Simple Summary
Cancer is a complex disease influenced by many factors that determine how genetic changes affect the function of encoded proteins, ultimately driving cancer development. While much pancreatic cancer research focuses on the four most frequently mutated genes (KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, and SMAD4), this review highlights the significant, but less-understood roles of further tumour suppressors, such as PTEN, KDM6A, and ARID1A in PDAC. Mutations in these genes are uncommon, but a reduced expression of their proteins is often observed in tumours. We present summaries of this data and emphasise the importance of research beyond the “big four” genes to better understand and combat this aggressive type of cancer.
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is frequently identified as the cancer type with the shortest probable survival time after diagnosis, and efforts to develop successful treatments have had a very limited impact in the clinic. One reason for the limited therapeutic options is the lack of appealing drug targets. The great majority of pancreatic cancers are classified as Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC), in which the genetic landscape is dominated by four genes: KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, and SMAD4. However, despite extensive knowledge of these genetic drivers, the development of effective therapies has seen only very limited success. Methods: Existing evidence indicates that mutations in the tumour suppressor gene PTEN are uncommon in PDAC (<10% cases). However, the loss of PTEN function through non-genetic mechanisms may be much more common and have a strong impact. We therefore summarise and review a large body of immunohistochemical studies that address the loss of PTEN in PDAC as well as a smaller number of studies addressing other implicated proteins, including KDM6A and ARID1A. Results: These studies show some loss of PTEN protein in more than half of PDAC cases. Furthermore, although genetic changes in genes including KDM6A/UTX and ARID1A are also uncommon, reduced expression of their encoded proteins is observed in many, perhaps most, cases of PDAC. Conclusions: These analyses, which go beyond genetics, highlight the broader set of cellular functions that are dysregulated in many pancreatic cancers and provide broader opportunities for treatment strategies. This review highlights the emerging importance of other drivers in PDAC, which are less well-studied in this context.
1. Introduction
More than 80% of primary cancers identified in the pancreas are defined as Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC). This represents one of the worst diagnoses amongst all malignancies, with recent data showing only 12% of patients surviving 5 years after diagnosis in the USA, with a median survival of around 6 months [1]. This is a very modest improvement on older data (which remain frequently reported); however, many parts of the world still see 5 year survival well below 12% [1]. Combined with a relatively high incidence, this results in pancreatic cancer now being the third most common cause of cancer death in the USA and Europe, after lung and colorectal cancer [1,2]. One factor in this poor prognosis is that diagnosis is commonly made only at the stage of advanced disease due to a lack of specific symptoms and tumour markers. Frequently, local invasion and distant metastasis occur prior to diagnosis, significantly lowering the possibility of curative surgery. Furthermore, PDAC very rarely responds well to chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and as will be discussed, there is a lack of effective targeted biological therapies [3]. A key histological feature of PDAC, which may contribute to its therapeutic resistance, is its unusually fibrous stroma. This desmoplasia is even observed in relatively early-stage tumours [4,5]. Addressing this point, a well-defined set of precursor lesions has been identified, which is believed to have the potential to progress into PDAC. These include changes generally termed Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia (PanIN), which are frequently subdivided into low-grade and high-grade lesions [6].
There are several less common types of cancer in the pancreas, including neuroendocrine tumours and acinar carcinomas. However, these will not be discussed in any detail in this review, except where relevant clinical studies mention pancreatic cancer without specifying whether the patients and samples are restricted to PDAC or also include other types of pancreatic cancer. This review will therefore focus specifically on PDAC, highlighting the significant, but less-understood roles of tumour suppressors, such as PTEN, KDM6A, and ARID1A in PDAC.
2. Genetics of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Genomic analyses of pancreatic cancer have consistently identified a well-recognised set of recurrent mutations, which are present in many, and in some studies the majority of these tumours [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. In particular, coding sequence variants in KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, and SMAD4 have been identified in all such studies, in most cases emerging as the four most commonly mutated genes. Most notably, activating missense mutations in KRAS are identified in almost all cases of PDAC, with observed rates in most patient cohorts >90% [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. KRAS mutations also appear to be a very early, probably initiating event in PDAC development, implied by their frequent discovery in PanIN lesions [16]. Furthermore, most PDAC cases also display loss-of-function mutations in TP53, with cohorts commonly showing rates in the 60–75% range. There appears to be less consistency in the observation of changes in the CDKN2A and SMAD4 tumour suppressor genes, with estimates for their functional loss ranging from 15% to 60%, perhaps contributed by different assessment technologies and differences between the analysed populations [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. While there is broad agreement that a KRAS mutation is an early and likely initiating event in PanIN/PDAC development, the sequence of subsequent genetic alterations remains less well understood. CDKN2A loss of function is often presented as a subsequent event during the progression through the stages of PanIN, while changes in TP53 and SMAD4 only occur later in well-developed PanIN lesions and during the progression to PDAC [17,18]. Therefore, an in-depth understanding of the evolution of PDAC is yet to be achieved, with particular attention being paid to whether mutations accumulate gradually or in a punctuated manner, as well as to how the cancer cell genetic landscape interacts with the tumour microenvironment [6,18].
Given the central role of KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, and SMAD4 in PDAC, we briefly summarise their biological functions and implications for tumour development. KRAS (Kirsten rat sarcoma virus) encodes the small-GTPase KRAS, which acts as an evolutionarily conserved switch-like activator of mitogenic and growth signalling in animal cells [19,20]. In the context of PDAC, one of the most significant pathways through which KRAS drives tumour progression is via the activation of the class 1 phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) enzymes and their synthesis of the lipid signal PIP3, which is removed by the tumour suppressor PTEN [19,20]. The TP53 tumour suppressor gene encodes the p53 transcription factor, which activates specific programmes of gene expression in response to cell stresses, including DNA damage. The responses activated by p53 target genes include cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, metabolic reprogramming, and depending on the context, cell death [21]. Unusually, the CDKN2A (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A) gene encodes two unrelated proteins with independent tumour suppressor functions, p14 ARF and p16 INK4A. The ARF protein is a key activator of p53 tumour suppressor function, which acts by protecting p53 from degradation, and the INK4A protein blocks the promotion of cell proliferation by the cyclin-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6 [22]. Finally, a significant minority of PDACs contain mutations in the SMAD4 gene, also sometimes referred to as Deleted in Pancreatic Cancer-4 (DPC4), with such mutations being less common in other types of cancer. The SMAD4 gene encodes a transcription factor that drives many of the effects of the intercellular signal protein Transforming Growth Factor beta (TGFβ). The SMAD4 protein forms hetero-oligomers with other SMAD proteins in response to TGFβ stimulation and, through effects on the transcription of its target genes, influences a diverse set of processes including cell cycle progression, cell migration, and angiogenesis [23].
A notable further feature revealed by these genomic studies is the relative homogeneity of these tumours, which are defined as pancreatic cancer, when compared to cancers identified in other organs. Cancers in almost all other organ systems display multiple clearly distinct cancer types, which themselves display greater apparent heterogeneity within their driving mutations, when compared to the picture observed in pancreatic cancer cohorts. These studies of pancreatic cancer also suggest that, despite a relatively homogeneous mutational landscape dominated by a few key drivers, additional genetic and non-genetic alterations contribute to PDAC heterogeneity and progression.
The consistent nature of less frequent genetic changes in PDAC indicates that additional genes also represent driver oncogenes and tumour suppressors (see Figure 1) [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. For example, almost all of the changes in MYC identified in around 5% of PDAC cases are amplifications, while almost all mutations of ARID1A present in 5–15% of PDAC cases are truncations [8,11,13,24]. This list of genes in which genetic changes are less frequently identified may indicate that functional changes in the relevant encoded proteins occur only through genetic mechanisms and only in a small subset of PDAC cancers. However, it is also possible that the function of these proteins is significant and modified in relatively many cases of PDAC, but by mechanisms not detected in these genomic studies.
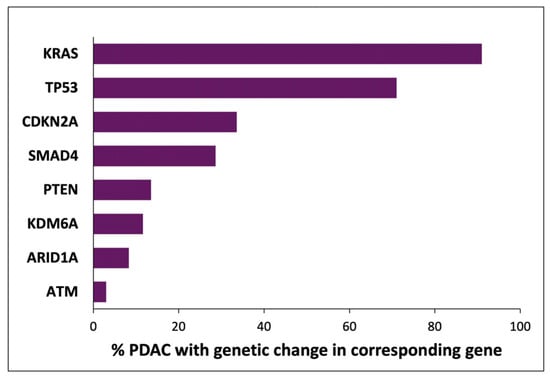
Figure 1.
Indicative fractions of PDAC cancers with genetic changes in selected genes. The frequency of genetic changes in each gene was calculated as the mean from multiple studies [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. The analyses and methods in these reports are not uniform, and the presented values represent an amalgamation of multiple classes of genetic changes. The genes discussed in this review and mutated in < 15% cases (PTEN, KDM6A, ARID1A, and ATM) are shown for relevance and were selected from a large number of genes (approx. 20) in which genetic changes were reported in 3–15% of PDACs.
For context, as mentioned above, genetic changes in CDKN2A and SMAD4 are each found in approximately one in three cases of PDAC [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Immunohistochemical analyses of the expression of the encoded proteins (the SMAD4 protein and the p16 INK4A and p14 ARF proteins encoded by the CDKN2A locus) report loss of SMAD4 protein expression in approximately 55% of PDAC samples [25,26,27,28,29,30,31] and loss of p16/INK4A and p14/ARF in a slightly higher fraction of cancers. Rates of reported loss of p16/INK4A (approx. 70%; range: 46–100%) are similar to those for p14/ARF (two studies reporting 65% and 68%) [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. Therefore, for both CDKN2A and SMAD4 loci, the frequency at which loss of protein expression is reported (Table 1) is approximately double the reported frequency of mutation, indicating common non-genomic mechanisms by which protein function is lost.

Table 1.
Summarised data from studies reporting the percentage of pancreatic cancer samples displaying immunohistochemical loss of SMAD4, p16/INK4A, and p14/ARF protein. The percentage of clinical samples reported as displaying loss of the relevant tumour suppressor protein in each study is shown. The details of scoring methods are found in each publication [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32].
3. Can PDAC Genetics and Stratification Inform Successful Therapy?
The last ten to fifteen years have seen substantial efforts to identify predictive genetic biomarkers for targeted therapy [33]. There have been some successes reported, including increased progression-free survival in germline BRCA mutant patients with metastatic PDAC treated with the PARP inhibitor Olaparib [34]. However, such BRCA mutations are present only in a small fraction of PDAC patients (approx. 5%) and consistent benefits on overall survival have not yet been seen [34,35], leaving the best use of these drugs in PDAC to be determined [36,37]. Success with the use of the novel KRAS inhibitor Sotorasib in lung cancer patients and colon cancer patients with cancers harbouring specifically G12C mutant KRAS protein [38,39] has raised hope for similar treatments for PDAC. The KRAS G12C mutation is rare in PDAC (approximately 1% of patients), and the selectivity of Sotorasib and other KRAS G12C selective inhibitors appears to rely on the presence of the novel cysteine residue in the switch II region close to the nucleotide-binding site of KRAS, requiring novel strategies to develop drugs targeting other KRAS mutants, which are more common in PDAC [40]. Despite these challenges, a number of inhibitors targeting KRAS G12D have emerged and are showing promise in early clinical trials [41,42].
In recent years, several efforts have been made to identify subtypes of PDAC to understand the disease better and to improve prognosis and therapy. These studies have revealed some consistent patterns, with multiple genetic and gene expression analyses aligning somewhat to identify PDAC subtypes. One subtype, often termed ‘classical,’ exhibits more epithelial and adherent characteristics, while an alternative subtype, referred to as ‘quasi-mesenchymal,’ ‘basal-like,’ or ‘squamous’, displays more mesenchymal traits [13,43,44,45]. However, consensus has yet to be reached regarding the relationship of this classification to further subtypes, associations with stromal or immune cell types, and chromosomal structural changes, as well as cancer morphology and histology [46,47]. Nevertheless, as the volume and quality of PDAC cohort data continue to grow alongside advancements in analytical techniques, improved outcomes for more patients are likely to follow.
The field of immune therapy for cancer has yielded many successes in the last fifteen or so years [48], and efforts have been made to apply immune therapy to pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, PDAC-specific therapeutic strategies have also been developed to target other non-immune aspects of the tumour microenvironment. Initial efforts have been largely unsuccessful [49]; however, an emerging understanding of the positive and negative impacts of the tumour stroma [50,51], intratumoural heterogeneity [52,53], and links to tumour genetics and subtypes should support the successful future use of these approaches in combination with others [54].
4. The Frequency of PTEN Protein Loss in PDAC Greatly Exceeds That of Reported Changes in the PTEN Gene
PTEN is one of the most frequently mutated tumour suppressor genes in human cancer [55,56]. Notably, it may provide the greatest selective advantage to tumours carrying mutations compared to other tumour suppressors [57]. In addition to mutations in the PTEN gene, numerous other mechanisms have been shown to occur in many cancers that reduce the function of the encoded PTEN phosphatase [55,58,59]. The dominant mechanism by which PTEN functions to oppose tumour formation is as a core inhibitory component of the oncogenic PI3K-AKT signalling network, in which it metabolises the primary lipid products of the class 1 phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks) [60,61]. PTEN is a phosphatase, which dephosphorylates position 3 of the inositol ring of PtdInsP3 and probably also PtdIns(3,4)P2 [59,60,62]. The loss of PTEN function in PDAC is particularly relevant given that KRAS directly binds to and activates the alpha, gamma, and delta isoforms of PI3K [63]. Consequently, PTEN loss is likely to amplify specific downstream signals driven by mutant KRAS.
An important consideration when analysing PTEN loss in tumours is that in some cancer types, PTEN appears to act as a dose-dependent tumour suppressor. Even partial reductions in PTEN protein function can significantly increase cancer risk [64,65]. This mechanism differs from the classical ‘two-hit’ model of recessive tumour suppressor genes, in which only total or near-total loss of function drives cancer.
Genotype–phenotype correlations [66,67] and high-throughput functional assessments of pathogenic PTEN variants provide further support for the hypothesis that a partial loss of PTEN function frequently drives tumour development. These studies indicate that many, if not most, cancer-associated variants retain substantial functional activity [68]. In contrast, for example, almost all cancer-associated mutations in TP53 show little or no functional activity [69]. Additionally, individuals with Li–Fraumeni and FAMMM syndromes, carrying TP53 and CDKN2A mutations respectively, are commonly found to develop cancers in which the remaining tumour suppressor gene copy is lost [70,71]. Cancers in individuals with PTEN Hamartoma Tumour Syndrome however, rarely display further gene loss [72].
It has been many years since the proposal, based on both human and mouse model data, that haploinsufficient PTEN loss may be a key driver of PDAC in combination with KRAS mutation [73]. Despite this, PTEN and other candidate drivers are often ignored in reviews of PDAC pathogenesis, perhaps because a mutation of the PTEN coding sequence is a rare event in pancreatic cancer. For example, at the time of writing (October 2024), the COSMIC database (https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic, (accessed on 9 July 2025)) shows 129 mutated samples from 3947 samples analysed (3.27%), and most published studies do not include PTEN in their lists of the most mutated genes in PDAC [7,8,10,11,24]. In cancers affecting other organ systems, the loss of a single copy of PTEN is more commonly observed as the mechanism driving loss of function compared to coding sequence mutations [33,44]. A similar picture is seen in PDAC studies, where all forms of genetic changes in PTEN are uncommon. Reports of PTEN shallow deletions (consistent with hemizygous single copy loss) are generally low (<20%), while deep deletions of PTEN are almost never identified [7,8,11,12,24,74].
Therefore, we subsequently analysed a substantial body of available data that has assessed the abundance of PTEN protein in PDAC tissue samples by immunohistochemistry. We were able to identify ten published research papers containing this data [73,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83], which are summarised in Table 1. As might be expected, these diverse studies use different scoring systems. For example, regarding details of their analysis and scoring of control non-neoplastic pancreatic tissues, Wartenberg and co-workers stated that 13.7% of control pancreatic tissue samples would be scored for ‘PTEN loss’ by the same criteria, which indicate 60% loss for PDAC samples [82]. Another study states that “matched non-neoplastic pancreatic tissue cores retained PTEN expression in all cases examined” [77]. Regardless, across these reports, a consistent picture emerges that PTEN protein is undetectable or scored as negative in approximately 30% of the PDAC patient samples and scored as relatively low or with a weak signal in approximately a further 25% of tumours (Table 2). This implies that lost or reduced PTEN function plays a role in driving cancer development in slightly more than half of PDAC cases. Notably, loss of PTEN protein in PDAC samples is associated with a higher tumour grade [76,82], metastasis [76,77,78], and shorter overall survival [75,76,77,81,83].

Table 2.
Summarised data from studies reporting the immunohistochemical analysis of PTEN protein levels in human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma samples. Different scoring systems were used in different studies, with studies scoring PTEN protein levels either with a digital positive/negative score or using three or four different levels (e.g., high/low/negative). Two studies were identified and excluded from analysis because they used antibodies that are known to give non-specific data in immunohistochemistry [84,85]. Where possible, samples identified as being from pancreatic cancer types other than PDAC were also excluded.
Researchers have attempted to implement many therapeutic approaches to target proteins and pathways commonly mutated in PDAC, such as KRAS (see Section 3 above) and p53, but this has proved to be challenging, with success in these efforts being currently limited to a small number of patients [86,87]. In contrast, there are a number of FDA-approved drugs that target PI3K, AKT, and mTOR, the three key kinases that make up the growth-promoting signalling network inhibited by PTEN [88,89,90]. Notably, in PDAC, therapeutic inhibition of the PI3K pathway is being explored, not only for its direct effects on cancer cells, but also for its potential benefits on the tumour stroma and anticancer immunity [91].
5. Diverse Drivers of PDAC Are Dysregulated at the Protein Level
In addition to genetic alterations, tumour suppressor function can also be affected at the protein level. Several tumour suppressors implicated in PDAC have been studied using immunohistochemistry to assess their protein abundance in tumour samples. The following subsections discuss key proteins whose expression is frequently reduced in PDAC, highlighting their potential roles in tumour development and progression. As described above, genomic studies of PDAC have identified a large number of implicated oncogenes and tumour suppressors in which mutations are identified in tumour samples, many of which do not play major roles in other cancer types. Several of these implicated tumour suppressors have been studied in more detail to investigate the abundance of their encoded proteins in pancreatic cancer samples by immunohistochemistry.
5.1. KDM6A/UTX Histone Demethylase
The KDM6A protein is a histone demethylase that also influences gene expression, potentially through the regulation of enhancer function independently of its catalytic activity. Furthermore, loss of KDM6A function has also been implicated in multiple cancers, such as acute myeloid and lymphoblastic leukaemias, myeloma, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and breast cancer, among others [92,93]. Mutations in the KDM6A gene, mostly deletions and truncations, are observed in 3–20% of PDAC samples, and the pancreatic-specific deletion of Kdm6a in mice leads to greatly accelerated Kras-driven pancreatic cancer [8,13,94,95]. Notably, tumour suppressor activity appears to be largely independent of catalytic activity [92,94]. The expression of the KDM6A protein in PDAC tumour tissue has been investigated by several groups (Table 3), all observing reduced expression of the tumour suppressor in a large proportion of patients’ tumours. The reported fractions of cancers with negative or reduced KDM6A protein in the four studies were 25%, 30%, 69%, and 78% [95,96,97,98]. Together, these data support the conclusion that the reduced expression of KDM6A may contribute to driving tumourigenesis in many, or perhaps most, pancreatic cancers.

Table 3.
Summarised data from studies reporting the immunohistochemical analysis of KDM6A protein levels in human PDAC samples. The details of positive/negative or high/low scoring methods are found in each publication [95,96,97,98].
5.2. ARID1A
The ARID1A gene encodes a component of the SWI-SNF chromatin remodelling complex and is subject to loss-of-function mutations in a range of cancer types, including ovarian, endometrial, colorectal, lung, and breast cancers [99,100]. The selective deletion of Arid1a in the pancreas of mice results in PanIN formation [101] and accelerates cancer development when combined with the tissue-specific expression of mutant KrasK12D or with Pten deletion [101,102]. Consistent with its role as a tumour suppressor in PDAC, ARID1A mutations, which are mostly deletions or truncations, are found in 5–15% of cases of the disease [8,11,13,24]. However, despite this relatively low frequency of genetic alterations, three independent studies of ARID1A protein abundance in pancreatic cancer tissue samples have reported lost or reduced ARID1A expression in 26%, 36%, and 51% of cases [103,104,105]. This is shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Summarised data from studies reporting the immunohistochemical analysis of ARID1A protein levels in human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma samples. The details of positive/negative or high/low scoring methods are found in each publication [103,104,105].
5.3. MAP2K4
The MAP2K4 gene, also known as MKK4, encodes a protein kinase that plays a role within Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) cascades, acting to phosphorylate and activate the MAPK family members JNK1, JNK2, and p38 in response to stresses and mitogens [106]. The selective deletion of MAP2K4/MKK4 in the pancreas of mice accelerates cancer development when combined with the tissue-specific expression of mutant KrasK12D [107]. Consistent with the potential to be a tumour suppressor in PDAC, reduced copy number and mutations of MAP2K4, including many deletions or truncations, are found in a small fraction of cases. Specific cohort analyses have identified these changes in 2%, 5%, and 24% of patients [8,13,24]. However, immunohistochemical analyses of the abundance of the MAP2K4 protein in pancreatic cancer tissue samples have provided somewhat conflicting data:some studies have reported higher levels of MAP2K4/MKK4 expression in PDAC tissue than in healthy pancreatic ducts, while others have reported a loss of expression [108,109,110,111]. One potential explanation for this discrepancy is a shift in MKK4 protein localisation, as observed in a recent large-scale study, from being predominantly cytoplasmic in healthy tissues to a more nuclear localisation in cancer cells [110]. There is also agreement in larger and more recent studies that loss of the MKK4 protein is associated with a poorer outcome in PDAC cohorts [109,110].
5.4. ATM
ATM is a large DNA-damage-activated protein kinase that contributes to the coordination of DNA repair and the maintenance of genome stability [112,113]. It is encoded by the ATM gene, in which homozygous loss-of-function germline mutations cause the inherited syndrome Ataxia-Telangiectasia, which is characterised by sensitivity to radiation and elevated cancer risk [113]. Similarly, heterozygous carriers of ATM mutations also have an increased risk of pancreatic cancer, and ATM mutations have been observed in approximately 5% of sporadic cases of PDAC [112]. In accordance with this tumour suppressor status, deletion of ATM in mice accelerates RAS-driven pancreatic cancer development and metastasis [114,115]. However, although there is an association of ATM protein loss in PDAC with shorter patient survival, a robust expression of ATM protein is retained in cancer cells in the vast majority (>80%) of PDAC cases [115,116,117]. This uncommon loss of ATM protein expression in PDAC may be related to data showing reduced survival in ATM-negative tumours, which retain the normal p53 protein, but in tumours with aberrant p53 (which comprise the majority of PDACs), ATM status had no effect on survival [116].
When considering the implications of ATM status, this should be viewed as part of the complex relationship between DNA repair and cancer: the loss of genome stability is an important characteristic driving many cancers, but it also makes cancer cells potentially susceptible to genotoxic therapies. This vulnerability is being investigated in multiple cancer types through the development of ATM inhibitors [118] and specifically in PDAC patients with germline BRCA1/2 mutations using the PARP inhibitor Olaparib [119,120], which provides some optimism for future patient outcomes.
5.5. GATA6
The GATA6 transcription factor plays an important role in early pancreatic development and cellular differentiation. In the context of PDAC, its expression has been proposed to influence immune infiltration [121]. GATA6 gene amplification is described in a small subset of PDAC samples (5–20% [8,24,122]), and an increased expression of the GATA6 protein relative to the normal ductal epithelium is reported in approximately half of PDAC cases [122,123]. Notably, high GATA6 expression is associated with the classical PDAC subtype, retained expression of E-Cadherin and CK5, and a longer relative overall survival [121,124,125].
6. Conclusions
Many factors affect how specific genetic changes in cancer cells control the function of encoded proteins and cancer development. For example, some tumour suppressor genes (e.g., TP53 and CDKN2A) usually have both gene copies mutated during the development of cancer, whereas others (e.g., PTEN) are more often observed to retain one unmutated gene copy. However, a comprehensive functional proteomic analysis of clinical samples remains far more challenging than an analogous genomic analysis. Therefore, it is easier to accumulate data that provide confidence in the pathogenic role of the former group of drivers than in the latter group, with the risk of overlooking important effects of the latter group.
We have reviewed data showing reduced levels of a set of tumour suppressor proteins in PDAC tissues observed in a substantial proportion of these cases (with findings summarised in Figure 2).
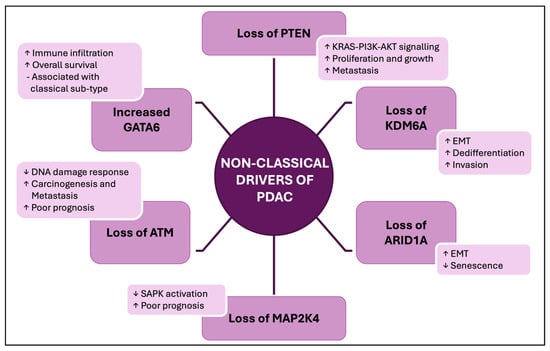
Figure 2.
A summary of the changes in tumour suppressor and oncoprotein functions commonly observed in PDAC, which are discussed in this review. Undefined abbreviations: EMT, Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition; SAPK, Stress-Activated Protein Kinase.
It is understandable that attention is focused on KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, and SMAD4, given the evidence for their central roles in the development of pancreatic cancer. Notably, the initial identification of PTEN, KDM6A, and ARID as tumour suppressor proteins was driven by the analysis of mutations in their encoding genes. Furthermore, this reliance on genetics for cancer driver identification is unlikely to change, given the challenges of discovery research to identify tumour suppressors through clinical proteomics.
In this review, we have addressed the non-genomic loss of tumour suppressor function. It should be noted that there are examples of oncogenes that are increased in function in many cases of PDACs in the absence of observed genetic changes. Perhaps most significantly, the increased activation of the Hippo pathway by an increased expression of the Yap1 protein in the absence of mutations appears to be a common (reported in 47% of cases) event in PDAC, in particular in the squamous/basal subtype [126]. The clinical significance of this is supported by data showing that Hippo pathway activation is able to bypass the dependence of PDAC on KRAS mutations and also drive resistance to KRAS G12C inhibitor therapy [127,128].
Regardless, a publication search of the PubMed database with the terms “pancreatic cancer”, “review”, and a selected gene name reveals >150 publications for each of the KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A and SMAD4 genes, but only 16 publications for PTEN, 8 for ARID1A, and a single review including KDM6A within its title or abstract. These analyses, which overlook or underplay other contributors such as PTEN, KDM6A, and ARID1A, may present a limited picture of PDAC pathogenesis. This is particularly true as evidence accumulates for functional links between these proteins [60,98,129,130,131,132,133,134] and highlights the need for future research into the roles of these proteins.
To date, there have only been a small number of studies that have investigated the abundance in PDAC tissues of MAP2K4, ATM, GATA6, and (to a lesser extent) ARID1A and KDM6A proteins. Therefore, while existing findings relating to these proteins appear significant, with few exceptions (e.g., GATA6 as a transcription factor driving early development of the pancreas), there is very limited understanding of why these proteins have specific associations with PDAC rather than other cancer types. Therefore, further data are required to deliver a solid understanding of their role in PDAC and its clinical significance.
PTEN, KDM6A, and ARID1A are not established targets for successful drugs, and their evident loss of function in PDAC does not provide therapeutic strategies that are well-validated in pancreatic cancer patients. However, each of these genes provides potential strategies that are currently under investigation for cancer treatment [135,136] (see Table 5), with some already approved for use in other types of cancer. For instance, the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signalling pathway is directly activated by KRAS and inhibited by PTEN, and several drug classes have been approved that inhibit components of this pathway. For example, inhibitors of mTOR are approved for the treatment of several cancers, including pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours, and they remain under investigation as PDAC therapies, although trials to date have yielded disappointing results [135,137]. Furthermore, inhibitors of class 1 PI3Ks and drugs inhibiting AKT have shown poor results in clinical trials as monotherapies but are now being used in combination therapy for certain groups of breast cancer subtypes. These drugs also remain under investigation in further settings, particularly in cancers displaying PIK3CA mutations or PTEN loss [138,139]. Strategies to target cancers with ARID1A and KDM6A deficiency are not as mature as those targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [99,140]; however, several recent promising results have been reported [97,141,142,143], offering hope for future research.

Table 5.
Selected ongoing clinical trials including PDAC patients, and with relevance to the proteins discussed in the review. Further details of each trial are available at clinicaltrials.gov. Additionally, there are approximately ten trials underway investigating the selective inhibitors of KRAS G12C that vary with regard to the drug and drug combinations, which are not listed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, L.M.P. and N.R.L.; methodology, L.M.P., R.B.-C., L.T.L., C.M. and N.R.L.; formal analysis, L.M.P., L.T.L., C.M. and N.R.L.; writing—original draft preparation, N.R.L.; writing—review and editing, L.M.P., R.B.-C., L.T.L., C.M. and N.R.L.; funding acquisition, N.R.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Research by the authors on pancreatic cancer has been funded by The Melville Trust for the Care and Cure of Cancer, PhD studentship LPorcza2019.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Partensky, C.; Bray, F. More Deaths from Pancreatic Cancer Than Breast Cancer in the EU by 2017. Acta Oncol. 2016, 55, 1158–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleeff, J.; Korc, M.; Apte, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Johnson, C.D.; Biankin, A.V.; Neale, R.E.; Tempero, M.; Tuveson, D.A.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamitopoulou, E. Tumour Microenvironment of Pancreatic Cancer: Immune landscape is Dictated by Molecular and Histopathological Features. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkan, M.; Hausmann, S.; Michalski, C.W.; Fingerle, A.A.; Dobritz, M.; Kleeff, J.; Friess, H. The Role of Stroma in Pancreatic Cancer: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notta, F.; Hahn, S.A.; Real, F.X. A Genetic Roadmap of Pancreatic Cancer: Still Evolving. Gut 2017, 66, 2170–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biankin, A.V.; Waddell, N.; Kassahn, K.S.; Gingras, M.C.; Muthuswamy, L.B.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.K.; Wilson, P.J.; Patch, A.M.; Wu, J.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Genomes Reveal Aberrations in Axon Guidance Pathway Genes. Nature 2012, 491, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, N.; Pajic, M.; Patch, A.M.; Chang, D.K.; Kassahn, K.S.; Bailey, P.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.; Nones, K.; Quek, K.; et al. Whole Genomes Redefine the Mutational Landscape of Pancreatic Cancer. Nature 2015, 518, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Dey, P.; Yao, W.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Draetta, G.F.; Maitra, A.; DePinho, R.A. Genetics and Biology of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.C.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Kamiyama, H.; Jimeno, A.; et al. Core Signaling Pathways in Human Pancreatic Cancers Revealed by Global Genomic Analyses. Science 2008, 321, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Yu, R.; Liu, R.; Liang, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, Y.W.; Guo, J.; et al. Genetic Aberrations in Chinese Pancreatic Cancer Patients and Their Association with Anatomic Location and Disease Outcomes. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, S.; Fukasawa, M.; Shindo, H.; Takahashi, E.; Hirose, S.; Fukasawa, Y.; Kawakami, S.; Hayakawa, H.; Kuratomi, N.; Kadokura, M.; et al. Clinical Significance of Genetic Alterations in Endoscopically Obtained Pancreatic Cancer Specimens. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Nones, K.; Johns, A.L.; Patch, A.M.; Gingras, M.C.; Miller, D.K.; Christ, A.N.; Bruxner, T.J.; Quinn, M.C.; et al. Genomic Analyses Identify Molecular Subtypes of Pancreatic Cancer. Nature 2016, 531, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biankin, A.V.; Maitra, A. Subtyping Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sausen, M.; Phallen, J.; Adleff, V.; Jones, S.; Leary, R.J.; Barrett, M.T.; Anagnostou, V.; Parpart-Li, S.; Murphy, D.; Kay Li, Q.; et al. Clinical Implications of Genomic Alterations in the Tumour and Circulation of Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, M.; Matthaei, H.; Wu, J.; Hong, S.M.; Yu, J.; Borges, M.; Hruban, R.H.; Maitra, A.; Kinzler, K.; Vogelstein, B.; et al. Presence of Somatic Mutations in Most Early-Stage Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 730–733.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, A.; Herman, J.; Schulick, R.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2011, 378, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, A.A.; Gallinger, S. Pancreatic Cancer Evolution and Heterogeneity: Integrating Omics and Clinical Data. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buday, L.; Downward, J. Many Faces of Ras Activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1786, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uprety, D.; Adjei, A.A. KRAS: From Undruggable to a Druggable Cancer Target. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 89, 102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Tavana, O.; Gu, W. Understanding the Complexity of p53 in a New Era of Tumor Suppression. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 946–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Sharpless, N.E. The Regulation of INK4/ARF in Cancer and Aging. Cell 2006, 127, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.J.; Chetty, R. Smad4/DPC4. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhi, A.D.; George, B.; Greenbowe, J.R.; Chung, J.; Suh, J.; Maitra, A.; Klempner, S.J.; Hendifar, A.; Milind, J.M.; Golan, T.; et al. Real-Time Targeted Genome Profile Analysis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas Identifies Genetic Alterations That Might Be Targeted With Existing Drugs or Used as Biomarkers. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2242–2253.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.Z.; Wang, W.Q.; Zhang, W.H.; Xu, H.X.; Gao, H.L.; Zhang, S.R.; Wu, C.T.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; et al. The Loss of SMAD4/DPC4 Expression Associated with a Strongly Activated Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Predicts Poor Prognosis in Resected Pancreatic Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4123–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masugi, Y.; Takamatsu, M.; Tanaka, M.; Hara, K.; Inoue, Y.; Hamada, T.; Suzuki, T.; Arita, J.; Hirose, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; et al. Post-Operative Mortality and Recurrence Patterns in Pancreatic Cancer According to KRAS Mutation and CDKN2A, p53, and SMAD4 Expression. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2023, 9, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biankin, A.V.; Morey, A.L.; Lee, C.S.; Kench, J.G.; Biankin, S.A.; Hook, H.C.; Head, D.R.; Hugh, T.B.; Sutherland, R.L.; Henshall, S.M. DPC4/Smad4 Expression and Outcome in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4531–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Park, Y.N.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, D.S.; Chi, H.S.; Kim, B.R. Clinical Significance of P16 Protein Expression Loss and Aberrant P53 Protein Expression in Pancreatic Cancer. Yonsei Med. J. 2005, 46, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geradts, J.; Wilentz, R.E.; Roberts, H. Immunohistochemical [Corrected] Detection of the Alternate INK4a-Encoded Tumor Suppressor Protein p14(ARF) in Archival Human Cancers and Cell Lines Using Commercial Antibodies: Correlation with P16(INK4a) Expression. Mod. Pathol. 2001, 14, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.Z.; Zhu, M.H.; Ni, C.R.; Li, F.M.; Zheng, J.M.; Gong, Z.J. Expression of Proteins in P53 (P14arf-Mdm2-P53-P21waf/Cip1) Pathway and Their Significance in Exocrine Pancreatic Carcinoma. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2004, 33, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwatate, Y.; Hoshino, I.; Ishige, F.; Itami, M.; Chiba, S.; Arimitsu, H.; Yanagibashi, H.; Nagase, H.; Yokota, H.; Takayama, W. Prognostic Significance of P16 Protein in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 13, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, M.; Okano, K.; Muraki, S.; Haba, R.; Maeba, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Yachida, S. Immunohistochemically Detected Expression of 3 Major Genes (CDKN2A/p16, TP53, and SMAD4/DPC4) Strongly Predicts Survival in Patients with Resectable Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, C.W.; O’Reilly, E.M. Next-Generation Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 18, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.Y.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishampayan, U.N. An Evaluation of Olaparib for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2021, 22, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’Baloula, J.; Tougeron, D.; Boileve, A.; Jeanbert, E.; Guimbaud, R.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Durand, A.; Turpin, A.; Quesada, S.; Blanc, J.F.; et al. Olaparib as Maintenance Therapy in Non Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Associated with Homologous Recombination Deficiency Profile: A French Retrospective Multicentric AGEO Real-World Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 212, 115051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, T.; Lupatsch, J.E.; Kossler, T.; Dedes, K.; Siebenhuner, A.R.; von Moos, R.; Wicki, A.; Schwenkglenks, M.E. Olaparib Not Cost-Effective as Maintenance Therapy for Platinum-Sensitive, BRCA1/2 Germline-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Fakih, M.G.; Strickler, J.H.; Desai, J.; Durm, G.A.; Shapiro, G.I.; Falchook, G.S.; Price, T.J.; Sacher, A.; Denlinger, C.S.; et al. KRAS(G12C) Inhibition with Sotorasib in Advanced Solid Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Li, B.T.; Dy, G.K.; Price, T.J.; Falchook, G.S.; Wolf, J.; Italiano, A.; Schuler, M.; Borghaei, H.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Sotorasib for Lung Cancers with KRAS p.G12C Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrem, J.M.; Peters, U.; Sos, M.L.; Wells, J.A.; Shokat, K.M. K-Ras(G12C) Inhibitors Allosterically Control GTP Affinity and Effector Interactions. Nature 2013, 503, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.C.; Li, C.Y.; Luo, L.B.; Li, X.; Jia, K.Y.; He, N.; Mao, S.Q.; Wang, W.Y.; Shao, C.C.; Liu, X.Y.; et al. Anti-tumor Efficacy of HRS-4642 and Its Potential Combination with Proteasome Inhibition in KRAS-Mutant Cancer. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 1286–1300.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.F.; Li, Y.T. New exploration of KRAS Inhibitors and the Mechanisms of Resistance. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated Genomic Characterization of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 185–203.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collisson, E.A.; Sadanandam, A.; Olson, P.; Gibb, W.J.; Truitt, M.; Gu, S.; Cooc, J.; Weinkle, J.; Kim, G.E.; Jakkula, L.; et al. Subtypes of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Their Differing Responses to Therapy. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffitt, R.A.; Marayati, R.; Flate, E.L.; Volmar, K.E.; Loeza, S.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Rashid, N.U.; Williams, L.A.; Eaton, S.C.; Chung, A.H.; et al. Virtual Microdissection Identifies Distinct Tumor- and Stroma-Specific Subtypes of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Liang, T. Subtyping for Pancreatic Cancer Precision Therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruff, S.M.; Pawlik, T.M. Molecular Classification and Pathogenesis of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma and Targeted Therapies: A Review. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2024, 29, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, A.D.; Fritz, J.M.; Lenardo, M.J. A Guide to Cancer Immunotherapy: From T Cell Basic Science to Clinical Practice. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.J.; Jaffee, E.M.; Zheng, L. The Tumour Microenvironment in Pancreatic Cancer—Clinical Challenges and Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Torphy, R.J.; Steiger, K.; Hongo, H.; Ritchie, A.J.; Kriegsmann, M.; Horst, D.; Umetsu, S.E.; Joseph, N.M.; McGregor, K.; et al. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Progression is Restrained by Stromal Matrix. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4704–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, X.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Hegde, S.; Lee, K.B.; Jiang, H.; Fields, R.C.; Pachter, J.A.; Lim, K.H.; DeNardo, D.G. Development of Resistance to FAK Inhibition in Pancreatic Cancer is Linked to Stromal Depletion. Gut 2020, 69, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, B.T.; Devisme, A.; Andrieux, G.; Vyas, F.; Aliar, K.; McCloskey, C.W.; Macklin, A.; Jang, G.H.; Denroche, R.; Romero, J.M.; et al. Spatially Confined Sub-Tumor Microenvironments in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell 2021, 184, 5577–5592.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, S.; Winter, P.S.; Navia, A.W.; Williams, H.L.; DenAdel, A.; Lowder, K.E.; Galvez-Reyes, J.; Kalekar, R.L.; Mulugeta, N.; Kapner, K.S.; et al. Microenvironment Drives Cell State, Plasticity, and Drug Response in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell 2021, 184, 6119–6137.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Cheng, S.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Z. Management of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer through Stromal Depletion and Immune Modulation. Medicina 2022, 58, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Garcia, V.; Tawil, Y.; Wise, H.M.; Leslie, N.R. Mechanisms of PTEN Loss in Cancer: It’s All About Diversity. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worby, C.A.; Dixon, J.E. Pten. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 641–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignell, G.R.; Greenman, C.D.; Davies, H.; Butler, A.P.; Edkins, S.; Andrews, J.M.; Buck, G.; Chen, L.; Beare, D.; Latimer, C.; et al. Signatures of Mutation and Selection in the Cancer Genome. Nature 2010, 463, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, N.R.; Foti, M. Non-Genomic Loss of PTEN Function in Cancer: Not in My Genes. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.S.; Salmena, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. The Functions and Regulation of the PTEN Tumour Suppressor. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Stephens, L.; Hawkins, P. PI3K signalling: The Path to Discovery and Understanding. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, M.; Kielkowska, A.; Chessa, T.; Anderson, K.E.; Barneda, D.; Pir, P.; Nakanishi, H.; Eguchi, S.; Koizumi, A.; Sasaki, J.; et al. PTEN Regulates PI(3,4)P(2) Signaling Downstream of Class I PI3K. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 566–580.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, R.; de Krijger, I.; Fritsch, K.; George, R.; Reason, B.; Kumar, M.S.; Diefenbacher, M.; Stamp, G.; Downward, J. RAS and RHO Families of GTPases Directly Regulate Distinct Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Isoforms. Cell 2013, 153, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimonti, A.; Carracedo, A.; Clohessy, J.G.; Trotman, L.C.; Nardella, C.; Egia, A.; Salmena, L.; Sampieri, K.; Haveman, W.J.; Brogi, E.; et al. Subtle Variations in Pten Dose Determine Cancer Susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.H.; Knudson, A.G.; Pandolfi, P.P. A Continuum Model for Tumour Suppression. Nature 2011, 476, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Escudero, I.; Oliver, M.D.; Andres-Pons, A.; Molina, M.; Cid, V.J.; Pulido, R. A comprehensive functional analysis of PTEN mutations: Implications in Tumor- and Autism-Related Syndromes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 4132–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, L.; Black, F.M.; Berg, J.N.; Eickholt, B.J.; Leslie, N.R. Functionally Distinct Groups of Inherited PTEN Mutations in Autism and Tumour Syndromes. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mighell, T.L.; Evans-Dutson, S.; O’Roak, B.J. A Saturation Mutagenesis Approach to Understanding PTEN Lipid Phosphatase Activity and Genotype-Phenotype Relationships. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonnier, V.; Leroy, B.; Rosenberg, S.; Soussi, T. Comprehensive Assessment of TP53 Loss of Function Using Multiple Combinatorial Mutagenesis Libraries. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, E.; Nell, R.J.; Verdijk, R.M.; Gruis, N.A.; van der Velden, P.A.; van Doorn, R. Loss of Wild-Type CDKN2A Is an Early Event in the Development of Melanoma in FAMMM Syndrome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 2298–2301.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetzer, Y.; Kagan, S.; Koifman, G.; Sarig, R.; Kogan-Sakin, I.; Charni, M.; Kaufman, T.; Zapatka, M.; Molchadsky, A.; Rivlin, N.; et al. The Onset of P53 Loss of Heterozygosity is Differentially Induced in Various Stem Cell Types and May Involve the loss of Either Allele. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, N.R.; Longy, M. Inherited PTEN Mutations and the Prediction of Phenotype. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 52, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Elpek, K.G.; Vinjamoori, A.; Zimmerman, S.M.; Chu, G.C.; Yan, H.; Fletcher-Sananikone, E.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. PTEN is a Major Tumor Suppressor in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Regulates an NF-Kappab-Cytokine Network. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidotto, T.; Melo, C.M.; Lautert-Dutra, W.; Chaves, L.P.; Reis, R.B.; Squire, J.A. Pan-Cancer Genomic Analysis Shows Hemizygous PTEN Loss Tumors are Associated with Immune Evasion and Poor Outcome. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeck, S.; Jung, A.; Laubender, R.P.; Neumann, J.; Egg, R.; Goritschan, C.; Vehling-Kaiser, U.; Winkelmann, C.; Fischer von Weikersthal, L.; Clemens, M.R.; et al. EGFR Pathway Biomarkers in Erlotinib-Treated Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: Translational Results from the Randomised, Crossover Phase 3 Trial AIO-PK0104. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Yao, R.; Huang, F.; Liu, X.; Nie, W. High Level of PTEN Expression is Associated with Low-Grade Liver Metastasis and Satisfactory Patient Survival in Pancreatic Cancer. Arch. Med. Res. 2011, 42, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, W.C.; Rashid, A.; Wang, H.; Katz, M.H.; Lee, J.E.; Pisters, P.W.; Wolff, R.A.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Fleming, J.B.; Wang, H. Loss of Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Expression is Associated with Recurrence and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Ren, J.; Tang, J. Expression of PTEN and KAI1 Tumor Suppressor Genes in Pancreatic Carcinoma and its Association with Different Pathological Factors. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jiang, K.; Lawson, D.; Cohen, C.; Siddiqui, M.T. Galectin-3 and PTEN Expression in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma, Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms and Gastrointestinal Tumors on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology. Acta Cytol. 2014, 58, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, N.A.; Schwock, J.; Iakovlev, V.; Pond, G.; Hedley, D.W.; Tsao, M.S. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Changes in Signaling Pathway Activation Downstream of Growth Factor Receptors in Pancreatic Duct Cell Carcinogenesis. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Xiong, J.; Li, T.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, K.; Wu, H.; Wang, C. Correlation Between Protein Expression of PTEN in Human Pancreatic Cancer and the Proliferation, Infiltration, Metastasis and Prognosis. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2006, 26, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wartenberg, M.; Centeno, I.; Haemmig, S.; Vassella, E.; Zlobec, I.; Galvan, J.A.; Neuenschwander, M.; Schlup, C.; Gloor, B.; Lugli, A.; et al. PTEN Alterations of the Stromal Cells Characterise an Aggressive Subpopulation of Pancreatic Cancer with Enhanced Metastatic Potential. Eur. J. Cancer. 2016, 65, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Shen, X.; Dong, X.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, K. Expression of the PTEN/FOXO3a/PLZF Signalling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer and its Significance in Tumourigenesis and Progression. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, N.R.; Yang, X.; Downes, C.P.; Weijer, C.J. PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-Dependent and -Independent Roles for PTEN in the Control of Cell Migration. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallares, J.; Bussaglia, E.; Martinez-Guitarte, J.L.; Dolcet, X.; Llobet, D.; Rue, M.; Sanchez-Verde, L.; Palacios, J.; Prat, J.; Matias-Guiu, X. Immunohistochemical Analysis of PTEN in Endometrial Carcinoma: A Tissue Microarray Study with a Comparison of Four Commercial Antibodies in Correlation with Molecular Abnormalities. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassin, O.; Oren, M. Drugging P53 in Cancer: One Protein, Many Targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.R.; Rosenberg, S.C.; McCormick, F.; Malek, S. RAS-Targeted Therapies: Is the Undruggable Drugged? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.C.; Oliveira, M.; Howell, S.J.; Dalenc, F.; Cortes, J.; Gomez Moreno, H.L.; Hu, X.; Jhaveri, K.; Krivorotko, P.; Loibl, S.; et al. Capivasertib in Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, M.C.; Gulluni, F.; Campa, C.C.; Martini, M.; Hirsch, E. Targeting PI3K Signaling in Cancer: Challenges and Advances. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wei, J.; Liu, P. Attacking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway for Targeted Therapeutic Treatment in Human Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Meng, L.H. Emerging Roles of Class I PI3K Inhibitors in Modulating Tumor Microenvironment and Immunity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.; Broun, A.; Ge, K. Lysine Demethylase KDM6A in Differentiation, Development, and Cancer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40, e00341-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Haaften, G.; Dalgliesh, G.L.; Davies, H.; Chen, L.; Bignell, G.; Greenman, C.; Edkins, S.; Hardy, C.; O’Meara, S.; Teague, J.; et al. Somatic Mutations of the Histone H3K27 Demethylase Gene UTX in Human Cancer. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andricovich, J.; Perkail, S.; Kai, Y.; Casasanta, N.; Peng, W.; Tzatsos, A. Loss of KDM6A Activates Super-Enhancers to Induce Gender-Specific Squamous-like Pancreatic Cancer and Confers Sensitivity to BET Inhibitors. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 512–526 e518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalisz, M.; Bernardo, E.; Beucher, A.; Maestro, M.A.; Del Pozo, N.; Millan, I.; Haeberle, L.; Schlensog, M.; Safi, S.A.; Knoefel, W.T.; et al. HNF1A Recruits KDM6A to Activate Differentiated Acinar Cell Programs that Suppress Pancreatic Cancer. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e102808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Shimada, S.; Akiyama, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Ogura, T.; Ogawa, K.; Ono, H.; Mitsunori, Y.; Ban, D.; Kudo, A.; et al. Loss of KDM6A Characterizes a Poor Prognostic Subtype of Human Pancreatic Cancer and Potentiates HDAC Inhibitor Lethality. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Jin, L.; Kim, H.S.; Tian, F.; Yi, Z.; Bedi, K.; Ljungman, M.; Pasca di Magliano, M.; Crawford, H.; Shi, J. KDM6A Loss Recruits Tumor-Associated Neutrophils and Promotes Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 4247–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Kong, F.; Kong, X.; Jiang, T.; Ma, M.; Zheng, S.; Guo, J.; Xie, K. Loss of GATA6-Mediated Up-Regulation of UTX Promotes Pancreatic Tumorigenesis and Progression. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, J.; Kato, S.; Sicklick, J.K.; Kurzrock, R. Targeting ARID1A Mutations in Cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 100, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.N.; Roberts, C.W. ARID1A Mutations in Cancer: Another Epigenetic Tumor Suppressor? Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.C.; Nassour, I.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, S.; Luo, X.; Lee, J.; Li, L.; Sun, X.; Nguyen, L.H.; Chuang, J.C.; et al. SWI/SNF Component ARID1A Restrains Pancreatic Neoplasia Formation. Gut 2019, 68, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, Y.; Fukuda, A.; Omatsu, M.; Namikawa, M.; Sono, M.; Masuda, T.; Araki, O.; Nagao, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ogawa, S.; et al. Loss of Arid1a and Pten in Pancreatic Ductal Cells Induces Intraductal Tubulopapillary Neoplasm via the YAP/TAZ Pathway. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 466–480.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numata, M.; Morinaga, S.; Watanabe, T.; Tamagawa, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Shiozawa, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Kameda, Y.; Okawa, S.; Rino, Y.; et al. The Clinical Significance of SWI/SNF Complex in Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Yu, S.; Jia, C.; Yan, J.; Lu, Z.; Chen, J. Loss of ARID1A Expression Correlates With Tumor Differentiation and Tumor Progression Stage in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533034618754475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Fukuda, A.; Ogawa, S.; Maruno, T.; Takada, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Hiramatsu, Y.; Araki, O.; Nagao, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; et al. ARID1A Maintains Differentiation of Pancreatic Ductal Cells and Inhibits Development of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma in Mice. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 194–209.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusgen, W.; Herdegen, T.; Waetzig, V. The bottleneck of JNK signaling: Molecular and Functional Characteristics of MKK4 and MKK7. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, C.C.; Harvey, E.; McMahon, R.F.; Finegan, K.G.; Connor, F.; Davis, R.J.; Tuveson, D.A.; Tournier, C. Impaired JNK Signaling Cooperates with KrasG12D Expression to Accelerate Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3344–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handra-Luca, A.; Lesty, C.; Hammel, P.; Sauvanet, A.; Rebours, V.; Martin, A.; Fagard, R.; Flejou, J.F.; Faivre, S.; Bedossa, P.; et al. Biological and Prognostic Relevance of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2012, 41, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.D.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wu, H.W.; Liang, Z.Y. A New Prognosis Prediction Model Combining TNM stage with MAP2K4 and JNK in Postoperative Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 217, 153313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, G.; Liang, Z.Y.; Zhou, W.X.; You, L.; Yuan, D.; Li, B.Q.; Guo, J.C.; Zhao, Y.P. Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of MKK4 and MKK7 in Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2019, 86, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, W.; Yun, K.J.; Ricci, F.; Zahurak, M.; Qiu, W.; Su, G.H.; Yeo, C.J.; Hruban, R.H.; Kern, S.E.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A. MAP2K4/MKK4 expression in Pancreatic Cancer: Genetic Validation of Immunohistochemistry and Relationship to Disease Course. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8516–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, S.A.; Schultz, C.W.; Azimi-Sadjadi, A.; Brody, J.R.; Pishvaian, M.J. ATM Dysfunction in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma and Associated Therapeutic Implications. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Paull, T.T. Cellular Functions of the Protein Kinase ATM and Their Relevance to Human Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 796–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosos, Y.; Escobar, D.; Chiang, M.Y.; Roys, K.; Valentine, V.; Valentine, M.B.; Rehg, J.E.; Sahai, V.; Begley, L.A.; Ye, J.; et al. ATM-Deficiency Increases Genomic Instability and Metastatic Potential in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.; Perkhofer, L.; Liebau, S.; Lin, Q.; Lechel, A.; Feld, F.M.; Hessmann, E.; Gaedcke, J.; Guthle, M.; Zenke, M.; et al. Loss of ATM Accelerates Pancreatic Cancer Formation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Saka, B.; Knight, S.; Borges, M.; Childs, E.; Klein, A.; Wolfgang, C.; Herman, J.; Adsay, V.N.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. Having Pancreatic Cancer with Tumoral Loss of ATM and Normal TP53 Protein Expression is Associated with a Poorer Prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranal, R.M.; Jiang, Z.; Hutchings, D.; Kryklyva, V.; Gauthier, C.; Fujikura, K.; Nanda, N.; Huang, B.; Skaro, M.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. Somatic Loss of ATM is a Late Event in Pancreatic Tumorigenesis. J. Pathol. 2023, 260, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Liang, Q.; Shi, J. Progress of ATM Inhibitors: Opportunities and Challenges. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 277, 116781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkhofer, L.; Gout, J.; Roger, E.; Kude de Almeida, F.; Baptista Simoes, C.; Wiesmuller, L.; Seufferlein, T.; Kleger, A. DNA Damage Repair as a Target in Pancreatic Cancer: State-of-the-art and Future Perspectives. Gut 2021, 70, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkhofer, L.; Schmitt, A.; Romero Carrasco, M.C.; Ihle, M.; Hampp, S.; Ruess, D.A.; Hessmann, E.; Russell, R.; Lechel, A.; Azoitei, N.; et al. ATM Deficiency Generating Genomic Instability Sensitizes Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells to Therapy-Induced DNA Damage. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5576–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eijck, C.W.F.; Real, F.X.; Malats, N.; Vadgama, D.; van den Bosch, T.P.P.; Doukas, M.; van Eijck, C.H.J.; Mustafa, D.A.M.; Dutch Pancreatic Cancer, G. GATA6 Identifies An Immune-Enriched Phenotype Linked to Favorable Outcomes in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer Undergoing Upfront Surgery. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwei, K.A.; Bashyam, M.D.; Kao, J.; Ratheesh, R.; Reddy, E.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Montgomery, K.; Giacomini, C.P.; Choi, Y.L.; Chatterjee, S.; et al. Genomic Profiling Identifies GATA6 as a Candidate Oncogene Amplified In Pancreatobiliary Cancer. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Luo, M.; Lakkur, S.; Lucito, R.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A. Frequent Genomic Copy Number Gain and Overexpression of GATA-6 in Pancreatic Carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokumai, T.; Omori, Y.; Ishida, M.; Ohtsuka, H.; Mizuma, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Maeda, C.; Ono, Y.; Mizukami, Y.; Miura, S.; et al. GATA6 and CK5 Stratify the Survival of Patients With Pancreatic Cancer Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibayama, T.; Hayashi, A.; Toki, M.; Kitahama, K.; Ho, Y.J.; Kato, K.; Yamada, T.; Kawamoto, S.; Kambayashi, K.; Ochiai, K.; et al. Combination Immunohistochemistry for CK5/6, p63, GATA6, and HNF4a Predicts Clinical Outcome In Treatment-Naive Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, B.; Yao, J.; Ferri-Borgogno, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, S.J.; Wang, Q.Y.; Yan, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, C.H.; Bang, S.M.; et al. YAP1 Oncogene is a Context-Specific Driver for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e130811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Yao, W.T.; Ying, H.Q.; Hua, S.J.; Liewen, A.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, C.J.; Sadanandam, A.; Hu, B.L.; et al. Yap1 Activation Enables Bypass of Oncogenic Kras Addiction in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell 2014, 158, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Z.Y.; Ranieri, M.; Li, S.; Sahu, S.; Liu, Y.Z.; Ban, Y.; Guidry, K.; Hu, H.; et al. Genome-Wide CRISPR Screens Identify Multiple Synthetic Lethal Targets That Enhance KRAS Inhibitor Efficacy. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 4095–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamagawa, H.; Fujii, M.; Togasaki, K.; Seino, T.; Kawasaki, S.; Takano, A.; Toshimitsu, K.; Takahashi, S.; Ohta, Y.; Matano, M.; et al. Wnt-deficient and Hypoxic Environment Orchestrates Squamous Reprogramming of human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2024, 26, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Luo, L.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pesic, M.; Cai, L.; Li, L. New Insight into the Role of SMAD4 Mutation/Deficiency in the Prognosis and Therapeutic Resistance of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Kobayashi, S.; Qiao, W.; Li, C.; Xiao, C.; Radaeva, S.; Stiles, B.; Wang, R.H.; Ohara, N.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Induction of Intrahepatic Cholangiocellular Carcinoma by Liver-Specific Disruption of Smad4 and Pten in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.C.; Wang, T.L.; Shih Ie, M. The Emerging Roles of ARID1A in Tumor Suppression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotman, L.C.; Pandolfi, P.P. PTEN and p53: Who will Get the Upper Hand? Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, K.; Xu, J.; Zairis, S.; Resnick-Silverman, L.; Abate, F.; Steinbach, N.; Ozturk, S.; Saal, L.H.; Su, T.; Cheung, P.; et al. p53 Maintains Baseline Expression of Multiple Tumor Suppressor Genes. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morran, D.C.; Wu, J.; Jamieson, N.B.; Mrowinska, A.; Kalna, G.; Karim, S.A.; Au, A.Y.; Scarlett, C.J.; Chang, D.K.; Pajak, M.Z.; et al. Targeting mTOR Dependency in Pancreatic Cancer. Gut 2014, 63, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revia, S.; Seretny, A.; Wendler, L.; Banito, A.; Eckert, C.; Breuer, K.; Mayakonda, A.; Lutsik, P.; Evert, M.; Ribback, S.; et al. Histone H3K27 Demethylase KDM6A is an Epigenetic Gatekeeper of mTORC1 Signalling in Cancer. Gut 2022, 71, 1613–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, Z.; Schneeweis, C.; Wirth, M.; Veltkamp, C.; Dantes, Z.; Feuerecker, B.; Ceyhan, G.O.; Knauer, S.K.; Weichert, W.; Schmid, R.M.; et al. MTOR Inhibitor-Based Combination Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belli, C.; Repetto, M.; Anand, S.; Porta, C.; Subbiah, V.; Curigliano, G. The Emerging Role of PI3K inhibitors For Solid Tumour Treatment And Beyond. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 2150–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervanidis, K.A.; D’Angelo, G.D.; Weisner, J.; Brandherm, S.; Rauh, D. Akt Inhibitor Advancements: From Capivasertib Approval to Covalent-Allosteric Promises. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 6052–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhong, X.D.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhu, M.H.; Tao, F.; Li, C.Y.; She, Q.S.; Yang, G.J.; Chen, J. The Role of Lysine-Specific Demethylase 6A (KDM6A) in Tumorigenesis and its Therapeutic Potentials in Cancer therapy. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 133, 106409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirt, C.K.; Booij, T.H.; Grob, L.; Simmler, P.; Toussaint, N.C.; Keller, D.; Taube, D.; Ludwig, V.; Goryachkin, A.; Pauli, C.; et al. Drug Screening and Genome Editing in Human Pancreatic Cancer Organoids Identifies Drug-Gene Interactions and Candidates for Off-Label Treatment. Cell Genom. 2022, 2, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botta, G.P.; Kato, S.; Patel, H.; Fanta, P.; Lee, S.; Okamura, R.; Kurzrock, R. SWI/SNF complex alterations as a biomarker of immunotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e150453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomihara, H.; Carbone, F.; Perelli, L.; Huang, J.K.; Soeung, M.; Rose, J.L.; Robinson, F.S.; Lissanu Deribe, Y.; Feng, N.; Takeda, M.; et al. Loss of ARID1A Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Sensitizes Pancreatic Tumors to Proteotoxic Stress. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).