Real World Outcomes of Patients with Aggressive Lymphoma and Autoimmune Disease Treated with CART
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Endpoints and Assessments
2.2. Statistical Analyses
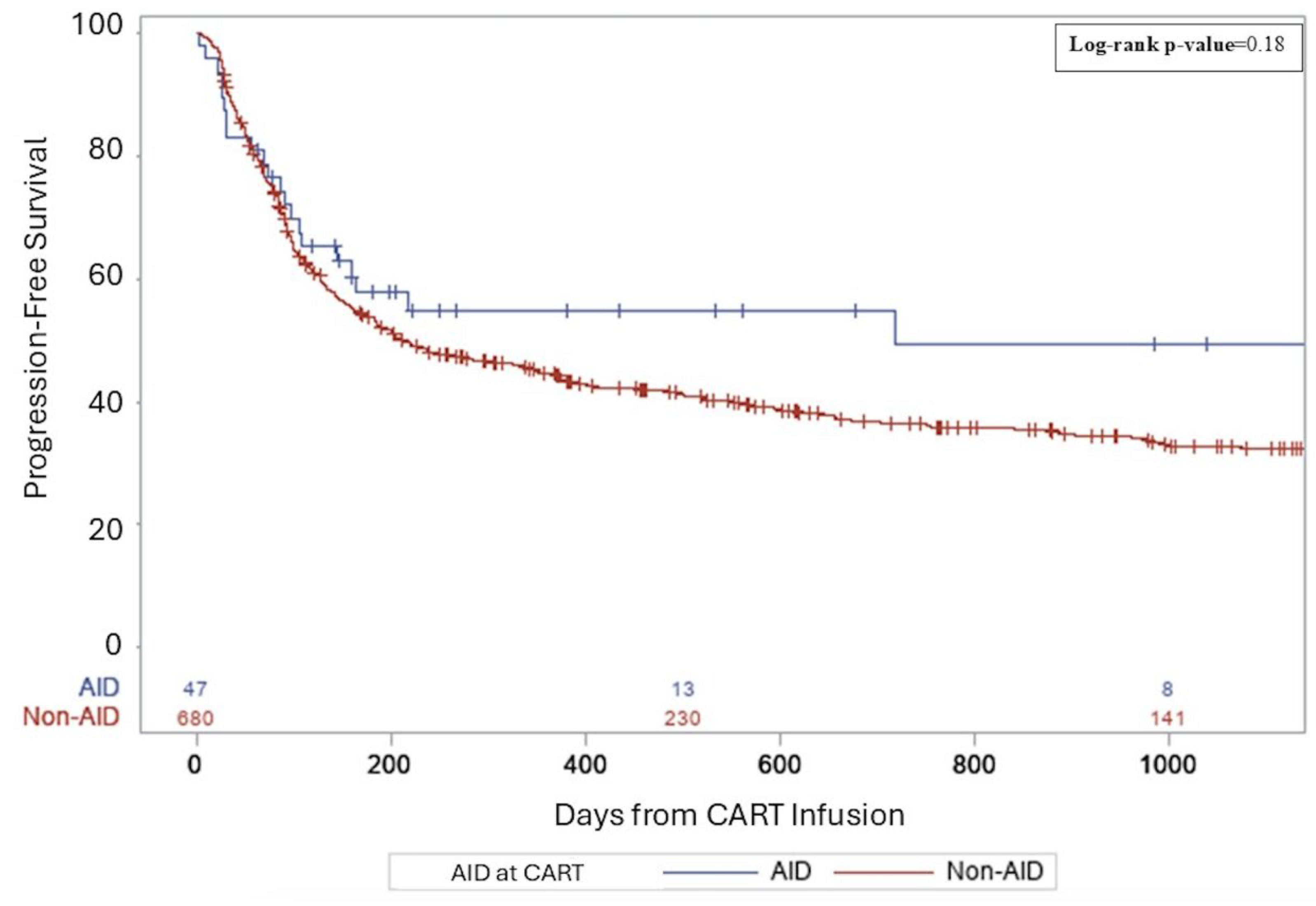
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Outcomes for B-NHL
3.2. Clinical Impact of CART on the Underlying AID
3.3. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AID | Autoimmune disease |
| B-NHL | B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| CART | Autologous chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy |
| IST | Immunosuppressive therapy |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematous |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| MG | Myasthenia gravis |
| ICANS | Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome |
| CRS | Cytokine release syndrome |
| IVIG | intravenous immunoglobulin G |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PFS | Progression free survival |
References
- Kleinstern, G.; Maurer, M.J.; Liebow, M.; Habermann, T.M.; Koff, J.L.; Allmer, C.; Witzig, T.E.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Micallef, I.N.; Johnston, P.B.; et al. History of autoimmune conditions and lymphoma prognosis. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zintzaras, E.; Voulgarelis, M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. The risk of lymphoma development in autoimmune diseases: A meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.A.; Gadalla, S.; Morton, L.M.; Landgren, O.; Pfeiffer, R.; Warren, J.L.; Berndt, S.I.; Ricker, W.; Parsons, R.; Engels, E.A. Population-based study of autoimmune conditions and the risk of specific lymphoid malignancies. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abend, A.H.; He, I.; Bahroos, N.; Christianakis, S.; Crew, A.B.; Wise, L.M.; Lipori, G.P.; He, X.; Murphy, S.N.; Herrick, C.D.; et al. Estimation of prevalence of autoimmune diseases in the United States using electronic health record data. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 135, e178722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayter, S.M.; Cook, M.C. Updated assessment of the prevalence, spectrum and case definition of autoimmune disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedby, K.E.; Vajdic, C.M.; Falster, M.; Engels, E.A.; Martínez-Maza, O.; Turner, J.; Hjalgrim, H.; Vineis, P.; Costantini, A.S.; Bracci, P.M.; et al. Autoimmune disorders and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes: A pooled analysis within the InterLymph Consortium. Blood 2008, 111, 4029–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azrielant, S.; Tiosano, S.; Watad, A.; Mahroum, N.; Whitby, A.; Comaneshter, D.; Cohen, A.D.; Amital, H. Correlation between systemic lupus erythematosus and malignancies: A cross-sectional population-based study. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, S.; Shabani, M.; Tabary, M.; Rayzan, E.; Rezaei, N. Lymphoma in the setting of autoimmune diseases: A review of association and mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 150, 102945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westin, J.R.; Oluwole, O.O.; Kersten, M.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Perales, M.-A.; Ghobadi, A.; Rapoport, A.P.; Sureda, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Farooq, U.; et al. Survival with axicabtagene ciloleucel in large B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T-cell therapy in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdar, M.; Solomon, S.R.; Arnason, J. Lisocabtagene maraleucel versus standard of care with salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation as second-line treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (TRANSFORM): Results from an interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 2294–2308. [Google Scholar]
- Thieblemont, C.; Karimi, Y.; Jurczak, W.; Cheah, C.Y.; Clausen, M.R.; Cunningham, D.; Do, Y.R.; Lewis, D.J.; Gasiorowski, R.; Kim, T.M.; et al. Subcutaneous epcoritamab induces deep, durable complete remissions in relapsed/refractory large b-cell lymphoma: Longer follow-up from the pivotal epcore NHL-1 trial. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S2), 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampotas, A.; Richter, J.; Isenberg, D.; Roddie, C. CAR-T cell therapy embarks on autoimmune disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2025, 60, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, E.H.; Ha, Y.J.; Lee, Y.J. Autoantibody biomarkers in rheumatic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, L.M.; Stohl, W. Belimumab and rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus: A tale of two B cell-targeting agents. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Alkrekshi, A.; Dasari, S.; Lin, H.T.C.; Elantably, D.; Armashi, A.R.A. CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in patients with concurrent B-cell Non-Hodgkin lymphoma and rheumatic autoimmune diseases: A propensity score matching study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2023, 58, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackensen, A.; Müller, F.; Mougiakakos, D.; Böltz, S.; Wilhelm, A.; Aigner, M.; Völkl, S.; Simon, D.; Kleyer, A.; Munoz, L.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, K.S.; Schlam, I.; Holtzman, N.G.; Peravali, M.; Richardson, P.K.; Dahiya, S.; Malkovska, V.; Rapoport, A.P. Safety and efficacy of CAR T cells in a patient with lymphoma and a coexisting autoimmune neuropathy. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 6019–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Ciurea, S.; Kamboh, H.; Miljkovic, M.; Mozaffar, T. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in neurological disorders. Neurology 2024, 103 (Suppl. 1), S119–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougiakakos, D.; Meyer, E.H.; Schett, G. CAR T cells in autoimmunity: Game changer or stepping stone? Blood 2025, 145, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schett, G.; Mackensen, A.; Mougiakakos, D. CAR T-cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Lancet 2023, 402, 2034–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghikia, A.; Schett, G.; Mougiakakos, D. B cell-targeting chimeric antigen receptor T cells as an emerging therapy in neuroimmunological diseases. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougiakakos, D.; Krönke, G.; Völkl, S.; Kretschmann, S.; Aigner, M.; Kharboutli, S.; Böltz, S.; Manger, B.; Mackensen, A.; Schett, G. CD19-targeted CAR T cells in refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, F.; Taubmann, J.; Bucci, L.; Wilhelm, A.; Bergmann, C.; Völkl, S.; Aigner, M.; Rothe, T.; Minopoulou, I.; Tur, C.; et al. CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in autoimmune disease—A case series with follow-up. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkt, W.; Freitag, M.; Claus, M.; Kolb, P.; Falcone, V.; Röhrich, M.; Rodon, L.; Deicher, F.; Andreeva, I.; Tretter, T.; et al. Third-generation CD19.CAR-T cell-containing combination therapy in Scl70+ systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghikia, A.; Hegelmaier, T.; Wolleschak, D.; Böttcher, M.; Pappa, V.; Motte, J.; Borie, D.; Gold, R.; Feist, E.; Schett, G.; et al. Clinical efficacy and autoantibody seroconversion with CD19-CAR T cell therapy in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and coexisting myasthenia gravis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1597–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghikia, A.; Hegelmaier, T.; Wolleschak, D.; Böttcher, M.; Desel, C.; Borie, D.; Motte, J.; Schett, G.; Schroers, R.; Gold, R.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cells for refractory myasthenia gravis. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 1104–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, F.; Richter, J.; Pfeffer, L.K.; Fehse, B.; Berger, S.C.; Reinhardt, S.; Kuhle, J.; Badbaran, A.; Rathje, K.; Gagelmann, N.; et al. CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in two patients with multiple sclerosis. Med 2024, 5, 550–558.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; DeStefano, V.M.; Wada, M.; Pinz, K.; Deener, G.; Shah, D.; Hagag, N.; et al. BCMA-CD19 compound CAR T cells for systemic lupus erythematosus: A phase 1 open-label clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1304–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Tian, D.S.; Zhou, L.Q.; Shang, K.; Huang, L.; Dong, M.-H.; You, Y.-F.; Xiao, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Anti-BCMA CAR T-cell therapy CT103A in relapsed or refractory AQP4-IgG seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: Phase 1 trial interim results. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blache, U.; Tretbar, S.; Koehl, U.; Mougiakakos, D.; Fricke, S. CAR T cells for treating autoimmune diseases. RMD Open 2023, 9, e002907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Non AID Patients (n = 680) | % | AID Patients (n = 47) | % | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age at diagnosis, years (range) | 58 | (17–85) | 61 | (28–83) | 0.15 |
| Sex | 0.72 | ||||
| Female | 243 | 35.7 | 18 | 38.3 | |
| Male | 437 | 64.3 | 29 | 61.7 | |
| Race | 0.03 | ||||
| White | 572 | 84.1 | 45 | 95.7 | |
| Non-White/unknown | 108 | 15.9 | 2 | 4.3 | |
| Ethnicity | 0.11 | ||||
| Non-Hispanic | 628 | 92.4 | 46 | 97.9 | |
| Hispanic | 44 | 6.5 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| Missing | 8 | 1.2 | 1 | 2.1 | |
| ECOG at dx | 0.18 | ||||
| 0–1 | 498 | 73.2 | 29 | 61.7 | |
| 2+ | 50 | 7.4 | 4 | 8.5 | |
| Missing | 132 | 19.4 | 14 | 29.8 | |
| IPI at dx | 0.22 | ||||
| 0–1 | 116 | 17.1 | 4 | 8.5 | |
| 2 | 118 | 17.4 | 13 | 27.7 | |
| 3 | 157 | 23.1 | 8 | 17.0 | |
| 4–5 | 86 | 12.6 | 5 | 10.6 | |
| Missing | 203 | 29.9 | 17 | 36.2 | |
| Autoimmune condition | < 0.01 | ||||
| None | 680 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| RA | 0 | 0.0 | 14 | 29.8 | |
| SLE | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 10.6 | |
| Sjogren’s | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 10.6 | |
| Crohn’s | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 10.6 | |
| Psoriasis/Psoriatic/Arthritis | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 10.6 | |
| Other | 0 | 0.0 | 13 | 27.7 | |
| Primary refractory disease with frontline therapy | 0.48 | ||||
| PD with frontline therapy | 97 | 14.3 | 3 | 6.4 | |
| Relapse within 6 months | 169 | 24.9 | 10 | 21.3 | |
| Relapse within 12 months | 139 | 20.4 | 10 | 21.3 | |
| DEL | 0.39 | ||||
| No | 339 | 49.9 | 22 | 46.8 | |
| Yes | 146 | 21.5 | 14 | 29.8 | |
| Missing | 195 | 28.7 | 11 | 23.4 | |
| DHL or THL | 0.67 | ||||
| No | 437 | 64.3 | 28 | 59.6 | |
| Yes | 106 | 15.6 | 7 | 14.9 | |
| Missing | 137 | 20.1 | 12 | 25.5 | |
| Bridging prior to CART | 0.61 | ||||
| No | 5 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| Yes | 329 | 48.4 | 20 | 42.6 | |
| Missing | 346 | 50.9 | 27 | 57.4 | |
| Frontline therapy | 0.32 | ||||
| R-CHOP | 418 | 61.5 | 26 | 55.3 | |
| DA-R-EPOCH | 122 | 17.9 | 7 | 14.9 | |
| R-ICE ** | 12 | 1.8 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| DHAP ** | 2 | 0.3 | 1 | 2.1 | |
| Hyper-CVAD | 8 | 1.2 | 1 | 2.1 | |
| R-ESHAP ** | 2 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| R-bendamustine | 21 | 3.1 | 1 | 2.1 | |
| Other | 47 | 6.9 | 4 | 8.5 | |
| Missing | 48 | 7.1 | 7 | 14.9 | |
| Median lines of prior therapy, (range) | 2 | (1–8) | 2 | (1–8) | 0.73 |
| Missing | 4 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| Autologous transplant prior to CART | 0.93 | ||||
| No | 546 | 80.3 | 38 | 80.9 | |
| Yes | 134 | 19.7 | 9 | 19.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altomare, N.J.; Herr, M.M.; Nair, N.M.; Stephens, D.M.; Cohen, J.B.; Epperla, N.; Cortese, M.; Bhansali, R.; Moyo, T.K.; Kenkre, V.; et al. Real World Outcomes of Patients with Aggressive Lymphoma and Autoimmune Disease Treated with CART. Cancers 2025, 17, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142358
Altomare NJ, Herr MM, Nair NM, Stephens DM, Cohen JB, Epperla N, Cortese M, Bhansali R, Moyo TK, Kenkre V, et al. Real World Outcomes of Patients with Aggressive Lymphoma and Autoimmune Disease Treated with CART. Cancers. 2025; 17(14):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142358
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltomare, Nicole J., Megan M. Herr, Nisha M. Nair, Deborah M. Stephens, Jonathon B. Cohen, Narendranath Epperla, Matthew Cortese, Rahul Bhansali, Tamara K. Moyo, Vaishalee Kenkre, and et al. 2025. "Real World Outcomes of Patients with Aggressive Lymphoma and Autoimmune Disease Treated with CART" Cancers 17, no. 14: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142358
APA StyleAltomare, N. J., Herr, M. M., Nair, N. M., Stephens, D. M., Cohen, J. B., Epperla, N., Cortese, M., Bhansali, R., Moyo, T. K., Kenkre, V., Ollila, T., Hess, B., Fitzgerald, L., Shouse, G., Davis, J. A., Jesme, C., Pelcovits, A., Moreira, J., Lin, A., ... Karmali, R., on behalf of the American BiTE and CART Consortium. (2025). Real World Outcomes of Patients with Aggressive Lymphoma and Autoimmune Disease Treated with CART. Cancers, 17(14), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142358









