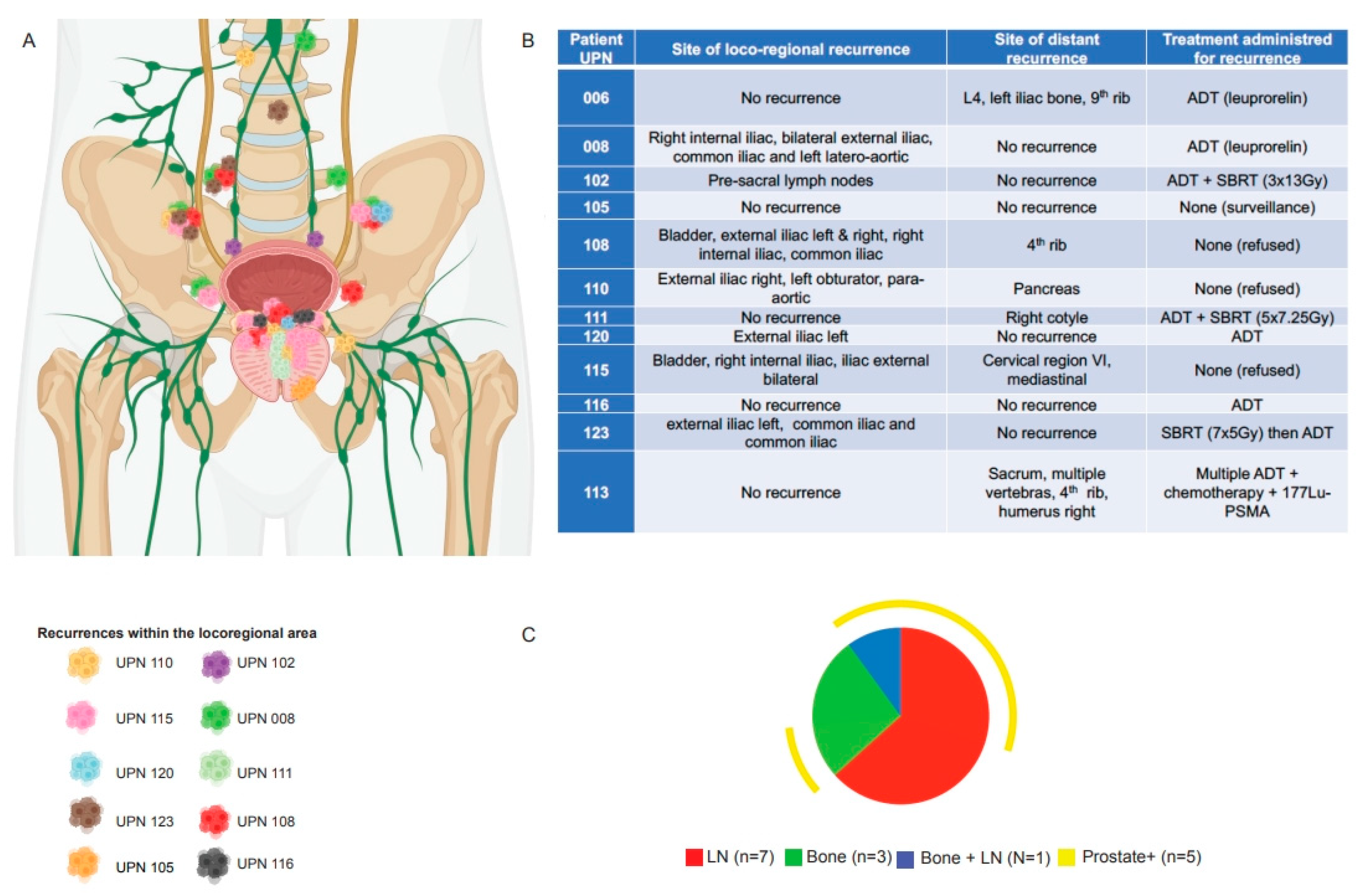
Additional Affiliation
Missing Citations
Text Correction
Newly Added Citations and References
- 18.
- Herrera, F.G.; Valerio, M.; Berthold, D.; Tawadros, T.; Meuwly, J.-Y.; Vallet, V.; Baumgartner, P.; Thierry, A.-C.; De Bari, B.; Jichlinski, P.; et al. 50-Gy Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy to the Dominant Intraprostatic Nodule: Results From a Phase 1a/b Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 103, 320–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.09.023.
- 22.
- Cloitre, M.; Valerio, M.; Mampuya, A.; Rakauskas, A.; Berthold, D.; Tawadros, T.; Meuwly, J.-Y.; Heym, L.; Duclos, F.; Vallet, V.; et al. Toxicity, Quality of Life, and PSA Control after 50 Gy Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy to the Dominant Intraprostatic Nodule with the Use of a Rectal Spacer: Results of a Phase I/II Study. BJR 2023, 96, 20220803. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20220803.
- 48.
- Katz, A.J.; Santoro, M.; Diblasio, F.; Ashley, R. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Localized Prostate Cancer: Disease Control and Quality of Life at 6 Years. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 118. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-8-118.
- 49.
- Musunuru, H.B.; D’Alimonte, L.; Davidson, M.; Ho, L.; Cheung, P.; Vesprini, D.; Liu, S.; Chu, W.; Chung, H.; Ravi, A.; et al. Phase 1-2 Study of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Including Regional Lymph Node Irradiation in Patients With High-Risk Prostate Cancer (SATURN): Early Toxicity and Quality of Life. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1438–1447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.07.2005.
- 50.
- Shikama, N.; Kumazaki, Y.; Miyazawa, K.; Nihei, K.; Hashimoto, S.; Tsukamoto, N. Rectal Toxicity After Extremely Hypofractionated Radiotherapy Using a Non-Isocentric Robotic Radiosurgery System for Early Stage Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2016, 7, 98–103. https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon986w.
- 51.
- Chen, L.N.; Suy, S.; Uhm, S.; Oermann, E.K.; Ju, A.W.; Chen, V.; Hanscom, H.N.; Laing, S.; Kim, J.S.; Lei, S.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: The Georgetown University Experience. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 58. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-8-58.
- 52.
- Murthy, V.; Gupta, M.; Mulye, G.; Maulik, S.; Munshi, M.; Krishnatry, R.; Phurailatpam, R.; Mhatre, R.; Prakash, G.; Bakshi, G. Early Results of Extreme Hypofractionation Using Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for High-Risk, Very High-Risk and Node-Positive Prostate Cancer. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 442–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2018.03.004.
- 53.
- Alayed, Y.; Cheung, P.; Vesprini, D.; Liu, S.; Chu, W.; Chung, H.; Musunuru, H.B.; Davidson, M.; Ravi, A.; Ho, L.; et al. SABR in High-Risk Prostate Cancer: Outcomes From 2 Prospective Clinical Trials With and Without Elective Nodal Irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.11.011.
- 54.
- Aluwini, S.; van Rooij, P.; Hoogeman, M.; Bangma, C.; Kirkels, W.J.; Incrocci, L.; Kolkman-Deurloo, I.-K. CyberKnife Stereotactic Radiotherapy as Monotherapy for Low- to Intermediate-Stage Prostate Cancer: Early Experience, Feasibility, and Tolerance. J. Endourol. 2010, 24, 865–869. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2009.0438.
- 55.
- Elias, E.; Helou, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheung, P.; Deabreu, A.; D’Alimonte, L.; Sethukavalan, P.; Mamedov, A.; Cardoso, M.; Loblaw, A. Dosimetric and Patient Correlates of Quality of Life after Prostate Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 112, 83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2014.06.009.
- 56.
- Vargas, C.E.; Hartsell, W.F.; Dunn, M.; Keole, S.R.; Doh, L.; Chang, J.; Larson, G.L. Image-Guided Hypofractionated Proton Beam Therapy for Low-Risk Prostate Cancer: Analysis of Quality of Life and Toxicity, PCG GU 002. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2016, 21, 207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpor.2016.01.002.
- 57.
- Madsen, B.L.; Hsi, R.A.; Pham, H.T.; Fowler, J.F.; Esagui, L.; Corman, J. Stereotactic Hypofractionated Accurate Radiotherapy of the Prostate (SHARP), 33.5 Gy in Five Fractions for Localized Disease: First Clinical Trial Results. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 67, 1099–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.10.050.
- 58.
- Alongi, F.; Cozzi, L.; Arcangeli, S.; Iftode, C.; Comito, T.; Villa, E.; Lobefalo, F.; Navarria, P.; Reggiori, G.; Mancosu, P.; et al. Linac Based SBRT for Prostate Cancer in 5 Fractions with VMAT and Flattening Filter Free Beams: Preliminary Report of a Phase II Study. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 171. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-8-171.
- 59.
- Głowacki, G.; Majewski, W.; Wojcieszek, P.; Grabinska, K.; Wozniak, G.; Miszczyk, L. Ultrahypofractionated CyberKnifeTM Based Stereotactic Radiotherapy versus Conventional Radiotherapy in Patients with Prostate Cancer–Acute Toxicity Evaluation in Two Phase II Prospective Studies. NEO 2017, 64, 599–604. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2017_421.
Reference
- Cloître, M.; Benkhaled, S.; Boughdad, S.; Schaefer, N.; Prior, J.O.; Zeverino, M.; Berthold, D.; Tawadros, T.; Meuwly, J.-Y.; Martel, P.; et al. Spatial Distribution of Recurrence and Long-Term Toxicity Following Dose Escalation to the Dominant Intra-Prostatic Nodule for Intermediate–High-Risk Prostate Cancer: Insights from a Phase I/II Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cloître, M.; Benkhaled, S.; Boughdad, S.; Schaefer, N.; Prior, J.O.; Zeverino, M.; Berthold, D.; Tawadros, T.; Meuwly, J.-Y.; Martel, P.; et al. Correction: Cloître et al. Spatial Distribution of Recurrence and Long-Term Toxicity Following Dose Escalation to the Dominant Intra-Prostatic Nodule for Intermediate–High-Risk Prostate Cancer: Insights from a Phase I/II Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 2097. Cancers 2025, 17, 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152496
Cloître M, Benkhaled S, Boughdad S, Schaefer N, Prior JO, Zeverino M, Berthold D, Tawadros T, Meuwly J-Y, Martel P, et al. Correction: Cloître et al. Spatial Distribution of Recurrence and Long-Term Toxicity Following Dose Escalation to the Dominant Intra-Prostatic Nodule for Intermediate–High-Risk Prostate Cancer: Insights from a Phase I/II Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 2097. Cancers. 2025; 17(15):2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152496
Chicago/Turabian StyleCloître, Minna, Sofian Benkhaled, Sarah Boughdad, Niklaus Schaefer, John O. Prior, Michele Zeverino, Dominik Berthold, Thomas Tawadros, Jean-Yves Meuwly, Paul Martel, and et al. 2025. "Correction: Cloître et al. Spatial Distribution of Recurrence and Long-Term Toxicity Following Dose Escalation to the Dominant Intra-Prostatic Nodule for Intermediate–High-Risk Prostate Cancer: Insights from a Phase I/II Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 2097" Cancers 17, no. 15: 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152496
APA StyleCloître, M., Benkhaled, S., Boughdad, S., Schaefer, N., Prior, J. O., Zeverino, M., Berthold, D., Tawadros, T., Meuwly, J.-Y., Martel, P., Rohner, C., Heym, L., Duclos, F., Vallet, V., Valerio, M., Bourhis, J., & Herrera, F. G. (2025). Correction: Cloître et al. Spatial Distribution of Recurrence and Long-Term Toxicity Following Dose Escalation to the Dominant Intra-Prostatic Nodule for Intermediate–High-Risk Prostate Cancer: Insights from a Phase I/II Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 2097. Cancers, 17(15), 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152496






